A Novel Blood Proteomic Signature for Prostate Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Blood Collection and Serum Isolation
2.3. Serum Immunodepletion and Filtration
2.4. PSA Measurement, Protein Digestion, and Peptide Isolation
2.5. SWATH Analysis
2.6. Processing of MS Proteomic Data
2.7. Biomarker Analysis and Development and Evaluation of Classification and Regression Models
2.8. Functional Annotation and Pathway Analysis
3. Results
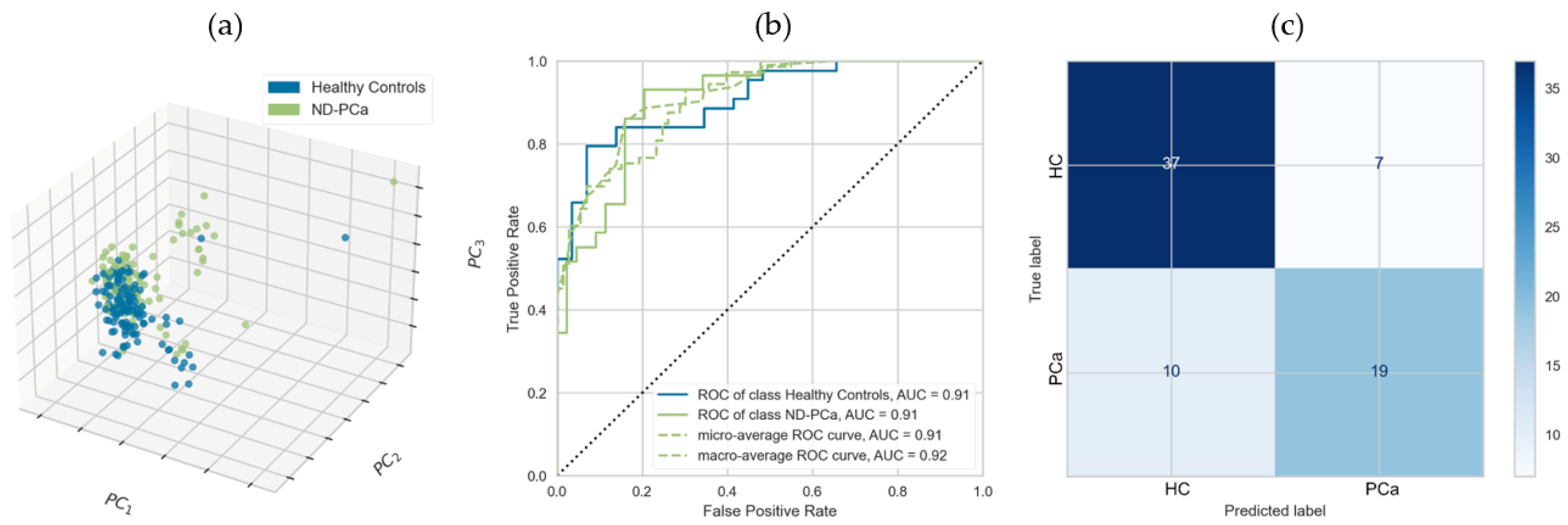
3.1. Serum Proteome Reveals a Signature of Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer Patients
3.2. Validation of Proteomic Biomarkers Using an External, Independent Cohort
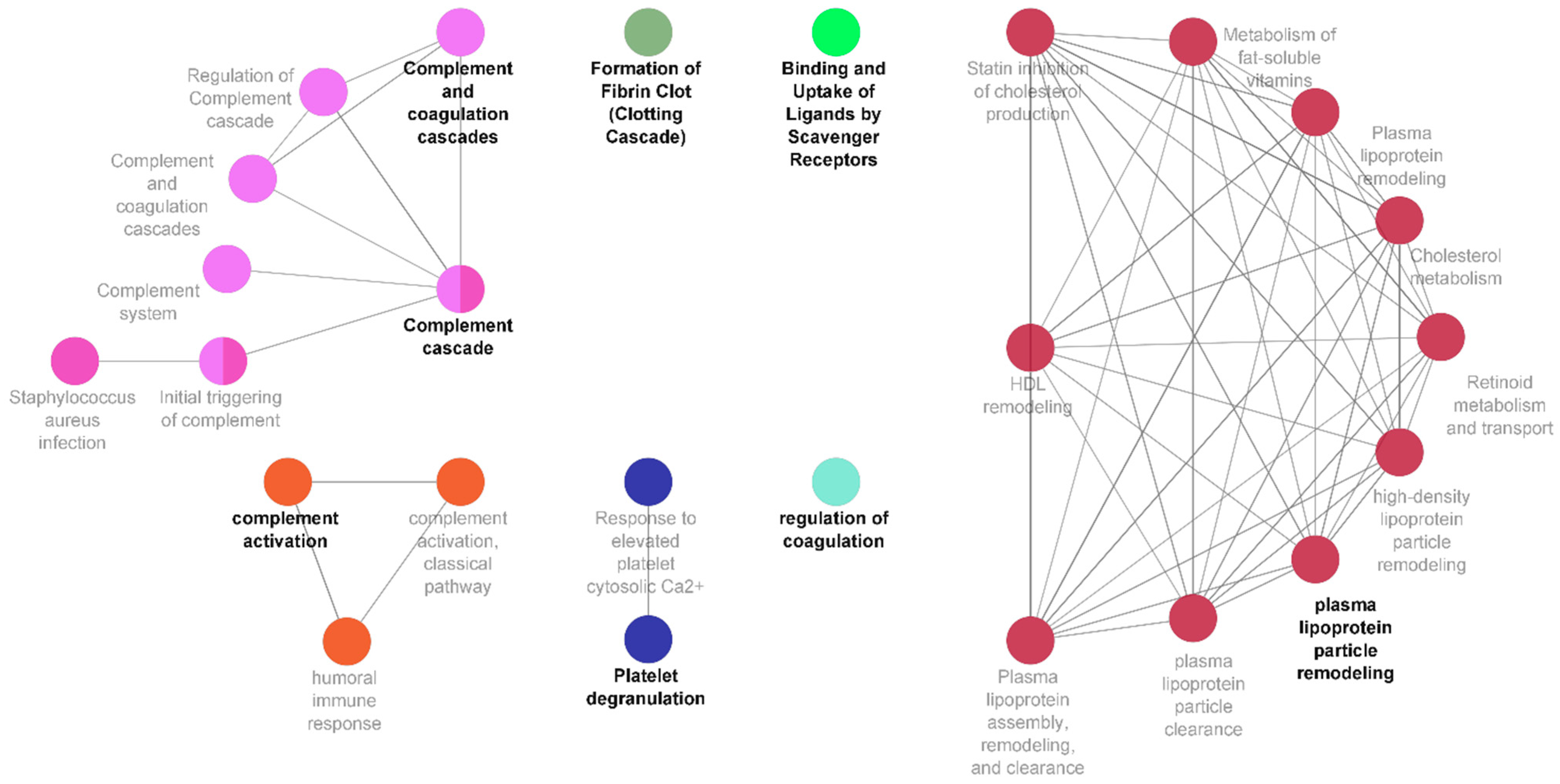
3.3. A Central Role for Complement and Coagulation Cascade in Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer
3.4. Treatment-Related Changes in the Proteomic Signature of Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prostate Cancer Statistics. Cancer Research UK. Available online: https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/statistics-by-cancer-type/prostate-cancer (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- USCS. Data Visualizations. 2021. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/cancer/uscs/dataviz/index.htm (accessed on 18 December 2022).
- Overview. Prostate Cancer: Diagnosis and Management. Guidance. NICE. 2021. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng131/chapter/recommendations (accessed on 4 January 2023).
