Recent Developments in the Field of Endoscopic Ultrasound for Diagnosis, Staging, and Treatment of Pancreatic Lesions
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Developments in the Diagnostic Role of EUS
2.1. Contrast-Enhanced EUS
2.2. Elastography
2.3. Needle-Based Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy and Microforceps Biopsies
2.4. Cystic Fluid Analysis and Genetic Analysis
2.5. The Role of Artificial Intelligence
2.6. Screening in High-Risk Patients
3. Devices and Modalities for Tissue Acquisition
3.1. MOSE
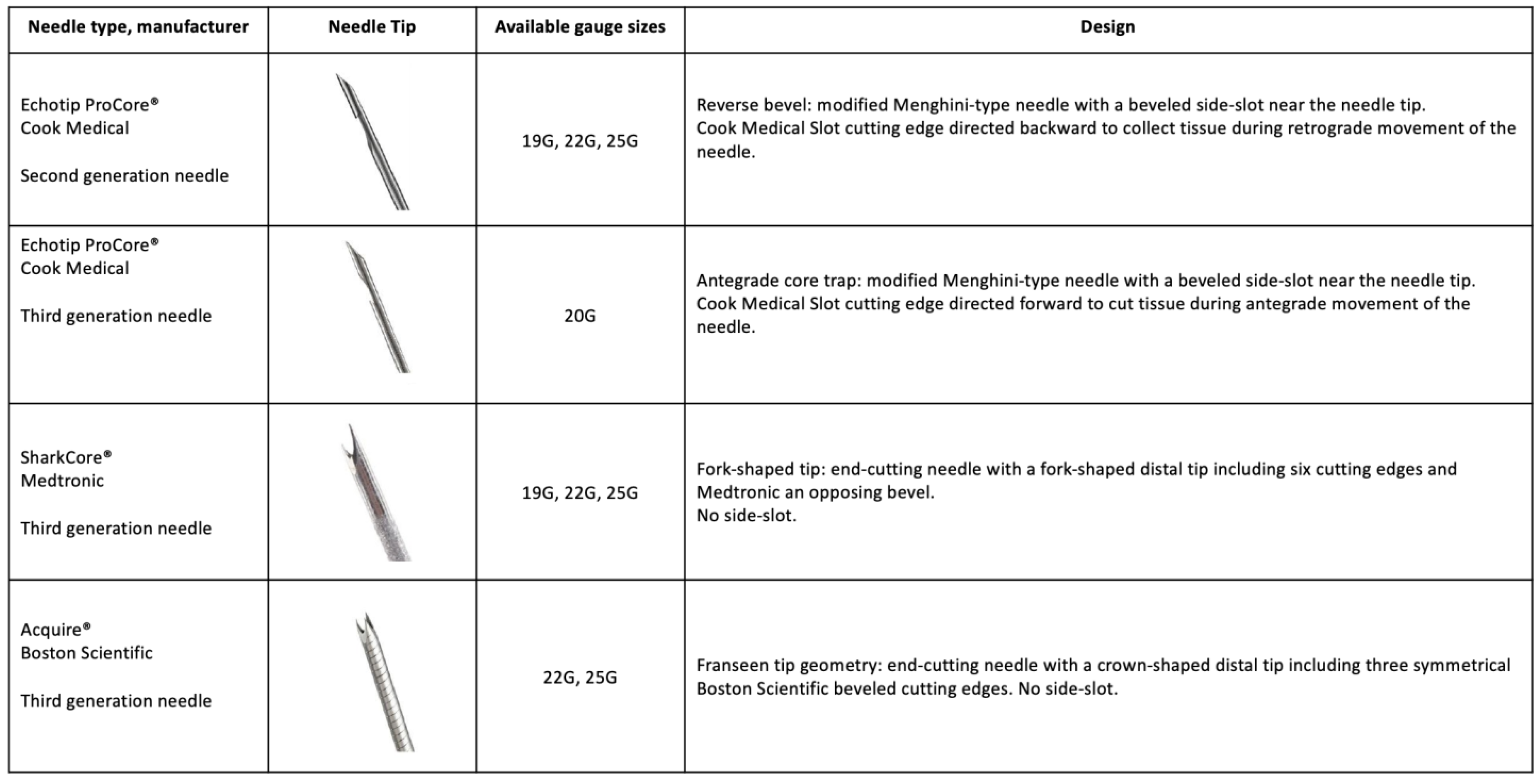
3.2. Needle Types for Tissue Acquisition
3.3. Sampling Techniques and Number of Needle Passes
4. Techniques for Local EUS-Guided Treatment
4.1. Radiofrequency Ablation
4.2. Additional Therapeutic Procedures
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| CEA | carcinoembryonic antigen |
| CE-EUS | contrast enhanced EUS |
| CEH-EUS | contrast enhanced harmonic mode EUS |
| EUS | endoscopic ultrasound |
| EUS-FNB | endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle biopsy |
| FNA | fine needle aspiration |
| FNB | fine needle biopsy |
| IPMN | intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm |
| MOSE | macroscopic on-site evaluation |
| MRCP | magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| nCLE | needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PDAC | pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| pNETs | pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors |
| RFA | radiofrequency ablation |
| ROSE | rapid on-site evaluation |
References
- Yousaf, M.N.; Chaudhary, F.S.; Ehsan, A.; Suarez, A.L.; Muniraj, T.; Jamidar, P.; Aslanian, H.R.; Farrell, J.J. Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and the management of pancreatic cancer. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2020, 7, e000408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, T.; Hara, K.; Mizuno, N.; Haba, S.; Okuno, N.; Koda, H.; Miyano, A.; Fumihara, D. Current status of artificial intelligence analysis for endoscopic ultrasonography. Dig. Endosc. 2021, 33, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, S.T.; Kelly, K.; Hollingsworth, M.A.; Thayer, S.P.; Ahlquist, D.A.; Andersen, D.K.; Batra, S.K.; Brentnall, T.A.; Canto, M.; Cleeter, D.F.; et al. Early Detection of Sporadic Pancreatic Cancer. Pancreas 2015, 44, 693–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machicado, J.D.; Obuch, J.C.; Goodman, K.A.; Schefter, T.E.; Frakes, J.; Hoffe, S.; Latifi, K.; Simon, V.C.; Santangelo, T.; Ezekwe, E.; et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound Placement of Preloaded Fiducial Markers Shortens Procedure Time Compared to Back-Loaded Markers. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 2749–2758.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslanian, H.R.; Lee, J.H.; Canto, M.I. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Pancreas Cancer Screening in High-Risk Individuals: Expert Review. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardeshna, D.R.; Cao, T.; Rodgers, B.; Onongaya, C.; Jones, D.; Chen, W.; Koay, E.J.; Krishna, S.G. Recent advances in the diagnostic evaluation of pancreatic cystic lesions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisotti, A.; Napoleon, B.; Facciorusso, A.; Cominardi, A.; Crinò, S.F.; Brighi, N.; Gincul, R.; Kitano, M.; Yamashita, Y.; Marchegiani, G.; et al. Contrast-enhanced EUS for the characterization of mural nodules within pancreatic cystic neoplasms: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 881–889.E5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmsen, F.