Disequilibrium between BRCA1 and BRCA2 Circular and Messenger RNAs Plays a Role in Breast Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. RNA Extraction
2.3. SEALigHTS Assay
2.3.1. Principle
2.3.2. Protocol
2.4. Ratio of circRNAs/mRNAs
3. Results
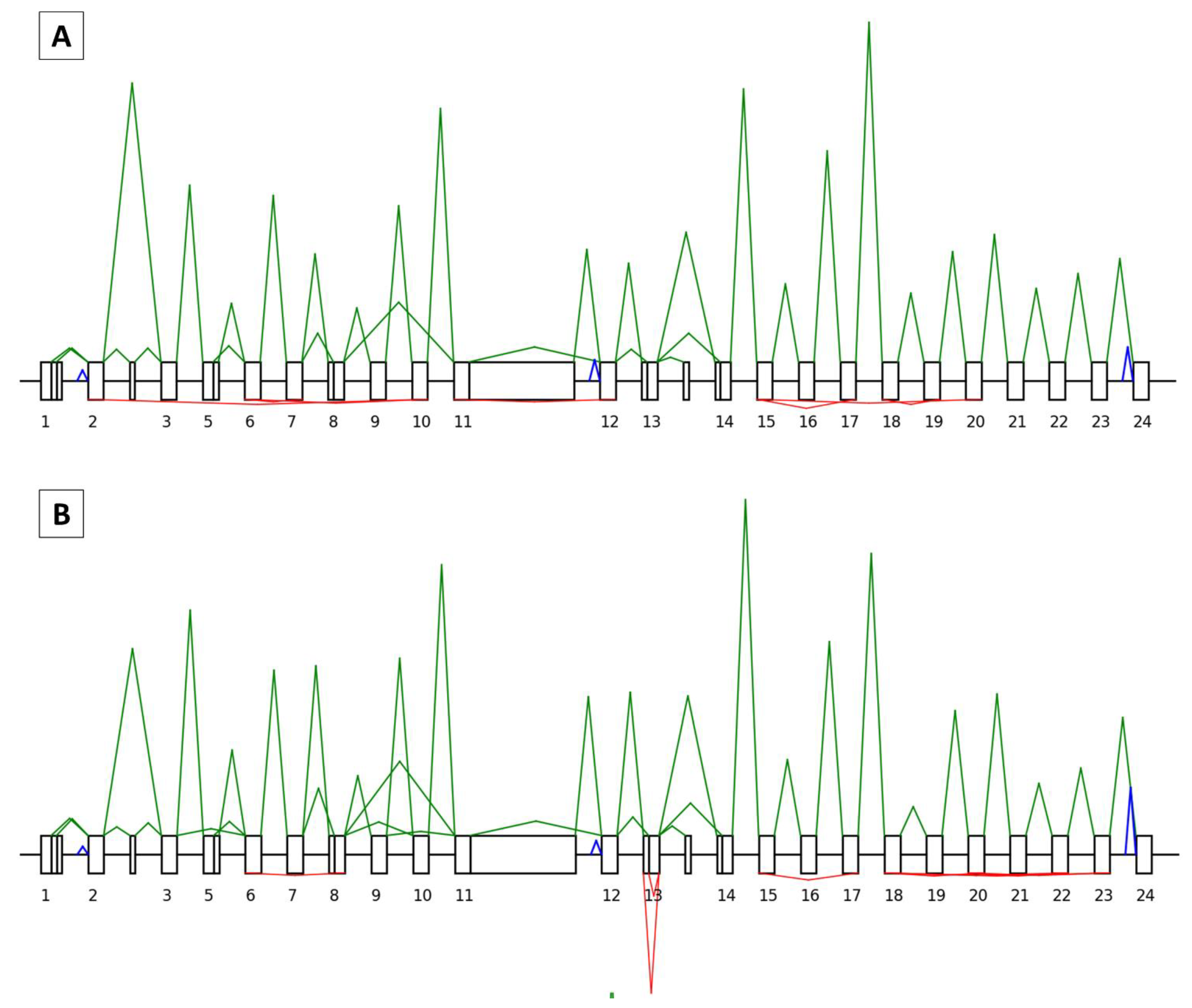
3.1. General Characteristics of the SEALigHTS Assay
3.2. SEALigHTS Assay Validation
3.2.1. Splicing Analyses
3.2.2. Backsplicing Analyses
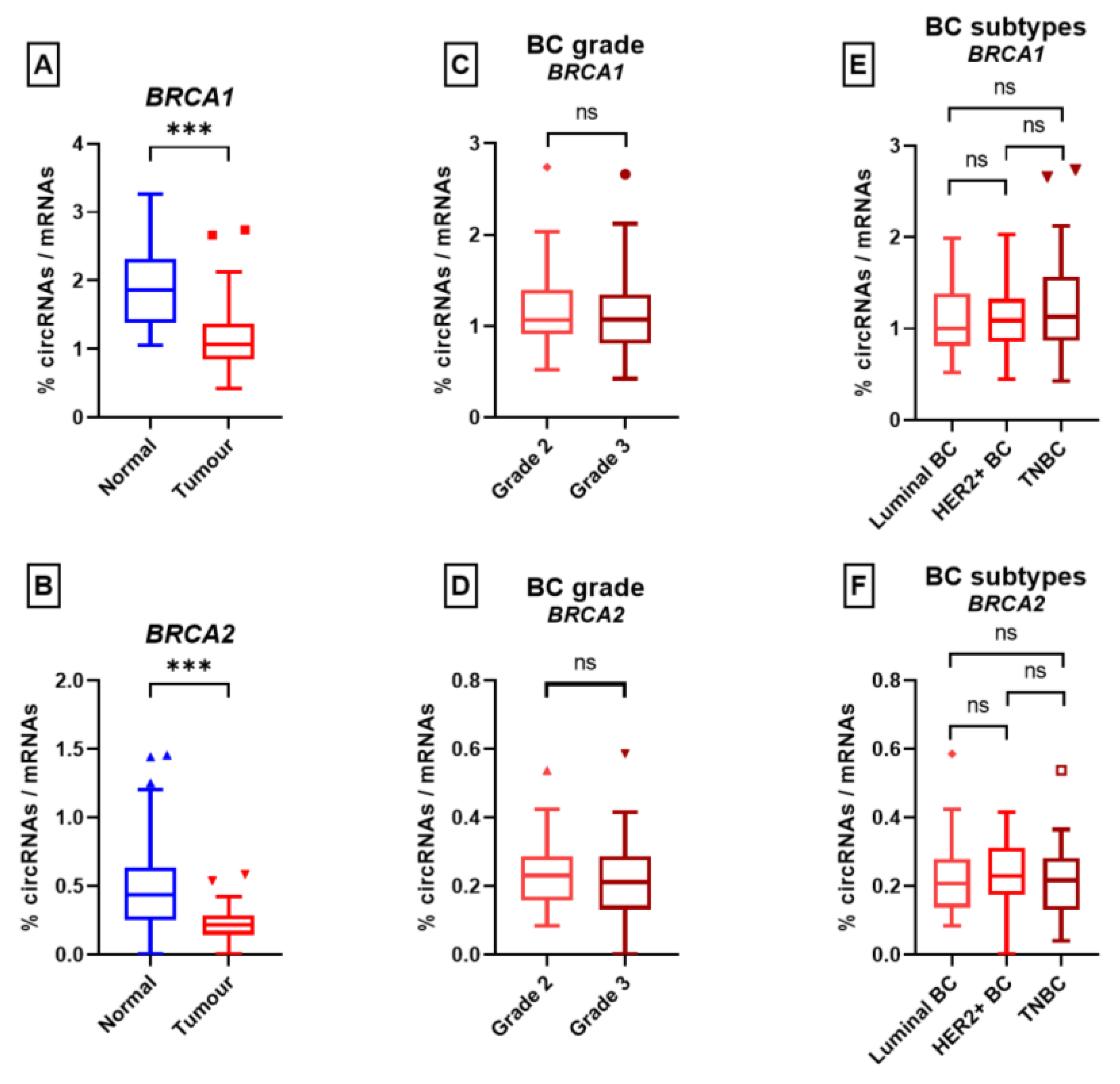
3.3. Research Set
3.3.1. Splicing Study
3.3.2. Backsplicing Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Shang, R.; Sun, W.; Dou, K.; Li, H. Circular RNA: A New Star of Noncoding RNAs. Cancer Lett. 2015, 365, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs Are Abundant, Conserved, and Associated with ALU Repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebbesen, K.K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J. Insights into Circular RNA Biology. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 1035–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilusz, J.E. Circular RNAs: Unexpected Outputs of Many Protein-Coding Genes. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J.; Damgaard, C.K. Circular RNA and MiR-7 in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5609–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.W.; Yang, W.; Liu, E.; Yang, Z.; Dhaliwal, P.; Yang, B.B. Foxo3 Circular RNA Retards Cell Cycle Progression via Forming Ternary Complexes with P21 and CDK2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 2846–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-Intron Circular RNAs Regulate Transcription in the Nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Lei, L.; Dong, S.; Liu, D. Circular RNA Hsa_circ_0068033 Acts as a Diagnostic Biomarker and Suppresses the Progression of Breast Cancer Through Sponging MiR-659. Oncotargets Ther. 2020, 13, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-Z.; Shao, C.-C.; Wang, X.-J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J.-Q.; Ouyang, Y.-X.; Feng, J.; Zhang, F.; Huang, W.-H.; Ying, Q.; et al. CircTADA2As Suppress Breast Cancer Progression and Metastasis via Targeting MiR-203a-3p/SOCS3 Axis. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. CircRNA Biogenesis Competes with Pre-MRNA Splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, J.; Gawad, C.; Wang, P.L.; Lacayo, N.; Brown, P.O. Circular RNAs Are the Predominant Transcript Isoform from Hundreds of Human Genes in Diverse Cell Types. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Choi, P.S.; Chaffer, C.L.; Labella, K.; Hwang, J.H.; Giacomelli, A.O.; Kim, J.W.; Ilic, N.; Doench, J.G.; Ly, S.H.; et al. An Alternative Splicing Switch in FLNB Promotes the Mesenchymal Cell State in Human Breast Cancer. eLife 2018, 7, e37184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karni, R.; de Stanchina, E.; Lowe, S.W.; Sinha, R.; Mu, D.; Krainer, A.R. The Gene Encoding the Splicing Factor SF2/ASF Is a Proto-Oncogene. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climente-González, H.; Porta-Pardo, E.; Godzik, A.; Eyras, E. The Functional Impact of Alternative Splicing in Cancer. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2215–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabot, B.; Shkreta, L. Defective Control of Pre–Messenger RNA Splicing in Human Disease. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 212, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Bigas, N.; Audit, B.; Ouzounis, C.; Parra, G.; Guigó, R. Are Splicing Mutations the Most Frequent Cause of Hereditary Disease? FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1900–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaton, A.J.B.Z.; Le Doussal, V.; Arnould, L.; Barlier, C.; Bellocq, J.P.; Ettore, F.; Fiche, M.; Jacquemier, J.; Grogan, G.M.; Mathieu, M.C.; et al. Voigt Recommandations Pour l’évaluation Immunohistochimique Des Récepteurs Hormonaux Sur Coupes En Paraffine Dans Les Carcinomes Mammaires Mise à Jour 1999. Ann. Pathol. 1999, 937, 280–375. [Google Scholar]
- Wolff, A.C.; Hammond, M.E.H.; Allison, K.H.; Harvey, B.E.; Mangu, P.B.; Bartlett, J.M.S.; Bilous, M.; Ellis, I.O.; Fitzgibbons, P.; Hanna, W.; et al. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Clinical Practice Guideline Focused Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2105–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Gao, J. A High-Throughput Method to Detect RNA Profiling by Integration of RT-MLPA with next Generation Sequencing Technology. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46071–46080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piton, N.; Ruminy, P.; Gravet, C.; Marchand, V.; Colasse, É.; Lamy, A.; Naoures Mear, C.L.; Bibeau, F.; Marguet, F.; Guisier, F.; et al. Ligation-Dependent RT-PCR: A New Specific and Low-Cost Technique to Detect ALK, ROS, and RET Rearrangements in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobée, V.; Drieux, F.; Marchand, V.; Sater, V.; Veresezan, L.; Picquenot, J.-M.; Viailly, P.-J.; Lanic, M.-D.; Viennot, M.; Bohers, E.; et al. Combining Gene Expression Profiling and Machine Learning to Diagnose B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drieux, F.; Ruminy, P.; Abdel-Sater, A.; Lemonnier, F.; Viailly, P.-J.; Fataccioli, V.; Marchand, V.; Bisig, B.; Letourneau, A.; Parrens, M.; et al. Defining Signatures of Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma with a Targeted 20-Marker Gene Expression Profiling Assay. Haematologica 2020, 105, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanic, M.