Causes of Death among Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma According to Chronic Liver Disease Etiology
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Variables of Interest
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
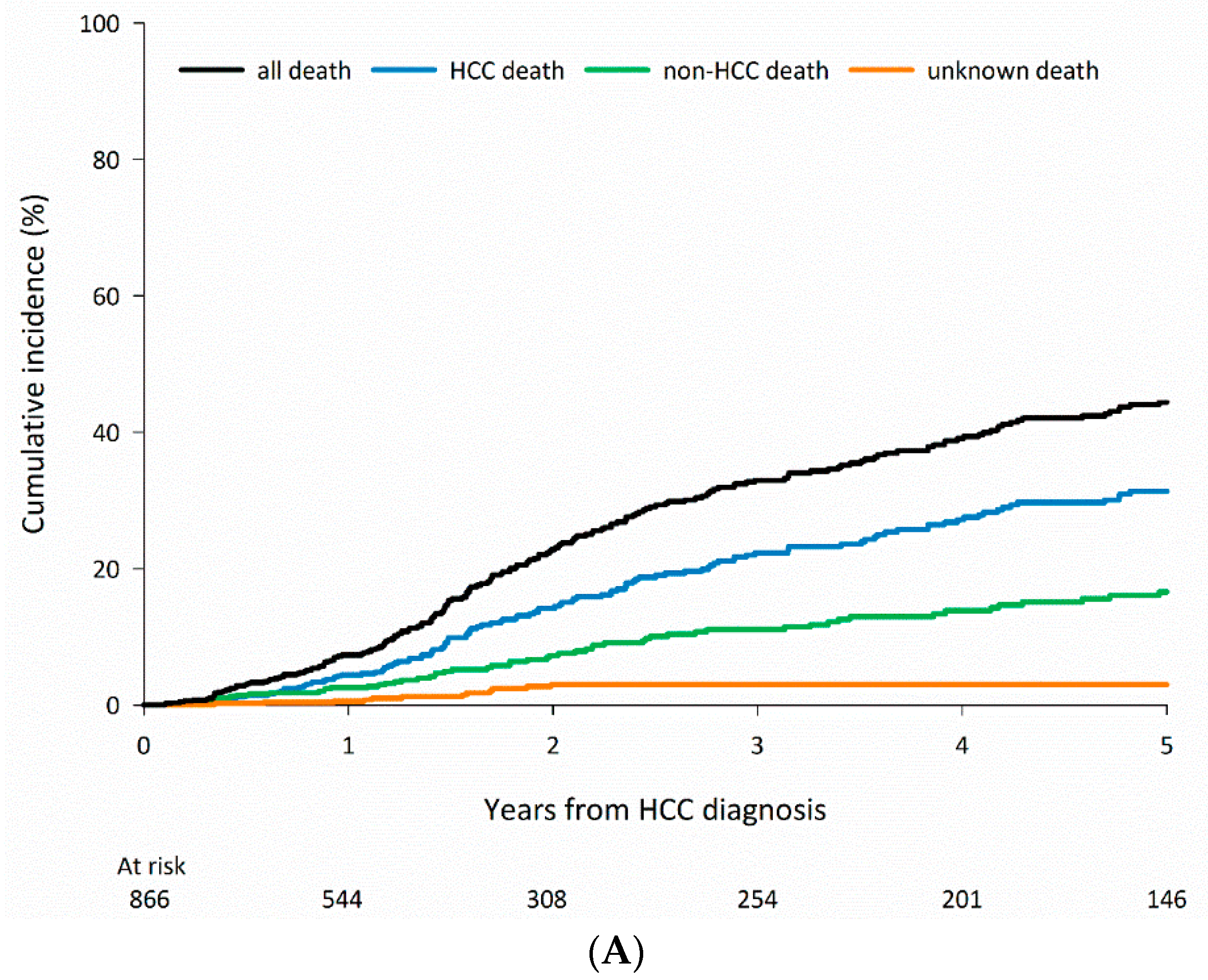
3.1. Characteristics of Patients According to CLD Etiology
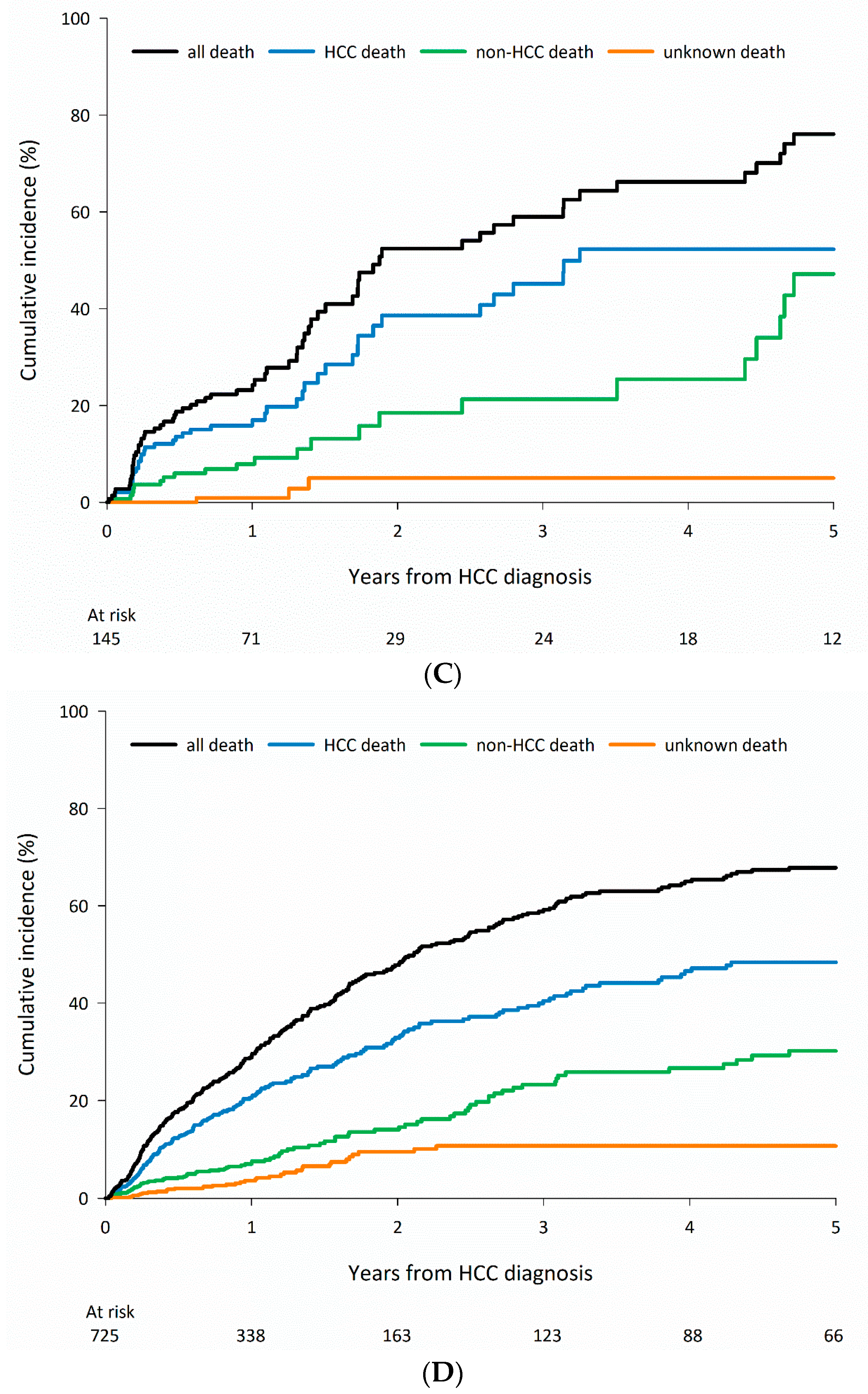
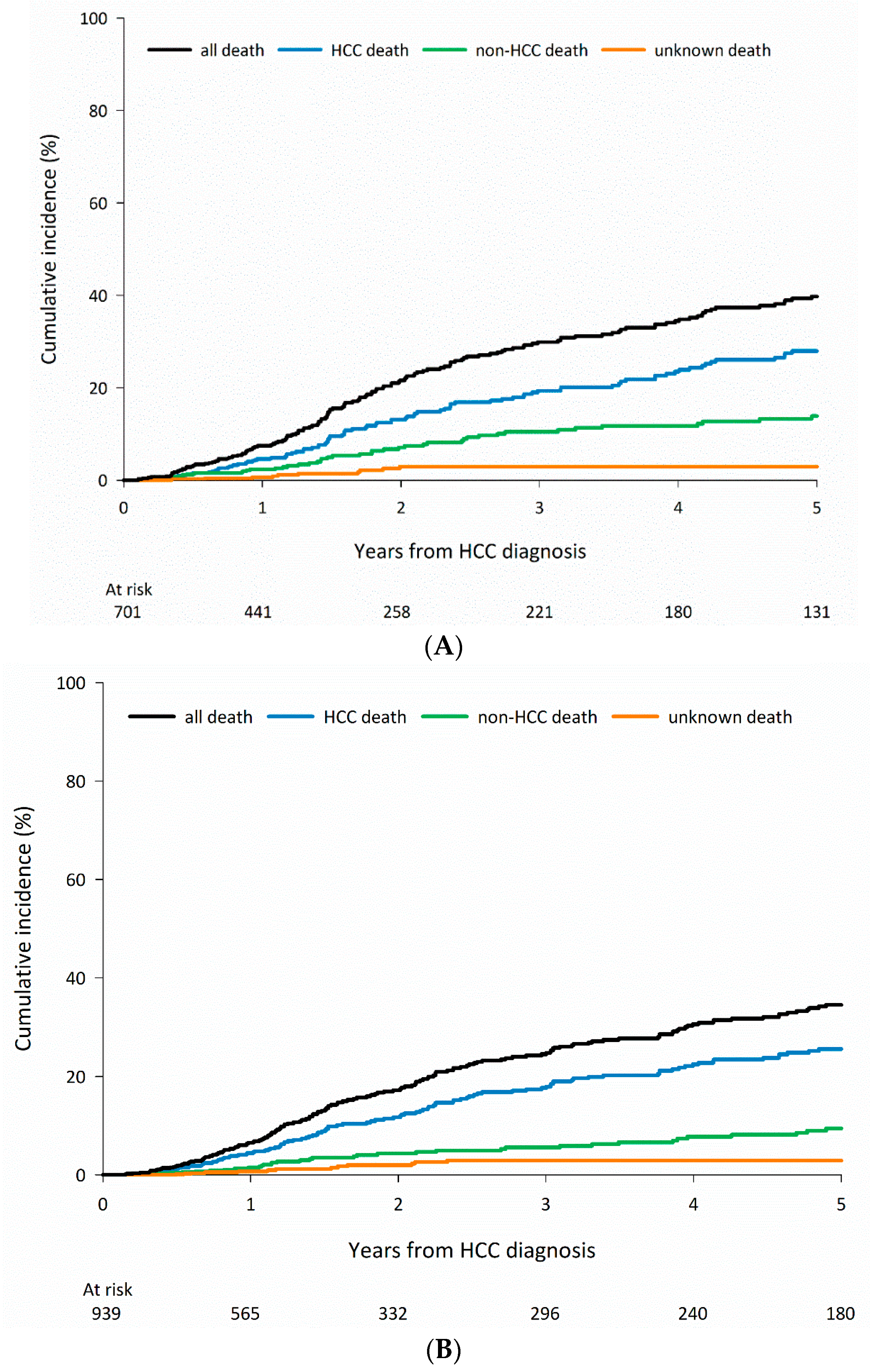
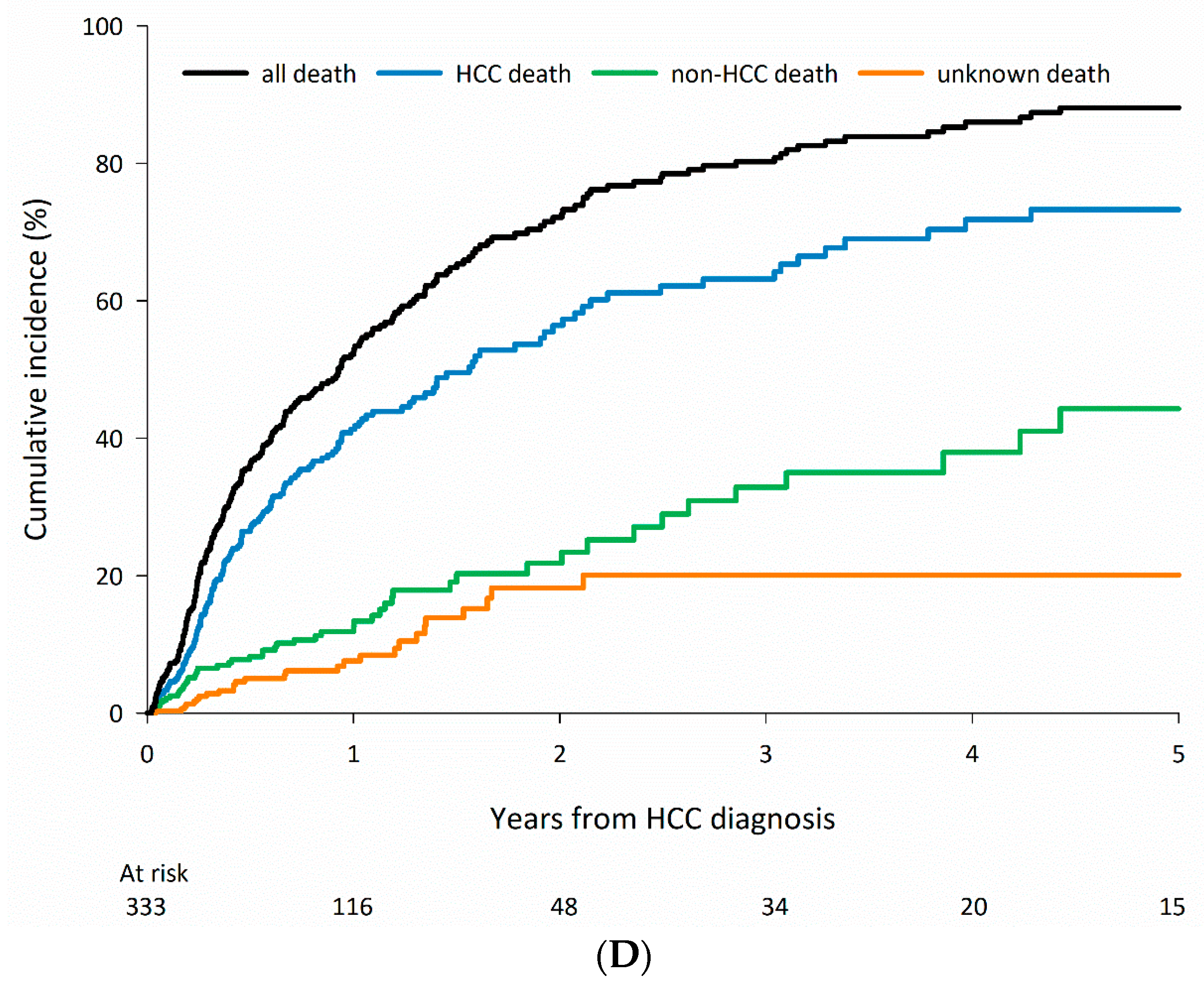
3.2. Cause-Specific Mortality According to CLD Etiology
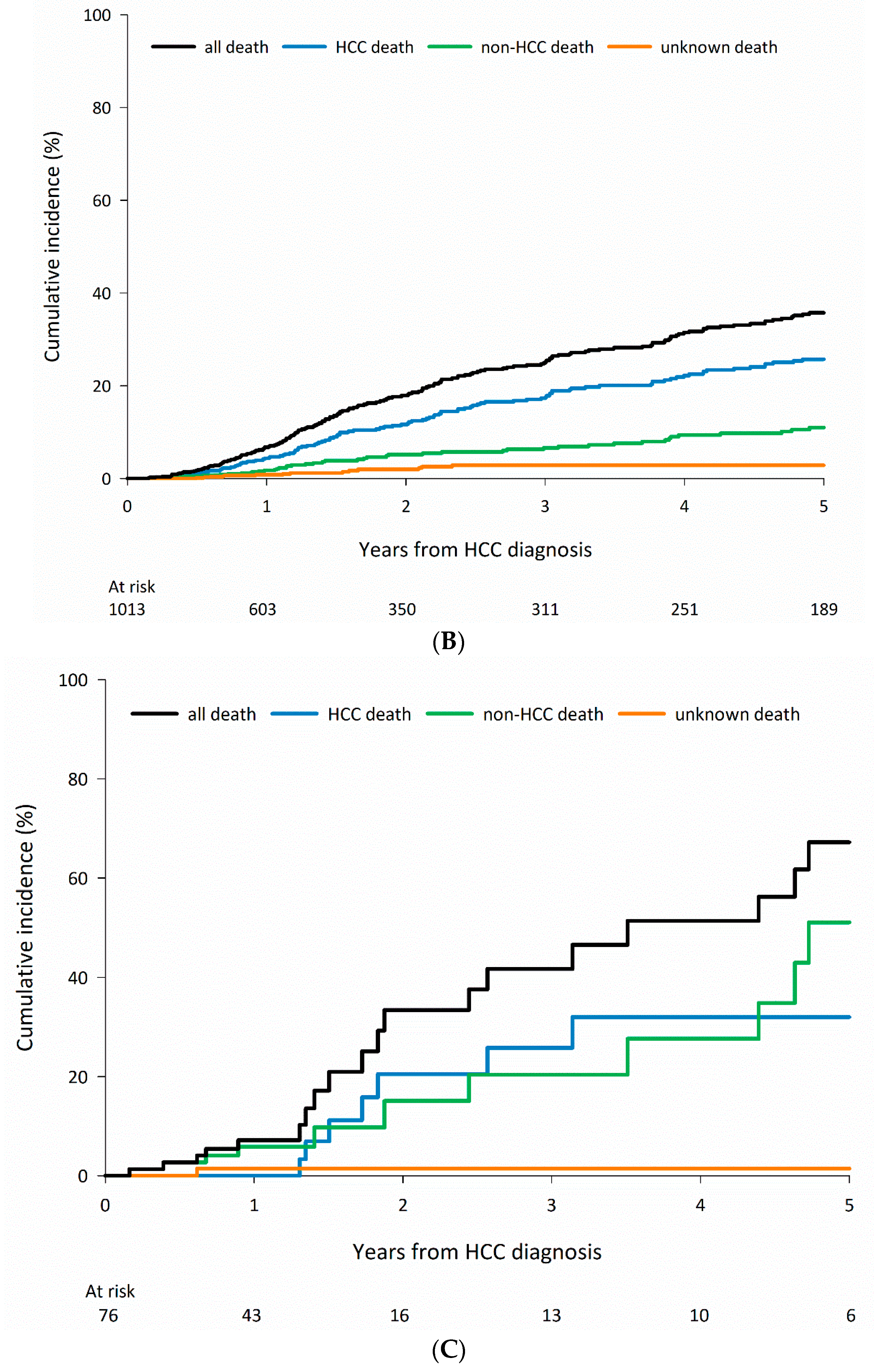
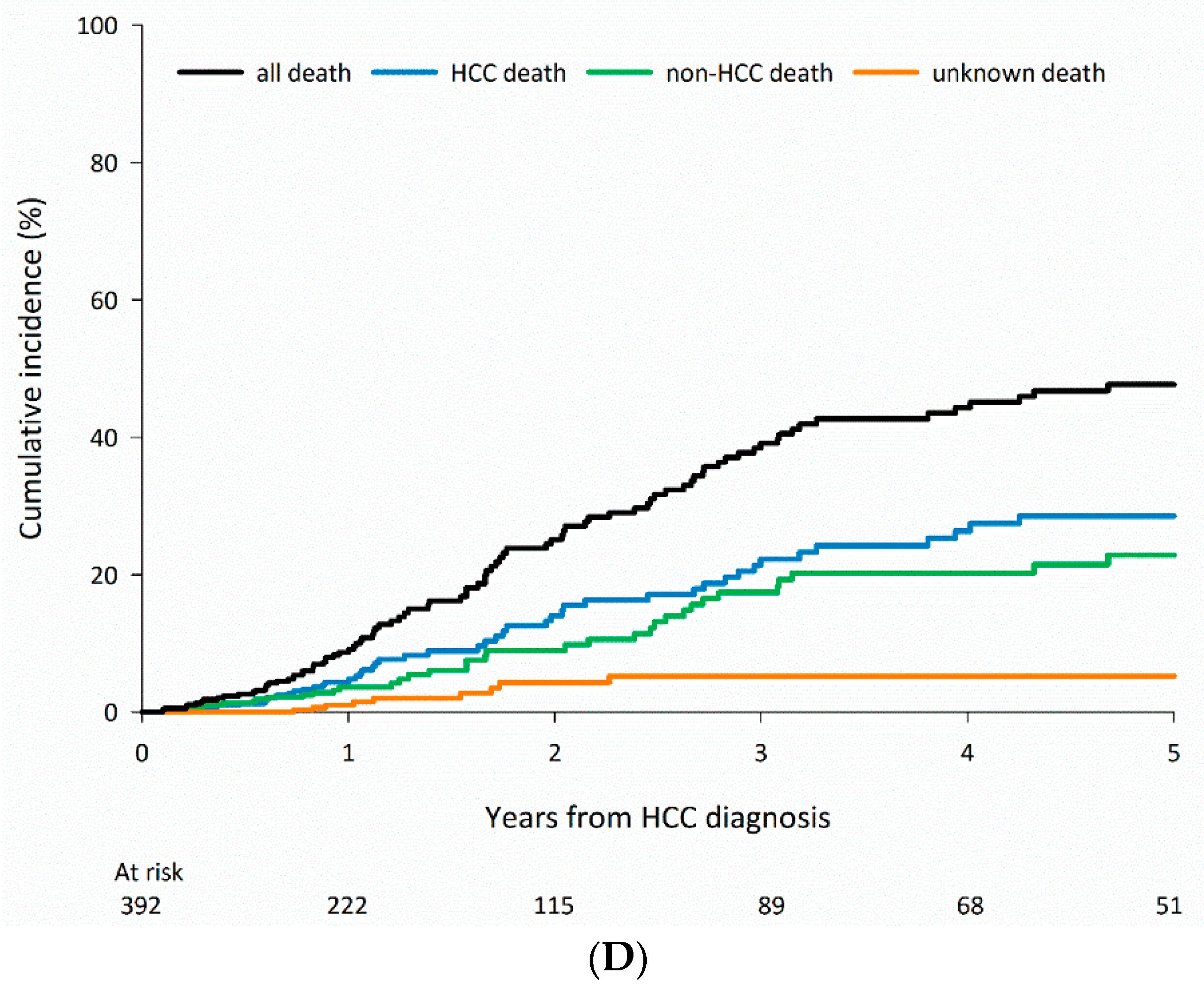
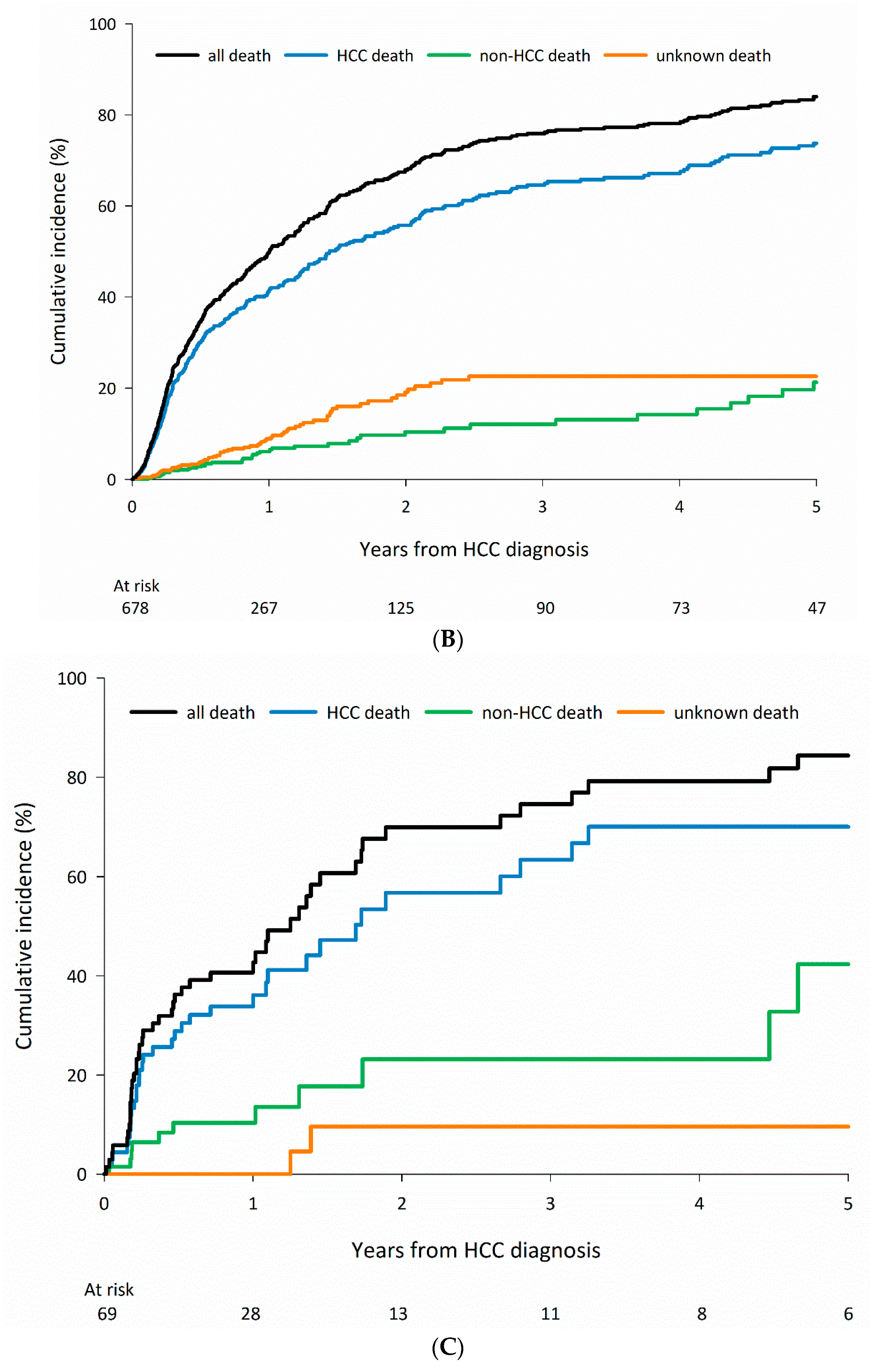
3.3. Cause-Specific Mortality among Patients Who Received Curative Treatments According to CLD Etiology
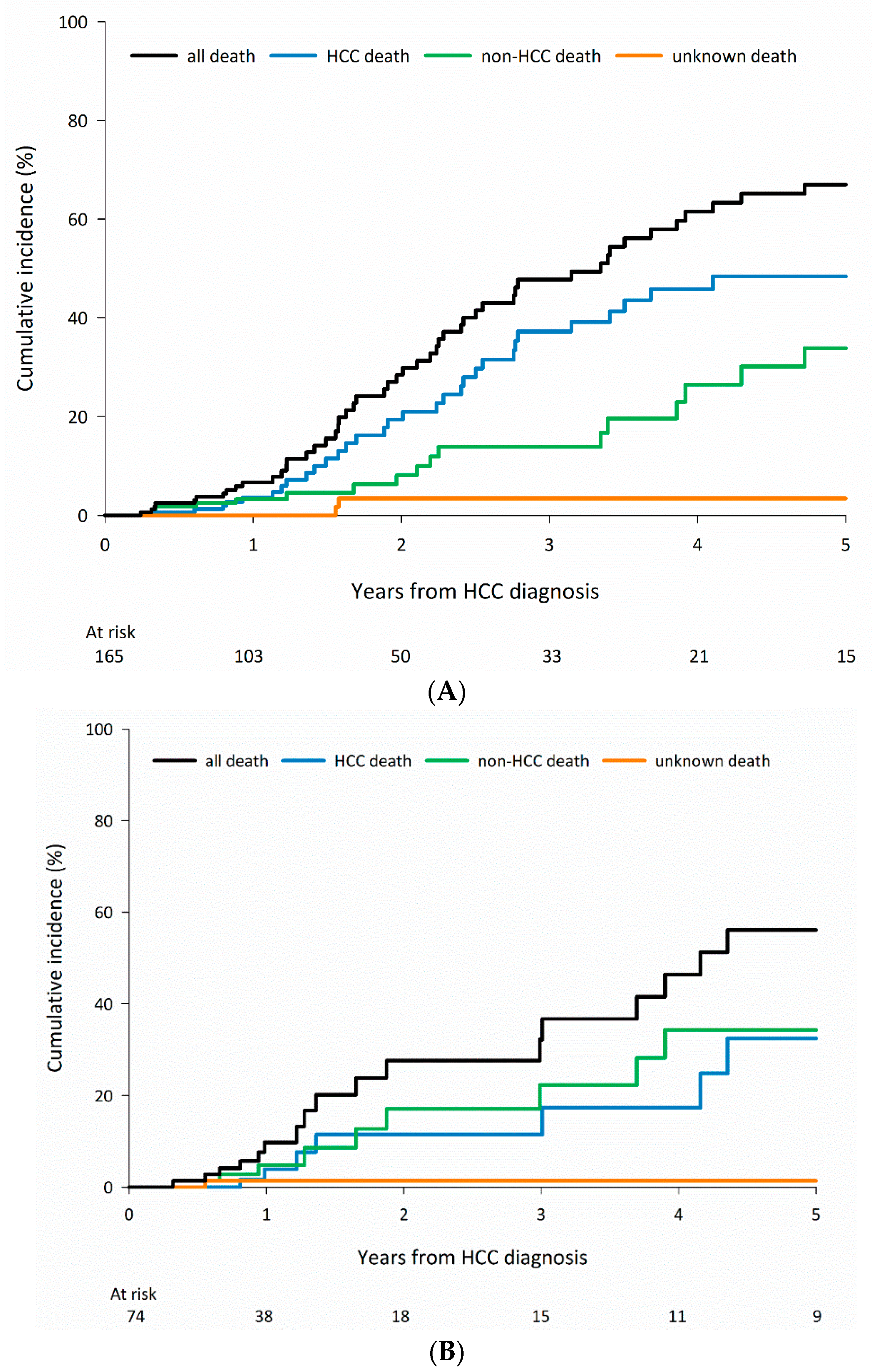
3.4. Cause-Specific Mortality in Patients Who Received Curative Treatments According to CLD Etiology and Stratified by Age
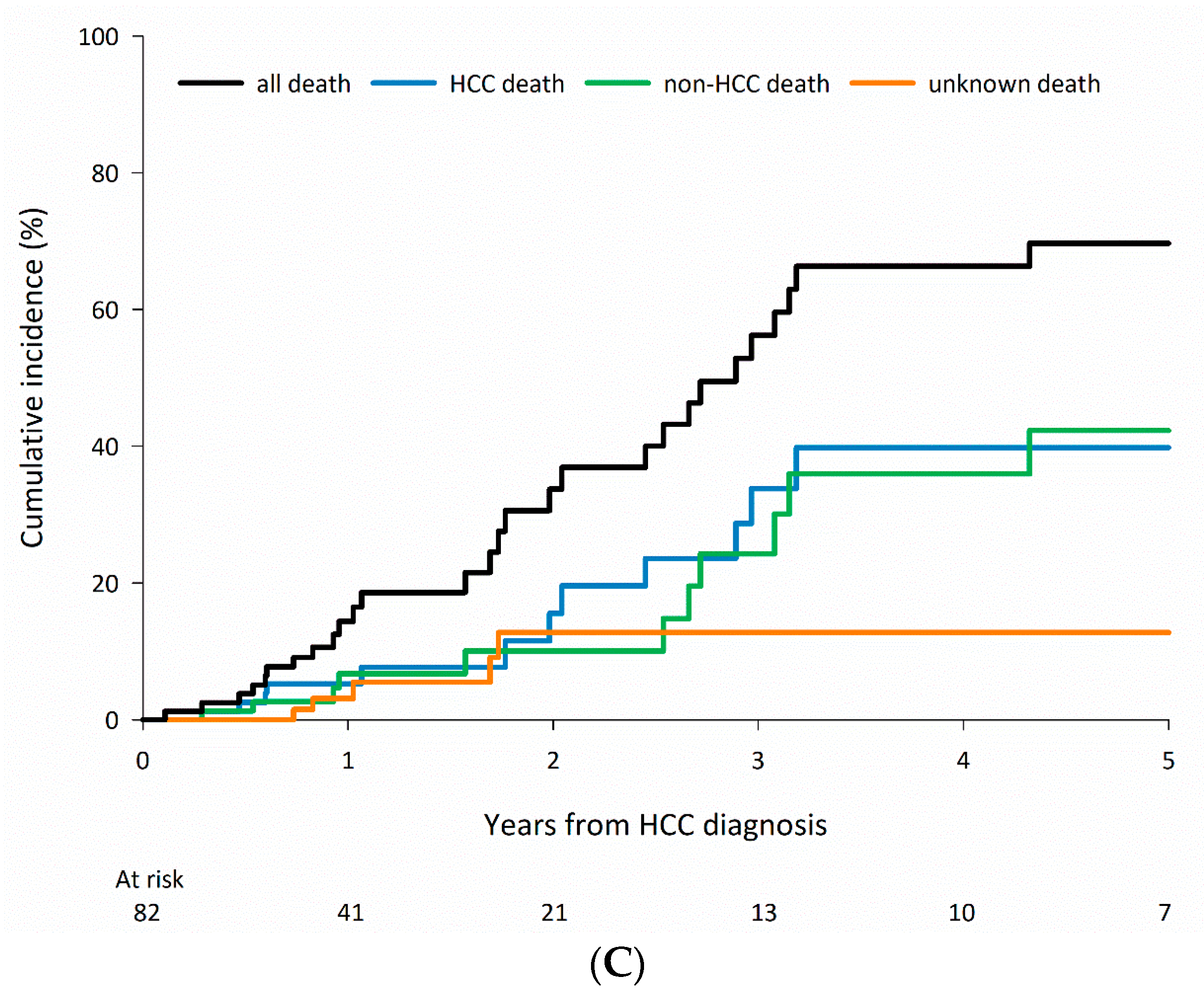
3.5. Cause-Specific Mortality in Patients Who Received Non-Curative Treatments According to CLD Etiology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, C.; Razavi, H.; Loomba, R.; Younossi, Z.; Sanyal, A.J. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology 2018, 67, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zou, B.; Yeo, Y.H.; Feng, Y.; Xie, X.; Lee, D.H.; Fujii, H.; Wu, Y.; Kam, L.Y.; Ji, F.; et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999-2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.; Cholankeril, G.; Yu, X.; Rana, A.; Natarajan, Y.; El-Serag, H.B.; Kramer, J.; Kanwal, F. Clinical Course and Outcomes of Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Related Hepatocellular Cancer (NAFLD-HCC). Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Joint Committee on Cancer. American Joint Committee on Cancer Staging Manual, 7th ed.; Edge, S.B., Byrd, D.R., Compton, C.C., Fritz, A.G., Greene, F.L., Trotti, A., III, Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; p. 175. [Google Scholar]
- Llovet, J.M.; Bru, C.; Bruix, J. Prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification. Semin. Liver Dis. 1999, 19, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, R.N.; Murray-Lyon, I.M.; Dawson, J.L.; Pietroni, M.C.; Williams, R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br. J. Surg. 1973, 60, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawrieh, S.; Dakhoul, L.; Miller, E.; Scanga, A.; deLemos, A.; Kettler, C.; Burney, H.; Liu, H.; Abu-Sbeih, H.; Chalasani, N.; et al. Characteristics, aetiologies and trends of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients without cirrhosis: A United States multicentre study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everhart, J.E.; Wright, E.C.; Goodman, Z.D.; Dienstag, J.L.; Hoefs, J.C.; Kleiner, D.E.; Ghany, M.G.; Mills, A.S.; Nash, S.R.; Govindarajan, S.; et al. Prognostic value of Ishak fibrosis stage: Findings from the hepatitis C antiviral long-term treatment against cirrhosis trial. Hepatology 2010, 51, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiha, G.; Ibrahim, A.; Helmy, A.; Sarin, S.K.; Omata, M.; Kumar, A.; Bernstien, D.; Maruyama, H.; Saraswat, V.; Chawla, Y.; et