The Superiority of Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI) PET/CT Versus FDG PET/CT in the Diagnosis of Various Malignancies
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
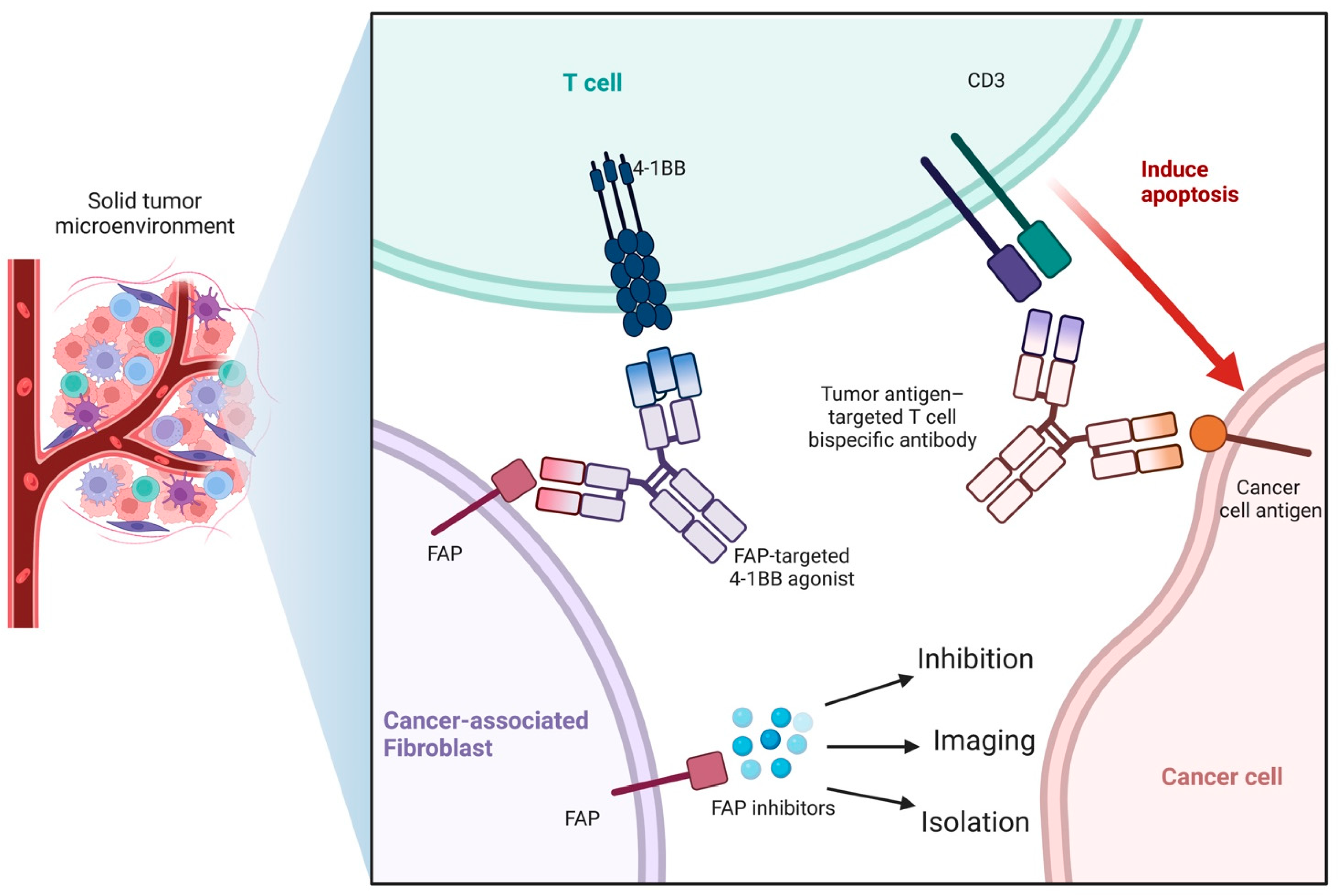
1.1. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs)
1.2. Fibroblast Activation Protein and Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI)
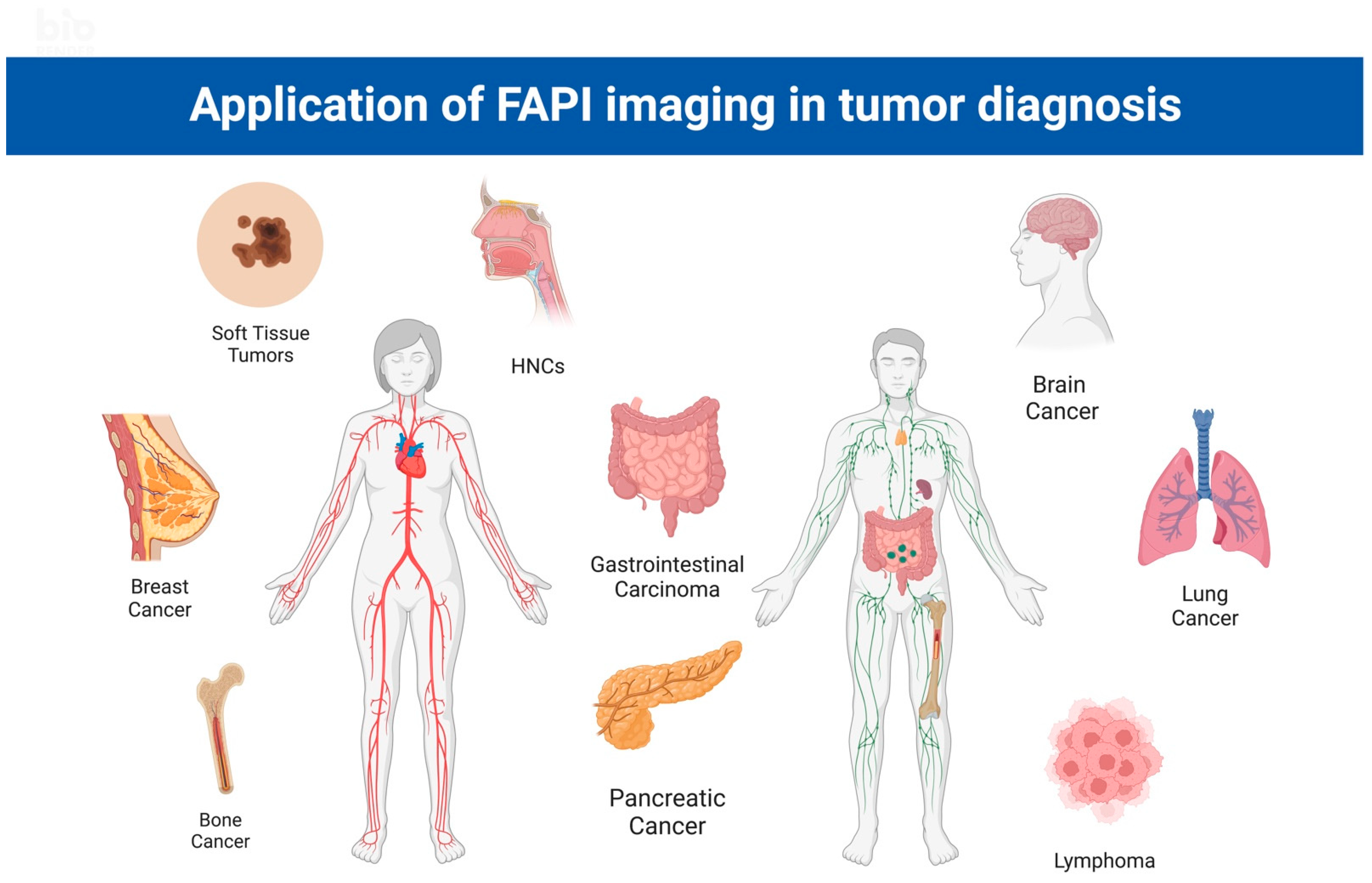
2. Application of FAPI PET/CT in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Cancers
2.1. Gastrointestinal Cancer
2.1.1. General Background, Gastric Cancer, and Peritoneal Cancer
2.1.2. Colorectal Cancer
2.1.3. Hepatobiliary and Pancreatic Carcinoma
| Tumor Type | No. of Patients | Clinical Setting | FAPI Patient Analysis | FAPI Lesion Analysis | FDG Patient Analysis | FDG Lesion Analysis | Ref. | ||||||||||||||
| Staging | Restaging | Treatment Status | TPR | FPR | TNR | FNR | TPR | FPR | TNR | FNR | TPR | FPR | TNR | FNR | TPR | FPR | TNR | FNR | |||
| HCC and ICC | 34 | 50% | 26% | 23 treatment-naïve | 96% | 0 | 100% | 4% | 87% | 0 | 100% | 13% | 65% | 0% | 100% | 35% | 65% | 0% | 100% | 35% | Guo, W. et al. [44] |
| HCC and ICC | 27 | 22% | 67% | 6 treatment-naïve | 100% | 7% | 93% | 0 | 96% | 0 | 100% | 4% | 58% | 0 | 100% | 42% | 89% | 0 | 100% | 11% | Siripongsatian, D. et al. [51] |
| PC | 36 | 53% | 26% | 23 treatment-naïve | 100% | 0 | 82% | 14% | 86% | 18% | 52% | 48% | 59% | 19% | 81% | 41% | Pang, Y. et al. [52] | ||||
| GC, CC and DC | 19 | 54% | 46% | Treatment-naïve | 100% | 0 | 89% | 11% | 71% | 39% | 57% | 43% | Pang, Y. et al. [53] | ||||||||
| GC | 56 | 80% | 20% | 45 treatment-naïve | 100% | 0 | 98% | 2% | 98% | 2% | 96% | 4% | Lin, R. et al. [54] | ||||||||
2.2. Brain Cancer
2.3. Neck and Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) Cancer
2.4. Lung Cancer
2.5. Breast Cancer
2.6. Bone Tumors
2.7. Soft Tissue Tumors
2.8. Other Cancer
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hajdu, S.I. A note from history: Landmarks in history of cancer, part 1. Cancer 2011, 117, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paget, S. The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1989, 8, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Lin, Y.; Shi, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, W.; Yin, W.; Dang, Y.; Chu, Y.; Fan, J.; He, R. FAP Promotes Immunosuppression by Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in the Tumor Microenvironment via STAT3–CCL2 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 4124–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Yu, D.-H.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, C.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.-H.; Ni, C.-R.; Zhu, M.-H. Expression of fibroblast activation protein in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma and its clinicopathological significance. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspriţoiu, V.M.; Stoica, I.; Bleotu, C.; Diaconu, C.C. Epigenetic Regulation of Angiogenesis in Development and Tumors Progression: Potential Implications for Cancer Treatment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 689962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.M.; Fusenig, N.E. Friends or foes—Bipolar effects of the tumour stroma in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffi, G.; Tuveson, D.A. Diversity and Biology of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 101, 147–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamson, E.J.; Keane, F.M.; Tholen, S.; Schilling, O.; Gorrell, M.D. Understanding fibroblast activation protein (FAP): Substrates, activities, expression and targeting for cancer therapy. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2014, 8, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, A.A.; Weiner, L.M. The role of fibroblast activation protein in health and malignancy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Song, E. Turning foes to friends: Targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loktev, A.; Lindner, T.; Mier, W.; Debus, J.; Altmann, A.; Jäger, D.; Giesel, F.; Kratochwil, C.; Barthe, P.; Roumestand, C.; et al. A Tumor-Imaging Method Targeting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loktev, A.; Lindner, T.; Burger, E.-M.; Altmann, A.; Giesel, F.; Kratochwil, C.; Debus, J.; Marme, F.; Jäger, D.; Mier, W.; et al. Development of Fibroblast Activation Protein-Targeted Radiotracers with Improved Tumor Retention. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, T.; Loktev, A.; Altmann, A.; Giesel, F.; Kratochwil, C.; Debus, J.; Jäger, D.; Mier, W.; Haberkorn, U. Development of Quinoline-Based Theranostic Ligands for the Targeting of Fibroblast Activation Protein. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1415–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanswell, P.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Rettig, W.J.; Welt, S.; Divgi, C.R.; Casper, E.S.; Finn, R.D.; Larson, S.M.; Old, L.J.; Scott, A.M. Population pharmacokinetics of antifibroblast activation protein monoclonal antibody F19 in cancer patients. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 51, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverman, P.; van der Geest, T.; Terry, S.Y.; Gerrits, D.; Walgreen, B.; Helsen, M.M.; Nayak, T.K.; Freimoser-Grundschober, A.; Waldhauer, I.; Hosse, R.J.; et al. Immuno-PET and Immuno-SPECT of Rheumatoid Arthritis with Radiolabeled Anti–Fibroblast Activation Protein Antibody Correlates with Severity of Arthritis. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meletta, R.; Muller Herde, A.; Chiotellis, A.; Isa, M.; Rancic, Z.; Borel, N.; Ametamey, S.M.; Krämer, S.D.; Schibli, R. Evaluation of the Radiolabeled Boronic Acid-Based FAP Inhibitor MIP-1232 for Atherosclerotic Plaque Imaging. Molecules 2015, 20, 2081–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesel, F.L.; Heussel, C.P.; Lindner, T.; Röhrich, M.; Rathke, H.; Kauczor, H.-U.; Debus, J.; Haberkorn, U.; Kratochwil, C. FAPI-PET/CT improves staging in a lung cancer patient with cerebral metastasis. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 1754–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varasteh, Z.; Mohanta, S.; Robu, S.; Braeuer, M.; Li, Y.; Omidvari, N.; Topping, G.; Sun, T.; Nekolla, S.G.; Richter, A.; et al. Molecular Imaging of Fibroblast Activity After Myocardial Infarction Using a 68Ga-Labeled Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor, FAPI-04. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Chen, X.; You, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Ren, S.; Huang, Q.; Hua, F.; Guan, Y.; et al. Comparison of [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 and [18F]-FDG for the detection of primary and metastatic lesions in patients with gastric cancer: A bicentric retrospective study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 49, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesel, F.L.; Kratochwil, C.; Lindner, T.; Marschalek, M.M.; Loktev, A.; Lehnert, W.; Debus, J.; Jäger, D.; Flechsig, P.; Altmann, A.; et al. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: Biodistribution and Preliminary Dosimetry Estimate of 2 DOTA-Containing FAP-Targeting Agents in Patients with Various Cancers. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochwil, C.; Flechsig, P.; Lindner, T.; Abderrahim, L.; Altmann, A.; Mier, W.; Adeberg, S.; Rathke, H.; Röhrich, M.; Winter, H.; et al. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: Tracer Uptake in 28 Different Kinds of Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesel, F.L.; Kratochwil, C.; Schlittenhardt, J.; Dendl, K.; Eiber, M.; Staudinger, F.; Kessler, L.; Fendler, W.P.; Lindner, T.; Koerber, S.A.; et al. Head-to-head intra-individual comparison of biodistribution and tumor uptake of 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET/CT in cancer patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 4377–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerber, S.A.; Staudinger, F.; Kratochwil, C.; Adeberg, S.; Haefner, M.F.; Ungerechts, G.; Rathke, H.; Winter, E.; Lindner, T.; Syed, M.; et al. The Role of68Ga-FAPI PET/CT for Patients with Malignancies of the Lower Gastrointestinal Tract: First Clinical Experience. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendl, K.; Koerber, S.A.; Finck, R.; Mokoala, K.M.G.; Staudinger, F.; Schillings, L.; Heger, U.; Röhrich, M.; Kratochwil, C.; Sathekge, M.; et al. 68Ga-FAPI-PET/CT in patients with various gynecological malignancies. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 4089–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, D.; Ma, L.; Wang, F. Fibroblast activation protein regulates tumor-associated fibroblasts and epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, P.; Tao, Z.; Tan, A. Low expression of miR-30a-5p induced the proliferation and invasion of oral cancer via promoting the expression of FAP. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20171027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurén, P. The Two Histological Main Types of Gastric Carcinoma: Diffuse and so-called Intestinal-Type Carcinoma. An Attempt at a Histo-Clinical Classification. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. 