- Trogdon, J.G.; Falchook, A.D.; Basak, R.; Carpenter, W.R.; Chen, R.C. Total Medicare Costs Associated with Diagnosis and Treatment of Prostate Cancer in Elderly Men. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PSA. North Bristol NHS Trust. Available online: https://www.nbt.nhs.uk/severn-pathology/requesting/test-information/psa (accessed on 18 March 2021).
- Richardson, T.D.; Oesterling, J.E. Age-Specific Reference Ranges for Serum Prostate-Specific Antigen. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 1997, 24, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrate, A.; Lughezzani, G.; Gadda, G.M.; Lista, G.; Kinzikeeva, E.; Fossati, N.; Larcher, A.; Dell’Oglio, P.; Mistretta, F.; Buffi, N.; et al. Clinical Use of [-2]ProPSA (P2PSA) and Its Derivatives (%p2PSA and Prostate Health Index) for the Detection of Prostate Cancer: A Review of the Literature. Korean J. Urol. 2014, 55, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, F.H.; Hugosson, J.; Roobol, M.J.; Tammela, T.L.J.; Ciatto, S.; Nelen, V.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Lujan, M.; Lilja, H.; Zappa, M.; et al. Screening and Prostate-Cancer Mortality in a Randomized European Study. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeb, S.; Carter, H.B.; Berndt, S.I.; Ricker, W.; Schaeffer, E.M. Complications after Prostate Biopsy: Data from SEER-Medicare. J. Urol. 2011, 186, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.R.; de Bastos, M.L.; Carvalho, M.; Guedes de Pinho, P. Biomarker Discovery in Human Prostate Cancer: An Update in Metabolomics Studies. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 9, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.L.; Jordan, K.W.; Ratai, E.M.; Sheng, J.; Adkins, C.B.; DeFeo, E.M.; Jenkins, B.G.; Ying, L.; McDougal, W.S.; Cheng, L.L. Metabolomic Imaging for Human Prostate Cancer Detection. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 16ra8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriole, G.L.; Crawford, E.D.; Grubb, R.L.; Buys, S.S.; Chia, D.; Church, T.R.; Fouad, M.N.; Isaacs, C.; Kvale, P.A.; Reding, D.J.; et al. Prostate Cancer Screening in the Randomized Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial: Mortality Results after 13 Years of Follow-Up. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knipper, S.; Graefen, M. Treatment Options for Localized Prostate Cancer. Onkologe 2019, 25, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amico, A.V.; Whittington, R.; Bruce Malkowicz, S.; Schultz, D.; Blank, K.; Broderick, G.A.; Tomaszewski, J.E.; Renshaw, A.A.; Kaplan, I.; Beard, C.J.; et al. Biochemical Outcome after Radical Prostatectomy, External Beam Radiation Therapy, or Interstitial Radiation Therapy for Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1998, 280, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourinho-Barbosa, R.R.; Srougi, V.; Nunes-Silva, I.; Baghdadi, M.; Rembeyo, G.; Eiffel, S.S.; Barret, E.; Rozet, F.; Galiano, M.; Cathelineau, X.; et al. Biochemical Recurrence after Radical Prostatectomy: What Does It Mean? Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2018, 44, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, A.; Liu, L.Y.; Nyalwidhe, J.O.; Semmes, O.J.; Vesprini, D.; Downes, M.R.; Boutros, P.C.; Liu, S.K.; Kislinger, T. Proteomic Discovery of Non-Invasive Biomarkers of Localized Prostate Cancer Using Mass Spectrometry. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2021, 18, 707–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geyer, P.E.; Holdt, L.M.; Teupser, D.; Mann, M. Revisiting Biomarker Discovery by Plasma Proteomics. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2017, 13, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geary, B.; Walker, M.J.; Snow, J.T.; Lee, D.C.H.; Pernemalm, M.; Maleki-Dizaji, S.; Azadbakht, N.; Apostolidou, S.; Barnes, J.; Krysiak, P.; et al. Identification of a Biomarker Panel for Early Detection of Lung Cancer Patients. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 3369–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, B.C.; Hunter, C.L.; Liu, Y.; Schilling, B.; Rosenberger, G.; Bader, S.L.; Chan, D.W.; Gibson, B.W.; Gingras, A.C.; Held, J.M.; et al. Multi-Laboratory Assessment of Reproducibility, Qualitative and Quantitative Performance of SWATH-Mass Spectrometry. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjo, S.I.; Santa, C.; Manadas, B. SWATH-MS as a Tool for Biomarker Discovery: From Basic Research to Clinical Applications. Proteomics 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajic, T.; Liu, Y.; Arvaniti, E.; Surinova, S.; Williams, E.G.; Schiess, R.; Hüttenhain, R.; Sethi, A.; Pan, S.; Brentnall, T.A.; et al. Similarities and Differences of Blood N-Glycoproteins in Five Solid Carcinomas at Localized Clinical Stage Analyzed by SWATH-MS. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 2819–2831.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, L.C.; Navarro, P.; Tate, S.; Röst, H.; Selevsek, N.; Reiter, L.; Bonner, R.; Aebersold, R. Targeted Data Extraction of the MS/MS Spectra Generated by Data-Independent Acquisition: A New Concept for Consistent and Accurate Proteome Analysis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2012, 11, O111.016717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittadi, R.; Franceschini, R.; Fortunato, A.; Zancan, M.; Barichello, M.; Tasca, A.; Giavarina, D.; Peloso, L.; Soffiati, G.; Gion, M. Interchangeability and Diagnostic Accuracy of Two Assays for Total and Free Prostate-Specific Antigen: Two Not Always Related Items. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2007, 22, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muazzam, A.; Chiasserini, D.; Kelsall, J.; Geifman, N.; Whetton, A.D.; Townsend, P.A. A Prostate Cancer Proteomics Database for Swath-Ms Based Protein Quantification. Cancers 2021, 13, 5580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.; Kuharev, J.; Gillet, L.C.; Bernhardt, O.M.; MacLean, B.; Röst, H.L.; Tate, S.A.; Tsou, C.C.; Reiter, L.; Distler, U.; et al. A Multicenter Study Benchmarks Software Tools for Label-Free Proteome Quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleman, J.; Rost, H.L.; Rosenberger, G.; Schmitt, U.; Malmstrom, L.; Malmstrom, J.; Levander, F. DIANA-Algorithmic Improvements for Analysis of Data-Independent Acquisition MS Data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberger, G.; Bludau, I.; Schmitt, U.; Heusel, M.; Hunter, C.L.; Liu, Y.; Maccoss, M.J.; Maclean, B.X.; Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Pedrioli, P.G.A.; et al. Statistical Control of Peptide and Protein Error Rates in Large-Scale Targeted Data-Independent Acquisition Analyses. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blattmann, P.; Heusel, M.; Aebersold, R. SWATH2stats: An R/Bioconductor Package to Process and Convert Quantitative SWATH-MS Proteomics Data for Downstream Analysis Tools. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Chang, C.Y.; Clough, T.; Broudy, D.; Killeen, T.; MacLean, B.; Vitek, O. MSstats: An R Package for Statistical Analysis of Quantitative Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomic Experiments. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2524–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGurk, K.A.; Dagliati, A.; Chiasserini, D.; Lee, D.; Plant, D.; Baricevic-Jones, I.; Kelsall, J.; Eineman, R.; Reed, R.; Geary, B.; et al. The Use of Missing Values in Proteomic Data-Independent Acquisition Mass Spectrometry to Enable Disease Activity Discrimination. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for Comprehensive and Integrative Metabolomics Data Analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2019, 68, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Machine Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Bengfort, B.; Bilbro, R. Yellowbrick: Visualizing the Scikit-Learn Model Selection Process. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGO: A Cytoscape Plug-in to Decipher Functionally Grouped Gene Ontology and Pathway Annotation Networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindea, G.; Galon, J.; Mlecnik, B. CluePedia Cytoscape Plugin: Pathway Insights Using Integrated Experimental and in Silico Data. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newcomer, L.M.; Stanford, J.L.; Blumenstein, B.A.; Brawer, M.K. Temporal Trends in Rates of Prostate Cancer: Declining Incidence of Advanced Stage Disease, 1974 to 1994. J. Urol. 1997, 158, 1427–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, I.M.; Pauler, D.K.; Goodman, P.J.; Tangen, C.M.; Lucia, M.S.; Parnes, H.L.; Minasian, L.M.; Ford, L.G.; Lippman, S.M.; Crawford, E.D.; et al. Prevalence of Prostate Cancer among Men with a Prostate-Specific Antigen Level ≤4.0 Ng per Milliliter. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 2239–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Minno, A.; Aveta, A.; Gelzo, M.; Tripodi, L.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Crocetto, F.; Imbimbo, C.; Castaldo, G. 8-Hydroxy-2-Deoxyguanosine and 8-Iso-Prostaglandin F2α: Putative Biomarkers to Assess Oxidative Stress Damage Following Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy (RARP). J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljubić, S.; Sermek, A.; Prgomet Sečan, A.; Prpić, M.; Jakšić, B.; Murgić, J.; Fröbe, A.; Ugarković, Đ.; Feliciello, I. Alpha Satellite RNA Levels Are Upregulated in the Blood of Patients with Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Genes 2022, 13, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevo, A.; Navaratnam, A.; Andrews, P. Prostate Cancer and the Role of Biomarkers. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 2120–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borque-Fernando, Á.; Rubio-Briones, J.; Esteban, L.M.; Dong, Y.; Calatrava, A.; Gómez-Ferrer, Á.; Gómez-Gómez, E.; Gil Fabra, J.M.; Rodríguez-García, N.; López González, P.; et al. Role of the 4Kscore Test as a Predictor of Reclassification in Prostate Cancer Active Surveillance. Prostate Cancer Prostat. Dis. 2019, 22, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyten, G.H.J.M.; Hessels, D.; Jannink, S.A.; Smit, F.P.; De Jong, H.; Cornel, E.B.; De Reijke, T.M.; Vergunst, H.; Kil, P.; Knipscheer, B.C.; et al. Prospective Multicentre Evaluation of PCA3 and TMPRSS2-ERG Gene Fusions as Diagnostic and Prognostic Urinary Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, M.; Nordström, T.; Aly, M.; Adolfsson, J.; Wiklund, P.; Brandberg, Y.; Thompson, J.; Wiklund, F.; Lindberg, J.; Presti, J.C.; et al. The Stockholm-3 (STHLM3) Model Can Improve Prostate Cancer Diagnostics in Men Aged 50–69 Yr Compared with Current Prostate Cancer Testing. Eur. Urol. Focus 2018, 4, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamil, B.S.; Mares, I. Title: Diagnostic Performance of ExosomeDxTM ’s ExoDxTMProstate Test and Opko Health’s 4kScore ®Test by Intelliscore Threshold. Available online: https://app.oxfordabstracts.com/events/1582/program-app/submission/205431 (accessed on 22 September 2021).
- Waterhouse, R.L.; Van Neste, L.; Moses, K.A.; Barnswell, C.; Silberstein, J.L.; Jalkut, M.; Tutrone, R.; Sylora, J.; Anglade, R.; Murdock, M.; et al. Evaluation of an Epigenetic Assay for Predicting Repeat Prostate Biopsy Outcome in African American Men. Urology 2019, 128, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metamark Seeing Rapid Uptake of Promark Proteomic Test for Prostate Cancer. Genomeweb. Available online: https://www.genomeweb.com/proteomics-protein-research/metamark-seeing-rapid-uptake-promark-proteomic-test-prostate-cancer (accessed on 23 September 2021).
