PARP Inhibitors in Breast and Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PARP Inhibitors across Different Tumour Types
2.1. PARP Inhibitor Therapy in Breast Cancer
2.2. PARP Inhibitor Therapy in Ovarian Cancer
2.3. PARP Inhibitor Therapy in Other Tumour Types
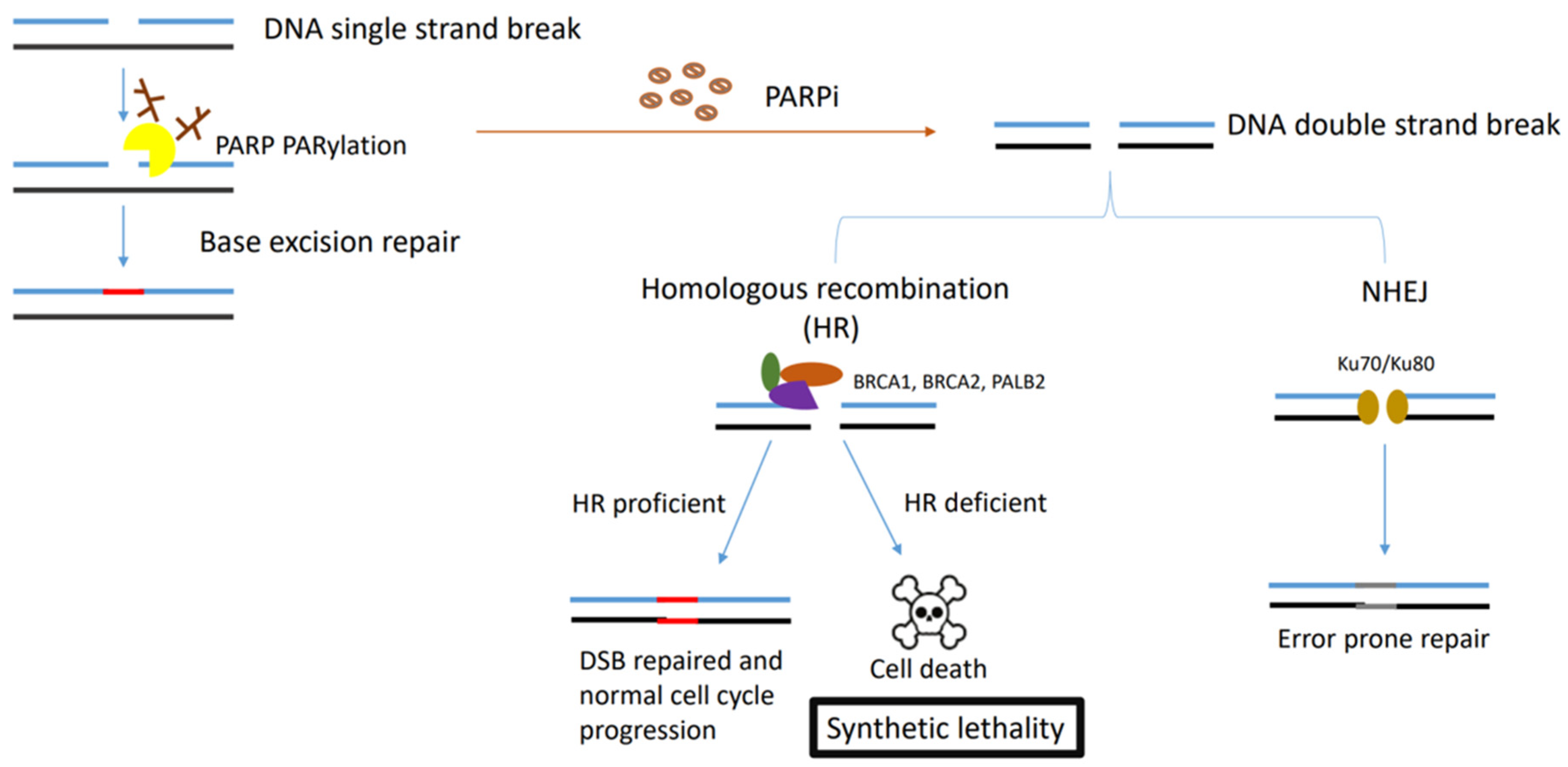
3. Challenges Facing PARP Inhibitors
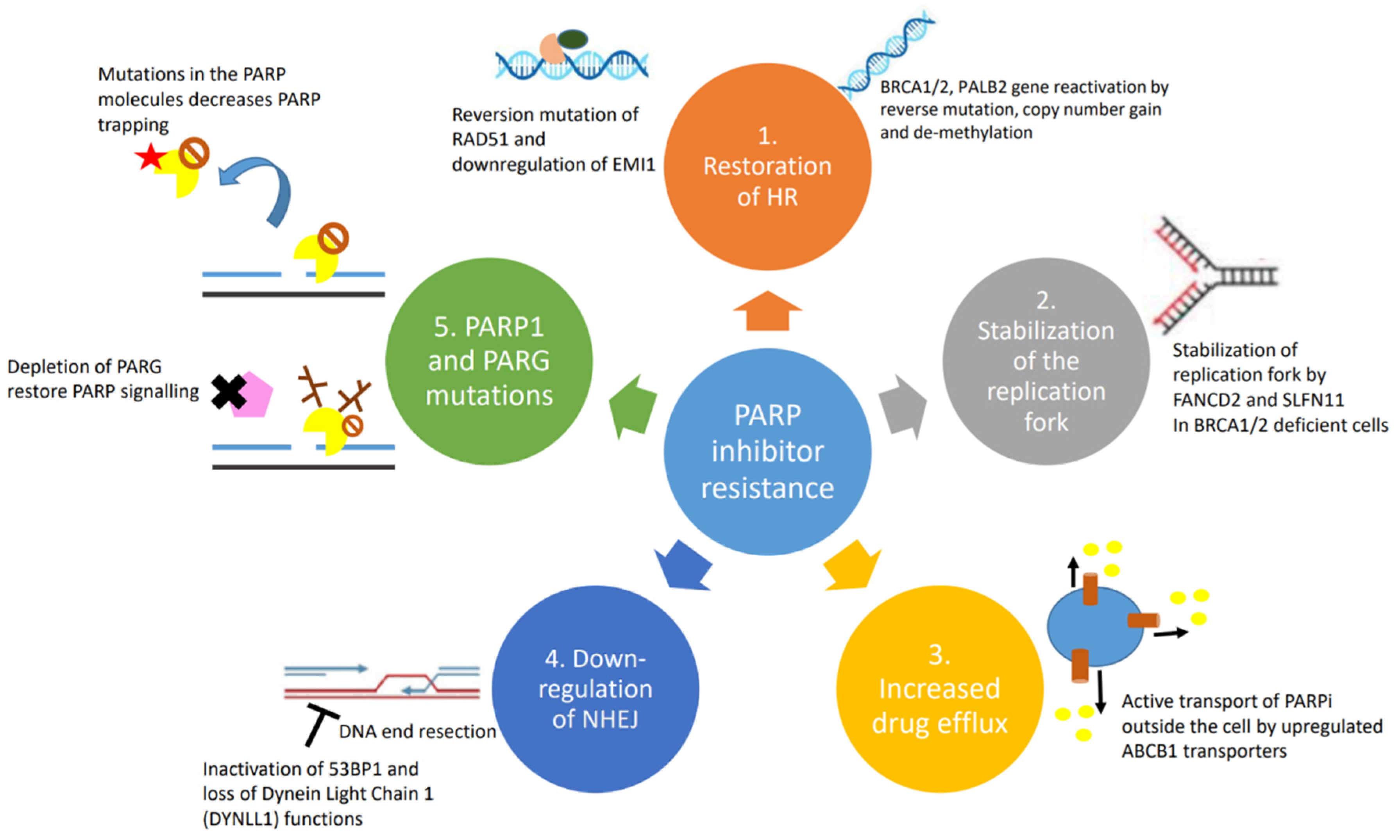
4. Causes and Mechanisms of PARP Inhibitor Resistance
4.1. Restoration of Homologous Recombination
4.2. Stabilization of the Replication Fork
4.3. Drug Efflux Pumps
4.4. Downregulation of NHEJ
4.5. PARP1 and PARG Mutations
5. Overcoming PARP Inhibitor Resistance through Combination Strategies
5.1. PARPi and Chemotherapy
5.2. PARPi and ATRi
5.3. PARPi and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
5.4. PARPI and Anti-Angiogenesis Agents
5.5. PARPI and PI3K
5.6. Inhibition of Polymerase Theta (POLQ) Synergizes with PARPi in Eliminating HR-Deficient Tumours
6. Cost-Effectiveness
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.H.; Tseng, W.L.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, M.L.; Chang, Y.L.; Sung, Y.J.; Chiou, S.H. Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase 1: Cellular Pluripotency, Reprogramming, and Tumorogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 15531–15545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldecott, K.W.; Aoufouchi, S.; Johnson, P.; Shall, S. XRCC1 polypeptide interacts with DNA polymerase beta and possibly poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase, and DNA ligase III is a novel molecular ‘nick-sensor’ in vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996, 24, 4387–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helleday, T.; Petermann, E.; Lundin, C.; Hodgson, B.; Sharma, R.A. DNA repair pathways as targets for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynahan, M.E.; Chiu, J.W.; Koller, B.H.; Jasin, M. Brca1 controls homology-directed DNA repair. Mol. Cell 1999, 4, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, G.; Brenneman, M.A.; Cui, T.X.; Donoviel, D.; Vogel, H.; Goodwin, E.H.; Chen, D.J.; Hasty, P. Deletion of Brca2 exon 27 causes hypersensitivity to DNA crosslinks, chromosomal instability, and reduced life span in mice. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2003, 36, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, S.; Thomas, H.D.; Mitchell, J.; Curtin, N.J. Exploiting the Achilles heel of cancer: The therapeutic potential of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors in BRCA2-defective cancer. Br. J. Radiol. 2008, 81, S6–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, H.E.; Schultz, N.; Thomas, H.D.; Parker, K.M.; Flower, D.; Lopez, E.; Kyle, S.; Meuth, M.; Curtin, N.J.; Helleday, T. Specific killing of BRCA2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Nature 2005, 434, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, H.; McCabe, N.; Lord, C.J.; Tutt, A.N.J.; Johnson, D.A.; Richardson, T.B.; Santarosa, M.; Dillon, K.J.; Hickson, I.; Knights, C.; et al. Targeting the DNA repair defect in BRCA mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature 2005, 434, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, J.; Huang, S.-N.; Das, B.B.; Renaud, A.; Zhang, Y.; Doroshow, J.H.; Ji, J.; Takeda, S.; Pommier, Y. Trapping of PARP1 and PARP2 by clinical PARP inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5588–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, N.; Turner, N.C.; Lord, C.J.; Kluzek, K.; Bialkowska, A.; Swift, S.; Giavara, S.; O’Connor, M.J.; Tutt, A.N.; Zdzienicka, M.Z.; et al. Deficiency in the repair of DNA damage by homologous recombination and sensitivity to poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8109–8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, P.C.; Boss, D.S.; Yap, T.A.; Tutt, A.; Wu, P.; Mergui-Roelvink, M.; Mortimer, P.; Swaisland, H.; Lau, A.; O’Connor, M.J.; et al. Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase in tumors from BRCA mutation carriers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.R.; Pignata, S.; Ledermann, J.A. Latest clinical evidence and further development of PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1366–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, B.