Radiotherapy for Recurrent Medulloblastoma in Children and Adolescents: Survival after Re-Irradiation and First-Time Irradiation
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cohort
2.2. Treatment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Ethical Approval
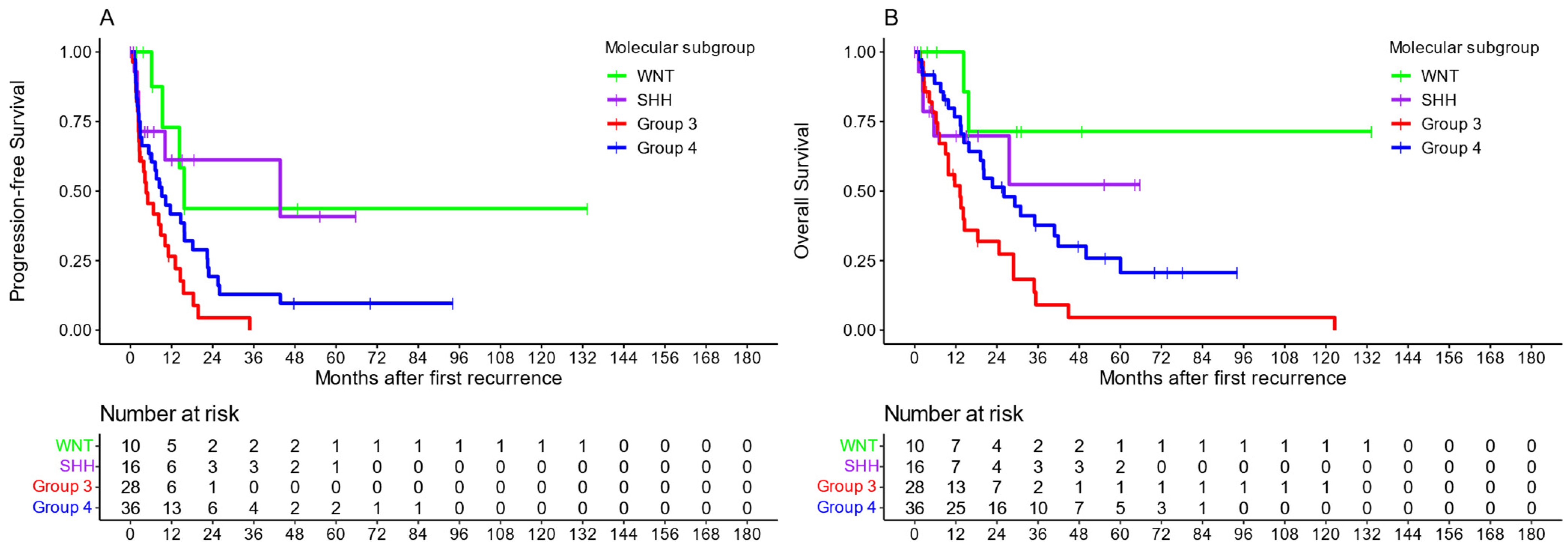
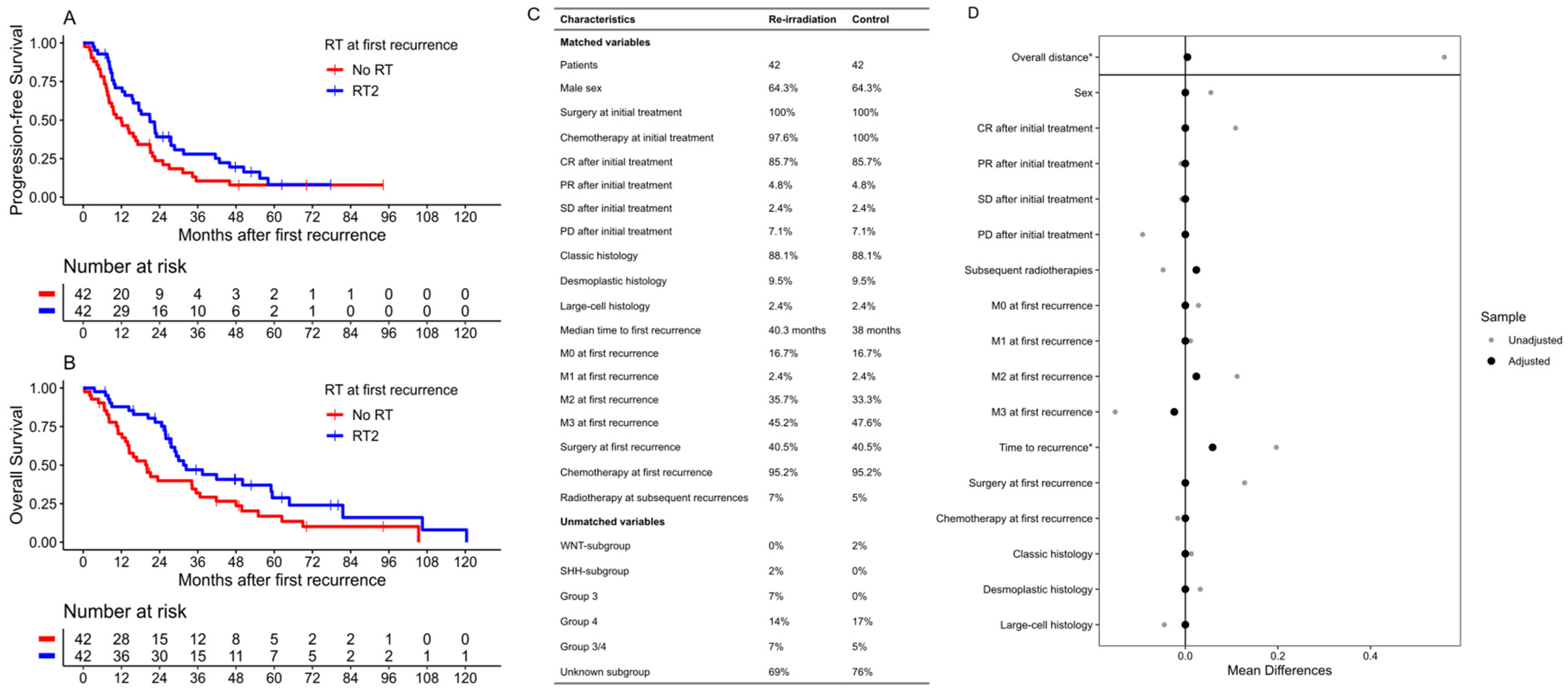
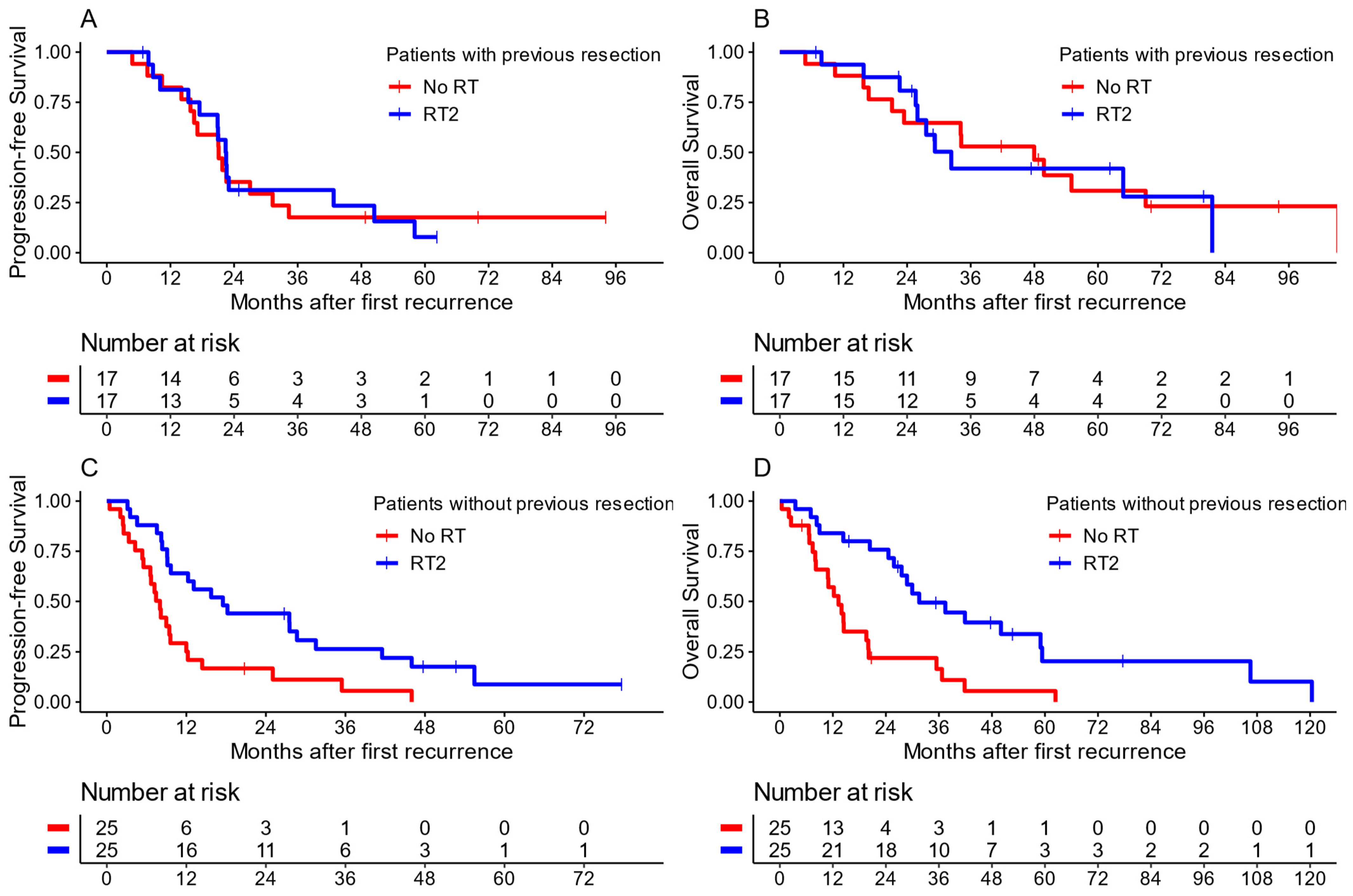
3. Results
3.1. Re-Irradiation
3.2. First Radiotherapy at First Recurrence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rieken, S.; Mohr, A.; Habermehl, D.; Welzel, T.; Lindel, K.; Witt, O.; Kulozik, A.E.; Wick, W.; Debus, J.; Combs, S.E. Outcome and prognostic factors of radiation therapy for medulloblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 81, e7–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seidel, C.; Heider, S.; Hau, P.; Glasow, A.; Dietzsch, S.; Kortmann, R.D. Radiotherapy in Medulloblastoma-Evolution of Treatment, Current Concepts and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2021, 13, 5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroni, L.V.; Freytes, C.; Fernandez Ponce, N.; Oller, A.; Pinto, N.; Gonzalez, A.; Maldonado, F.R.; Sampor, C.; Rugilo, C.; Lubieniecki, F.; et al. Craniospinal irradiation as part of re-irradiation for children with recurrent medulloblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2021, 155, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.L.; Armstrong, C.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Wu, S.; Wallace, D.; Bonner, M.J.; Schreiber, J.; Swain, M.; Chapieski, L.; Mabbott, D.; et al. Processing speed, attention, and working memory after treatment for medulloblastoma: An international, prospective, and longitudinal study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3494–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moxon-Emre, I.; Bouffet, E.; Taylor, M.D.; Laperriere, N.; Scantlebury, N.; Law, N.; Spiegler, B.J.; Malkin, D.; Janzen, L.; Mabbott, D. Impact of craniospinal dose, boost volume, and neurologic complications on intellectual outcome in patients with medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottensmeier, H.; Schlegel, P.G.; Eyrich, M.; Wolff, J.E.; Juhnke, B.O.; von Hoff, K.; Frahsek, S.; Schmidt, R.; Faldum, A.; Fleischhack, G.; et al. Treatment of children under 4 years of age with medulloblastoma and ependymoma in the HIT2000/HIT-REZ 2005 trials: Neuropsychological outcome 5 years after treatment. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, S.L.; Goloubeva, O.; Reddick, W.E.; Glass, J.O.; Gajjar, A.; Kun, L.; Merchant, T.E.; Mulhern, R.K. Patterns of intellectual development among survivors of pediatric medulloblastoma: A longitudinal analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 2302–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallen, G.; Resch, A.; Calaminus, G.; Wiener, A.; Leiss, U.; Pletschko, T.; Friedrich, C.; Langer, T.; Grabow, D.; Driever, P.H.; et al. Strategies to improve the quality of survival for childhood brain tumour survivors. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2015, 19, 619–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milker-Zabel, S.; Zabel, A.; Thilmann, C.; Zuna, I.; Hoess, A.; Wannenmacher, M.; Debus, J. Results of three-dimensional stereotactically-guided radiotherapy in recurrent medulloblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2002, 60, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, D.S.; Sarhan, N.; Ramaswamy, V.; Nobre, L.; Yee, R.; Taylor, M.D.; Hawkins, C.; Bartels, U.; Huang, A.; Tabori, U.; et al. Re-irradiation for children with recurrent medulloblastoma in Toronto, Canada: A 20-year experience. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 145, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetmore, C.; Herington, D.; Lin, T.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Gajjar, A.; Merchant, T.E. Reirradiation of recurrent medulloblastoma: Does clinical benefit outweigh risk for toxicity? Cancer 2014, 120, 3731–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunkel, I.J.; Gardner, S.L.; Garvin, J.H., Jr.; Goldman, S.; Shi, W.; Finlay, J.L. High-dose carboplatin, thiotepa, and etoposide with autologous stem cell rescue for patients with previously irradiated recurrent medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2010, 12, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massimino, M.; Gandola, L.; Spreafico, F.; Biassoni, V.; Luksch, R.; Collini, P.; Solero, C.N.; Simonetti, F.; Pignoli, E.; Cefalo, G.; et al. No salvage using high-dose chemotherapy plus/minus reirradiation for relapsing previously irradiated medulloblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 73, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowski, S.; Gerber, N.U.; von Hoff, K.; Gnekow, A.; Bode, U.; Graf, N.; Berthold, F.; Henze, G.; Wolff, J.E.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; et al. Treatment of early childhood medulloblastoma by postoperative chemotherapy and deferred radiotherapy. Neuro Oncol. 