-J.; Domagk, D.; Dietrich, C.; Hocke, M. Discriminating chronic pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer: Contrast-enhanced EUS and multidetector computed tomography in direct comparison. Endosc. Ultrasound 2018, 7, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, K.; Ishikawa, T.M.; Ohno, E.M.; Mizutani, Y.M.; Iida, T.; Furukawa, K.M.; Nakamura, M.M.; Honda, T.M.; Ishigami, M.M.; Kawashima, H.M.; et al. Differentiation Between Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm of the Pancreas and Nonfunctional Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasm Using Endoscopic Ultrasound. Pancreas 2022, 51, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, P.E.; Alessandrino, F.; Bellizzi, A.; Mortele, K.J. Non-hyperfunctioning pancreatic endocrine tumors: Multimodality imaging features with histopathological correlation. Abdom. Imaging 2015, 40, 2398–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, S.; Bassi, C.; Salvia, R.; Malleo, G.; Marchegiani, G.; Rebours, V.; Levy, P.; Partelli, S.; Suleiman, S.L.; A Banks, P.; et al. Low progression of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms with worrisome features and high-risk stigmata undergoing non-operative management: A mid-term follow-up analysis. Gut 2016, 66, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Study Group on Cystic Tumours of the Pancreas. European evidence-based guidelines on pancreatic cystic neoplasms. Gut 2018, 67, 789–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoto, S.; Kitano, M.; Fukasawa, M.; Ashida, R.; Kato, H.; Shiomi, H.; Sugimori, K.; Kanno, A.; Chiba, Y.; Takano, S.; et al. Tissue harmonic versus contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography for the diagnosis of pancreatic tumors: Prospective multicenter study. Dig. Endosc. 2021, 34, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, Y.; Iwashita, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Mita, N.; Uemura, S.; Yoshida, K.; Iwata, K.; Mukai, T.; Yasuda, I.; Shimizu, M. Efficacy of Contrast-Enhanced Harmonic Endoscopic Ultrasound for Pancreatic Solid Tumors with a Combination of Qualitative and Quantitative Analyses: A Prospective Pilot Study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 67, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, R.; Kamata, K.; Hara, A.; Tanaka, H.; Okamoto, A.; Yamazaki, T.; Nakai, A.; Omoto, S.; Minaga, K.; Yamao, K.; et al. Utility of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography for predicting the prognosis of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Dig. Endosc. 2020, 33, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, A.L.; Cazacu, I.; Burtea, D.E.; Harbiyeli, I.C.; Bejinariu, N.; Popescu, C.; Serbanescu, M.; Tabacelia, D.; Copaescu, C.; Bhutani, M.; et al. Quantitative contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasound in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: Can we predict survival using perfusion parameters? A pilot study. Med. Ultrason. 