al. Asian-Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL) consensus guidelines on invasive and non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis: A 2016 update. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Regalia, E.; Doci, R.; Andreola, S.; Pulvirenti, A.; Bozzetti, F.; Montalto, F.; Ammatuna, M.; Morabito, A.; Gennari, L. Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; El-Serag, H.B.; Thrift, A.P. Predictors of five-year survival among patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States: An analysis of SEER-Medicare. Cancer Causes Control 2021, 32, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of alcohol-related liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 154–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaibori, M.; Yoshii, K.; Yokota, I.; Hasegawa, K.; Nagashima, F.; Kubo, S.; Kon, M.; Izumi, N.; Kadoya, M.; Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan; et al. Impact of Advanced Age on Survival in Patients Undergoing Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Report of a Japanese Nationwide Survey. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torpy, J.M.; Lynm, C.; Glass, R.M. Frailty in older adults. JAMA 2006, 296, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.W.; Yong, C.C.; Lin, C.C.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, C.L.; Cheng, Y.F.; Wang, J.H.; Yen, Y.H. Six months as a cutoff time point to define early recurrence after liver resection of hepatocellular carcinoma based on post-recurrence survival. Updates Surg. 2021, 73, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hester, C.A.; Rich, N.E.; Singal, A.G.; Yopp, A.C. Comparative Analysis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis- Versus Viral Hepatitis- and Alcohol-Related Liver Disease-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2019, 17, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, M.A.; Singal, A.G.; Kum, H.C.; Lee, Y.T.; Park, S.; Rich, N.E.; Noureddin, M.; Yang, J.D. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the United States. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 21, 670–680.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.D.; Targher, G. NAFLD: A multisystem disease. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S47–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| HCV, n = 1415 | HBV, n = 1691 | Alcohol, n = 145 | All Negative, n = 725 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 66 (60–73) | 60 (52–67) | 59 (51.5–65) | 68 (60–76) | <0.001 |
| Male | 833 (58.9%) | 1394 (82.4%) | 141 (97.2%) | 503 (69.4%) | <0.001 |
| Method of HCC diagnosis | <0.001 | ||||
| Clinical | 559 (39.5%) | 631 (37.3%) | 68 (46.9%) | 231 (31.9%) | |
| Pathological | 856 (60.5%) | 1061 (62.7%) | 77 (53.1%) | 494 (68.1%) | |
| Tumor size (mm) | 30 (21–50) | 35 (23–75) | 32 (21.5–82.5) | 48 (28–95) | <0.001 |
| 7th edition AJCC stage | <0.001 | ||||
| 1 | 742 (52.4%) | 826 (48.8%) | 60 (41.4%) | 328 (45.2%) | |
| 2 | 317 (22.4%) | 283 (16.7%) | 39 (26.9%) | 115 (15.9%) | |