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Schmutzler, R.K.; Audeh, M.W.; Friedlander, M.; Balmaña, J.; Mitchell, G.; Fried, G.; Stemmer, S.M.; Hubert, A.O.; et al. Olaparib monotherapy in patients with advanced cancer and a germline BRCA1/2 mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robson, M.E.; Tung, N.; Conte, P.; Im, S.A.; Senkus, E.; Xu, B.; Masuda, N.; Delaloge, S.; Li, W.; Armstrong, A.; et al. OlympiAD final overall survival and tolerability results: Olaparib versus chemotherapy treatment of physician’s choice in patients with a germline BRCA mutation and HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litton, J.K.; Rugo, H.S.; Ettl, J.; Hurvitz, S.A.; Gonçalves, A.; Lee, K.-H.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Yerushalmim, R.; Mina, L.A.; Martin, M.; et al. Talazoparib in Patients with Advanced Breast Cancer and a Germline BRCA Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loibl, S.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Untch, M.; Sikov, W.M.; Rugo, H.S.; McKee, M.D.; Huober, J.; Golshan, M.; Minckwitz, G.; Maag, D.; et al. Addition of the PARP inhibitor veliparib plus carboplatin or carboplatin alone to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer (BrighTNess): A randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutt, A.N.J.; Garber, J.E.; Kaufman, B.; Viale, G.; Fumagalli, D.; Rastogi, P.; Gelber, R.D.; Azambuja, E.D.; Fielding, A.; Balmana, J.; et al. Adjuvant Olaparib for Patients with BRCA1- or BRCA2-Mutated Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2394–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Martín, A.; Pothuri, B.; Vergote, I.; DePont Christensen, R.; Graybill, W.; Mirza, M.R.; McCormick, C.; Lorusso, D.; Hoskins, P.; Freyer, G.; et al. Niraparib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Advanced Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Moore, K.N.; Colombo, N.; Scambia, G.; Kim, B.G.; Oaknin, A.; Friedlander, M.; Lisyanskaya, A.; Floquet, A.; Leary, A.; et al. Maintenance olaparib for patients with newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer and a BRCA mutation (SOLO1/GOG 3004): 5-year follow-up of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1721–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray-Coquard, I.; Pautier, P.; Pignata, S.; Pérol, D.; González-Martín, A.; Berger, R.; Fujiwara, K.; Vergote, I.; Colombo, N.; Maenpaa, J.; et al. Olaparib plus Bevacizumab as First-Line Maintenance in Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2416–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monk, B.J.; Parkinson, C.; Lim, M.C.; O’Malley, D.M.; Oaknin, A.; Wilson, M.K.; Coleman, T.L.; Lorusso, D.; Bessette, P.; Ghamande, S.; et al. A Randomized, Phase III Trial to Evaluate Rucaparib Monotherapy as Maintenance Treatment in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Ovarian Cancer (ATHENA–MONO/GOG-3020/ENGOT-ov45). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3952–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penson, R.T.; Valencia, R.V.; Cibula, D.; Colombo, N.; Leath, C.A., 3rd; Bidziński, M.; Kim, J.-W.; Nam, J.H.; Madry, R.; Hernandez, C.; et al. Olaparib Versus Nonplatinum Chemotherapy in Patients With Platinum-Sensitive Relapsed Ovarian Cancer and a Germline BRCA1/2 Mutation (SOLO3): A Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujade-Lauraine, E.; Ledermann, J.A.; Selle, F.; Gebski, V.; Penson, R.T.; Oza, A.M.; Korach, J.; Huzarski, T.; Poveda, A.; Pignata, S.; et al. Olaparib tablets as maintenance therapy in patients with platinum-sensitive, relapsed ovarian cancer and a BRCA1/2 mutation (SOLO2/ENGOT-Ov21): A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledermann, J.; Harter, P.; Gourley, C.; Friedlander, M.; Vergote, I.; Rustin, G.; Scott, C.; Meier, W.; Shapira-Frommer, R.; Safra, T.; et al. Olaparib Maintenance Therapy in Platinum-Sensitive Relapsed Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.R.; Monk, B.J.; Herrstedt, J.; Oza, A.M.; Mahner, S.; Redondo, A.; Fabbro, M.; Ledermann, J.A.; Lorusso, D.; Vergote, I.; et al. Niraparib Maintenance Therapy in Platinum-Sensitive, Recurrent Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2154–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swisher, E.M.; Lin, K.K.; Oza, A.M.; Scott, C.L.; Giordano, H.; Sun, J.; Konecny, G.E.; Coleman, R.L.; Tinker, A.V.; O’Malley, D.M.; et al. Rucaparib in relapsed, platinum-sensitive high-grade ovarian carcinoma (ARIEL2 Part 1): An international, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.L.; Oza, A.M.; Lorusso, D.; Aghajanian, C.; Oaknin, A.; Dean, A.; Colombo, N.; Weberpals, J.I.; Clamp, A.; Scambia, G.; et al. Rucaparib maintenance treatment for recurrent ovarian carcinoma after response to platinum therapy (ARIEL3): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 1949–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bono, J.; Mateo, J.