-D.; Le Loarer, F.; Rainville, V.; Sater, V.; Viennot, M.; Beaussire, L.; Viailly, P.-J.; Angot, E.; Hostein, I.; Jardin, F.; et al. Detection of Sarcoma Fusions by a Next-Generation Sequencing Based–Ligation-Dependent Multiplex RT-PCR Assay. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, G.; Rousselin, A.; Goardon, N.; Castéra, L.; Harter, V.; Legros, A.; Muller, E.; Fouillet, R.; Brault, B.; Smirnova, A.S.; et al. Detecting Splicing Patterns in Genes Involved in Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 25, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Lai, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, Z.; Meng, Z.; Wang, P.; Hu, Z.; et al. RJunBase: A Database of RNA Splice Junctions in Human Normal and Cancerous Tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D201–D211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Diermeier, S.D. Circular RNAs: Potential Applications as Therapeutic Targets and Biomarkers in Breast Cancer. Non-Coding RNA 2021, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.M.; Chalbatani, G.M.; Berland, L.; Cruz De los Santos, M.; Raj, P.; Jalali, S.A.; Gharagouzloo, E.; Ivan, C.; Dragomir, M.P.; Calin, G.A. A New World of Biomarkers and Therapeutics for Female Reproductive System and Breast Cancers: Circular RNAs. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Bai, X.; Zeng, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z. CircRNA-MiRNA-MRNA in Breast Cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 523, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, X.; Gong, J.; Hou, Z.; Jiang, K.; Wang, Q.; et al. CircPTEN1, a Circular RNA Generated from PTEN, Suppresses Cancer Progression through Inhibition of TGF-β/Smad Signaling. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmayr-Heyda, A.; Reiner, A.T.; Auer, K.; Sukhbaatar, N.; Aust, S.; Bachleitner-Hofmann, T.; Mesteri, I.; Grunt, T.W.; Zeillinger, R.; Pils, D. Correlation of Circular RNA Abundance with Proliferation—Exemplified with Colorectal and Ovarian Cancer, Idiopathic Lung Fibrosis and Normal Human Tissues. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| BRCA1 Circular RNAs NORMAL | BRCA1 Circular RNAs TUMOR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular RNA Name | Relative Proportion of BRCA1 circRNAs (%) | Frequency (%) (n = 38) | Ratio of circRNA/mRNA (%) | Relative Proportion to BRCA1 circRNAs (%) | Frequency (%) (n = 90) | Ratio of circRNA/mRNA (%) |
