Frequency of Germline and Somatic BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations in Prostate Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
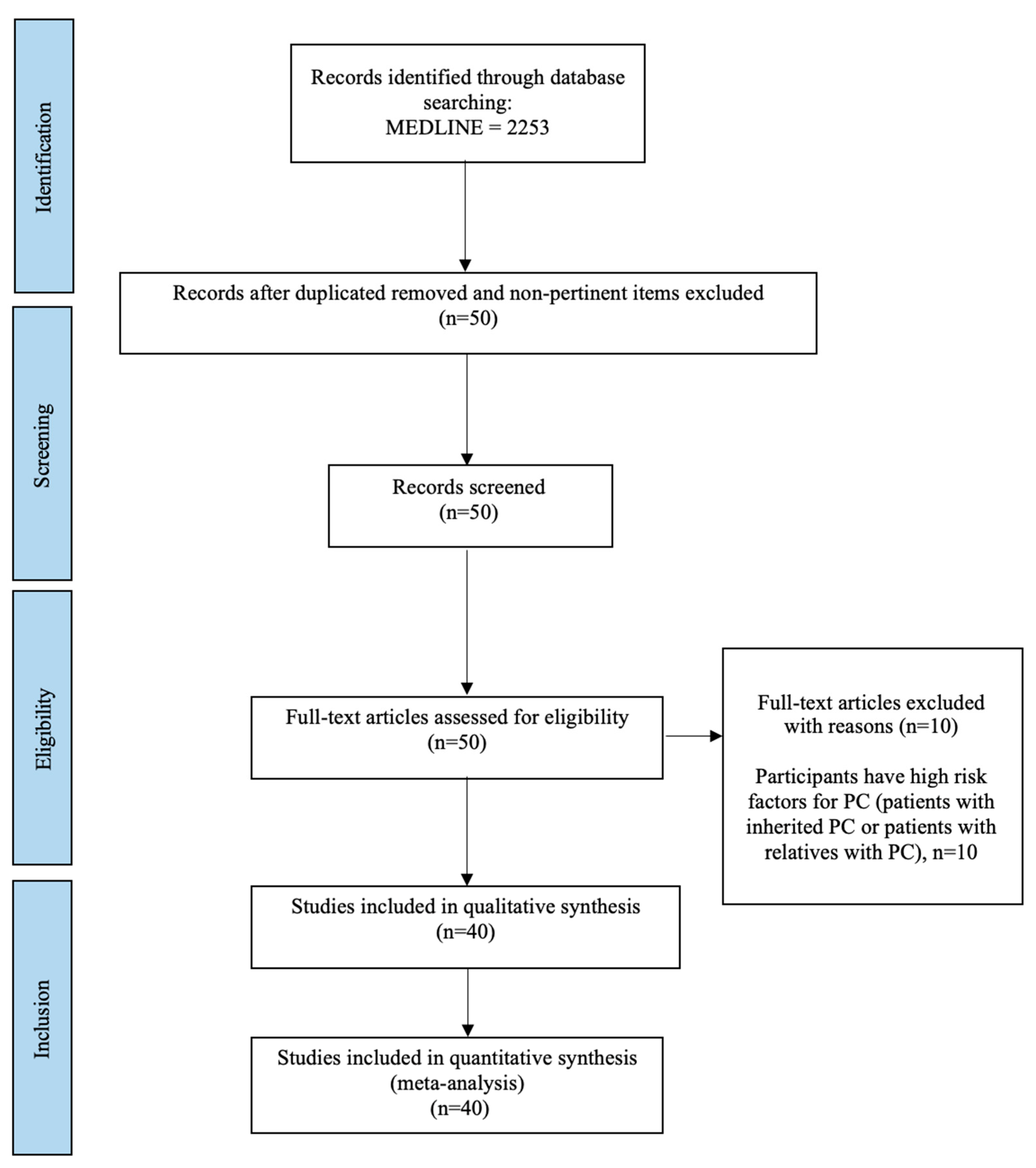
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Methods
2.5. Role of Funding Source
3. Results
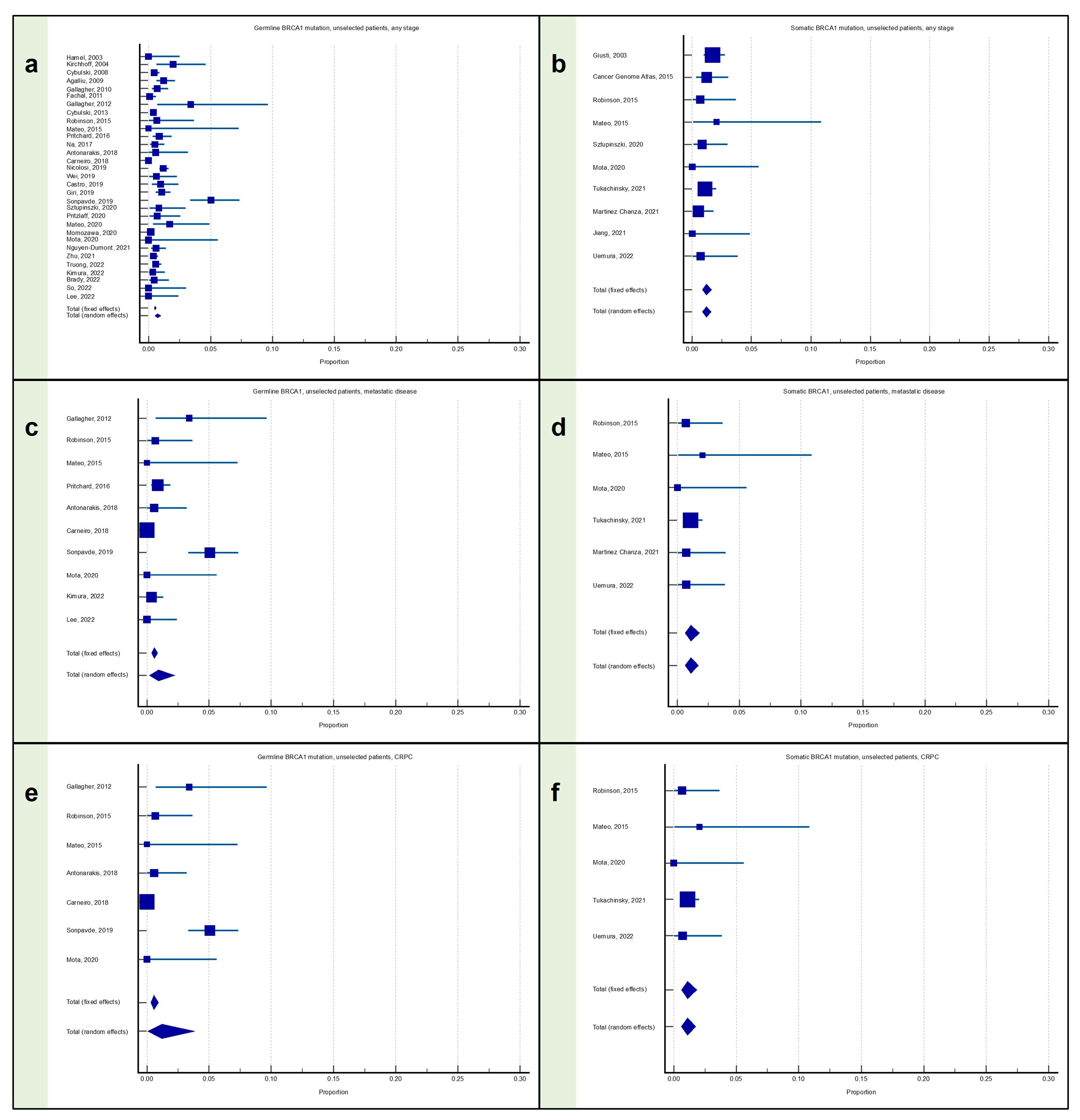
3.1. Meta-Analysis: Proportion of Patients with Prostate Cancer with BRCA1 Mutation
3.1.1. Proportion of Patients with Any Stage PC with BRCA1 Mutation
3.1.2. Proportion of Patients with Metastatic PC with BRCA1 Mutation
3.1.3. Proportion of Patients with mCRPC with BRCA1 Mutation
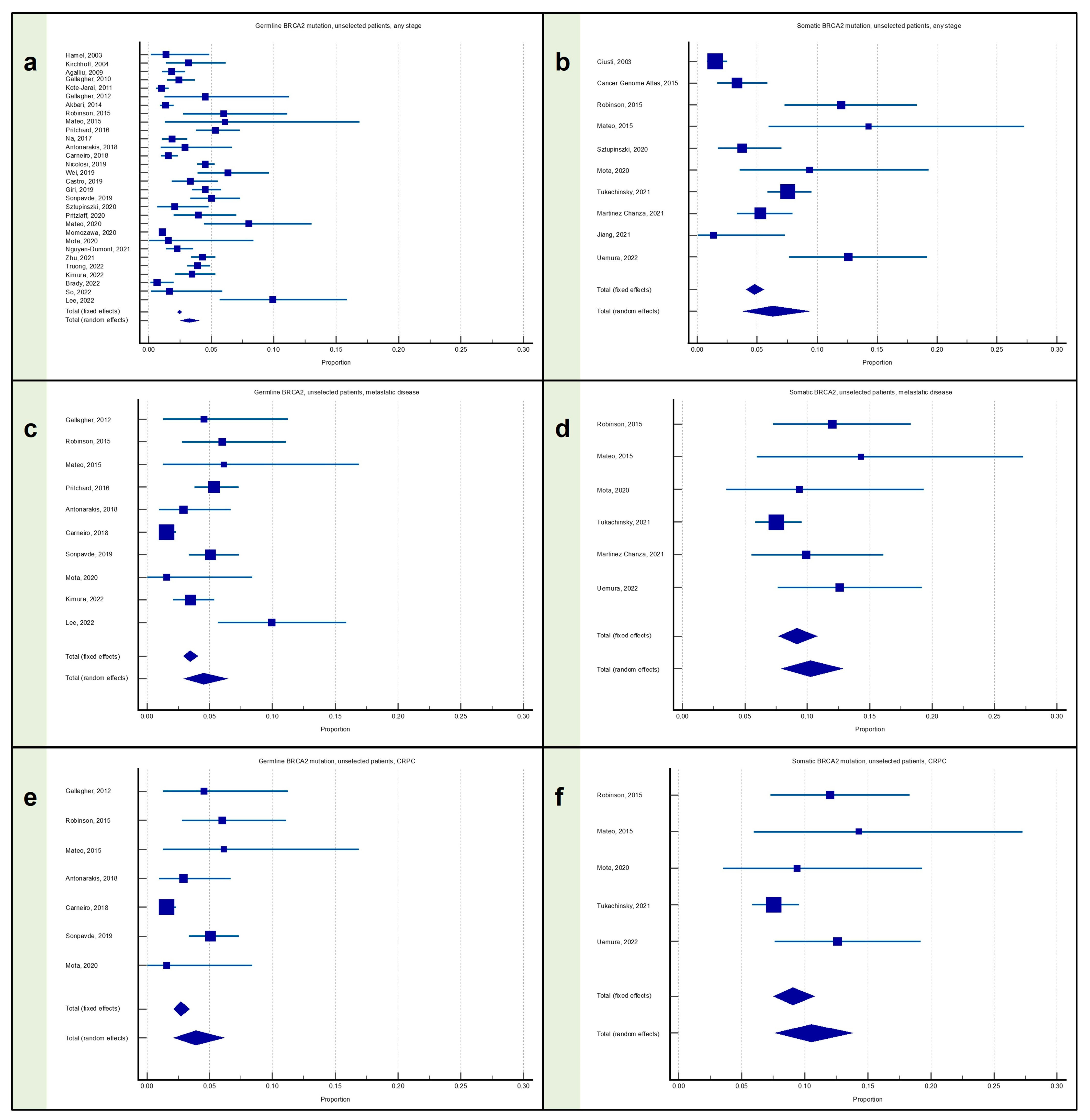
3.2. Meta-Analysis: Proportion of Patients with Prostate Cancer with BRCA2 Mutation
3.2.1. Proportion of Patients with Any Stage PC with BRCA2 Mutation
3.2.2. Proportion of Patients with Metastatic PC with BRCA2 Mutation
3.2.3. Proportion of Patients with mCRPC with BRCA2 Mutation
3.3. Meta-Analysis: Proportion of Patients with Prostate Cancer with Any BRCA Mutation
3.3.1. Proportion of Patients with Any Stage PC with Any BRCA Mutation
3.3.2. Proportion of Patients with Metastatic PC with Any BRCA Mutation
3.3.3. Proportion of Patients with mCRPC with Any BRCA Mutation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Giusti, 2003 | 940 | 1.702 | 0.976 to 2.749 | 29.05 | 29.05 |
| Cancer Genome Atlas, 2015 | 333 | 1.201 | 0.328 to 3.047 | 10.31 | 10.31 |
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 0.667 | 0.0169 to 3.658 | 4.66 | 4.66 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 2.041 | 0.0517 to 10.854 | 1.54 | 1.54 |
| Sztupinszki, 2020 | 240 | 0.833 | 0.101 to 2.978 | 7.44 | 7.44 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 5.601 | 2.01 | 2.01 |
| Tukachinsky, 2021 | 837 | 1.075 | 0.493 to 2.031 | 25.87 | 25.87 |
| Martinez Chanza, 2021 | 399 | 0.501 | 0.0608 to 1.799 | 12.35 | 12.35 |
| Jiang, 2021 | 74 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 4.863 | 2.32 | 2.32 |
| Uemura, 2022 | 143 | 0.699 | 0.0177 to 3.835 | 4.45 | 4.45 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 3229 | 1.199 | 0.853 to 1.637 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 3229 | 1.199 | 0.853 to 1.603 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 5.9758 |
| DF | 9 |
| Significance level | p = 0.7423 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 0.00% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 0.00 to 43.62 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | −0.6710 |
| 95% CI | −1.9905 to 0.6484 |
| Significance level | p = 0.2746 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | −0.2000 |
| Significance level | p = 0.4208 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Giusti, 2003 | 940 | 1.489 | 0.817 to 2.486 | 29.05 | 11.84 |
| Cancer Genome Atlas, 2015 | 333 | 3.303 | 1.660 to 5.834 | 10.31 | 11.11 |
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 12.000 | 7.269 to 18.301 | 4.66 | 9.95 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 14.286 | 5.942 to 27.242 | 1.54 | 7.18 |
| Sztupinszki, 2020 | 240 | 3.750 | 1.729 to 6.999 | 7.44 | 10.71 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 9.375 | 3.519 to 19.297 | 2.01 | 7.94 |
| Tukachinsky, 2021 | 837 | 7.527 | 5.832 to 9.528 | 25.87 | 11.79 |
| Martinez Chanza, 2021 | 399 | 5.263 | 3.287 to 7.933 | 12.35 | 11.29 |
| Jiang, 2021 | 74 | 1.351 | 0.0342 to 7.301 | 2.32 | 8.34 |
| Uemura, 2022 | 143 | 12.587 | 7.634 to 19.162 | 4.45 | 9.86 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 3229 | 4.766 | 4.058 to 5.558 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 3229 | 6.294 | 3.792 to 9.375 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 82.8977 |
| DF | 9 |
| Significance level | p < 0.0001 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 89.14% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 82.15 to 93.40 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 3.0217 |
| 95% CI | −1.6936 to 7.7370 |
| Significance level | p = 0.1777 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.1556 |
| Significance level | p = 0.5312 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Giusti, 2003 | 940 | 3.191 | 2.163 to 4.525 | 29.05 | 12.62 |
| Cancer Genome Atlas, 2015 | 333 | 4.505 | 2.543 to 7.321 | 10.31 | 11.47 |
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 12.667 | 7.801 to 19.072 | 4.66 | 9.79 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 16.327 | 7.322 to 29.657 | 1.54 | 6.36 |
| Sztupinszki, 2020 | 240 | 4.583 | 2.310 to 8.053 | 7.44 | 10.88 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 9.375 | 3.519 to 19.297 | 2.01 | 7.24 |
| Tukachinsky, 2021 | 837 | 8.602 | 6.791 to 10.710 | 25.87 | 12.53 |
| Martinez Chanza, 2021 | 399 | 5.764 | 3.689 to 8.524 | 12.35 | 11.74 |
| Jiang, 2021 | 74 | 1.351 | 0.0342 to 7.301 | 2.32 | 7.71 |
| Uemura, 2022 | 143 | 13.287 | 8.193 to 19.969 | 4.45 | 9.67 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 3229 | 6.072 | 5.274 to 6.950 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 3229 | 7.183 | 4.892 to 9.874 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 56.8386 |
| DF | 9 |
| Significance level | p < 0.0001 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 84.17% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 72.49 to 90.89 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 2.1709 |
| 95% CI | −1.8631 to 6.2049 |
| Significance level | p = 0.2498 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.1556 |
| Significance level | p = 0.5312 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Hamel, 2003 | 146 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 2.495 | 0.45 | 1.97 |
| Kirchhoff, 2004 | 251 | 1.992 | 0.650 to 4.587 | 0.77 | 2.64 |
| Cybulski, 2008 | 1793 | 0.446 | 0.193 to 0.877 | 5.51 | 4.45 |
| Agalliu, 2009 | 979 | 1.226 | 0.635 to 2.131 | 3.01 | 4.07 |
| Gallagher, 2010 | 832 | 0.721 | 0.265 to 1.563 | 2.56 | 3.94 |
| Fachal, 2011 | 905 | 0.110 | 0.00280 to 0.614 | 2.78 | 4.01 |
| Gallagher, 2012 | 88 | 3.409 | 0.709 to 9.641 | 0.27 | 1.41 |
| Cybulski, 2013 | 3750 | 0.373 | 0.204 to 0.626 | 11.52 | 4.72 |
