Antiandrogen-Equipped Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Selectively Inhibit Androgen Receptor (AR) and AR-Splice Variant (AR-SV) in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. HDAC Inhibition and AR-Binding Assays
2.2. Cell Lines and Reagents
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay
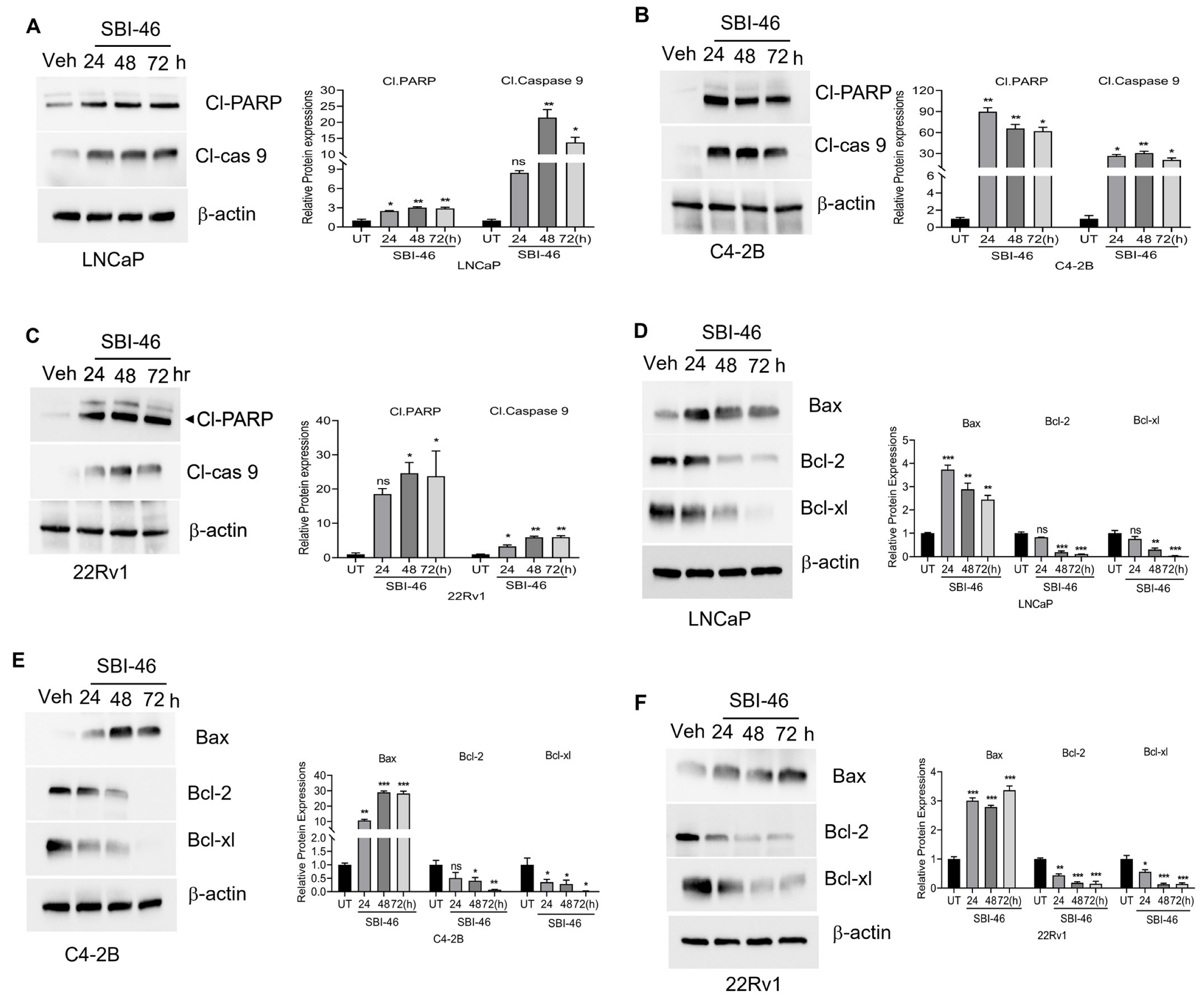
2.5. Apoptosis Assay
2.6. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Xenograft Studies
2.9. Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
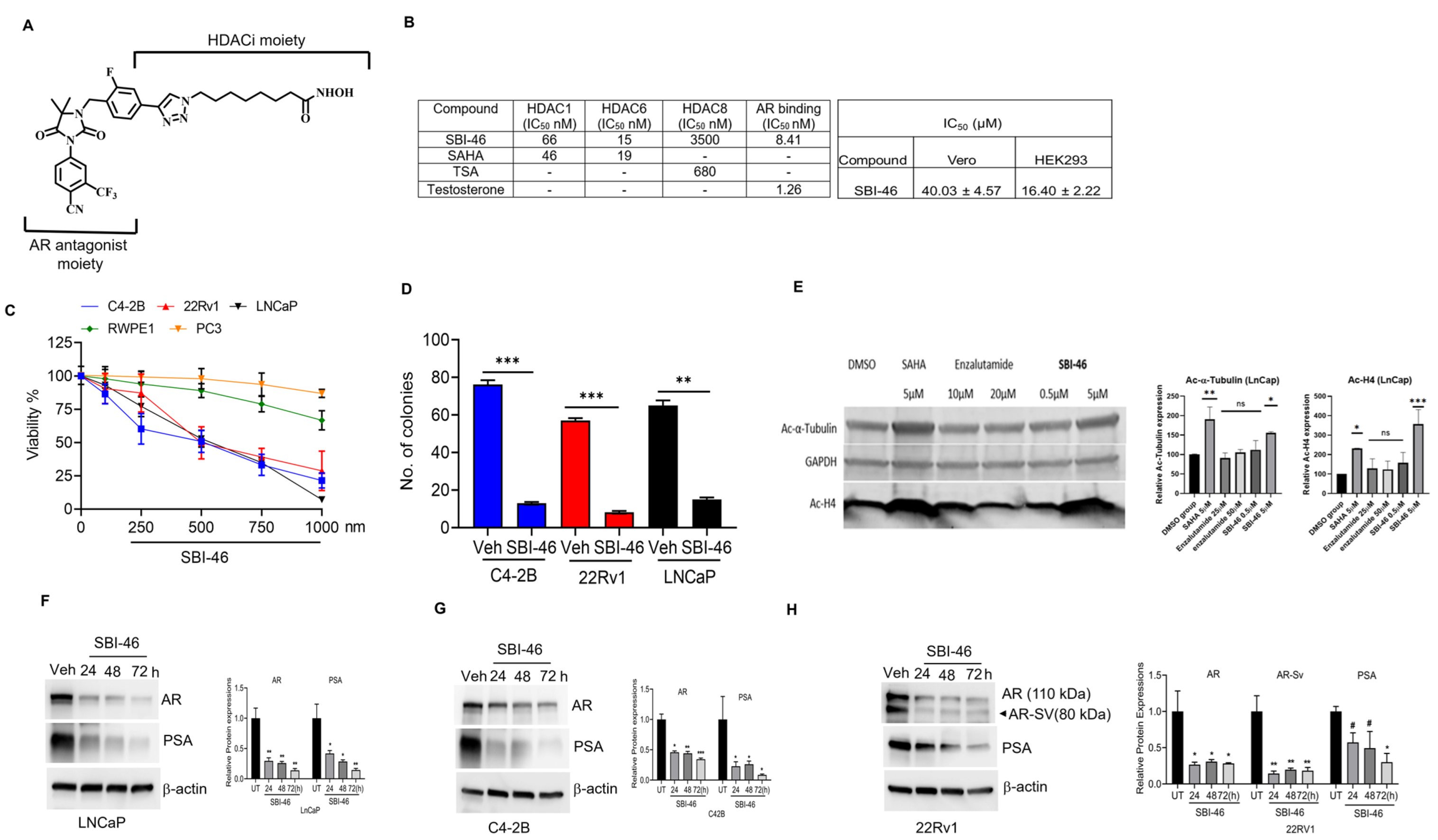
3.1. SBI-46 Inhibits HDACs and Tightly Binds to AR In Vitro
3.2. SBI-46 Selectively Inhibits the Viability of AR+ and AR-SV CRPC Cells
3.3. SBI-46 Inhibits HDACs Intracellularly
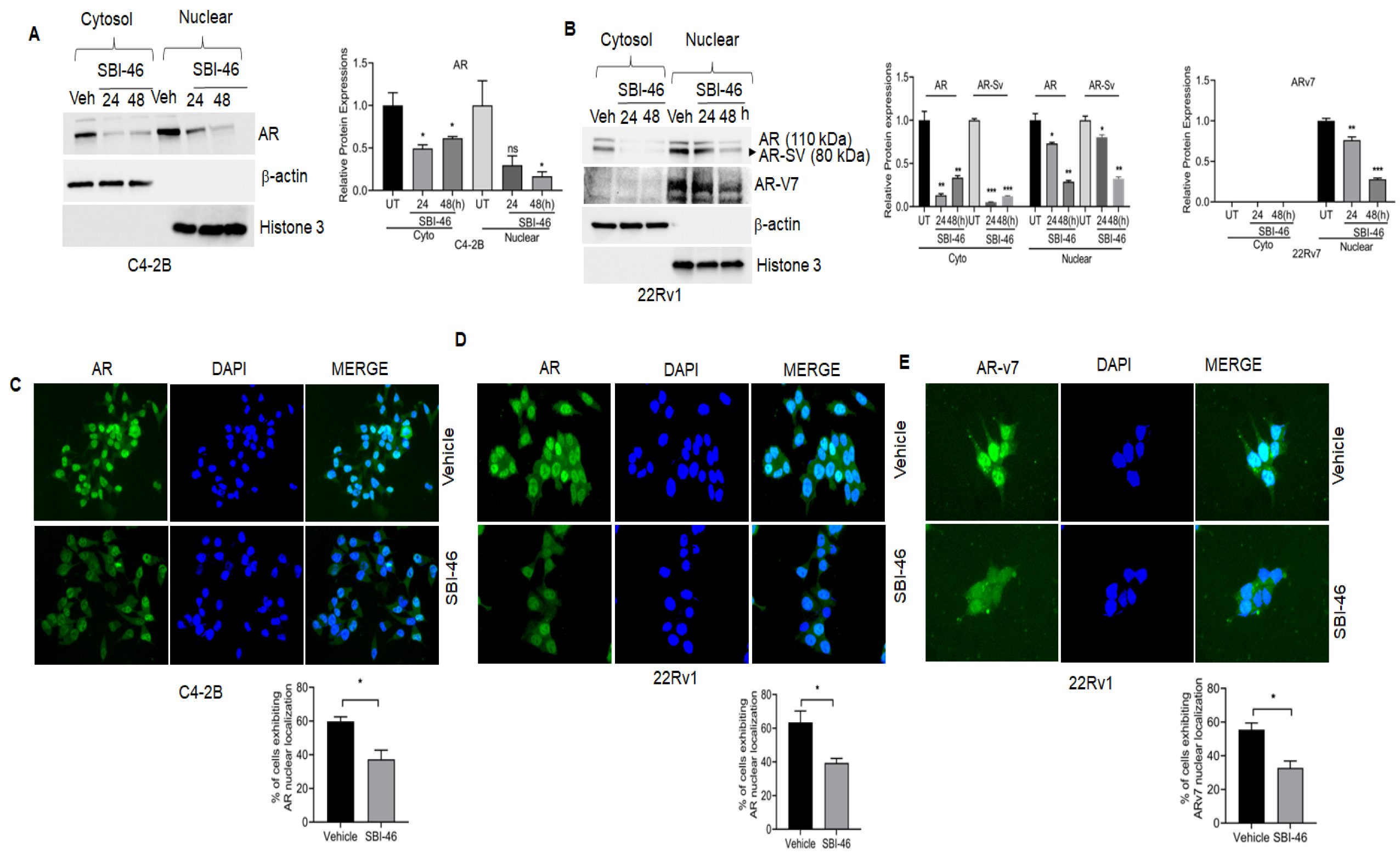
3.4. SBI-46 Inhibits AR and AR-SV in CRPC
3.5. SBI-46 Blocks Nuclear AR Localization in DHT-Treated CRPC Cells
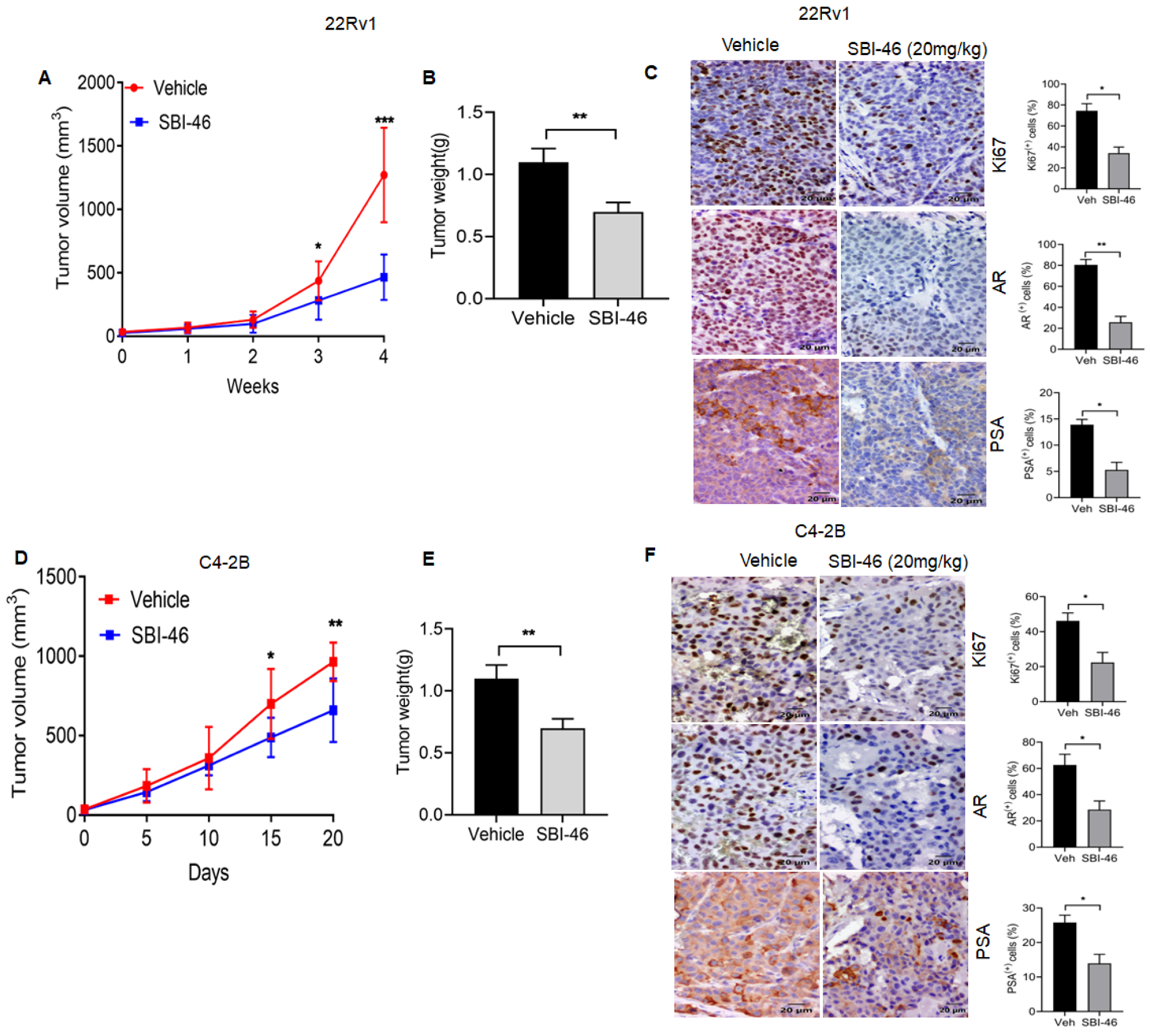
3.6. SBI-46 Represses Tumor Growth in an In Vivo Xenograft Model of CRPC
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbier, R.H.; Chau, C.; Figg, W. Androgen receptor splice variant 7 (AR-V7) and AR full-length (AR-FL) as predictive biomarkers of therapeutic resistance: Partners in crime? BJU Int. 2019, 124, 549–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, K.-I. Splicing Factors Have an Essential Role in Prostate Cancer Progression and Androgen Receptor Signaling. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Dai, B.; Ye, D.; Kong, Y.; Chang, K.; Jia, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, G. Constitutively Active AR-V7 Plays an Essential Role in the Development and Progression of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, A.; Coleman, I.; Yuan, W.; Sprenger, C.; Dolling, D.; Rodrigues, D.N.; Russo, J.W.; Figueiredo, I.; Bertan, C.; Seed, G.; et al. Androgen receptor splice variant-7 expression emerges with castration resistance in prostate cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 129, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.; Dong, J.; Robertson, M.J.; Basil, P.; Coarfa, C.; Weigel, N.L. Androgen receptor and its splice variant, AR-V7, differentially induce mRNA splicing in prostate cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohler, M.; Sikdar, A.; Ponnusamy, S.; Hwang, D.