| 3 | 250 (17.7%) | 391 (23.1%) | 26 (17.9%) | 183 (25.2%) | |
| 4 | 89 (6.3%) | 164 (9.7%) | 17 (11.7%) | 81 (11.2%) | |
| Unknown | 17 (1.2%) | 28 (1.7%) | 3 (2.1%) | 18 (2.5%) | |
| Tumor number by imaging studies | 0.436 | ||||
| Single | 870 (61.5%) | 1032 (61.0%) | 79 (54.5%) | 443 (61.1%) | |
| Multiple | 545 (38.5%) | 660 (39.0%) | 66 (45.5%) | 282 (38.9%) | |
| BCLC stage | <0.001 | ||||
| 0 | 214 (15.1%) | 220 (13.0%) | 18 (12.4%) | 47 (6.5%) | |
| A | 581 (41.1%) | 592 (35.0%) | 45 (31.0%) | 205 (28.3%) | |
| B | 240 (17.0%) | 344 (20.3%) | 34 (23.4%) | 190 (26.2%) | |
| C | 283 (20.0%) | 421 (24.9) | 36 (24.8) | 215 (29.7%) | |
| D | 69 (4.9%) | 82 (4.8%) | 9 (6.2%) | 45 (6.2%) | |
| Unknown | 28 (2.0%) | 33 (2.0%) | 3 (2.1%) | 23 (3.2%) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.5 (22.3–27.3) | 24.5 (22.1–27.3) | 24.8 (22.0–27.4) | 25.0 (22.6–28.0) | 0.048 |
| AFP | 0.001 | ||||
| ≥20 ng/ml | 741 (52.4%) | 902 (53.3%) | 64 (44.1%) | 329 (45.4%) | |
| <20 ng/ml | 674 (47.6%) | 790 (46.7%) | 81 (55.9%) | 396 (54.6%) | |
| Cirrhosis | <0.001 | ||||
| Yes | 1062 (75.3%) | 1157 (68.4%) | 100 (69.4%) | 444 (61.8%) | |
| No | 348 (24.7%) | 534 (31.6%) | 44 (30.6%) | 275 (38.2%) | |
| Unknown | |||||
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 1.0 (0.8–1.3) | 1.0 (0.8–1.2) | 1.1 (0.9–1.4) | 1.1 (0.8–1.5) | <0.001 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.1 (0.8–1.6) | 1.0 (0.8–1.6) | 1.3 (0.8–2.3) | 1.0 (0.7–1.5) | <0.001 |
| INR | 1.0 (1.0–1.1) | 1.0 (1.0–1.1) | 1.0 (1.1–1.2) | 1.0 (1.0–1.1) | <0.001 |
| Child Pugh class | <0.001 | ||||
