Unveiling the RKIP and EGFR Inverse Relationship in Solid Tumors: A Case Study in Cervical Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Silico Analysis
2.2. Tissue Samples
2.3. Immunohistochemistry Analysis (IHC) for RKIP
2.4. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
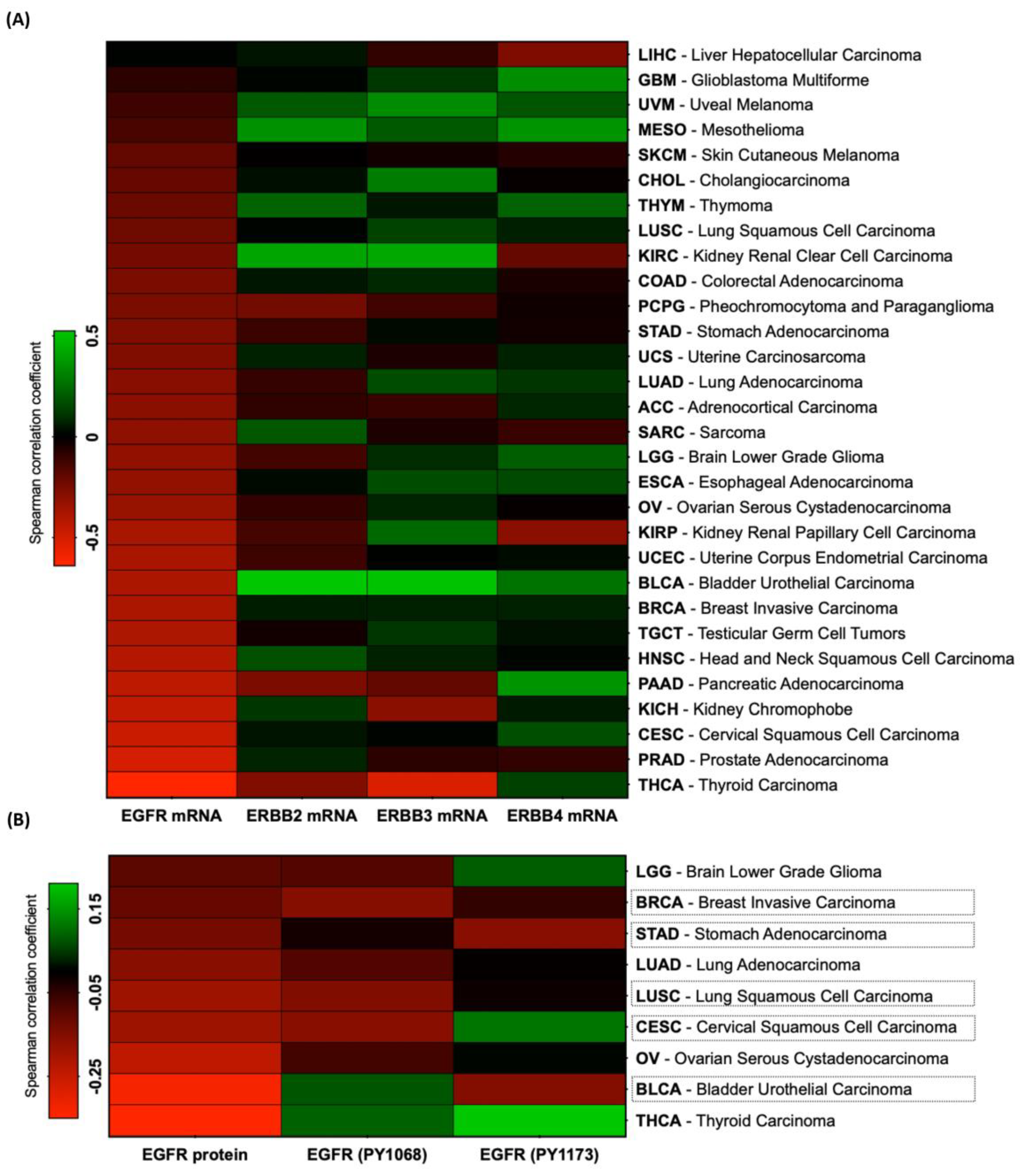
3.1. Correlation between RKIP and HER Receptor Expression in Solid Tumors
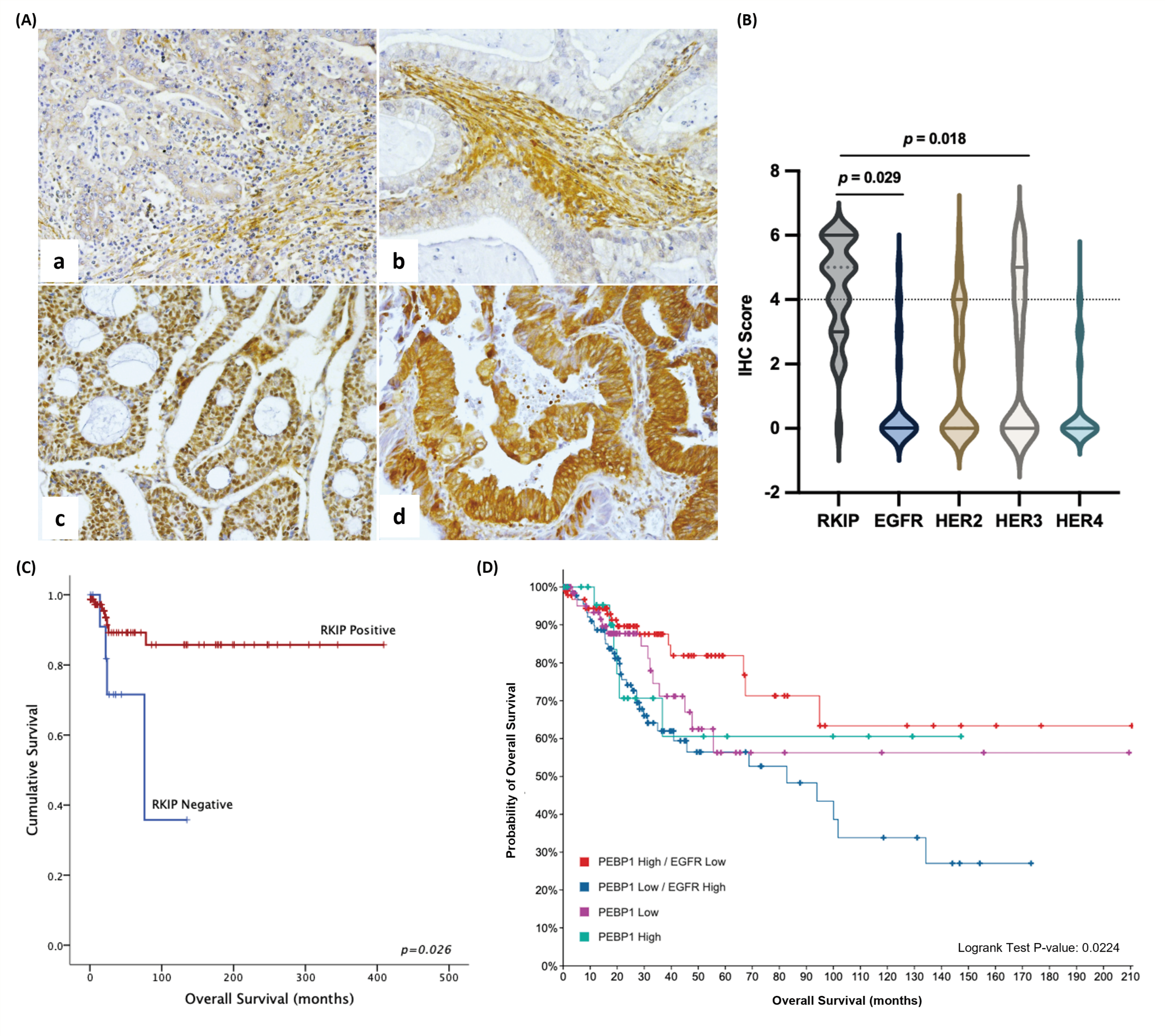
3.2. Clinical Impact of the RKIP/EGFR Negative Feedback Loop in Cervical Cancer
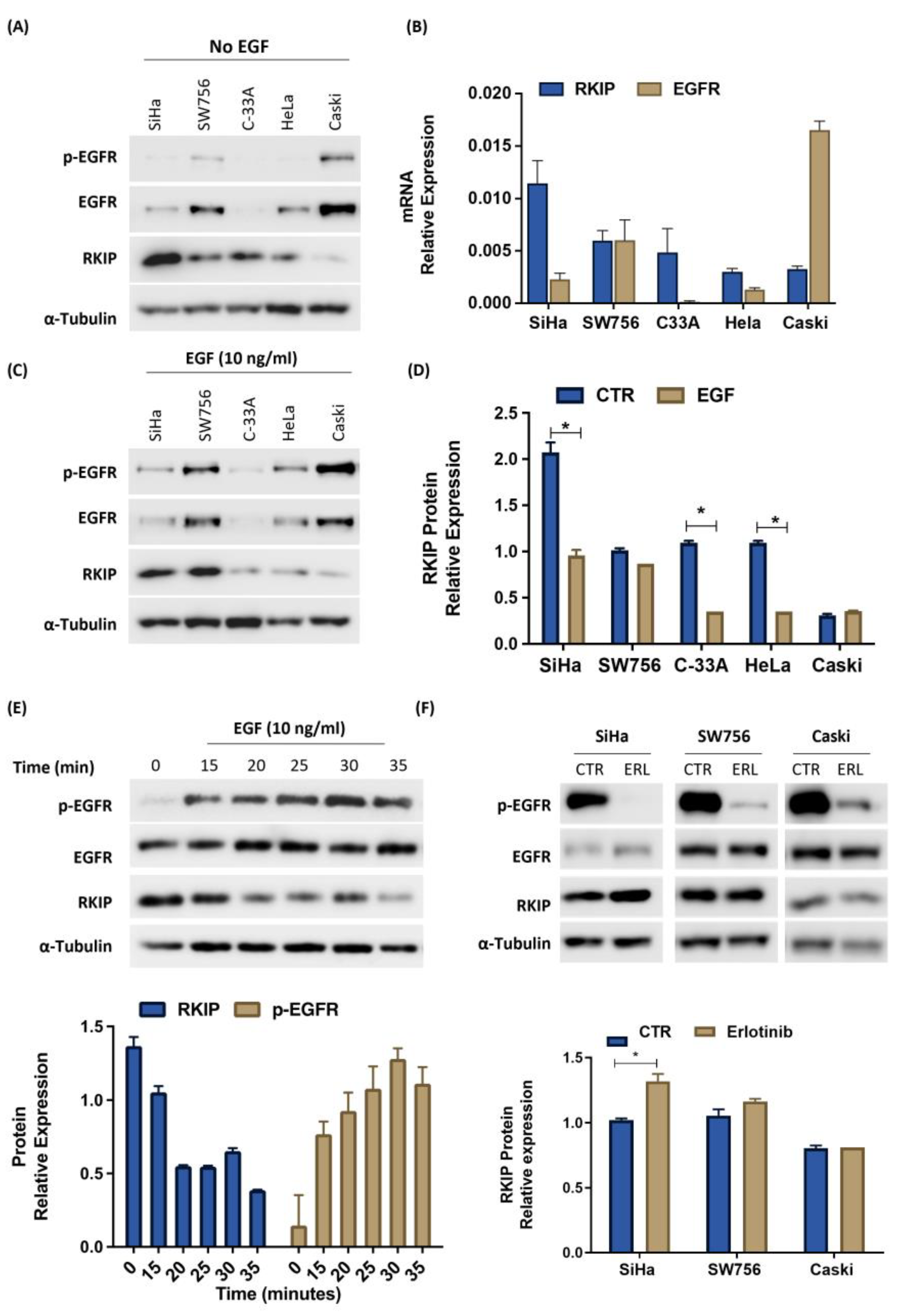
3.3. Oncogenic Interplay between RKIP and EGFR Cervical Cancer Models
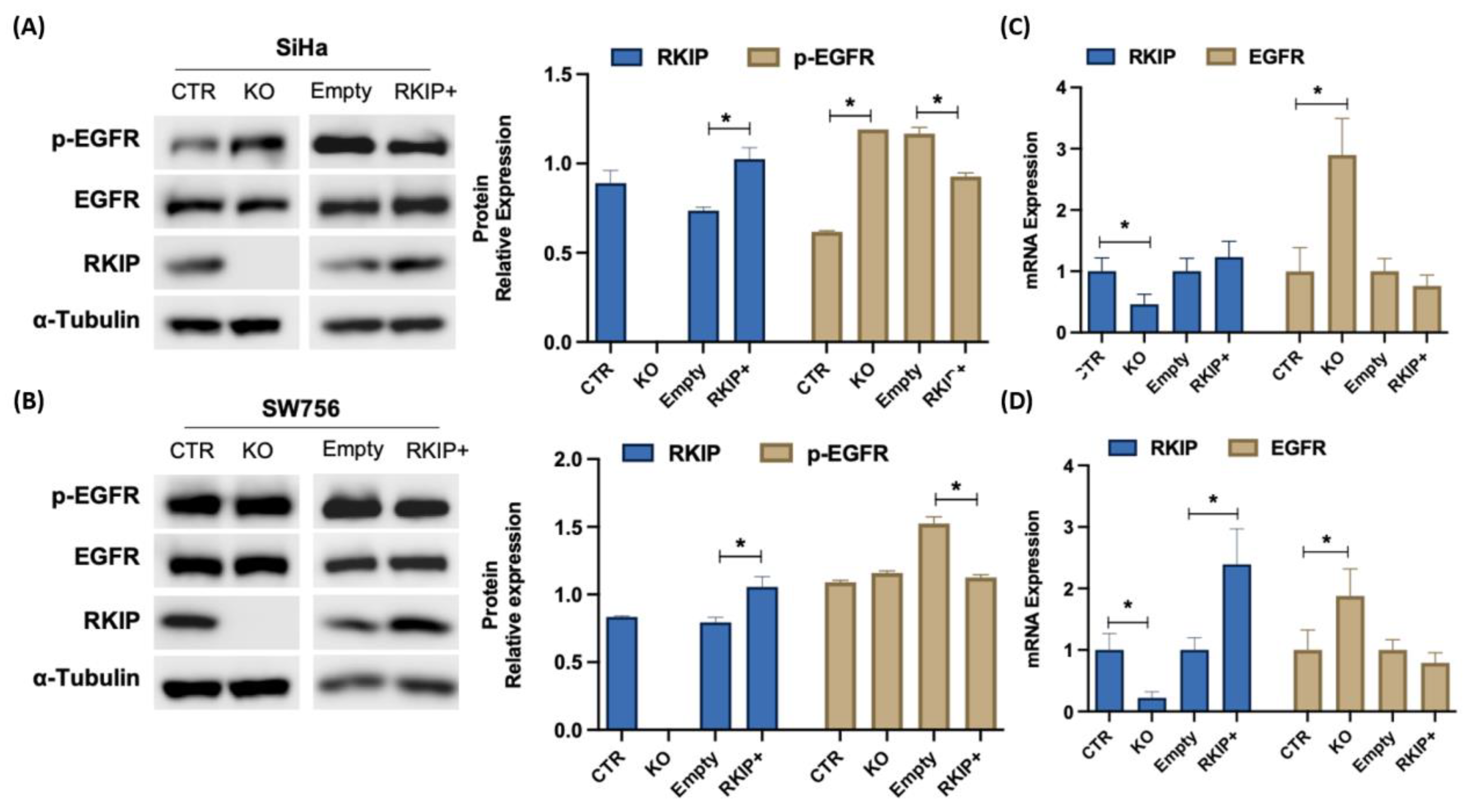
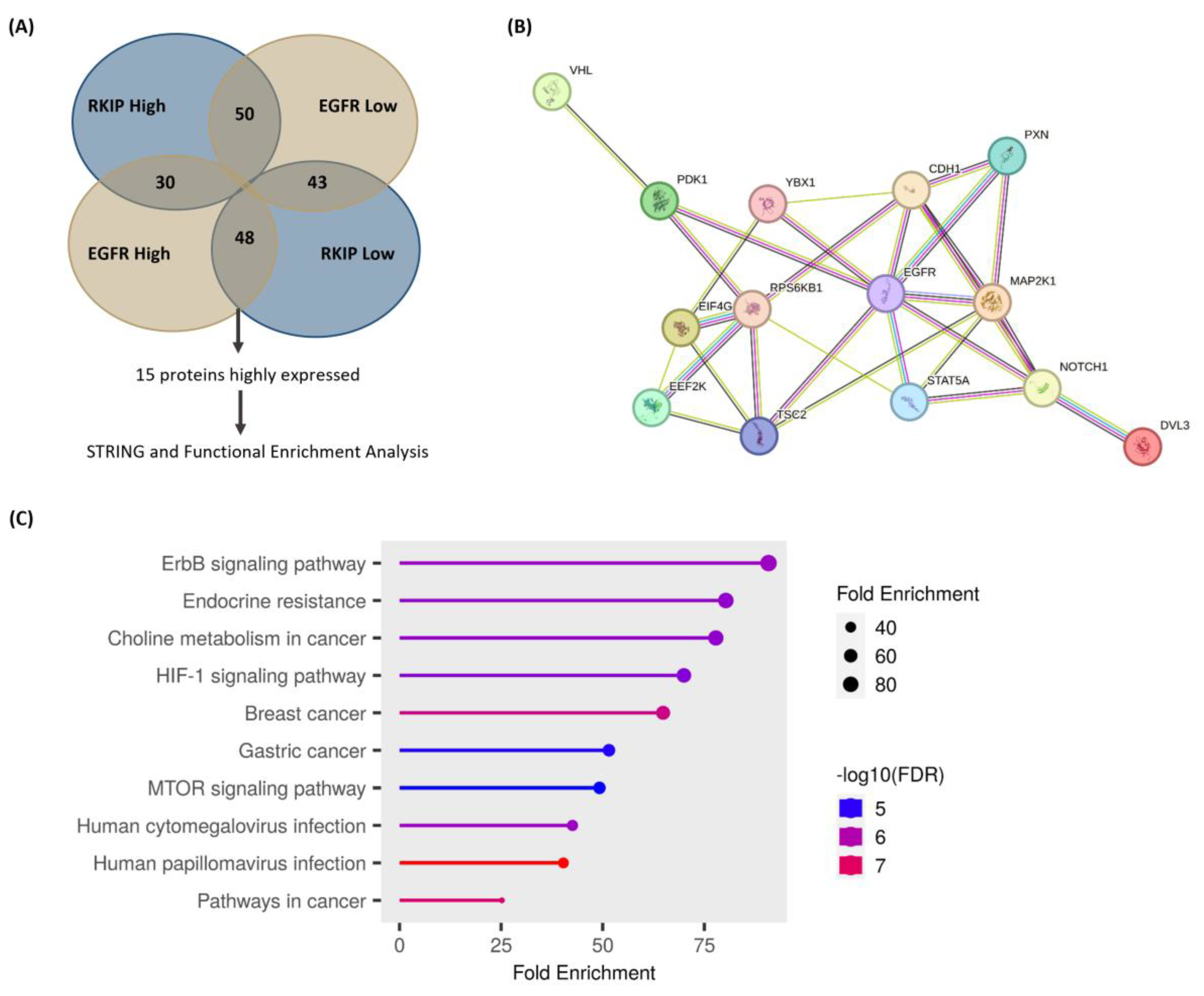
3.4. Molecular Signature of RKIP and EGFR Negative Feedback Loop in Cervical Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, M.A.; Benedet, J.L.; Odicino, F.; Maisonneuve, P.; Beller, U.; Creasman, W.T.; Heintz, A.P.; Ngan, H.Y.; Pecorelli, S. Carcinoma of the Cervix Uteri. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2006, 95, S43–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueñas-Gonzalez, A.; Serrano-Olvera, A.; Cetina, L.; Coronel, J. New Molecular Targets against Cervical Cancer. Int. J. Womens Health 2014, 6, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, H.J.; Ulak, R.; Ki, K.D.; Lee, J.M. Cytotoxic and Targeted Systemic Therapy in Advanced and Recurrent Cervical Cancer: Experience from Clinical Trials. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2014, 232, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, K.S.; Sill, M.W.; Penson, R.T.; Huang, H.; Ramondetta, L.M.; Landrum, L.M.; Oaknin, A.; Reid, T.J.; Leitao, M.M.; Michael, H.E.; et al. Bevacizumab for Advanced Cervical Cancer: Final Overall Survival and Adverse Event Analysis of a Randomised, Controlled, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial (Gynecologic Oncology Group 240). Lancet 2017, 390, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, N.; Dubot, C.; Lorusso, D.; Caceres, M.V.; Hasegawa, K.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Tewari, K.S.; Salman, P.; Hoyos Usta, E.; Yañez, E.; et al. Pembrolizumab for Persistent, Recurrent, or Metastatic Cervical Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1856–1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrriquez, E.N.; Zakhour, M.; Salani, R. Precision Medicine for Cervical Cancer. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2022, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, O.; Silva-Oliveira, R.; Cury, F.P.; Barbosa, A.M.; Granja, S.; Evangelista, A.F.; Marques, F.; Miranda-Gonçalves, V.; Cardoso-Carneiro, D.; de Paula, F.E.; et al. HER Family Receptors Are Important Theranostic Biomarkers for Cervical Cancer: Blocking Glucose Metabolism Enhances the Therapeutic Effect of HER Inhibitors. Theranostics 2017, 7, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J.; Ferguson, K.M. The EGFR Family: Not So Prototypical Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a020768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Parker, B.A.; Schwab, R.; Kurzrock, R. HER2 Aberrations in Cancer: Implications for Therapy. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arteaga, C.L. ErbB-Targeted Therapeutic Approaches in Human Cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 284, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, J.M.; Valge-Archer, V.E. Development Trends for Monoclonal Antibody Cancer Therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawver, L.K.; Slamon, D.; Ullrich, A. Smart Drugs: Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Cancer Cell 2002, 1, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonkers, J.; Berns, A. Oncogene Addiction: Sometimes a Temporary Slavery. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 535–538. [Google Scholar]
- Vakiani, E.; Solit, D.B. KRAS and BRAF: Drug Targets and Predictive Biomarkers. J. Pathol. 2011, 223, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Cappuzzo, F. Predictive Value of EGFR and HER2 Overexpression in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Oncogene 2009, 28 (Suppl. S1), S32–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, M.M.; Morrison, D.K. Integrating Signals from RTKs to ERK/MAPK. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3113–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso-Carneiro, D.; Raquel-Cunha, A.; Pinheiro, J.; Gabriela-Freitas, M.; Fontão, P.; Reis, R.M.; Martinho, O. Implications of RKIP Protein in Cancer Prognosis and Therapy Response: A Literature Update. In Prognostic and Therapeutic Applications of RKIP in Cancer; Bonavida, B., Baritaki, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 389–414. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, A.A.; Howitt, B.E.; Myers, A.P.