-J.; He, Y.; Miller, D.; Narayanan, R. An Overview of Next-Generation Androgen Receptor-Targeted Therapeutics in Development for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, S.; Van Der Poel, H.G.; Bergman, A.M.; Zwart, W.; Prekovic, S. Enzalutamide therapy for advanced prostate cancer: Efficacy, resistance and beyond. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, R31–R52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, N.; Herdman, M.; Pavesi, M.; De Phung, D.; Naidoo, S.; Beer, T.M.; Tombal, B.; Loriot, Y.; Ivanescu, C.; Parli, T.; et al. Health-related quality of life effects of enzalutamide in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: An in-depth post hoc analysis of EQ-5D data from the PREVAIL trial. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2017, 15, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okegawa, T.; Ninomiya, N.; Masuda, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Tambo, M.; Nutahara, K. AR-V7 in circulating tumor cells cluster as a predictive biomarker of abiraterone acetate and enzalutamide treatment in castration-resistant prostate cancer patients. Prostate 2018, 78, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagawa, S.T.; Antonarakis, E.S.; Gjyrezi, A.; Galletti, G.; Kim, S.; Worroll, D.; Stewart, J.; Zaher, A.; Szatrowski, T.P.; Ballman, K.V.; et al. Expression of AR-V7 and ARv567es in Circulating Tumor Cells Correlates with Outcomes to Taxane Therapy in Men with Metastatic Prostate Cancer Treated in TAXYNERGY. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 1880–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucchiara, V.; Yang, J.C.; Mirone, V.; Gao, A.C.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Evans, C.P. Epigenomic Regulation of Androgen Receptor Signaling: Potential Role in Prostate Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2017, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali, P.; Pranpat, M.; Bradner, J.; Balasis, M.; Fiskus, W.; Guo, F.; Rocha, K.; Kumaraswamy, S.; Boyapalle, S.; Atadja, P.; et al. Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: A novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26729–26734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsbie, D.S.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Borsu, L.; Scher, H.I.; Rosen, N.; Sawyers, C.L. Histone deacetylases are required for androgen receptor function in hormone-sensitive and cas-trate-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckschlager, T.; Plch, J.; Stiborova, M.; Hrabeta, J. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Anticancer Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.-A.; Wen, W.-L.; Chang, J.-W.; Wei, T.-T.; Tan, Y.-H.C.; Salunke, S.; Chen, C.-T.; Chen, C.-S.; Wang, Y.-C. A Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Exhibits Antitumor Activity via Apoptosis Induction, F-Actin Disruption and Gene Acetylation in Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, Z.; Diermeier, S.; Hanif, M.; Rosengren, R.J. Understanding Failure and Improving Treatment Using HDAC Inhibitors for Prostate Cancer. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancurova, I.; Uddin, M.M.; Zou, Y.; Vancura, A. Combination Therapies Targeting HDAC and IKK in Solid Tumors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 39, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryder, B.; Akbashev, M.J.; Rood, M.K.; Raftery, E.D.; Meyers, W.M.; Dillard, P.; Khan, S.; Oyelere, A.K. Selectively Targeting Prostate Cancer with Antiandrogen Equipped Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2550–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, N.R.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Kolluru, V.; Ankem, M.; Damodaran, C.; Vadhanam, M.V. A natural molecule, urolithin A, downregulates androgen receptor activation and suppresses growth of prostate cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, B.; Dahiya, N.R.; Tyagi, A.; Kolluru, V.; Saran, U.; Baby, B.V.; States, J.C.; Haddad, A.Q.; Ankem, M.K.; Damodaran, C. Chronic exposure to cadmium induces a malignant transformation of benign prostate epithelial cells. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, A.; Kolluru, V.; Chandrasekaran, B.; Saran, U.; Sharma, A.K.; Ankem, M.K.; Damodaran, C. ASR488, a novel small molecule, activates an mRNA binding protein, CPEB1, and inhibits the growth of bladder cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, B.; Pal, D.; Kolluru, V.; Tyagi, A.; Baby, B.; Dahiya, N.R.; Youssef, K.; Alatassi, H.; Ankem, M.K.; Sharma, A.K.; et al. The chemopreventive effect of withaferin A on spontaneous and inflammation-associated colon carcinogenesis models. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 1537–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkidou, K.; Gaughan, L.; Cook, S.; Leung, H.Y.; Neal, D.E.; Robson, C.N. Upregulation and Nuclear Recruitment of HDAC1 in Hormone Refractory Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2004, 59, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.; Wang, Y.; Dar, J.A.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Nelson, J.B.; Wang, Z. HDAC6 Regulates Androgen Receptor Hypersensitivity and Nuclear Localization via Modulating Hsp90 Acetylation in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Mol. Endocrinol. 2009, 23, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodji, Q.H.; Kornacki, J.R.; McDonald, J.F.; Mrksich, M.; Oyelere, A.K. Design and structure activity relationship of tumor-homing histone deacetylase inhibitors conjugated to folic and pteroic acids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 96, 340–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bantscheff, M.; Hopf, C.; Savitski, M.M.; Dittmann, A.; Grandi, P.; Michon, A.-M.; Schlegl, J.; Abraham, Y.; Becher, I.; Bergamini, G.; et al. Chemoproteomics profiling of HDAC inhibitors reveals selective targeting of HDAC complexes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Kim, Y.; Min, G.E.; Ahn, H. Dihydrotestosterone enhances castration-resistant prostate cancer cell proliferation through STAT5 activation via glucocorticoid receptor pathway. Prostate 2014, 74, 1240–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Horn, J.L.; Banda, K.; Goodman, A.Z.; Lim, Y.; Jana, S.; Arora, S.; Germanos, A.A.; Wen, L.; Hardin, W.R.; et al. The androgen receptor regulates a druggable translational regulon in advanced prostate cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, H.I.; Fizazi, K.; Saad, F.; Taplin, M.-E.; Sternberg, C.N.; Miller, K.; De Wit, R.; Mulders, P.; Chi, K.N.; Shore, N.D.; et al. Increased Survival with Enzalutamide in Prostate Cancer after Chemotherapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Wei, D.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Guo, P.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Jiang, Y.; Luo, Y. Construction of enzalutamide-resistant cell model of prostate cancer and preliminary screening of potential drug-resistant genes. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 1776–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Li, L.; Du, Z.; Quan, Z.; Yuan, M.; Cheng, H.; Gao, Y.; Luo, C.; Wu, X. Combination of phospholipase Cepsilon knockdown with GANT61 sensitizes castrationresistant prostate cancer cells to enzalutamide by suppressing the androgen receptor signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 2689–2702. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Heemers, H.; Sharifi, N. Androgen Signaling in Prostate Cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2017, 7, a030452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcuve, G.P.; Khan, D.H.; Davie, J.R. Roles of histone deacetylases in epigenetic regulation: Emerging paradigms from studies with inhibitors. Clin. Epigenetics 2012, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Kim, J.-S. A short guide to histone deacetylases including recent progress on class II enzymes. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosati, R.; Chen, B.; Patki, M.; McFall, T.; Ou, S.; Heath, E.; Ratnam, M.; Qin, Z. Hybrid Enzalutamide Derivatives with Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Activity Decrease Heat Shock Protein 90 and Androgen Receptor Levels and Inhibit Viability in Enzalutamide-Resistant C4-2 Prostate Cancer Cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 90, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraweera, A.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Combination Therapy with Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (HDACi) for the Treatment of Cancer: Achieving the Full Therapeutic Potential of HDACi. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, D.; Rampias, T. HDAC Inhibitors: Dissecting Mechanisms of Action to Counter Tumor Heterogeneity. Cancers 2021, 13, 3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, M. HDAC inhibitors still need a home run, despite recent approval. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 225–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Karsh, L.I.; Nissenblatt, M.J.; Canfield, S.E. Androgen Receptor Splice Variant, AR-V7, as a Biomarker of Resistance to Androgen Axis-Targeted Therapies in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2019, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Armstrong, C.M.; Lou, W.; Lombard, A.P.; Cucchiara, V.; Gu, X.; Yang, J.C.; Nadiminty, N.; Pan, C.