Infliximab, a Monoclonal Antibody against TNF-α, Inhibits NF-κB Activation, Autotaxin Expression and Breast Cancer Metastasis to Lungs
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Animals
2.3. Orthotopic Breast Cancer Models in Syngeneic Mice
2.4. Lung Nodule Measurement
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. RT-PCR
2.8. ATX Assay
2.9. Cytokine/Chemokine Measurements
2.10. Clonogenic Assay
2.11. Database
2.12. Statistics
3. Results
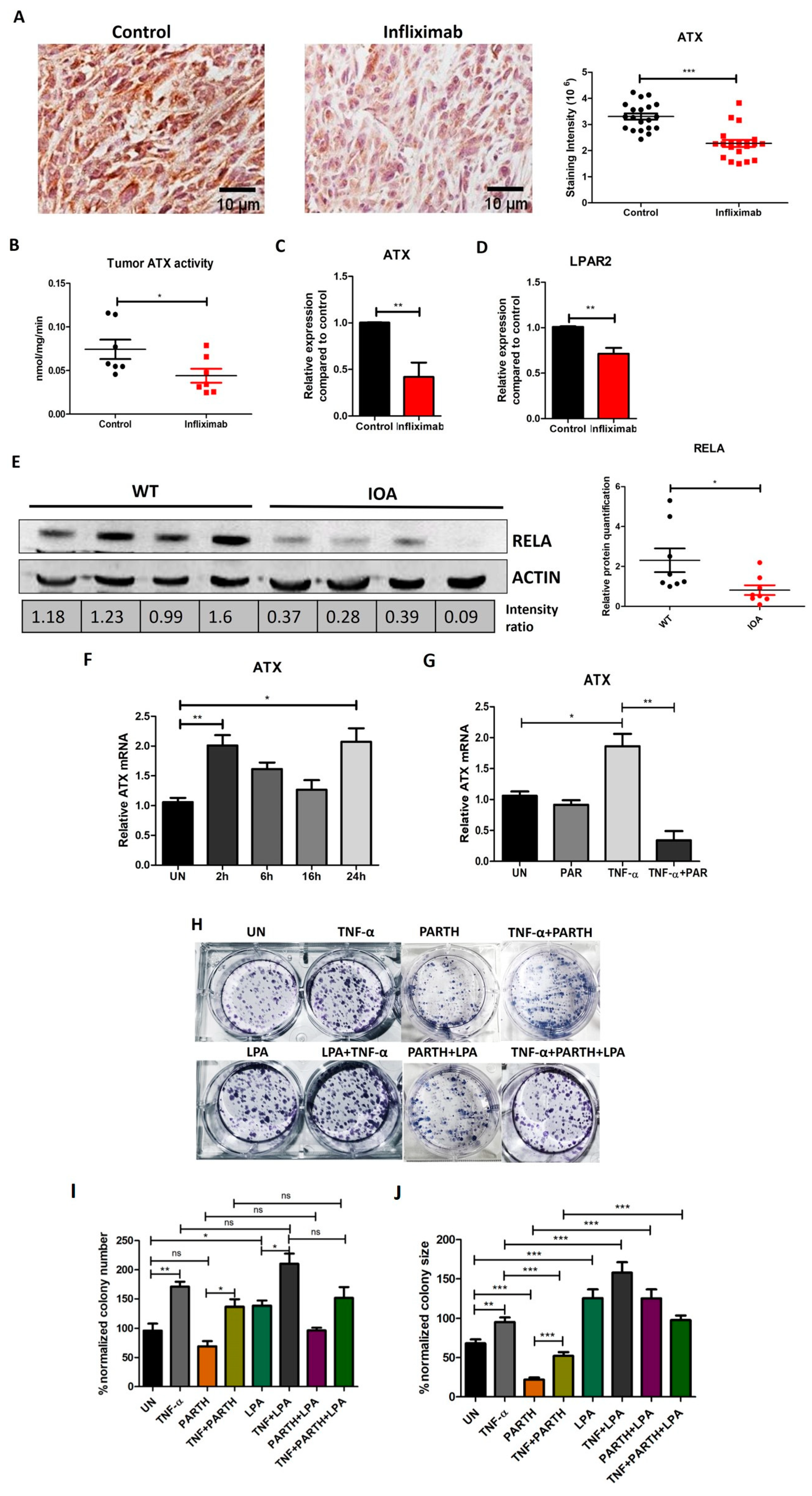
3.1. Effect of Infliximab on Breast Cancer Metastasis to Lungs
3.2. Infliximab Alters Concentrations of Cytokines in Plasma and Breast Tumors in a Syngeneic Mouse Model
3.3. Infliximab Treatment Decreases Inflammation-Related Genes and NF-κB Activation in Breast Tumors in a Syngeneic Mouse Model
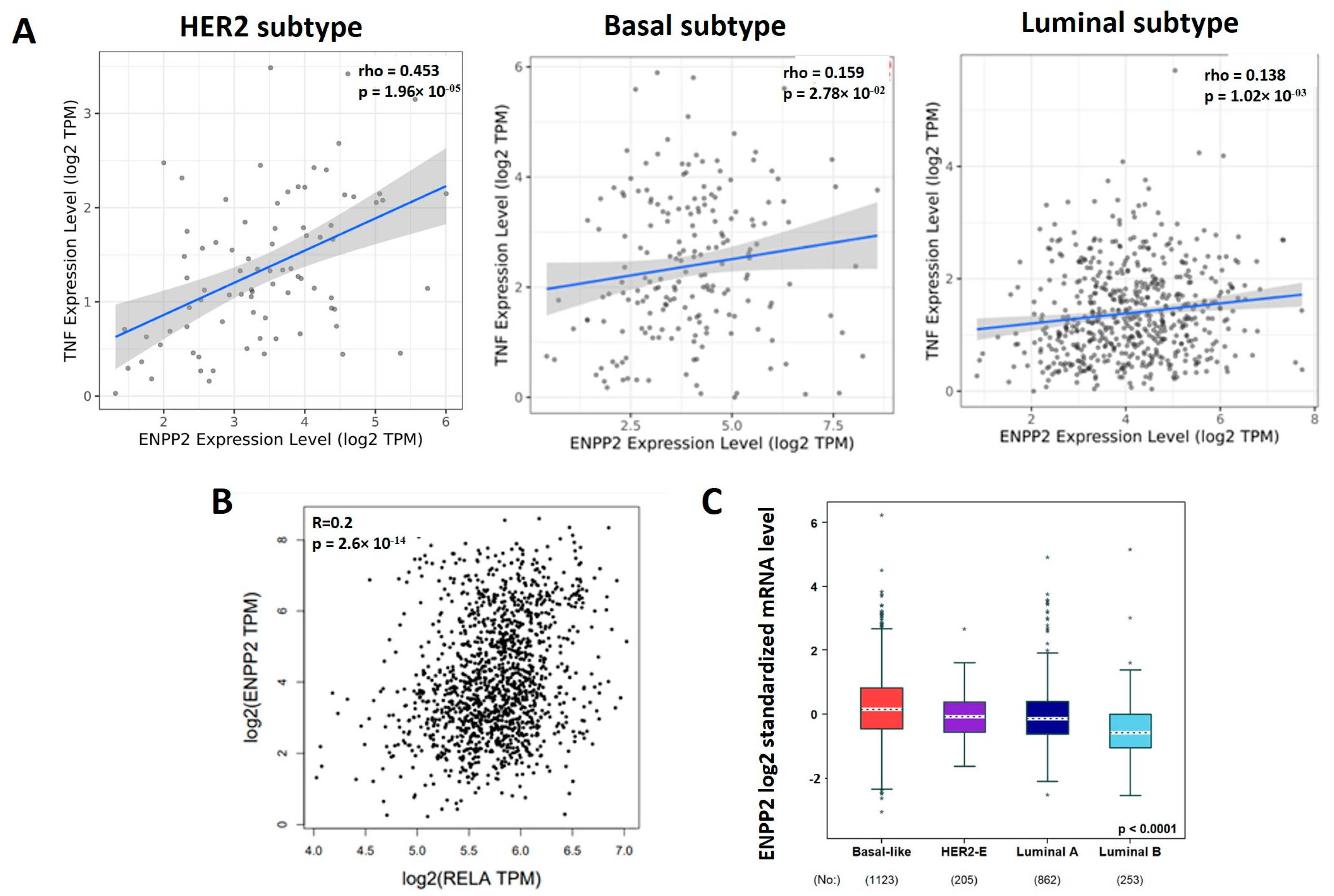
3.4. TNF-α, RELA and ATX Are Positively Correlated in Breast Cancer Patients
3.5. TNF-α Induced NF-κB and ATX Activity Are Correlated in Breast Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATX | Autotaxin |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LPA | Lysophosphatidic acid, lysophosphatidate |
| LPAR | LPA receptor |
| LPP | Lipid phosphate phosphatase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha |
| RELA | RELA protooncogene (NF-κBsubunit) |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
References
- Greten, F.R.; Grivennikov, S.I. Inflammation and Cancer: Triggers, Mechanisms, and Consequences. Immunity 2019, 51, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAndrew, N.P.; Bottalico, L.; Mesaros, C.; Blair, I.A.; Tsao, P.Y.; Rosado, J.M.; Ganguly, T.; Song, S.J.; Gimotty, P.A.; Mao, J.J.; et al. Effects of systemic inflammation on relapse in early breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatelia, K.; Singh, K.; Singh, R. TLRs: Linking inflammation and breast cancer. Cell Signal. 2014, 26, 2350–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Murri, A.M.; Bartlett, J.M.; Canney, P.A.; Doughty, J.C.; Wilson, C.; McMillan, D.C. Evaluation of an inflammation-based prognostic score (GPS) in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkaya, H.; Kim, G.I.; Davis, A.; Malik, F.; Henry, N.L.; Ithimakin, S.; Quraishi, A.A.; Tawakkol, N.; D’Angelo, R.; Paulson, A.K.; et al. Activation of an IL6 inflammatory loop mediates trastuzumab resistance in HER2+ breast cancer by expanding the cancer stem cell population. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 570–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Smyth, M.J. Targeting cancer-related inflammation in the era of immunotherapy. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2017, 95, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colotta, F.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A. Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: Links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, B.P. TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB/Snail pathway in cancer cell migration and invasion. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 102, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Tao, D.; Fang, Y.; Deng, C.