1965, 64, 31–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, K.; Chen, W.T.; Iwasa, S.; Jin, X.; Yamane, T.; Ooi, A.; Mitsumata, M. Seprase, a Membrane-Type Serine Protease, Has Different Expression Patterns in Intestinal- and Diffuse-Type Gastric Cancer. Oncology 2003, 65, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, Y.; Kono, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Fujii, H.; Yamane, T.; Mitsumata, M.; Chen, W.-T. The Expression of a Type II Transmembrane Serine Protease (Seprase) in Human Gastric Carcinoma. Oncology 2004, 67, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Qian, C.; Hu, Z.; Fei, B.; Zhou, H. Biomarkers in Tumor Microenvironment? Upregulation of Fibroblast Activation Protein-α Correlates with Gastric Cancer Progression and Poor Prognosis. OMICS A J. Integr. Biol. 2017, 21, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; He, X.; Jiao, F.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Ren, X.; Li, Q. Fibroblast Activation Protein-α-Positive Fibroblasts Promote Gastric Cancer Progression and Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wu, J.; Xu, B.; Wang, J.; Liang, L.; Guo, Y.; Peng, M.; Zhao, Y.; Liao, Q. Fibroblast activation protein α-positive pancreatic stellate cells promote the migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer by CXCL1-mediated Akt phosphorylation. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyyounouski, M.K.; Klump, W.J.; Konski, A.; Wu, H.; Adler, L.P. FDG PET Imaging of Signet-Ring Cell Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2005, 30, 118–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Yang, X.; Ng, Y.L.; Yu, X.; Huo, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, C.; Li, L.; et al. First total-body kinetic modeling and parametric imaging of dynamic 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET in pancreatic and gastric cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2023, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, S.; Jin, X.; Okada, K.; Mitsumata, M.; Ooi, A. Increased expression of seprase, a membrane-type serine protease, is associated with lymph node metastasis in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2003, 199, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, L.R.; Lee, H.O.; Lee, J.S.; Klein-Szanto, A.; Watts, P.; Ross, E.A.; Chen, W.-T.; Cheng, J.D. Clinical Implications of Fibroblast Activation Protein in Patients with Colon Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikberg, M.L.; Edin, S.; Lundberg, I.V.; Van Guelpen, B.; Dahlin, A.M.; Rutegård, J.; Stenling, R.; Öberg, Å.; Palmqvist, R. High intratumoral expression of fibroblast activation protein (FAP) in colon cancer is associated with poorer patient prognosis. Tumor Biol. 2013, 34, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kömek, H.; Can, C.; Kaplan, I.; Gündoğan, C.; Kepenek, F.; Karaoglan, H.; Demirkıran, A.; Ebinç, S.; Güzel, Y.; Gündeş, E. Comparison of [68 Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT and [18F]FDG PET/CT in colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 3898–3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumgay, H.; Arnold, M.; Ferlay, J.; Lesi, O.; Cabasag, C.J.; Vignat, J.; Laversanne, M.; McGlynn, K.A.; Soerjomataram, I. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 1598–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Gong, Y.; Cai, C.; Li, P.; Chen, J.; Xing, S.; Chen, J.; Peng, S.; et al. The Expression of FAP in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells is Induced by Hypoxia and Correlates with Poor Clinical Outcomes. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 3278–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; He, Q.; Jiang, S.; Li, M.; Xue, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, S.; Peng, H.; Liang, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. [18F]FAPI PET/CT in the evaluation of focal liver lesions with [18F]FDG non-avidity. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 50, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Pang, Y.; Yao, L.; Zhao, L.; Fan, C.; Ke, J.; Guo, P.; Hao, B.; Fu, H.; Xie, C.; et al. Imaging fibroblast activation protein in liver cancer: A single-center post hoc retrospective analysis to compare [68Ga]Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT versus MRI and [18F]-FDG PET/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 48, 1604–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, J.; Pang, Y.; Fu, K.; Shang, Q.; Wu, H.; Sun, L.; Lin, Q.; Chen, H. Fibroblast activation protein-based theranostics in cancer research: A state-of-the-art review. Theranostics 2022, 12, 1557–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, J.; Pang, Y.; Fang, J.; Fu, K.; Meng, L.