Venetoclax for Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Pediatric Patients: A Texas Medical Center Experience
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Response and Adverse Event Evaluation
2.3. Statistical Analysis
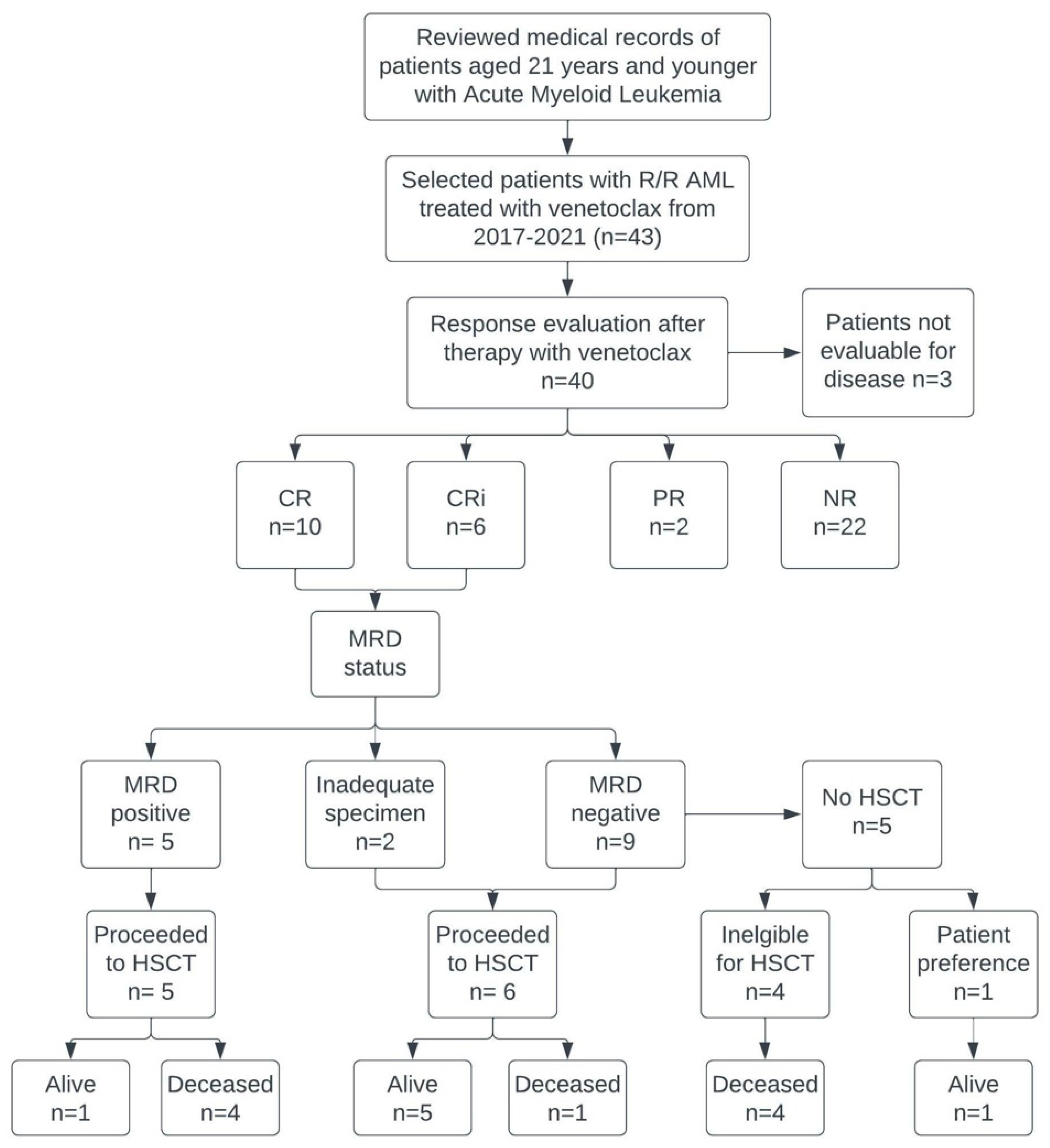
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Treatment
3.3. Safety Profile
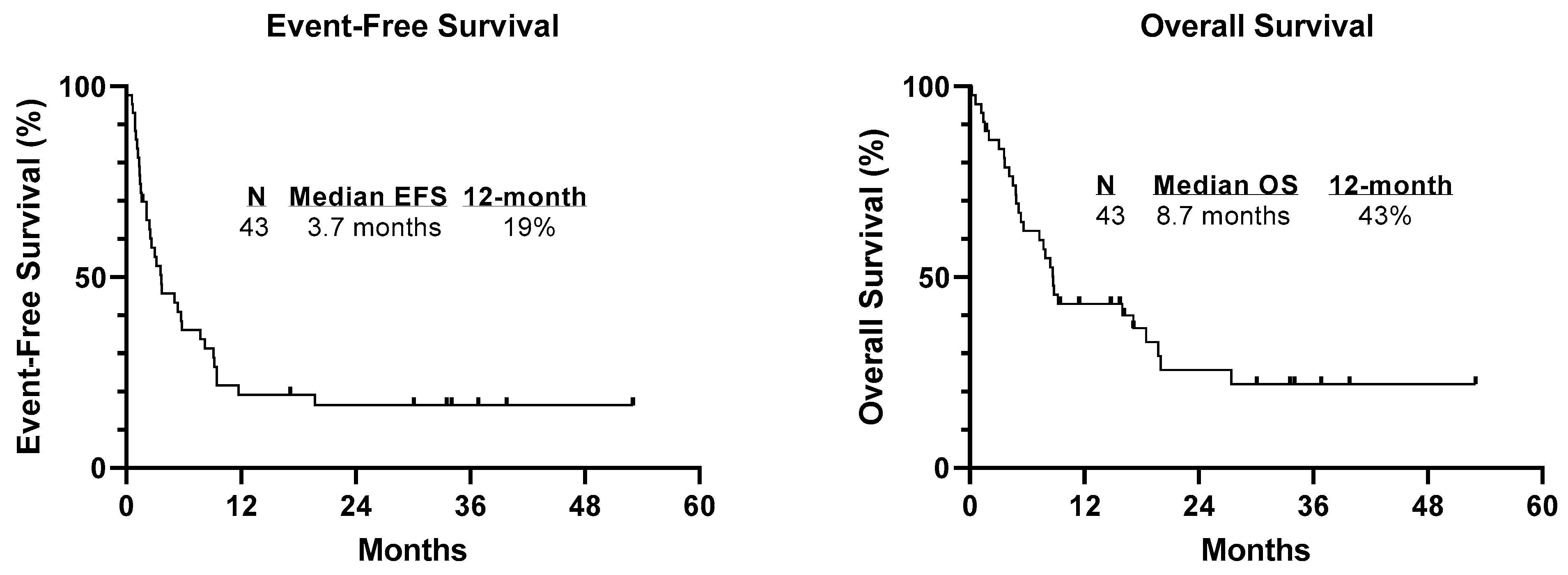
3.4. Response
3.5. Response with Venetoclax and Hypomethylating Agent
3.6. Prognostic Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Rooij, J.D.; Zwaan, C.M.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M. From Biology to Clinical Management. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaspers, G.J.; Zimmermann, M.; Reinhardt, D.; Gibson, B.E.; Tamminga, R.Y.; Aleinikova, O.; Armendariz, H.; Dworzak, M.; Ha, S.Y.; Hasle, H.; et al. Improved outcome in pediatric relapsed acute myeloid leukemia: Results of a randomized trial on liposomal daunorubicin by the International BFM Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pui, C.-H.; Carroll, W.L.; Meshinchi, S.; Arceci, R.J. Biology, risk stratification, and therapy of pediatric acute leukemias: An update. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gamis, A.S.; Alonzo, T.A.; Meshinchi, S.; Sung, L.; Gerbing, R.B.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hirsch, B.A.; Kahwash, S.B.; Heerema-McKenney, A.; Winter, L.; et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin in children and adolescents with de novo acute myeloid leukemia improves event-free survival by reducing relapse risk: Results from the randomized phase III Children’s Oncology Group trial AAML0531. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3021–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorman, M.F.; Ji, L.; Ko, R.H.; Barnette, P.; Bostrom, B.; Hutchinson, R.; Raetz, E.; Seibel, N.L.; Twist, C.J.; Eckroth, E.; et al. Outcome for children treated for relapsed or refractory acute myelogenous leukemia (rAML): A Therapeutic Advances in Childhood Leukemia (TACL) Consortium study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 55, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwaan, C.M.; Kolb, E.A.; Reinhardt, D.; Abrahamsson, J.; Adachi, S.; Aplenc, R.; De Bont, E.S.J.M.; De Moerloose, B.; Dworzak, M.; Gibson, B.E.S.; et al. Collaborative Efforts Driving Progress in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2949–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rasche, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Steidel, E.; Alonzo, T.; Aplenc, R.; Bourquin, J.P.; Boztug, H.; Cooper, T.; Gamis, A.S.; Gerbing, R.B.; et al. Survival Following Relapse in Children with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Report from AML-BFM and COG. Cancers 2021, 13, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, G.; Tasian, S.K. Relapsed pediatric acute myeloid leukaemia: State-of-the-art in 2023. Haematologica 2023. (Early view). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.H.; Montesinos, P.; Ivanov, V.; DiNardo, C.D.; Novak, J.; Laribi, K.; Kim, I.; Stevens, D.A.; Fiedler, W.; Pagoni, M.; et al. Venetoclax plus LDAC for newly diagnosed AML ineligible for intensive chemotherapy: A phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trial. Blood 2020, 135, 2137–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Jonas, B.A.; Pullarkat, V.; Thirman, M.J.; Garcia, J.S.; Wei, A.H.; Konopleva, M.; Döhner, H.; Letai, A.; Fenaux, P.; et al. Azacitidine and Venetoclax in Previously Untreated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. New Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, V.A.; DiNardo, C.; Konopleva, M. Venetoclax-based therapies for acute myeloid leukemia. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2019, 32, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souers, A.J.; Leverson, J.D.; Boghaert, E.R.; Ackler, S.L.; Catron, N.D.; Chen, J.; Dayton, B.D.; Ding, H.; Enschede, S.H.; Fairbrother, W.J.; et al. ABT-199, a potent and selective BCL-2 inhibitor, achieves antitumor activity while sparing platelets. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffioen, M.S.; de Leeuw, D.C.; Janssen, J.; Smit, L. Targeting Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Venetoclax; Biomarkers for Sensitivity and Rationale for Venetoclax-Based Combination Therapies. Cancers 2022, 14, 3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Pratz, K.; Pullarkat, V.; Jonas, B.A.; Arellano, M.; Becker, P.S.; Frankfurt, O.; Konopleva, M.; Wei, A.H.; Kantarjian, H.M.; et al. Venetoclax combined with decitabine or azacitidine in treatment-naive, elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2019, 133, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winters, A.C.; Maloney, K.W.; Treece, A.L.; Gore, L.; Franklin, A.K. Single-center pediatric experience with venetoclax and azacitidine as treatment for myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2020, 67, e28398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, A.; Trabal, A.; McCall, D.; Khazal, S.; Toepfer, L.; Bell, D.H.; Roth, M.; Mahadeo, K.M.; Nunez, C.; Short, N.J.; et al. Venetoclax for Children and Adolescents with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Lymphoblastic Lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karol, S.E.; Alexander, T.B.; Budhraja, A.; Pounds, S.B.; Canavera, K.; Wang, L.; Wolf, J.; Klco, J.M.; Mead, P.E.; Das Gupta, S.; et al. Venetoclax in combination with cytarabine with or without idarubicin in children with relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia: A phase 1, dose-escalation study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.; Thiele, J.; Borowitz, M.J.; Le Beau, M.M.