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, J. TNF-Alpha Promotes Invasion and Metastasis via NF-Kappa B Pathway in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2017, 23, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Cao, C.; Li, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Ye, L. Inflammatory factor TNF-alpha promotes the growth of breast cancer via the positive feedback loop of TNFR1/NF-kappaB (and/or p38)/p-STAT3/HBXIP/TNFR1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 58338–58352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercogliano, M.F.; Bruni, S.; Elizalde, P.V.; Schillaci, R. Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha Blockade: An Opportunity to Tackle Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shostak, K.; Chariot, A. NF-kappaB, stem cells and breast cancer: The links get stronger. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.K.; Jana, D.; Patil, P.S.; Chaudhari, K.S.; Chattopadhyay, B.K.; Chikkala, B.R.; Mandal, S.; Chowdhary, P. Role of NF-kappaB as a Prognostic Marker in Breast Cancer: A Pilot Study in Indian Patients. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 4, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Taguchi, Y.; Ito-Kureha, T.; Semba, K.; Yamaguchi, N.; Inoue, J. NF-kappaB non-cell-autonomously regulates cancer stem cell populations in the basal-like breast cancer subtype. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, H.L.; Nagari, A.; Kraus, W.L. TNFalpha signaling exposes latent estrogen receptor binding sites to alter the breast cancer cell transcriptome. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartikasari, A.E.R.; Huertas, C.S.; Mitchell, A.; Plebanski, M. Tumor-Induced Inflammatory Cytokines and the Emerging Diagnostic Devices for Cancer Detection and Prognosis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 692142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerebours, F.; Vacher, S.; Andrieu, C.; Espie, M.; Marty, M.; Lidereau, R.; Bieche, I. NF-kappa B genes have a major role in inflammatory breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindley, D.N.; Tang, X.; Meng, G.; Benesch, M.G.K. Role of Adipose Tissue-Derived Autotaxin, Lysophosphatidate Signaling, and Inflammation in the Progression and Treatment of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesch, M.G.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Curtis, J.M.; McMullen, T.P.; Brindley, D.N. Regulation of autotaxin expression and secretion by lysophosphatidate and sphingosine 1-phosphate. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magkrioti, C.; Galaris, A.; Kanellopoulou, P.; Stylianaki, E.A.; Kaffe, E.; Aidinis, V. Autotaxin and chronic inflammatory diseases. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 104, 102327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Curtis, J.M.; Brindley, D.N. Doxycycline attenuates breast cancer related inflammation by decreasing plasma lysophosphatidate concentrations and inhibiting NF-kappaB activation. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesch, M.G.K.; Tang, X.; Brindley, D.N. Autotaxin and Breast Cancer: Towards Overcoming Treatment Barriers and Sequelae. Cancers 2020, 12, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Murph, M.; Panupinthu, N.; Mills, G.B. ATX-LPA receptor axis in inflammation and cancer. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3695–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauck, T.; Kadam, S.; Heinz, K.; Garcia Peraza, M.; Schmid, R.; Kremer, A.E.; Wolf, K.; Bauer, A.; Horch, R.E.; Arkudas, A.; et al. Influence of the autotaxin-lysophosphatidic acid axis on cellular function and cytokine expression in different breast cancer cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.M.; Xu, Y.; Skill, N.J.; Sheng, H.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, M.; Saxena, R.; Maluccio, M.A. Autotaxin expression and its connection with the TNF-alpha-NF-kappaB axis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Morris, A.J.; Deken, M.A.; Brindley, D.N. Autotaxin Inhibition with IOA-289 Decreases Breast Tumor Growth in Mice Whereas Knockout of Autotaxin in Adipocytes Does Not. Cancers 2023, 15, 2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euer, N.; Schwirzke, M.; Evtimova, V.; Burtscher, H.; Jarsch, M.; Tarin, D.; Weidle, U.H. Identification of genes associated with metastasis of mammary carcinoma in metastatic versus non-metastatic cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2002, 22, 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, H.; Wakabayashi, H.; Naito, Y.; Kato, S.; Nakagawa, T.; Matsumine, A.; Sudo, A. Anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy inhibits lung metastasis in an osteosarcoma cell line. Oncology 2015, 88, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obchoei, S.; Weakley, S.M.; Wongkham, S.; Wongkham, C.; Sawanyawisuth, K.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Cyclophilin A enhances cell proliferation and tumor growth of liver fluke-associated cholangiocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.S. Current implications of cyclophilins in human cancers. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 29, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhai, Q.; Bharadwaj, U.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Fisher, W.E.; Chen, C.; Yao, Q. Cyclophilin A is overexpressed in human pancreatic cancer cells and stimulates cell proliferation through CD147. Cancer 2006, 106, 2284–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fu, J.; Zeng, Z.; Cohen, D.; Li, J.; Chen, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W509–W514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jezequel, P.; Gouraud, W.; Ben Azzouz, F.; Guerin-Charbonnel, C.; Juin, P.P.; Lasla, H.; Campone, M. bc-GenExMiner 4.5: New mining module computes breast cancer differential gene expression analyses. Database 2021, 2021, baab007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Kang, B.