| A | 1125 (79.5%) | 1398 (82.6%) | 100 (69.0%) | 591 (81.5%) | |
| B | 229 (16.2%) | 212 (12.5%) | 39 (26.9%) | 100 (13.8%) | |
| C | 38 (2.7%) | 62 (3.7%) | 6 (4.1%) | 15 (2.1%) | |
| Unknown | 23 (1.6%) | 20 (1.2%) | 0 | 19 (2.6%) | |
| Treatment | <0.001 | ||||
| Transplant | 54 (3.8%) | 58 (3.4%) | 5 (3.4%) | 16 (2.2%) | |
| Resection | 398 (28.1%) | 640 (37.8%) | 38 (26.2%) | 243 (33.5%) | |
| Ablation | 414 (29.3%) | 316 (18.7%) | 33 (22.8%) | 133 (18.3%) | |
| Best supportive care | 73 (5.2%) | 87 (5.1%) | 12 (8.3%) | 43 (5.9%) | |
| Chemotherapy | 10 (0.7%) | 35 (2.1%) | 2 (1.4%) | 14 (1.9%) | |
| TAE/TACE | 328 (23.2%) | 318 (18.8%) | 39 (26.9%) | 168 (23.2%) | |
| Target therapy | 95 (6.7%) | 186 (11.0%) | 11 (7.6%) | 77 (10.6%) | |
| Radiation therapy | 43 (3.0%) | 52 (3.1%) | 5 (3.4%) | 31 (4.3%) |
| Group | Cause of Mortality | 1-Year | 3-Year | 5-Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total, N = 3976 | Any cause | 883 (22.2) | 1426 (35.9) | 1593 (40.1) |
| HCC-related | 639 (72.4) | 987 (69.2) | 1098 (68.9) | |
| Non-HCC-related | 158 (17.9) | 283 (19.8) | 339 (21.3) | |
| Unknown | 86 (9.7) | 156 (10.9) | 156 (9.8) | |
| HCV, n = 1415 | Any cause | 269 (19.0) | 493 (34.8) | 561 (39.6) |
| HCC-related | 189 (70.3) | 339 (68.8) | 385 (68.6) | |
| Non-HCC-related | 62 (23.0) | 118 (23.9) | 140 (25.0) | |
| Unknown | 18 (6.7) | 36 (7.3) | 36 (6.4) | |
| HBV, n = 1691 | Any cause | 384 (22.7) | 577 (34.1) | 644 (38.1) |
| HCC-related | 295 (76.8) | 424 (73.5) | 472 (73.3) | |
| Non-HCC-related | 42 (10.9) | 72 (12.5) | 91 (14.1) | |
