Phenotypic Characterization of Colorectal Liver Metastases: Capsule versus No Capsule and the Potential Role of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
3. Results
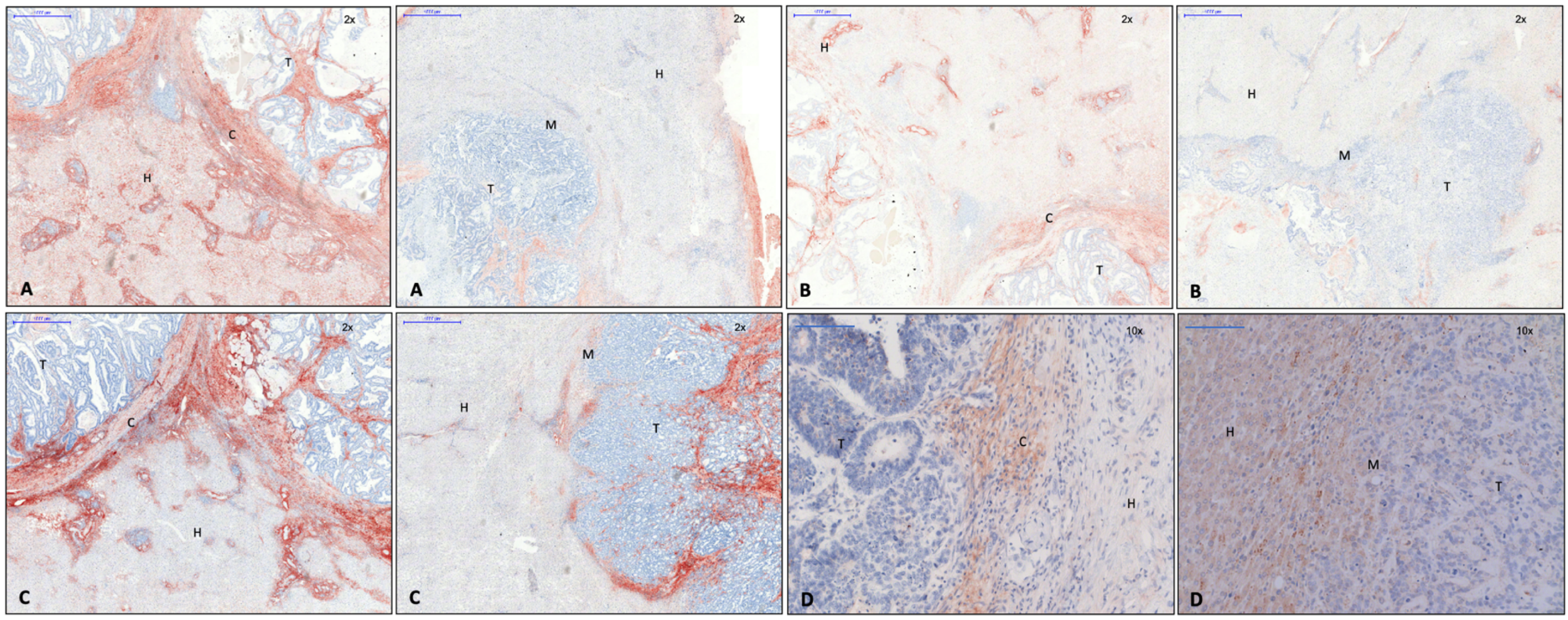
3.1. Identification of Capsule Components and Analysis of Their Arrangement
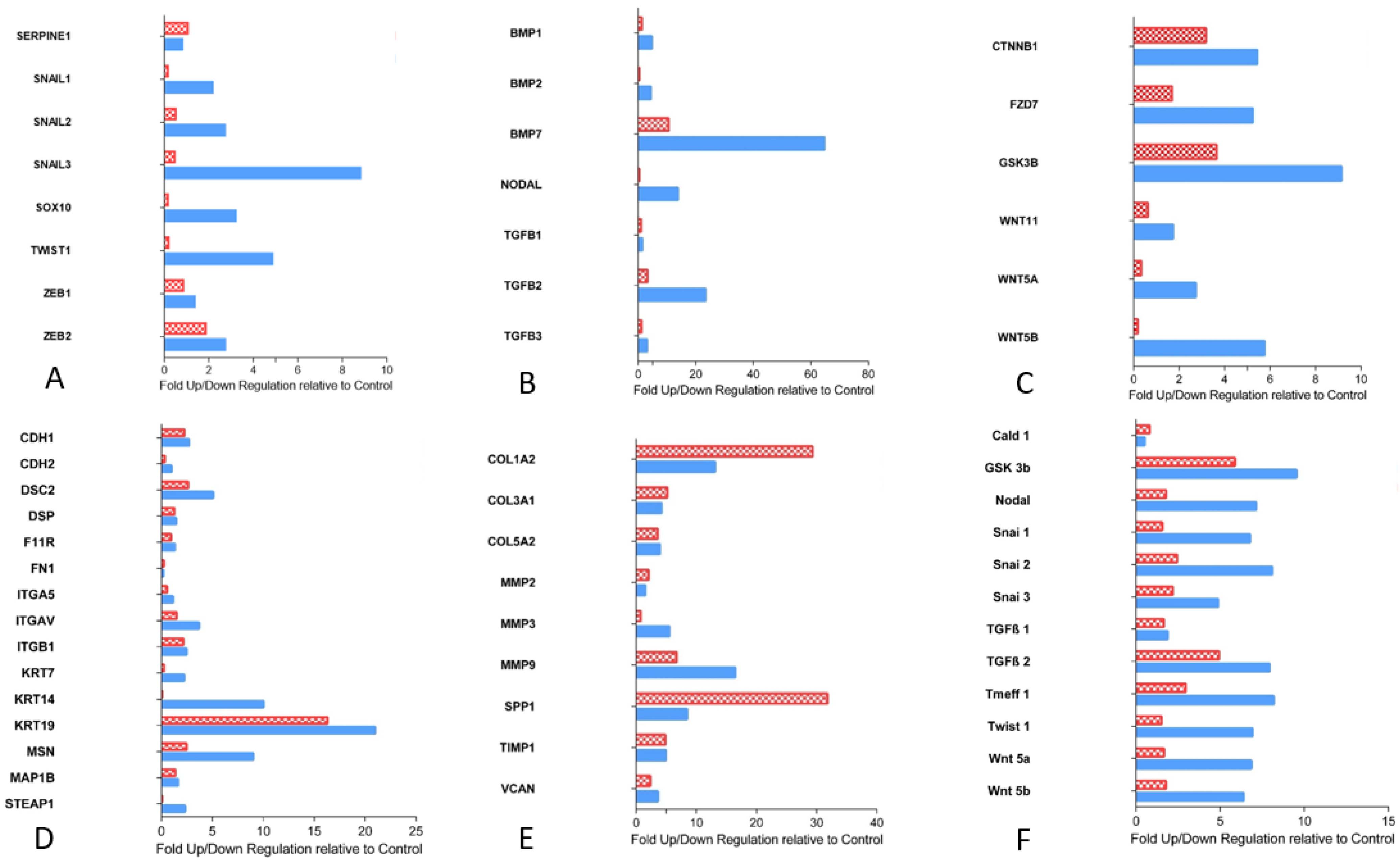
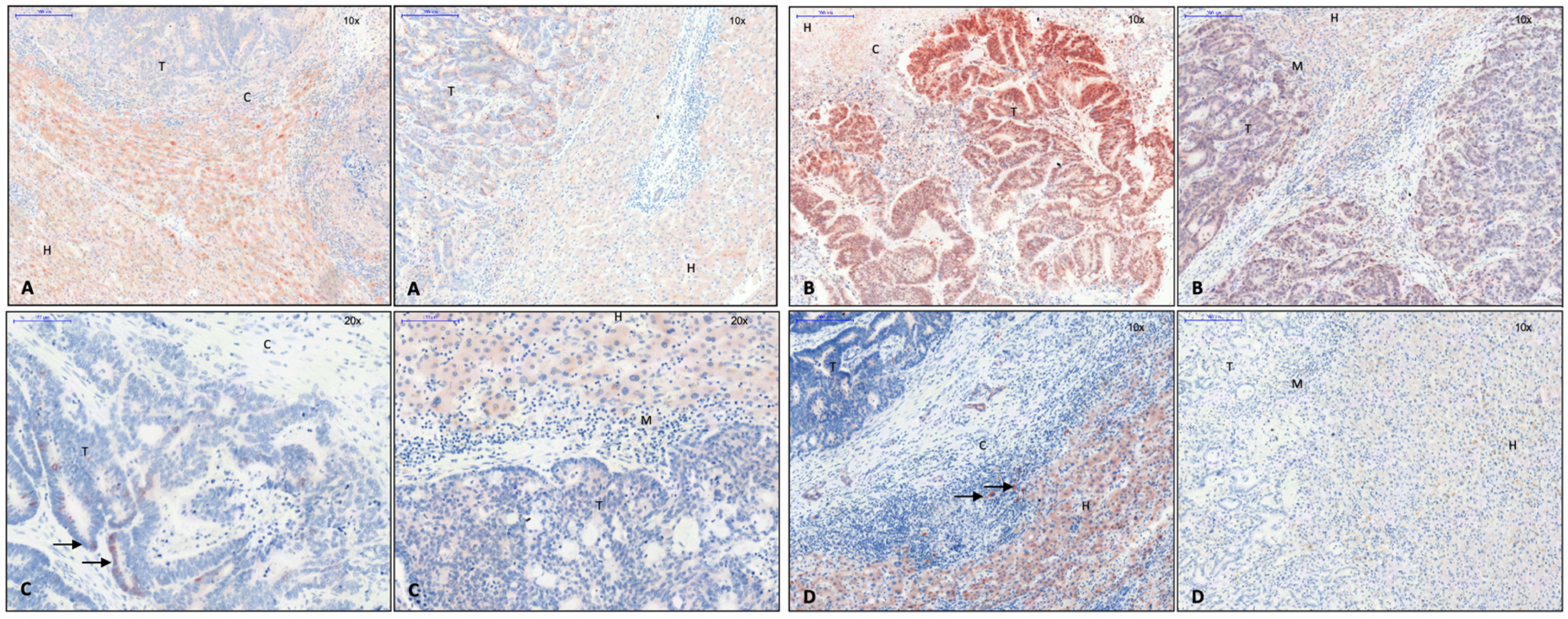
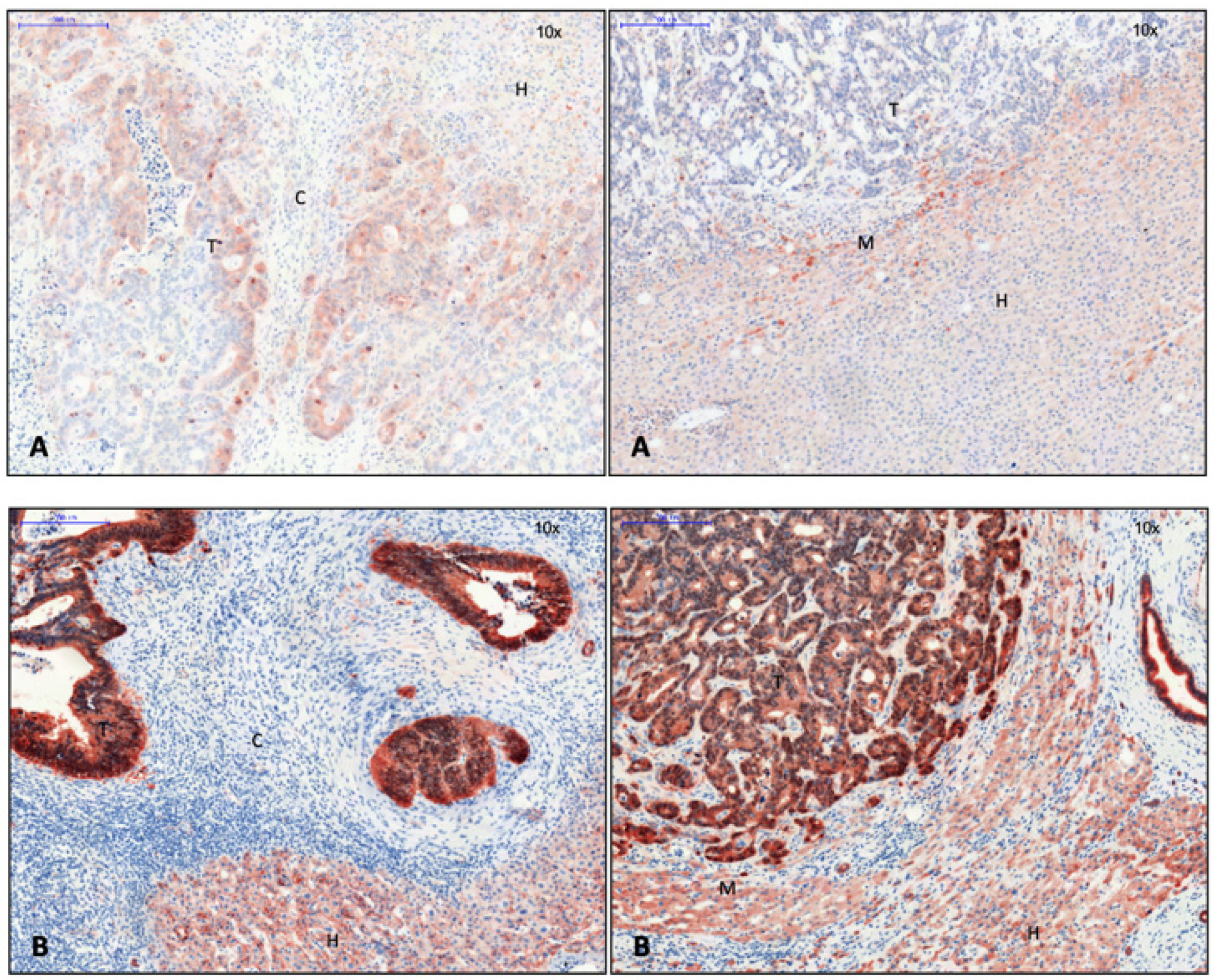
3.2. EMT Activity in CRLM with and without Capsule
3.2.1. Transcription Factors Involved in EMT
3.2.2. Proteins of TGF-ß Superfamily
3.2.3. Essential Gene Products Involved in wnt Pathway
3.2.4. Cell Junction Proteins
3.2.5. Gene Products of Relevance for Extracellular Matrix
3.2.6. Tumor Suppressor Gene
3.2.7. Custom Arrays: Quantitative Validation of EMT Arrays
4. Discussion
4.1. Activity of EMT at the Tumor Margin: Formation of a Fibrous Capsule Versus Invasive Tumor Growth
4.2. Encapsulated Versus Non-Encapsulated CRLM: A Case of Carcinoma Cell Grading and Tumor Growth Potential
4.3. Identified Capsule Components Suggest Mesenchymal Cells as a Potential Source
4.4. Matrix Architecture May Determine Capsule Function
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A-SMA | α smooth muscle actin |
| BMP | bone morphogenetic protein |
| CD | cluster of differentiation |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CRC | colorectal carcinoma |
| CRLM | colorectal liver metastases |
| CK | cytokeratin |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EMT | epithelial mesenchymal transition |
| MAP-kinase | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MAP1b | microtubule associated protein 1b |
| MMTV | Mouse mammary tumor virus |
| MET | mesenchymal epithelial transition |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteases |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| pGSK-3-β | phosphorylated glycogen synthase kinase |
| PNS | peripheral nervous system |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| SOX 10 | SRY-box transcription factor 10 |
| SRY | sex-determining region Y |