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W556–W560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, R.; Esmaeili, R.; Mirzaei, R.; Bidad, K.; de Lima, S.; Ajami, M.; Shirzad, H.; Hadjati, J.; Majidzadeh, A.K. Study of the tumor microenvironment during breast cancer progression. Cancer Cell Int. 2017, 17, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Shapiro, D.J. The immune system and inflammation in breast cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 382, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laha, D.; Grant, R.; Mishra, P.; Nilubol, N. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor in Manipulating the Immunological Response of Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 656908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripsianis, G.; Papadopoulou, E.; Anagnostopoulos, K.; Botaitis, S.; Katotomichelakis, M.; Romanidis, K.; Kontomanolis, E.; Tentes, I.; Kortsaris, A. Coexpression of IL-6 and TNF-alpha: Prognostic significance on breast cancer outcome. Neoplasma 2014, 61, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montfort, A.; Colacios, C.; Levade, T.; Andrieu-Abadie, N.; Meyer, N.; Segui, B. The TNF Paradox in Cancer Progression and Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Ma, D.; Gao, R.F.; Yu, K.D. Effect of Ki-67 Expression Levels and Histological Grade on Breast Cancer Early Relapse in Patients with Different Immunohistochemical-based Subtypes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, M.; Meignan, S.; Volkel, P.; Angrand, P.O.; Chopin, V.; Bidan, N.; Toillon, R.A.; Adriaenssens, E.; Lagadec, C.; Le Bourhis, X. Vimentin Promotes the Aggressiveness of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells Surviving Chemotherapeutic Treatment. Cells 2021, 10, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.; Rajak, S.; Tewari, A.; Gupta, P.; Chattopadhyay, N.; Sinha, R.A.; Chakravarti, B. Multifaceted role of chemokines in solid tumors: From biology to therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Bhat, V.; Berdnikov, A.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Buchel, E.; Safneck, J.; Marshall, A.J.; Murphy, L.C.; Postovit, L.M.; et al. Paracrine Crosstalk between Fibroblasts and ER+ Breast Cancer Cells Creates an IL1beta-Enriched Niche that Promotes Tumor Growth. iScience 2019, 19, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparano, J.A.; O’Neill, A.; Graham, N.; Northfelt, D.W.; Dang, C.T.; Wolff, A.C.; Sledge, G.W.; Miller, K.D. Inflammatory cytokines and distant recurrence in HER2-negative early breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, M.; Zanotto, M.; Malpeli, G.; Bassi, G.; Perbellini, O.; Chilosi, M.; Bifari, F.; Krampera, M. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) induced by inflammatory priming elicits mesenchymal stromal cell-like immune-modulatory properties in cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.H.; Zhu, H.; Liu, L.S.; Huang, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Sun, X.P.; Chang, C.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhai, K. Tumour Necrosis Factor-alpha Gene Polymorphism Is Associated with Metastasis in Patients with Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Lee, J.R.; Kim, K.J.; Jun, J.H.; Hwang, H.J.; Lee, W.; Nam, S.H.; Oh, J.E.; Yoo, Y.C. Identification for antitumor effects of tramadol in a xenograft mouse model using orthotopic breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pileczki, V.; Braicu, C.; Gherman, C.D.