| Unknown | 47 (12.2) | 81 (14.0) | 81 (12.6) | |
| Alcohol, n = 145 | Any cause | 34 (23.4) | 57 (39.3) | 66 (45.5) |
| HCC-related | 23 (67.6) | 38 (66.7) | 41 (62.1) | |
| Non-HCC-related | 10 (29.4) | 16 (28.1) | 22 (33.3) | |
| Unknown | 1 (2.9) | 3 (5.3) | 3 (4.5) | |
| All negative, n = 725 | Any cause | 196 (27.0) | 299 (41.2) | 322 (44.4) |
| HCC-related | 132 (67.3) | 186 (62.2) | 200 (62.1) | |
| Non-HCC-related | 44 (22.4) | 77 (25.8) | 86 (26.7) | |
| Unknown | 20 (10.2) | 36 (12.0) | 36 (11.2) |
| Group | Cause of Mortality | 1-Year | 3-Year | 5-Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total, N = 2347 | Any cause | 154 (6.6) | 402 (17.1) | 496 (21.1) |
| HCC-related | 88 (57.1) | 242 (60.2) | 302 (60.9) | |
| Non-HCC-related | 51 (33.1) | 122 (30.3) | 156 (31.5) | |
| Unknown | 15 (9.7) | 38 (9.5) | 38 (7.7) | |
| HCV, n = 866 | Any cause | 58 (6.7) | 164 (18.9) | 202 (23.3) |
| HCC-related | 34 (58.6) | 101 (61.6) | 126 (62.4) | |
| Non-HCC-related | 20 (34.5) | 50 (30.5) | 63 (31.2) | |
| Unknown | 4 (6.9) | 13 (7.9) | 13 (6.4) | |
| HBV, n = 1013 | Any cause | 61 (6.0) | 144 (14.2) | 184 (18.2) |
| HCC-related | 39 (63.9) | 94 (65.3) | 122 (66.3) | |
| Non-HCC-related | 15 (24.6) | 35 (24.3) | 47 (25.5) | |
| Unknown | 7 (11.5) | 15 (10.4) | 15 (8.2) | |
| Alcohol, n = 76 | Any cause | 5 (6.6) | 14 (18.4) | 19 (25.0) |
| HCC-related | 0 (0.0) | 6 (42.9) | 7 (36.8) | |
| Non-HCC-related | 4 (80.0) | 7 (50.0) | 11 (57.9) | |
| Unknown | 1 (20.0) | 1 (7.1) | 1 (5.3) | |