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Palescandolo, E.; Van Hummelen, P.; MacConaill, L.E.; Shoni, M.; Wagle, N.; Jones, R.T.; et al. Oncogenic Mutations in Cervical Cancer: Genomic Differences between Adenocarcinomas and Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Cervix. Cancer 2013, 119, 3776–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, O.; Pinto, F.; Granja, S.; Miranda-Goncalves, V.; Moreira, M.A.; Ribeiro, L.F.; di Loreto, C.; Rosner, M.R.; Longatto-Filho, A.; Reis, R.M. RKIP Inhibition in Cervical Cancer Is Associated with Higher Tumor Aggressive Behavior and Resistance to Cisplatin Therapy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandamme, D.; Herrero, A.; Al-Mulla, F.; Kolch, W. Regulation of the MAPK Pathway by Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2014, 19, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yesilkanal, A.E.; Rosner, M.R. Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein (RKIP) as a Metastasis Suppressor: Regulation of Signaling Networks in Cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2014, 19, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, K.; Schmid, E.; Deiss, K. RKIP: A Governor of Intracellular Signaling. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2014, 19, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.X.; Jung, D.; Yao, R. ShinyGO: A Graphical Gene-Set Enrichment Tool for Animals and Plants. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2628–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein-Protein Association Networks with Increased Coverage, Supporting Functional Discovery in Genome-Wide Experimental Datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatla, N.; Berek, J.S.; Cuello Fredes, M.; Denny, L.A.; Grenman, S.; Karunaratne, K.; Kehoe, S.T.; Konishi, I.; Olawaiye, A.B.; Prat, J.; et al. Revised FIGO Staging for Carcinoma of the Cervix Uteri. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2019, 145, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenciarelli, C.; Marei, H.E.; Zonfrillo, M.; Pierimarchi, P.; Paldino, E.; Casalbore, P.; Felsani, A.; Vescovi, A.L.; Maira, G.; Mangiola, A. PDGF Receptor Alpha Inhibition Induces Apoptosis in Glioblastoma Cancer Stem Cells Refractory to Anti-Notch and Anti-EGFR Treatment. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, F.; Pértega-Gomes, N.; Pereira, M.S.; Vizcaíno, J.R.; Monteiro, P.; Henrique, R.M.; Baltazar, F.; Andrade, R.P.; Reis, R.M. T-box Transcription Factor Brachyury Is Associated with Prostate Cancer Progression and Aggressiveness. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4949–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z. ErbB Receptors and Cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1652, 3–35. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, R.I.; Gee, J.M.; Harper, M.E. EGFR and Cancer Prognosis. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37 (Suppl. S4), S9–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.J.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, G.M. Immunohistochemical Detection of Raf Kinase Inhibitor Protein in Normal Cervical Tissue and Cervical Cancer Tissue. J. Int. Med. Res. 2011, 39, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longatto-Filho, A.; Pinheiro, C.; Martinho, O.; Moreira, M.A.; Ribeiro, L.F.; Queiroz, G.S.; Schmitt, F.C.; Baltazar, F.; Reis, R. Molecular Characterization of EGFR, PDGFRA and VEGFR2 in Cervical Adenosquamous Carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Shrieve, D.C.; Zempolich, K.A.; Lee, R.J.; Hammond, E.; Handrahan, D.L.; Gaffney, D.K. Correlation between Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Family (EGFR, HER2, HER3, HER4), Phosphorylated Akt (P-Akt), and Clinical Outcomes after Radiation Therapy in Carcinoma of the Cervix. Gynecol. Oncol. 2005, 99, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannetti, E.; Labots, M.; Dekker, H.; Galvani, E.; Lind, J.S.; Sciarrillo, R.; Honeywell, R.; Smit, E.F.; Verheul, H.M.; Peters, G.J. Molecular Mechanisms and Modulation of Key Pathways Underlying the Synergistic Interaction of Sorafenib with Erlotinib in Non-Small-Cell-Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Cells. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trakul, N.; Menard, R.E.; Schade, G.R.; Qian, Z.; Rosner, M.R. Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein Regulates Raf-1 but Not B-Raf Kinase Activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 24931–24940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Nakamura, K.; Takeda, T.; Chiwaki, F.; Banno, K.; Aoki, D.; Takeshita, F.; Sasaki, H. Aurora Kinase Blockade Drives De Novo Addiction of Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma to Druggable EGFR Signaling. Oncogene 2022, 41, 2326–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eves, E.M.; Shapiro, P.; Naik, K.; Klein, U.R.; Trakul, N.; Rosner, M.R. Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein Regulates Aurora B Kinase and the Spindle Checkpoint. Mol. Cell 2006, 23, 561–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosner, M.R. MAP kinase meets mitosis: A role for Raf Kinase Inhibitory Protein in spindle checkpoint regulation. Cell