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 0.667 | 0.0169 to 3.658 | 0.46 | 2.00 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 7.252 | 0.15 | 0.91 |
| Pritchard, 2016 | 692 | 0.867 | 0.319 to 1.878 | 2.13 | 3.78 |
| Na, 2017 | 799 | 0.501 | 0.137 to 1.277 | 2.46 | 3.90 |
| Antonarakis, 2018 | 172 | 0.581 | 0.0147 to 3.197 | 0.53 | 2.17 |
| Carneiro, 2018 | 1534 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 0.240 | 4.71 | 4.37 |
| Nicolosi, 2019 | 3607 | 1.192 | 0.864 to 1.602 | 11.08 | 4.71 |
| Wei, 2019 | 316 | 0.633 | 0.0767 to 2.267 | 0.97 | 2.92 |
| Castro, 2019 | 419 | 0.955 | 0.261 to 2.426 | 1.29 | 3.26 |
| Giri, 2019 | 1328 | 1.054 | 0.578 to 1.762 | 4.08 | 4.28 |
| Sonpavde, 2019 | 514 | 5.058 | 3.331 to 7.324 | 1.58 | 3.48 |
| Sztupinszki, 2020 | 240 | 0.833 | 0.101 to 2.978 | 0.74 | 2.58 |
| Pritzlaff, 2020 | 277 | 0.722 | 0.0876 to 2.584 | 0.85 | 2.76 |
| Mateo, 2020 | 175 | 1.714 | 0.355 to 4.928 | 0.54 | 2.19 |
| Momozawa, 2020 | 7636 | 0.183 | 0.100 to 0.307 | 23.46 | 4.87 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 5.601 | 0.20 | 1.12 |
| Nguyen-Dumont, 2021 | 833 | 0.600 | 0.195 to 1.395 | 2.56 | 3.94 |
| Zhu, 2021 | 1836 | 0.381 | 0.153 to 0.784 | 5.64 | 4.46 |
| Truong, 2022 | 1883 | 0.584 | 0.292 to 1.043 | 5.79 | 4.47 |
| Kimura, 2022 | 549 | 0.364 | 0.0441 to 1.310 | 1.69 | 3.55 |
| Brady, 2022 | 437 | 0.458 | 0.0555 to 1.643 | 1.35 | 3.30 |
| So, 2022 | 120 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 3.027 | 0.37 | 1.75 |
| Lee, 2022 | 151 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 2.413 | 0.47 | 2.01 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 32,525 | 0.530 | 0.454 to 0.615 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 32,525 | 0.733 | 0.506 to 1.003 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 159.5048 |
| DF | 30 |
| Significance level | p < 0.0001 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 81.19% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 74.05 to 86.37 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 1.4944 |
| 95% CI | 0.03504 to 2.9537 |
| Significance level | p = 0.0451 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.09247 |
| Significance level | p = 0.4649 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Hamel, 2003 | 146 | 1.370 | 0.166 to 4.861 | 0.49 | 2.62 |
| Kirchhoff, 2004 | 251 | 3.187 | 1.386 to 6.183 | 0.84 | 3.12 |
| Agalliu, 2009 | 979 | 1.839 | 1.093 to 2.890 | 3.28 | 3.89 |
| Gallagher, 2010 | 832 | 2.404 | 1.474 to 3.688 | 2.79 | 3.83 |
| Kote-Jarai, 2011 | 1832 | 1.037 | 0.626 to 1.615 | 6.14 | 4.05 |
| Gallagher, 2012 | 88 | 4.545 | 1.252 to 11.231 | 0.30 | 2.10 |
| Akbari, 2014 | 1904 | 1.366 | 0.894 to 1.994 | 6.38 | 4.06 |
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 6.000 | 2.780 to 11.084 | 0.51 | 2.65 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 6.122 | 1.281 to 16.866 | 0.17 | 1.50 |
| Pritchard, 2016 | 692 | 5.347 | 3.792 to 7.295 | 2.32 | 3.76 |
| Na, 2017 | 799 | 1.877 | 1.054 to 3.078 | 2.68 | 3.82 |
| Antonarakis, 2018 | 172 | 2.907 | 0.950 to 6.653 | 0.58 | 2.78 |
| Carneiro, 2018 | 1534 | 1.565 | 1.005 to 2.319 | 5.14 | 4.02 |
| Nicolosi, 2019 | 3607 | 4.547 | 3.890 to 5.278 | 12.09 | 4.15 |
| Wei, 2019 | 316 | 6.329 | 3.908 to 9.606 | 1.06 | 3.30 |
| Castro, 2019 | 419 | 3.341 | 1.839 to 5.543 | 1.41 | 3.49 |
| Giri, 2019 | 1328 | 4.518 | 3.465 to 5.778 | 4.45 | 3.98 |
| Sonpavde, 2019 | 514 | 5.058 | 3.331 to 7.324 | 1.73 | 3.61 |
| Sztupinszki, 2020 | 240 | 2.083 | 0.680 to 4.795 | 0.81 | 3.08 |
| Pritzlaff, 2020 | 277 | 3.971 | 1.999 to 6.994 | 0.93 | 3.20 |
| Mateo, 2020 | 175 | 8.000 | 4.443 to 13.058 | 0.59 | 2.80 |
| Momozawa, 2020 | 7636 | 1.087 | 0.867 to 1.346 | 25.59 | 4.20 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 1.562 | 0.0396 to 8.401 | 0.22 | 1.77 |
| Nguyen-Dumont, 2021 | 833 | 2.281 | 1.379 to 3.539 | 2.79 | 3.83 |
| Zhu, 2021 | 1836 | 4.303 | 3.421 to 5.334 | 6.16 | 4.05 |
| Truong, 2022 | 1883 | 3.930 | 3.098 to 4.909 | 6.31 | 4.06 |
| Kimura, 2022 | 549 | 3.461 | 2.096 to 5.352 | 1.84 | 3.65 |
| Brady, 2022 | 437 | 0.686 | 0.142 to 1.993 | 1.47 | 3.52 |
| So, 2022 | 120 | 1.667 | 0.202 to 5.891 | 0.41 | 2.42 |
| Lee, 2022 | 151 | 9.934 | 5.667 to 15.855 | 0.51 | 2.66 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 29,813 | 2.473 | 2.300 to 2.656 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 29,813 | 3.246 | 2.539 to 4.037 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 320.7889 |
| DF | 29 |
| Significance level | p < 0.0001 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 90.96% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 88.22 to 93.06 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 2.4186 |
| 95% CI | 0.3057 to 4.5316 |
| Significance level | p = 0.0264 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.07126 |
| Significance level | p = 0.5802 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Hamel, 2003 | 146 | 1.370 | 0.166 to 4.861 | 0.43 | 3.02 |
| Kirchhoff, 2004 | 251 | 5.179 | 2.786 to 8.694 | 0.75 | 3.37 |
| Agalliu, 2009 | 979 | 2.962 | 1.993 to 4.227 | 2.90 | 3.83 |
| Gallagher, 2010 | 832 | 3.125 | 2.051 to 4.545 | 2.46 | 3.80 |
| Gallagher, 2012 | 88 | 7.955 | 3.258 to 15.705 | 0.26 | 2.60 |
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 6.667 | 3.243 to 11.918 | 0.45 | 3.04 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 6.122 | 1.281 to 16.866 | 0.15 | 2.04 |
| Pritchard, 2016 | 692 | 6.214 | 4.533 to 8.279 | 2.05 | 3.76 |
| Na, 2017 | 799 | 2.378 | 1.438 to 3.689 | 2.37 | 3.79 |
| Antonarakis, 2018 | 172 | 3.488 | 1.291 to 7.438 | 0.51 | 3.14 |
| Carneiro, 2018 | 1534 | 1.565 | 1.005 to 2.319 | 4.54 | 3.90 |
| Nicolosi, 2019 | 3607 | 5.739 | 5.002 to 6.548 | 10.67 | 3.97 |
| Wei, 2019 | 316 | 6.962 | 4.414 to 10.351 | 0.94 | 3.49 |
| Castro, 2019 | 419 | 4.296 | 2.566 to 6.705 | 1.24 | 3.60 |
| Giri, 2019 | 1328 | 5.572 | 4.400 to 6.945 | 3.93 | 3.88 |
| Sonpavde, 2019 | 514 | 10.117 | 7.648 to 13.055 | 1.52 | 3.68 |
| Sztupinszki, 2020 | 240 | 2.917 | 1.181 to 5.917 | 0.71 | 3.35 |
| Pritzlaff, 2020 | 277 | 4.693 | 2.522 to 7.892 | 0.82 | 3.42 |
| Mateo, 2020 | 175 | 9.714 | 5.761 to 15.098 | 0.52 | 3.15 |
