Lenalidomide Maintenance and Measurable Residual Disease in a Real-World Multiple Myeloma Transplanted Population Receiving Different Treatment Strategies Guided by Access to Novel Drugs in Brazil
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
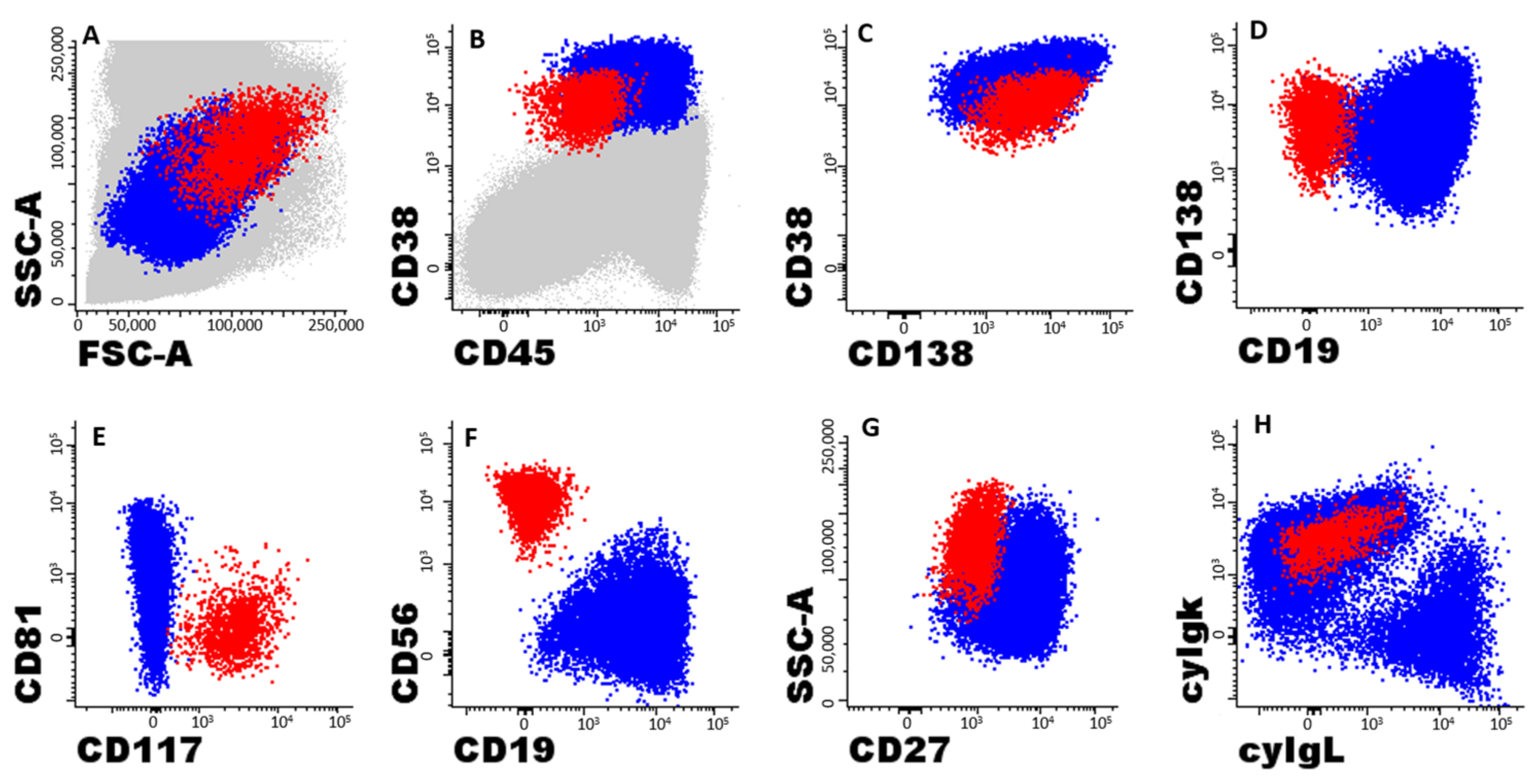
2. Material and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, S.K.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Gertz, M.A.; Buadi, F.K.; Pandey, S.; Kapoor, P.; Dingli, D.; Hayman, S.R.; Leung, N.; et al. Continued improvement in survival in multiple myeloma: Changes in early mortality and outcomes in older patients. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimopoulos, M.A.; Moreau, P.; Terpos, E.; Mateos, M.V.; Zweegman, S.; Cook, G.; Delforge, M.; Hájek, R.; Schjesvold, F.; Cavo, M.; et al. Multiple Myeloma: EHA-ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up. Hemasphere 2021, 5, e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, B.; Puig, N.; Cedena, M.T.; Rosiñol, L.; Cordón, L.; Vidriales, M.B.; Burgos, L.; Flores-Montero, J.; Sanoja-Flores, L.; Lopez-Anglada, L.; et al. Measurable Residual Disease by Next-Generation Flow Cytometry in Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attal, M.; Lauwers-Cances, V.; Hulin, C.; Leleu, X.; Caillot, D.; Escoffre, M.; Arnulf, B.; Macro, M.; Belhadj, K.; Garderet, L.; et al. Lenalidomide, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone with Transplantation for Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, N.S.; Kaufman, J.L.; Dhodapkar, M.V.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Almaula, D.K.; Heffner, L.T.; Gupta, V.A.; Boise, L.H.; Lonial, S.; Nooka, A.K. Long-Term Follow-Up Results of Lenalidomide, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone Induction Therapy and Risk-Adapted Maintenance Approach in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahuerta, J.J.; Paiva, B.; Vidriales, M.B.; Cordón, L.; Cedena, M.T.; Puig, N.; Martinez-Lopez, J.; Rosiñol, L.; Gutierrez, N.C.; Martín-Ramos, M.L.; et al. Depth of Response in Multiple Myeloma: A Pooled Analysis of Three PETHEMA/GEM Clinical Trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2900–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Montero, J.; de Tute, R.; Paiva, B.; Perez, J.J.; Böttcher, S.; Wind, H.; Sanoja, L.; Puig, N.; Lecrevisse, Q.; Vidriales, M.B.; et al. Immunophenotype of normal vs. myeloma plasma cells: Toward antibody panel specifications for MRD detection in multiple myeloma. Cytometry B Clin. Cytom. 2016, 90, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, B.; Vidriales, M.B.; Cerveró, J.; Mateo, G.; Pérez, J.J.; Montalbán, M.A.; Sureda, A.; Montejano, L.; Gutiérrez, N.C.; García de Coca, A.; et al. Multiparameter flow cytometric remission is the most relevant prognostic factor for multiple myeloma patients who undergo autologous stem cell transplantation. Blood 2008, 112, 4017–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgren, O.; Devlin, S.; Boulad, M.; Mailankody, S. Role of MRD status in relation to clinical outcomes in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients: A meta-analysis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2016, 51, 1565–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munshi, N.C.