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Cazzola, M.; Vardiman, J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 2391–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheson, B.D.; Bennett, J.M.; Kopecky, K.J.; Büchner, T.; Willman, C.L.; Estey, E.H.; Schiffer, C.A.; Doehner, H.; Tallman, M.S.; Lister, T.A.; et al. Revised recommendations of the International Working Group for Diagnosis, Standardization of Response Criteria, Treatment Outcomes, and Reporting Standards for Therapeutic Trials in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 4642–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Jorgensen, J.L.; Wang, S.A. How Do We Use Multicolor Flow Cytometry to Detect Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Myeloid Leukemia? Clin. Lab. Med. 2017, 37, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Wei, A.H.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Craddock, C.; DiNardo, C.D.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Godley, L.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood 2022, 140, 1345–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Rausch, C.R.; Benton, C.; Kadia, T.; Jain, N.; Pemmaraju, N.; Daver, N.; Covert, W.; Marx, K.R.; Mace, M.; et al. Clinical experience with the BCL2-inhibitor venetoclax in combination therapy for relapsed and refractory acute myeloid leukemia and related myeloid malignancies. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senapati, J.; Dhawan, R.; Aggarwal, M.; Kumar, P.; Kumar Vishwanathan, G.; Dass, J.; Tyagi, S.; Mahapatra, M.; Seth, T. Venetoclax and azacitidine (VenAZA) combination therapy in young unfit patients with AML: A perspective from a developing country. Leuk. Lymphoma 2021, 62, 1514–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Maiti, A.; Rausch, C.R.; Pemmaraju, N.; Naqvi, K.; Daver, N.G.; Kadia, T.M.; Borthakur, G.; Ohanian, M.; Alvarado, Y.; et al. 10-day decitabine with venetoclax for newly diagnosed intensive chemotherapy ineligible, and relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukaemia: A single-centre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e724–e736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaut, D.; Burkenroad, A.; Duong, T.; Feammelli, J.; Sasine, J.; Schiller, G. Venetoclax combination therapy in relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia: A single institution experience. Leuk. Res. 2020, 90, 106314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenold, M.E.; Moskoff, B.N.; Benjamin, D.J.; Hoeg, R.T.; Rosenberg, A.S.; Abedi, M.; Tuscano, J.M.; Jonas, B.A. Outcomes of Adults with Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treated with Venetoclax Plus Hypomethylating Agents at a Comprehensive Cancer Center. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 649209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Tiong, I.S.; Quaglieri, A.; MacRaild, S.; Loghavi, S.; Brown, F.C.; Thijssen, R.; Pomilio, G.; Ivey, A.; Salmon, J.M.; et al. Molecular patterns of response and treatment failure after frontline venetoclax combinations in older patients with AML. Blood 2020, 135, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsia, E.; McCullough, K.; Joshi, M.; Cook, J.; Alkhateeb, H.B.; Al-Kali, A.; Begna, K.; Elliott, M.; Hogan, W.; Litzow, M.; et al. Venetoclax and hypomethylating agents in acute myeloid leukemia: Mayo Clinic series on 86 patients. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 1511–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukier, M.; Kadia, T.; Konopleva, M.; Alotaibi, A.S.; Alfayez, M.; Loghavi, S.; Patel, K.P.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Cortes, J.; Samra, B.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes in patients with acute myeloid leukemia with concurrent FLT3-ITD and IDH mutations. Cancer 2021, 127, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Xiong, X.; Li, X.; Lu, W.; He, X.; Jin, X.; Sun, R.; Lyu, H.; Yuan, T.; Sun, T.; et al. Low-dose decitabine plus venetoclax is safe and effective as post-transplant maintenance therapy for high-risk acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 3636–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, B.; Arslan, S.; Koller, P.; Murata-Collins, J.; Afkhami, M.; Pillai, R.; Gaal, K.; Salhotra, A.; Al Malki, M.M.; Aribi, A.; et al. Outcomes of Venetoclax and Hypomethylating Agents (HMA) in Adult Patients with KMT2A-Rearranged Leukemias. Blood 2021, 138 (Suppl. 1), 3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivtsov, A.V.; Evans, K.; Gadrey, J.Y.; Eschle, B.K.; Hatton, C.; Uckelmann, H.J.; Ross, K.N.; Perner, F.; Olsen, S.N.; Pritchard, T.; et al. A Menin-MLL Inhibitor Induces Specific Chromatin Changes and Eradicates Disease in Models of MLL-Rearranged Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 660–673.e611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard-Carpentier, G.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Tang, G.; Yin, C.C.; Khoury, J.D.; Issa, G.C.; Haddad, F.; Jain, N.; Ravandi, F.; Short, N.J.; et al. Outcomes of acute lymphoblastic leukemia with KMT2A (MLL) rearrangement: The MD Anderson experience. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 5415–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, J.A.; Guest, E.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Loken, M.R.; Brodersen, L.E.; Kolb, E.A.; Aplenc, R.; Meshinchi, S.; Raimondi, S.C.; et al. Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin Improves Event-Free Survival and Reduces Relapse in Pediatric KMT2A-Rearranged AML: Results from the Phase III Children′s Oncology Group Trial AAML0531. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3149–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowiez, C.A.; Loghavi, S.; Kadia, T.M.; Daver, N.; Borthakur, G.; Pemmaraju, N.; Naqvi, K.; Alvarado, Y.; Yilmaz, M.; Short, N.; et al. Outcomes of older patients with NPM1-mutated AML: Current treatments and the promise of venetoclax-based regimens. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, G.C.; Bidikian, A.; Venugopal, S.; Konopleva, M.Y.; DiNardo, C.D.; Kadia, T.M.; Borthakur, G.; Jabbour, E.J.; Pemmaraju, N.; Yilmaz, M.; et al. Clinical outcomes associated with NPM1 mutations in patients with relapsed or refractory AML. Blood Adv. 2022, 7, 933–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient Characteristics | |
|---|---|
| Characteristic | No. of Patients (%) |
| Median age, years (range) | 17 (0.6–21) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 26 (60) |
| Female | 17 (40) |
| Race | |
| Asian | 3 (7) |
| African American | 4 (9) |
| Hispanic | 18 (42) |
| Caucasian | 18 (42) |
| Number of prior regimens | |
| 1 | 9 (21) |
| 2 | 15 (35) |
| 3 | 8 (19) |
| ≥4 | 11 (26) |
| Number of prior HSCT | |
| 0 | 26 (60) |
| 1 | 11 (26) |
| ≥2 | 6 (14) |
| Genetics | |
| KMT2A | 17 (40) |
| FLT3-ITD | 10 (23) |
| WT1 | 13 (30) |
| Monosomy 7 | 5 (12) |
| NPM1 | 4 (9) |
| RAS | 4 (9) |
| TP53 | 3 (7) |
| RUNX1-RUNX1T1 | 3 (7) |
| Inv (3) | 3 (7) |
| CEBPA | 2 (5) |
| IDH1/2 | 2 (5) |
| 5q- | 1 (2) |
| ASXL1 | 1 (2) |
| NUP98 | 1 (2) |
| Inv (16) | 0 (0) |
| Patient | Age/Sex | Cytogenetics | NGS and PCR | Prior Therapy Number | Prior HSCT | Venetoclax Regimen | Dosing mg/m2 | Cycles | Best Response | Toxicity | Directly to HSCT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.66/M | KMT2A | PTPN11 | 2 | No | (1) ARAC/VEN; (2) AZA/VEN | 66 | 2 | NR | None | No |
| 2 | 1/F | t(8;12), FLT3-ITD | Negative | 3 | No | AZA/VEN | 93 | 1 | NR | None | No |
| 3 | 2/M | KMT2A | BCR-ABL | 2 | Yes (2) | AZA/VEN | 83 | 1 | CR | TLS | No |
| 4 | 2/M | KMT2A | Negative | 5 | Yes (2) | AZA/VEN | 85 | 3 | CR | None | No |
| 5 | 3/F | KDM5A | Negative | 2 | No | AZA/VEN | 342 | 2 | CR | Thrombocytopenia, Anemia | Yes |
| 6 | 4/M | KMT2A | Negative | 4 | Yes (2) | DEC/VEN | 479 | 1 | NE | TLS, Sepsis | No |
| 7 | 5/M | Complex karyotype | PTPN11 | 1 | Yes (2) | (1) AZA/VEN/ trametinib; (2) AZA/VEN | 93 | 3 | PR | None | No |
| 8 | 6/F | KMT2A | ASXL1 | 5 | No | (1) DEC/VEN; (2) AZA/VEN | 322 | 2 | NR | Pancytopenia, Pneumonia | No |
| 9 | 7/F | RUNX1-RUNX1T1, Inversion 8 | Negative | 2 | No | AZA/VEN | 83 | 1 | CR | None | No |
| 10 | 9/M | KMT2A | Negative | 2 | Yes | AZA/VEN | 163 | 1 | NR | Diarrhea | No |
| 11 | 10/M | KMT2A, FLT3-ITD | STAG2 | 1 | No | AZA/VEN/GO/TKI | 247 | 1 | NR | Hemolytic anemia | Yes |