| BRCA1_circRNA_20-18 | 10.94 | 84.21 (32) | 4.73 | 11.18 | 92.22 (83) | 2.57 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_7-6 | 10.83 | 89.47 (34) | 4.68 | 7.93 | 87.78 (79) | 1.82 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_17-15 | 10.31 | 92.11 (35) | 4.46 | 9.49 | 92.22 (83) | 2.18 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_19-18 | 7.19 | 78.95 (30) | 3.11 | 5.80 | 84.44 (76) | 1.33 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_3-2 | 5.42 | 44.74 (17) | 2.34 | 2.17 | 46.67 (42) | 0.50 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_10-2 | 5.00 | 68.42 (26) | 2.16 | 3.78 | 72.22 (65) | 0.87 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_22-20 | 3.65 | 50 (19) | 1.58 | 4.81 | 87.78 (79) | 1.11 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_10-6 | 3.33 | 44.74 (17) | 1.44 | 2.66 | 63.33 (57) | 0.61 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_12-11 | 3.33 | 55.26 (21) | 1.44 | 5.25 | 84.44 (76) | 1.21 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_23-18 | 3.33 | 55.26 (21) | 1.44 | 5.15 | 81.11 (73) | 1.18 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_19-15 | 3.23 | 52.63 (20) | 1.40 | 2.59 | 72.22 (65) | 0.60 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_8-6 | 2.81 | 55.26 (21) | 1.22 | 2.08 | 56.67 (51) | 0.48 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_23-20 | 2.71 | 42.11 (16) | 1.17 | 5.51 | 81.11 (73) | 1.27 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_21-18 | 2.40 | 34.21 (13) | 1.04 | 2.68 | 63.33 (57) | 0.62 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_8-3 | 2.08 | 42.11 (16) | 0.90 | 2.91 | 76.67 (69) | 0.67 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_5q-3 | 1.67 | 13.16 (5) | 0.72 | 0.71 | 22.22 (20) | 0.16 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_22-18 | 1.56 | 31.58 (12) | 0.68 | 2.37 | 61.11 (55) | 0.54 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_23-15 | 1.46 | 28.95 (11) | 0.63 | 1.24 | 43.33 (39) | 0.28 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_7-5 | 1.35 | 28.95 (11) | 0.59 | 1.69 | 41.11 (37) | 0.39 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_20-15 | 1.15 | 18.42 (7) | 0.50 | 1.75 | 55.56 (50) | 0.40 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_22-15 | 1.04 | 26.32 (10) | 0.45 | 1.69 | 57.78 (52) | 0.39 |
| BRCA2 Circular RNAs NORMAL | BRCA2 Circular RNAs TUMOR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular RNA Name | Relative Proportion to BRCA1 circRNAs (%) | Frequency (%) (n = 38) | Ratio of circRNA/mRNA (%) | Relative Proportion to BRCA1 circRNAs (%) | Frequency (%) (n = 90) | Ratio of circRNA/mRNA (%) |