| Momozawa, 2020 | 7636 | 1.270 | 1.031 to 1.547 | 22.59 | 4.00 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 1.562 | 0.0396 to 8.401 | 0.19 | 2.30 |
| Nguyen-Dumont, 2021 | 833 | 2.881 | 1.855 to 4.257 | 2.47 | 3.80 |
| Zhu, 2021 | 1836 | 4.684 | 3.763 to 5.753 | 5.43 | 3.92 |
| Truong, 2022 | 1883 | 4.514 | 3.621 to 5.552 | 5.57 | 3.92 |
| Kimura, 2022 | 549 | 3.825 | 2.383 to 5.788 | 1.63 | 3.70 |
| Brady, 2022 | 437 | 1.144 | 0.373 to 2.650 | 1.30 | 3.62 |
| So, 2022 | 120 | 1.667 | 0.202 to 5.891 | 0.36 | 2.87 |
| Swami, 2022 | 7707 | 7.967 | 7.372 to 8.594 | 22.80 | 4.00 |
| Lee, 2022 | 151 | 9.934 | 5.667 to 15.855 | 0.45 | 3.05 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 33,784 | 4.174 | 3.964 to 4.393 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 33,784 | 4.466 | 3.376 to 5.700 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 632.0792 |
| DF | 28 |
| Significance level | p < 0.0001 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 95.57% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 94.50 to 96.43 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 0.4449 |
| 95% CI | −2.6280 to 3.5179 |
| Significance level | p = 0.7687 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.03941 |
| Significance level | p = 0.7641 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 0.667 | 0.0169 to 3.658 | 10.86 | 10.86 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 2.041 | 0.0517 to 10.854 | 3.60 | 3.60 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 5.601 | 4.68 | 4.68 |
| Tukachinsky, 2021 | 837 | 1.075 | 0.493 to 2.031 | 60.29 | 60.29 |
| Martinez Chanza, 2021 | 141 | 0.709 | 0.0180 to 3.888 | 10.22 | 10.22 |
| Uemura, 2022 | 143 | 0.699 | 0.0177 to 3.835 | 10.36 | 10.36 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 1384 | 1.096 | 0.618 to 1.794 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 1384 | 1.096 | 0.616 to 1.710 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 1.4171 |
| DF | 5 |
| Significance level | p = 0.9224 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 0.00% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 0.00 to 13.04 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 0.01503 |
| 95% CI | −1.4005 to 1.4305 |
| Significance level | p = 09779 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.06667 |
| Significance level | p = 0.8510 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 12.000 | 7.269 to 18.301 | 10.86 | 16.64 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 14.286 | 5.942 to 27.242 | 3.60 | 7.26 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 9.375 | 3.519 to 19.297 | 4.68 | 9.02 |
| Tukachinsky, 2021 | 837 | 7.527 | 5.832 to 9.528 | 60.29 | 34.95 |
| Martinez Chanza, 2021 | 141 | 9.929 | 5.535 to 16.098 | 10.22 | 15.99 |
| Uemura, 2022 | 143 | 12.587 | 7.634 to 19.162 | 10.36 | 16.14 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 1384 | 9.161 | 7.696 to 10.802 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 1384 | 10.256 | 7.921 to 12.854 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 8.1196 |
| DF | 5 |
| Significance level | p = 0.1498 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 38.42% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 0.00 to 75.53 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 2.1365 |
| 95% CI | 0.4976 to 3.7754 |
| Significance level | p = 0.0224 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.06667 |
| Significance level | p = 0.8510 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 12.667 | 7.801 to 19.072 | 10.86 | 15.82 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 16.327 | 7.322 to 29.657 | 3.60 | 6.40 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 9.375 | 3.519 to 19.297 | 4.68 | 8.05 |
| Tukachinsky, 2021 | 837 | 8.602 | 6.791 to 10.710 | 60.29 | 39.34 |
| Martinez Chanza, 2021 | 141 | 10.638 | 6.078 to 16.939 | 10.22 | 15.12 |
| Uemura, 2022 | 143 | 13.287 | 8.193 to 19.969 | 10.36 | 15.28 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 1384 | 10.115 | 8.580 to 11.822 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 1384 | 10.940 | 8.732 to 13.364 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 7.0496 |
| DF | 5 |
| Significance level | p = 0.2170 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 29.07% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 0.00 to 70.93 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 1.9127 |
| 95% CI | 0.2041 to 3.6213 |
| Significance level | p = 0.0359 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.3333 |
| Significance level | p = 0.3476 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Gallagher, 2012 | 88 | 3.409 | 0.709 to 9.641 | 2.24 | 8.49 |
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 0.667 | 0.0169 to 3.658 | 3.80 | 9.81 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 7.252 | 1.26 | 6.77 |
| Pritchard, 2016 | 692 | 0.867 | 0.319 to 1.878 | 17.44 | 11.87 |
| Antonarakis, 2018 | 172 | 0.581 | 0.0147 to 3.197 | 4.35 | 10.09 |
| Carneiro, 2018 | 1534 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 0.240 | 38.64 | 12.26 |
| Sonpavde, 2019 | 514 | 5.058 | 3.331 to 7.324 | 12.96 | 11.63 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 5.601 | 1.64 | 7.58 |
| Kimura, 2022 | 549 | 0.364 | 0.0441 to 1.310 | 13.84 | 11.69 |
| Lee, 2022 | 151 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 2.413 | 3.83 | 9.82 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 3963 | 0.583 | 0.371 to 0.873 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 3963 | 0.935 | 0.192 to 2.229 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 80.7401 |
| DF | 9 |
| Significance level | p < 0.0001 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 88.85% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 81.60 to 93.25 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 1.9459 |
| 95% CI | −2.5292 to 6.4209 |
| Significance level | p = 0.3454 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.1111 |
| Significance level | p = 0.6547 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Gallagher, 2012 | 88 | 4.545 | 1.252 to 11.231 | 2.24 | 7.64 |