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Rawstron, A.C.; Owen, R.G.; Child, J.A.; Thakurta, A.; Sherrington, P.; Samur, M.K.; Georgieva, A.; Anderson, K.C.; et al. Association of Minimal Residual Disease With Superior Survival Outcomes in Patients With Multiple Myeloma: A Meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, B.; van Dongen, J.J.; Orfao, A. New criteria for response assessment: Role of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma. Blood 2015, 125, 3059–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Tute, R.M.; Rawstron, A.C.; Gregory, W.M.; Child, J.A.; Davies, F.E.; Bell, S.E.; Cook, G.; Szubert, A.J.; Drayson, M.T.; Jackson, G.H.; et al. Minimal residual disease following autologous stem cell transplant in myeloma: Impact on outcome is independent of induction regimen. Haematologica 2016, 101, e69–e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Paiva, B.; Anderson, K.C.; Durie, B.; Landgren, O.; Moreau, P.; Munshi, N.; Lonial, S.; Bladé, J.; Mateos, M.V.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group consensus criteria for response and minimal residual disease assessment in multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e328–e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, E.; Schütz, N.; Peña, C.; Ruiz-Argüelles, G.; Hopkins, C.R.; Bove, V.; Villano, F.; Andino, L.; Suárez, L.; Martínez, H.; et al. Significant differences in access to tests and treatments for multiple myeloma between public and private systems in Latin America. Results of a Latin American survey. GELAMM (Grupo de Estudio Latino Americano de Mieloma Múltiple). Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessoa de Magalhães Filho, R.J.; Crusoe, E.; Riva, E.; Bujan, W.; Conte, G.; Navarro Cabrera, J.R.; Garcia, D.K.; Vega, G.Q.; Macias, J.; Oliveros Alvear, J.W.; et al. Analysis of Availability and Access of Anti-myeloma Drugs and Impact on the Management of Multiple Myeloma in Latin American Countries. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2019, 19, e43–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrieta-Álvarez, I.; Steensma, D.P.; Olivares-Gazca, J.C.; Olivares-Gazca, M.; León-Peña, A.; Cantero-Fortiz, Y.; García-Navarrete, Y.I.; Cruz-Mora, A.; Ruiz-Argüelles, A.; Ruiz-Delgado, G.J.; et al. Treatment of Persons with Multiple Myeloma in Underprivileged Circumstances: Real-World Data from a Single Institution. Acta Haematol. 2020, 143, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, P.L.; Holstein, S.A.; Petrucci, M.T.; Richardson, P.G.; Hulin, C.; Tosi, P.; Bringhen, S.; Musto, P.; Anderson, K.C.; Caillot, D.; et al. Lenalidomide Maintenance After Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation in Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3279–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, S.V.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Palumbo, A.; Blade, J.; Merlini, G.; Mateos, M.V.; Kumar, S.; Hillengass, J.; Kastritis, E.; Richardson, P.