2022, 24, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salom, F.; Prat, F. Current role of endoscopic ultrasound in the diagnosis and management of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 14, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, E.; Kawashima, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Iida, T.; Suzuki, H.; Uetsuki, K.; Yashika, J.; Yamada, K.; Yoshikawa, M.; Gibo, N.; et al. Diagnostic performance of endoscopic ultrasonography-guided elastography for solid pancreatic lesions: Shear-wave measurements versus strain elastography with histogram analysis. Dig. Endosc. 2020, 33, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghiu, M.; Sparchez, Z.; Rusu, I.; Bolboacă, S.D.; Seicean, R.; Pojoga, C.; Seicean, A. Direct Comparison of Elastography Endoscopic Ultrasound Fine-Needle Aspiration and B-Mode Endoscopic Ultrasound Fine-Needle Aspiration in Diagnosing Solid Pancreatic Lesions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Medranda, C.; I Olmos, J.; Puga-Tejada, M.; Oleas, R.; Baquerizo-Burgos, J.; Arevalo-Mora, M.; Zavala, R.D.V.; Nebel, J.A.; Loffredo, D.C.; Pitanga-Lukashok, H. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided through-the-needle microforceps biopsy and needle-based confocal laser-endomicroscopy increase detection of potentially malignant pancreatic cystic lesions: A single-center study. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 14, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoleon, B.; Palazzo, M.; Lemaistre, A.-I.; Caillol, F.; Palazzo, L.; Aubert, A.; Buscail, L.; Maire, F.; Morellon, B.M.; Pujol, B.; et al. Needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy of pancreatic cystic lesions: A prospective multicenter validation study in patients with definite diagnosis. Endoscopy 2018, 51, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.G.; Hart, P.A.; DeWitt, J.M.; DiMaio, C.J.; Kongkam, P.; Napoleon, B.; Othman, M.O.; Tan, D.M.Y.; Strobel, S.G.; Stanich, P.; et al. EUS-guided confocal laser endomicroscopy: Prediction of dysplasia in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 91, 551–563.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, Z.L.; Satyavada, S.; Simons-Linares, R.; Mok, S.R.; Moreno, B.M.; Aparicio, J.R.; Chahal, P. Intracystic Glucose and Carcinoembryonic Antigen in Differentiating Histologically Confirmed Pancreatic Mucinous Neoplastic Cysts. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 117, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, T.R.; Paleti, S.; Rustagi, T. Molecular analysis of EUS-acquired pancreatic cyst fluid for KRAS and GNAS mutations for diagnosis of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasia and mucinous cystic lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 93, 1019–1033.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniccia, A.; Polanco, P.M.; Boone, B.A.; Wald, A.I.; McGrath, K.; Brand, R.E.; Khalid, A.; Kubiliun, N.; O'Broin-Lennon, A.M.; Park, W.G.; et al. Prospective, Multi-Institutional, Real-Time Next-Generation Sequencing of Pancreatic Cyst Fluid Reveals Diverse Genomic Alterations that Improve the Clinical Management of Pancreatic Cysts. Gastroenterology 2022, 164, 117–133.E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vege, S.S.; Ziring, B.; Jain, R.; Moayyedi, P.; Adams, M.A.; Dorn, S.D.; Dudley-Brown, S.L.; Flamm, S.L.; Gellad, Z.F.; Gruss, C.B.; et al. American Gastroenterological Association Institute Guideline on the Diagnosis and Management of Asymptomatic Neoplastic Pancreatic Cysts. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 819–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Fernández-del Castillo, C.; Kamisawa, T.; Jang, J.Y.; Levy, P.; Ohtsuka, T.; Salvia, R.; Shimizu, Y.; Tada, M.; Wolfgang, C.L. Revisions of international consensus Fukuoka guidelines for the management of IPMN of the pancreas. Pancreatology 2017, 17, 738–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.; Facciorusso, A.; Khan, S.; Madhu, D.; Kassab, L.; Ponnada, S.; Chandan, S.; Crino, S.; Kochhar, G.; Adler, D.; et al. Pooled diagnostic parameters of artificial intelligence in EUS image analysis of the pancreas: A descriptive quantitative review. Endosc. Ultrasound 2022, 11, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, L.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, N.; Tang, A.; Hu, S. Application of a novel artificial intelligence system in guiding the targeted puncture of a pancreatic mass. Endoscopy 2021, 54, E500–E501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Yao, L.; Ding, X.; Chen, D.; Wu, H.; Lu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, L.; An, P.; et al. Deep learning–based pancreas segmentation and station recognition system in EUS: Development and validation of a useful training tool (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 874–885.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.; Keswani, R.N.; Petersen, B.; Edmundowicz, S.A.; Walsh, C.M.; Huang, C.; Cohen, J.; Cote, G. Training in EUS and ERCP: Standardizing methods to assess competence. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 87, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, H.; Sherazi, S.A.A.; Gupta, S.; Perisetti, A.; Achebe, I.; Ali, A.; Tharian, B.; Thosani, N.; Sharma, N.R. Application of artificial intelligence in diagnosis of pancreatic malignancies by endoscopic ultrasound: A systemic review. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2022, 15, 17562848221093873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, T.; Hayakawa, M.; Suzuki, H.; Ohno, E.; Mizutani, Y.; Iida, T.; Fujishiro, M.; Kawashima, H.; Hotta, K. Development of a Novel Evaluation Method for Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Biopsy in Pancreatic Diseases Using Artificial Intelligence. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goggins, M.; Overbeek, K.A.; Brand, R.; Syngal, S.; Del Chiaro, M.; Bartsch, D.K.; Bassi, C.; Carrato, A.; Farrell, J.; Fishman, E.K.; et al. Management of patients with increased risk for familial pancreatic cancer: Updated recommendations from the International Cancer of the Pancreas Screening (CAPS) Consortium. Gut 2019, 69, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbeek, K.A.; Levink, I.J.M.; Koopmann, B.D.M.; Harinck, F.; Konings, I.C.A.W.; Ausems, M.G.E.M.; Wagner, A.; Fockens, P.; van Eijck, C.H.; Koerkamp, B.G.; et al. Long-term yield of pancreatic cancer surveillance in high-risk individuals. Gut 2021, 71, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domagk, D.; Oppong, K.W.; Aabakken, L.; Czakó, L.; Gyökeres, T.; Manes, G.; Meier, P.; Poley, J.-W.; Ponchon, T.; Tringali, A.; et al. Performance measures for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic ultrasound: A European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Quality Improvement Initiative. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 1448–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harinck, F.; Konings, I.C.A.W.; Kluijt, I.; Poley, J.W.; Van Hooft, J.E.; Van Dullemen, H.M.; Nio, C.Y.; Krak, N.C.; Hermans, J.J.; Aalfs, C.M.; et al. A multicentre comparative prospective blinded analysis of EUS and MRI for screening of pancreatic cancer in high-risk individuals. Gut 2015, 65, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.; Friedman, M.; Feldman, D.; Krishnan, K.; Casey, B.; Pisuchpen, N.; Kambadakone, A.; Chung, D.C. Concordance of EUS and MRI/MRCP findings among high-risk individuals undergoing pancreatic cancer screening. Pancreatology 2022, 22, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corral, J.E.; Mareth, K.F.; Riegert-Johnson, D.L.; Das, A.; Wallace, M.B. Diagnostic Yield from Screening Asymptomatic Individuals at High Risk for Pancreatic Cancer: A Meta-analysis of Cohort Studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiavillano, B.; Frazzoni, L.; Togliani, T.; Fabbri, C.; Tarantino, I.; De Luca, L.; Staiano, T.; Binda, C.; Signoretti, M.; Eusebi, L.H.; et al. Macroscopic on-site evaluation (MOSE) of specimens from solid lesions acquired during EUS-FNB: Multicenter study and comparison between needle gauges. Endosc. Int. Open 2021, 9, E901–E906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, B.P.; Madhu, D.; Reddy, N.; Chara, B.S.; Khan, S.R.; Garg, G.; Kassab, L.L.; Muthusamy, A.K.; Singh, A.; Chandan, S.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy sampling by macroscopic on-site evaluation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 96, 909–917.E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiavillano, B.; Crinò, S.F.; Facciorusso, A.; Di Matteo, F.; Barbera, C.; Larghi, A.; Rizzatti, G.; Carrara, S.; Spadaccini, M.; Auriemma, F.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy with or without macroscopic on-site evaluation: A randomized controlled noninferiority trial. Endoscopy 2022, 55, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.-W.; So, H.; Hwang, J.; Ko, S.; Oh, D.; Song, T.; Park, D.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.-H. Macroscopic on-site evaluation after EUS-guided fine needle biopsy may replace rapid on-site evaluation. Endosc. Ultrasound 2021, 10, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Ni, M.; Wang, P.; Zheng, J.; Sun, Q.; Xu, G.; Peng, C.; Shen, S.; Zhang, W.; Huang, S.; et al. Diagnostic value of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration with rapid on-site evaluation performed by endoscopists in solid pancreatic lesions: A prospective, randomized controlled trial. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crinò, S.F.; Di Mitri, R.; Nguyen, N.Q.; Tarantino, I.; de Nucci, G.; Deprez, P.H.; Carrara, S.; Kitano, M.; Shami, V.M.; Fernández-Esparrach, G.; et al. Endoscopic Ultrasound–guided Fine-needle Biopsy with or Without Rapid On-site Evaluation for Diagnosis of Solid Pancreatic Lesions: A Randomized Controlled Non-Inferiority Trial. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 899–909.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkolfakis, P.; Crinò, S.F.; Tziatzios, G.; Ramai, D.; Papaefthymiou, A.; Papanikolaou, I.S.; Triantafyllou, K.; Arvanitakis, M.; Lisotti, A.; Fusaroli, P.; et al. Comparative diagnostic performance of end-cutting fine-needle biopsy needles for EUS tissue sampling of solid pancreatic masses: A network meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2022, 95, 1067–1077.E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Xu, X.; Li, P. A Meta-Analysis Comparing Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Fine-needle Aspiration with Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Fine-needle Biopsy. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2022, 56, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Haddad, M.; Wallace, M.B.; Brugge, W.; Lakhtakia, S.; Li, Z.-S.; Sethi, A.; Pleskow, D.; Nguyen, C.C.; Pannala, R.; DeWitt, J.M.; et al. Fine-needle aspiration of pancreatic cystic lesions: A randomized study with long-term follow-up comparing standard and flexible needles. Endoscopy 2020, 53, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza Ladd, A.; Casner, N.; Cherukuri, S.V.; Garcia, C.; Padilla, O.; Dwivedi, A.; Hakim, N. Fine Needle Biopsies of Solid Pancreatic Lesions: Tissue Acquisition Technique and Needle Design Do Not Impact Specimen Adequacy. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 67, 4549–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ren, Y.; Chen, S.; Jin, Y.; Xie, H.; Yu, L.; Peng, K.; Xia, Y.; Pan, D.; Lu, J.; et al. The Wet Suction Technique Enhances the Diagnostic Efficacy and Aspirate Quality of EUS-FNA for Solid Lesions. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2022, 57, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, T.; Tian, L.; Deng, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yin, H.; Long, X.; Pan, S.; Yang, Z.; Luo, W.; et al. Comparison between modified wet suction and dry suction technique for endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle biopsy in pancreatic solid lesions. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 36, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.-D.; Wang, K.-X.; Zhou, W.; Li, S.-Y.; Jiang, H.; Gao, L.; Li, J.; Kong, X.-Y.; Yang, L.; Fang, A.-Q. Optimal number of needle passes during EUS-guided fine-needle biopsy of solid pancreatic lesions with 22G ProCore needles and different suction techniques: A randomized controlled trial. Endosc. Ultrasound 2021, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouw, R.E.; Barret, M.; Biermann, K.; Bisschops, R.; Czakó, L.; Gecse, K.B.; de Hertogh, G.; Hucl, T.; Iacucci, M.; Jansen, M.; et al. Endoscopic tissue sampling–Part 1: Upper gastrointestinal and hepatopancreatobiliary tracts. European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Guideline. Endoscopy 2021, 53, 1174–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacevic, B.; Vilmann, P. EUS tissue acquisition: From A to B. Endosc. Ultrasound 2020, 9, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polkowski, M.; Jenssen, C.C.; Kaye, P.V.; Carrara, S.; Deprez, P.; Ginès, A.; Fernández-Esparrach, G.G.; Eisendrath, P.; Aithal, G.P.; Arcidiacono, P.P.; et al. Technical aspects of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)-guided sampling in gastroenterology: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technical Guideline–March 2017. Endoscopy 2017, 49, 989–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthet, M.; Giovannini, M.; Gasmi, M.; Lesavre, N.; Boustière, C.; Napoleon, B.; LaQuiere, A.; Koch, S.; Vanbiervliet, G.; Gonzalez, J.