Risk Classification of Bladder Cancer by Gene Expression and Molecular Subtype
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Sample Collection and RNA Extraction
2.3. Gene Expression Custom Panel and NanoString Analysis
2.4. PD-L1 mRNA Quantification by RT-qPCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
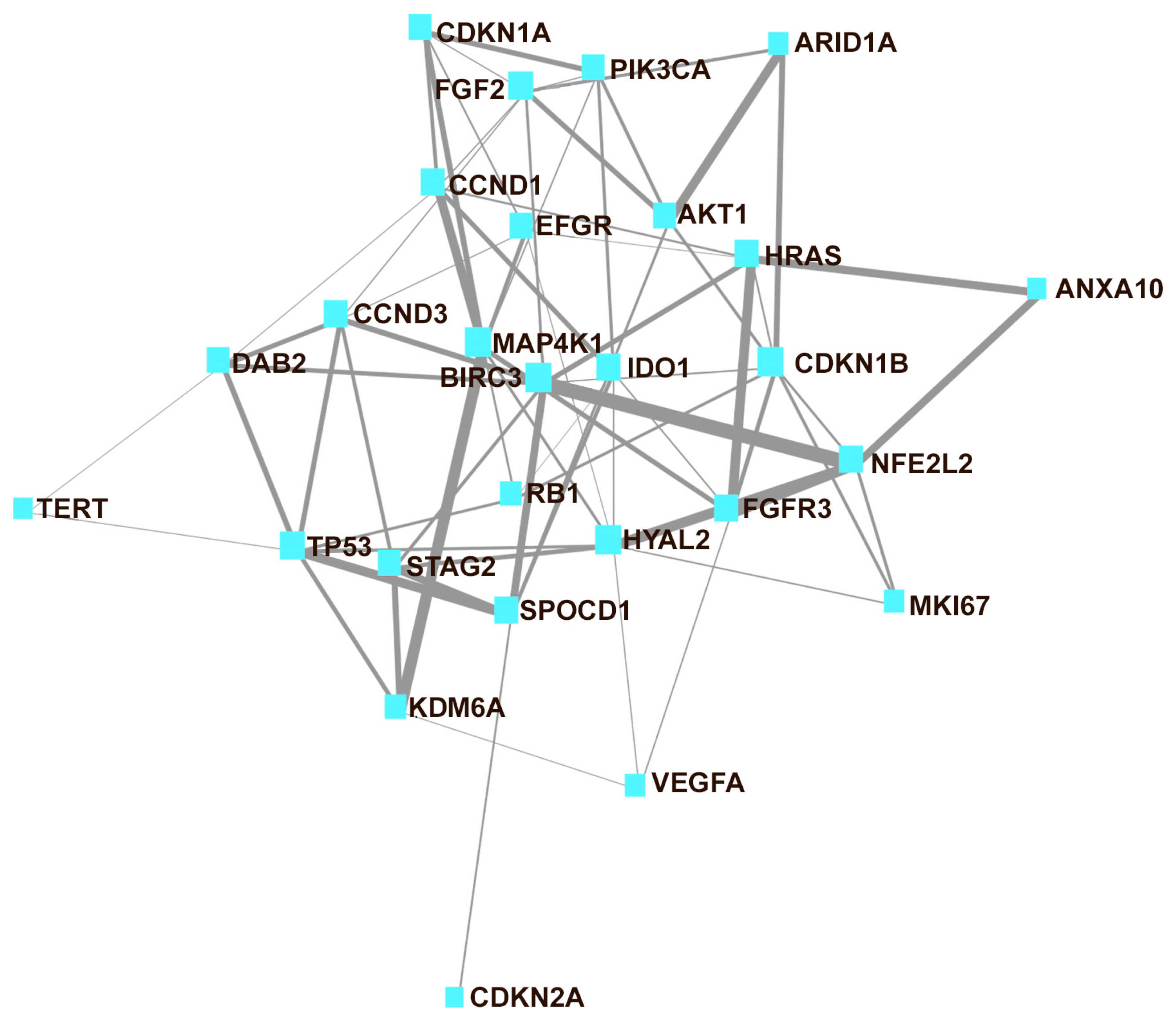
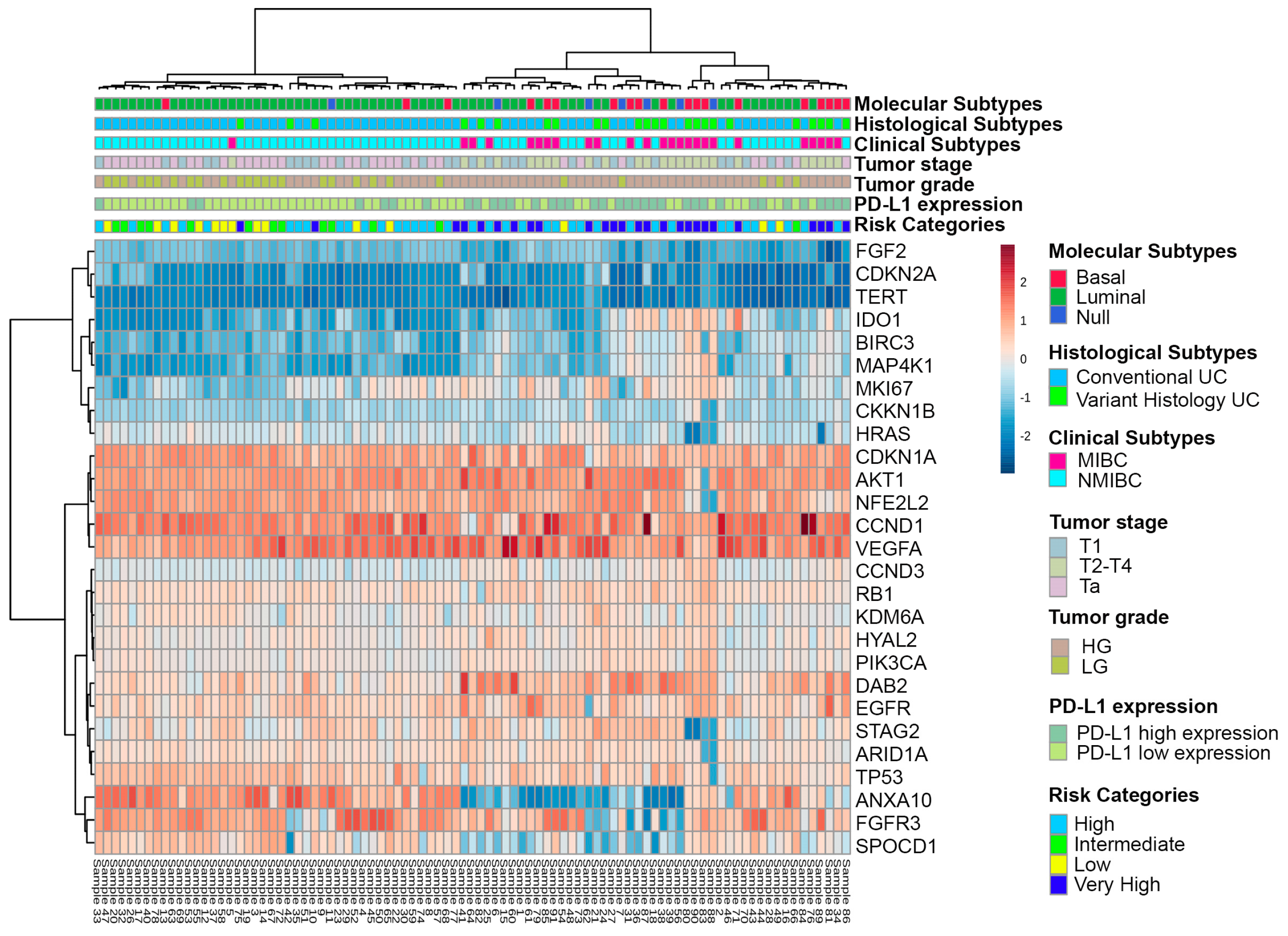
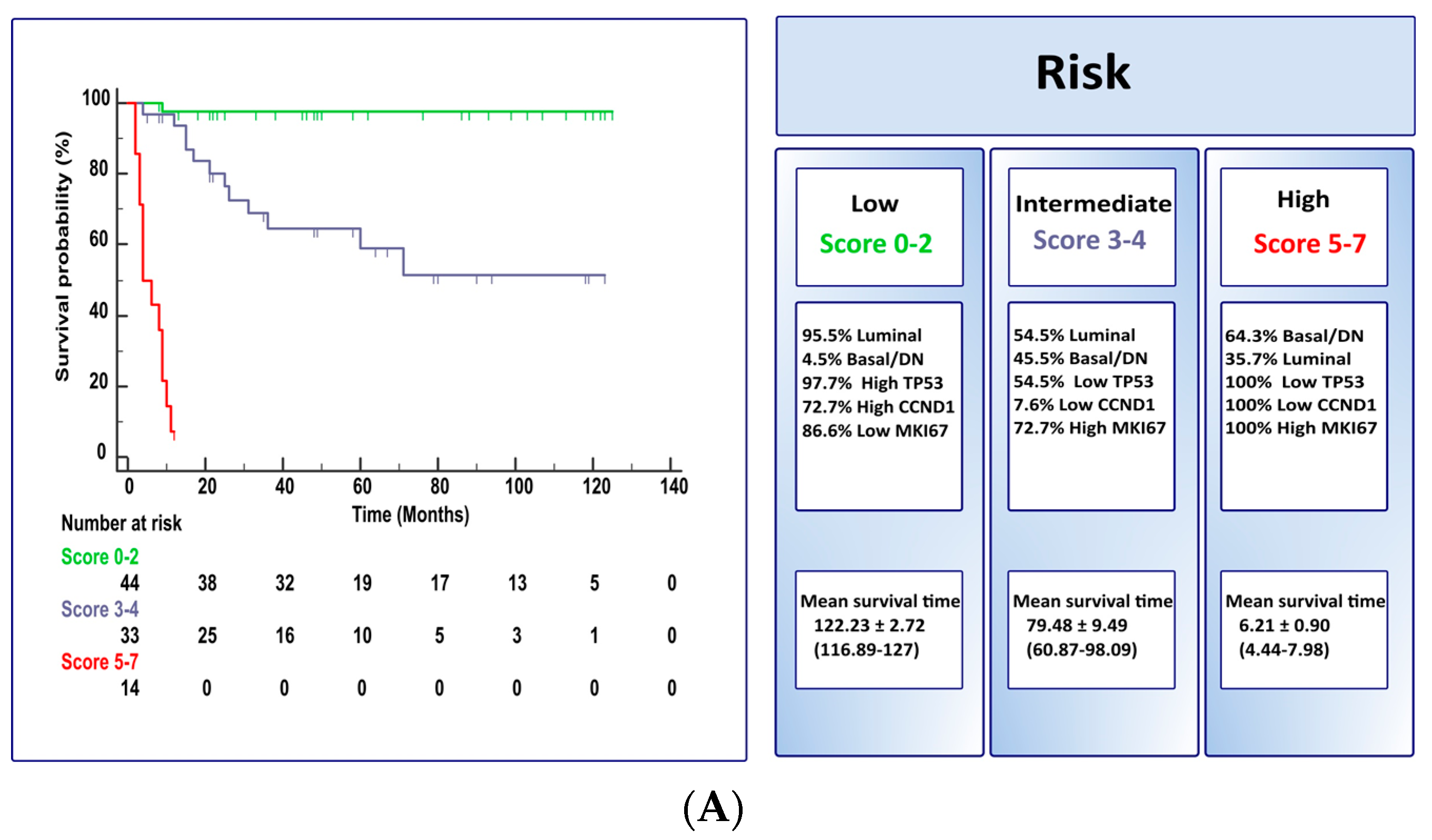
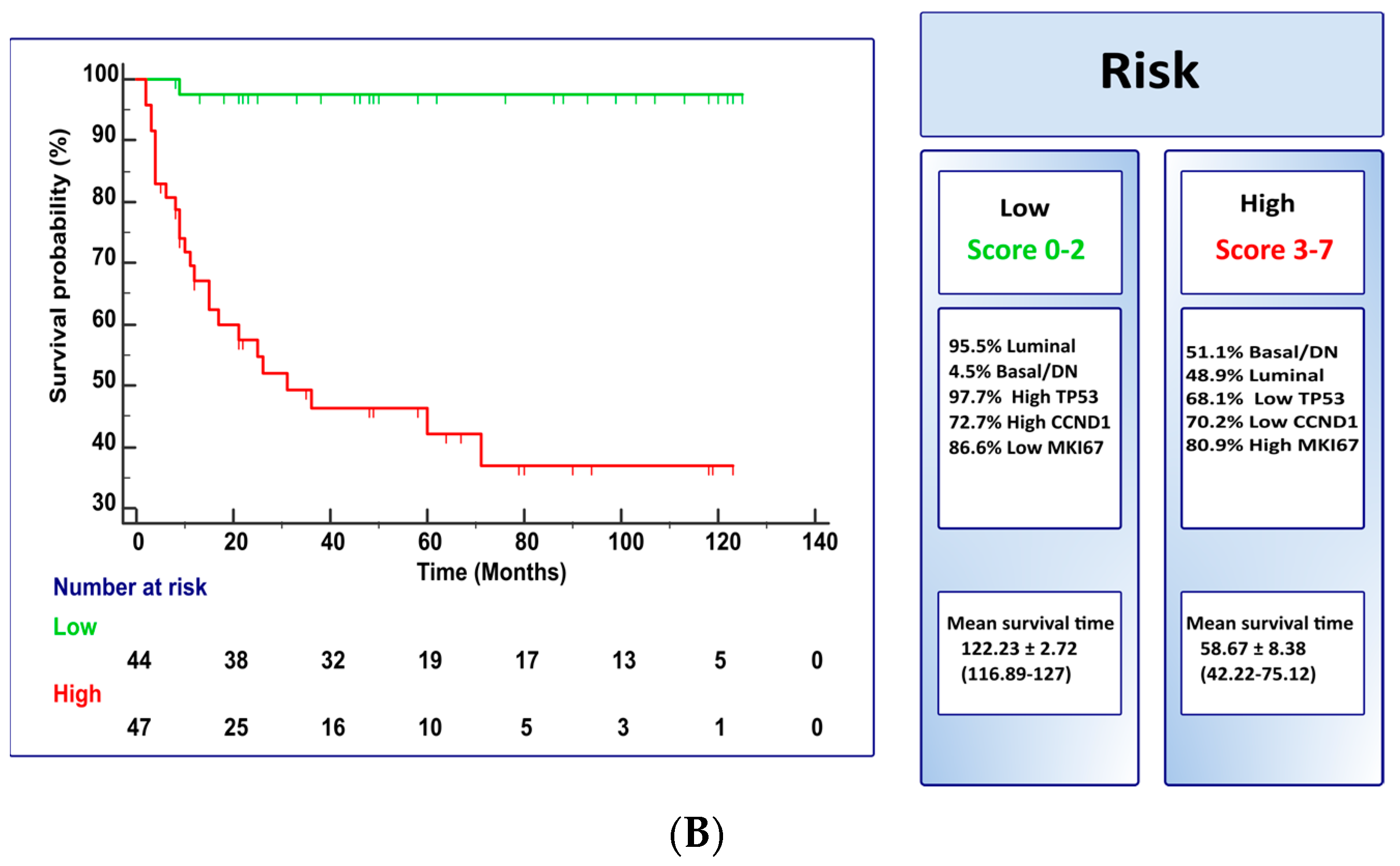
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Beltran, A. Bladder cancer: Clinical and pathological profile. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. Suppl. 2008, 42, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babjuk, M.; Burger, M.; Capoun, O.; Cohen, D.; Comperat, E.M.; Dominguez Escrig, J.L.; Gontero, P.; Liedberg, F.; Masson-Lecomte, A.; Mostafid, A.H.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer (Ta, T1, and Carcinoma in Situ). Eur. Urol. 2022, 81, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guallar-Garrido, S.; Julian, E. Bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG) Therapy for Bladder Cancer: An Update. Immunotargets Ther. 2020, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Cimadamore, A.; Blanca, A.; Massari, F.; Vau, N.; Scarpelli, M.; Cheng, L.; Montironi, R. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for the Treatment of Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotan, Y.; de Jong, J.J.; Liu, V.Y.T.; Bismar, T.A.; Boorjian, S.A.; Huang, H.C.; Davicioni, E.; Mian, O.Y.; Wright, J.L.; Necchi, A.; et al. Patients with Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer with Nonluminal Subtype Derive Greatest Benefit from Platinum Based Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. J. Urol. 2022, 207, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research, Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of urothelial bladder carcinoma. Nature 2014, 507, 315–322. [CrossRef]
- Sjodahl, G.; Eriksson, P.; Liedberg, F.; Hoglund, M. Molecular classification of urothelial carcinoma: Global mRNA classification versus tumour-cell phenotype classification. J. Pathol. 2017, 242, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollberg, P.; Chebil, G.; Eriksson, P.; Sjodahl, G.; Liedberg, F. Molecular subtypes applied to a population-based modern cystectomy series do not predict cancer-specific survival. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebola, J.; Aguiar, P.; Blanca, A.; Montironi, R.; Cimadamore, A.; Cheng, L.; Henriques, V.; Lobato-Faria, P.; Lopez-Beltran, A. Predicting outcomes in non-muscle invasive (Ta/T1) bladder cancer: The role of molecular grade based on luminal/basal phenotype. Virchows Arch. 2019, 475, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, A.; de Reynies, A.; Allory, Y.; Sjodahl, G.; Robertson, A.G.; Seiler, R.; Hoadley, K.A.; Groeneveld, C.S.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Choi, W.; et al. A Consensus Molecular Classification of Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2020, 77, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morera, D.S.; Hasanali, S.L.; Belew, D.; Ghosh, S.; Klaassen, Z.; Jordan, A.R.; Wang, J.; Terris, M.K.; Bollag, R.J.; Merseburger, A.S.; et al. Clinical Parameters Outperform Molecular Subtypes for Predicting Outcome in Bladder Cancer: Results from Multiple Cohorts, Including TCGA. J. Urol. 2020, 203, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Cimadamore, A.; Montironi, R.; Cheng, L. Molecular pathology of urothelial carcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2021, 113, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanguedolce, F.; Zanelli, M.; Palicelli, A.; Ascani, S.; Zizzo, M.; Cocco, G.; Bjornebo, L.; Lantz, A.; Falagario, U.G.; Cormio, L.; et al. Are We Ready to Implement Molecular Subtyping of Bladder Cancer in Clinical Practice? Part 1: General Issues and Marker Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Blanca, A.; Cimadamore, A.; Gogna, R.; Montironi, R.; Cheng, L. Molecular Classification of Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Using NanoString-Based Gene Expression Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Shankar, E.; Lin, S.; Singh, V.; Chan, E.R.; Cao, S.; Fu, P.; MacLennan, G.T.; Ponsky, L.E.; Gupta, S. Identification of Key Genes Associated with Progression and Prognosis of Bladder Cancer through Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Li, Z.; Lai, Y.; Lu, Z.; Lei, H.; He, C.; He, Z. A 7-gene signature predicts the prognosis of patients with bladder cancer. BMC Urol. 2022, 22, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goux, C.; Vacher, S.; Schnitzler, A.; Barry Delongchamps, N.; Zerbib, M.; Peyromaure, M.; Sibony, M.; Allory, Y.; Bieche, I.; Damotte, D.; et al. Assessment of prognostic implication of a panel of oncogenes in bladder cancer and identification of a 3-gene signature associated with recurrence and progression risk in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardos, J.; Rose, T.L.; Manocha, U.; Wobker, S.E.; Damrauer, J.S.; Bivalaqua, T.J.; Kates, M.; Moore, K.J.; Parker, J.S.; Kim, W.Y. Development and validation of a NanoString BASE47 bladder cancer gene classifier. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallden, B.; Storhoff, J.; Nielsen, T.; Dowidar, N.; Schaper, C.; Ferree, S.; Liu, S.; Leung, S.; Geiss, G.; Snider, J.; et al. Development and verification of the PAM50-based Prosigna breast cancer gene signature assay. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyerer, V.; Stoehr, R.; Bertz, S.; Lange, F.; Geppert, C.I.; Wach, S.; Taubert, H.; Sikic, D.; Wullich, B.; Hartmann, A.; et al. Prognostic impact of molecular muscle-invasive bladder cancer subtyping approaches and correlations with variant histology in a population-based mono-institutional cystectomy cohort. World J. Urol. 2021, 39, 4011–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olkhov-Mitsel, E.; Yu, Y.; Lajkosz, K.; Liu, S.K.; Vesprini, D.; Sherman, C.G.; Downes, M.R. Development of a Clinically Applicable NanoString-Based Gene Expression Classifier for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer Molecular Stratification. Cancers 2022, 14, 4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netto, G.J.; Amin, M.B.; Berney, D.M.; Comperat, E.M.; Gill, A.J.; Hartmann, A.; Menon, S.; Raspollini, M.R.; Rubin, M.A.; Srigley, J.R.; et al. The 2022 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part B: Prostate and Urinary Tract Tumors. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.B.; Greene, F.L.; Edge, S.B.; Compton, C.C.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Brookland, R.K.; Meyer, L.; Gress, D.M.; Byrd, D.R.; Winchester, D.P. The Eighth Edition AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Kwast, T.; Liedberg, F.; Black, P.C.; Kamat, A.; van Rhijn, B.W.G.; Algaba, F.; Berman, D.M.; Hartmann, A.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Samaratunga, H.; et al. International Society of Urological Pathology Expert Opinion on Grading of Urothelial Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. Focus 2022, 8, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, D.G.; Gordon, N.S.; Boucher, R.H.; Pirrie, S.J.; Baxter, L.; Ott, S.; Silcock, L.; Whalley, C.M.; Stockton, J.D.; Beggs, A.D.; et al. Targeted deep sequencing of urothelial bladder cancers and associated urinary DNA: A 23-gene panel with utility for non-invasive diagnosis and risk stratification. BJU Int. 2019, 124, 532–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbineni, H.; Alwhaibi, A.; Goc, A.; Gao, F.; Pruitt, A.; Somanath, P.R. Genetic deletion and pharmacological inhibition of Akt1 isoform attenuates bladder cancer cell proliferation, motility and invasion. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 764, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathe, A.; Nawroth, R. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Bladder Cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1655, 335–350. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.T.; Hui, G.; Mathis, C.; Chamie, K.; Pantuck, A.J.; Drakaki, A. The Current Status and Future Role of the Phosphoinositide 3 Kinase/AKT Signaling Pathway in Urothelial Cancer: An Old Pathway in the New Immunotherapy Era. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2018, 16, e269–e276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Deng, J.; Zhou, S.; Xiao, D.; Long, J.; Zhang, N.; He, C.; Mo, M.; Yang, X. Dual Inhibition of Pirarubicin-Induced AKT and ERK Activations by Phenformin Sensitively Suppresses Bladder Cancer Growth. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; He, C.; Zheng, S.; Wu, C.; Ren, M.; Shan, Y. AKT1/HK2 Axis-mediated Glucose Metabolism: A Novel Therapeutic Target of Sulforaphane in Bladder Cancer. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 17, 202100738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munksgaard, P.P.; Mansilla, F.; Brems Eskildsen, A.S.; Fristrup, N.; Birkenkamp-Demtröder, K.; Ulhøi, B.P.; Borre, M.; Agerbæk, M.; Hermann, G.G.; Orntoft, T.F.; et al. Low ANXA10 expression is associated with disease aggressiveness in bladder cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Heijden, A.G.; Mengual, L.; Lozano, J.J.; Ingelmo-Torres, M.; Ribal, M.J.; Fernández, P.L.; Oosterwijk, E.; Schalken, J.A.; Alcaraz, A.; Witjes, J.A. A five-gene expression signature to predict progression in T1G3 bladder cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 64, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Wang, C.; Ding, Y.; Xu, D.; Qian, S.; Shen, H.; Qi, J. ARID1A upregulation predicts better survival in patients with urothelial bladder carcinoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrak, A.; Palanduz, S.; Coskunpinar, E.; Sanli, O.; Armagan, A.; Karakus, S.; Topaktas, R.; Cefle, K.; Ozturk, S.; Ucur, A. Roles of Signal Transducer Pathways in Investigation of Biopsies from Patients with Bladder Tumors. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 201–205. [Google Scholar]
- Alhalabi, O.; Hahn, A.W.; Msaouel, P.; Andreev-Drakhlin, A.Y.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Naing, A.; Piha-Paul, S.; Filip, J.; Pant, S.; Yap, T.A.; et al. Molecular Profiling of Metastatic Bladder Cancer Early-Phase Clinical Trial Participants Predicts Patient Outcomes. Mol. Cancer. Res. 2021, 19, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmunt, J.; Kim, J.; Reardon, B.; Perera-Bel, J.; Orsola, A.; Rodriguez-Vida, A.; Wankowicz, S.A.; Bowden, M.; Barletta, J.A.; Morote, J.; et al. Genomic Predictors of Good Outcome, Recurrence, or Progression in High-Grade T1 Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 4476–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivas, P.; Lalani, A.A.; Pond, G.R.; Nagy, R.J.; Faltas, B.; Agarwal, N.; Gupta, S.V.; Drakaki, A.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; Wang, J.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Alterations in Advanced Urothelial Carcinoma and Association with Clinical Outcomes: A Pilot Study. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 3, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Ho, J.N.; Jin, H.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, S.E.; Hong, S.K.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, E.S.; Byun, S.S. Upregulated expression of BCL2, MCM7, and CCNE1 indicate cisplatin-resistance in the set of two human bladder cancer cell lines: T24 cisplatin sensitive and T24R2 cisplatin resistant bladder cancer cell lines. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2016, 57, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yin, L.