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 6.000 | 2.780 to 11.084 | 3.80 | 9.45 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 6.122 | 1.281 to 16.866 | 1.26 | 5.60 |
| Pritchard, 2016 | 692 | 5.347 | 3.792 to 7.295 | 17.44 | 12.87 |
| Antonarakis, 2018 | 172 | 2.907 | 0.950 to 6.653 | 4.35 | 9.87 |
| Carneiro, 2018 | 1534 | 1.565 | 1.005 to 2.319 | 38.64 | 13.62 |
| Sonpavde, 2019 | 514 | 5.058 | 3.331 to 7.324 | 12.96 | 12.43 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 1.562 | 0.0396 to 8.401 | 1.64 | 6.51 |
| Kimura, 2022 | 549 | 3.461 | 2.096 to 5.352 | 13.84 | 12.54 |
| Lee, 2022 | 151 | 9.934 | 5.667 to 15.855 | 3.83 | 9.47 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 3963 | 3.439 | 2.894 to 4.054 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 3963 | 4.514 | 2.932 to 6.418 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 48.7604 |
| DF | 9 |
| Significance level | p < 0.0001 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 81.54% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 67.17 to 89.62 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 2.5522 |
| 95% CI | −0.4949 to 5.5992 |
| Significance level | p = 0.0895 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | −0.02222 |
| Significance level | p = 0.9287 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Gallagher, 2012 | 88 | 7.955 | 3.258 to 15.705 | 0.76 | 7.55 |
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 6.667 | 3.243 to 11.918 | 1.29 | 8.71 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 6.122 | 1.281 to 16.866 | 0.43 | 6.02 |
| Pritchard, 2016 | 692 | 6.214 | 4.533 to 8.279 | 5.93 | 10.54 |
| Antonarakis, 2018 | 172 | 3.488 | 1.291 to 7.438 | 1.48 | 8.97 |
| Carneiro, 2018 | 1534 | 1.565 | 1.005 to 2.319 | 13.14 | 10.89 |
| Sonpavde, 2019 | 514 | 10.117 | 7.648 to 13.055 | 4.41 | 10.33 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 1.562 | 0.0396 to 8.401 | 0.56 | 6.74 |
| Kimura, 2022 | 549 | 3.825 | 2.383 to 5.788 | 4.71 | 10.38 |
| Swami, 2022 | 7707 | 7.967 | 7.372 to 8.594 | 65.99 | 11.13 |
| Lee, 2022 | 151 | 9.934 | 5.667 to 15.855 | 1.30 | 8.73 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 11,670 | 6.561 | 6.119 to 7.026 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 11,670 | 5.842 | 3.721 to 8.405 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 156.4338 |
| DF | 10 |
| Significance level | p < 0.0001 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 93.61% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 90.42 to 95.73 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | −1.2792 |
| 95% CI | −5.3286 to 2.7702 |
| Significance level | p = 0.4930 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | −0.01818 |
| Significance level | p = 0.9379 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 0.667 | 0.0169 to 3.658 | 12.10 | 12.10 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 2.041 | 0.0517 to 10.854 | 4.01 | 4.01 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 5.601 | 5.21 | 5.21 |
| Tukachinsky, 2021 | 837 | 1.075 | 0.493 to 2.031 | 67.15 | 67.15 |
| Uemura, 2022 | 143 | 0.699 | 0.0177 to 3.835 | 11.54 | 11.54 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 1243 | 1.104 | 0.601 to 1.853 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 1243 | 1.104 | 0.600 to 1.758 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 1.4098 |
| DF | 4 |
| Significance level | p = 0.8425 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 0.00% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 0.00 to 44.46 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 0.03864 |
| 95% CI | −1.9079 to 1.9852 |
| Significance level | p = 0.9536 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.0000 |
| Significance level | p = 1.0000 |
| Study | Sample size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 12.000 | 7.269 to 18.301 | 12.10 | 20.83 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 14.286 | 5.942 to 27.242 | 4.01 | 10.15 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 9.375 | 3.519 to 19.297 | 5.21 | 12.33 |
| Tukachinsky, 2021 | 837 | 7.527 | 5.832 to 9.528 | 67.15 | 36.38 |
| Uemura, 2022 | 143 | 12.587 | 7.634 to 19.162 | 11.54 | 20.32 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 1243 | 9.045 | 7.512 to 10.775 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 1243 | 10.523 | 7.635 to 13.812 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 7.9212 |
| DF | 4 |
| Significance level | p = 0.0945 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 49.50% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 0.00 to 81.49 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 2.2040 |
| 95% CI | −0.01351 to 4.4216 |
| Significance level | p = 0.0508 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.2000 |
| Significance level | p = 0.6242 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 12.667 | 7.801 to 19.072 | 12.10 | 20.28 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 16.327 | 7.322 to 29.657 | 4.01 | 9.23 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 9.375 | 3.519 to 19.297 | 5.21 | 11.37 |
| Tukachinsky, 2021 | 837 | 8.602 | 6.791 to 10.710 | 67.15 | 39.41 |
| Uemura, 2022 | 143 | 13.287 | 8.193 to 19.969 | 11.54 | 19.71 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 1243 | 10.026 | 8.415 to 11.828 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 1243 | 11.263 | 8.485 to 14.378 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 6.9426 |
| DF | 4 |
| Significance level | p = 0.1390 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 42.38% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 0.00 to 78.81 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 1.9919 |
| 95% CI | −0.3078 to 4.2916 |
| Significance level | p = 0.0704 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.6000 |
| Significance level | p = 0.1416 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Gallagher, 2012 | 88 | 3.409 | 0.709 to 9.641 | 3.45 | 13.51 |
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 0.667 | 0.0169 to 3.658 | 5.86 | 14.67 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 7.252 | 1.94 | 11.75 |