2009, 11, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, R.G.; Wilne, S.H.; Robinson, K.J.; Ironside, J.W.; Cox, T.; Chong, W.K.; Michalski, A.; Campbell, R.H.; Bailey, C.C.; Thorp, N.; et al. Primary postoperative chemotherapy without radiotherapy for treatment of brain tumours other than ependymoma in children under 3 years: Results of the first UKCCSG/SIOP CNS 9204 trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grill, J.; Sainte-Rose, C.; Jouvet, A.; Gentet, J.C.; Lejars, O.; Frappaz, D.; Doz, F.; Rialland, X.; Pichon, F.; Bertozzi, A.I.; et al. Treatment of medulloblastoma with postoperative chemotherapy alone: An SFOP prospective trial in young children. Lancet Oncol. 2005, 6, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.M.; Richardson, S.; Schwalbe, E.C.; Hicks, D.; Lindsey, J.C.; Crosier, S.; Rafiee, G.; Grabovska, Y.; Wharton, S.B.; Jacques, T.S.; et al. Time, pattern, and outcome of medulloblastoma relapse and their association with tumour biology at diagnosis and therapy: A multicentre cohort study. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, K.; Mynarek, M.; Zwiener, I.; Siegler, N.; Zimmermann, M.; Christiansen, H.; Budach, W.; Henke, G.; Warmuth-Metz, M.; Pietsch, T.; et al. Postponed is not canceled: Role of craniospinal radiation therapy in the management of recurrent infant medulloblastoma--an experience from the HIT-REZ 1997 & 2005 studies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 88, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kameda-Smith, M.M.; Wang, A.; Abdulhadi, N.; Voth, R.; Sergeant, A.; Maharaj, A.; Bakhshinyan, D.; Adile, A.A.; Pai, A.M.; Ajani, O.; et al. Salvage Therapy for Childhood Medulloblastoma: A Single Center Experience. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 46, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.; Tong, Y.; Robinson, G.; Thompson, M.C.; Currle, D.S.; Eden, C.; Kranenburg, T.A.; Hogg, T.; Poppleton, H.; Martin, J.; et al. Subtypes of medulloblastoma have distinct developmental origins. Nature 2010, 468, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.D.; Northcott, P.A.; Korshunov, A.; Remke, M.; Cho, Y.J.; Clifford, S.C.; Eberhart, C.G.; Parsons, D.W.; Rutkowski, S.; Gajjar, A.; et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: The current consensus. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.W.; Orr, B.A.; Wu, G.; Gururangan, S.; Lin, T.; Qaddoumi, I.; Packer, R.J.; Goldman, S.; Prados, M.D.; Desjardins, A.; et al. Vismodegib Exerts Targeted Efficacy Against Recurrent Sonic Hedgehog-Subgroup Medulloblastoma: Results from Phase II Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium Studies PBTC-025B and PBTC-032. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2646–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, V.; Torrejon, J.; Kariyawasam, D.; Berlanga, P.; Guerrini-Rousseau, L.; Ayrault, O.; Varlet, P.; Tauziede-Espariat, A.; Puget, S.; Bolle, S.; et al. Clinical and molecular analysis of smoothened inhibitors in Sonic Hedgehog medulloblastoma. Neurooncol. Adv. 2021, 3, vdab097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajjar, A.; Robinson, G.W.; Smith, K.S.; Lin, T.; Merchant, T.E.; Chintagumpala, M.; Mahajan, A.; Su, J.; Bouffet, E.; Bartels, U.; et al. Outcomes by Clinical and Molecular Features in Children with Medulloblastoma Treated with Risk-Adapted Therapy: Results of an International Phase III Trial (SJMB03). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, D.R.; Fleischhack, G.; Milde, T.; Pajtler, K.W. The Current Landscape of Targeted Clinical Trials in Non-WNT/Non-SHH Medulloblastoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mynarek, M.; Milde, T.; Padovani, L.; Janssens, G.O.; Kwiecien, R.; Mosseri, V.; Clifford, S.C.; Doz, F.; Rutkowski, S. SIOP PNET5 MB Trial: History and Concept of a Molecularly Stratified Clinical Trial of Risk-Adapted Therapies for Standard-Risk Medulloblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakst, R.L.; Dunkel, I.J.; Gilheeney, S.; Khakoo, Y.; Becher, O.; Souweidane, M.M.; Wolden, S.L. Reirradiation for recurrent medulloblastoma. Cancer 2011, 117, 4977–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T.; Maitre, M.; Sastri, G.J.; Krishnatry, R.; Shirsat, N.; Epari, S.; Sahay, A.; Chinnaswamy, G.; Patil, V.; Shetty, P.; et al. Outcomes of salvage re-irradiation in recurrent medulloblastoma correlate with age at initial diagnosis, primary risk-stratification, and molecular subgrouping. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 144, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balter-Seri, J.; Mor, C.; Shuper, A.; Zaizov, R.; Cohen, I.J. Cure of recurrent medulloblastoma: The contribution of surgical resection at relapse. Cancer 1997, 79, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalski, J.M.; Janss, A.J.; Vezina, L.G.; Smith, K.S.; Billups, C.A.; Burger, P.C.; Embry, L.M.; Cullen, P.L.; Hardy, K.K.; Pomeroy, S.L.; et al. Children’s Oncology Group Phase III Trial of Reduced-Dose and Reduced-Volume Radiotherapy with Chemotherapy for Newly Diagnosed Average-Risk Medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2685–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gururangan, S.; Krauser, J.; Watral, M.A.; Driscoll, T.; Larrier, N.; Reardon, D.A.; Rich, J.N.; Quinn, J.A.; Vredenburgh, J.J.; Desjardins, A.; et al. Efficacy of high-dose chemotherapy or standard salvage therapy in patients with recurrent medulloblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2008, 10, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, D.C.; Gargan, L.; Weprin, B.E.; Mulne, A.F.; Elterman, R.D.; Munoz, L.; Giller, C.A.; Winick, N.J. Impact of site of tumor recurrence upon survival for children with recurrent or progressive medulloblastoma. J. Neurosurg. 