-M. Long-term outcome after EUS-guided radiofrequency ablation: Prospective results in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and pancreatic cystic neoplasms. Endosc. Int. Open 2021, 9, E1178–E1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, R.; Mohammed, A.; Singh, A.; Harnegie, M.; Rustagi, T.; Stevens, T.; Chahal, P. EUS-guided radiofrequency and ethanol ablation for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc. Ultrasound 2022, 11, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollapudi, L.A.; Tyberg, A. EUS-RFA of the pancreas: Where are we and future directions. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadaccini, M.; Di Leo, M.; Iannone, A.; Hoff, D.v.D.; Fugazza, A.; Galtieri, P.A.; Pellegatta, G.; Maselli, R.; Anderloni, A.; Colombo, M.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided ablation of solid pancreatic lesions: A systematic review of early outcomes with pooled analysis. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 14, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, J.B.; Revanur, V.; Forcione, D.G.; Bechtold, M.L.; Puli, S.R. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fiducial marker placement in pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 12, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, S.; Bispo, M.; Leite, S.; Moreira, T.; Caldeira, A.; Moutinho-Ribeiro, P.; Nunes, N.; on behalf of the Portuguese Group for Ultrasound in Gastroenterology (GRUPUGE). GRUPUGE Perspective: Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Tattooing and Fiducial Placement in Pancreatic Cancer. GE Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 28, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
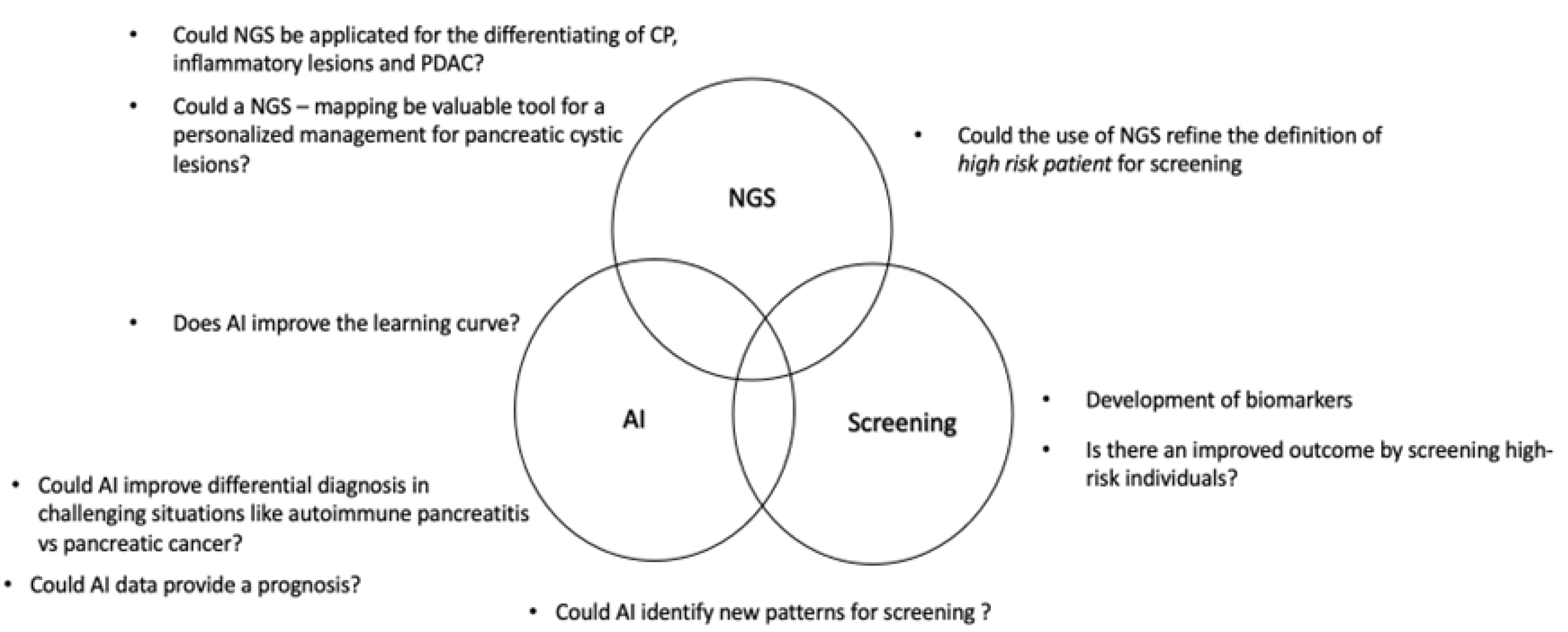
| Study (Year) | Study Type | Objective | Data type | AI | Results | Application | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mohan et al., 2022 | Meta-analysis 11 studies 2001–2020 | Overall performance of AI in: -Diagnosis and characterization of solid PL -Differentiate PC from non-neoplastic tissue -Differentiate malignancy from CP -Diagnosis of PC | -EUS elastography -EUS images -EUS—videos -CEH-EUS | Fractal-based quantitative analysis NN algorithm SVM | -Overall accuracy 85.8% -Sens 91.8% -Spec 84.6% -PPV 87.4% -NPV 91.4% -Heterogeneity 57% | Superior diagnostic results with the combination of AI and newer core-biopsy needles in EUS evaluation of solid masses | -Heterogeneity -Absence of prospective data |
| Yu et al., 2022 | Case report | Guiding punction of pancreatic masses by differentiating cancerous, non-cancerous, and necrotic regions | N/A | Deep CNN | Improving the diagnostic accuracy of EUS FNA | ||
| Zhang et al., 2020 | Cross-over 8 participants | BP-MASTER® -Test the performance of classifying the previously learned stations of pancreatic EUS -Pancreatic tissue and blood vessel segmentation | -EUS images -EUS videos | Deep learning | -Classification accuracy 86% -Comparable accuracy between endoscopists and AI -Improvement of trainee’s accuracy for classification and segmentation | Shortening the pancreatic EUS learning curve Improving EUS quality control | -Duodenal bulb station non studied |
| Goyal et al., 2022 | Systematic review 11 studies | Study the effectiveness of AI with EUS in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer -Differentiating PC from CP -Differentiating malignant from benign IPMNs | -Retrospective EUS images and videos -Real time collected EUS images | ANN CNN SVM | Performance in recognition of pancreatic malignancy: -Sens 83–100% -Spec 50–99% -Accuracy 80–97.5% -PC vs. CP ANN -Sens 88–100% -Spec 50–94% -SVM -Sens 96% -Spec 93% -Accuracy 94% CNN -Sens 90% -Spec 75% Benign vs. malignant IPMNs CNN -Sens 95.7% -Spec 92.6% -Accuracy 94% | -Improvement of pancreatic malignancy recognition even in presence of chronic pancreatitis -SVM method simpler and highly performant | |