| 12 | 11/F | KMT2A | WT1 | 3 | No | AZA/VEN | 237 | 2 | NR | Pancytopenia | No |
| 13 | 14/M | KMT2A | WT1, EED, PHF6, CSF3R | 1 | No | AZA/VEN | 227 | 2 | CR | None | Yes |
| 14 | 14/F | Del 5q | TP53 | 1 | No | AZA/VEN | 64 | 2 | NR | None | No |
| 15 | 14/M | FLT3-ITD | WT1 | 2 | Yes | AZA/VEN | 61 | 1 | NR | Pancytopenia | No |
| 16 | 14/M | Negative | Negative | 2 | No | AZA, VEN | 374 | 2 | CR | None | No |
| 17 | 15/M | FLT3-ITD, NUP98-NSD1 | PTPN11, WT1 | 2 | Yes | (1) AZA/VEN; (2) CLIA/GO/VEN; (3) CDK inhibitor/VEN | (1) 63 (2,3) 138 | 6 | NR | TLS, thrombocytopenia, FNA | No |
| 18 | 16/F | KMT2A | STAT5 | 3 | No | AZA/VEN | 75 | 2 | PR | Pancytopenia, Sepsis | No |
| 19 | 17/F | t(9;11), KMT2A | PRPF40B, WT1 | 2 | No | CLIA/Ven/GO | 153 | 1 | CRi | FNA | Yes |
| 20 | 17/M | FLT3-ITD, inversion 3, monosomy 7 | CALR, CBL, PTPN11, STAT5A, WT1 | 2 | No | (1) FLAG/GO/TKI/VEN; (2) Cladribine/ARAC/arsenic/ TKI/VEN | (1) 62; (2) 124 | (1) 1 (2) 1 | NR | FNA | No |
| 21 | 17/M | KMT2A | PTPN11 | 4 | Yes | AZA/VEN | 56 | 4 | NR | None | No |
| 22 | 17/F | Negative | Negative | 6 | Yes (2) | AZA/VEN | 263 | 1 | NR | Neutropenia | No |
| 23 | 18/M | Negative | IKZF1, NF1, PTPN11, DNMT3A | 3 | Yes | DEC/VEN | 122 | 3 | NR | FNA | No |
| 24 | 18/M | KMT2A | Negative | 3 | Yes | DEC/VEN | 67 | 1 | NR | None | No |
| 25 | 18/M | KMT2A | JAK1 | 1 | No | AZA/VEN | 167 | 1 | NE | None | Yes |
| 26 | 18/F | MECOM(EVI1), Inv 3, monosomy 7 | CUX1, WT1, PTNP11 | 4 | No | (1) FLAG-IDA/VEN (2) VEN/Mcl-1 inhibitor | (1) 41 (2) 117 | (1) 1 (2) 1 | NR | Elevated liver enzymes | No |
| 27 | 19/M | MECOM(EVI1)r, Inv 3, monosomy 7 | NRAS, WT1 | 2 | No | DEC/ VEN | (1) 92 (2) 46 | 3 | CRi | FNA | Yes |
| 28 | 19/M | t (3;3), monosomy 7, FLT3-ITD | BCORL1, PTPN11 | 7 | No | (1) FLAG, VEN/TKI (2) DEC/VEN/TKI (3) VEN/TKI (4) DEC/VEN/TKI (5) VEN/TKI | 126 | (1) 1 (2) 2 (3) 1 (4) 3 (5) 9 | NR/stable disease | FNA, Nausea | No |
| 29 | 20/F | NPM1, t(4;8), t(7;8) | BCORL1, NPM1, PTPN11, WT1 | 5 | Yes | DEC/VEN | 118 | 1 | NE | None | No |
| 30 | 20/F | Negative | WT1 | 4 | No | DEC/ VEN | 90 | 2 | NR | None | No |
| 31 | 20/F | Negative | NRAS, KRAS | 3 | No | AZA/VEN | 50 | 4 | CRi | FNA | Yes |
| 32 | 20/M | Monosomy 7 | KRAS | 3 | No | (1) DEC/VEN (2) CLIA/VEN/GO | (1) 93 (2) 47 | (1) 9 (2) 1 | CRi | FNA | Yes |
| 33 | 20/M | KMT2A | SMC1A | 1 | Yes | FLAG-Ida/VEN | 110 | 2 | CRi | FNA | Yes |
| 34 | 20/M | FLT3-ITD | IDH2; NPM1 | 2 | Yes | DEC/VEN/GO | 105 | 1 | NR | None | No |
| 35 | 20/F | KMT2A | Negative | 2 | Yes | AZA/VEN | 75 | 2 | CR | Klebsiella sepsis | No |
| 36 | 21/M | IDH2 | IDH2 | 1 | No | FLAG-Ida/VEN | 44 | 2 | CR | FNA, Sepsis | Yes |
| 37 | 21/F | FLT3-1868a | PIGA, WT1 | 5 | Yes (2) | AZA/VEN/gilteritinib | 60 | 1 | NR | FNA | No |
| 38 | 21/F | RUNX1-RUNX1T1; | Negative | 2 | No | DEC/GO/VEN | 118 | 4 | CR | FNA | No |