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. TNF-alpha gene knockout in triple negative breast cancer cell line induces apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 14, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, A.C.; Pathanjeli, P.; Wu, Z.; Bao, L.; Goo, L.E.; Yates, J.A.; Oliver, C.R.; Soellner, M.B.; Merajver, S.D. IL-4/IL-13 Stimulated Macrophages Enhance Breast Cancer Invasion Via Rho-GTPase Regulation of Synergistic VEGF/CCL-18 Signaling. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Sarkissyan, M.; Paico, K.; Wu, Y.; Vadgama, J.V. MCP-1 is overexpressed in triple-negative breast cancers and drives cancer invasiveness and metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Shi, G.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, W.; Wu, Y. Interferon-gamma inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenasebright cancer stem cells in the 4T1 mouse model of breast cancer. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 135, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckel, M.C.; Wolfson, A.; Slachta, C.A.; Schwarting, R.; Salgame, P.; Katsetos, C.D.; Platsoucas, C.D. Human breast tumor cells express IL-10 and IL-12p40 transcripts and proteins, but do not produce IL-12p70. Cell Immunol. 2011, 266, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stender, J.D.; Nwachukwu, J.C.; Kastrati, I.; Kim, Y.; Strid, T.; Yakir, M.; Srinivasan, S.; Nowak, J.; Izard, T.; Rangarajan, E.S.; et al. Structural and Molecular Mechanisms of Cytokine-Mediated Endocrine Resistance in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cell 2017, 65, 1122–1135.e1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor-kappaB: The enemy within. Cancer Cell 2004, 6, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Neriah, Y.; Karin, M. Inflammation meets cancer, with NF-kappaB as the matchmaker. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtois, G.; Gilmore, T.D. Mutations in the NF-kappaB signaling pathway: Implications for human disease. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6831–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.; Karin, M. Autocrine IL-6 signaling: A key event in tumorigenesis? Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, D.R.; Hurt, E.M.; Farrar, W.L. The role of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 2502–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Karl, M.N.; Wang, W.; Starich, B.; Tan, H.; Kiemen, A.; Pucsek, A.B.; Kuo, Y.H.; Russo, G.C.; Pan, T.; et al. Engineered bispecific antibodies targeting the interleukin-6 and -8 receptors potently inhibit cancer cell migration and tumor metastasis. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 3430–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplanski, G. Interleukin-18: Biological properties and role in disease pathogenesis. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 281, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Cheon, S.; Cho, D. The dual effects of interleukin-18 in tumor progression. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 4, 329–335. [Google Scholar]