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Yu, X.; Yao, J.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Exploring the five different genes associated with PKCα in bladder cancer based on gene expression microarray. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 1759–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, B.; Li, W.; Yang, Y.; Wu, S. The impact of cyclin D1 overexpression on the prognosis of bladder cancer: A meta-analysis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 12, 1477–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Ordóñez, J.L.; Otero, A.P.; Blanca, A.; Sevillano, V.; Sanchez-Carbayo, M.; Muñoz, E.; Cheng, L.; Montironi, R.; de Alava, E. Cyclin D3 gene amplification in bladder carcinoma in situ. Virchows Arch. 2010, 457, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreis, N.-N.; Louwen, F.; Yuan, J. The Multifaceted p21 (Cip1/Waf1/CDKN1A) in Cell Differentiation, Migration and Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Kwiatkowski, D.J. Combined CDKN1A/TP53 mutation in bladder cancer is a therapeutic target. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, A.G.; Kim, J.; Al-Ahmadie, H.; Bellmunt, J.; Guo, G.; Cherniack, A.D.; Hinoue, T.; Laird, P.W.; Hoadley, K.A.; Akbani, R.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Cell 2017, 171, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akli, S.; Zhang, X.Q.; Bondaruk, J.; Tucker, S.L.; Czerniak, P.B.; Benedict, W.F.; Keyomarsi, K. Low molecular weight cyclin E is associated with p27-resistant, high-grade, high-stage and invasive bladder cancer. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 1468–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassar, A.H.; Adib, E.; Akl, E.W.; Abou Alaiwi, S.; Nuzzo, P.V.; Mouhieddine, T.H.; Sonpavde, G.P.; Haddad, R.; Giannakis, M.; Hodi, F.S.; et al. CDKN2A alterations as markers of immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) resistance in urothelial carcinoma (UC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 475-475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itami, Y.; Miyake, M.; Ohnishi, S.; Tatsumi, Y.; Gotoh, D.; Hori, S.; Morizawa, Y.; Iida, K.; Ohnishi, K.; Nakai, Y.; et al. Disabled Homolog 2 (DAB2) Protein in Tumor Microenvironment Correlates with Aggressive Phenotype in Human Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hsieh, J.T.; Kong, Z. The ATM inhibitor KU55933 sensitizes radioresistant bladder cancer cells with DAB2IP gene defect. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2015, 91, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, A.A.; Hussain, Z.F.; Irfan, M.; Khan, E.Y.; Faridi, N.; Naqvi, H.; Khan, A.; Edhi, M.M. Prognostic significance of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) over expression in urothelial carcinoma of urinary bladder. BMC Urol. 2018, 18, 018–0373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangouei, A.S.; Barjasteh, A.H.; Rahimi, H.R.; Mojarrad, M.; Moghbeli, M. Role of tyrosine kinases in bladder cancer progression: An overview. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kessel, K.E.M.; Zuiverloon, T.C.M.; Alberts, A.R.; Boormans, J.L.; Zwarthoff, E.C. Targeted therapies in bladder cancer: An overview of in vivo research. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2015, 12, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaravinos, A.; Volanis, D.; Lambrou, G.I.; Delakas, D.; Spandidos, D.A. Role of the angiogenic components, VEGFA, FGF2, OPN and RHOC, in urothelial cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNiel, E.A.; Tsichlis, P.N. Analyses of publicly available genomics resources define FGF-2-expressing bladder carcinomas as EMT-prone, proliferative tumors with low mutation rates and high expression of CTLA-4, PD-1 and PD-L1. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2017, 2, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Ochoa, A.; McConkey, D.J.; Aine, M.; Höglund, M.; Kim, W.Y.; Real, F.X.; Kiltie, A.E.; Milsom, I.; Dyrskjøt, L.; et al. Genetic Alterations in the Molecular Subtypes of Bladder Cancer: Illustration in the Cancer Genome Atlas Dataset. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loriot, Y.; Necchi, A.; Park, S.H.; Garcia-Donas, J.; Huddart, R.; Burgess, E.; Fleming, M.; Rezazadeh, A.; Mellado, B.; Varlamov, S.; et al. Erdafitinib in Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kompier, L.C.; Lurkin, I.; van der Aa, M.N.; van Rhijn, B.W.; van der Kwast, T.H.; Zwarthoff, E.C. FGFR3, HRAS, KRAS, NRAS and PIK3CA mutations in bladder cancer and their potential as biomarkers for surveillance and therapy. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 0013821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, S.; Enokida, H.; Yoshino, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Yonemori, M.; Sakaguchi, T.; Osako, Y.; Nakagawa, M. HRAS as a potential therapeutic target of salirasib RAS inhibitor in bladder cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Gutierrez, P.R.; Kwenda, E.P.; Donelan, W.; O’Malley, P.; Crispen, P.L.; Kusmartsev, S. Hyal2 Expression in Tumor-Associated Myeloid Cells Mediates Cancer-Related Inflammation in Bladder Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.S.; Jou, Y.C.; Tsai, H.T.; Cheong, I.S.; Tzai, T.S. Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase-1 expression predicts poorer survival and up-regulates ZEB2 expression in human early stage bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matheus, L.H.G.; Dalmazzo, S.V.; Brito, R.B.O.; Pereira, L.A.; de Almeida, R.J.; Camacho, C.P.; Dellê, H. 1-Methyl-D-tryptophan activates aryl hydrocarbon receptor, a pathway associated with bladder cancer progression. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 020–07371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.E.; Porten, S.P.; Grossfeld, G.D.; Meng, M.V. Role of Indoleamine-2,3-Dioxygenase Inhibitors in Salvage Therapy for Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 47, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Wu, S.; Yang, L. hsa-miR-96 up-regulates MAP4K1 and IRS1 and may function as a promising diagnostic marker in human bladder urothelial carcinomas. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 5, 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, K.; Jeong, C.W.; Kwak, C.; Kim, H.H.; Ku, J.H. Significance of Ki-67 in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 100614–100630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, N.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Ding, Z.; Chen, X.; Deng, Y. Prognostic value of ki67 in BCG-treated non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: A meta-analysis and systematic review. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e019635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, H.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Hayes, J.D. NRF2 and the Ambiguous Consequences of Its Activation during Initiation and the Subsequent Stages of Tumourigenesis. Cancers 2020, 12, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dueñas, M.; Martínez-Fernández, M.; García-Escudero, R.; Villacampa, F.; Marqués, M.; Saiz-Ladera, C.; Duarte, J.; Martínez, V.; Gómez, M.J.; Martín, M.L.; et al. PIK3CA gene alterations in bladder cancer are frequent and associate with reduced recurrence in non-muscle invasive tumors. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R.L.; McPherson, H.R.; Kettlewell, L.; Shnyder, S.D.; Hurst, C.D.; Alder, O.; Knowles, M.A. PIK3CA dependence and sensitivity to therapeutic targeting in urothelial carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 016–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquila, L.; Ohm, J.; Woloszynska-Read, A. The role of STAG2 in bladder cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 131, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelo, A.; Prip, F.; Harris, B.T.; Solomon, D.; Berry, D.L.; Chaldekas, K.; Kumar, A.; Simko, J.; Jensen, J.B.; Bhattacharyya, P.; et al. STAG2 Is a Biomarker for Prediction of Recurrence and Progression in Papillary Non-Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4145–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachakonda, P.S.; Hosen, I.; de Verdier, P.J.; Fallah, M.; Heidenreich, B.; Ryk, C.; Wiklund, N.P.; Steineck, G.; Schadendorf, D.; Hemminki, K.; et al. TERT promoter mutations in bladder cancer affect patient survival and disease recurrence through modification by a common polymorphism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17426–17431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, N.; Rinaldetti, S.; Cheikh, B.B.; Zhou, Q.; Hass, E.P.; Jones, R.T.; Joshi, M.; LaBarbera, D.V.; Knott, S.R.V.; Cech, T.R.; et al. TRIM28 is a transcriptional activator of the mutant TERT promoter in human bladder cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2102423118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarese, C.; Massari, F.; Blanca, A.; Tortora, G.; Montironi, R.; Cheng, L.; Scarpelli, M.; Raspollini, M.R.; Vau, N.; Fonseca, J.; et al. Tp53 and its potential therapeutic role as a target in bladder cancer. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2017, 21, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fus, Ł.P.; Górnicka, B. Role of angiogenesis in urothelial bladder carcinoma. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2016, 69, 258–263. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Requena, M.J.; Luque, R.J.; Alvarez-Kindelan, J.; Quintero, A.; Blanca, A.M.; Rodriguez, M.E.; Siendones, E.; Montironi, R. Cyclin D3 expression in primary Ta/T1 bladder cancer. J. Pathol. 2006, 209, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Luque, R.J.; Alvarez-Kindelan, J.; Quintero, A.; Merlo, F.; Carrasco, J.C.; Requena, M.J.; Montironi, R. Prognostic factors in stage T1 grade 3 bladder cancer survival: The role of G1-S modulators (p53, p21Waf1, p27kip1, Cyclin D1, and Cyclin D3) and proliferation index (ki67-MIB1). Eur. Urol. 2004, 45, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintero, A.; Alvarez-Kindelan, J.; Luque, R.J.; Gonzalez-Campora, R.; Requena, M.J.; Montironi, R.; Lopez-Beltran, A. Ki-67 MIB1 labelling index and the prognosis of primary TaT1 urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 59, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Beltran, A.; Luque, R.J.; Alvarez-Kindelan, J.; Quintero, A.; Merlo, F.; Requena, M.J.; Montironi, R. Prognostic factors in survival of patients with stage Ta and T1 bladder urothelial tumors: The role of G1-S modulators (p53, p21Waf1, p27Kip1, cyclin D1, and cyclin D3), proliferation index, and clinicopathologic parameters. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2004, 122, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crocetto, F.; Russo, G.; Di Zazzo, E.; Pisapia, P.; Mirto, B.F.; Palmieri, A.; Pepe, F.; Bellevicine, C.; Russo, A.; La Civita, E.; et al. Liquid Biopsy in Prostate Cancer Management-Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aveta, A.; Cacciapuoti, C.; Barone, B.; Di Zazzo, E.; Del Giudice, F.; Maggi, M.; Ferro, M.; Terracciano, D.; Busetto, G.M.; Lucarelli, G.; et al. The Impact of Meat Intake on Bladder Cancer Incidence: Is It Really a Relevant Risk? Cancers 2022, 14, 4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, S.; Calistri, D.; Gurioli, G.; Carretta, E.; Serra, L.; Gunelli, R.; Zoli, W.; Casadio, V. Copy number analysis of 24 oncogenes: MDM4 identified as a putative marker for low recurrence risk in non muscle invasive bladder cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12458–12468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietzak, E.J.; Zabor, E.C.; Bagrodia, A.; Armenia, J.; Hu, W.; Zehir, A.; Funt, S.; Audenet, F.; Barron, D.; Maamouri, N.; et