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Wu, H.; Sun, L.; et al. Development of Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor-Based Dimeric Radiotracers with Improved Tumor Retention and Antitumor Efficacy. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 3640–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.J.; Alpaugh, R.K.; Palazzo, I.; Meropol, N.J.; Rogatko, A.; Xu, Z.; Hoffman, J.P.; Weiner, L.M.; Cheng, J.D. Fibroblast Activation Protein and Its Relationship to Clinical Outcome in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2008, 37, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, A.; Li, C.-P.; Buza, E.L.; Blomberg, R.; Govindaraju, P.; Avery, D.; Monslow, J.; Hsiao, M.; Puré, E. Fibroblast activation protein augments progression and metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e92232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, C.; Jones, J.O.; Kraman, M.; Wells, R.J.; Deonarine, A.; Chan, D.S.; Connell, C.M.; Roberts, E.W.; Zhao, Q.; Caballero, O.L.; et al. Targeting CXCL12 from FAP-expressing carcinoma-associated fibroblasts synergizes with anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20212–20217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunderson, A.J.; Yamazaki, T.; Mccarty, K.; Phillips, M.; Alice, A.; Bambina, S.; Zebertavage, L.; Friedman, D.; Cottam, B.; Newell, P.; et al. Blockade of fibroblast activation protein in combination with radiation treatment in murine models of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siripongsatian, D.; Promteangtrong, C.; Kunawudhi, A.; Kiatkittikul, P.; Boonkawin, N.; Chinnanthachai, C.; Jantarato, A.; Chotipanich, C. Comparisons of Quantitative Parameters of Ga-68-Labelled Fibroblast Activating Protein Inhibitor (FAPI) PET/CT and [18F]F-FDG PET/CT in Patients with Liver Malignancies. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2022, 24, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Shang, Q.; Meng, T.; Zhao, L.; Feng, L.; Wang, S.; Guo, P.; Wu, X.; Lin, Q.; et al. Positron emission tomography and computed tomography with [68Ga]Ga-fibroblast activation protein inhibitors improves tumor detection and staging in patients with pancreatic cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Luo, Z.; Hao, B.; Wu, H.; Lin, Q.; Sun, L.; Chen, H. Comparison of 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG Uptake in Gastric, Duodenal, and Colorectal Cancers. Radiology 2021, 298, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Lin, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Zang, J.; Miao, W. [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT in the evaluation of gastric cancer: Comparison with [18F]FDG PET/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 2960–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röhrich, M.; Loktev, A.; Wefers, A.K.; Altmann, A.; Paech, D.; Adeberg, S.; Windisch, P.; Hielscher, T.; Flechsig, P.; Floca, R.; et al. IDH-wildtype glioblastomas and grade III/IV IDH-mutant gliomas show elevated tracer uptake in fibroblast activation protein–specific PET/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 2569–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wen, B.; Tian, Y.; Chen, J.; He, Y. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT Findings in a Rare Presacral Myxopapillary Ependymoma. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, C. Elevated 68Ga-FAPI Uptake by Primary Benign Intraosseous Meningioma. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, 994–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Geng, J.; Zhang, C. Presacral Benign Schwannoma Mimics Malignancy on 18F-FDG and 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeman, J.E.; Li, J.-G.; Pei, X.; Venigalla, P.; Zumsteg, Z.S.; Katsoulakis, E.; Lupovitch, E.; McBride, S.M.; Tsai, C.J.; Boyle, J.O.; et al. Patterns of Treatment Failure and Postrecurrence Outcomes Among Patients With Locally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma After Chemoradiotherapy Using Modern Radiation Techniques. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1487–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldi, P.; Leccisotti, L.; Bussu, F.; Miccichè, F.; Rufini, V. Role of (18)F-FDG PET-CT in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2013, 33, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscolo-Rizzo, P.; Zorzi, M.; Del Mistro, A.; Da Mosto, M.C.; Tirelli, G.; Buzzoni, C.; Rugge, M.; Polesel, J.; Guzzinati, S. The evolution of the epidemiological landscape of head and neck cancer in Italy: Is there evidence for an increase in the incidence of potentially HPV-related carcinomas? PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterio, D.; Marvaso, G.; Ferrari, A.; Volpe, S.; Orecchia, R.