Simple Summary
Identifying ALK fusions in advanced non-small-cell lung carcinoma (aNSCLC) is mandatory for targeted therapy. Current methods use ALK IHC, ALK FISH, or NGS, but face challenges due to low fusion frequency, possible tissue exhaustion, and test limitations. We compared RNA NGS with ALK IHC and ALK FISH in 1246 NSCLC cases, finding RNA NGS faster and equally effective. This suggests the need to replace systematic ALK IHC with RNA NGS reflex testing for more efficient assessments of ALK status.
Abstract
The identification of ALK fusions in advanced non-small-cell lung carcinoma (aNSCLC) is mandatory for targeted therapy. The current diagnostic approach employs an algorithm using ALK immunohistochemistry (IHC) screening, followed by confirmation through ALK FISH and/or next-generation sequencing (NGS). Challenges arise due to the infrequency of ALK fusions (3–7% of aNSCLC), the suboptimal specificity of ALK IHC and ALK FISH, and the growing molecular demands placed on small tissue samples, leading to interpretative, tissue availability, and time-related issues. This study investigates the effectiveness of RNA NGS as a reflex test for identifying ALK fusions in NSCLC, with the goal of replacing ALK IHC in the systematic screening process. The evaluation included 1246 NSCLC cases using paired techniques: ALK IHC, ALK FISH, and ALK NGS. ALK IHC identified 51 positive cases (4%), while RNA NGS detected ALK alterations in 59 cases (4.8%). Of the 59 ALK-positive cases identified via NGS, 53 (89.8%) were confirmed to be positive. This included 51 cases detected via both FISH and IHC, and 2 cases detected only via FISH, as they were completely negative according to IHC. The combined reporting time for ALK IHC and ALK FISH averaged 13 days, whereas ALK IHC and RNA NGS reports were obtained in an average of 4 days. These results emphasize the advantage of replacing systematic ALK IHC screening with RNA NGS reflex testing for a more comprehensive and accurate assessment of ALK status.
1. Introduction
Detecting ALK rearrangements in stage IIIB/IV non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NS-NSCLC) patients is pivotal for their eligibility for targeted therapy, particularly involving first- and second-generation ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors [1,2].
Hence, there is a pressing need to systematically screen for ALK rearrangements in cases of advanced non-squamous NSCLC (aNS-NSCLC) at baseline [3].
For years, FISH analysis has been the benchmark method for detecting ALK rearrangements, while it is a time-consuming process requiring specialized equipment and high expertise for interpreting various signal variants. ALK:EML4 fusions often exhibit a short break pattern, leading to potential misinterpretation and false-negative results, though this can be mitigated by using the ALK::EML4 fusion probe [4].
Some samples fail to meet FISH analysis criteria due to various quality-related issues and a very low percentage of tumor cells. With the advent of high-performance rabbit monoclonal antibodies, immunohistochemistry (IHC) has become a valuable alternative to FISH. While easier to interpret and not requiring specialized equipment like FISH, IHC cannot replace FISH unless standardized and properly validated [2,5].
Despite the high concordance rate between IHC and FISH, routine practice sometimes yields discordant results due to technical issues and the diverse properties of ALK protein produced by different ALK fusion variants [6,7].
Moreover, next-generation sequencing (NGS) can detect ALK fusion in FISH-negative cases, with NGS recently overtaking FISH as the predominant ALK testing method [8,9]. This trend is anticipated to persist, given that multiple NGS methodologies can identify a wide range of actionable gene alterations. Current guidelines from ESMO and NCCN for NSCLC advocate for extensive molecular profiling, reinforcing this practice [3,10]. The continuous discovery of therapeutic molecular targets for NS-NSCLC has increased the number of predictive biomarkers that need to be evaluated before any treatment. These biomarkers include EGFR, ALK, ROS1, BRAF, RET, NTRK, MET, KRAS, and HER2 [3]. However, in routine clinical practice, sequentially testing for genomic alterations in each of these genes poses several challenges. Firstly, the turnaround times (TATs) needed to obtain the results can significantly delay the initiation of targeted treatments. Secondly, some tests may be impractical or yield uncertain or false-negative results, particularly when dealing with small tissue biopsies or samples with low tumor content. This can lead to insufficient amounts of extracted nucleic acid or an inadequate number of visible tumor cells on tissue sections [11].