- Thong-Ngam, D.; Tangkijvanich, P.; Lerknimitr, R.; Mahachai, V.; Theamboonlers, A.; Poovorawan, Y. Diagnostic role of serum interleukin-18 in gastric cancer patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 4473–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Kim, K.E. Interleukin-18 Is a Prognostic Biomarker Correlated with CD8+ T Cell and Natural Killer Cell Infiltration in Skin Cutaneous Melanoma. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, S.A.; Zaki, S.A.; El-Maghraby, S.M.; Kadry, D.Y. Importance of serum IL-18 and RANTES as markers for breast carcinoma progression. J. Egypt. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 17, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Merendino, R.A.; Gangemi, S.; Ruello, A.; Bene, A.; Losi, E.; Lonbardo, G.; Purello-Dambrosio, F. Serum levels of interleukin-18 and sICAM-1 in patients affected by breast cancer: Preliminary considerations. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2001, 16, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, N.; Li, W.; Fujimoto, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Katagiri, T.; Okamura, H.; Miyoshi, Y. High Serum Levels of Interleukin-18 Are Associated With Worse Outcomes in Patients With Breast Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 5009–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanzaki, H.; Chatterjee, A.; Hossein Nejad Ariani, H.; Zhang, X.; Chung, S.; Deng, N.; Ramanujan, V.K.; Cui, X.; Greene, M.I.; Murali, R. Disabling the Nuclear Translocalization of RelA/NF-kappaB by a Small Molecule Inhibits Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Growth. Breast Cancer (Dove Med. Press) 2021, 13, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Han, X.; Lu, C.; Yang, T.; Qiao, P.; Sun, Y.; Yu, Z. Ubiquitination of NF-kappaB p65 by FBXW2 suppresses breast cancer stemness, tumorigenesis, and paclitaxel resistance. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesch, M.G.; Tang, X.; Maeda, T.; Ohhata, A.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Kok, B.P.; Dewald, J.; Hitt, M.; Curtis, J.M.; McMullen, T.P.; et al. Inhibition of autotaxin delays breast tumor growth and lung metastasis in mice. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 2655–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmings, D.G.; Brindley, D.N. Signalling by lysophosphatidate and its health implications. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.; Wannecq, E.; Descotes, F.; Jansen, S.; Deux, B.; Ribeiro, J.; Serre, C.M.; Gres, S.; Bendriss-Vermare, N.; Bollen, M.; et al. Cancer cell expression of autotaxin controls bone metastasis formation in mouse through lysophosphatidic acid-dependent activation of osteoclasts. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deken, M.A.; Niewola-Staszkowska, K.; Peyruchaud, O.; Mikulcic, N.; Antolic, M.; Shah, P.; Cheasty, A.; Tagliavini, A.; Nizzardo, A.; Pergher, M.; et al. Characterization and translational development of IOA-289, a novel autotaxin inhibitor for the treatment of solid tumors. Immunooncol. Technol. 