Leptomeningeal Disease (LMD) in Patients with Melanoma Metastases
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
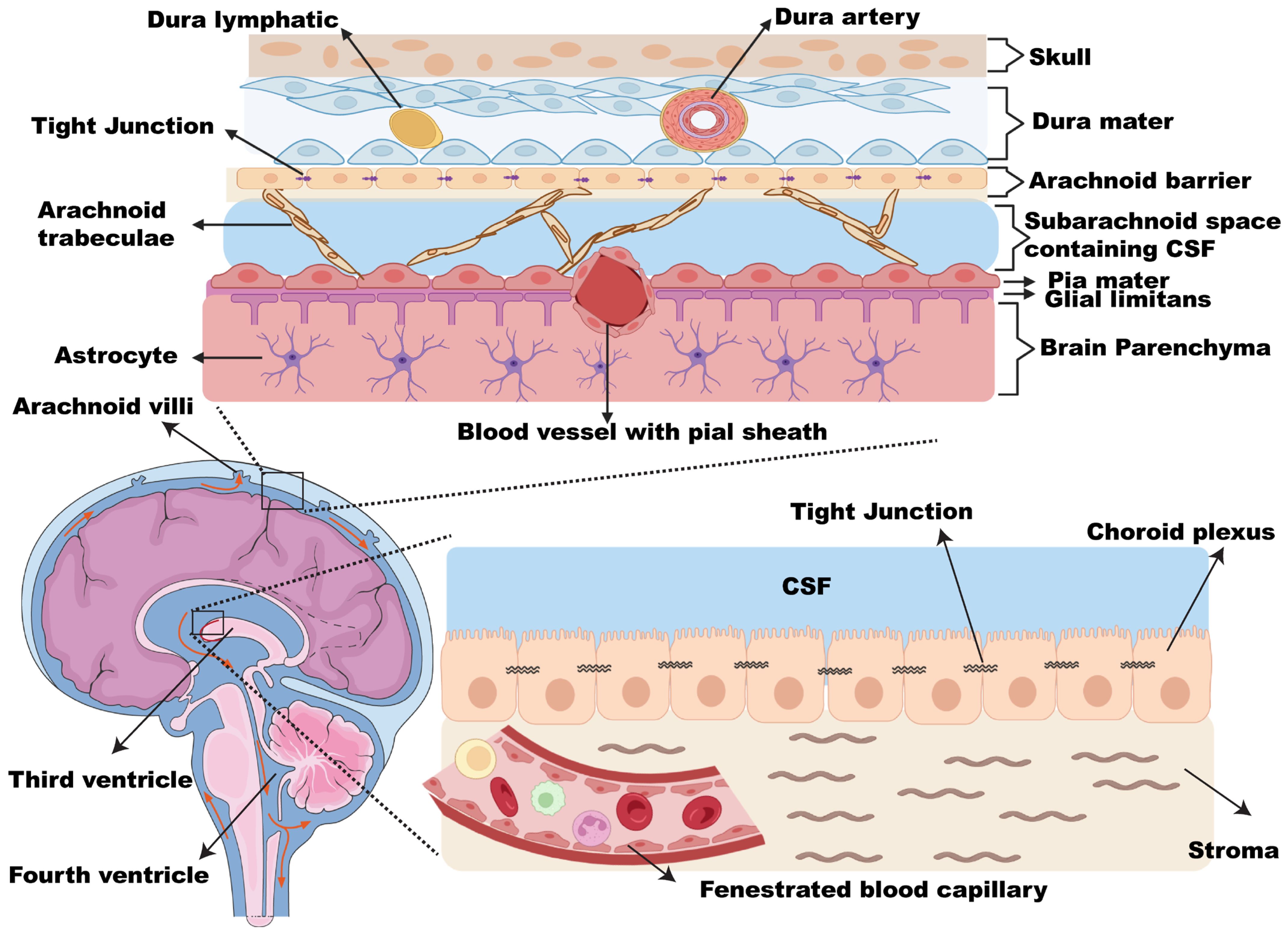
2. Leptomeninges and CSF Biology
2.1. Leptomeninges
2.2. CSF
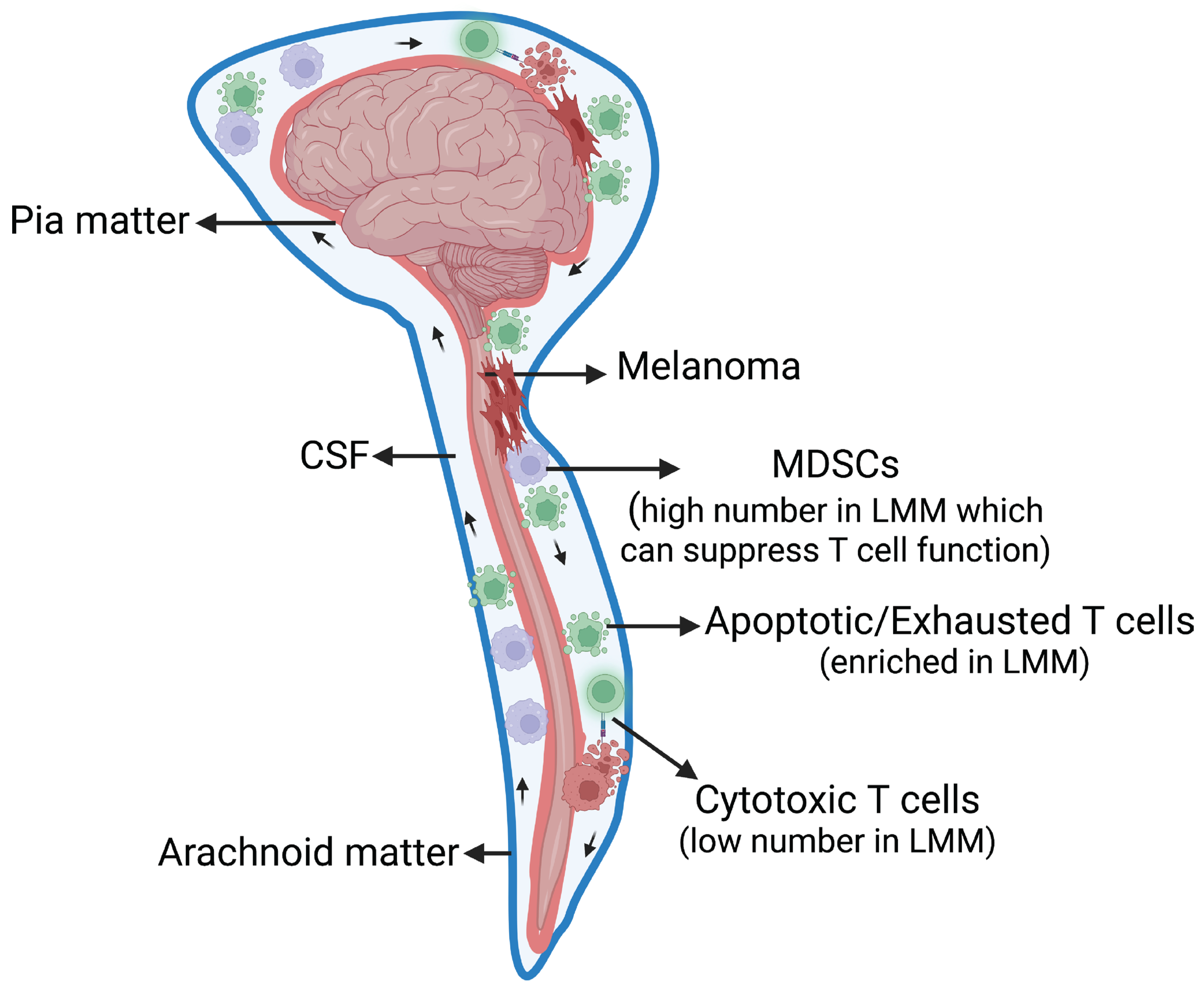
3. LMM Pathophysiology
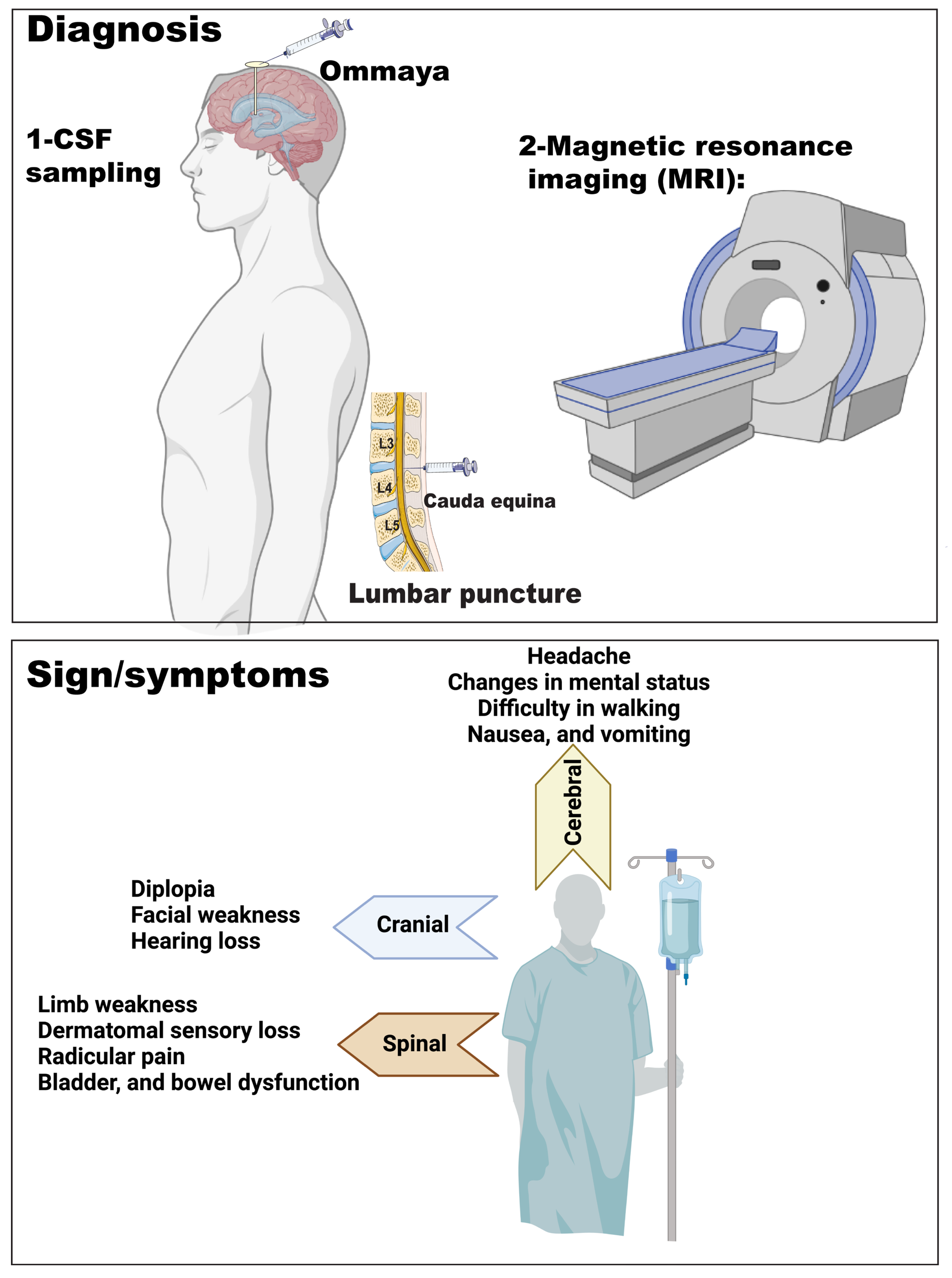
4. Clinical Signs and Symptoms of LMD
5. LMD Diagnosis
5.1. Imaging
5.2. CSF Analysis
5.3. Diagnostic Criteria for LMD
6. LMM Prognosis
7. LMM Treatment
7.1. Radiation Therapy
7.2. Systemic Therapy
7.3. Intrathecal (IT) Therapy
7.4. Response to Treatment
7.5. Palliative and Supportive Care
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morton, R.; Ko, A.l.; Silbergeld, D.L. 40–Brain Metastasis. In Principles of Neurological Surgery, 4th ed.; Ellenbogen, R.G., Sekhar, L.N., Kitchen, N.D., da Silva, H.B., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 586–592.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rhun, E.; Weller, M.; Brandsma, D.; Van den Bent, M.; de Azambuja, E.; Henriksson, R.; Boulanger, T.; Peters, S.; Watts, C.; Wick, W.; et al. EANO–ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumours†. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, iv84–iv99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batool, A.; Kasi, A. Leptomeningeal Carcinomatosis; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK499862/ (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Pan, Z.; Yang, G.