| Antonarakis, 2018 | 172 | 0.581 | 0.0147 to 3.197 | 6.71 | 14.90 |
| Carneiro, 2018 | 1534 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 0.240 | 59.54 | 16.49 |
| Sonpavde, 2019 | 514 | 5.058 | 3.331 to 7.324 | 19.98 | 16.06 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 0.000 | 0.000 to 5.601 | 2.52 | 12.62 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 2571 | 0.562 | 0.311 to 0.934 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 2571 | 1.207 | 0.0526 to 3.839 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 78.5852 |
| DF | 6 |
| Significance level | p < 0.0001 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 92.36% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 86.81 to 95.58 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 2.4198 |
| 95% CI | −3.9590 to 8.7987 |
| Significance level | p = 0.3743 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | −0.04762 |
| Significance level | p = 0.8806 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Gallagher, 2012 | 88 | 4.545 | 1.252 to 11.231 | 3.45 | 11.73 |
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 6.000 | 2.780 to 11.084 | 5.86 | 14.50 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 6.122 | 1.281 to 16.866 | 1.94 | 8.60 |
| Antonarakis, 2018 | 172 | 2.907 | 0.950 to 6.653 | 6.71 | 15.16 |
| Carneiro, 2018 | 1534 | 1.565 | 1.005 to 2.319 | 59.54 | 20.91 |
| Sonpavde, 2019 | 514 | 5.058 | 3.331 to 7.324 | 19.98 | 19.09 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 1.562 | 0.0396 to 8.401 | 2.52 | 10.01 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 2571 | 2.691 | 2.101 to 3.391 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 2571 | 3.895 | 2.132 to 6.158 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 25.7604 |
| DF | 6 |
| Significance level | p = 0.0002 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 76.71% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 51.20 to 88.88 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 2.2629 |
| 95% CI | −0.7550 to 5.2808 |
| Significance level | p = 0.1118 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.04762 |
| Significance level | p = 0.8806 |
| Study | Sample Size | Proportion (%) | 95% CI | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Random | ||||
| Gallagher, 2012 | 88 | 7.955 | 3.258 to 15.705 | 3.45 | 13.42 |
| Robinson, 2015 | 150 | 6.667 | 3.243 to 11.918 | 5.86 | 14.68 |
| Mateo, 2015 | 49 | 6.122 | 1.281 to 16.866 | 1.94 | 11.54 |
| Antonarakis, 2018 | 172 | 3.488 | 1.291 to 7.438 | 6.71 | 14.94 |
| Carneiro, 2018 | 1534 | 1.565 | 1.005 to 2.319 | 59.54 | 16.72 |
| Sonpavde, 2019 | 514 | 10.117 | 7.648 to 13.055 | 19.98 | 16.23 |
| Mota, 2020 | 64 | 1.562 | 0.0396 to 8.401 | 2.52 | 12.46 |
| Total (fixed effects) | 2571 | 3.500 | 2.824 to 4.283 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Total (random effects) | 2571 | 5.255 | 2.177 to 9.569 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Q | 71.1738 |
| DF | 6 |
| Significance level | p < 0.0001 |
| I2 (inconsistency) | 91.57% |
| 95% CI for I2 | 85.20 to 95.20 |
| Egger’s test | |
| Intercept | 2.8014 |
| 95% CI | −2.9857 to 8.5884 |
| Significance level | p = 0.2685 |
| Begg’s test | |
| Kendall’s Tau | 0.04762 |
| Significance level | p = 0.8806 |
References
- Kuchenbaecker, K.B.; Hopper, J.L.; Barnes, D.R.; Phillips, K.A.; Mooij, T.M.; Roos-Blom, M.J.; Jervis, S.; van Leeuwen, F.E.; Milne, R.L.; Andrieu, N.; et al. Risks of Breast, Ovarian, and Contralateral Breast Cancer for BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers. JAMA 2017, 317, 2402–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindo, K.; Yu, J.; Suenaga, M.; Fesharakizadeh, S.; Cho, C.; Macgregor-Das, A.; Siddiqui, A.; Witmer, P.D.; Tamura, K.; Song, T.J.; et al. Deleterious Germline Mutations in Patients with Apparently Sporadic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3382–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bono, J.; Mateo, J.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Shore, N.; Sandhu, S.; Chi, K.N.; Sartor, O.; Agarwal, N.; Olmos, D.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, J.; Porta, N.; Bianchini, D.; McGovern, U.; Elliott, T.; Jones, R.; Syndikus, I.; Ralph, C.; Jain, S.; Varughese, M.; et al. Olaparib in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer with DNA repair gene aberrations (TOPARP-B): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaeffer, E.M.; Srinivas, S.; Adra, N.; An, Y.; Barocas, D.; Bitting, R.; Bryce, A.; Chapin, B.; Cheng, H.H.; D’Amico, A.V.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Prostate Cancer, Version 1.2023. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar]
- Anscher, M.S.; Chang, E.; Gao, X.; Gong, Y.; Weinstock, C.; Bloomquist, E.; Adeniyi, O.; Charlab, R.; Zimmerman, S.; Serlemitsos-Day, M.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Rucaparib for the Treatment of Patients with Deleterious BRCA-Mutated Metastatic Castrate-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Oncologist 2021, 26, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abida, W.; Patnaik, A.; Campbell, D.; Shapiro, J.; Bryce, A.H.; McDermott, R.; Sautois, B.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Bambury, R.M.; Voog, E.; et al. Rucaparib in Men With Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer Harboring a BRCA1 or BRCA2 Gene Alteration. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3763–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemminki, K. Familial risk and familial survival in prostate cancer. World J. Urol. 2012, 30, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, A.; Incorvaia, L.; Capoluongo, E.; Tagliaferri, P.; Gori, S.; Cortesi, L.; Genuardi, M.; Turchetti, D.; De Giorgi, U.; Di Maio, M.; et al. Implementation of preventive and predictive BRCA testing in patients with breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and prostate cancer: A position paper of Italian Scientific Societies. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, C.; Castro, E.; Fizazi, K.; Heidenreich, A.; Ost, P.; Procopio, G.; Tombal, B.; Gillessen, S. Prostate cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1119–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.; Alkhushaym, N.; Fallatah, S.; Althagafi, A.; Aljadeed, R.; Alsowaida, Y.; Jeter, J.; Martin, J.R.; Babiker, H.M.; McBride, A.; et al. The association of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations with prostate cancer risk, frequency, and mortality: A meta-analysis. Prostate 2019, 79, 880–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusti, R.M.; Rutter, J.L.; Duray, P.H.; Freedman, L.S.; Konichezky, M.; Fisher-Fischbein, J.; Greene, M.H.; Maslansky, B.; Fischbein, A.; Gruber, S.B.; et al. A twofold increase in BRCA mutation related prostate cancer among Ashkenazi Israelis is not associated with distinctive histopathology. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhoff, T.; Kauff, N.D.; Mitra, N.; Nafa, K.; Huang, H.; Palmer, C.; Gulati, T.; Wadsworth, E.; Donat, S.; Robson, M.E.; et al. BRCA mutations and risk of prostate cancer in Ashkenazi Jews. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 2918–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybulski, C.; Górski, B.; Gronwald, J.; Huzarski, T.; Byrski, T.; Debniak, T.; Jakubowska, A.; Wokołorczyk, D.; Gliniewicz, B.; Sikorski, A.; et al. BRCA1 mutations and prostate cancer in Poland. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2008, 17, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agalliu, I.; Gern, R.; Leanza, S.; Burk, R.D. Associations of high-grade prostate cancer with BRCA1 and BRCA2 founder mutations. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, D.J.; Gaudet, M.M.; Pal, P.; Kirchhoff, T.; Balistreri, L.; Vora, K.; Bhatia, J.; Stadler, Z.; Fine, S.W.; Reuter, V.; et al. Germline BRCA mutations denote a clinicopathologic subset of prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2115–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kote-Jarai, Z.; Leongamornlert, D.; Saunders, E.; Tymrakiewicz, M.; Castro, E.; Mahmud, N.; Guy, M.; Edwards, S.; O’Brien, L.; Sawyer, E.; et al. BRCA2 is a moderate penetrance gene contributing to young-onset prostate cancer: Implications for genetic testing in prostate cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fachal, L.; Gómez-Caamaño, A.; Celeiro-Muñoz, C.; Peleteiro, P.; Blanco, A.; Carballo, A.; Forteza, J.; Carracedo, A.; Vega, A. BRCA1 mutations do not increase prostate cancer risk: Results from a meta-analysis including new data. Prostate 2011, 71, 1768–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, D.J.; Cronin, A.M.; Milowsky, M.I.; Morris, M.J.; Bhatia, J.; Scardino, P.T.; Eastham, J.A.; Offit, K.; Robson, M.E. Germline BRCA mutation does not prevent response to taxane-based therapy for the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer. BJU Int. 2012, 109, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybulski, C.; Wokołorczyk, D.; Kluźniak, W.; Jakubowska, A.; Górski, B.; Gronwald, J.; Huzarski, T.; Kashyap, A.; Byrski, T.; Dębniak, T.; et al. An inherited NBN mutation is associated with poor prognosis prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, M.R.; Wallis, C.J.; Toi, A.; Trachtenberg, J.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A.; Nam, R.K. The impact of a BRCA2 mutation on mortality from screen-detected prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1238–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeshouse, A.; Ahn, J.; Akbani, R.; Ally, A.; Amin, S.; Andry, C.D.; Annala, M.; Aprikian, A.; Armenia, J.; Arora, A.; et al. The Molecular Taxonomy of Primary Prostate Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.; Van Allen, E.M.; Wu, Y.M.; Schultz, N.; Lonigro, R.J.; Mosquera, J.M.; Montgomery, B.; Taplin, M.E.; Pritchard, C.C.; Attard, G.; et al. Integrative clinical genomics of advanced prostate cancer. Cell 2015, 161, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Mateo, J.; Walsh, M.F.; De Sarkar, N.; Abida, W.; Beltran, H.; Garofalo, A.; Gulati, R.; Carreira, S.; Eeles, R.; et al. Inherited DNA-Repair Gene Mutations in Men with Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, R.; Zheng, S.L.; Han, M.; Yu, H.; Jiang, D.; Shah, S.; Ewing, C.M.; Zhang, L.; Novakovic, K.; Petkewicz, J.; et al. Germline Mutations in ATM and BRCA1/2 Distinguish Risk for Lethal and Indolent Prostate Cancer and are Associated with Early Age at Death. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonarakis, E.S.; Lu, C.; Luber, B.; Liang, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Silberstein, J.L.; Piana, D.; Lai, Z.; Isaacs, W.B.; et al. Germline DNA-repair Gene Mutations and Outcomes in Men with Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer Receiving First-line Abiraterone and Enzalutamide. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, B.A.; Collier, K.A.; Nagy, R.J.; Pamarthy, S.; Sagar, V.; Fairclough, S.; Odegaard, J.; Lanman, R.B.; Costa, R.; Taxter, T.; et al. Acquired Resistance to Poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase Inhibitor Olaparib in BRCA2-Associated Prostate Cancer Resulting from Biallelic BRCA2 Reversion Mutations Restores Both Germline and Somatic Loss-of-Function Mutations. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2018, 2, PO.17.00176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolosi, P.; Ledet, E.; Yang, S.; Michalski, S.; Freschi, B.; O’Leary, E.; Esplin, E.D.; Nussbaum, R.L.; Sartor, O. Prevalence of Germline Variants in Prostate Cancer and Implications for Current Genetic Testing Guidelines. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, E.; Romero-Laorden, N.; Del Pozo, A.; Lozano, R.; Medina, A.; Puente, J.; Piulats, J.M.; Lorente, D.; Saez, M.I.; Morales-Barrera, R.; et al. PROREPAIR-B: A Prospective Cohort Study of the Impact of Germline DNA Repair Mutations on the Outcomes of Patients With Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, V.N.; Hegarty, S.E.; Hyatt, C.; O’Leary, E.; Garcia, J.; Knudsen, K.E.; Kelly, W.K.; Gomella, L.G. Germline genetic testing for inherited prostate cancer in practice: Implications for genetic testing, precision therapy, and cascade testing. Prostate 2019, 79, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonpavde, G.; Agarwal, N.; Pond, G.R.; Nagy, R.J.; Nussenzveig, R.H.; Hahn, A.W.; Sartor, O.; Gourdin, T.S.; Nandagopal, L.; Ledet, E.M.