| All negative, n = 392 | Any cause | 30 (7.7) | 80 (20.4) | 91 (23.2) |
| HCC-related | 15 (50.0) | 41 (51.3) | 47 (51.6) | |
| Non-HCC-related | 12 (40.0) | 30 (37.5) | 35 (38.5) | |
| Unknown | 3 (10.0) | 9 (11.3) | 9 (9.9) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yen, Y.-H.; Kee, K.-M.; Li, W.-F.; Liu, Y.-W.; Wang, C.-C.; Hu, T.-H.; Tsai, M.-C.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-Y. Causes of Death among Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma According to Chronic Liver Disease Etiology. Cancers 2023, 15, 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061687
Yen Y-H, Kee K-M, Li W-F, Liu Y-W, Wang C-C, Hu T-H, Tsai M-C, Kuo Y-H, Lin C-Y. Causes of Death among Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma According to Chronic Liver Disease Etiology. Cancers. 2023; 15(6):1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061687
Chicago/Turabian StyleYen, Yi-Hao, Kwong-Ming Kee, Wei-Feng Li, Yueh-Wei Liu, Chih-Chi Wang, Tsung-Hui Hu, Ming-Chao Tsai, Yuan-Hung Kuo, and Chih-Yun Lin. 2023. "Causes of Death among Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma According to Chronic Liver Disease Etiology" Cancers 15, no. 6: 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061687
APA StyleYen, Y.-H., Kee, K.-M., Li, W.-F., Liu, Y.-W., Wang, C.-C., Hu, T.-H., Tsai, M.-C., Kuo, Y.-H., & Lin, C.-Y. (2023). Causes of Death among Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma According to Chronic Liver Disease Etiology. Cancers, 15(6), 1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15061687