| Steap 1 | six transmembrane epithelial antigen of the prostate 1 |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor β |
| TIMP | tissue-inhibitor metalloproteases |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor α |
| TWIST | time without symptoms of disease and toxicity of treatment gene |
| Wnt | wingless-type MMTV integration site family |
| ZEB | zinc finger E-box binding homeobox |
References
- Brunner, S.M.; Kesselring, R.; Rubner, C.; Martin, M.; Jeiter, T.; Boerner, T.; Ruemmele, P.; Schlitt, H.J.; Fichtner-Feigl, S. Prognosis according to histochemical analysis of liver metastases removed at liver resection. Br. J. Surg. 2014, 101, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, K.; Yamamoto, J.; Moriya, Y.; Akasu, T.; Kosuge, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Hirohashi, S. Macroscopic intrabiliary growth of liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Surgery 1999, 126, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, J.; Sugihara, K.; Kosuge, T.; Takayama, T.; Shimada, K.; Yamasaki, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Hirohashi, S. Pathologic support for limited hepatectomy in the treatment of liver metastases from colorectal cancer. Ann. Surg. 1995, 221, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunevicius, R.; Nakanishi, H.; Ito, S.; Kozaki, K.I.; Kato, T.; Tatematsu, M.; Yasui, K. Clinicopathological significance of fibrotic capsule formation around liver metastasis from colorectal cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 127, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knijn, N.; de Ridder, J.A.; Punt, C.J.; de Wilt, J.H.; Nagtegaal, I.D. Histopathological evaluation of resected colorectal cancer liver metastases: What should be done? Histopathology 2013, 63, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, K.; Yamamoto, J.; Kosuge, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Nakanishi, Y.; Hirohashi, S. Fibrous pseudocapsule of metastatic liver tumors from colorectal carcinoma. Clinicopathologic study of 152 first resection cases. Cancer 2000, 89, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson, B.; Stenram, U.; Tranberg, K.G. Resection of colorectal liver metastases: 25-year experience. World J. Surg. 1998, 22, 268–276; discussion 276–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Galon, J. The immune contexture in human tumours: Impact on clinical outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, P.-J.; van der Stok, E.P.; Teuwen, L.-A.; van den Eynden, G.G.; Illemann, M.; Frentzas, S.; Majeed, A.W.; Eefsen, R.L.; van den Braak, R.R.J.C.; Lazaris, A.; et al. International consensus guidelines for scoring the histopathological growth patterns of liver metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1427–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiagen GmbH. RNeasy FFPE Handbook: For Purification of Total RNA from Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Sections; 2014; pp. 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Qiagen GmbH. RT2 PreAMP cDNA Synthesis Handbook: For Synthesis and Preamplification of cDNA from For Synthesis and Preamplification of cDNA from Small RNA Samples and RNA from Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Samples; 2011; pp. 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Saiki, R.K.; Gelfand, D.H.; Stoffel, S.; Scharf, S.J.; Higuchi, R.; Horn, G.T.; Mullis, K.B.; Erlich, H.A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science 1988, 239, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiagen GmbH. RT2 Profiler PCR Array Handbook: For Pathway-Focused Gene Expression Profiling Using Real-Time RT-PCR; 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffl, M.W. Real-time RT-PCR: Neue Ansätze zur exakten mRNA Quantifizierung. BIOspektrum 1/04. BIOspektrum 2004, 10, 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, K.; Moody, C.J. Caldesmon: A calmodulin-binding actin-regulatory protein. Cell Calcium. 1986, 7, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, C.-M. Caldesmon as a therapeutic target for proliferative vascular diseases. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, E.R. Molecular Genetics of Colorectal Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2011, 6, 479–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeGolvan, M.P.; Resnick, M. Pathobiology of colorectal cancer hepatic metastases with an emphasis on prognostic factors. J. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 102, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gras, B.; Jacqueroud, L.; Wierinckx, A.; Lamblot, C.; Fauvet, F.; Lachuer, J.; Puisieux, A.; Ansieau, S. Snail family members unequally trigger EMT and thereby differ in their ability to promote the neoplastic transformation of mammary epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Heng, L.; Zhong, L.; Su, X.; Rong, R.; Hu, S.; Liu, W.; Jia, B.; et al. SOX10, a novel HMG-box-containing tumor suppressor, inhibits growth and metastasis of digestive cancers by suppressing the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 10571–10583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisberg, M.; Hanai, J.-I.; Sugimoto, H.; Mammoto, T.; Charytan, D.; Strutz, F.; Kalluri, R. BMP-7 counteracts TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and reverses chronic renal injury. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.N. Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP) signaling in development and human diseases. Genes Dis. 2014, 1, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeisberg, M.; Bottiglio, C.; Kumar, N.; Maeshima, Y.; Strutz, F.; Müller, G.A.; Kalluri, R. Bone morphogenic protein-7 inhibits progression of chronic renal fibrosis associated with two genetic mouse models. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2003, 285, F1060–F1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, Y.; Long, X.; Xiao, P.; Ren, X.; Yu, J. BMP signaling and its paradoxical effects in tumorigenesis and dissemination. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78206–78218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chougule, P.; Sumitran-Holgersso, S. Cytokeratins of the Liver and Intestine Epithelial Cells during Development and Disease. In Cytokeratins—Tools in Oncology; Hamilton, G., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jonsdottir, H.R.; Arason, A.J.; Palsson, R.; Franzdottir, S.R.; Gudbjartsson, T.; Isaksson, H.J.; Gudmundsson, G.; Gudjonsson, T.; Magnusson, M.K. Basal cells of the human airways acquire mesenchymal traits in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and in culture. Lab. Investig. 2015, 95, 1418–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastuszak, M.; Groszewski, K.; Dyrla, P.; Wojtuń, S.; Gil, J. Cytokeratins in gastroenterology. Systematic review. Gastroenterol. Rev. 2015, 10, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offenberg, H.; Brunner, N.; Mansilla, F.; Torben, F.O.; Birkenkamp-Demtroder, K. TIMP-1 expression in human colorectal cancer is associated with TGF-B1, LOXL2, INHBA1, TNF-AIP6 and TIMP-2 transcript profiles. Mol. Oncol. 2008, 2, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, A.H.; Raufman, J.-P.; Xie, G. The role of matrix metalloproteinases in colorectal cancer. Cancers 2014, 6, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenskiöld, M.; Holmdahl, L.; Falk, P.; Ivarsson, M.-L. Increased plasma MMP-2 protein expression in lymph node-positive patients with colorectal cancer. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2005, 20, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshio, T.; Morita, T.; Kimura, Y.; Tsujii, M.; Hayashi, N.; Sobue, K. Caldesmon suppresses cancer cell invasion by regulating podosome/invadopodium formation. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 3777–3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Cai, Y.; Xie, T.; Shi, M.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, B. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta regulates Snail and β-catenin expression during Fas-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition in gastrointestinal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 2734–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Marck, V.L.; Bracke, M.E. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Human Cancer: Landes Bioscience; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Coulson-Thomas, V.J.; Coulson-Thomas, Y.M.; Gesteira, T.F.; de Paula, C.A.A.; Mader, A.M.; Waisberg, J.; Pinhal, M.A.; Friedl, A.; Toma, L.; Nader, H.B. Colorectal cancer desmoplastic reaction up-regulates collagen synthesis and restricts cancer cell invasion. Cell Tissue Res. 2011, 346, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Feng, B.; Dong, T.; Yan, G.; Tan, B.; Shen, H.; Huang, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, P.; et al. Up-regulation of type I collagen during tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer revealed by quantitative proteomic analysis. J. Proteom. 2013, 94, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardelli, C.; Sakko, A.J.; Ween, M.P.; Russell, D.L.; Horsfall, D.J. The biological role and regulation of versican levels in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pukkila, M.; Kosunen, A.; Ropponen, K.; Virtaniemi, J.; Kellokoski, J.; Kumpulainen, E.; Pirinen, R.; Nuutinen, J.; Johansson, R.; Kosma, V.-M. High stromal versican expression predicts unfavourable outcome in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 60, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirinen, R.; Leinonen, T.; Böhm, J.; Johansson, R.; Ropponen, K.; Kumpulainen, E.; Kosma, V.-M. Versican in nonsmall cell lung cancer: Relation to hyaluronan, clinicopathologic factors, and prognosis. Hum. Pathol. 2005, 36, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardelli, C.; Mayne, K.; Sykes, P.; Raymond, W.A.; McCaul, K.; Marshall, V.R.; Horsfall, D.J. Elevated levels of versican but not decorin predict disease progression in early-stage prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levental, K.R.; Yu, H.; Kass, L.; Lakins, J.N.; Egeblad, M.; Erler, J.T.; Fong, S.F.T.; Csiszar, K.; Giaccia, A.; Weninger, W.; et al. Matrix Crosslinking Forces Tumor Progression by Enhancing Integrin signaling. Cell 2009, 139, 891–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
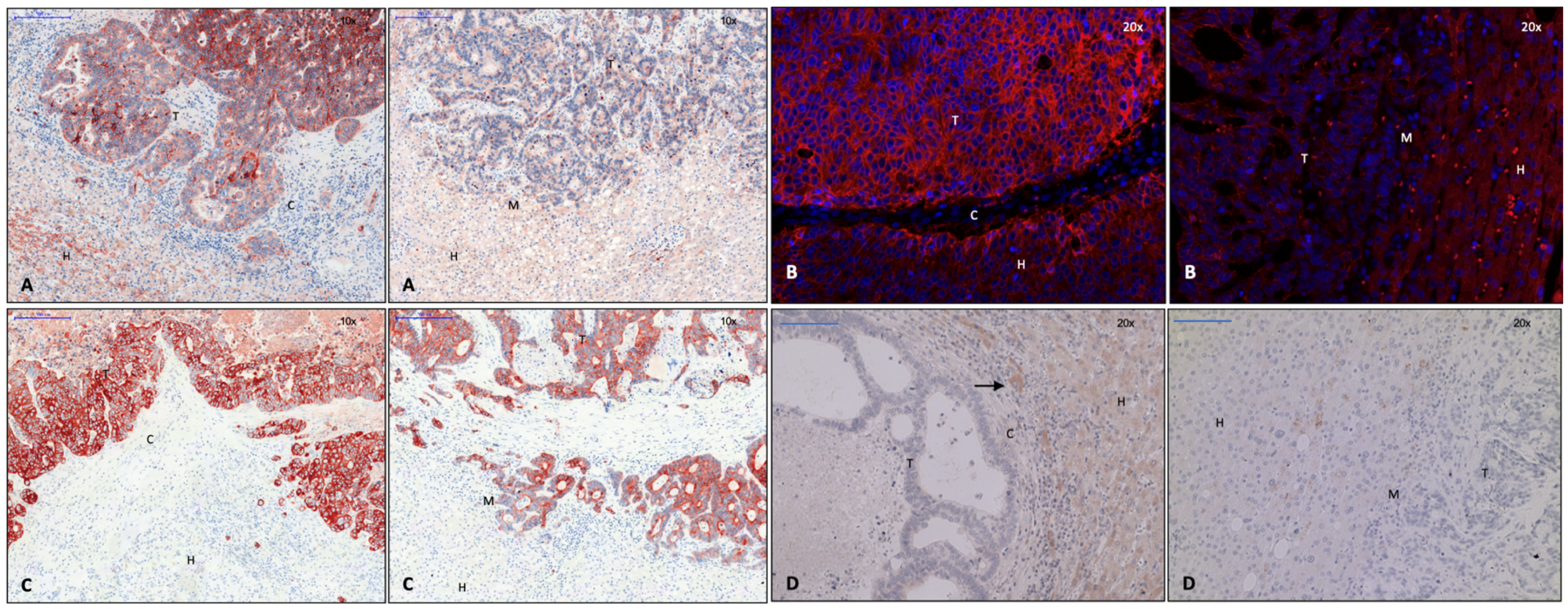
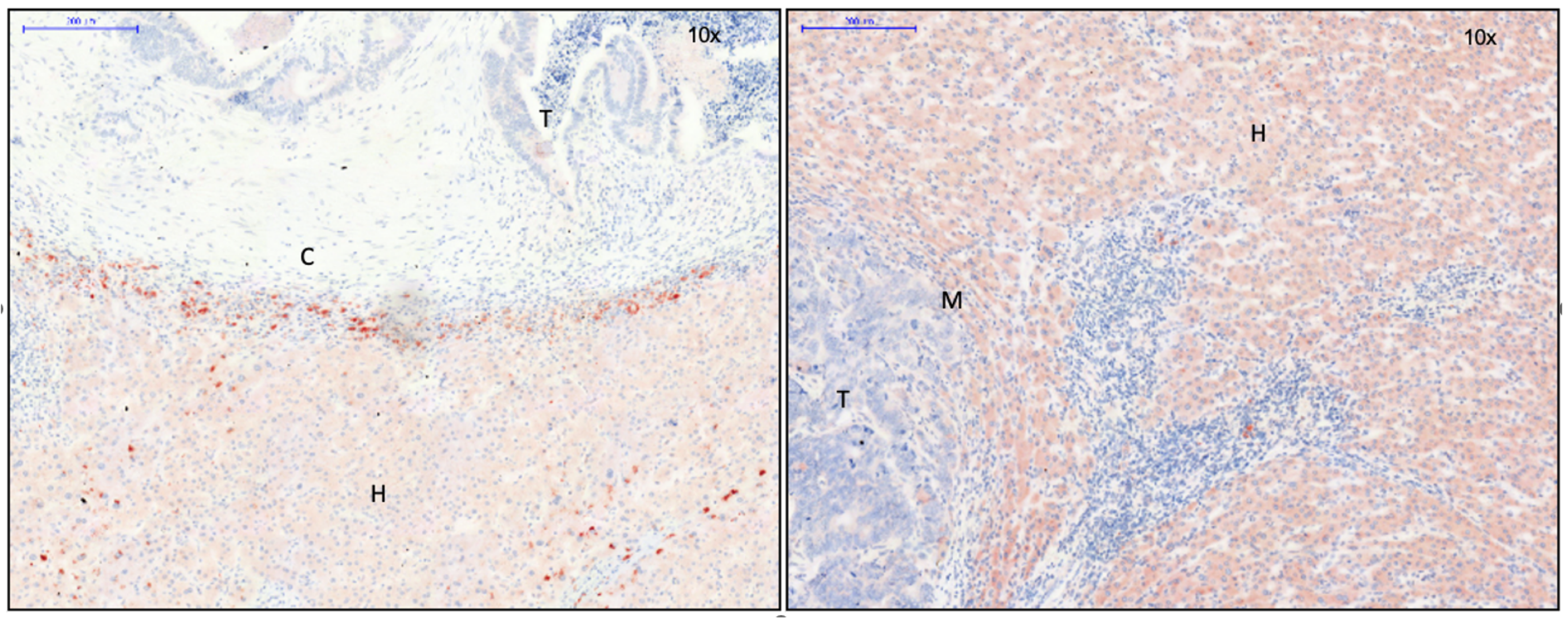
