Overall Survival and Prognostic Factors in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A National Cancer Database Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulkes, W.D.; Smith, I.E.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Triple-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivers, K.F.; Lund, M.J.; Porter, P.L.; Liff, J.M.; Flagg, E.W.; Coates, R.J.; Eley, J.W. The epidemiology of triple-negative breast cancer, including race. Cancer Causes Control 2009, 20, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, Y.H. A Study on the Factors and Prediction Model of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer for Public Health Promotion. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassam, F.; Enright, K.; Dent, R.; Dranitsaris, G.; Myers, J.; Flynn, C.; Fralick, M.; Kumar, R.; Clemons, M. Survival outcomes for patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: Implications for clinical practice and trial design. Clin. Breast Cancer 2009, 9, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Pinilla, S.M.; Sarrio, D.; Honrado, E.; Hardisson, D.; Calero, F.; Benitez, J.; Palacios, J. Prognostic significance of basal-like phenotype and fascin expression in node-negative invasive breast carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therasse, P.; Arbuck, S.G.; Eisenhauer, E.A.; Wanders, J.; Kaplan, R.S.; Rubinstein, L.; Verweij, J.; Van Glabbeke, M.; van Oosterom, A.T.; Christian, M.C.; et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2000, 92, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, R.; Hanna, W.M.; Trudeau, M.; Rawlinson, E.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Pattern of metastatic spread in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2009, 115, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandapati, A.; Lukong, K.E. Triple negative breast cancer: Approved treatment options and their mechanisms of action. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 3701–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Ashley, S.; Steele, D.; Ashworth, A.; Lakhani, S.R.; Smith, I.E. Basal-like breast carcinomas: Clinical outcome and response to chemotherapy. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 59, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, K.R.; Brown, M.; Cress, R.D.; Parise, C.A.; Caggiano, V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: A population-based study from the California cancer Registry. Cancer 2007, 109, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, K.E.; Haiderali, A.; Huang, M.; Schwartzberg, L.S. Real-world effectiveness outcomes in patients diagnosed with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Future Oncol. 2021, 17, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, R.; Trudeau, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Hanna, W.M.; Kahn, H.K.; Sawka, C.A.; Lickley, L.A.; Rawlinson, E.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4429–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilimoria, K.Y.; Stewart, A.K.; Winchester, D.P.; Ko, C.Y. The National Cancer Data Base: A powerful initiative to improve cancer care in the United States. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2008, 15, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boffa, D.J.; Rosen, J.E.; Mallin, K.; Loomis, A.; Gay, G.; Palis, B.; Thoburn, K.; Gress, D.; McKellar, D.P.; Shulman, L.N.; et al. Using the National Cancer Database for Outcomes Research: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, A.; Kong, S.; Cheung, W.Y. Eligibility of real-world patients with metastatic breast cancer for clinical trials. Breast 2020, 54, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, I.Y.; Yan, A.T.; Earle, C.C.; Trudeau, M.E.; Eisen, A.; Chan, K.K.W. Comparison of outcomes in a population-based cohort of metastatic breast cancer patients receiving anti-HER2 therapy with clinical trial outcomes. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 181, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Karantza, V.; Aktan, G.; Lala, M. Current treatment landscape for patients with locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: A systematic literature review. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, A.; Berg, T.; Jensen, M.B.; Jakobsen, E.; Nielsen, H.M.; Kümler, I.; Glavicic, V.; Jensen, J.D.; Knoop, A. Real-World Survival and Treatment Regimens Across First- to Third-Line Treatment for Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer 2023, 17, 11782234231203292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swede, H.; Sarwar, A.; Magge, A.; Braithwaite, D.; Cook, L.S.; Gregorio, D.I.; Jones, B.A.; Hoag, J.R.; Gonsalves, L.; Salner, A.L.; et al. Mortality risk from comorbidities independent of triple-negative breast cancer status: NCI-SEER-based cohort analysis. Cancer Causes Control 2016, 27, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, E.; Maisonneuve, P.; Rotmensz, N.; Cancello, G.; Iorfida, M.; Balduzzi, A.; Galimberti, V.; Veronesi, P.; Luini, A.; Pruneri, G.; et al. Heterogeneity of triple-negative breast cancer: Histologic subtyping to inform the outcome. Clin. Breast Cancer 2013, 13, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkenhol, M.C.A.; Vreuls, W.; Wauters, C.A.P.; Mol, S.J.J.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; Bult, P. Histological subtypes in triple negative breast cancer are associated with specific information on survival. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2020, 46, 151490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, U.; Budhathoki, P.; Gaire, S.; Yadav, S.K.; Shah, A.; Adhikari, A.; Choong, G.; Couzi, R.; Giridhar, K.V.; Leon-Ferre, R.A.; et al. Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors in triple-negative invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 200, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, D.; Gligorov, J.; André, F.; Cameron, D.