- Mohler, J.L.; Armstrong, A.J.; Bahnson, R.R.; D’Amico, A.V.; Davis, B.J.; Eastham, J.A.; Enke, C.A.; Farrington, T.A.; Higano, C.S.; Horwitz, E.M.; et al. Prostate Cancer, Version 1.2016: Featured Updates to the NCCN Guidelines. JNCCN J. Nat. Comprehens. Cancer Netw. 2016, 14, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.E.; Feng, F.Y.; Ghadessi, M.; Erho, N.; Crisan, A.; Buerki, C.; Sundi, D.; Mitra, A.P.; Vergara, I.A.; Thompson, D.J.S.; et al. A Genomic Classifier Predicting Metastatic Disease Progression in Men with Biochemical Recurrence after Prostatectomy. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2014, 17, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorff, T.B.; Blanchard, S.; Carruth, P.; Wagner, J.; Kuhn, P.; Chaudhry, A.; Adkins, L.; Thomas, S.; Martirosyan, H.; Chu, P.; et al. A Phase I Study to Evaluate PSCA-Targeting Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T Cells for Patients with PSCA+ Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (MCRPC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, TPS250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pye, H.; Ahmed, H.; Heavey, S.; Stopka-Farooqui, U.; Johnston, E.; Schiess, R.; Gillessen, S.; Punwani, S.; Emberton, M.; Whitaker, H. Evaluation of Proclarix, a Prostate Cancer Risk Score, Used Together with Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Diagnosis of Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcila-Ruiz, M.J.; Assimos, D.G.; Brucker, B.M.; Chancellor, M.B.; Druskin, S.C.; Curtis Nickel, J.; Partin, A.W.; Shapiro, E. Best of the 2017 AUA Annual Meeting: Highlights From the 2017 American Urological Association Annual Meeting, May 12–16, 2017, Boston, MA, USA. Rev. Urol. 2017, 19, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cima, I.; Schiess, R.; Wild, P.; Kaelin, M.; Schüffler, P.; Lange, V.; Picotti, P.; Ossola, R.; Templeton, A.; Schubert, O.; et al. Cancer Genetics-Guided Discovery of Serum Biomarker Signatures for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Prostate Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3342–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hand, D.J. Measuring Classifier Performance: A Coherent Alternative to the Area under the ROC Curve. Mach. Learn. 2009, 77, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikkinen, K.A.O.; Dahm, P.; Lytvyn, L.; Heen, A.F.; Vernooij, R.W.M.; Siemieniuk, R.A.C.; Wheeler, R.; Vaughan, B.; Fobuzi, A.C.; Blanker, M.H.; et al. Prostate Cancer Screening with Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test: A Clinical Practice Guideline. BMJ 2018, 362, k3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklin, D.; Hajishengallis, G.; Yang, K.; Lambris, J.D. Complement: A Key System for Immune Surveillance and Homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamidi, S.; Hone, S.; Kirschfink, M. The Complement System in Cancer: Ambivalence between Tumour Destruction and Promotion. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, V.J.; Huber-Lang, M.; Ward, P.A. Complement in Lung Disease. Autoimmunity 2006, 39, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.F.; Ward, P.A. Role of C5a in Inflammatory Responses. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 821–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.A.; Assiri, A.M.; Broering, D.C. Complement and Macrophage Crosstalk during Process of Angiogenesis in Tumor Progression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2015, 22, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurianz, K.; Ziegler, S.; Garcia-Schuler, H.; Kraus, S.; Bohana-Kashtan, O.; Fishelson, Z.; Kirschfink, M. Complement Resistance of Tumor Cells: Basal and Induced Mechanisms. Mol. Immunol. 