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, T.; Gao, Y.; Dong, L. Leptomeningeal metastases from a primary central nervous system melanoma: A case report and literature review. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 12, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Perez-Soler, R. Leptomeningeal metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, e43–e55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smalley, K.S.; Fedorenko, I.V.; Kenchappa, R.S.; Sahebjam, S.; Forsyth, P.A. Managing leptomeningeal melanoma metastases in the era of immune and targeted therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figura, N.B.; Rizk, V.T.; Armaghani, A.J.; Arrington, J.A.; Etame, A.B.; Han, H.S.; Czerniecki, B.J.; Forsyth, P.A.; Ahmed, K.A. Breast leptomeningeal disease: A review of current practices and updates on management. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 177, 277–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.D.; Bindal, S.; Bassett, R.L., Jr.; Haydu, L.E.; McCutcheon, I.E.; Heimberger, A.B.; Li, J.; O’Brien, B.J.; Guha-Thakurta, N.; Tetzlaff, M.T.; et al. Predictors of survival in metastatic melanoma patients with leptomeningeal disease (LMD). J. Neurooncol. 2019, 142, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oinino, S.; Rodrigues, I.; Boulanger, T.; Andre, C.; Bonneterre, J.; Zairi, F.; Mortier, L.; Desmedt, E.; Templier, C.; Rhun, E.L. Prognosis of leptomeningeal metastases from melanoma: A case series of 28 patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, e13550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizer, J.J.; Hwu, W.