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group updated criteria for the diagnosis of multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, e538–e548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, B.; Martinez-Lopez, J.; Vidriales, M.B.; Mateos, M.V.; Montalban, M.A.; Fernandez-Redondo, E.; Alonso, L.; Oriol, A.; Teruel, A.I.; de Paz, R.; et al. Comparison of immunofixation, serum free light chain, and immunophenotyping for response evaluation and prognostication in multiple myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1627–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Montero, J.; Sanoja-Flores, L.; Paiva, B.; Puig, N.; García-Sánchez, O.; Böttcher, S.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Pérez-Morán, J.J.; Vidriales, M.B.; García-Sanz, R.; et al. Next Generation Flow for highly sensitive and standardized detection of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroz, M.; Came, N.; Lin, P.; Chen, W.; Yuan, C.; Lagoo, A.; Monreal, M.; de Tute, R.; Vergilio, J.A.; Rawstron, A.C.; et al. Consensus guidelines on plasma cell myeloma minimal residual disease analysis and reporting. Cytometry B Clin. Cytom. 2016, 90, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonça de Pontes, R.; Flores-Montero, J.; Sanoja-Flores, L.; Puig, N.; Pessoa de Magalhães, R.J.; Corral-Mateos, A.; Salgado, A.B.; García-Sánchez, O.; Pérez-Morán, J.; Mateos, M.V.; et al. B-Cell Regeneration Profile and Minimal Residual Disease Status in Bone Marrow of Treated Multiple Myeloma Patients. Cancers 2021, 13, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.K.; Rajkumar, V.; Kyle, R.A.; van Duin, M.; Sonneveld, P.; Mateos, M.V.; Gay, F.; Anderson, K.C. Multiple myeloma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawstron, A.C.; de Tute, R.M.; Haughton, J.; Owen, R.G. Measuring disease levels in myeloma using flow cytometry in combination with other laboratory techniques: Lessons from the past 20 years at the Leeds Haematological Malignancy Diagnostic Service. Cytometry B Clin. Cytom. 2016, 90, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliva, S.; Bruinink, D.H.O.; Rihova, L.; D’Agostino, M.; Pantani, L.; Capra, A.; van der Holt, B.; Troia, R.; Petrucci, M.T.; Villanova, T.; et al. Minimal residual disease assessment by multiparameter flow cytometry in transplant-eligible myeloma in the EMN02/HOVON 95 MM trial. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpos, E.; Kostopoulos, I.V.; Kastritis, E.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Migkou, M.; Rousakis, P.; Argyriou, A.T.; Kanellias, N.; Fotiou, D.; Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou, E.; et al. Impact of Minimal Residual Disease Detection by Next-Generation Flow Cytometry in Multiple Myeloma Patients with Sustained Complete Remission after Frontline Therapy. Hemasphere 2019, 3, e300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungria, V.T.; Maiolino, A.; Martinez, G.; Duarte, G.O.; Bittencourt, R.; Peters, L.; Colleoni, G.; Oliveira, L.C.; Crusoé, E.; Coelho, É.; et al. Observational study of multiple myeloma in Latin America. Ann Hematol 2017, 96, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crusoe, E.Q.; Higashi, F.; Martinez, G.; Bittencourt, R.; Pinto Neto, J.V.; Sousa, L.; Santucci, R.; Magalhães, R.J.P.; Colli, G.; Nunes, R.F.M.; et al. Superiority of the triple combination of bortezomib, cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone versus cyclophosphamide, thalidomide and dexamethasone in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, eligible for transplantation. Hematol. Transfus. Cell Ther. 2020, 42, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, P.; Goldschmidt, H.; Rosiñol, L.; Bladé, J.; Lahuerta, J.J.; Cavo, M.; Tacchetti, P.; Zamagni, E.; Attal, M.; Lokhorst, H.M.; et al. Bortezomib-based versus nonbortezomib-based induction treatment before autologous stem-cell transplantation in patients with previously untreated multiple myeloma: A meta-analysis of phase III randomized, controlled trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3279–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalina, T.; Flores-Montero, J.; van der Velden, V.H.; Martin-Ayuso, M.; Böttcher, S.; Ritgen, M.; Almeida, J.; Lhermitte, L.; Asnafi, V.; Mendonça, A.; et al. EuroFlow standardization of flow cytometer instrument settings and immunophenotyping protocols. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1986–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrot, A.; Lauwers-Cances, V.; Corre, J.; Robillard, N.; Hulin, C.; Chretien, M.L.; Dejoie, T.; Maheo, S.; Stoppa, A.M.; Pegourie, B.; et al. Minimal residual disease negativity using deep sequencing is a major prognostic factor in multiple myeloma. Blood 2018, 132, 2456–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina, A.; Puig, N.; Flores-Montero, J.; Jimenez, C.; Sarasquete, M.E.; Garcia-Alvarez, M.; Prieto-Conde, I.; Chillon, C.; Alcoceba, M.; Gutierrez, N.C.; et al. Comparison of next-generation sequencing (NGS) and next-generation flow (NGF) for minimal residual disease (MRD) assessment in multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2020, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, B.; Korde, N.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Smith, E.L.; Shah, U.; Mailankody, S.; Hultcrantz, M.; Hassoun, H.; Lu, S.X.; Tan, C.; et al. Dynamics of minimal residual disease in patients with multiple myeloma on continuous lenalidomide maintenance: A single-arm, single-centre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e422–e432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Tute, R.M.; Pawlyn, C.; Cairns, D.A.; Davies, F.E.; Menzies, T.; Rawstron, A.; Jones, J.R.; Hockaday, A.; Henderson, R.; Cook, G.; et al. Minimal Residual Disease After Autologous Stem-Cell Transplant for Patients With Myeloma: Prognostic Significance and the Impact of Lenalidomide Maintenance and Molecular Risk. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, G.H.; Davies, F.E.; Pawlyn, C.; Cairns, D.A.; Striha, A.; Collett, C.; Hockaday, A.; Jones, J.R.; Kishore, B.; Garg, M.; et al. Lenalidomide maintenance versus observation for patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (Myeloma XI): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiolino, A.; Hungria, V.T.; Garnica, M.; Oliveira-Duarte, G.; Oliveira, L.C.; Mercante, D.R.; Miranda, E.C.; Quero, A.A.; Peres, A.L.; Barros, J.C.; et al. Thalidomide plus dexamethasone as a maintenance therapy after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation improves progression-free survival in multiple myeloma. Am. J. Hematol. 2012, 87, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, P.; Al-Sukhun, S.; Blanchard, C.; Shulman, L.N. Access to Cancer Therapeutics in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2016, 35, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavo, M.; Gay, F.; Beksac, M.; Pantani, L.; Petrucci, M.T.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Dozza, L.; van der Holt, B.; Zweegman, S.; Oliva, S.; et al. Autologous haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation versus bortezomib-melphalan-prednisone, with or without bortezomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone consolidation therapy, and lenalidomide maintenance for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma (EMN02/HO95): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e456–e468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxi, S.M.; Beall, R.; Yang, J.; Mackey, T.K. A multidisciplinary review of the policy, intellectual property rights, and international trade environment for access and affordability to essential cancer medications. Glob. Health 2019, 15, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, S.D. How should we pay the piper when he’s calling the tune? On the long-term affordability of cancer care in the United States. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables Studied at Diagnosis | M-Lenalidomide n = 18 | No Lenalidomide n = 35 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 57.5 (40–67) | 59 (43–70) | 0.56 |
| Gender * (% female) | 61% (11/18) | 45.7% (16/35) | 0.22 |
| Subtype of MM * | 0.90 | ||
| IgG | 67% (12/18) | 63% (22/35) | |
| IgA | 11% (2/18) | 17% (6/35) | |
| LC | 17% (3/18) | 17% (6/35) | |
| NS | 5% (1/18) | 3% (1/35) | |
| Monoclonal component (serum) | 1.40 | 2.50 | 0.77 |
| g/dl | (0–11) | (0–10.1) | |
| Monoclonal component (urine) | 0.80 | 0.85 | 0.74 |
| g/24 h | (0.37–6) | (0–15.8) | |
| Hemoglobin g/L | 115 (69–146) | 100 (49–152) | 0.18 |
| Creatinine mg/dl | 0.8 (0.6–5.2) | 0.9 (0.5–8.6) | 0.16 |
| Calcium mg/dl | 9.4 (7.7–17) | 9.5 (8–14) | 0.98 |
| Bone Lesions * | 94% (17/18) | 91% (32/35) | 0.58 |
| DS Stage * | 0.14 | ||
| II-A and II-B | 44% (8/18) | 26% (9/35) | |
| III-A and III-B | 56%(10/18) | 74% (26/35) | |
| ISS Stage | 0.23 | ||
| I | 56% (10/18) | 31.5% (11/35) | |
| II | 22% (4/18) | 37% (13/35) | |
| III | 22% (4/18) | 31.5% (11/35) | |
| Albumin g/dl | 3.8 (1.9–6.6) | 3.7 (1.4–5.0) | 0.16 |
| Beta2-microglobulin mg/L | 3.1 (1.8–11.3) | 3.6 (1.1–33.3) | 0.88 |
| Induction treatment * | 0.001 | ||
| CTD | 17% (3/18) | 69% (24/35) | |
| VCD | 83% (15/18) | 31% (11/35) | |
| Response after ASCT * | 0.42 | ||
| CR and sCR | 56% (10/18) | 49% (17/35) | |
| VGPR and PR | 44% (8/18) | 51% (18/35) | |
| MRD | 0.59 | ||
| MRD− | 39% (7/18) | 40% (14/35) | |