1999, 36, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishelson, Z.; Donin, N.; Zell, S.; Schultz, S.; Kirschfink, M. Obstacles to Cancer Immunotherapy: Expression of Membrane Complement Regulatory Proteins (MCRPs) in Tumors. Mol. Immunol. 2003, 40, 109–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skerka, C.; Chen, Q.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement Factor H Related Proteins (CFHRs). Mol. Immunol. 2013, 56, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, H.; Han, S.R.; Lee, S.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Yoo, S.M.; Lee, M.S. Activation of the Complement System in an Osteosarcoma Cell Line Promotes Angiogenesis through Enhanced Production of Growth Factors. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stallone, G.; Netti, G.S.; Cormio, L.; Castellano, G.; Infante, B.; Pontrelli, P.; Divella, C.; Selvaggio, O.; Spadaccino, F.; Ranieri, E.; et al. Modulation of Complement Activation by Pentraxin-3 in Prostate Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Horner, J.W.; Paul, E.; Shang, X.; Troncoso, P.; Deng, P.; Jiang, S.; Chang, Q.; Spring, D.J.; Sharma, P.; et al. Effective Combinatorial Immunotherapy for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Nature 2017, 543, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eruslanov, E.; Stoffs, T.; Kim, W.J.; Daurkin, I.; Gilbert, S.M.; Su, L.M.; Vieweg, J.; Daaka, Y.; Kusmartsev, S. Expansion of CCR8+ Inflammatory Myeloid Cells in Cancer Patients with Urothelial and Renal Carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Peng, G.; Huang, H.; Liu, F.; Kong, D.P.; Dong, K.Q.; Dai, L.H.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, K.J.; Yang, J.; et al. Blocking the Feedback Loop between Neuroendocrine Differentiation and Macrophages Improves the Therapeutic Effects of Enzalutamide (MDV3100) on Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 708–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleissner, C.A. Macrophage Phenotype Modulation by CXCL4 in Atherosclerosis. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Mo, J.; Pang, M.; Chen, Z.; Feng, F.; Xie, P.; Yang, B. Identification of HCG18 and MCM3AP-AS1 That Associate with Bone Metastasis, Poor Prognosis and Increased Abundance of M2 Macrophage Infiltration in Prostate Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 1533033821990064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnon, C.; Hall, S.J.; Lin, J.; Xue, X.; Gerber, L.; Freedland, S.J.; Frenette, P.S. Autonomic Nerve Development Contributes to Prostate Cancer Progression. Science 2013, 341, 6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahalka, A.H.; Arnal-Estapé, A.; Maryanovich, M.; Nakahara, F.; Cruz, C.D.; Finley, L.W.S.; Frenette, P.S. Adrenergic Nerves Activate an Angio-Metabolic Switch in Prostate Cancer. Science 2017, 358, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BenEzra, D. Angiogenesis—Critical Assessment of in-Vitro Assays and in—Vivo Models. In Angiogenesis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Steuber, T.; Tennstedt, P.; Macagno, A.; Athanasiou, A.; Wittig, A.; Huber, R.; Golding, B.; Schiess, R.; Gillessen, S. Thrombospondin 1 and Cathepsin D Improve Prostate Cancer Diagnosis by Avoiding Potentially Unnecessary Prostate Biopsies. BJU Int. 2019, 123, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ito, R.; Oue, N.; Zhu, X.; Kitadai, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Nakayama, H.; Yasui, W. Expression of Thrombospondin-1 Is Correlated with Microvessel Density in Gastric Carcinoma. Virchows Archiv. 