| BRCA2_circRNA_7-3 | 22.34 | 50 (19) | 2.76 | 26.13 | 76.67 (69) | 1.48 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_7-4 | 19.68 | 55.26 (21) | 2.43 | 21.18 | 76.67 (69) | 1.20 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_18-17 | 12.23 | 44.74 (17) | 1.51 | 12.61 | 61.11 (55) | 0.71 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_7-5 | 6.91 | 21.05 (8) | 0.85 | 5.97 | 48.89 (44) | 0.34 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_9-9 | 4.79 | 21.05 (8) | 0.59 | 2.10 | 24.44 (22) | 0.12 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_26-13 | 4.26 | 21.05 (8) | 0.53 | 0.67 | 8.89 (8) | 0.04 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_21-20 | 3.72 | 7.89 (3) | 0.46 | 1.51 | 18.89 (17) | 0.09 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_13-11 | 3.19 | 13.16 (5) | 0.39 | 7.39 | 47.78 (43) | 0.42 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_4-3 | 3.19 | 13.16 (5) | 0.39 | 3.61 | 32.22 (29) | 0.20 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_14-13 | 2.66 | 13.16 (5) | 0.33 | 1.43 | 14.44 (13) | 0.08 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_10-4 | 2.13 | 7.89 (3) | 0.26 | 1.01 | 10 (9) | 0.06 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_13-12 | 2.13 | 5.26 (2) | 0.26 | 0.76 | 10 (9) | 0.04 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_6q-2 | 2.13 | 10.53 (4) | 0.26 | 0.76 | 10 (9) | 0.04 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_10-5 | 1.60 | 7.89 (3) | 0.20 | 0.67 | 7.78 (7) | 0.04 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_10-8 | 1.60 | 7.89 (3) | 0.20 | 1.43 | 17.78 (16) | 0.08 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_11-11 | 1.60 | 7.89 (3) | 0.20 | 1.18 | 13.33 (12) | 0.07 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_10-3 | 1.06 | 5.26 (2) | 0.13 | 1.01 | 12.22 (11) | 0.06 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_19-17 | 1.06 | 5.26 (2) | 0.13 | 3.28 | 32.22 (29) | 0.19 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_24-19 | 1.06 | 5.26 (2) | 0.13 | 2.10 | 20 (18) | 0.12 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_24-22 | 1.06 | 5.26 (2) | 0.13 | 1.76 | 16.67 (15) | 0.10 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_24-21 | 0.53 | 2.63 (1) | 0.07 | 2.44 | 28.89 (26) | 0.14 |
| BRCA1 Circular RNAs NORMAL | BRCA1 Circular RNAs TUMOR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular RNA Name | Relative proportion to BRCA1 circRNAs (%) | Frequency (%) (n = 38) | Ratio of circRNA/mRNA (%) | Relative Proportion to BRCA1 circRNAs (%) | Frequency (%) (n = 90) | Ratio of circRNA/mRNA (%) |
| BRCA1_circRNA_5q-3 | 1.67 | 13.16 (5) | 0.72 | 0.71 | 22.22 (20) | 0.16 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_23-8p | 1.15 | 23.68 (9) | 0.50 | 0.76 | 40 (36) | 0.18 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_19-17 | 1.04 | 21.05 (8) | 0.45 | 0.85 | 38.89 (35) | 0.19 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_18-2 | 0.63 | 13.16 (5) | 0.27 | 0.25 | 14.44 (13) | 0.06 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_16-3 | 0.52 | 13.16 (5) | 0.23 | 0.07 | 4.44 (4) | 0.02 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_23-22 | 0.42 | 10.53 (4) | 0.18 | 0.10 | 6.67 (6) | 0.02 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_10-8 | 0.31 | 7.89 (3) | 0.14 | 0.66 | 27.78 (25) | 0.15 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_20-20 | 0.31 | 5.26 (2) | 0.14 | 0.41 | 11.11 (10) | 0.09 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_12-6 | 0.10 | 2.63 (1) | 0.05 | 0.19 | 12.22 (11) | 0.04 |
| BRCA1_circRNA_21-20 | 0.10 | 2.63 (1) | 0.05 | 0.10 | 6.67 (6) | 0.02 |
| BRCA2 Circular RNAs NORMAL | BRCA2 Circular RNAs TUMOR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular RNA Name | Relative Proportion to BRCA1 circRNAs (%) | Frequency (%) (n = 38) | Ratio circRNA/mRNA (%) | Relative Proportion to BRCA1 circRNAs (%) | Frequency (%) (n = 90) | Ratio circRNA/mRNA (%) |
| BRCA2_circRNA_7-5 | 6.91 | 21.05 (8) | 0.85 | 5.97 | 48.89 (44) | 0.34 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_9-9 | 4.79 | 21.05 (8) | 0.59 | 2.10 | 24.44 (22) | 0.12 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_26-13 | 4.26 | 21.05 (8) | 0.53 | 0.67 | 8.89 (8) | 0.04 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_13-12 | 2.13 | 5.26 (2) | 0.26 | 0.76 | 10 (9) | 0.04 |
| BRCA2_circRNA_6q-2 | 2.13 | 10.53 (4) | 0.26 | 0.76 | 10 (9) | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Levacher, C.; Viennot, M.; Drouet, A.; Beaussire, L.; Coutant, S.; Théry, J.-C.; Baert-Desurmont, S.; Laé, M.; Ruminy, P.; Houdayer, C. Disequilibrium between BRCA1 and BRCA2 Circular and Messenger RNAs Plays a Role in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072176
Levacher C, Viennot M, Drouet A, Beaussire L, Coutant S, Théry J-C, Baert-Desurmont S, Laé M, Ruminy P, Houdayer C. Disequilibrium between BRCA1 and BRCA2 Circular and Messenger RNAs Plays a Role in Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(7):2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072176
Chicago/Turabian StyleLevacher, Corentin, Mathieu Viennot, Aurélie Drouet, Ludivine Beaussire, Sophie Coutant, Jean-Christophe Théry, Stéphanie Baert-Desurmont, Marick Laé, Philippe Ruminy, and Claude Houdayer. 2023. "Disequilibrium between BRCA1 and BRCA2 Circular and Messenger RNAs Plays a Role in Breast Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 7: 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072176
APA StyleLevacher, C., Viennot, M., Drouet, A., Beaussire, L., Coutant, S., Théry, J.-C., Baert-Desurmont, S., Laé, M., Ruminy, P., & Houdayer, C. (2023). Disequilibrium between BRCA1 and BRCA2 Circular and Messenger RNAs Plays a Role in Breast Cancer. Cancers, 15(7), 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072176