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA alterations in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer 2019, 125, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo, J.; Carreira, S.; Sandhu, S.; Miranda, S.; Mossop, H.; Perez-Lopez, R.; Nava Rodrigues, D.; Robinson, D.; Omlin, A.; Tunariu, N.; et al. DNA-Repair Defects and Olaparib in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.M.; Saidian, A.; Shaya, J.; Nonato, T.; Cabal, A.; Randall, J.M.; Millard, F.; Stewart, T.; Rose, B.; Tamayo, P.; et al. The Prognostic Significance of Homologous Recombination Repair Pathway Alterations in Metastatic Hormone Sensitive Prostate Cancer. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2022, 20, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, M.K.; Ahn, H.K.; Huh, J.; Kim, K.H. Germline pathogenic variants in unselected Korean men with prostate cancer. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2022, 63, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, L.; Newcomb, L.F.; Zhu, K.; Zheng, Y.; Boyer, H.; Sarkar, N.; McKenney, J.K.; Brooks, J.D.; Carroll, P.R.; Dash, A.; et al. Germline mutations in penetrant cancer predisposition genes are rare in men with prostate cancer selecting active surveillance. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 4332–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swami, U.; Zimmerman, R.M.; Nussenzveig, R.H.; Hernandez, E.J.; Jo, Y.; Sayegh, N.; Wesolowski, S.; Kiedrowski, L.A.; Barata, P.C.; Lemmon, G.H.; et al. Genomic landscape of advanced prostate cancer patients with BRCA1 versus BRCA2 mutations as detected by comprehensive genomic profiling of cell-free DNA. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 966534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, N.; Kotar, K.; Foulkes, W.D. Founder mutations in BRCA1/2 are not frequent in Canadian Ashkenazi Jewish men with prostate cancer. BMC Med. Genet. 2003, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wu, J.; Gu, W.; Qin, X.; Dai, B.; Lin, G.; Gan, H.; Freedland, S.J.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, D. Germline DNA Repair Gene Mutation Landscape in Chinese Prostate Cancer Patients. Eur. Urol. 2019, 76, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Mizuno, K.; Shiota, M.; Narita, S.; Terada, N.; Fujimoto, N.; Ogura, K.; Hatano, S.; Iwasaki, Y.; Hakozaki, N.; et al. Prognostic significance of pathogenic variants in BRCA1, BRCA2, ATM and PALB2 genes in men undergoing hormonal therapy for advanced prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 1680–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, H.; Breen, K.; Nandakumar, S.; Sjoberg, D.D.; Kemel, Y.; Mehta, N.; Lenis, A.T.; Reisz, P.A.; Carruthers, J.; Benfante, N.; et al. Gene-based Confirmatory Germline Testing Following Tumor-only Sequencing of Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2023, 83, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, H.; Oya, M.; Kamoto, T.; Sugimoto, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Morita, K.; Koto, R.; Takahashi, M.; Nii, M.; Shin, E.; et al. The prevalence of gene mutations in homologous recombination repair pathways in Japanese patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer in real-world clinical practice: The multi-institutional observational ZENSHIN study. Cancer Med. 2022, 12, 5265–5274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Hu, X.; Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, M.; Zhao, H.; Gao, R.; Huang, Z.; Lu, J. Homologous recombination repair gene mutations in Chinese localized and locally advanced prostate cancer patients. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 224, 153507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, H.; Li, Y.; Ng, C.F.; Zhou, F.; He, C.; Sun, G.; Ni, Y.; Chiu, P.K.F.; et al. Inherited Mutations in Chinese Men with Prostate Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2021, 20, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen-Dumont, T.; Dowty, J.G.; MacInnis, R.J.; Steen, J.A.; Riaz, M.; Dugué, P.A.; Renault, A.L.; Hammet, F.; Mahmoodi, M.; Theys, D.; et al. Rare Germline Pathogenic Variants Identified by Multigene Panel Testing and the Risk of Aggressive Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Chanza, N.; Bernard, B.; Barthelemy, P.; Accarain, A.; Paesmans, M.; Desmyter, L.; T’Kint de Roodenbeke, D.; Gil, T.; Sideris, S.; Roumeguere, T.; et al. Prevalence and clinical impact of tumor BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in patients presenting with localized or metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic. Dis. 2022, 25, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukachinsky, H.; Madison, R.W.; Chung, J.H.; Gjoerup, O.V.; Severson, E.A.; Dennis, L.; Fendler, B.J.; Morley, S.; Zhong, L.; Graf, R.P.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA in 3,334 Patients with Advanced Prostate Cancer Identifies Targetable BRCA Alterations and AR Resistance Mechanisms. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3094–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momozawa, Y.; Iwasaki, Y.; Hirata, M.; Liu, X.; Kamatani, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Sugano, K.; Yoshida, T.; Murakami, Y.; Matsuda, K.; et al. Germline Pathogenic Variants in 7636 Japanese Patients with Prostate Cancer and 12366 Controls. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2020, 112, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, J.; Seed, G.; Bertan, C.; Rescigno, P.; Dolling, D.; Figueiredo, I.; Miranda, S.; Nava Rodrigues, D.; Gurel, B.; Clarke, M.; et al. Genomics of lethal prostate cancer at diagnosis and castration resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1743–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritzlaff, M.; Tian, Y.; Reineke, P.; Stuenkel, A.J.; Allen, K.; Gutierrez, S.; Jackson, M.; Dolinsky, J.S.; LaDuca, H.; Xu, J.; et al. Diagnosing hereditary cancer predisposition in men with prostate cancer. Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mota, J.M.; Barnett, E.; Nauseef, J.T.; Nguyen, B.; Stopsack, K.H.; Wibmer, A.; Flynn, J.R.; Heller, G.; Danila, D.C.; Rathkopf, D.; et al. Platinum-Based Chemotherapy in Metastatic Prostate Cancer with DNA Repair Gene Alterations. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztupinszki, Z.; Diossy, M.; Krzystanek, M.; Borcsok, J.; Pomerantz, M.M.; Tisza, V.; Spisak, S.; Rusz, O.; Csabai, I.; Freedman, M.L.; et al. Detection of Molecular Signatures of Homologous Recombination Deficiency in Prostate Cancer with or without BRCA1/2 Mutations. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2673–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, T.H.; Adelman, C.; Barnicle, A.; Kozarewa, I.; Luke, S.; Lai, Z.; Hollis, S.; Dougherty, B.; Harrington, E.A.; Kang, J.; et al. Homologous Recombination Repair Gene Mutation Characterization by Liquid Biopsy: A Phase II Trial of Olaparib and Abiraterone in Metastatic Castrate-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathkopf, D.; Chi, K.; Olmos, D.; Cheng, H.; Agarwal, N.; Graff, J.; Sandhu, S.; Hayreh, V.; Lopez-Gitlitz, A.; Francis, P.; et al. AMPLITUDE: A study of niraparib in combination with abiraterone acetate plus prednisone (AAP) versus AAP for the treatment of patients with deleterious germline or somatic homologous recombination repair (HRR) gene-altered metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (mCSPC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, TPS176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.N.; Rathkopf, D.E.; Smith, M.R.; Efstathiou, E.; Attard, G.; Olmos, D.; Lee, J.Y.; Small, E.J.; Gomes, A.J.; Roubaud, G.; et al. Phase 3 MAGNITUDE study: First results of niraparib (NIRA) with abiraterone acetate and prednisone (AAP) as first-line therapy in patients (pts) with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) with and without homologous recombination repair (HRR) gene alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Mateo, J.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Shore, N.; Sandhu, S.; Chi, K.N.; Sartor, O.; Agarwal, N.; Olmos, D.; et al. Survival with Olaparib in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2345–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubara, N.; de Bono, J.; Olmos, D.; Procopio, G.; Kawakami, S.; Ürün, Y.; van Alphen, R.; Flechon, A.; Carducci, M.A.; Choi, Y.D.; et al. Olaparib Efficacy in Patients with Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer and BRCA1, BRCA2, or ATM Alterations Identified by Testing Circulating Tumor DNA. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| BRCA1 | BRCA2 | BRCA1/2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germline | Somatic | Germline | Somatic | Germline | Somatic | |
| Patients with any stage PC | ||||||
| Number of studies | 31 | 10 | 30 | 10 | 29 | 10 |
| Number of patients | 32,525 | 3229 | 29,813 | 3229 | 33,784 | 3229 |
| % (fixed effect) | 0.53 (95% CI: 0.45–0.62) | 1.20 (95% CI: 0.85–1.64) | 2.47 (95% CI: 2.30–2.66) | 4.77 (95% CI: 4.06–5.56) | 4.17 (95% CI: 3.96–4.39) | 6.07 (95% CI: 5.27–6.95) |
| % (random effect) | 0.73 (95% CI: 0.51–1.00) | 1.20 (95% CI: 0.85–1.60) | 3.25 (95% CI: 2.54–4.04) | 6.29 (95% CI: 3.79–9.38) | 4.47 (95% CI: 3.38–5.70) | 7.18 (95% CI: 4.89–9.87) |
| Heterogeneity I2 (p-value) | 81.19% (p < 0.0001) | 0.00% (p = 0.7423) | 90.96% (p < 0.0001) | 89.14% (p < 0.0001) | 95.57% (p < 0.0001) | 84.17% (p < 0.0001) |
| Metastatic PC patients | ||||||
| Number of studies | 10 | 6 | 10 | 6 | 11 | 6 |
| Number of patients | 3963 | 1384 | 3963 | 1384 | 11,670 | 1384 |
| % (fixed effect) | 0.58 (95% CI: 0.37–0.87) | 1.10 (95% CI: 0.62–1.79) | 3.44 (95% CI: 2.89–4.05) | 9.16 (95% CI: 7.70–10.80) | 6.56 (95% CI: 6.12–7.03) | 10.12 (95% CI: 8.58–11.82) |
| % (random effect) | 0.94 (95% CI: 0.19–2.23) | 1.10 (95% CI: 0.62–1.71) | 4.51 (95% CI: 2.93–6.42) | 10.26 (95% CI: 7.92–12.85) | 5.84 (95% CI: 3.72–8.41) | 10.94 (95% CI: 8.73–13.36) |
| Heterogeneity I2 (p-value) | 88.85% (p < 0.0001) | 0.00% (p = 0.9224) | 81.54% (p < 0.0001) | 38.42% (p = 0.1498) | 93.61% (p < 0.0001) | 29.07% (p = 0.2170) |
| mCRPC patients | ||||||
| Number of studies | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 |
| Number of patients | 2571 | 1243 | 2571 | 1243 | 2571 | 1243 |
| % (fixed effect) | 0.56 (95% CI: 0.31–0.93) | 1.10 (95% CI: 0.60–1.85) | 2.69 (95% CI: 2.10–3.39) | 9.05 (95% CI: 7.51–10.78) | 3.50 (95% CI: 2.82–4.28) | 10.03 (95% CI: 8.42–11.83) |
| % (random effect) | 1.21 (95% CI: 0.05–3.84) | 1.10 (95% CI: 0.60–1.76) | 3.90 (95% CI: 2.13–6.16) | 10.52 (95% CI: 7.64–13.81) | 5.26 (95% CI: 2.18–9.57) | 11.26 (95% CI: 8.49–14.38) |
| Heterogeneity I2 (p-value) | 92.36% (p < 0.0001) | 0.00% (p = 0.8425) | 76.71% (p = 0.0002) | 49.50% (p = 0.0945) | 91.57% (p < 0.0001) | 42.38% (p = 0.1390) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valsecchi, A.A.; Dionisio, R.; Panepinto, O.; Paparo, J.; Palicelli, A.; Vignani, F.; Di Maio, M. Frequency of Germline and Somatic BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations in Prostate Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092435
Valsecchi AA, Dionisio R, Panepinto O, Paparo J, Palicelli A, Vignani F, Di Maio M. Frequency of Germline and Somatic BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations in Prostate Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2023; 15(9):2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092435
Chicago/Turabian StyleValsecchi, Anna Amela, Rossana Dionisio, Olimpia Panepinto, Jessica Paparo, Andrea Palicelli, Francesca Vignani, and Massimo Di Maio. 2023. "Frequency of Germline and Somatic BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations in Prostate Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 15, no. 9: 2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092435
APA StyleValsecchi, A. A., Dionisio, R., Panepinto, O., Paparo, J., Palicelli, A., Vignani, F., & Di Maio, M. (2023). Frequency of Germline and Somatic BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations in Prostate Cancer: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 15(9), 2435. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15092435