Currently, the utility of IHC for ALK screening is under scrutiny, paving the way for RNA NGS reflex testing, capable of examining all necessary genomic alterations associated with available targeted therapies in a single step in routine clinical practice [3].
This study aimed to compare ALK rearrangement screening results using IHC and RNA NGS in a large single-center cohort of NS-NSCLC patients, with ALK FISH results as a reference. Additionally, we compared the TATs for obtaining these results.
2. Patients and Methods
Between January 2016 and December 2023, 1246 NS-NSCLC consecutive patients were tested systematically via ALK IHC, and DNA and RNA NGS (Laboratory of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, IHU RespirERA, Nice, France; Figure 1).

Figure 1.
CONSORT flow diagram of the study.
Diagnoses were made on a morphological and IHC basis according to the recommendations of the 2015 WHO classification for lung cancer, with the IASLC/ATS/ERS-recommended modifications, by senior lung pathologists (M.I., E.L, S.L, V.H., and P.H.) [12].
The TAT was defined as the duration between receiving the final histological diagnosis reports and the electronic validation of the molecular reports.
All tumor specimens were used with informed signed consent from the patients. The study was approved by the local ethics committee (Human Research Ethics Committee, Nice University Hospital Center/Hospital-related Biobank BB-0033-00025; http://www.biobank-cotedazur.fr/, accessed on 15 March 2024) and was performed in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki.
2.1. ALK Immunohistochemistry
FFPE sections were freshly cut, resulting in a thickness of 4 μm. Within a maximum of one day after sectioning, the slides were stained using IHC. All IHC staining procedures were carried out on a Ventana BenchMark Ultra automated immunostainer (Ventana Medical Systems, Roche Group, Tucson, AZ, USA) [5,13,14]. Following CC1 antigen retrieval, tissue sections were incubated with the primary rabbit monoclonal antibody anti-ALK (Clone D5F3, prediluted, Ventana Medical Systems). OptiView DAB IHC Detection Kit (Ventana Medical Systems) and OptiView Amplification Kit (Ventana Medical Systems) were used according to the manufacturer’s technical instructions to visualize the bound anti-ALK primary antibody. ALK-Lung Analyte Control (HCL009, HistoCyte Laboratories, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK) was used as a positive external control for all tests.
All the procedures were accredited in the laboratory under the ISO 15189 norm [15] (COFRAC n°8-3034).
Every specimen was examined and evaluated by five pathologists (M.I., E.L.M., S.L., V.H., and P.H.). The Ventana ALK Scoring Interpretation Guide was used for the interpretation of the ALK IHC assay. Cases were scored positive if strong granular cytoplasmic brown staining in tumor cells (any percentage of positive tumor cells) was present [5]. After initial calibration according to the interpretation guide and conducting annual internal quality controls for ALK IHC interpretation, the concordance rate among the five pathologists reached 100% in this study.
2.2. ALK Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization
The Abbott ALK break-apart probe (Vysis LSI ALK Dual Color; Abbott Molecular, Rungis, France) was used on 4 µm thick FFPE tissue sections, according to the manufacturer’s technical instructions, as detailed in previous studies [16]. Every specimen was examined and evaluated by one senior pathologist (E.L.M.). This ALK FISH assay was accredited in the laboratory according to the ISO 15189 norm (COFRAC n°8-3034).
2.3. Ultra-Fast Next-Generation Sequencing
Patients included in the study underwent fast DNA- and RNA-based NGS as a form of reflex testing at the LPCE (Nice University Hospital, France), accredited under the ISO 15189 vs. 2022 norm for somatic genomic testing by NGS in routine clinical practice (www.cofrac.fr, accessed on 15 March 2024).
Nucleic acids were extracted using Maxwell RSC Instrument (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) with the Maxwell RSC FFPE Plus DNA kit or the Maxwell RSC RNA FFPE kit (Promega). Concentrations were measured using the Qubit Fluorometric quantification assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) with Qubit RNA HS Assay Kit and Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit.