2007, 107, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajjar, A.; Mulhern, R.K.; Heideman, R.L.; Sanford, R.A.; Douglass, E.C.; Kovnar, E.H.; Langston, J.A.; Jenkins, J.J.; Kun, L.E. Medulloblastoma in very young children: Outcome of definitive craniospinal irradiation following incomplete response to chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 1994, 12, 1212–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Smith, K.S.; Deng, M.; Terhune, C.; Robinson, G.W.; Orr, B.A.; Liu, A.P.Y.; Lin, T.; Billups, C.A.; Chintagumpala, M.; et al. Clinical Outcomes and Patient-Matched Molecular Composition of Relapsed Medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Remke, M.; Bouffet, E.; Faria, C.C.; Perreault, S.; Cho, Y.J.; Shih, D.J.; Luu, B.; Dubuc, A.M.; Northcott, P.A.; et al. Recurrence patterns across medulloblastoma subgroups: An integrated clinical and molecular analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafay-Cousin, L.; Smith, A.; Chi, S.N.; Wells, E.; Madden, J.; Margol, A.; Ramaswamy, V.; Finlay, J.; Taylor, M.D.; Dhall, G.; et al. Clinical, Pathological, and Molecular Characterization of Infant Medulloblastomas Treated with Sequential High-Dose Chemotherapy. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.; Hill, R.M.; Kui, C.; Lindsey, J.C.; Grabovksa, Y.; Keeling, C.; Pease, L.; Bashton, M.; Crosier, S.; Vinci, M.; et al. Emergence and maintenance of actionable genetic drivers at medulloblastoma relapse. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Taylor, M.D. Medulloblastoma: From Myth to Molecular. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, V.; Remke, M.; Adamski, J.; Bartels, U.; Tabori, U.; Wang, X.; Huang, A.; Hawkins, C.; Mabbott, D.; Laperriere, N.; et al. Medulloblastoma subgroup-specific outcomes in irradiated children: Who are the true high-risk patients? Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, N.; Ramaswamy, V.; Remke, M.; Pfaff, E.; Shih, D.J.; Martin, D.C.; Castelo-Branco, P.; Baskin, B.; Ray, P.N.; Bouffet, E.; et al. Subgroup-specific prognostic implications of TP53 mutation in medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2927–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, A.S.; Krailo, M.; Chi, S.; Villaluna, D.; Springer, L.; Williams-Hughes, C.; Fouladi, M.; Gajjar, A. Temozolomide with irinotecan versus temozolomide, irinotecan plus bevacizumab for recurrent medulloblastoma of childhood: Report of a COG randomized Phase II screening trial. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e29031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrl, A.; Chocholous, M.; Kieran, M.W.; Azizi, A.A.; Prucker, C.; Czech, T.; Dieckmann, K.; Schmook, M.T.; Haberler, C.; Leiss, U.; et al. Antiangiogenic metronomic therapy for children with recurrent embryonal brain tumors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2012, 59, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaab, C.; Adolph, J.E.; Tippelt, S.; Mikasch, R.; Obrecht, D.; Mynarek, M.; Rutkowski, S.; Pfister, S.M.; Milde, T.; Witt, O.; et al. Local and Systemic Therapy of Recurrent Medulloblastomas in Children and Adolescents: Results of the P-HIT-REZ 2005 Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Teuff, G.; Castaneda-Heredia, A.; Dufour, C.; Jaspan, T.; Calmon, R.; Devos, A.; McHugh, K.; Leblond, P.; Frappaz, D.; Aerts, I.; et al. Phase II study of temozolomide and topotecan (TOTEM) in children with relapsed or refractory extracranial and central nervous system tumors including medulloblastoma with post hoc Bayesian analysis: A European ITCC study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Overall, n = 293 1 | First Irradiation, n = 39 1 | Re-Irradiation, n = 56 1 | No Re-Irradiation, n = 184 1 | No Radiation, n = 14 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||||
| male | 206 (70%) | 31 (79%) | 40 (71%) | 128 (70%) | 7 (50%) |
| female | 87 (30%) | 8 (21%) | 16 (29%) | 56 (30%) | 7 (50%) |
| Age at first recurrence; years (IQR) | 9.4 (6.2, 13.0) | 4.6 (3.4, 6.3) | 11.2 (8.4, 14.7) | 11.0 (7.8, 14.2) | 2.7 (2.1, 3.5) |
| Time to first recurrence from initial diagnosis; months (IQR) | 21.6 (15.1, 42.1) | 16.2 (13.7, 20.5) | 32.7 (23.2, 47.7) | 22.2 (15.6, 42.9) | 14.8 (8.8, 15.5) |
| Molecular subgroup | |||||
| WNT | 10 (9.3%) | 1 (5.9%) | 0 (0%) | 9 (13%) | 0 (0%) |
| SHH | 16 (15%) | 7 (41%) | 1 (6.7%) | 4 (5.8%) | 4 (67%) |
| Group 3 | 28 (26%) | 7 (41%) | 3 (20%) | 16 (23%) | 2 (33%) |
| Group 4 | 36 (34%) | 1 (5.9%) | 7 (47%) | 28 (41%) | 0 (0%) |
| Group 3/4 | 17 (16%) | 1 (5.9%) | 4 (27%) | 12 (17%) | 0 (0%) |
| Resection during initial treatment | 280 (96%) | 39 (100%) | 53 (95%) | 174 (95%) | 14 (100%) |
| GTR | 167 (60%) | 27 (69%) | 34 (64%) | 98 (56%) | 8 (57%) |
| NTR | 74 (26%) | 8 (21%) | 12 (23%) | 50 (29%) | 4 (29%) |
| STR | 35 (13%) | 4 (10%) | 7 (13%) | 23 (13%) | 1 (7.1%) |
| Biopsy | 4 (1.4%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (1.7%) | 1 (7.1%) |