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Shore, N.; Sandhu, S.; Chi, K.N.; Sartor, O.; Agarwal, N.; Olmos, D.; et al. Olaparib for Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2091–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golan, T.; Hammel, P.; Reni, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Macarulla, T.; Hall, M.J.; Park, J.-O.; Hochhauser, D.; Arnold, D.; Oh, D.-Y.; et al. Maintenance Olaparib for Germline BRCA-Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenia, J.; Wankowicz, S.A.M.; Liu, D.; Gao, J.; Kundra, R.; Reznik, E.; Chatila, W.K.; Chakravarty, D.; Han, G.C.; Coleman, I.; et al. The long tail of oncogenic drivers in prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, J.; Carreira, S.; Sandhu, S.; Miranda, S.; Mossop, H.; Perez-Lopez, R.; Rodrigues, D.N.; Robinson, D.; Omlin, A.; Tunariu, N.; et al. DNA-Repair Defects and Olaparib in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, N.; Wiechno, P.; Alekseev, B.; Sala, N.; Jones, R.; Kocak, I.; Chiuri, V.E.; Jassem, J.; Flechon, A.; Redfern, C.; et al. Olaparib combined with abiraterone in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindler, H.L.; Hammel, P.; Reni, M.; Cutsem, E.V.; Macarulla, T.; Hall, M.J.; Park, J.O.; Hochhauser, D.; Arnold, D.; Oh, D.-Y.; et al. Overall Survival Results from the POLO Trial: A Phase III Study of Active Maintenance Olaparib Versus Placebo for Germline BRCA-Mutated Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3929–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindler, H.L.; Hammel, P.; Reni, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Mercade, T.M.; Hall, M.J.; Park, J.-O.; Hochhauser, D.; Arnold, D.; Oh, D.-Y.; et al. Olaparib as maintenance treatment following first-line platinum-based chemotherapy (PBC) in patients (pts) with a germline BRCA mutation and metastatic pancreatic cancer (mPC): Phase III POLO trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. 18), LBA4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, P.C.; Yap, T.A.; Boss, D.S.; Carden, C.P.; Mergui-Roelvink, M.; Gourley, C.; Greve, J.D.; Lubinski, J.; Shanley, S.; Messiou, C.; et al. Poly(ADP)-ribose polymerase inhibition: Frequent durable responses in BRCA carrier ovarian cancer correlating with platinum-free interval. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2512–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audeh, M.W.; Carmichael, J.; Penson, R.T.; Friedlander, M.; Powell, B.; Bell-McGuinn, K.M.; Scott, C.; Weitzel, J.N.; Oaknin, A.; Loman, N.; et al. Oral poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor olaparib in patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations and recurrent ovarian cancer: A proof-of-concept trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobalina, L.; Armenia, J.; Irving, E.; O’Connor, M.; Forment, J. A meta-analysis of reversion mutations in BRCA genes identifies signatures of DNA end-joining repair mechanisms driving therapy resistance. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, W.; Swisher, E.M.; Karlan, B.Y.; Agarwal, M.K.; Higgins, J.; Friedman, C.; Villegas, E.; Jacquemont, C.; Farrugia, D.J.; Couch, F.J.; et al. Secondary mutations as a mechanism of cisplatin resistance in BRCA2-mutated cancers. Nature 2008, 451, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Nam, H.J. PARP Inhibitors: Clinical Limitations and Recent Attempts to Overcome Them. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.L.; Brough, R.; Lord, C.J.; Natrajan, R.; Vatcheva, R.; Levine, D.A.; Boyd, J.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Ashworth, A. Resistance to therapy caused by intragenic deletion in BRCA2. Nature 2008, 451, 1111–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondrashova, O.; Nguyen, M.; Shield-Artin, K.; Tinker, A.V.; Teng, N.N.; Harrell, M.I.; Kuiper, M.J.; Ho, G.-Y.; Barker, H.; Jasin, M.; et al. Secondary Somatic Mutations Restoring RAD51C and RAD51D Associated with Acquired Resistance to the PARP Inhibitor Rucaparib in High-Grade Ovarian Carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 984–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspers, J.E.; Kersbergen, A.; Boon, U.; Sol, W.; van Deemter, L.; Zander, S.A.; Drost, R.; Wientjens, E.; Ji, J.; Aly, A.; et al. Loss of 53BP1 causes PARP inhibitor resistance in Brca1-mutated mouse mammary tumors. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwman, P.; Aly, A.; Escandell, J.M.; Pieterse, M.; Bartkova, J.; van der Gulden, H.; Hiddingh, S.; Thanasoula, M.; Kulkarni, A.; Yang, Q.; et al. 53BP1 loss rescues BRCA1 deficiency and is associated with triple-negative and BRCA-mutated breast cancers. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Chapman, J.R.; Brandsma, I.; Yuan, J.; Mistrik, M.; Bouwman, P.; Bartkova, J.; Gogola, E.; Warmerdam, D.; Barazas, M.; et al. REV7 counteracts DNA double-strand break resection and affects PARP inhibition. Nature 2015, 521, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taglialatela, A.; Alvarez, S.; Leuzzi, G.; Sannino, V.; Ranjha, L.; Huang, J.-W.; Madubata, C.; Anand, R.; Levy, B.; Rabadan, R.; et al. Restoration of replication fork stability in BRCA1-and BRCA2-deficient cells by inactivation of SNF2-family fork remodelers. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 414–430.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kais, Z.; Rondinelli, B.; Holmes, A.; O’Leary, C.; Kozono, D.; D’Andrea, A.D.; Ceccaldi, R. FANCD2 Maintains Fork Stability in BRCA1/2-Deficient Tumors and Promotes Alternative End-Joining DNA Repair. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 2488–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, S.J.; Krastev, D.B.; Brandsma, I.; Dréan, A.; Song, F.; Aleksandrov, R.; Harrell, M.I.; Menon, M.; Brough, R.; Campbell, H.; et al. Genome-wide and high-density CRISPR-Cas9 screens identify point mutations in PARP1 causing PARP inhibitor resistance. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyanathan, A.; Sawers, L.; Gannon, A.L.; Chakravarty, P.; Scott, A.L.; Bray, S.E.; Ferguson, M.J.; Smith, G. ABCB1 (MDR1) induction defines a common resistance mechanism in paclitaxel- and olaparib-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, L.J.; Sandhu, S.; Chen, L.; Campbell, J.; Kozarewa, I.; Fenwick, K.; Assiotis, I.; Rodrigues, D.N.; Filho, J.S.R.; Moreno, V.; et al. Secondary mutations in BRCA2 associated with clinical resistance to a PARP inhibitor. J. Pathol. 2013, 229, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, K.K.; Swisher, E.M.; Taniguchi, T. Secondary mutations of BRCA1/2 and drug resistance. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishvaian, M.J.; Biankin, A.V.; Bailey, P.; Chang, D.K.; Laheru, D.; Wolfgang, C.L.; Brody, J.R. BRCA2 secondary mutation-mediated resistance to platinum and PARP inhibitor-based therapy in pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 1021–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lheureux, S.; Bruce, J.P.; Burnier, J.V.; Karakasis, K.; Shaw, P.A.; Clarke, B.A.; Yang, S.Y.C.; Quevedo, R.; Li, T.; Dowar, M.; et al. Somatic BRCA1/2 Recovery as a Resistance Mechanism After Exceptional Response to Poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase Inhibition. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patch, A.M.; Christie, E.L.; Etemadmoghadam, D.; Garsed, D.W.; George, J.; Fereday, S.; Nones, K.; Cowin, P.; Alsop, K.; Bailey, P.J.; et al. Whole-genome characterization of chemoresistant ovarian cancer. Nature 2015, 521, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Krais, J.J.; Bernhardy, A.J.; Nicolas, E.; Cai, K.Q.; Harrell, M.I.; Kim, H.H.; George, E.; Swisher, E.M.; Simpkins, F.; et al. RING domain-deficient BRCA1 promotes PARP inhibitor and platinum resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3145–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Burness, M.L.; Martin-Trevino, R.; Guy, J.; Bai, S.; Harouaka, R.; Brooks, M.D.; Shang, L.; Fox, A.; Luther, T.K.; et al. RAD51 Mediates Resistance of Cancer Stem Cells to PARP Inhibition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzio, A.; Puccini, J.; Kwon, Y.; Maverakis, N.K.; Arbini, A.; Sung, P.; Bar-Sagi, D.; Pagano, M. The F-Box Domain-Dependent Activity of EMI1 Regulates PARPi Sensitivity in Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 224–237.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, K.E. Poly-ADP-ribosyl-polymerase inhibitor resistance mechanisms and their therapeutic implications. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 31, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, J.; Tang, S.W.; Leo, E.; Baechler, S.A.; Redon, C.E.; Zhang, H.; Al Abo, M.; Rajapakse, V.N.; Nakamura, E.; Jenkins, L.M.M.; et al. SLFN11 Blocks Stressed Replication Forks Independently of ATR. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 371–384.