Genomic alterations were detected using ion semiconductor sequencing (Ion Torrent™ Technology, Thermo Fisher Scientific) on Ion Torrent™ Genexus™ Integrated Sequencer, following the manufacturer’s technical instructions, as previously described [17,18]. The Oncomine™ Precision Assay GX (OPA, Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number A46291) was used, covering 50 key genes—45 for DNA mutations, 18 for fusions, and 14 for copy number variants (CNVs), including a 5′/3′ expression imbalance caller for novel fusion detection. The Genexus sequencer could sequence up to 16 samples per run. [17,18].
3. Results
The main epidemiological, clinical, and pathological data of the enrolled patients are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Main epidemiological and pathological data of the 1246 patients with NS-NSCLC included in the study.
ALK IHC was assessed in 1246 cases of NS-NSCLC, revealing unequivocal positive staining in 51 out of 1246 cases (4%) (Figure 2).
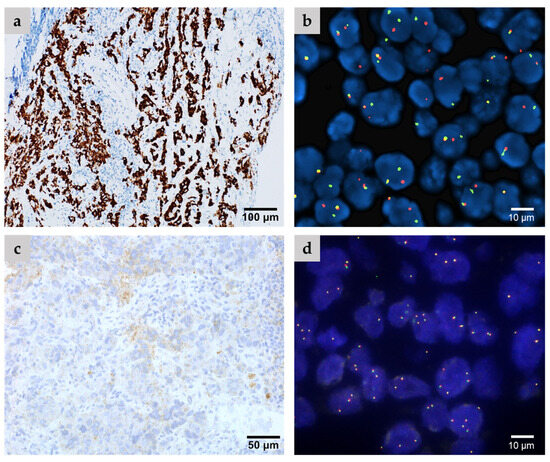
Figure 2.
Representative cases include (a,b) an ALK-positive case confirmed via both IHC (a) and FISH analysis (b), as well as (c,d) an ALK-negative case demonstrating non-specific staining according to IHC (c) and negative FISH analysis (d).
ALK FISH analysis yielded positive results in 53 out of 1246 cases (4.2%). Among these cases, there were two cases where non-specific staining was observed and recorded as negative by IHC, but ALK 5′/3′-end expression imbalance was detected via RNA NGS.
RNA NGS analysis identified ALK alterations in 59 out of 1246 cases (4.7%) (Figure 3).

Figure 3.
RNA NGS-detected ALK fusions in the study.
A positive ALK result of NGS analysis was confirmed in 53 out of 59 cases (89.8%), comprising 51 cases identified via both FISH and IHC, and 2 cases detected solely via FISH due to completely negative IHC results (Figure 4A). Additionally, five cases were false positives according to RNA NGS, showing ALK 5′/3′-end expression imbalance, but tested negative via both FISH and IHC, while one case was FISH-negative but exhibited non-specific staining under IHC (Figure 4A).
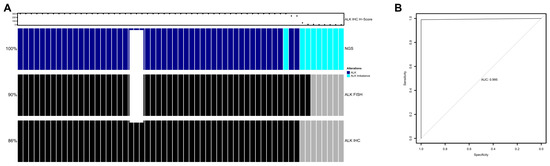
Figure 4.
(A) Overview of ALK fusion detection using NGS (ALK-positive, dark blue; ALK 5′/3′-end expression imbalance, turquoise), ALK FISH (ALK-positive, black; ALK-negative, gray), and ALK IHC (ALK-positive, black; ALK-negative, gray). Each column represents one patient. The IHC H-score is shown above. (B) Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve for the detection of ALK via NGS compared with IHC H-score in the full cohort of 1246 patients.
In the full cohort, the area under the curve using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was 0.995. Based on the Youden J method, an optimal cut-off was defined as an H-score of 145. At this cutoff, specificity was 98.99%, sensitivity was 100%, NPV was 100%, and PPV was 98.04% for the ALK RNA NGS test compared with IHC (Figure 4B).
The average TAT to obtain DNA and RNA NGS reports was 4 days, ranging from 3 to 8 days. For both the ALK IHC and ALK FISH reports, the total mean TAT was 13 days. Specifically, the ALK IHC report took an average of 2 days (ranging from 2 to 5 days), while the ALK FISH report took an average of 13 days (ranging from 6 to 21 days).
