The Genetic and Immunologic Landscape Underlying the Risk of Malignant Progression in Laryngeal Dysplasia
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- Previous history of invasive laryngeal cancer
- -
- Previous laryngeal surgical procedures or treatments
- -
- Immunitary diseases or concurrent medical treatments interfering with the immunitary system function (i.e., sclerodermia, rheumatoid arthritis, steroid immunosuppressive treatments, etc.)
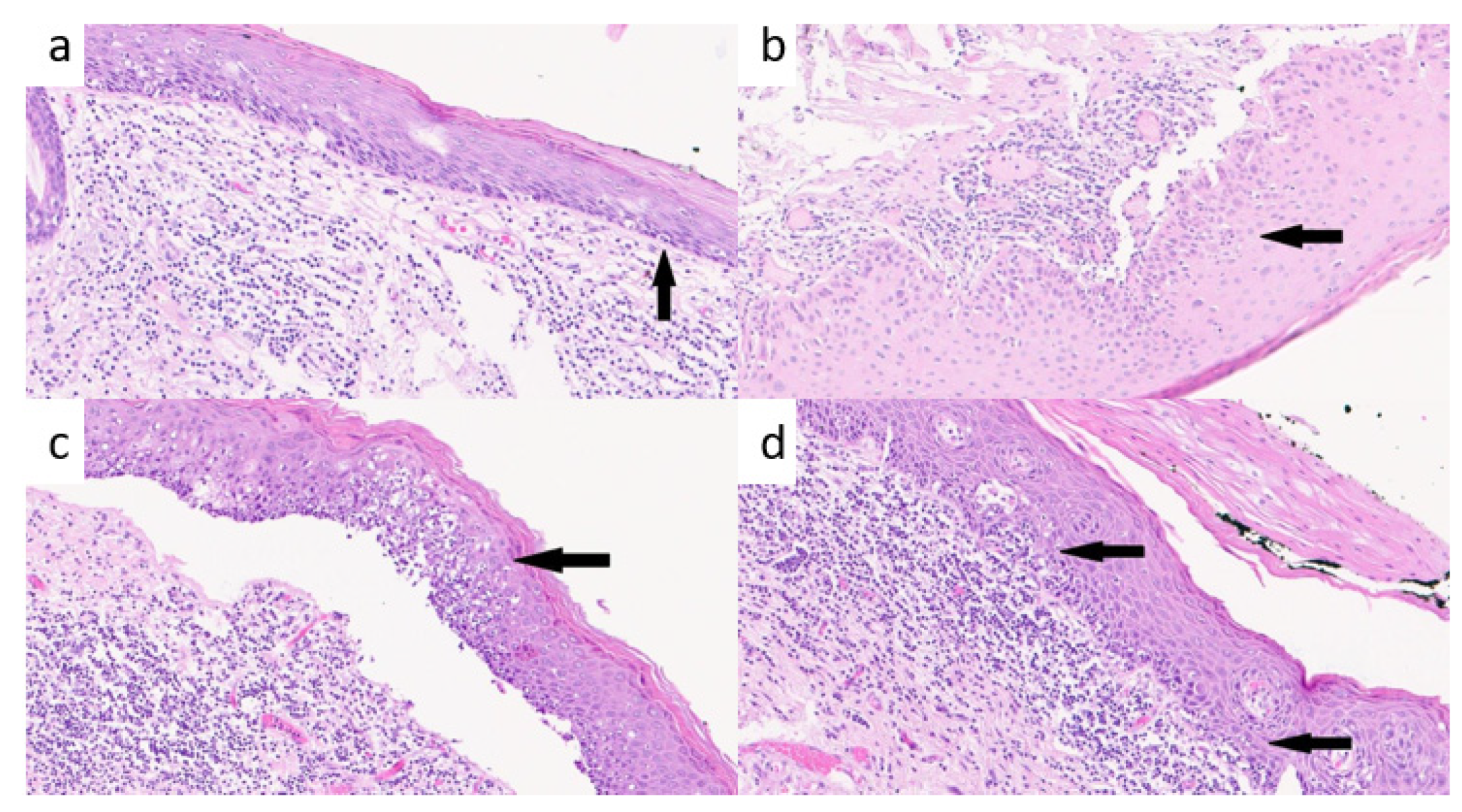
2.1. Histopathological Evaluation of TILs
2.2. Genetic Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
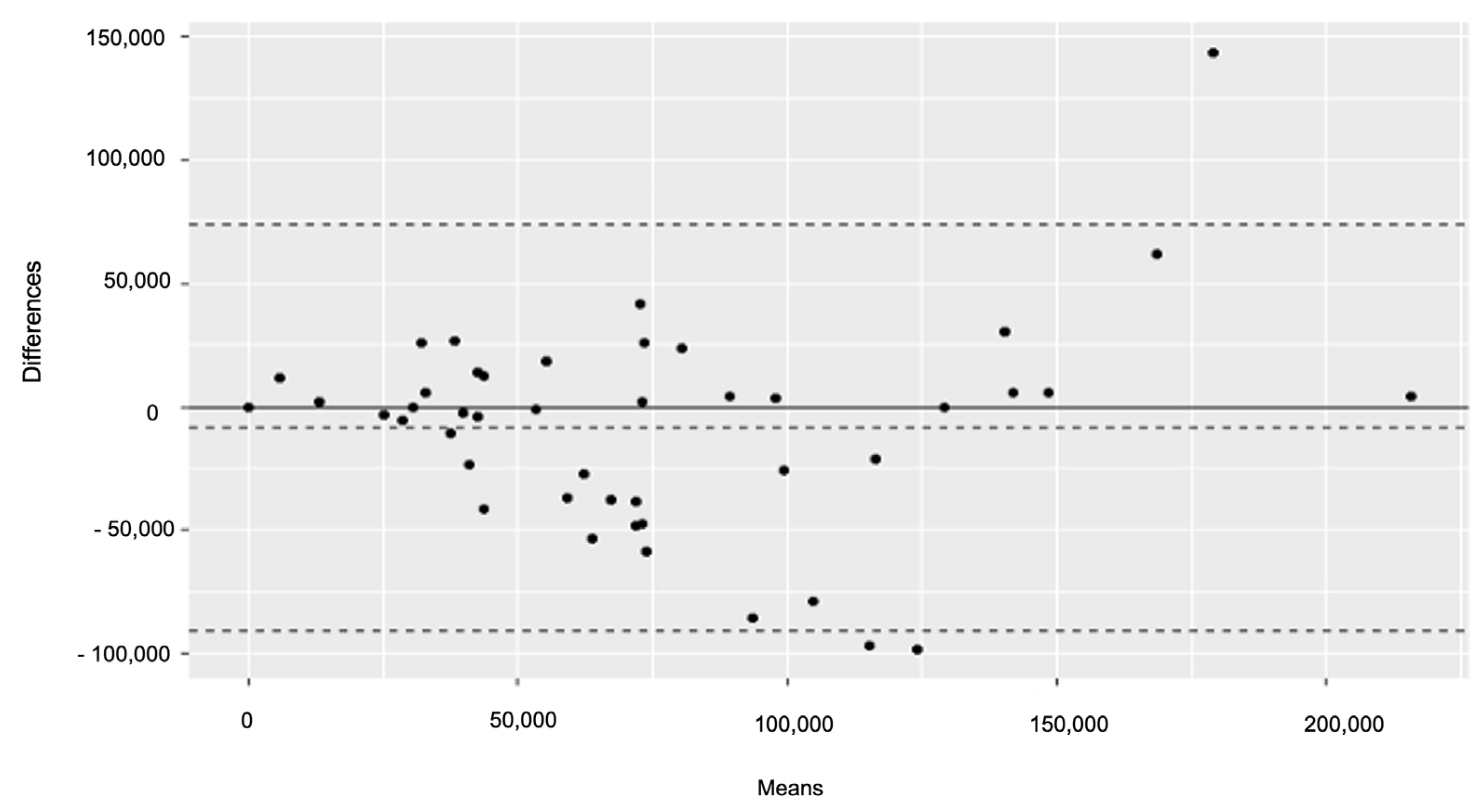
2.3.1. TILs Analysis
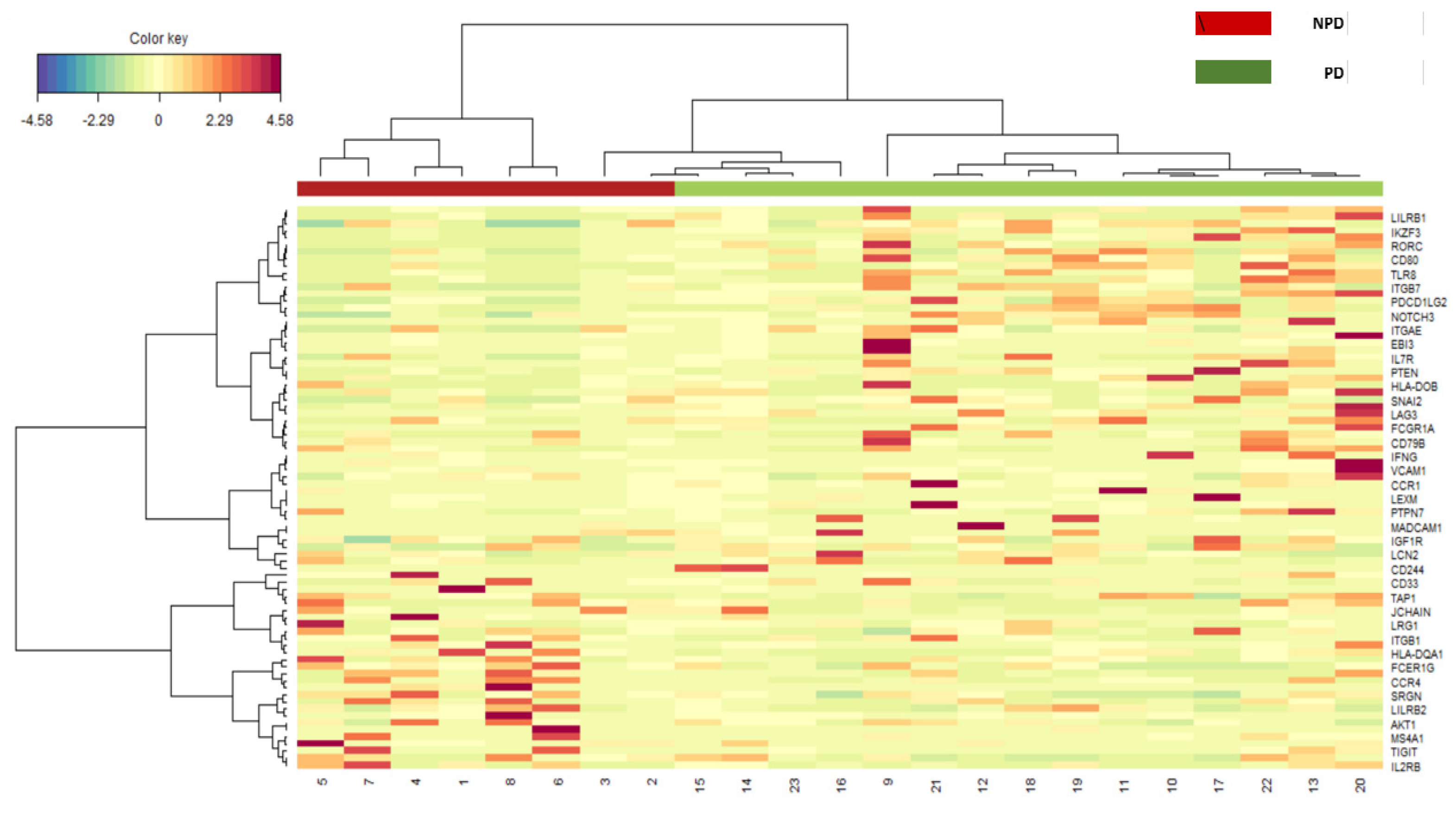
2.3.2. Gene Expression Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TILs Analysis
3.2. Gene Expression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nocini, R.; Molteni, G.; Mattiuzzi, C.; Lippi, G. Updates on larynx cancer epidemiology. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 32, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lips, M.; Speyer, R.; Zumach, A.; Kross, K.W.; Kremer, B. Supracricoid laryngectomy and dysphagia: A systematic literature review. Laryngoscope 2015, 125, 2143–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Califano, J.; Van Der Riet, P.; Westra, W.; Nawroz, H.; Clayman, G.; Piantadosi, S.; Corio, R.; Lee, D.; Greenberg, B.; Koch, W.; et al. Genetic progression model for head and neck cancer: Implications for field cancerization. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 2488–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Califano, J.; Westra, W.H.; Meininger, G.; Corio, R.; Koch, W.M.; Sidransky, D. Genetic progression and clonal relationship of recurrent premalignant head and neck lesions. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.D. Laryngeal dysplasia, squamous cell carcinoma, and variants. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2017, 10, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hulst, A.M.; Kroon, W.; Van Der Linden, E.S.; Nagtzaam, L.; Ottenhof, S.R.; Wegner, I.; Gunning, A.C.; Grolman, W.; Braunius, W.W. Grade of dysplasia and malignant transformation in adults with premalignant laryngeal lesions. Head Neck 2016, 38, E2284–E2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.; De Santi, S.; Tagliabue, M.; De Benedetto, L.; Zorzi, S.; Pietrobon, G.; Herman, I.; Maffini, F.; Chiocca, S.; Corso, F.; et al. Laryngeal dysplasia: Oncological outcomes in a large cohort of patients treated in a tertiary comprehensive cancer centre. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2021, 42, 102861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Yoon, T.M.; Lee, J.K.; Lim, S.C. Predictive factors of recurrence and malignant transformation in vocal cord leukoplakia. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 272, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falco, M.; Tammaro, C.; Takeuchi, T.; Cossu, A.M.; Scafuro, G.; Zappavigna, S.; Itro, A.; Addeo, R.; Scrima, M.; Lombardi, A.; et al. Overview on Molecular Biomarkers for Laryngeal Cancer: Looking for New Answers to an Old Problem. Cancers 2022, 14, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliabue, M.; Maffini, F.; Fumagalli, C.; Gandini, S.; Lepanto, D.; Corso, F.; Cacciola, S.; Ranghiero, A.; Rappa, A.; Vacirca, D.; et al. A role for the immune system in advanced laryngeal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remacle, M.; Eckel, H.E.; Antonelli, A.; Brasnu, D.; Chevalier, D.; Friedrich, G.; Olofsson, J.; Rudert, H.H.; Thumfart, W.; De Vincentiis, M.; et al. Endoscopic cordectomy. a proposal for a classification by the Working Committee, European Laryngological Society. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2000, 257, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remacle, M.; Van Haverbeke, C.; Eckel, H.; Bradley, P.; Chevalier, D.; Djukic, V.; de Vicentiis, M.; Friedrich, G.; Olofsson, J.; Peretti, G.; et al. Proposal for revision of the European Laryngological Society classification of endoscopic cordectomies. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2007, 264, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihm, M.C.; Clemente, C.G.; Cascinelli, N. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in lymph node melanoma metastases: A histopathologic prognostic indicator and an expression of local immune response. Lab. Investig. 1996, 74, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bosisio, F.M.; Antoranz, A.; van Herck, Y.; Bolognesi, M.M.; Marcelis, L.; Chinello, C.; Wouters, J.; Magni, F.; Alexopoulos, L.; Stas, M.; et al. Functional heterogeneity of lymphocytic patterns in primary melanoma dissected through single-cell multiplexing. eLife 2020, 9, e53008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lian, J.W.; Chin, Y.-P.; Wang, L.; Lian, A.; Murphy, G.F.; Zhou, L. Assessing the Prognostic Significance of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Patients with Melanoma Using Pathologic Features Identified by Natural Language Processing. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2126337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledderose, S.; Ledderose, C.; Penkava, J.; Ledderose, G.J. Prognostic Value of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Sinonasal Mucosal Melanoma. Laryngoscope 2022, 132, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javier Palarea-Albaladejo, J.A. zCompositions—R package for multivariate imputation of left-censored data under a compositional approach. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 143, 85–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.P.; Lee, B.K.B.; Lau, S.H.; Kallarakkal, T.G.; Zaini, Z.M.; Lye, B.K.W.; Zain, R.B.; Sathasivam, H.P.; Yeong, J.P.S.; Savelyeva, N.; et al. Transcriptional analysis highlights three distinct immune profiles of high-risk oral epithelial dysplasia. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 954567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, C.G.; Mihm, M.C., Jr.; Bufalino, R.; Zurrida, S.; Collini, P.; Cascinelli, N. Prognostic value of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in the vertical growth phase of primary cutaneous melanoma. Cancer 1996, 77, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gail, M.H.; Brinton, L.A.; Byar, D.P.; Corle, D.K.; Green, S.B.; Schairer, C.; Mulvihill, J.J. Projecting Individualized Probabilities of Developing Breast Cancer for White Females Who Are Being Examined Annually. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1989, 81, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Carson, W.F., 4th; Cavassani, K.A.; Connett, J.M.; Kunkel, S.L. CCR6 as a mediator of immunity in the lung and gut. Exp. Cell Res. 2011, 317, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero-Campo, P.; Buffone, M.G.; Benencia, F.; Conejo-Garcia, J.; Rinaudo, P.F.; Gerton, G.L. A Role for the Chemokine Receptor CCR6 in Mammalian Sperm Motility and Chemotaxis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2014, 229, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosche, L.; Knippertz, I.; König, C.; Royzman, D.; Wild, A.B.; Zinser, E.; Sticht, H.; Muller, Y.A.; Steinkasserer, A.; Lechmann, M. The CD83 Molecule—An Important Immune Checkpoint. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, A.I.; Joseph, C.; Kurozumi, S.; Mohammed, O.J.; Miligy, I.M.; Green, A.R.; Rakha, E.A. Myxovirus resistance 1 (MX1) is an independent predictor of poor outcome in invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 181, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calmon, M.F.; Rodrigues, R.V.; Kaneto, C.M.; Moura, R.P.; Silva, S.D.; Mota, L.D.C.; Pinheiro, D.G.; Torres, C.; de Carvalho, A.F.; Cury, P.M.; et al. Epigenetic Silencing of CRABP2 and MX1 in Head and Neck Tumors. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chirshev, E.; Hojo, N.; Suzuki, T.; Bertucci, A.; Pierce, M.; Perry, C.; Wang, R.; Zink, J.; Glackin, C.; et al. The epithelial–mesenchymal transcription factor snai1 represses transcription of the tumor suppressor miRNA let-7 in cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battula, V.L.; Evans, K.W.; Hollier, B.G.; Shi, Y.; Marini, F.C.; Ayyanan, A.; Wang, R.-Y.; Brisken, C.; Guerra, R.; Andreeff, M.; et al. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition-Derived Cells Exhibit Multilineage Differentiation Potential Similar to Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 1435–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unternaehrer, J.J.; Zhao, R.; Kim, K.; Cesana, M.; Powers, J.T.; Ratanasirintrawoot, S.; Onder, T.; Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A.; Daley, G.Q. The Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Factor SNAIL Paradoxically Enhances Reprogramming. Stem Cell Rep. 2014, 3, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmeda, D.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Flores, J.M.; Fabra, A.; Portillo, F.; Cano, A. SNAI1 Is Required for Tumor Growth and Lymph Node Metastasis of Human Breast Carcinoma MDA-MB-231 Cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11721–11731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wu, Y.; Helman, J.I.; Wen, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, L. CXCR4 Promotes Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Migration and Invasion through Inducing Expression of MMP-9 and MMP-13 via the ERK Signaling Pathway. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Qian, S.-M. CD44v6-O-MWNTS-Loaded Gemcitabine and CXCR4 siRNA Improves the Anti-tumor Effectiveness of Ovarian Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 687322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubaki, M.; Genno, S.; Takeda, T.; Matsuda, T.; Kimura, N.; Yamashita, Y.; Morii, Y.; Shimomura, K.; Nishida, S. Rhosin Suppressed Tumor Cell Metastasis through Inhibition of Rho/YAP Pathway and Expression of RHAMM and CXCR4 in Melanoma and Breast Cancer Cells. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, A.N.; Brown, M.H.; Law, S.K.A.; McKnight, A.J.; Tomlinson, M.G.; van der Merwe, P.A. The Leucocyte Antigen Factsbook; Academic Press Ltd.: London, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Chavin, K.D.; Qin, L.; Lin, J.; Woodward, J.; Baliga, P.; Kato, K.; Yaglta, H.; Bromberg, J.S. Anti-CD48 (murine CD2 ligand) mAbs suppress cell mediated immunity in vivo. Int. Immunol. 1994, 6, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cycon, K.A.; Mulvaney, K.; Rimsza, L.M.; Persky, D.; Murphy, S.P. Histone deacetylase inhibitors activate CIITA and MHC class II antigen expression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Immunology 2013, 140, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Tang, D.; Li, S.-J.; Zhou, J.; Hsueh, C.-Y.; Zhao, D.-D.; Heng, Y.; Tao, L.; Lu, L.-M. Link between CIITA rs3087456 polymorphism and the risk of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma in a Chinese population. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Cheng, Z.; Dong, F.; Quan, L.; Cui, L.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, T.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Pang, Y.; et al. Enhanced expression of FCER1G predicts positive prognosis in multiple myeloma. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1182–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Barajon, I.; Garlanda, C. IL-1 and IL-1 regulatory pathways in cancer progression and therapy. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 281, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evoronov, E.; Ecarmi, Y.; Apte, R.N. The role IL-1 in tumor-mediated angiogenesis. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkabets, M.; Ribeiro, V.S.G.; Dinarello, C.A.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Di Santo, J.; Apte, R.N.; Vosshenrich, C.A.J. IL-1β regulates a novel myeloid-derived suppressor cell subset that impairs NK cell development and function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 3347–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, J.; De Ley, M.; Opdenakker, G.; Billiau, A.; De Somer, P.; Van Beeumen, J. Homogeneous interferon-inducing 22K factor is related to endogenous pyrogen and interleukin-1. Nature 1985, 314, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanam, A.; Gibson-Corley, K.N.; Love-Homan, L.; Ihejirika, N.; Simons, A.L. Interleukin-1 blockade overcomes erlotinib resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 76087–76100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Li, F.; Tong, L.; Chen, C.; Yuan, B. Effects of in IL-1B/IL-1RN variants on the susceptibility to head and neck cancer in a chinese Han population. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdebenito, S.; Malik, S.; Luu, R.; Valdebenito, S.; Malik, S.; Luu, R.; Loudig, O.; Mitchell, M.; Okafo, G.; Bhat, K.; et al. Tunneling nanotubes, TNT, communicate glioblastoma with surrounding non-tumor astrocytes to adapt them to hypoxic and metabolic tumor conditions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietsch, G.N.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y.; Morishima, C.; Chow, L.Q.; Disis, M.L.; Hershberg, R.M. Coordinated Activation of Toll-Like Receptor8 (TLR8) and NLRP3 by the TLR8 Agonist, VTX-2337, Ignites Tumoricidal Natural Killer Cell Activity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, R.M.; Lim, C.M.; Matthews, M.; Dietsch, G.; Hershberg, R.; Ferris, R.L. TLR8 stimulation enhances cetuximab-mediated natural killer cell lysis of head and neck cancer cells and dendritic cell cross-priming of EGFR-specific CD8+ T cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | NPDy n = 31 (100%) | PDy n = 15 (100%) | p-Value 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.2 | ||
| Female | 8 (26%) | 1 (6.7%) | |
| Male | 23 (74%) | 14 (93%) | |
| Age, Median (IQR) | 58 (54, 64) | 66 (56, 70) | 0.2 |
| Smoking | 0.8 | ||
| Never | 4 (13%) | 3 (20%) | |
| Current | 13 (42%) | 6 (40%) | |
| Former | 14 (45%) | 6 (40%) | |
| Cancer site | 0.6 | ||
| Glottis | 27 (87%) | 13 (87%) | |
| Supraglottis | 2 (6.5%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Glottis + Supraglottis | 2 (6.5%) | 2 (13%) | |
| Histological Grade | 0.029 | ||
| mild SIN | 11 (35%) | 3 (20%) | |
| Intermediate SIN | 10 (32%) | 1 (6.7%) | |
| severe SIN | 10 (32%) | 11 (73%) | |
| Multifocal | 0.4 | ||
| No | 26 (84%) | 11 (73%) | |
| Yes | 5 (16%) | 4 (27%) |
| Characteristics | NPDy n = 31 (100%) | PDy n = 15 (100%) | p-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Examiner 1 | |||
| Distribution 1 | 0.3 | ||
| Homogeneus | 1 (3.2%) | 2 (13%) | |
| Eterogeneus | 28 (90%) | 13 (87%) | |
| Not evaluable (NE) | 2 (6.5%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Brisk 1 | 0.011 | ||
| No | 4 (13%) | 8 (53%) | |
| Yes | 25 (81%) | 7 (47%) | |
| Heterogenous-NE | 2 (6.5%) | 0 (0%) | |
| High-TILs 1 | 69,268 (46,175–103,503) | 105,892 (72,054–190,685) | 0.022 |
| Low-TILs 1 | 18,312 (11,146–39,411) | 47,771 (30,652–101,114) | 0.001 |