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.; Xu, B.; Wardley, A.; Kaen, D.; Andrade, L.; et al. Primary results from IMpassion131, a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised phase III trial of first-line paclitaxel with or without atezolizumab for unresectable locally advanced/metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Adams, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Schneeweiss, A.; Barrios, C.H.; Iwata, H.; Diéras, V.; Hegg, R.; Im, S.A.; Shaw Wright, G.; et al. Atezolizumab and Nab-Paclitaxel in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2108–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.; Rugo, H.S.; Cescon, D.W.; Im, S.A.; Yusof, M.M.; Gallardo, C.; Lipatov, O.; Barrios, C.H.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Iwata, H.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittendorf, E.A.; Philips, A.V.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Qiao, N.; Wu, Y.; Harrington, S.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Akcakanat, A.; et al. PD-L1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Xu, D.; Tang, B.; Ren, Y.; Han, Y.; Liang, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Expression of programmed death ligand-1 and programmed death-1 in samples of invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast and its correlation with prognosis. Anticancer Drugs 2018, 29, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, H.G.; Malmgren, J.A.; Atwood, M.K. Triple-negative breast cancer in the elderly: Prognosis and treatment. Breast J. 2017, 23, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayson, D.; Payne, J.I.; Michael, J.C.R.; Tsuruda, K.M.; Abdolell, M.; Barnes, P.J. Impact of Detection Method and Age on Survival Outcomes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Population-Based Cohort Analysis. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, e955–e960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Perez, E.A.; Hong, R.; Li, Q.; Xu, B. Age-Related Disparity in Immediate Prognosis of Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A Population-Based Study from SEER Cancer Registries. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltoni, R.; Ravaioli, S.; Bronte, G.; Mazza, M.; Cerchione, C.; Massa, I.; Balzi, W.; Cortesi, M.; Zanoni, M.; Bravaccini, S. Chronological age or biological age: What drives the choice of adjuvant treatment in elderly breast cancer patients? Transl. Oncol. 2022, 15, 101300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, P.G.; Murphy, C.G.; Mallam, D.; Accordino, M.; Patil, S.; Howard, J.; Omuro, A.; Beal, K.; Seidman, A.D.; Hudis, C.A.; et al. Limited overall survival in patients with brain metastases from triple negative breast cancer. Breast J. 2012, 18, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkitaraman, R.; Joseph, T.; Dhadda, A.; Chaturvedi, A.; Upadhyay, S. Prognosis of patients with triple-negative breast cancer and brain metastasis. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 21, 729–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Cao, J.; Shao, Z.; Wang, Z. Incidence, pattern and prognosis of brain metastases in patients with metastatic triple negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Tong, Y.; Zhu, X.; Shen, K.; Zhu, J.; Chen, X. Prolonged Time to Adjuvant Chemotherapy Initiation Was Associated with Worse Disease Outcome in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morante, Z.; Ruiz, R.; Araujo, J.M.; Pinto, J.A.; Cruz-Ku, G.; Urrunaga-Pastor, D.; Namuche, F.; Flores, C.; Mantilla, R.; Luján, M.G.; et al. Impact of the Delayed Initiation of Adjuvant Chemotherapy in the Outcome of Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2021, 21, 239–246.e234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgaleta, A.M.; Burguete, A.B.; Gutiérrez, L.R.; Nuín, E.B.; Felipe, G.A.; de la Vega, F.A. Local treatment in oligometastasis from breast cancer: An overview. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 25, 2861–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, M.J.; Mokbel, K. Locoregional therapy in de novo metastatic breast cancer. The unanswered question. Breast 2021, 58, 170–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, J.M.; Gao, F.; Bumb, C.; Ellis, M.J.; Ma, C.X. Racial differences in outcomes of triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 138, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S.; Broglio, K.; Kau, S.W.; Green, M.C.; Giordano, S.H.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Buchholz, T.A.; Albarracin, C.; Yang, W.T.; Hennessy, B.T.; et al. Triple receptor-negative breast cancer: The effect of race on response to primary systemic treatment and survival outcomes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, K.M.; Cole, S.R.; Tse, C.K.; Perou, C.M.; Carey, L.A.; Foulkes, W.D.; Dressler, L.G.; Geradts, J.; Millikan, R.C. Intrinsic breast tumor subtypes, race, and long-term survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 6100–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schettini, F.; Chic, N.; Brasó-Maristany, F.; Paré, L.; Pascual, T.; Conte, B.; Martínez-Sáez, O.; Adamo, B.; Vidal, M.; Barnadas, E.; et al. Clinical, pathological, and PAM50 gene expression features of HER2-low breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gampenrieder, S.P.; Dezentjé, V.; Lambertini, M.; de Nonneville, A.; Marhold, M.; Le Du, F.; Salgado, A.C.; Costa, D.A.; Vaz Batista, M.; Ruché, N.C.; et al. Influence of HER2 expression on prognosis in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer-results from an international, multicenter analysis coordinated by the AGMT Study Group. ESMO Open 2023, 8, 100747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Jacot, W.; Yamashita, T.; Sohn, J.; Vidal, M.; Tokunaga, E.; Tsurutani, J.; Ueno, N.T.; Prat, A.; Chae, Y.S.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in Previously Treated HER2-Low Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Food & Drug administration. Oncology (Cancer)/Hematologic Malignancies Approval Notifications. 2023. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/oncology-cancer-hematologic-malignancies-approval-notifications (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Robson, M.E.; Im, S.A.; Senkus, E.; Xu, B.; Domchek, S.M.; Masuda, N.; Delaloge, S.; Tung, N.; Armstrong, A.; Dymond, M.; et al. OlympiAD extended follow-up for overall survival and safety: Olaparib versus chemotherapy treatment of physician’s choice in patients with a germline BRCA mutation and HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 184, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litton, J.K.