4. Discussion
This study demonstrated that implementing an ultrafast DNA and RNA NGS approach at baseline can significantly enhance reflex testing for ALK rearrangements in NS-NSCLC.
Overall, our findings prompted us to discontinue the ALK IHC screening approach and the sequential ALK IHC/ALK FISH algorithm in our laboratory in favor of the RNA NGS approach. We also emphasize the importance of FISH analysis as the preferred orthogonal method for confirming ambiguous ALK results showing ALK imbalance identified via RNA NGS.
Among the patients with NSCLC, ALK gene alterations occur in approximately 3–7% of cases, consistent with findings from previous series [19,20]. Our study cohort demonstrated a similar prevalence of ALK alterations as reported in NSCLC patients [19,20]. DNA and RNA NGS results were obtained within an average of four working days. In contrast, ALK IHC results were available within an average of 2 working days, but confirmation of positivity required an additional 13 working days (a range of 6–21 days) under ALK FISH.
The decision to move away from routine ALK IHC screening in patients with NS-NSCLC was justified by various factors, particularly based on the findings of our study. ALK status assessment through IHC has limitations, as evidenced by several false-negative results that were confirmed by discrepancies with ALK FISH results [21]. Furthermore, the choice of anti-ALK antibody is crucial due to the variability in specificity and sensitivity among commercial antibodies. The ALK (D5F3) CDx IHC assay stands out as the sole IHC assay approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the standalone testing of ALK rearrangements in NSCLC, owing to its high performance and clinical validation [22]. Finally, in numerous cases, both ALK IHC and ALK FISH are redundantly performed, leading to increased associated costs, increased workload in the pathology laboratory, and longer TATs for obtaining reports. Importantly, this practice can also deplete tumor tissue reserves, especially in cases of small biopsies or when tumor cell percentages are low [23].
Our findings showed excellent agreement between ALK FISH results and those obtained from RNA NGS. RNA NGS was conducted concurrently with DNA NGS testing, enabling a comprehensive assessment of essential gene statuses at the baseline for NS-aNSCLC.
NGS offers the ability to analyze a broad panel of driver alterations simultaneously, requiring a smaller specimen volume compared with sequential analysis of driver oncogenes like EGFR, KRAS, BRAF, HER2, MET, ALK, ROS1, NTRK, and RET [24]. There are two primary NGS approaches: DNA-based NGS and hybrid capture-based NGS. DNA-based NGS can target predefined breakpoints. The reported sensitivity and specificity of DNA-based NGS assays for detecting ALK rearrangements in NSCLC diagnosed via FISH and IHC are 85% and 79%, respectively [25]. In contrast, hybrid capture-based NGS has the capability to analyze most breakpoints, including those that are unknown [26].
Previously, a significant limitation of relying solely on NGS for evaluating ALK rearrangements was the delay in obtaining results. This delay could hinder the timely administration of targeted therapy due to issues related to sample organization, workflow, and sequencing methods [24]. However, the development of a new ultra-fast NGS system has revolutionized this process, delivering results within an average of four days for positive cases. This surpasses the turnaround time of sequentially using ALK IHC followed by ALK FISH [17,18,27]. It is important to note that RNA NGS can identify all fusion partners of the ALK gene and can enable the detection of short deletions that might not be detectable with ALK FISH [28,29,30]. Although DNA-based sequencing can identify rearrangements of fusion genes within intron regions, these sequences often differ from messenger RNA (mRNA) fusions. This underscores the fact that RNA NGS is indeed the preferred approach for evaluating the ALK status [31]. Furthermore, it is important to highlight that in certain cases, ALK fusions are detected through imbalance assessment, which can be confusing due to its lower specificity [21]. If an ALK fusion is identified through expression imbalance or with a low number of reads, it is recommended to conduct orthogonal testing using FISH to enhance specificity [27,32].
Interestingly, capture-based NGS can detect ALK rearrangements in blood samples noninvasively with high sensitivity and specificity. This approach also enables the monitoring of tumor dynamics and identification of drug-resistant mutations [33].
There are several approaches to target enrichment for RNA next-generation sequencing (NGS), including amplicon-based, hybrid capture, and anchored multiplex methods. Each has its advantages and disadvantages [34].