al. Genomic Differences Between “Primary” and “Secondary” Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer as a Basis for Disparate Outcomes to Cisplatin-based Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.; Jiang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. The prognostic value of six survival-related genes in bladder cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Tang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Qian, K.; Ju, L.; Xiao, Y. Development and Validation of a Six-Gene Prognostic Signature for Bladder Cancer. Front Genet. 2021, 12, 758612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascione, C.M.; Napolitano, F.; Esposito, D.; Servetto, A.; Belli, S.; Santaniello, A.; Scagliarini, S.; Crocetto, F.; Bianco, R.; Formisano, L. Role of FGFR3 in bladder cancer: Treatment landscape and future challenges. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2023, 115, 102530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, M.; Lopez-Beltran, A. Biological and clinical perspectives of TERT promoter mutation detection on bladder cancer diagnosis and management. Hum. Pathol 2022, 133, 56–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crocetto, F.; Barone, B.; Ferro, M.; Busetto, G.M.; La Civita, E.; Buonerba, C.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Terracciano, D.; Schalken, J.A. Liquid biopsy in bladder cancer: State of the art and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2022, 170, 103577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Control | 5 (5.2) |
| Tumor | 91 (94.8) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 85 (88.5) |
| Female | 11 (11.5) |
| Age, yr, median ± SD (range) | 73 ± 10.48 (43–95) |
| Followup (median ± SD, range), in months | 46 ± 40.51 (2–125) |
| Molecular Subtypes | |
| Luminal | 65 (71.4) |
| Basal | 19 (20.9) |
| Null | 7 (7.7) |
| Histologic Subtype | |
| UC-conventional | 67 (73.6) |
| UC-with variant histology | 24 (26.4) |
| Clinical Subtypes | |
| NMIBC | 66 (72.5) |
| MIBC | 25 (27.5) |
| Tumor stage * | |
| Ta | 36 (39.5) |
| T1 | 30 (33.0) |
| T2-T4 | 25 (27.5) |
| Tumor Grade (WHO 2022) | |
| High-grade | 63 (69.2) |
| Low-grade | 28 (30.8) |
| PD-L1 expression | |
| High expression | 36 (40) |
| Low expression | 54 (60) |
| Risk categories ** | |
| Low | 14 (15.4) |
| Intermediate | 13 (14.3) |
| High | 38 (41.8) |
| Very High | 26 (28.6) |
| Recurrence event in NMIBC | |
| Yes | 36 (54.5) |
| No | 30 (45.5) |
| Progression event in NMIBC | |
| Yes | 7 (10.6) |
| No | 59 (89.4) |
| Survival (NMIBC and MIBC) | |
| NED | 34 (37.4) |
| AWD | 3 (3.3) |
| DBC | 26 (28.6) |
| DOC | 28 (30.7) |
| Gene Descriptor | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Prognosis | Target Therapy | ||
| AKT1 | AKT serine/threonine kinase 1 | [27,28] | [29,30,31,32] |
| ANXA10 | Annexin A10 | [33,34] | |
| ARID1A | AT-Rich Interaction Domain 1A | [35,36,37,38,39] | |
| BIRC3 | Baculoviral IAP Repeat Containing 3 | [40,41] | |
| CCND1 | Cyclin D1 | [36,42] | |
| CCND3 | Cyclin D3 | [36,43] | |
| CDKN1A | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21) | [27,44] | [44,45] |
| CDKN1B | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27, Kip1) | [46,47] | |
| CDKN2A | Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2 (p16) | [27,38,48] | [48] |
| DAB2 | Disabled homolog 2 | [34,49] | [50] |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor | [39,51,52] | [53] |
| FGF2 | Fibroblast growth factor 2 | [54,55] | |
| FGFR3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | [19,27,36,37,39,56] | [53,57] |
| HRAS | HRas proto-oncogene, GTPase | [27,36,58] | [59] |
| HYAL2 | Hyaluronidase 2 | [34,60] | |
| IDO1 | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 | [61,62] | [62,63] |
| KDM6A | Lysine demethylase 6A | [27,56] | |