| Antibody | Host | Reactivity | Clonality | Dilution | Dwell Time AEC | Producer Catalogue Number | Concentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-Catenin | Rabbit | Human, Mouse, Rat, Ape, Zebrafish | Polyclonal | 1:50 | 4 min | CellSignaling #9562 | |
| Caldesmon 1 | Rabbit | Human | Polyclonal, Clone: RB19749 | 1:10 | 1.5 min | Abgent AP6609c | 0.25 mg/mL |
| Collagen 1 | Mouse | Human, Rat, Cow, Game, Pig, Rabbit | Monoclonal, Clone: COL-1 | 1:200 | 2 min | Abcam Ab90395 | |
| Col 3 | Mouse | Human, Mouse, Rat | Monoclonal, Clone: Col-29 | 1:25 | 3 min | Abcam Ab82354 | |
| Col 5 | Mouse | Human, Sheep, Rabbit, Cow, Dog, Pig, Kangaroo | Monoclonal, Clone: 1E2-E4/Col5 | 1:25 | 3 min | Abcam Ab112551 | |
| Cy3 Secondary antibody | Goat | IgG Rabbit | Polyclonal | 1:100 | - | Abcam Ab6939 | |
| E-Cadherin | Rabbit | Human, Mouse | Monoclonal | 1:100 | 3.5 min | CellSignaling 24E10, #3195 | |
| Fibronectin 1 | Mouse | Human | Monoclonal, Clone: IST-4 | 1:200 | 2.5 min | Sigma-Aldrich F0916 | |
| Phospho-GSK-3 α, β (Ser21/9) | Rabbit | Human, Mouse, Rabbit, Ape, Zebrafish | Polyclonal | 1:50 | 3 min | CellSignaling #9331 | |
| Keratin 19 (BA17) | Mouse | Human | Monoclonal | 1:200 | 2 min | CellSignaling #4558 | |
| MAP1b | Mouse | Human, Rat, Cow | Monoclonal, Clone: 3G5 | 1:100 | 3 min | Abcam Ab79195 | |
| Snail 1 | Mouse | Human | Monoclonal | 1:50 | 1 min | LifeSpanBioSciences, Inc. LS-C161335 | |
| Snail 3 | Rabbit | Human | Polyclonal | 1:150 | 2 min | Sigma-Aldrich HPA016757 | 0.18 mg/mL |
| Sox 10 | Mouse | Human | Monoklonal, Clone: 1E6 | 1:200 | 1 min | Sigma-Aldrich SAB1402361-100UG | 1 mg/mL |
| Tomoregulin 1 | Goat | Human, Mouse, Rat | Polyclonal | 1:100 | 3 min | Biorbyt Orb101484 | 0.5 mg/mL |
| Twist 1 | Mouse | Human | Monoclonal, Clone: 3E10 | 1:100 | 5 min | Abcam Ab135180 | 0.5 mg/mL |
| Versican | Mouse | Human | Monoclonal, Clone: 8.S.270 | 1:150 | 3 min | US Biological L1350A | ~~1 mg/mL |
| No Capsule (N = 138; 62.2%) | Capsule (N = 84; 37.8%) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colon/Rectum | 81/57 | 52/32 | 0.673 |
| Synchronous/Metachronous liver metastasis | 63/75 | 35/49 | 0.580 |