Amplicon-based enrichment has high sensitivity for detecting known variants, is quick and cost-effective, and requires relatively small amounts of input RNA. However, it is limited to detecting known variants and is less effective for novel or complex rearrangements. It also has the potential for amplification bias and a limited dynamic range [34].
Hybrid capture can detect a broad range of variant types, including novel fusions and splice variants. It offers high specificity and coverage uniformity, making it suitable for high-throughput applications. On the downside, it is more expensive and time-consuming compared with amplicon-based methods, requires larger amounts of input RNA, and can potentially capture off-target sequences, leading to noise [34].
Anchored multiplex PCR is effective for identifying gene fusions, including those with unknown partners, and has a flexible design that allows for the detection of various types of rearrangements. It offers high sensitivity and specificity. However, it involves complex design and optimization, is costlier compared with amplicon-based methods, and requires a moderate amount of input RNA [34].
The Oncomine assay, an example of an anchored multiplex PCR method, is specifically designed for detecting gene fusions and variants in cancer research. It has high sensitivity and specificity for detecting a wide range of gene fusions, including those with unknown partners [35]. It features a streamlined workflow and comprehensive coverage of relevant cancer genes, and is suitable for use with limited RNA samples, such as those obtained from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissues. However, the assay can be relatively expensive compared with simpler methods and requires careful design and optimization to ensure comprehensive coverage and accurate detection. While effective for fusion detection, it may be less suitable for detecting other types of variants or for applications requiring whole-transcriptome analysis. Additionally, interpreting the results can be complex and may require specialized bioinformatics tools and expertise [35].
Simultaneous performance of DNA and RNA NGS enables comprehensive assessment of various genomic alterations that are essential for baseline evaluation in NS-NSCLC. This approach facilitates the investigation of key genetic changes necessary for understanding the molecular profile of aNS-NSCLC at the outset [3].
In this context, it is important to highlight that the simultaneous presence of driver oncogene mutations along with an ALK rearrangement may have implications for predicting diverse clinical outcomes in patients with aNS-NSCLC [36]. Nevertheless, several constraints may hinder the implementation of the new algorithm described above in routine clinical practice. First, unlike IHC platforms, which are widely available in most pathology laboratories, NGS approaches are not uniformly accessible across all countries or even within organizations and institutions within a single country [37]. Second, even if NGS approaches are accessible, their use may be limited due to the high costs and possible lack of reimbursement, which can result in longer TATs for obtaining results that may not align with international guidelines [38]. Considering their reduced expenses and shorter TATs, IHC and/or rapid RT-PCR can be viable alternatives for evaluating ALK status [37,39,40]. Notably, in small biopsies or when there is an extremely low content of tumor cells, the IHC and FISH methods can be indispensable as they might be the sole methods capable of detecting therapeutic targets. This is particularly worrisome as NGS might produce false-negative results in cases of inadequate nucleic acid quantity and/or quantity [41]. Unlike RNA NGS, the ALK FISH assay might yield false-negative results, especially in cases with small deletions [42]. Additionally, ALK FISH entails relatively higher costs, and technical challenges, requiring a sufficient number of tumor cells, and can be labor-intensive.
Therefore, the integration of diverse approaches for assessing ALK status within pathology laboratories is crucial. ALK FISH serves as a valuable orthogonal tool alongside ALK IHC to confirm doubtful NGS and/or RT-PCR results, particularly in young and/or non-smoking patients. Furthermore, cutting-edge in situ technologies like multiplex IHC, incorporating various antibodies including anti-ALK antibodies, can conserve tissue material and expedite TATs by simultaneously providing results for different targetable molecules.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our study underscores the recommendation to discontinue IHC for evaluating ALK rearrangement status in NS-NSCLC in favor of adopting ultrafast RNA NGS reflex testing as the preferred method. However, ALK FISH remains valuable for validating diagnoses in cases of uncertain NGS results or when dealing with very small tissue biopsies containing few tumor cells. Additionally, ALK FISH may be considered in specific circumstances, such as with young and/or non-smoker patients, or based on specific requests from physicians.