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A. Modern radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2019, 46, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, D.L.; Harris, J.; Yao, M.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Opanowski, A.; Levering, A.; Ang, K.K.; Trotti, A.M.; Garden, A.S.; Jones, C.U.; et al. Metabolic Tumor Volume as a Prognostic Imaging-Based Biomarker for Head-and-Neck Cancer: Pilot Results From Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Protocol 0522. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 91, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Ou, X.; Xia, Z.; Guan, Q.; Hu, S.; Yang, Z.; Song, S. The Added Value of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer of Unknown Primary with 18F-FDG–Negative Findings. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Promteangtrong, C.; Siripongsatian, D.; Jantarato, A.; Kunawudhi, A.; Kiatkittikul, P.; Yaset, S.; Boonkawin, N.; Chotipanich, C. Head-to-Head Comparison of 68Ga-FAPI-46 and 18F-FDG PET/CT for Evaluation of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Single-Center Exploratory Study. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Yao, S.; Miao, W. Pleural Metastasis of Papillary Thyroid Cancer Depicted by 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, 467–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Wei, Q.; Yu, W. Cancer-associated fibroblasts in radiotherapy: Challenges and new opportunities. Cell Commun. Signal. 2019, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Han, C.; Wang, S.; Fang, P.; Ma, Z.; Xu, L.; Yin, R. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: An emerging target of anti-cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhrich, M.; Syed, M.; Liew, D.P.; Giesel, F.L.; Liermann, J.; Choyke, P.L.; Wefers, A.K.; Ritz, T.; Szymbara, M.; Schillings, L.; et al. 68Ga-FAPI-PET/CT improves diagnostic staging and radiotherapy planning of adenoid cystic carcinomas—Imaging analysis and histological validation. Radiother. Oncol. 2021, 160, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.; Flechsig, P.; Liermann, J.; Windisch, P.; Staudinger, F.; Akbaba, S.; Koerber, S.A.; Freudlsperger, C.; Plinkert, P.K.; Debus, J.; et al. Fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI) PET for diagnostics and advanced targeted radiotherapy in head and neck cancers. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 2836–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Liu, F.; Huang, J.; Ruan, W.; Liu, Q.; Gai, Y.; Hu, F.; Jiang, D.; Hu, Y.; Yang, K.; et al. A head-to-head comparison of 68Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and 18F-FDG PET/MR in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A prospective study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 3228–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; You, Z.; Mou, C.; Hu, Z.; Liu, H. Esophagitis Mimicking Esophageal Cancer on 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 47, 279–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballal, S.; Yadav, M.P.; Moon, E.S.; Rösch, F.; ArunRaj, S.T.; Agarwal, S.; Tripathi, M.; Sahoo, R.K.; Bal, C. First-in-Human Experience With 177Lu-DOTAGA.(SA.FAPi)2 Therapy in an Uncommon Case of Aggressive Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Clinically Mimicking as Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, e444–e445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Aisner, D.L.; Wood, D.E.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A.; Dilling, T.J.; Dobelbower, M.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 5.2018. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 807–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhao, L.; He, Z. Performance of Whole-Body PET/CT for the Detection of Distant Malignancies in Various Cancers: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treglia, G.; Sadeghi, R.; Annunziata, S.; Lococo, F.; Cafarotti, S.; Bertagna, F.; Prior, J.O.; Ceriani, L.; Giovanella, L. Diagnostic Accuracy of 18F-FDG-PET and PET/CT in the Differential Diagnosis between Malignant and Benign Pleural Lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acad. Radiol. 2014, 21, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.A.; Shin, K.M.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, B.-T.; Kim, H.; Kwon, O.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Chung, M.J. Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Staging: Efficacy Comparison of Integrated PET/CT versus 3.0-T Whole-Body MR Imaging. Radiology 2008, 248, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toloza, E.M.; Harpole, L.; Detterbeck, F.; McCrory, D.C. Invasive Staging of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: A review of the current evidence. Chest 2003, 123, 157S–166S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, C.; Kepenek, F.; Kömek, H.; Gündoğan, C.; Kaplan, I.; Taşdemir, B.; Güzel, Y.; Agüloğlu, N.; Karaoğlan, H. Comparison of 18F-FDG PET/CT and 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2022, 43, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, B.; Wu, J.; Pang, Y.; Sun, L.; Chen, H. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT in Assessment of Leptomeningeal Metastases in a Patient With Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 45, 784–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Cheng, K.; Fu, Z.; Zheng, J.; Mu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Yu, J.; Yuan, S. [18F]AlF-NOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT uptake in metastatic lesions on PET/CT imaging might distinguish different pathological types of lung cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 49, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballal, S.; Yadav, M.P.; Moon, E.S.; Kramer, V.S.; Roesch, F.; Kumari, S.; Tripathi, M.; ArunRaj, S.T.; Sarswat, S.; Bal, C. Biodistribution, pharmacokinetics, dosimetry of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA.SA.FAPi, and the head-to-head comparison with [18F]F-FDG PET/CT in patients with various cancers. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 48, 1915–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Lv, J.; Hou, P.; Liu, S.; Chen, P.; Wang, M.; Zhou, C.; Wang, X. Clinical Utility of F-18 Labeled Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI) for Primary Staging in Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Prospective Study. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2022, 24, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Tang, G.; Hu, K.; Liu, X.; Zhou, W.; Li, H.; Huang, S.; Han, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhong, J.; et al. Comparison of 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET/CT in the Evaluation of Advanced Lung Cancer. Radiology 2022, 303, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, X.; Xu, X.; Ding, J.; Liu, T.; Jiang, J.; Li, N.; Zhu, H.; Yang, Z. Dynamic PET/CT Imaging of 68Ga-FAPI-04 in Chinese Subjects. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 651005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Welch, K.; Wang, L.; Kong, F.-M. Negative Predictive Value of Positron Emission Tomography and Computed Tomography for Stage T1-2N0 Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2012, 13, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Pang, Y.; Meng, T.; Chen, H. Differentiation of Reactive Lymph Nodes and Tumor Metastatic Lymph Nodes With 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT in a Patient With Squamous Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wu, J.; Yang, S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y. Organizing Pneumonia With Intense 68Ga-FAPI Uptake Mimicking Lung Cancer on 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, 223–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, J.; Yamazaki, K.; Tsukamoto, E.; Tamaki, N.; Onodera, Y.; Otake, T.; Morikawa, T.; Kinoshita, I.; Dosaka-Akita, H.; Nishimura, M. Mediastinal Lymph Node Staging by FDG-PET in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Analysis of False-Positive FDG-PET Findings. Respiration 2003, 70, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt-Cuellar, S.L.; Carter, B.W.; Palacio, D.; Erasmus, J.J. Pitfalls and Limitations in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Staging. Semin. Roentgenol. 2015, 50, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liao, T.; Rao, Z.; Gong, W.; Ou, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C. Comparison of the Relative Diagnostic Performance of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and [18F]FDG PET/CT for the Detection of Bone Metastasis in Patients With Different Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 737827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kömek, H.; Can, C.; Güzel, Y.; Oruç, Z.; Gündoğan, C.; Yildirim, Ö.A.; Kaplan, I.; Erdur, E.; Yıldırım, M.S.; Çakabay, B. 68Ga-FAPI-04 PET/CT, a new step in breast cancer imaging: A comparative pilot study with the 18F-FDG PET/CT. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2021, 35, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Simms, A.E.; Mazur, A.; Wang, S.; León, N.R.; Jones, B.; Aziz, N.; Kelly, T. Fibroblast activation protein-α promotes tumor growth and invasion of breast cancer cells through non-enzymatic functions. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2011, 28, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garin-Chesa, P.; Old, L.J.; Rettig, W.J. Cell surface glycoprotein of reactive stromal fibroblasts as a potential antibody target in human epithelial cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 7235–7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, X.; Yu, L.; Huang, X.; Liao, Z.; Xian, Q. Expression and role of fibroblast activation protein-alpha in microinvasive breast carcinoma. Diagn. Pathol. 2011, 6, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.K.; Jung, W.H.; Koo, J.S. Expression of cancer-associated fibroblast-related proteins differs between invasive lobular carcinoma and invasive ductal carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 159, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.Y.; Lee, Y.K.; Koo, J.S. Expression of cancer-associated fibroblast-related proteins in adipose stroma of breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 8685–8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Nie, Y.; Qu, S.; Liao, J.-Y.; Cui, X.; Yao, H.; Zeng, Y.; Su, F.; Song, E.; Liu, Q. miR-21 Induces Myofibroblast Differentiation and Promotes the Malignant Progression of Breast Phyllodes Tumors. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4341–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.J.; Pollock, C.B.; Kelly, K. Mechanisms of cancer metastasis to the bone. Cell Res. 2005, 15, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundy, G. Metastasis to bone: Causes, consequences and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Oronzo, S.; Coleman, R.; Brown, J.; Silvestris, F. Metastatic bone disease: Pathogenesis and therapeutic options: Up-date on bone metastasis management. J. Bone Oncol. 2019, 15, 100205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Younis, M.H.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, W.; Lan, X. Clinical summary of fibroblast activation protein inhibitor-based radiopharmaceuticals: Cancer and beyond. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 2844–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Pang, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Hao, B.; Wu, J.; Wei, J.; Wu, S.; Zhao, L.; Luo, Z.; et al. Comparison of [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 and [18F] FDG PET/CT for the diagnosis of primary and metastatic lesions in patients with various types of cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2020, 47, 1820–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.; Chen, S.; He, L.; Liu, W.; Zhang, C. Intense 68Ga-FAPI Uptake in a Patient With Myositis Ossificans: Mimicking Bone Malignancy. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, 638–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, S.; Miao, W. Both [68Ga]Ga-FAPI and [18F]FDG PET/CT missed bone metastasis in a patient with breast cancer. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 4519–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendl, K.; Finck, R.; Giesel, F.L.; Kratochwil, C.; Lindner, T.; Mier, W.; Cardinale, J.; Kesch, C.; Röhrich, M.; Rathke, H.; et al. FAP imaging in rare cancer entities—First clinical experience in a broad spectrum of malignancies. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 49, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerber, S.A.; Finck, R.; Dendl, K.; Uhl, M.; Lindner, T.; Kratochwil, C.; Röhrich, M.; Rathke, H.; Ungerechts, G.; Adeberg, S.; et al. Novel FAP ligands enable improved imaging contrast in sarcoma patients due to FAPI-PET/CT. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 3918–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, L.; Ferdinandus, J.; Hirmas, N.; Bauer, S.; Dirksen, U.; Zarrad, F.; Nader, M.; Chodyla, M.; Milosevic, A.; Umutlu, L.; et al. 68Ga-FAPI as a Diagnostic Tool in Sarcoma: Data from the 68Ga-FAPI PET Prospective Observational Trial. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratochwil, C.; Giesel, F.L.; Rathke, H.; Fink, R.; Dendl, K.; Debus, J.; Mier, W.; Jäger, D.; Lindner, T.; Haberkorn, U. [153Sm]Samarium-labeled FAPI-46 radioligand therapy in a patient with lung metastases of a sarcoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 3011–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdinandus, J.; Costa, P.F.; Kessler, L.; Weber, M.; Hirmas, N.; Kostbade, K.; Bauer, S.; Schuler, M.; Ahrens, M.; Schildhaus, H.