| Singular/Multiple liver metastasis | 51/87 | 33/51 | 0.776 |
| No Chemo/Chemo (within 3 months prior to liver resection) | 71/67 | 50/34 | 0.268 |
| T1/2/3/4 (primary tumor) | 6/11/89/29 | 1/14/55/13 | 0.112 |
| N 0/1/2 (primary tumor) | 35/51/49 | 40/23/20 | 0.004 * |
| G1/2/3 (primary tumor) | 1/104/31 | 1/63/19 | 0.939 |
| No Capsule (N = 14) | Capsule (N = 20) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colon/Rectum | 9/5 | 10/10 | 0.495 |
| Synchronous/Metachronous liver metastasis | 8/6 | 3/17 | 0.023 * |
| Singular/Multiple liver metastasis | 4/10 | 8/12 | 0.717 |
| No Chemo/Chemo (within 3 months prior to liver resection) | 14/0 | 20/0 | |
| T1/2/3/4 (primary tumor) | 0/1/10/3 | 0/6/13/1 | 0.133 |
| N 0/1/2 (primary tumor) | 2/5/7 | 11/3/6 | 0.051 |
| G1/2/3 (primary tumor) | 0/11/3 | 1/15/4 | 0.697 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fleig, C.; Evert, K.; Schlitt, H.J.; Fichtner-Feigl, S.; Brunner, S.M. Phenotypic Characterization of Colorectal Liver Metastases: Capsule versus No Capsule and the Potential Role of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition. Cancers 2023, 15, 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041056
Fleig C, Evert K, Schlitt HJ, Fichtner-Feigl S, Brunner SM. Phenotypic Characterization of Colorectal Liver Metastases: Capsule versus No Capsule and the Potential Role of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041056
Chicago/Turabian StyleFleig, Claudia, Katja Evert, Hans J. Schlitt, Stefan Fichtner-Feigl, and Stefan M. Brunner. 2023. "Phenotypic Characterization of Colorectal Liver Metastases: Capsule versus No Capsule and the Potential Role of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041056
APA StyleFleig, C., Evert, K., Schlitt, H. J., Fichtner-Feigl, S., & Brunner, S. M. (2023). Phenotypic Characterization of Colorectal Liver Metastases: Capsule versus No Capsule and the Potential Role of Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition. Cancers, 15(4), 1056. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041056