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Mina, L.A.; Rugo, H.S.; Lee, K.H.; Gonçalves, A.; Diab, S.; Woodward, N.; Goodwin, A.; Yerushalmi, R.; et al. Talazoparib versus chemotherapy in patients with germline BRCA1/2-mutated HER2-negative advanced breast cancer: Final overall survival results from the EMBRACA trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardia, A.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Tolaney, S.M.; Loirat, D.; Punie, K.; Oliveira, M.; Brufsky, A.; Sardesai, S.D.; Kalinsky, K.; Zelnak, A.B.; et al. Sacituzumab Govitecan in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
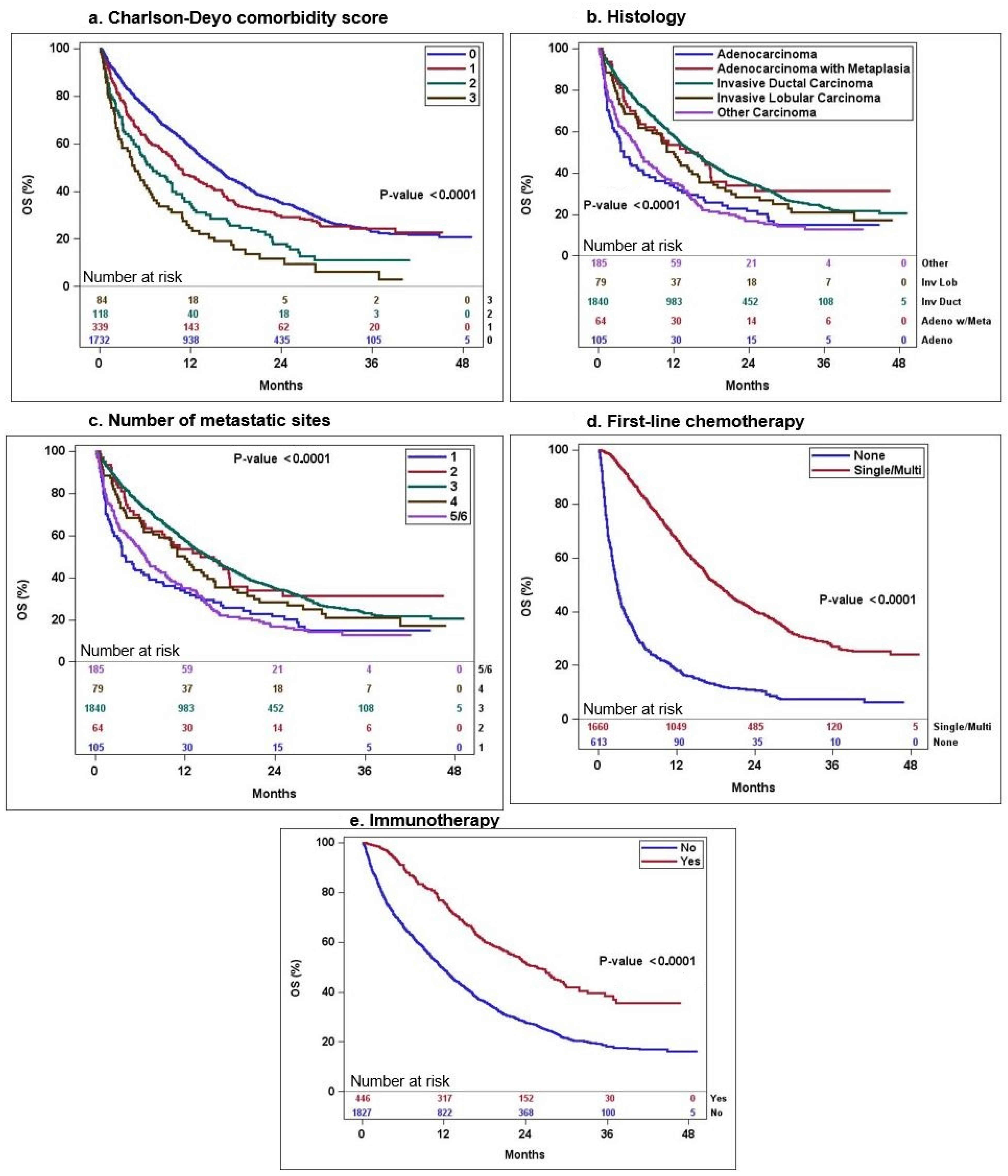
| No. of Patients (% of Total Patients) | Median OS in Months (95% CI) | Log-Rank p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 12-Month Survival Estimates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographic Characteristics | |||||
| Age | <0.0001 | ||||
| 19–40 | 179 (7.9) | 15.5 (13.2–18.2) | Reference | 0.64 (0.57–0.72) | |
| 41–70 | 1435 (63.1) | 15.6 (14.2–16.7) | 1.05 (0.87–1.27) | 0.58 (0.55–0.60) | |
| 71–90 | 659 (29) | 9.6 (8.0–11.4) | 1.52 (1.24–1.85) | 0.44 (0.41–0.48) | |
| Race | 0.2033 | ||||
| Caucasian | 1532 (67.4) | 13.6 (12.7–14.8) | Reference | 0.54 (0.52–0.57) | |
| African–American | 638 (28.1) | 13.4 (11.9–15.2) | 1.02 (0.91–1.14) | 0.54 (0.5–0.58) | |
| Other | 103 (4.5) | 16.9 (12.3–28.3) | 0.8 (0.62–1.03) | 0.6 (0.51–0.71) | |
| Charlson-Deyo score | <0.0001 | ||||
| 0 | 1732 (76.2) | 15.3 (14.3–16.3) | Reference | 0.59 (0.56–0.61) | |
| 1 | 339 (14.9) | 10.4 (9.1–13.1) | 1.22 (1.06–1.41) | 0.46 (0.41–0.52) | |
| 2 | 118 (5.2) | 6.9 (5.2–9.6) | 1.8 (1.47–2.22) | 0.35 (0.27–0.45) | |
| 3 or more | 84 (3.7) | 4.6 (2.9–6.9) | 2.46 (1.94–3.12) | 0.25 (0.17–0.36) | |
| Clinicopathologic/Cancer Characteristics | |||||
| Histology | <0.0001 | ||||
| Invasive ductal carcinoma | 1840 (81) | 15.2 (14.1–16.3) | Reference | 0.58 (0.56–0.60) | |
| Invasive lobular carcinoma | 79 (3.5) | 12 (8.5–16.0) | 1.23 (0.95–1.60) | 0.49 (0.39–0.61) | |
| Adenocarcinoma with metaplasia | 64 (2.8) | 14.0 (8.9–20.3) | 1.0 (0.73–1.4) | 0.54 (0.43–0.68) | |
| Adenocarcinoma NOS | 105 (4.6) | 4.0 (2.9–8.1) | 1.89 (1.51–2.37) | 0.33 (0.25–0.44) | |
| Other carcinoma | 185 (8.1) | 6.7 (5.2–9.3) | 1.83 (1.55–2.17) | 0.35 (0.29–0.43) | |
| HER-2 IHC expression | |||||
| 0 | 1217 (53.5) | 13.1 (12.2–14.5) | 0.3099 | Reference | 0.53 (0.50–0.56) |
| 1+ | 634 (27.9) | 14.2 (12.5–16.1) | 0.95 (0.84–1.07) | 0.55 (0.51–0.59) | |
| 2+ | 422 (18.6) | 14.7 (12.8–17.2) | 0.91 (0.79–1.04) | 0.57 (0.53–0.62) | |
| No. of metastatic sites | <0.0001 | ||||
| 1 | 1129 (49.7) | 19.8 (18.1–22.2) | Reference | 0.67 (0.65–0.70) | |
| 2 | 603 (26.5) | 11 (9.8–12.3) | 1.72 (1.53–1.94) | 0.47 (0.43–0.51) | |
| 3 | 328 (14.4) | 9.1 (6.9–11.2) | 1.99 (1.72–2.30) | 0.43 (0.38–0.49) | |
| 4 | 157 (6.9) | 4.6 (3.5–5.6) | 3.16 (2.62–3.80) | 0.24 (0.18–0.32) | |