-X.; Evans, C.P.; et al. Niclosamide and Bicalutamide Combination Treatment Overcomes Enzalutamide- and Bicalutamide-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzi, L.; Benedetti, R.; Altucci, L.; Rastelli, G. Design of Dual Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylase 6 and Heat Shock Protein 90. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11473–11480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Zheng, H.; Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Min, X.; Dai, S.; Zhou, W.; Chen, Z.; Xu, G.; Chen, Y. Discovery of a novel AR/HDAC6 dual inhibitor for prostate cancer treatment. Aging 2021, 13, 6982–6998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Bai, S.; Li, D.; Ma, T.; Sartor, O.; Flemington, E.K.; Zhang, H.; et al. Interplay between Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Androgen Receptor Splice Variants Mediates Castration Resistance. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, H.I.; Graf, R.P.; Schreiber, N.A.; McLaughlin, B.; Lu, D.; Louw, J.; Danila, D.C.; Dugan, L.; Johnson, A.; Heller, G.; et al. Nuclear-specific AR-V7 Protein Localization is Necessary to Guide Treatment Selection in Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollock, J.; Wardell, S.E.; Parent, A.A.; Stagg, D.; Ellison, S.J.; Alley, H.M.; Chao, C.A.; Lawrence, S.A.; Stice, J.P.; Spasojevic, I.; et al. Inhibiting androgen receptor nuclear entry in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoodi, K.Z.; Xu, Y.; Dar, J.A.; Eisermann, K.; Pascal, L.E.; Parrinello, E.; Ai, J.; Johnston, P.A.; Nelson, J.B.; Wipf, P.; et al. Inhibition of Androgen Receptor Nuclear Localization and Castration-Resistant Prostate Tumor Growth by Pyrroloimidazole-based Small Molecules. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2120–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Chen, S.; Ng, P.; Bubley, G.J.; Nelson, P.S.; Mostaghel, E.A.; Marck, B.; Matsumoto, A.M.; Simon, N.I.; Wang, H.; et al. Intratumoral De Novo Steroid Synthesis Activates Androgen Receptor in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer and Is Upregulated by Treatment with CYP17A1 Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6503–6513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, J.A.; Guns, E.S.; Lubik, A.A.; Adomat, H.H.; Hendy, S.C.; Wood, C.A.; Ettinger, S.L.; Gleave, M.E.; Nelson, C.C. Androgen Levels Increase by Intratumoral De novo Steroidogenesis during Progression of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 