2003, 442, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.N.; Albo, D.; Tuszynski, G.P. Fibroblasts Promote Breast Cancer Cell Invasion by Upregulating Tumor Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Production. Surgery 2002, 132, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, T.; Alaseem, A.; Chinnaiyan, A.; Dhandayuthapani, S.; Kanagasabai, T.; Alhazzani, K.; Dondapati, P.; Alobid, S.; Natarajan, U.; Schwartz, R.; et al. MDM2 Overexpression Modulates the Angiogenesis-Related Gene Expression Profile of Prostate Cancer Cells. Cells 2018, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K. The Multi-Functional Serpin, Protein C Inhibitor: Beyond Thrombosis and Hemostasis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 2017–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagelgans, A.; Jandeck, C.; Friedemann, M.; Donchin, A.; Richter, S.; Menschikowski, M. Identification of CpG Sites of SERPINA5 Promoter with Opposite Methylation Patterns in Benign and Malignant Prostate Cells. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 6609–6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, B.M.; Eisenberg, M.L.; Hotaling, J.M. Male Infertility: A Biomarker of Individual and Familial Cancer Risk. Fertil. Steril. 2018, 109, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loizzo, D.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Rogers, D.; Cerrato, C.; di Meo, N.A.; Autorino, R.; Mirone, V.; Ferro, M.; Porta, C.; Stella, A.; et al. Novel Insights into Autophagy and Prostate Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messner, C.B.; Demichev, V.; Wendisch, D.; Michalick, L.; White, M.; Freiwald, A.; Textoris-Taube, K.; Vernardis, S.I.; Egger, A.S.; Kreidl, M.; et al. Ultra-High-Throughput Clinical Proteomics Reveals Classifiers of COVID-19 Infection. Cell Syst. 2020, 11, 11.e4–24.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | Age (Years) | PSA (ng/mL) | Gleason Score | Tumour Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Newly Diagnosed Prostate Cancer Patients (PCa-ND) | ||||
| Active Surveillance (PCa-AS) (n = 41) | 68 (±8) | 9.7 (±9.6) | HGPIN (n = 1) 3 + 3 (n = 33) 3 + 4 (n = 1) NA (n = 6) | T1–T3 (no nodal spread and no metastasis) |
| Pre-treatment (PCa-pre) (n = 47) | 64 (±6) | 8.1 (±5.1) | 2 + 2 (n = 1) 3 + 3 (n = 32) 3 + 4 (n = 12) NA (n = 2) | T1–T3 (no nodal spread and no metastasis) |
| Post Treatment (PCa-post) | ||||
| Post prostatectomy (n = 12) | 63 (±6) | 8.6 (±5.5) | N/A | N/A |
| Post radiotherapy (n = 13) | 63 (±6) | 11.9 (±24.7) | N/A | N/A |
| Healthy Controls (HC) | ||||
| Healthy Control (n = 131) | 66 (±10) | 0.8 (±0.6) | N/A | NA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muazzam, A.; Spick, M.; Cexus, O.N.F.; Geary, B.; Azhar, F.; Pandha, H.; Michael, A.; Reed, R.; Lennon, S.; Gethings, L.A.; et al. A Novel Blood Proteomic Signature for Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041051
Muazzam A, Spick M, Cexus ONF, Geary B, Azhar F, Pandha H, Michael A, Reed R, Lennon S, Gethings LA, et al. A Novel Blood Proteomic Signature for Prostate Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(4):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041051
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuazzam, Ammara, Matt Spick, Olivier N. F. Cexus, Bethany Geary, Fowz Azhar, Hardev Pandha, Agnieszka Michael, Rachel Reed, Sarah Lennon, Lee A. Gethings, and et al. 2023. "A Novel Blood Proteomic Signature for Prostate Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 4: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041051
APA StyleMuazzam, A., Spick, M., Cexus, O. N. F., Geary, B., Azhar, F., Pandha, H., Michael, A., Reed, R., Lennon, S., Gethings, L. A., Plumb, R. S., Whetton, A. D., Geifman, N., & Townsend, P. A. (2023). A Novel Blood Proteomic Signature for Prostate Cancer. Cancers, 15(4), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15041051