| 39 | 21/M | RUNX1-RUNX1T1 | CEBPA, KIT, STATSA | 3 | No | DEC/VEN | 60 | 1 | NR | Sepsis (R. Mucilaginosa) | No |
| 40 | 21/F | FLT3-ITD, NPM1 | NPM1, RUNX1, SH2B3, TP53, WT1 | 4 | Yes | (1) DEC/VEN/TKI (2) AZA/VEN | (1) 134 (2) 268 | (1) 1 (2) 3 | CR | FNA | Yes |
| 41 | 21/M | Negative | CEBPA, WT1 | 2 | No | (1) ARAC/VEN (2) DEC/VEN | 37 | (1) 1 (2) 1 | NR | FNA | No |
| 42 | 21/M | KMT2A | KRAS, NRAS, BRINP3, TP53 | 1 | No | DEC/VEN | 52 | 1 | NR | FNA | No |
| 43 | 21/M | FLT3-ITD | NPM1, GATA2 | 1 | No | CLIA, VEN | 50 | 2 | CRi | FNA (S. viridans) | Yes |
| Adverse Event, n (%) | Grade ≥ 3 | Grade 3, n | Grade 4, n | Grade 5, n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Febrile neutropenia | 16 (37) | 16 | 0 | 0 |
| Non-febrile neutropenia | 5 (12) | 1 | 4 | 0 |
| Anemia | 6 (14) | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 6 (14) | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Sepsis | 5 (12) | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| Tumor lysis syndrome | 3 (7) | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Nausea/vomiting | 1 (2) | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Elevated ALT/AST | 1 (2) | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Pneumonia | 1 (2) | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trabal, A.; Gibson, A.; He, J.; McCall, D.; Roth, M.; Nuñez, C.; Garcia, M.; Buzbee, M.; Toepfer, L.; Bidikian, A.; et al. Venetoclax for Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Pediatric Patients: A Texas Medical Center Experience. Cancers 2023, 15, 1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071983
Trabal A, Gibson A, He J, McCall D, Roth M, Nuñez C, Garcia M, Buzbee M, Toepfer L, Bidikian A, et al. Venetoclax for Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Pediatric Patients: A Texas Medical Center Experience. Cancers. 2023; 15(7):1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071983
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrabal, Adriana, Amber Gibson, Jiasen He, David McCall, Michael Roth, Cesar Nuñez, Miriam Garcia, Meredith Buzbee, Laurie Toepfer, Aram Bidikian, and et al. 2023. "Venetoclax for Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Pediatric Patients: A Texas Medical Center Experience" Cancers 15, no. 7: 1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071983
APA StyleTrabal, A., Gibson, A., He, J., McCall, D., Roth, M., Nuñez, C., Garcia, M., Buzbee, M., Toepfer, L., Bidikian, A., Daver, N., Kadia, T., Short, N. J., Issa, G. C., Ravandi, F., DiNardo, C. D., Montalban Bravo, G., Garces, S., Marcogliese, A., ... Cuglievan, B. (2023). Venetoclax for Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Pediatric Patients: A Texas Medical Center Experience. Cancers, 15(7), 1983. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15071983