Author Contributions
Original draft writing, resources, and reviewing, M.I., S.G., G.R., V.L.-F., S.L. (Salomé Lalvée), O.B., K.Z., K.W., C.B., E.L.-M., S.L. (Sandra Lassalle), E.LM., S.H., V.H. and P.H.; reviewing and editing, M.I., S.H. and P.H.; supervision, administration, resources, reviewing, and editing, M.I. and P.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the French government managed by “Agence Nationale de la Recherche” under the France 2030 program, reference ANR-23-IAHU-007.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Nice (Approval Code: #CRBMTA2023-16.04 Approval Date: 16 October 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
M.I. received honoraria from AstraZeneca, and MSD. P.H. received honoraria from Sanofi, Amgen, Roche, BMS, AstraZeneca, Abbvie, Qiagen, Pfizer, Janssen, Pierre Fabre, ThermoFisher Scientific, Biodena, Diaceutics, Biocartis, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, Bayer, Novartis, and Bayer. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.W.; Wu, Y.L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, L.E.; Kerr, K.M.; Menis, J.; Mok, T.S.; Nestle, U.; Passaro, A.; Peters, S.; Planchard, D.; Smit, E.F.; Solomon, B.J.; et al. Oncogene-addicted metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosele, F.; Remon, J.; Mateo, J.; Westphalen, C.B.; Barlesi, F.; Lolkema, M.P.; Normanno, N.; Scarpa, A.; Robson, M.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; et al. Recommendations for the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) for patients with metastatic cancers: A report from the ESMO Precision Medicine Working Group. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1491–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camidge, D.R.; Kono, S.A.; Flacco, A.; Tan, A.C.; Doebele, R.C.; Zhou, Q.; Crino, L.; Franklin, W.A.; Varella-Garcia, M. Optimizing the detection of lung cancer patients harboring anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene rearrangements potentially suitable for ALK inhibitor treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 5581–5590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynes, M.W.; Sholl, L.M.; Dietel, M.; Schuuring, E.; Tsao, M.S.; Yatabe, Y.; Tubbs, R.R.; Hirsch, F.R. An International Interpretation Study Using the ALK IHC Antibody D5F3 and a Sensitive Detection Kit Demonstrates High Concordance between ALK IHC and ALK FISH and between Evaluators. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabillic, F.; Hofman, P.; Ilie, M.; Peled, N.; Hochmair, M.; Dietel, M.; Von Laffert, M.; Gosney, J.R.; Lopez-Rios, F.; Erb, G.; et al. ALK IHC and FISH discordant results in patients with NSCLC and treatment response: For discussion of the question-to treat or not to treat? ESMO Open 2018, 3, e000419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabillic, F.; Gros, A.; Dugay, F.; Begueret, H.; Mesturoux, L.; Chiforeanu, D.C.; Dufrenot, L.; Jauffret, V.; Dachary, D.; Corre, R.; et al. Parallel FISH and immunohistochemical studies of ALK status in 3244 non-small-cell lung cancers reveal major discordances. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clave, S.; Rodon, N.; Pijuan, L.; Diaz, O.; Lorenzo, M.; Rocha, P.; Taus, A.; Blanco, R.; Bosch-Barrera, J.; Reguart, N.; et al. Next-generation Sequencing for ALK and ROS1 Rearrangement Detection in Patients With Non-small-cell Lung Cancer: Implications of FISH-positive Patterns. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, e421–e429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.M.; Wu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Niu, H.; Curran, E.A.; Lovly, C.M.; Humphries, M.J. Real-world ALK Testing Trends in Patients With Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in the United States. Clin. Lung Cancer 2023, 24, e39–e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aisner, D.L.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.R.; Bharat, A.; Bruno, D.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A.; et al. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 497–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penault-Llorca, F.; Kerr, K.M.; Garrido, P.; Thunnissen, E.; Dequeker, E.; Normanno, N.; Patton, S.J.; Fairley, J.; Kapp, J.; de Ridder, D.; et al. Expert opinion on NSCLC small specimen biomarker testing—Part 2: Analysis, reporting, and quality assessment. Virchows Arch. 2022, 481, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Burke, A.P.; Marx, A.; Nicholson, A.G. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart, 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, A.T.; Kim, D.W.; Nakagawa, K.; Seto, T.; Crino, L.; Ahn, M.J.; De Pas, T.; Besse, B.; Solomon, B.J.; Blackhall, F.; et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doebele, R.C.; Pilling, A.B.; Aisner, D.L.; Kutateladze, T.G.; Le, A.T.; Weickhardt, A.J.; Kondo, K.L.; Linderman, D.J.; Heasley, L.E.; Franklin, W.A.; et al. Mechanisms of resistance to crizotinib in patients with ALK gene rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 1472–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 15189:2022; Medical Laboratories—Requirements for Quality and Competence. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Ilie, M.I.; Bence, C.; Hofman, V.; Long-Mira, E.; Butori, C.; Bouhlel, L.; Lalvee, S.; Mouroux, J.; Poudenx, M.; Otto, J.; et al. Discrepancies between FISH and immunohistochemistry for assessment of the ALK status are associated with ALK ‘borderline’-positive rearrangements or a high copy number: A potential major issue for anti-ALK therapeutic strategies. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, M.; Hofman, V.; Bontoux, C.; Heeke, S.; Lespinet-Fabre, V.; Bordone, O.; Lassalle, S.; Lalvee, S.; Tanga, V.; Allegra, M.; et al. Setting Up an Ultra-Fast Next-Generation Sequencing Approach as Reflex Testing at Diagnosis of Non-Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer; Experience of a Single Center (LPCE, Nice, France). Cancers 2022, 14, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacharias, M.; Absenger, G.; Kashofer, K.; Wurm, R.; Lindenmann, J.; Terbuch, A.; Konjic, S.; Sauer, S.; Gollowitsch, F.; Gorkiewicz, G.; et al. Reflex testing in non-small cell lung carcinoma using DNA- and RNA-based next-generation sequencing-a single-center experience. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 4221–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreenivas, A.; Janku, F.; Gouda, M.A.; Chen, H.Z.; George, B.; Kato, S.; Kurzrock, R. ALK fusions in the pan-cancer setting: Another tumor-agnostic target? NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, S.; Conde, E.; Alonso, M.; Illarramendi, A.; Bote de Cabo, H.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Paz-Ares, L.; Lopez-Rios, F. A narrative review of methods for the identification of ALK fusions in patients with non-small cell lung carcinoma. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, S.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Gadgeel, S.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, D.W.; Ou, S.I.; Perol, M.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Rosell, R.; et al. Alectinib versus Crizotinib in Untreated ALK-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Q.; Roy-Chowdhuri, S. Small but powerful: The promising role of small specimens for biomarker testing. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2020, 9, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uruga, H.; Mino-Kenudson, M. ALK (D5F3) CDx: An immunohistochemistry assay to identify ALK-positive NSCLC patients. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2018, 11, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letovanec, I.; Finn, S.; Zygoura, P.; Smyth, P.; Soltermann, A.; Bubendorf, L.; Speel, E.J.; Marchetti, A.; Nonaka, D.; Monkhorst, K.; et al. Evaluation of NGS and RT-PCR Methods for ALK Rearrangement in European NSCLC Patients: Results from the European Thoracic Oncology Platform Lungscape Project. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.; Wang, L.; Arcila, M.E.; Balasubramanian, S.; Greenbowe, J.R.; Ross, J.S.; Stephens, P.; Lipson, D.; Miller, V.A.; Kris, M.G.; et al. Broad, Hybrid Capture-Based Next-Generation Sequencing Identifies Actionable Genomic Alterations in Lung Adenocarcinomas Otherwise Negative for Such Alterations by Other Genomic Testing Approaches. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3631–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofman, V.; Heeke, S.; Bontoux, C.; Chalabreysse, L.; Barritault, M.; Bringuier, P.P.; Fenouil, T.; Benzerdjeb, N.; Begueret, H.; Merlio, J.P.; et al. Ultrafast Gene Fusion Assessment for Nonsquamous NSCLC. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2023, 4, 100457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazdal, D.; Hofman, V.; Christopoulos, P.; Ilie, M.; Stenzinger, A.; Hofman, P. Fusion-positive non-small cell lung carcinoma: Biological principles, clinical practice, and diagnostic implications. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2022, 61, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitiushkina, N.V.; Romanko, A.A.; Preobrazhenskaya, E.V.; Tiurin, V.I.; Ermachenkova, T.I.; Martianov, A.S.; Mulkidjan, R.S.; Sokolova, T.N.; Kholmatov, M.M.; Bizin, I.V.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the test for 5′-/3′-end mRNA unbalanced expression as a screening tool for ALK and ROS1 fusions in lung cancer. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 3226–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, J.N.; Bloom, R.; Forys, J.T.; Hiken, J.; Armstrong, J.R.; Branson, J.; McNulty, S.; Velu, P.D.; Pepin, K.; Abel, H.; et al. Genomic heterogeneity of ALK fusion breakpoints in non-small-cell lung cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2018, 31, 791–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benayed, R.; Offin, M.; Mullaney, K.; Sukhadia, P.; Rios, K.; Desmeules, P.; Ptashkin, R.; Won, H.; Chang, J.; Halpenny, D.; et al. High Yield of RNA Sequencing for Targetable Kinase Fusions in Lung Adenocarcinomas with No Mitogenic Driver Alteration Detected by DNA Sequencing and Low Tumor Mutation Burden. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4712–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeer-Florin, A.; Duruisseaux, M.; Pinsolle, J.; Dubourd, S.; Mondet, J.; Phillips Houlbracq, M.; Magnat, N.; Faure, J.; Chatagnon, A.; de Fraipont, F.; et al. ALK fusion variants detection by targeted RNA-next generation sequencing and clinical responses to crizotinib in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2018, 116, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Brannon, A.R.; Ferris, L.A.; Campbell, C.D.; Lin, J.J.; Schultz, K.R.; Ackil, J.; Stevens, S.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; et al. Tracking the Evolution of Resistance to ALK Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors through Longitudinal Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2018, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.R. Target Enrichment Approaches for Next-Generation Sequencing Applications in Oncology. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, H.L.; Walsh, K.; Diamond, A.; Oniscu, A.; Deans, Z.C. Validation of the Oncomine() focus panel for next-generation sequencing of clinical tumour samples. Virchows Arch. 2018, 473, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, L.; Yan, C.; Ulivi, P.; Denis, M.G.; Christopoulos, P.; et al. Concomitant mutation status of ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancers and its prognostic impact on patients treated with crizotinib. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadal, E.; Bautista, D.; Cabezon-Gutierrez, L.; Ortega, A.L.; Torres, H.; Carcedo, D.; Ruiz de Alda, L.; Garcia, J.F.; Vieitez, P.; Rojo, F. Clinical and economic impact of current ALK rearrangement testing in Spain compared with a hypothetical no-testing scenario. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindeman, N.I.; Cagle, P.T.; Aisner, D.L.; Arcila, M.E.; Beasley, M.B.; Bernicker, E.; Colasacco, C.; Dacic, S.; Hirsch, F.R.; Kerr, K.; et al. Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Guideline From the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buglioni, A.; Caffes, P.L.; Hessler, M.G.; Mansfield, A.S.; Lo, Y.C. Clinical Utility Validation of an Automated Ultrarapid Gene Fusion Assay for NSCLC. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2022, 3, 100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depoilly, T.; Garinet, S.; van Kempen, L.C.; Schuuring, E.; Clave, S.; Bellosillo, B.; Ercolani, C.; Buglioni, S.; Siemanowski, J.; Merkelbach-Bruse, S.; et al. Multicenter Evaluation of the Idylla GeneFusion in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Mol. Diagn. 2022, 24, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, E.; Rojo, F.; Gomez, J.; Enguita, A.B.; Abdulkader, I.; Gonzalez, A.; Lozano, D.; Mancheno, N.; Salas, C.; Salido, M.; et al. Molecular diagnosis in non-small-cell lung cancer: Expert opinion on ALK and ROS1 testing. J. Clin. Pathol. 2022, 75, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canterbury, C.R.; Fernandes, H.; Crapanzano, J.P.; Murty, V.V.; Mansukhani, M.M.; Shu, C.A.; Szabolcs, M.; Saqi, A. ALK Gene Rearrangements in Lung Adenocarcinomas: Concordance of Immunohistochemistry, Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization, RNA In Situ Hybridization, and RNA Next-Generation Sequencing Testing. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2021, 2, 100223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).