| MRD+ | 61% (11/18) | 60% (21/35) |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median PFS (Months) | HR | 95th CI | p-Value | HR | 95th CI | p-Value | |
| Age at diagnosis | |||||||
| <58 | 37 | 1 | |||||
| ≥58 | 28 | 1.7 | (0.69–4.37) | 0.23 | |||
| DS | |||||||
| II-A | 38 | 1 | |||||
| II-B | NR | 0.34 | (0.06–2.06) | 0.86 | |||
| III-A | 27 | (0.08–7.88) | |||||
| III-B | 31 | (0.49–5.99) | |||||
| ISS | |||||||
| I | 36 | 1 | |||||
| II | 23 | 0.79 | (0.25–2.46) | 0.44 | |||
| III | 35 | (0.54–4.51) | |||||
| Induction therapy | |||||||
| CTD | 34 | 1 | |||||
| VCD | 35 | 1.99 | (0.79–4.99) | 1.13 | |||
| Maintenance therapy | |||||||
| No | 29 | 1 | |||||
| Yes | NR | 5.78 | (1.34–24.95) | 0.003 | 7.05 | (1.6–30.72) | 0.001 |
| Status post ASCT | |||||||
| CR | 44 | 1 | |||||
| Non-CR | 30 | 4.69 | (0.18–1.17) | 0.10 | |||
| MRD | |||||||
| Positive | 42 | 1 | |||||
| Negative | NR | 2.62 | (0.94–7.29) | 0.049 | 3.37 | (1.19–9.57) | 0.014 |
| MRD and M-Len | |||||||
| MRD− or + and MLen+ | 1 | ||||||
| MRD− No MLen | 44 | 2.98 | (0.58–15.4) | 0.19 | |||
| MRD+ No MLen | 35 | 9.22 | (2.06–41.2) | 0.004 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salgado, A.B.d.S.; Magalhães, R.J.P.; Pontes, R.M.; Barbosa, E.d.S.; Flores-Montero, J.; Sanoja-Flores, L.; Land, M.G.P.; Pimenta, G.; Dutra, H.d.S.; Costa, E.S.; et al. Lenalidomide Maintenance and Measurable Residual Disease in a Real-World Multiple Myeloma Transplanted Population Receiving Different Treatment Strategies Guided by Access to Novel Drugs in Brazil. Cancers 2023, 15, 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051605
Salgado ABdS, Magalhães RJP, Pontes RM, Barbosa EdS, Flores-Montero J, Sanoja-Flores L, Land MGP, Pimenta G, Dutra HdS, Costa ES, et al. Lenalidomide Maintenance and Measurable Residual Disease in a Real-World Multiple Myeloma Transplanted Population Receiving Different Treatment Strategies Guided by Access to Novel Drugs in Brazil. Cancers. 2023; 15(5):1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051605
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalgado, Anna Beatriz dos Santos, Roberto Jose Pessoa Magalhães, Robéria M. Pontes, Eduarda da Silva Barbosa, Juan Flores-Montero, Luzalba Sanoja-Flores, Marcelo Gerardin Poirot Land, Glicinia Pimenta, Hélio dos Santos Dutra, Elaine S. Costa, and et al. 2023. "Lenalidomide Maintenance and Measurable Residual Disease in a Real-World Multiple Myeloma Transplanted Population Receiving Different Treatment Strategies Guided by Access to Novel Drugs in Brazil" Cancers 15, no. 5: 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051605
APA StyleSalgado, A. B. d. S., Magalhães, R. J. P., Pontes, R. M., Barbosa, E. d. S., Flores-Montero, J., Sanoja-Flores, L., Land, M. G. P., Pimenta, G., Dutra, H. d. S., Costa, E. S., Orfao, A., & Maiolino, A. (2023). Lenalidomide Maintenance and Measurable Residual Disease in a Real-World Multiple Myeloma Transplanted Population Receiving Different Treatment Strategies Guided by Access to Novel Drugs in Brazil. Cancers, 15(5), 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15051605