| Ishikawa et al., 2022 | Retrospective | -Study the usefulness of AI in predicting the EUS-FNB sample quality for histopathological examination | -Stereomicroscopic images of EUS-FNB specimens | CNN and deep learning Contrastive learning | -AI evaluation using contrastive learning is comparable to MOSE performed by EUS experts -Diagnostic accuracy with deep learning not as high as MOSE performed by experts | Increasing the objectivity of the evaluation | Small sample size |
| Study (Year) | Study Type | Study Sample | Objective | Localization | Device | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mangiavillano et al., 2021 | Multicenter study | 378 patients | Diagnostic yield and accuracy of MOSE with different needle sizes | Pancreatic and extra-pancreatic lesions | Procore® Acquire® Echotip ultra® Sharkcore® | Association with the diagnostic yield of MOSE -larger needle diameter -≥3 needle passes |
| Gkolfakis et al., 2022 | Network meta-analysis | 16 RCTs 1934 patients | Compare the diagnostic accuracy of available FNB needles for sampling of solid pancreatic lesions | Solid pancreatic lesions | 22/25G FNA 20 G Side-fenestrated forward-facing bevel 22 G Franseen 19/22/25 G Fork-tip 21/22 G Menghini-tip 22/25 G Reverse bevel | Franseen 22 G -AUC 0.89 for accuracy 0.94 for adequacy Fork-tip needles 22 G -0.76 for accuracy -0.73 for adequacy 25 G Franseen and 25 G Fork-tip needles were not superior to 22 G reverse-bevel needles |
| Li et al., 2022 | Meta-analysis | 18 RCTs 2718 patients | Compare the diagnostic value and safety of FNA and FNB—needles | Pancreatic and extra-pancreatic lesions | -Solid pancreatic lesions: no difference in diagnostic accuracy -Overall gastrointestinal lesions: better diagnostic accuracy with FNB needles | |
| Al-Haddad et al., 2021 | Multicenter prospective randomized trial | 250 patients | Impact of three FNA needles on -diagnostic accuracy -accrue fluid for tumor markers | Pancreatic cystic lesions | 19 G Fle x19 G 22 G | -Overall success rate for aspiration: higher for 19 G Flex and 22 G compared with 19 G -No difference in the percentage of cyst volume aspirated by needle type |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poiraud, M.; Gkolfakis, P.; Arvanitakis, M. Recent Developments in the Field of Endoscopic Ultrasound for Diagnosis, Staging, and Treatment of Pancreatic Lesions. Cancers 2023, 15, 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092547
Poiraud M, Gkolfakis P, Arvanitakis M. Recent Developments in the Field of Endoscopic Ultrasound for Diagnosis, Staging, and Treatment of Pancreatic Lesions. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092547
Chicago/Turabian StylePoiraud, Marie, Paraskevas Gkolfakis, and Marianna Arvanitakis. 2023. "Recent Developments in the Field of Endoscopic Ultrasound for Diagnosis, Staging, and Treatment of Pancreatic Lesions" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092547
APA StylePoiraud, M., Gkolfakis, P., & Arvanitakis, M. (2023). Recent Developments in the Field of Endoscopic Ultrasound for Diagnosis, Staging, and Treatment of Pancreatic Lesions. Cancers, 15(9), 2547. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092547