-J.; Panageas, K.S.; Wilton, A.; Baldwin, D.E.; Bailey, E.; von Althann, C.; Lamb, L.A.; Alvarado, G.; Bilsky, M.H.; et al. Brain and leptomeningeal metastases from cutaneous melanoma: Survival outcomes based on clinical features. Neuro-Oncology 2008, 10, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorti, E.; Kebir, S.; Ahmed, M.S.; Keyvani, K.; Umutlu, L.; Kanaki, T.; Zaremba, A.; Reinboldt-Jockenhoefer, F.; Knispel, S.; Gratsias, E.; et al. Leptomeningeal disease from melanoma—Poor prognosis despite new therapeutic modalities. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 148, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tétu, P.; Sirven-Villaros, L.; Cuzzubbo, S.; Ursu, R.; Baroudjian, B.; Delyon, J.; Nataf, F.; De Margerie-Mellon, C.; Allayous, C.; Lefevre, W.; et al. Impact of New Systemic Treatment and Radiotherapy in Melanoma Patients with Leptomeningeal Metastases. Cancers 2020, 12, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Cancer Statistics Working Group. U.S. Cancer Statistics Data Visualizations Tool, based on 2019 Submission Data (1999–2017): U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Cancer Institute. Available online: https://gis.cdc.gov/Cancer/USCS/#/AtAGlance/ (accessed on 12 January 2022).