| 5 or 6 | 56 (2.4) | 2.6 (2.2– 5) | 4.61 (3.47–6.13) | 0.17 (0.10–0.31) | |
| Site of metastatic involvement (subgroup analysis in those with single metastatic site only after excluding brain metastases) | 0.0001 | ||||
| LN only | 233 | 24.4 (21.8–33.5) | Reference | 0.8 (0.75–0.85) | |
| Bone only | 317 | 18.9 (16.6–24.7) | 1.36 (1.08–1.72) | 0.67 (0.61–0.72) | |
| Liver only | 165 | 15.6 (13.3–19.4) | 1.67 (1.29–2.17) | 0.61 (0.54–0.69) | |
| Lung only | 286 | 22.8 (17.6–26.5) | 1.23 (0.97–1.56) | 0.7 (0.65–0.76) | |
| Other only | 83 | 12.3 (10.2–23.0) | 1.85 (1.34–2.55) | 0.5 (0.41–0.63) | |
| Location of metastases | <0.0001 | ||||
| Cranial only | 45 (2) | 11.8 (7.2–19.8) | Reference | 0.47 (0.34–0.64) | |
| Cranial + extra-cranial | 204 (9) | 5.3 (4.5–7.2) | 1.7 (1.16–2.49) | 0.32 (0.26–0.4) | |
| Extra-cranial only | 2024 (89) | 14.6 (13.6–15.8) | 0.86 (0.60–1.22) | 0.57 (0.55–0.59) | |
| Treatment characteristics | |||||
| First-line chemotherapy | <0.0001 | ||||
| None | 613 (27) | 2.9 (2.6–3.3) | Reference | 0.18 (0.15–0.22) | |
| Single-agent | 714 (31.4) | 16.4 (14.6–18.4) | 0.29 (0.25–0.33) | 0.61 (0.58–0.65) | |
| Multi-agent | 946 (41.6) | 19.9 (18.1–22) | 0.23 (0.21–0.26) | 0.71 (0.68–0.74) | |
| Immunotherapy | <0.0001 | ||||
| No | 1827 (80.4) | 11.5 (10.9–12.6) | Reference | 0.49 (0.47–0.51) | |
| Yes | 446 (19.6) | 25.6 (22.3–29.1) | 0.49 (0.42–0.56) | 0.76 (0.72–0.80) | |
| Time from Dx to systemic therapy | <0.0001 | ||||
| None | 579 (25.5) | 2.7 (2.4–3.1) | Reference | 0.47 (0.39–0.56) | |
| <2 weeks | 138 (6.1) | 10.8 (9.2–15) | 0.34 (0.28–0.43) | 0.61 (0.57–0.66) | |
| 2–4 weeks | 425 (18.7) | 15.6 (14.2–16.8) | 0.26 (0.23–0.31) | 0.71 (0.68–0.73) | |
| >4 weeks | 1131 (49.8) | 20.6 (19.3–22.6) | 0.21 (0.18–0.23) | 0.17 (0.14–0.2) | |
| Surgery of distant site (LN or other site) | <0.0001 | ||||
| No | 2134 (93.9) | 13.1 (12.5–14.1) | Reference | 0.53 (0.51–0.55) | |
| Yes | 106 (4.7) | 29.2 (23.0–NE) | 0.50 (0.38–0.66) | 0.76 (0.69–0.85) | |
| Radiation to the distant site | 0.0204 | ||||
| No | 1603 (70.5) | 12.6 (11.5–13.6) | Reference | 0.51 (0.49–0.54) | |
| Yes | 482 (21.2) | 14.7 (12.7–17.5) | 0.86 (0.76–0.98) | 0.57 (0.53–0.61) | |
| Palliative treatment (to alleviate symptoms) | |||||
| No | 1721 (75.7) | 14.5 (13.5–15.6) | 0.0037 | Reference | 0.56 (0.54–0.59) |
| Yes | 552 (24.3) | 11.3 (10.0–12.9) | 1.18 (1.06–1.32) | 0.48 (0.44–0.53) | |
| No. of Patients | Median OS in Months (95% CI) | Log-Rank p-Value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | 12-Month Survival Estimates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charlson-Deyo comorbidity score 0; no. of patients = 1732 (76.2%) | |||||
| First-line chemotherapy | <0.0001 | ||||
| None | 401 | 3.3 (2.9–4.0) | Reference | 0.22 (0.18–0.27) | |
| Single-agent | 550 | 17.3 (15.5–19.7) | 0.31 (0.27–0.36) | 0.65 (0.61–0.69) | |
| Multi-agent | 781 | 20.1 (18.4–22.4) | 0.26 (0.23–0.3) | 0.72 (0.69–0.75) | |
| Charlson-Deyo comorbidity score 1; no. of patients = 339 (14.9%) | |||||
| First-line chemotherapy | <0.0001 | ||||