-U.; et al. Initial clinical experience with 90Y-FAPI-46 radioligand therapy for advanced stage solid tumors: A case series of nine patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macpherson, R.E.; Pratap, S.; Tyrrell, H.; Khonsari, M.; Wilson, S.; Gibbons, M.; Whitwell, D.; Giele, H.; Critchley, P.; Cogswell, L.; et al. Retrospective audit of 957 consecutive 18F-FDG PET–CT scans compared to CT and MRI in 493 patients with different histological subtypes of bone and soft tissue sarcoma. Clin. Sarcoma Res. 2018, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charest, M.; Hickeson, M.; Lisbona, R.; Novales-Diaz, J.-A.; Derbekyan, V.; Turcotte, R.E. FDG PET/CT imaging in primary osseous and soft tissue sarcomas: A retrospective review of 212 cases. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2009, 36, 1944–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.J.; Johnny Ong, C.-A.; Tan, J.W.-S.; Ching Teo, M.C. Utility of positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) imaging in the evaluation of sarcomas: A systematic review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2019, 143, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Hu, S.; Yan, W.; Luo, Z.; Song, S. Head-to-head evaluation of [18F]FDG and [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT in recurrent soft tissue sarcoma. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 2889–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Gong, W.; Zhang, C. Increased 68Ga-FAPI Activity in Malignant Melanoma of the Nasal Cavity. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, 147–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokoala, K.; Emil, N.; Lawal, I.; Antke, C.; Giesel, F.L.; Sathekge, M. [68Ga]Ga-FAPI versus [18F]F-FDG in malignant melanoma: Complementary or counterpoint? Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 2445–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erol Fenercioğlu, O.; Beyhan, E.; Ergül, N.; Arslan, E.; Çermik, T.F. 18F-FDG PET/CT and 68Ga-FAPI-4 PET/CT Findings of Bilateral Knee Osteoarthritis in a Patient With Uveal Malignant Melanoma. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, e144–e146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, G.; Wright, G.; Dave, S.S.; Xiao, W.; Powell, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, W.; Tan, B.; Goldschmidt, N.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Stromal Gene Signatures in Large-B-Cell Lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augsten, M. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts as Another Polarized Cell Type of the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Wei, M.; Wang, S.; Wang, G.; Lai, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X. Detecting Fibroblast Activation Proteins in Lymphoma Using 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, Y.; Yao, Z.M.; Cheng, Z. Hepatic Lesion of Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma Revealed by Al18F-NOTA-FAPI-04 PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 47, e49–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, J.; Lin, Z.; Yao, S.; Miao, W. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma Revealed by 68Ga-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 46, e421–e423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Y.; Zhou, H.; Alhaskawi, A.; Wang, Z.; Lai, J.; Yao, C.; Liu, Z.; Hasan Abdullah Ezzi, S.; Goutham Kota, V.; Hasan Abdulla Hasan Abdulla, M.; et al. The Superiority of Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI) PET/CT Versus FDG PET/CT in the Diagnosis of Various Malignancies. Cancers 2023, 15, 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041193
Dong Y, Zhou H, Alhaskawi A, Wang Z, Lai J, Yao C, Liu Z, Hasan Abdullah Ezzi S, Goutham Kota V, Hasan Abdulla Hasan Abdulla M, et al. The Superiority of Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI) PET/CT Versus FDG PET/CT in the Diagnosis of Various Malignancies. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041193
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Yanzhao, Haiying Zhou, Ahmad Alhaskawi, Zewei Wang, Jingtian Lai, Chengjun Yao, Zhenfeng Liu, Sohaib Hasan Abdullah Ezzi, Vishnu Goutham Kota, Mohamed Hasan Abdulla Hasan Abdulla, and et al. 2023. "The Superiority of Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI) PET/CT Versus FDG PET/CT in the Diagnosis of Various Malignancies" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041193
APA StyleDong, Y., Zhou, H., Alhaskawi, A., Wang, Z., Lai, J., Yao, C., Liu, Z., Hasan Abdullah Ezzi, S., Goutham Kota, V., Hasan Abdulla Hasan Abdulla, M., & Lu, H. (2023). The Superiority of Fibroblast Activation Protein Inhibitor (FAPI) PET/CT Versus FDG PET/CT in the Diagnosis of Various Malignancies. Cancers, 15(4), 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041193