| Average Count 1 | 49,363 (29,855–69,665) | 74,841 (47,969–147,890) | 0.009 |
| Density 20X 1 | 34,634 (23,089–51,752) | 52,946 (36,027–95,342) | 0.019 |
| Density 20X2 1 | 9156 (4976–19,705) | 23,885 (15,326–50,557) | 0.001 |
| Average Density 1 | 24,283 (14,928–34,833) | 37,420 (23,985–73,945) | 0.008 |
| Examiner 2 | |||
| Distribution 1 | 0.5 | ||
| Homogeneus | 28 (90%) | 15 (100%) | |
| Not evaluable (NE) | 3 (9.7%) | 0 (0%) | |
| Brisk 1 | 0.002 | ||
| No | 5 (16%) | 10 (67%) | |
| Yes | 23 (74%) | 5 (33%) | |
| Heterogenous-NE | 3 (9.7%) | 0 (0%) | |
| High-TILs 1 | 97,930 (54,936–151,672) | 160,032(103,105–203,025) | 0.028 |
| Low-TILs 1 | 15,127 (9554–33,439) | 71,656 (27,468–86,783) | 0.005 |
| Average Count 1 | 60,549 (33,503–90,764) | 107,484 (69,068–142,118) | 0.011 |
| Density 20X 1 | 48,965 (27,468–75,836) | 80,016 (51,552–101,513) | 0.031 |
| Density 20X/2 1 | 7564 (4777–15,724) | 35,828 (13,734–43,392) | 0.004 |
| Average Density 1 | 26,871 (17,217–45,382) | 53,742 (34,534–71,059) | 0.011 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, F.; Maffini, F.; Lepanto, D.; Vacirca, D.; Taormina, S.V.; De Berardinis, R.; Gandini, S.; Vignati, S.; Ranghiero, A.; Rappa, A.; et al. The Genetic and Immunologic Landscape Underlying the Risk of Malignant Progression in Laryngeal Dysplasia. Cancers 2023, 15, 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041117
Chu F, Maffini F, Lepanto D, Vacirca D, Taormina SV, De Berardinis R, Gandini S, Vignati S, Ranghiero A, Rappa A, et al. The Genetic and Immunologic Landscape Underlying the Risk of Malignant Progression in Laryngeal Dysplasia. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041117
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Francesco, Fausto Maffini, Daniela Lepanto, Davide Vacirca, Sergio Vincenzo Taormina, Rita De Berardinis, Sara Gandini, Silvano Vignati, Alberto Ranghiero, Alessandra Rappa, and et al. 2023. "The Genetic and Immunologic Landscape Underlying the Risk of Malignant Progression in Laryngeal Dysplasia" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041117
APA StyleChu, F., Maffini, F., Lepanto, D., Vacirca, D., Taormina, S. V., De Berardinis, R., Gandini, S., Vignati, S., Ranghiero, A., Rappa, A., Chiocca, S., Barberis, M., Tagliabue, M., & Ansarin, M. (2023). The Genetic and Immunologic Landscape Underlying the Risk of Malignant Progression in Laryngeal Dysplasia. Cancers, 15(4), 1117. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041117