| None | 111 | 2.4 (1.7–3.3) | Reference | 0.15 (0.09–0.24) | |
| Single-agent | 112 | 13.1 (9.6–17.7) | 0.28 (0.21–0.38) | 0.51 (0.43–0.62) | |
| Multi-agent | 116 | 19.9 (16.4–29.1) | 0.19 (0.14–0.26) | 0.7 (0.62–0.79) | |
| Charlson-Deyo comorbidity score 2; no. of patients = 118 (5.2%) | |||||
| First-line chemotherapy | <0.0001 | ||||
| None | 52 | 2.2 (1.4–3.4) | Reference | 0.08 (0.03–0.21) | |
| Single-agent | 31 | 13.2 (10.9–NE) | 0.19 (0.11–0.33) | 0.57 (0.41–0.77) | |
| Multi-agent | 35 | 16.8 (8.6–25.2) | 0.21 (0.13–0.35) | 0.54 (0.4–0.74) | |
| Charlson-Deyo comorbidity score = 3 or more; no. of patients = 84 (3.7%) | |||||
| First-line chemotherapy | <0.0001 | ||||
| None | 49 | 2.2 (1.5–3.7) | Reference | 0.1 (0.04–0.24) | |
| Single-agent | 21 | 10.9 (5.3–21.2) | 0.3 (0.16–0.54) | 0.41 (0.24–0.7) | |
| Multi-agent | 14 | 12.1 (7.5–NE) | 0.28 (0.14–0.56) | 0.5 (0.3–0.84) | |
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | Overall p-Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Charlson-Deyo score | <0.0001 | |
| 0 | Reference | |
| 1 | 1.23 (1.07–1.42) | |
| 2 | 1.57 (1.27–1.93) | |
| 3 | 1.97 (1.55- 2.51) | |
| Histology | <0.0001 | |
| Invasive ductal carcinoma | Reference | |
| Invasive lobular carcinoma | 1.04 (0.80–1.35) | |
| Adenocarcinoma with metaplasia | 0.83 (0.60–1.14) | |
| Adenocarcinoma NOS | 1.29 (1.03–1.62) | |
| Other carcinoma | 1.54 (1.29–1.82) | |
| No. of metastatic sites | <0.0001 | |
| 1 | Reference | |
| 2 | 1.90 (1.69–2.15) | |
| 3 | 2.16 (1.86–2.5) | |
| 4 | 3.58 (2.96–4.33) | |
| 5 or 6 | 4.81 (3.61–6.42) | |
| First-line chemotherapy | <0.0001 | |
| None | Reference | |
| Single-agent or multi-agent | 0.28 (0.25–0.32) | |
| Immunotherapy | <0.0001 | |
| No | Reference | |
| Yes | 0.56 (0.49–0.65) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kesireddy, M.; Elsayed, L.; Shostrom, V.K.; Agarwal, P.; Asif, S.; Yellala, A.; Krishnamurthy, J. Overall Survival and Prognostic Factors in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A National Cancer Database Analysis. Cancers 2024, 16, 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16101791
Kesireddy M, Elsayed L, Shostrom VK, Agarwal P, Asif S, Yellala A, Krishnamurthy J. Overall Survival and Prognostic Factors in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A National Cancer Database Analysis. Cancers. 2024; 16(10):1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16101791
Chicago/Turabian StyleKesireddy, Meghana, Lina Elsayed, Valerie K. Shostrom, Priyal Agarwal, Samia Asif, Amulya Yellala, and Jairam Krishnamurthy. 2024. "Overall Survival and Prognostic Factors in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A National Cancer Database Analysis" Cancers 16, no. 10: 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16101791
APA StyleKesireddy, M., Elsayed, L., Shostrom, V. K., Agarwal, P., Asif, S., Yellala, A., & Krishnamurthy, J. (2024). Overall Survival and Prognostic Factors in Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: A National Cancer Database Analysis. Cancers, 16(10), 1791. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16101791