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottenberg, S.; Jaspers, J.E.; Kersbergen, A.; van der Burg, E.; Nygren, A.O.; Zander, S.A.; Derksen, P.W.B.; de Bruin, M.; Zevenhoven, J.; Lau, A.; et al. High sensitivity of BRCA1-deficient mammary tumors to the PARP inhibitor AZD2281 alone and in combination with platinum drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17079–17084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzolini, C.; Paus, E.; Buclin, T.; Kim, R.B. Polymorphisms in human MDR1 (P-glycoprotein): Recent advances and clinical relevance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 75, 13–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isono, M.; Niimi, A.; Oike, T.; Hagiwara, Y.; Sato, H.; Sekine, R.; Yoshida, Y.; Isobe, S.-Y.; Obuse, C.; Nishi, R.; et al. BRCA1 Directs the Repair Pathway to Homologous Recombination by Promoting 53BP1 Dephosphorylation. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, M.; Lottersberger, F.; Buonomo, S.B.; Sfeir, A.; de Lange, T. 53BP1 regulates DSB repair using Rif1 to control 5’ end resection. Science 2013, 339, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noordermeer, S.M.; Adam, S.; Setiaputra, D.; Barazas, M.; Pettitt, S.J.; Ling, A.K.; Olivieri, M.; Alvarez-Quilon, A.; Moatti, N.; Zimmermann, M.; et al. The shieldin complex mediates 53BP1-dependent DNA repair. Nature 2018, 560, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.J.; Meghani, K.; Caron, M.C.; Yang, C.; Ronato, D.A.; Bian, J.; Sharma, A.; Moore, J.; Niraj, J.; Detappe, A.; et al. DYNLL1 binds to MRE11 to limit DNA end resection in BRCA1-deficient cells. Nature 2018, 563, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogola, E.; Duarte, A.A.; de Ruiter, J.R.; Wiegant, W.W.; Schmid, J.A.; de Bruijn, R.; James, D.I.; Llobet, S.G.; Vis, D.J.; Annunziato, S.; et al. Selective Loss of PARG Restores PARylation and Counteracts PARP Inhibitor-Mediated Synthetic Lethality. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 1078–1093.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, R.L.; Fleming, G.F.; Brady, M.F.; Swisher, E.M.; Steffensen, K.D.; Friedlander, M.; Okamoto, A.; Moore, K.N.; Benbaruch, N.E.; Werner, T.L.; et al. Veliparib with First-Line Chemotherapy and as Maintenance Therapy in Ovarian Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2403–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plummer, R.; Lorigan, P.; Steven, N.; Scott, L.; Middleton, M.R.; Wilson, R.H.; Mulligan, E.; Curtin, N.; Wang, D.; Dewji, R.; et al. A phase II study of the potent PARP inhibitor, Rucaparib (PF-01367338, AG014699), with temozolomide in patients with metastatic melanoma demonstrating evidence of chemopotentiation. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, R.A.; Lindeman, G.J.; Clemons, M.; Wildiers, H.; Chan, A.; McCarthy, N.J.; Singer, C.F.; Lowe, E.S.; Watkins, C.L.; Carmichael, J.; et al. Phase I trial of the oral PARP inhibitor olaparib in combination with paclitaxel for first- or second-line treatment of patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samol, J.; Ranson, M.; Scott, E.; Macpherson, E.; Carmichael, J.; Thomas, A.; Cassidy, J. Safety and tolerability of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor, olaparib (AZD2281) in combination with topotecan for the treatment of patients with advanced solid tumors: A phase I study. Investig. New Drugs 2012, 30, 1493–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, R.A.; Lindeman, G.J.; Clemons, M.; Wildiers, H.; Chan, A.; McCarthy, N.J.; Lowe, E.S.; Kemsley, K.; Carmichael, J. Safety and efficacy of the oral PARP inhibitor olaparib (AZD2281) in combination with paclitaxel for the first- or second-line treatment of patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: Results from the safety cohort of a phase I/II multicenter trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28 (Suppl. 15), 1018. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Xu, H.; George, E.; Hallberg, D.; Kumar, S.; Jagannathan, V.; Medvedev, S.; Kinose, Y.; Devins, K.; Verma, P.; et al. Combining PARP with ATR inhibition overcomes PARP inhibitor and platinum resistance in ovarian cancer models. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murai, J.; Feng, Y.; Yu, G.K.; Ru, Y.; Tang, S.W.; Shen, Y.; Pommier, Y. Resistance to PARP inhibitors by SLFN11 inactivation can be overcome by ATR inhibition. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 76534–76550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, H.; Hafez, N.; Doroshow, D.; Sohal, D.; Keedy, V.; Do, K.T.; LoRusso, P.; Jürgensmeier, J.; Avedissian, M.; Sklar, J.; et al. Ceralasertib-Mediated ATR Inhibition Combined with Olaparib in Advanced Cancers Harboring DNA Damage Response and Repair Alterations (Olaparib Combinations). JCO Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, PO.20.00439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, P.D.; Wethington, S.L.; Pagan, C.; Latif, N.; Tanyi, J.; Martin, L.P.; Morgan, M.; Burger, R.A.; Haggerty, A.; Zarrin, H.; et al. Combination ATR and PARP Inhibitor (CAPRI): A phase 2 study of ceralasertib plus olaparib in patients with recurrent, platinum-resistant epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021, 163, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Flies, D.B.; Marjon, N.A.; Mantia-Smaldone, G.; Ronner, L.; Gimotty, P.A.; Adams, S.F. CTLA-4 Blockade Synergizes Therapeutically with PARP Inhibition in BRCA1-Deficient Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Yi, M.; Qin, S.; Chu, Q.; Luo, S.; Wu, K. Prospects for combining immune checkpoint blockade with PARP inhibition. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Niimi, A.; Yasuhara, T.; Permata, T.B.M.; Hagiwara, Y.; Isono, M.; Nuryadi, E.; Sekine, R.; Oike, T.; Kakoti, S.; et al. DNA double-strand break repair pathway regulates PD-L1 expression in cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, E.J.; Zimmer, A.; Padget, M.; Cimino-Mathews, A.; Nair, J.R.; Liu, Y.; Swisher, E.M.; Hodge, J.W.; Nixon, A.B.; Nichols, E.; et al. Combination of PARP Inhibitor Olaparib, and PD-L1 Inhibitor Durvalumab, in Recurrent Ovarian Cancer: A Proof-of-Concept Phase II Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4268–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, C.C.B.; Westermann, A.M.; Boere, I.A.; Witteveen, P.O.; Ottevanger, P.B.; Sonke, G.S.; Lalisang, R.I.; Putter, H.; Kranenbarg, E.M.K.; Braak, J.P.B.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of durvalumab with olaparib in metastatic or recurrent endometrial cancer (phase II DOMEC trial). Gynecol. Oncol. 2022, 165, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayak, S.; Tolaney, S.M.; Schwartzberg, L.; Mita, M.; McCann, G.; Tan, A.R.; Wahner-Hendrickson, A.E.; Forero, A.; Anders, C.; Wulf, G.M.; et al. Open-label Clinical Trial of Niraparib Combined With Pembrolizumab for Treatment of Advanced or Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Waggoner, S.; Vidal, G.A.; Mita, M.; Moroney, J.W.; Holloway, R.; Le, L.V.; Sachdev, J.C.; Chapman-Davis, E.; Colon-Otero, G.; et al. Single-Arm Phases 1 and 2 Trial of Niraparib in Combination With Pembrolizumab in Patients With Recurrent Platinum-Resistant Ovarian Carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1141–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domchek, S.M.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Im, S.A.; Park, Y.H.; Delord, J.P.; Italiano, A.; Alexandre, J.; You, B.; Bastian, S.; Kreb, M.G.; et al. Olaparib and durvalumab in patients with germline BRCA-mutated metastatic breast cancer (MEDIOLA): An open-label, multicentre, phase 1/2, basket study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1155–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.-A.; Xu, B.; Li, W.; Robson, M.; Ouyang, Q.; Yeh, D.-C.; Iwata, H.; Park, Y.H.; Sohn, J.H.; Tseng, L.M.; et al. Olaparib monotherapy for Asian patients with a germline BRCA mutation and HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer: OlympiAD randomized trial subgroup analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drew, Y.; de Jonge, M.; Hong, S.H.; Park, Y.H.; Wolfer, A.; Brown, J.; Ferguson, M.; Gore, M.E.; Alvarez, R.H.; Gresty, C.; et al. An open-label, phase II basket study of olaparib and durvalumab (MEDIOLA): Results in germline BRCA-mutated (gBRCAm) platinum-sensitive relapsed (PSR) ovarian cancer (OC). Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 149, 246–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Oliva, D.; Aguilar-Quesada, R.; O’Valle, F.; Muñoz-Gámez, J.A.; Martínez-Romero, R.; García del Moral, R.; Almodóvar, J.M.R.D.; Villuendas, R.; Piris, M.A.; Oliver, F.J. Inhibition of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Modulates Tumor-Related Gene Expression, Including Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Activation, during Skin Carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5744–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindra, R.S.; Schaffer, P.J.; Meng, A.; Woo, J.; Måseide, K.; Roth, M.E.; Lizardi, P.; Hedley, D.W.; Bristow, R.G.; Glazer, P.M. Down-regulation of Rad51 and decreased homologous recombination in hypoxic cancer cells. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 8504–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.J.; Yang, K.; Taylor-Harding, B.; Wiedemeyer, W.R.; Buckanovich, R.J. VEGFR3 inhibition chemosensitizes ovarian cancer stemlike cells through down-regulation of BRCA1 and BRCA2. Neoplasia 2014, 16, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.F.; Barry, W.T.; Birrer, M.; Lee, J.M.; Buckanovich, R.J.; Fleming, G.F.; Rimel, B.; Buss, M.K.; Nattam, S.; Hurteau, J.; et al. Combination cediranib and olaparib versus olaparib alone for women with recurrent platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer: A randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.R.; Åvall Lundqvist, E.; Birrer, M.J.; dePont Christensen, R.; Nyvang, G.B.; Malander, S.; Anttila, M.; Werner, T.L.; Lund, B.; Lindahl, G.; et al. Niraparib plus bevacizumab versus niraparib alone for platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer (NSGO-AVANOVA2/ENGOT-ov24): A randomised, phase 2, superiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1409–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lheureux, S.; Oaknin, A.; Garg, S.; Bruce, J.P.; Madariaga, A.; Dhani, N.C.; Bowering, V.; White, J.; Accardi, S.; Tan, Q.; et al. EVOLVE: A Multicenter Open-Label Single-Arm Clinical and Translational Phase II Trial of Cediranib Plus Olaparib for Ovarian Cancer after PARP Inhibition Progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4206–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Jiang, N.; Xiang, L.; Li, T.; Roberts, T.M.; Zhao, J.J.; Cheng, H.; et al. Combined inhibition of PI3K and PARP is effective in the treatment of ovarian cancer cells with wild-type PIK3CA genes. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 142, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, M.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Bian, X.; Wang, X.; Roberts, T.M.; Zhao, J.J.; Liu, P.; Cheng, H. Effective use of PI3K inhibitor BKM120 and PARP inhibitor Olaparib to treat PIK3CA mutant ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13153–13166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batalini, F.; Xiong, N.; Tayob, N.; Polak, M.; Eismann, J.; Cantley, L.C.; Shapiro, G.I.; Adalsteinsson, V.; Winer, E.P.; Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; et al. Phase 1b Clinical Trial with Alpelisib plus Olaparib for Patients with Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Barry, W.T.; Birrer, M.; Westin, S.N.; Cadoo, K.A.; Shapiro, G.I.; Mayer, E.L.; O’Cearbhaill, R.E.; Coleman, R.L.; Kochupurakkal, B.; et al. Olaparib and α-specific PI3K inhibitor alpelisib for patients with epithelial ovarian cancer: A dose-escalation and dose-expansion phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.A.; Kristeleit, R.; Michalarea, V.; Pettitt, S.J.; Lim, J.S.J.; Carreira, S.; Road, D.; Miller, R.; Riisnaes, R.; Miranda, S.; et al. Phase I Trial of the PARP Inhibitor Olaparib and AKT Inhibitor Capivasertib in Patients with BRCA1/2- and Non-BRCA1/2-Mutant Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1528–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westin, S.N.; Labrie, M.; Litton, J.K.; Blucher, A.; Fang, Y.; Vellano, C.P.; Marszalek, J.R.; Feng, N.; Ma, X.Y.; Reason, A.; et al. Phase Ib Dose Expansion and Translational Analyses of Olaparib in Combination with Capivasertib in Recurrent Endometrial, Triple-Negative Breast, and Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 6354–6365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfeir, A.; Symington, L.S. Microhomology-Mediated End Joining: A Back-up Survival Mechanism or Dedicated Pathway? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 701–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.D.; Doublié, S. DNA polymerase θ (POLQ), double-strand break repair, and cancer. DNA Repair 2016, 44, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccaldi, R.; Liu, J.C.; Amunugama, R.; Hajdu, I.; Primack, B.; Petalcorin, M.I.; O’Conner, K.W.; Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Elledge, S.J.; Boulton, S.J.; et al. Homologous-recombination-deficient tumours are dependent on Polθ-mediated repair. Nature 2015, 518, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemée, F.; Bergoglio, V.; Fernandez-Vidal, A.; Machado-Silva, A.; Pillaire, M.J.; Bieth, A.; Gentil, C.; Baker, L.; Martin, A.L.; Leduc, C.; et