2023, 18, 100384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benesch, M.G.; Wu, R.; Tang, X.; Brindley, D.N.; Ishikawa, T.; Takabe, K. Autotaxin production in the human breast cancer tumor microenvironment mitigates tumor progression in early breast cancers. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 2790–2813. [Google Scholar]
- Olsson, L.T.; Williams, L.A.; Midkiff, B.R.; Kirk, E.L.; Troester, M.A.; Calhoun, B.C. Quantitative analysis of breast cancer tissue composition and associations with tumor subtype. Hum. Pathol. 2022, 123, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvorak, H.F. Tumors: Wounds that do not heal. Similarities between tumor stroma generation and wound healing. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Tang, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Curtis, J.M.; McMullen, T.P.W.; Brindley, D.N. Dexamethasone decreases the autotaxin-lysophosphatidate-inflammatory axis in adipose tissue: Implications for the metabolic syndrome and breast cancer. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 1899–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Wuest, M.; Tang, X.; Dufour, J.; Zhao, Y.; Curtis, J.M.; McMullen, T.P.W.; Murray, D.; Wuest, F.; Brindley, D.N. Repeated Fractions of X-Radiation to the Breast Fat Pads of Mice Augment Activation of the Autotaxin-Lysophosphatidate-Inflammatory Cycle. Cancers 2019, 11, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, M.; Singh, R. TRIMs: Selective recruitment at different steps of the NF-kappaB pathway-determinant of activation or resolution of inflammation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6069–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Nowak, D.E.; Brasier, A.R. A TNF-induced gene expression program under oscillatory NF-kappaB control. BMC Genom. 2005, 6, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shinde, A.; Tang, X.; Singh, R.; Brindley, D.N. Infliximab, a Monoclonal Antibody against TNF-α, Inhibits NF-κB Activation, Autotaxin Expression and Breast Cancer Metastasis to Lungs. Cancers 2024, 16, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010052
Shinde A, Tang X, Singh R, Brindley DN. Infliximab, a Monoclonal Antibody against TNF-α, Inhibits NF-κB Activation, Autotaxin Expression and Breast Cancer Metastasis to Lungs. Cancers. 2024; 16(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010052
Chicago/Turabian StyleShinde, Anjali, Xiaoyun Tang, Rajesh Singh, and David N. Brindley. 2024. "Infliximab, a Monoclonal Antibody against TNF-α, Inhibits NF-κB Activation, Autotaxin Expression and Breast Cancer Metastasis to Lungs" Cancers 16, no. 1: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010052
APA StyleShinde, A., Tang, X., Singh, R., & Brindley, D. N. (2024). Infliximab, a Monoclonal Antibody against TNF-α, Inhibits NF-κB Activation, Autotaxin Expression and Breast Cancer Metastasis to Lungs. Cancers, 16(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16010052