Div. 2007, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| Mutual Exclusivity | Co-Expression | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | Neither | A Not B | B Not A | Both | Log2 OR | p-Value * | Tendency | Spearman Correlation | p-Value * |
| PEBP1 | EGFR | 8480 | 510 | 835 | 25 | −1.006 | <0.001 | Mutual exclusivity | −0.32 | 7.18 × 10−229 |
| PEBP1 | ERBB4 | 8972 | 499 | 343 | 36 | 0.916 | <0.001 | Co-occurrence | 0.04 | 1.099 × 10−5 |
| PEBP1 | ERBB2 | 8476 | 469 | 839 | 66 | 0.508 | 0.008 | Co-occurrence | 0.06 | 9.32 × 10−10 |
| PEBP1 | ERBB3 | 8792 | 491 | 523 | 44 | 0.591 | 0.010 | Co-occurrence | 0.07 | 1.09 × 10−10 |
| Protein | Cytoband | p-Value | q-Value * | Molecular Function 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | 7p11.2 | 0.00 | 0.00 | RTK signaling |
| NOTCH1 | 9q34.3 | 1.05 × 10−13 | 1.06 × 10−11 | NOTCH signaling |
| EEF2K | 16p12.2 | 1.504 × 10−6 | 8.466 × 10−5 | Protein synthesis |
| VHL | 3p25.3 | 1.668 × 10−6 | 8.466 × 10−5 | HIF-1 signaling |
| EIF4G1 | 3q27.1 | 3.610 × 10−6 | 1.466 × 10−4 | RNA binding and transport |
| p-EGFR (Tyr1068) | 6.903 × 10−6 | 2.335 × 10−4 | RTK signaling | |
| DVL3 | 3q27.1 | 9.316 × 10−5 | 1.576 × 10−3 | Wnt signaling |
| STAT5A | 17q21.2 | 2.484 × 10−4 | 3.843 × 10−3 | JAK-STAT signaling pathway |
| MAP2K1 | 15q22.31 | 2.650 × 10−4 | 3.843 × 10−3 | MAPK signaling |
| YBX1 | 1p34.2 | 7.978 × 10−4 | 9.527 × 10−3 | mRNA splicing |
| p-PDK1 (Ser241) | 9.093 × 10−4 | 0.0103 | HIF-1 signaling | |
| RPS6KB1 | 17q23.1 | 1.719 × 10−3 | 0.0174 | mTOR and PI3K/AKT signaling |
| TSC2 | 16p13.3 | 2.189 × 10−3 | 0.0212 | mTOR and PI3K/AKT signaling |