| MAP4K1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 1 | [34,64] | |
| MKI67 | Marker of proliferation Ki-67 | [65,66] | |
| NFE2L2 | NFE2 like bZIP transcription factor 2 | [56,67] | |
| PIK3CA | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha | [27,37,39,68] | [29,30,69] |
| RB1 | RB transcriptional corepressor 1 | [39,56] | |
| SPOCD1 | SPOC domain containing 1 | [34] | |
| STAG2 | Stromal Antigen 2 | [70,71] | |
| TERT | Telomerase reverse transcriptase | [27,72] | [73] |
| TP53 | Tumor protein p53 | [27,37,38,39,74] | [45,74] |
| VEGFA | Vascular endothelial growth factor A | [54,75] | [53] |
| Gene | t-Test | FDR | AUC | Optimal Cut-Off |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HRAS | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.80 | 2.48 |
| CDKN1A | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.80 | 3.4 |
| MAP4K1 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.79 | 2.01 |
| NFE2L2 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.79 | 3.43 |
| TP53 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.84 | 3.06 |
| FGF2 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.80 | 1.86 |
| IDO1 | <0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.76 | 2.08 |
| DAB2 | <0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.77 | 3.16 |
| FGFR3 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.81 | 3.29 |
| ANXA10 | 0.0003 | 0.0008 | 0.75 | 3.05 |
| CCND1 | 0.0008 | 0.0020 | 0.76 | 3.77 |
| AKT1 | 0.0011 | 0.0024 | 0.73 | 3.56 |
| SPOCD1 | 0.0012 | 0.0025 | 0.74 | 2.87 |
| ARID1A | 0.0021 | 0.0041 | 0.68 | 2.93 |
| MKI67 | 0.0023 | 0.0042 | 0.70 | 2.6 |
| CCND3 | 0.0039 | 0.0065 | 0.71 | 2.71 |
| BIRC3 | 0.0044 | 0.0070 | 0.68 | 2.28 |
| VEGFA | 0.0150 | 0.0225 | 0.66 | 3.72 |
| STAG2 | 0.0173 | 0.0246 | 0.57 | 3.09 |
| Factors | β | HR | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular subtypes | 1.277 | 3.584 | |
| Luminal | 0 | ||
| Basal/Null | 1 | ||
| TP53 expression | −2.408 | 0.090 | |
| High | 0 | ||
| Low | 2 | ||
| CCND1 expression | −2.710 | 0.067 | |
| High | 0 | ||
| Low | 2 | ||
| MKI67 expression | 2.808 | 16.579 | |
| High | 2 | ||
| Low | 0 | ||
| Total score | 0–7 | ||
| Model A | |||||
| Low Risk (score 0–2) | Intermediate Risk (score 3–4) | High Risk (score 5–7) | |||
| 43 (97.7%) NMIBC | 22 (66.7%) NMIBC | 1 (7.1%) NMIBC | |||
| 1 (2.3%) MIBC | 11 (33.3%) MIBC | 13 (92.9%) MIBC | |||
| Model B | |||||
| Low Risk (score 0–2) | High Risk (score 3–7) | ||||
| 43 (97.7%) NMIBC | 23 (48.9%) NMIBC | ||||
| 1 (2.3%) MIBC | 24 (51.1%) MIBC | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blanca, A.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Lopez-Porcheron, K.; Gomez-Gomez, E.; Cimadamore, A.; Bilé-Silva, A.; Gogna, R.; Montironi, R.; Cheng, L. Risk Classification of Bladder Cancer by Gene Expression and Molecular Subtype. Cancers 2023, 15, 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072149
Blanca A, Lopez-Beltran A, Lopez-Porcheron K, Gomez-Gomez E, Cimadamore A, Bilé-Silva A, Gogna R, Montironi R, Cheng L. Risk Classification of Bladder Cancer by Gene Expression and Molecular Subtype. Cancers. 2023; 15(7):2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072149
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlanca, Ana, Antonio Lopez-Beltran, Kevin Lopez-Porcheron, Enrique Gomez-Gomez, Alessia Cimadamore, Andreia Bilé-Silva, Rajan Gogna, Rodolfo Montironi, and Liang Cheng. 2023. "Risk Classification of Bladder Cancer by Gene Expression and Molecular Subtype" Cancers 15, no. 7: 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072149
APA StyleBlanca, A., Lopez-Beltran, A., Lopez-Porcheron, K., Gomez-Gomez, E., Cimadamore, A., Bilé-Silva, A., Gogna, R., Montironi, R., & Cheng, L. (2023). Risk Classification of Bladder Cancer by Gene Expression and Molecular Subtype. Cancers, 15(7), 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15072149