- Arnold, M.; Singh, D.; Laversanne, M.; Vignat, J.; Vaccarella, S.; Meheus, F.; Cust, A.E.; de Vries, E.; Whiteman, D.C.; Bray, F. Global Burden of Cutaneous Melanoma in 2020 and Projections to 2040. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkoris, C.P. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. How does cancer reach the pia-arachnoid? Cancer 1983, 51, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rhun, E.; Taillibert, S.; Chamberlain, M.C. Carcinomatous meningitis: Leptomeningeal metastases in solid tumors. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2013, 4, S265–S288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, P.C.; Fischbein, N.J.; McCalmont, T.H.; Kashani-Sabet, M.; Zettersten, E.M.; Liu, A.Y.; Weissman, J.L. Perineural spread of malignant melanoma of the head and neck: Clinical and imaging features. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2004, 25, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, K.; Jeong, J. Developmental biology of the meninges. Genesis 2019, 57, e23288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeeb, N.; Deep, A.; Griessenauer, C.J.; Mortazavi, M.M.; Watanabe, K.; Loukas, M.; Tubbs, R.S.; Cohen-Gadol, A.A. The intracranial arachnoid mater. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2013, 29, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brat, D.J. 2—Normal Brain Histopathology. In Practical Surgical Neuropathology: A Diagnostic Approach, 2nd ed.; Perry, A., Brat, D.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, S.A.; Krabak, M.J. Leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 1999, 25, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, J.V.; Dick, A.D.; McMenamin, P.G.; Roberts, F.; Pearlman, E. Chapter 1—Anatomy of the eye and orbit. In The Eye, 4th ed.; Forrester, J.V., Dick, A.D., McMenamin, P.G., Roberts, F., Pearlman, E., Eds.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 1–102.e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernau, W.; Vernau, K.A.; Sue Bailey, C. Chapter 26—Cerebrospinal Fluid. In Clinical Biochemistry of Domestic Animals, 6th ed.; Kaneko, J.J., Harvey, J.W., Bruss, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; pp. 769–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.L.; Jacob, L.; Boisserand, L. Lymphatic system in central nervous system. Med. Sci. 2019, 35, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.C. Chapter 9—Delivery Considerations for Targeting the Choroid Plexus–Cerebrospinal Fluid Route. In The Choroid Plexus and Cerebrospinal Fluid; Neman, J., Chen, T.C., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hladky, S.B.; Barrand, M.A. Mechanisms of fluid movement into, through and out of the brain: Evaluation of the evidence. Fluids Barriers CNS 2014, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piña, Y.; Gramatzki, D.; Forsyth, P.; Lee, E.Q.; Le Rhun, E. Leptomeningeal Disease. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 36, 189–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neman, J.; Termini, J.; Wilczynski, S.; Vaidehi, N.; Choy, C.; Kowolik, C.M.; Li, H.; Hambrecht, A.C.; Roberts, E.; Jandial, R. Human breast cancer metastases to the brain display GABAergic properties in the neural niche. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boire, A.; Zou, Y.; Shieh, J.; Macalinao, D.G.; Pentsova, E.; Massagué, J. Complement Component 3 Adapts the Cerebrospinal Fluid for Leptomeningeal Metastasis. Cell 2017, 168, 1101–1113.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.-M.; Kim, S.; Joo, J.; Shin, K.H.; Gwak, H.-S.; Lee, S.H. Incidence and risk factors for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in breast cancer patients with parenchymal brain metastases. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2012, 52, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.-Y.; Hsieh, K.L.-C.; Tsang, Y.-M.; Cheung, W.-K.; Hsieh, C.-H. Primary leptomeningeal melanoma. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 21, 1051–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley, I.; Chen, Z.; Phadke, M.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Wyatt, C.; Evernden, B.; Messina, J.L.; Sarnaik, A.; Sondak, V.K.; et al. Single-Cell Characterization of the Immune Microenvironment of Melanoma Brain and Leptomeningeal Metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4109–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, R.E.; Richardson, E.K.; Toh, H.C. Revisiting the role of CD4+ T-cells in cancer immunotherapy—New insights into old paradigms. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varin, A.; Gordon, S. Alternative activation of macrophages: Immune function and cellular biology. Immunobiology 2009, 214, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostuni, R.; Kratochvill, F.; Murray, P.J.; Natoli, G. Macrophages and cancer: From mechanisms to therapeutic implications. Trends Immunol. 2015, 36, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Lan, H. Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor metastasis: Biological roles and clinical therapeutic applications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendrowicz, E.; Sas, Z.; Bremer, E.; Rygiel, T.P. The Role of Macrophages in Cancer Development and Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastaki Khoshbin, A.; Eskian, M.; Keshavarz-Fathi, M.; Rezaei, N. Roles of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Cancer Metastasis: Immunosuppression and Beyond. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2019, 67, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solito, S.; Pinton, L.; Mandruzzato, S. In Brief: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer. J. Pathol. 2017, 242, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhang, L.; Ju, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, C.; Guan, M.; Pan, S. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the characteristics of cerebrospinal fluid tumour environment in breast cancer and lung cancer leptomeningeal metastases. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakadan, S.M.; Alvarez-Breckenridge, C.A.; Markson, S.C.; Kim, A.E.; Klein, R.H.; Nayyar, N.; Navia, A.W.; Kuter, B.M.; Kolb, K.E.; Bihun, I.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic correlates of immunotherapy response within the tumor microenvironment of leptomeningeal metastases. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapunda, J.A.; Tibar, H.; Regragui, W.; Engelhardt, B. How Does the Immune System Enter the Brain? Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 805657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, B.; Vajkoczy, P.; Weller, R.O. The movers and shapers in immune privilege of the CNS. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakoyiannis, I. CSF: A key player in brain’s immunity. Lab Anim. 2022, 51, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalley, I.; Law, V.; Wyatt, C.; Evernden, B.; Fang, B.; Koomen, J.M.; Welsh, E.A.; Macaulay, R.J.B.; Forsyth, P.A.; Smalley, K.S.M. Proteomic Analysis of CSF from Patients with Leptomeningeal Melanoma Metastases Identifies Signatures Associated with Disease Progression and Therapeutic Resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2163–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, R.M.; Cannon, A.; Reynolds, J.V.; Lysaght, J.; Lynam-Lennon, N. Complement in Tumourigenesis and the Response to Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, A.; Yan, J. The Role of Membrane Bound Complement Regulatory Proteins in Tumor Development and Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flood, C.; Akinwunmi, J.; Lagord, C.; Daniel, M.; Berry, M.; Jackowski, A.; Logan, A. Transforming Growth Factor-β1 in the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Titers Derived from Exogenous and Endogenous Sources. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2001, 21, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morganti-Kossmann, M.C.; Hans, V.H.; Lenzlinger, P.M.; Dubs, R.; Ludwig, E.; Trentz, O.; Kossmann, T. TGF-beta is elevated in the CSF of patients with severe traumatic brain injuries and parallels blood-brain barrier function. J. Neurotrauma 1999, 16, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Cheng, R. Chapter 5—Neurovascular physiology and neurocritical care. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Hetts, S.W., Cooke, D.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 176, pp. 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Bertalan, M.S.; Brastianos, P.K. Leptomeningeal metastasis from systemic cancer: Review and update on management. Cancer 2018, 124, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maller, V.V.; Gray, R.I. Noncommunicating Hydrocephalus. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2016, 37, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bönig, L.; Möhn, N.; Ahlbrecht, J.; Wurster, U.; Raab, P.; Puppe, W.; Sühs, K.-W.; Stangel, M.; Skripuletz, T.; Schwenkenbecher, P. Leptomeningeal Metastasis: The Role of Cerebrospinal Fluid Diagnostics. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.-W.; Jeong, I.H.; Joung, A.; Cho, H.J.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.J. Leptomeningeal metastasis: Clinical experience of 519 cases. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 56, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; Twijnstra, A. Presenting features and value of diagnostic procedures in leptomeningeal metastases. Neurology 1999, 53, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, M.; Junck, L.; Brandsma, D.; Soffietti, R.; Ruda, R.; Raizer, J.; Boogerd, W.; Taillibert, S.; Groves, M.D.; Le Rhun, E.; et al. Leptomeningeal metastases: A RANO proposal for response criteria. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, L.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Brandes, A.A.; Peereboom, D.M.; Galanis, E.; Lin, N.U.; Soffietti, R.; Macdonald, D.R.; Chamberlain, M.; Perry, J.; et al. The Neurologic Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (NANO) scale: A tool to assess neurologic function for integration into the Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology (RANO) criteria. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 19, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.L.; Perez, H.R.; Jacks, L.M.; Panageas, K.S.; Deangelis, L.M. Leptomeningeal metastases in the MRI era. Neurology 2010, 74, 1449–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rhun, E.; Ruda, R.; Devos, P.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Brandsma, D.; Perez Segura, P.; Soffietti, R.; Weller, M. Diagnosis and treatment patterns for patients with leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors across Europe. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ineichen, B.V.; Tsagkas, C.; Absinta, M.; Reich, D.S. Leptomeningeal enhancement in multiple sclerosis and other neurological diseases: A systematic review and Meta-Analysis. NeuroImage Clin. 2022, 33, 102939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidis, N. The diagnostic and therapeutic management of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15 (Suppl. 4), iv285–iv291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.P. Chapter 36—Imaging of noninfectious inflammatory disorders of the spinal cord. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Masdeu, J.C., González, R.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 136, pp. 733–746. [Google Scholar]
- Debnam, J.M.; Mayer, R.R.; Chi, T.L.; Ketonen, L.; Weinberg, J.S.; Wei, W.; Groves, M.D.; Guha-Thakurta, N. Most common sites on MRI of intracranial neoplastic leptomeningeal disease. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2017, 45, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginat, D.T.; Meyers, S.P. Intracranial Lesions with High Signal Intensity on T1-weighted MR Images: Differential Diagnosis. RadioGraphics 2012, 32, 499–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, L.M.; Boutros, D. Leptomeningeal Metastasis. Cancer Investig. 2005, 23, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rhun, E.; Devos, P.; Weller, J.; Seystahl, K.; Mo, F.; Compter, A.; Berghoff, A.S.; Jongen, J.L.M.; Wolpert, F.; Ruda, R.; et al. Prognostic validation and clinical implications of the EANO ESMO classification of leptomeningeal metastasis from solid tumors. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, J.W.; Nagpal, S.; Iv, M.; Zeineh, M.; Gubens, M.A.; Ramchandran, K.; Neal, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A. Prolonged survival of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in the modern treatment era. Clin. Lung Cancer 2014, 15, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwinska, A.; Rudnicka, H.; Murawska, M. Breast cancer leptomeningeal metastasis: Propensity of breast cancer subtypes for leptomeninges and the analysis of factors influencing survival. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rhun, E.; Taillibert, S.; Zairi, F.; Kotecki, N.; Devos, P.; Mailliez, A.; Servent, V.; Vanlemmens, L.; Vennin, P.; Boulanger, T.; et al. A retrospective case series of 103 consecutive patients with leptomeningeal metastasis and breast cancer. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 113, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.W. Alcohol: Acute and Chronic Use and Postmortem Findings. In Encyclopedia of Forensic and Legal Medicine, 2nd ed.; Payne-James, J., Byard, R.W., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 84–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magill, S.T.; Choy, W.; Nguyen, M.P.; McDermott, M.W. Ommaya Reservoir Insertion: A Technical Note. Cureus 2020, 12, e7731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, C.M.; Forbes, R.B. Diagnostic Lumbar Puncture. Ulster Med. J. 2014, 83, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glass, J.P.; Melamed, M.; Chernik, N.L.; Posner, J.B. Malignant cells in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Mean. Posit. CSF Cytol. 