| PXN | 12q24.23 | 2.521 × 10−3 | 0.0213 | Cell junction/ECM organization |
| CDH1 | 16q22.1 | 2.800 × 10−3 | 0.0219 | Cell junction/ECM organization |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardoso-Carneiro, D.; Pinheiro, J.; Fontão, P.; Nogueira, R.; Gabriela-Freitas, M.; Raquel-Cunha, A.; Mendes, A.; Longatto-Filho, A.; Marques, F.; Moreira, M.A.R.; et al. Unveiling the RKIP and EGFR Inverse Relationship in Solid Tumors: A Case Study in Cervical Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16122182
Cardoso-Carneiro D, Pinheiro J, Fontão P, Nogueira R, Gabriela-Freitas M, Raquel-Cunha A, Mendes A, Longatto-Filho A, Marques F, Moreira MAR, et al. Unveiling the RKIP and EGFR Inverse Relationship in Solid Tumors: A Case Study in Cervical Cancer. Cancers. 2024; 16(12):2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16122182
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardoso-Carneiro, Diana, Joana Pinheiro, Patrícia Fontão, Rosete Nogueira, Maria Gabriela-Freitas, Ana Raquel-Cunha, Adriana Mendes, Adhemar Longatto-Filho, Fábio Marques, Marise A. R. Moreira, and et al. 2024. "Unveiling the RKIP and EGFR Inverse Relationship in Solid Tumors: A Case Study in Cervical Cancer" Cancers 16, no. 12: 2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16122182
APA StyleCardoso-Carneiro, D., Pinheiro, J., Fontão, P., Nogueira, R., Gabriela-Freitas, M., Raquel-Cunha, A., Mendes, A., Longatto-Filho, A., Marques, F., Moreira, M. A. R., Reis, R. M., & Martinho, O. (2024). Unveiling the RKIP and EGFR Inverse Relationship in Solid Tumors: A Case Study in Cervical Cancer. Cancers, 16(12), 2182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16122182