| Chemotherapy during initial treatment | 288 (98%) | 37 (95%) | 54 (96%) | 183 (99%) | 14 (100%) |
| Chang stage at first recurrence | |||||
| M0 | 51 (17%) | 12 (31%) | 9 (16%) | 26 (14%) | 4 (29%) |
| M1 | 6 (2.0%) | 1 (2.6%) | 2 (3.6%) | 2 (1.1%) | 1 (7.1%) |
| M2 | 83 (28%) | 11 (28%) | 21 (38%) | 46 (25%) | 5 (36%) |
| M3 | 153 (52%) | 15 (38%) | 24 (43%) | 110 (60%) | 4 (29%) |
| M4 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Resection at first recurrence | 117 (40%) | 16 (41%) | 33 (59%) | 61 (33%) | 5 (36%) |
| GTR | 54 (46%) | 7 (39%) | 12 (36%) | 33 (54%) | 2 (40%) |
| NTR | 18 (15%) | 5 (28%) | 5 (15%) | 7 (11%) | 1 (20%) |
| STR | 16 (14%) | 4 (22%) | 3 (9.1%) | 7 (11%) | 2 (40%) |
| Biopsy | 29 (25%) | 2 (11%) | 13 (39%) | 14 (23%) | 0 (0%) |
| Chemotherapy at first recurrence | 267 (91%) | 33 (85%) | 53 (95%) | 170 (92%) | 11 (79%) |
| CSI at first recurrence | 48 (16%) | 36 (92%) | 12 (21%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adolph, J.E.; Fleischhack, G.; Tschirner, S.; Rink, L.; Dittes, C.; Mikasch, R.; Dammann, P.; Mynarek, M.; Obrecht-Sturm, D.; Rutkowski, S.; et al. Radiotherapy for Recurrent Medulloblastoma in Children and Adolescents: Survival after Re-Irradiation and First-Time Irradiation. Cancers 2024, 16, 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111955
Adolph JE, Fleischhack G, Tschirner S, Rink L, Dittes C, Mikasch R, Dammann P, Mynarek M, Obrecht-Sturm D, Rutkowski S, et al. Radiotherapy for Recurrent Medulloblastoma in Children and Adolescents: Survival after Re-Irradiation and First-Time Irradiation. Cancers. 2024; 16(11):1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111955
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdolph, Jonas E., Gudrun Fleischhack, Sebastian Tschirner, Lydia Rink, Christine Dittes, Ruth Mikasch, Philipp Dammann, Martin Mynarek, Denise Obrecht-Sturm, Stefan Rutkowski, and et al. 2024. "Radiotherapy for Recurrent Medulloblastoma in Children and Adolescents: Survival after Re-Irradiation and First-Time Irradiation" Cancers 16, no. 11: 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111955
APA StyleAdolph, J. E., Fleischhack, G., Tschirner, S., Rink, L., Dittes, C., Mikasch, R., Dammann, P., Mynarek, M., Obrecht-Sturm, D., Rutkowski, S., Bison, B., Warmuth-Metz, M., Pietsch, T., Pfister, S. M., Pajtler, K. W., Milde, T., Kortmann, R.-D., Dietzsch, S., Timmermann, B., & Tippelt, S., on behalf of the German GPOH HIT-Network. (2024). Radiotherapy for Recurrent Medulloblastoma in Children and Adolescents: Survival after Re-Irradiation and First-Time Irradiation. Cancers, 16(11), 1955. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16111955