6407–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhtaniemi, R.; Sipilä, P.; Junnila, A.; Oksala, R.; Knuuttila, M.; Mehmood, A.; Aho, E.; Laajala, T.D.; Aittokallio, T.; Laiho, A.; et al. High intratumoral dihydrotestosterone is associated with antiandrogen resistance in VCaP prostate cancer xenografts in castrated mice. iScience 2022, 25, 104287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Xia, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, C.; Jiang, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, H. Inhibition of EGFR signaling with Spautin-1 represents a novel therapeutics for prostate cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chandrasekaran, B.; Tapadar, S.; Wu, B.; Saran, U.; Tyagi, A.; Johnston, A.; Gaul, D.A.; Oyelere, A.K.; Damodaran, C. Antiandrogen-Equipped Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Selectively Inhibit Androgen Receptor (AR) and AR-Splice Variant (AR-SV) in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC). Cancers 2023, 15, 1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061769
Chandrasekaran B, Tapadar S, Wu B, Saran U, Tyagi A, Johnston A, Gaul DA, Oyelere AK, Damodaran C. Antiandrogen-Equipped Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Selectively Inhibit Androgen Receptor (AR) and AR-Splice Variant (AR-SV) in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC). Cancers. 2023; 15(6):1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061769
Chicago/Turabian StyleChandrasekaran, Balaji, Subhasish Tapadar, Bocheng Wu, Uttara Saran, Ashish Tyagi, Alexis Johnston, David A. Gaul, Adegboyega K. Oyelere, and Chendil Damodaran. 2023. "Antiandrogen-Equipped Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Selectively Inhibit Androgen Receptor (AR) and AR-Splice Variant (AR-SV) in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC)" Cancers 15, no. 6: 1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061769
APA StyleChandrasekaran, B., Tapadar, S., Wu, B., Saran, U., Tyagi, A., Johnston, A., Gaul, D. A., Oyelere, A. K., & Damodaran, C. (2023). Antiandrogen-Equipped Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Selectively Inhibit Androgen Receptor (AR) and AR-Splice Variant (AR-SV) in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC). Cancers, 15(6), 1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061769