1979, 29, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perske, C.; Nagel, I.; Nagel, H.; Strik, H. CSF cytology—The ongoing dilemma to distinguish neoplastic and inflammatory lymphocytes. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2011, 39, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, B.J.; Douglas, V.C.; Tihan, T.; Rubenstein, J.L.; Josephson, S.A. A systematic approach to the diagnosis of suspected central nervous system lymphoma. JAMA Neurol. 2013, 70, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Girón, R.; Pantanowitz, L. Cerebrospinal fluid cytology in nonmalignant aseptic meningeal disorders. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2017, 45, 1020–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommer, M.; Nagy, A.; Schöpflin, C.; Pauls, S.; Ringhoffer, M.; Schmid, M. Cerebrospinal fluid pleocytosis. Cancer Cytopathol. 2011, 119, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torzewski, M.; Lackner, K.J. Cerebrospinal fluid cytology: A highly diagnostic method for the detection of diseases of the central nervous system. LaboratoriumsMedizin 2016, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sener, U.; Kumthekar, P.; Boire, A. Advances in the diagnosis, evaluation, and management of leptomeningeal disease. Neurooncol. Adv. 2021, 3, v86–v95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, M.; Soffietti, R.; Raizer, J.; Rudà, R.; Brandsma, D.; Boogerd, W.; Taillibert, S.; Groves, M.D.; Le Rhun, E.; Junck, L.; et al. Leptomeningeal metastasis: A Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology critical review of endpoints and response criteria of published randomized clinical trials. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.C.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells Detected by the CellSearch System in Patients with Metastatic Breast Colorectal and Prostate Cancer. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010, 617421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rhun, E.; Tu, Q.; De Carvalho Bittencourt, M.; Farre, I.; Mortier, L.; Cai, H.; Kohler, C.; Faure, G.C. Detection and quantification of CSF malignant cells by the CellSearch® technology in patients with melanoma leptomeningeal metastasis. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoli, M.R.; Chang, C.-C.; Kageshita, T.; Wang, X.; McCarthy, J.B.; Ferrone, S. Human High Molecular Weight-Melanoma-Associated Antigen (HMW-MAA): A Melanoma Cell Surface Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan (MSCP) with Biological and Clinical Significance. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 24, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, M.; Singh, P.; Kotchetkov, I.S.; Skakodub, A.; Meng, A.; Tamer, C.; Young, R.J.; Reiner, A.S.; Panageas, K.S.; Ramanathan, L.V.; et al. Quantitative assessment of circulating tumor cells in cerebrospinal fluid as a clinical tool to predict survival in leptomeningeal metastases. J. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 157, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballester, L.Y.; Glitza Oliva, I.C.; Douse, D.Y.; Chen, M.M.; Lan, C.; Haydu, L.E.; Huse, J.T.; Roy-Chowdhuri, S.; Luthra, R.; Wistuba, I.I.; et al. Evaluating Circulating Tumor DNA From the Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients With Melanoma and Leptomeningeal Disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 77, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorenko, I.V.; Evernden, B.; Kenchappa, R.S.; Sahebjam, S.; Ryzhova, E.; Puskas, J.; McIntosh, L.; Caceres, G.; Magliocco, A.; Etame, A.; et al. A rare case of leptomeningeal carcinomatosis in a patient with uveal melanoma: Case report and review of literature. Melanoma Res. 2016, 26, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momtaz, P.; Pentsova, E.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Diamond, E.; Hyman, D.; Merghoub, T.; You, D.; Gasmi, B.; Viale, A.; Chapman, P.B. Quantification of tumor-derived cell free DNA(cfDNA) by digital PCR (DigPCR) in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with BRAFV600 mutated malignancies. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 85430–85436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichberg, D.G.; Achua, J.K.; Locatelli, E.; Shah, A.H.; Komotar, R.J.; Ghods, A.J. Primary diffuse leptomeningeal melanomatosis: Case report and review of the literature. World Neurosurg. 2019, 122, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, B.; Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, J.; Zhong, W.; Tu, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z. Unique genetic profiles from cerebrospinal fluid cell-free DNA in leptomeningeal metastases of EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer: A new medium of liquid biopsy. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straathof, C.S.; de Bruin, H.G.; Dippel, D.W.; Vecht, C.J. The diagnostic accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in leptomeningeal metastasis. J. Neurol. 1999, 246, 810–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freilich, R.J.; Krol, G.; DeAngelis, L.M. Neuroimaging and cerebrospinal fluid cytology in the diagnosis of leptomeningeal metastasis. Ann. Neurol. 1995, 38, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.C.; Newman, W.; Patanowitz, L.; Branstetter, B.F.; Amankulor, N.; Tarhini, A.A. Long-term control of leptomeningeal disease after radiation therapy and nivolumab in a metastatic melanoma patient. Immunotherapy 2020, 12, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, C.; Salzmann, M.; Steinbrecher, A.; Herbst, R.; Hassel, J.C. Durable complete remission of leptomeningeal melanoma by intrathecal methotrexate maintained with systemic ipilimumab. Immunotherapy 2021, 13, 1079–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, J.; Saria, M.; Grewal, H.K.; Kesari, S. Neoplastic meningitis resulting from hematological malignancies: Pharmacokinetic considerations and maximizing outcome. Clin. Investig. 2011, 1, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayar, G.; Ejikeme, T.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Elsamadicy, A.A.; Blackwell, K.L.; Clarke, J.M.; Lad, S.P.; Fecci, P.E. Leptomeningeal disease: Current diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 73312–73328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, F.; Baumert, B.G.; Schäfer, N.; Hattingen, E.; Scheffler, B.; Herrlinger, U.; Glas, M. Therapy of leptomeningeal metastasis in solid tumors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 43, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, Y.; Konishi, K.; Ejima, Y. Utility of whole brain radiation therapy for leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 25, 1432–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Wen, L.; Lai, M.; Zhou, Z.; Shan, C.; Li, S.; Lin, T.; Wu, J.; Wang, W.; Xu, S.; et al. Whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) for leptomeningeal metastasis from NSCLC in the era of targeted therapy: A retrospective study. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 15, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, I.; Blank, C.U.; Brandsma, D. Clinical and radiological response of leptomeningeal melanoma after whole brain radiotherapy and ipilimumab. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 1976–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Mehta, U.N.; Dsouza, L.H.; Guadagnolo, B.A.; Sanders, D.L.; Kim, K.B. Long-term stabilization of leptomeningeal disease with whole-brain radiation therapy in a patient with metastatic melanoma treated with vemurafenib: A case report. Melanoma Res. 2013, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.J.; Wijetunga, N.A.; Yamada, J.; Wolden, S.; Mehallow, M.; Goldman, D.A.; Zhang, Z.; Young, R.J.; Kris, M.G.; Yu, H.A.; et al. Clinical trial of proton craniospinal irradiation for leptomeningeal metastases. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.T.; Wijetunga, N.A.; Pentsova, E.; Wolden, S.; Young, R.J.; Correa, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Steckler, A.; Bucwinska, W.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Proton Craniospinal Irradiation Versus Photon Involved-Field Radiotherapy for Patients With Solid Tumor Leptomeningeal Metastasis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3858–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Rhun, E.; Preusser, M.; van den Bent, M.; Andratschke, N.; Weller, M. How we treat patients with leptomeningeal metastases. ESMO Open 2019, 4, e000507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Genomic Classification of Cutaneous Melanoma. Cell 2015, 161, 1681–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbie, R.; Ferguson, P.; Molina-Aguilar, C.; Adams, D.J.; Robles-Espinoza, C.D. Melanoma subtypes: Genomic profiles, prognostic molecular markers and therapeutic possibilities. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.Y.; Miller, D.M.; Tsao, H. Somatic driver mutations in melanoma. Cancer 2017, 123, 2104–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.B.; Hauschild, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.B.; Ascierto, P.; Larkin, J.; Dummer, R.; Garbe, C.; Testori, A.; Maio, M.; et al. Improved Survival with Vemurafenib in Melanoma with BRAF V600E Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosman, J.A.; Kim, K.B.; Schuchter, L.; Gonzalez, R.; Pavlick, A.C.; Weber, J.S.; McArthur, G.A.; Hutson, T.E.; Moschos, S.J.; Flaherty, K.T.; et al. Survival in BRAF V600–Mutant Advanced Melanoma Treated with Vemurafenib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trunzer, K.; Pavlick, A.C.; Schuchter, L.; Gonzalez, R.; McArthur, G.A.; Hutson, T.E.; Moschos, S.J.; Flaherty, K.T.; Kim, K.B.; Weber, J.S.; et al. Pharmacodynamic effects and mechanisms of resistance to vemurafenib in patients with metastatic melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Queirolo, P.; Picasso, V.; Spagnolo, F. Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition for the treatment of BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eroglu, Z.; Ribas, A. Combination therapy with BRAF and MEK inhibitors for melanoma: Latest evidence and place in therapy. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2015, 8, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Baik, C.; Kirkwood, J.M. Clinical Development of BRAF plus MEK Inhibitor Combinations. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakji-Dupré, L.; Le Rhun, E.; Templier, C.; Desmedt, E.; Blanchet, B.; Mortier, L. Cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of vemurafenib in patients treated for brain metastatic BRAF-V600 mutated melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2015, 25, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, N.; Scheffler, B.; Stuplich, M.; Schaub, C.; Kebir, S.; Rehkämper, C.; Mack, F.; Niehusmann, P.; Simon, M.; Greschus, S.; et al. Vemurafenib for Leptomeningeal Melanomatosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, e173–e174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glitza, I.C.; Ferguson, S.D.; Guha-Thakurta, N. Rapid resolution of leptomeningeal disease with targeted therapy in a metastatic melanoma patient. J. Neuro Oncol. 2017, 133, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Barcena, E.; Mehta, U.N.; Rohlfs, M.L.; Kumar, A.J.; Penas-Prado, M.; Kim, K.B. Prolonged survival of a patient with metastatic leptomeningeal melanoma treated with BRAF inhibition-based therapy: A case report. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floudas, C.S.; Chandra, A.B.; Xu, Y. Vemurafenib in leptomeningeal carcinomatosis from melanoma: A case report of near-complete response and prolonged survival. Melanoma Res. 2016, 26, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, K.; Roudaia, L.; Buhlaiga, N.; Del Rincon, S.V.; Papneja, N.; Miller, W.H. A Review of Cancer Immunotherapy: From the Past, to the Present, to the Future. Curr. Oncol. 2020, 27, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellman, I.; Coukos, G.; Dranoff, G. Cancer immunotherapy comes of age. Nature 2011, 480, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkona, S.; Diamandis, E.P.; Blasutig, I.M. Cancer immunotherapy: The beginning of the end of cancer? BMC Med. 2016, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Allison, J.P. The future of immune checkpoint therapy. Science 2015, 348, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Acevedo, J.A.; Kimbrough, E.O.; Lou, Y. Next generation of immune checkpoint inhibitors and beyond. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansh, M. Ipilimumab and cancer immunotherapy: A new hope for advanced stage melanoma. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2011, 84, 381–389. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, J.S.; D’Angelo, S.P.; Minor, D.; Hodi, F.S.; Gutzmer, R.; Neyns, B.; Hoeller, C.; Khushalani, N.I.; Miller, W.H.; Lao, C.D.; et al. Nivolumab versus chemotherapy in patients with advanced melanoma who progressed after anti-CTLA-4 treatment (CheckMate 037): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Schadendorf, D.; Lipson, E.J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Matamala, L.; Castillo Gutiérrez, E.; Rutkowski, P.; Gogas, H.J.; Lao, C.D.; De Menezes, J.J.; et al. Relatlimab and Nivolumab versus Nivolumab in Untreated Advanced Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolin, K.; Ernstoff, M.S.; Hamid, O.; Lawrence, D.; McDermott, D.; Puzanov, I.; Wolchok, J.D.; Clark, J.I.; Sznol, M.; Logan, T.F.; et al. Ipilimumab in patients with melanoma and brain metastases: An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.A.; Saiag, P.; Robert, C.; Grob, J.-J.; Flaherty, K.T.; Arance, A.