al. DNA polymerase theta up-regulation is associated with poor survival in breast cancer, perturbs DNA replication, and promotes genetic instability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13390–13395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillaire, M.J.; Selves, J.; Gordien, K.; Gourraud, P.A.; Gentil, C.; Danjoux, M.; Do, C.; Negre, V.; Bieth, A.; Guimbaud, R.; et al. A ‘DNA replication’ signature of progression and negative outcome in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 876–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos-Gomez, P.A.; Gong, F.; Nair, N.; Miller, K.M.; Lazzerini-Denchi, E.; Sfeir, A. Mammalian polymerase θ promotes alternative NHEJ and suppresses recombination. Nature 2015, 518, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, G.; Wang, A.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Werba, G.; Weissinger, D.; Zhao, E.; Dhara, S.; Hernandez, R.E.; Ackermann, A.; et al. POLQ inhibition elicits an immune response in homologous recombination-deficient pancreatic adenocarcinoma via cGAS/STING signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 28, e165934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Gelot, C.; Pantelidou, C.; Li, A.; Yücel, H.; Davis, R.E.; Färkkilä, A.; Kochupurakkal, B.; Syed, A.; Shapiro, G.I.; et al. A first-in-class Polymerase Theta Inhibitor selectively targets Homologous-Recombination-Deficient Tumors. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; He, C.; Tong, Y.; Fang, Q.; Mi, X.; Chen, L.; Xin, W.; Fang, L. Cost-effectiveness of PARP inhibitors in malignancies: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0279286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolford, J.E.; Bai, J.; Moore, K.N.; Kristeleit, R.; Monk, B.J.; Tewari, K.S. Cost-effectiveness of niraparib, rucaparib, and olaparib for treatment of platinum-resistant, recurrent ovarian carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 157, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, R.; Havrilesky, L.J.; Myers, E.R.; Secord, A.A.; Dottino, J.A.; Berchuck, A.; Moss, H.A. Cost-effectiveness analysis comparing “PARP inhibitors-for-all” to the biomarker-directed use of PARP inhibitor maintenance therapy for newly diagnosed advanced stage ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 159, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oplustil O’Connor, L.; Rulten, S.L.; Cranston, A.N.; Odedra, R.; Brown, H.; Jaspers, J.E.; Jones, L.; Knights, C.; Evers, B.; Ting, A.; et al. The PARP Inhibitor AZD2461 Provides Insights into the Role of PARP3 Inhibition for Both Synthetic Lethality and Tolerability with Chemotherapy in Preclinical Models. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6084–6094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Tumour Type | Drug | Population | Clinical Setting | Significant Results | Study Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast cancer | Veliparib |
|
|
| [17] |
| Breast cancer | Olaparib |
|
|
| [18] |
| Breast cancer | Talazoparib |
|
|
| [16] |
| Breast cancer | Olaparib |
|
|
| [15] |
| Ovarian cancer | Niraparib |
|
|
| [19] |
| Ovarian Cancer | Olaparib |
|
|
| [20] |
| Ovarian Cancer | Olaparib |
|
|
| [21] |
| Ovarian cancer | Rucaparib |
|
|
| [22] |
| Ovarian Cancer | Olaparib |
|
|
| [23] |
| Ovarian Cancer | Olaparib |
|
|
| [24] |
| Ovarian Cancer | Olaparib |
|
|
| [25] |
| Ovarian Cancer | Niraparib |
|
|
| [26] |
| Ovarian Cancer | Rucaparib |
|
|
| [27] |
| Ovarian Cancer | Rucaparib |
|
|
| [28] |
| Prostate Cancer | Olaparib |
|
|
| [29] |
| Pancreatic Cancer | Olaparib |
|
|
| [30] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.S.Y.; Jie, Y.E.; Cheng, S.W.; Ling, G.L.; Ming, H.V.Y. PARP Inhibitors in Breast and Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082357
Wang SSY, Jie YE, Cheng SW, Ling GL, Ming HVY. PARP Inhibitors in Breast and Ovarian Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(8):2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082357
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Samuel S. Y., Yeo Ee Jie, Sim Wey Cheng, Goh Liuh Ling, and Heong Valerie Yue Ming. 2023. "PARP Inhibitors in Breast and Ovarian Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 8: 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082357
APA StyleWang, S. S. Y., Jie, Y. E., Cheng, S. W., Ling, G. L., & Ming, H. V. Y. (2023). PARP Inhibitors in Breast and Ovarian Cancer. Cancers, 15(8), 2357. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15082357