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Thomas, L.; Lesimple, T.; Mortier, L.; et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with BRAFV600-mutant melanoma brain metastases (COMBI-MB): A multicentre, multicohort, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Forsyth, P.A.; Algazi, A.; Hamid, O.; Hodi, F.S.; Moschos, S.J.; Khushalani, N.I.; Lewis, K.; Lao, C.D.; Postow, M.A.; et al. Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Melanoma Metastatic to the Brain. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geukes Foppen, M.H.; Brandsma, D.; Blank, C.U.; van Thienen, J.V.; Haanen, J.B.; Boogerd, W. Targeted treatment and immunotherapy in leptomeningeal metastases from melanoma. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1138–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arasaratnam, M.; Hong, A.; Shivalingam, B.; Wheeler, H.; Guminksi, A.D.; Long, G.V.; Menzies, A.M. Leptomeningeal melanoma-A case series in the era of modern systemic therapy. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2018, 31, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Ren, H.; Zhao, L.; Yin, J.; Feng, G.; Wang, J.; Guan, H. Neurological immune-related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: A review of the literature. Asia-Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 16, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuzzubbo, S.; Tetu, P.; Guegan, S.; Ursu, R.; Belin, C.; Sirven Villaros, L.; Mazoyer, J.; Lheure, C.; Lebbe, C.; Baroudjian, B.; et al. Reintroduction of immune-checkpoint inhibitors after immune-related meningitis: A case series of melanoma patients. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panneerselvam, K.; Wang, Y. S3528 Immune-Mediated Colitis Induced by Intrathecal Nivolumab. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2021, 116, S1449–S1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lishner, M.; Perrin, R.G.; Feld, R.; Messner, H.A.; Tuffnell, P.G.; Elhakim, T.; Matlow, A.; Curtis, J.E. Complications associated with Ommaya reservoirs in patients with cancer. The Princess Margaret Hospital experience and a review of the literature. Arch. Intern. Med. 1990, 150, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosse, R.; Doonan, B.; Ali, A.; Barish, J.; Narayan, P.; Welniak, S.; Jester, G.; Delaune, J.; Heldermon, C.D. A retrospective review of complication rates of Ommaya reservoir placement for intrathecal medication administration. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, e18532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprangers, B.E.N.; Cosmai, L.; Porta, C. 16—Conventional chemotherapy. In Onco-Nephrology; Finkel, K.W., Perazella, M.A., Cohen, E.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 127–153.e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Selamoglu, Z.; Ksenija, S.M.; Pezzani, R.; Redaelli, M.; Cho, W.C.; Kobarfard, F.; Rajabi, S.; Martorell, M.; Kumar, P.; et al. Liposomal Cytarabine as Cancer Therapy: From Chemistry to Medicine. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassan, R.; Masciulli, A.; Intermesoli, T.; Audisio, E.; Rossi, G.; Pogliani, E.M.; Cassibba, V.; Mattei, D.; Romani, C.; Cortelezzi, A.; et al. Randomized trial of radiation-free central nervous system prophylaxis comparing intrathecal triple therapy with liposomal cytarabine in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2015, 100, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glitza, I.C.; Rohlfs, M.; Guha-Thakurta, N.; Bassett, R.L., Jr.; Bernatchez, C.; Diab, A.; Woodman, S.E.; Yee, C.; Amaria, R.N.; Patel, S.P.; et al. Retrospective review of metastatic melanoma patients with leptomeningeal disease treated with intrathecal interleukin-2. ESMO Open 2018, 3, e000283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaulen, L.D.; Gumbinger, C.; Hinz, F.; Kessler, T.; Winkler, F.; Bendszus, M.; Sahm, F.; Wick, W. Intraventricular immune checkpoint inhibition with nivolumab in relapsed primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2022, 4, vdac051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, V.; Chen, Z.; Vena, F.; Smalley, I.; Macaulay, R.; Evernden, B.R.; Tran, N.; Pina, Y.; Puskas, J.; Caceres, G.; et al. A preclinical model of patient-derived cerebrospinal fluid circulating tumor cells for experimental therapeutics in leptomeningeal disease from melanoma. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24, 1673–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, S.; Sharma, D. 5—Neuroanesthesia and Monitoring for Cranial and Complex Spinal Surgery. In Principles of Neurological Surgery, 4th ed.; Ellenbogen, R.G., Sekhar, L.N., Kitchen, N.D., da Silva, H.B., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 87–102.e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omuro, A.M.P.; Lallana, E.C.; Bilsky, M.H.; DeAngelis, L.M. Ventriculoperitoneal shunt in patients with leptomeningeal metastasis. Neurology 2005, 64, 1625–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Park, J.B.; Gwak, H.S.; Kwon, J.W.; Shin, S.H.; Yoo, H. Clinical outcome of cerebrospinal fluid shunts in patients with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 17, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, N.; Fick, T.; Nandoe Tewarie, R.; Broekman, M.L. Management of hydrocephalus in patients with leptomeningeal metastases: An ethical approach to decision-making. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 140, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bander, E.D.; Yuan, M.; Reiner, A.S.; Garton, A.L.A.; Panageas, K.S.; Brennan, C.W.; Tabar, V.; Moss, N.S. Cerebrospinal fluid diversion for leptomeningeal metastasis: Palliative, procedural and oncologic outcomes. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 154, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, H.L.; Mulvey, M.R.; Bennett, M.I. Cancer-Related Neuropathic Pain. Cancers 2019, 11, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monsour, M.A.; Kelly, P.D.; Chambless, L.B. Antiepileptic Drugs in the Management of Cerebral Metastases. Neurosurg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 31, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khaled, M.L.; Tarhini, A.A.; Forsyth, P.A.; Smalley, I.; Piña, Y. Leptomeningeal Disease (LMD) in Patients with Melanoma Metastases. Cancers 2023, 15, 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061884
Khaled ML, Tarhini AA, Forsyth PA, Smalley I, Piña Y. Leptomeningeal Disease (LMD) in Patients with Melanoma Metastases. Cancers. 2023; 15(6):1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061884
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhaled, Mariam Lotfy, Ahmad A. Tarhini, Peter A. Forsyth, Inna Smalley, and Yolanda Piña. 2023. "Leptomeningeal Disease (LMD) in Patients with Melanoma Metastases" Cancers 15, no. 6: 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061884
APA StyleKhaled, M. L., Tarhini, A. A., Forsyth, P. A., Smalley, I., & Piña, Y. (2023). Leptomeningeal Disease (LMD) in Patients with Melanoma Metastases. Cancers, 15(6), 1884. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061884





