Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: From Biology to Treatment
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. VHL/Targeted Therapies
3. Immunotherapy
4. Cytoreductive Nephrectomy
5. Radiation Therapy
6. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A.; Thandra, K.C.; Saginala, K.; Mohammed, A.; Vakiti, A.; Rawla, P.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma. World J. Oncol. 2020, 11, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muss, H.B. Interferon therapy of metastatic renal cell cancer. Semin. Surg. Oncol. 1988, 4, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klapper, J.A.; Downey, S.G.; Smith, F.O.; Yang, J.C.; Hughes, M.S.; Kammula, U.S.; Sherry, R.M.; Royal, R.E.; Steinberg, S.M.; Rosenberg, S. High-dose interleukin-2 for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A retrospective analysis of response and survival in patients treated in the surgery branch at the National Cancer Institute between 1986 and 2006. Cancer 2008, 113, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keefe, S.M.; Nathanson, K.L.; Rathmell, W.K. The molecular biology of renal cell carcinoma. Semin. Oncol. 2013, 40, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melmon, K.L.; Rosen, S.W. Lindau’s Disease. Review of the Literature and Study of a Large Kindred. Am. J. Med. 1964, 36, 595–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seizinger, B.R.; Rouleau, G.A.; Ozelius, L.J.; Lane, A.H.; Farmer, G.E.; Lamiell, J.M.; Haines, J.; Yuen, J.W.; Collins, D.; Majoor-Krakauer, D.; et al. Von Hippel-Lindau disease maps to the region of chromosome 3 associated with renal cell carcinoma. Nature 1988, 332, 268–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaelin, W.G., Jr. The von Hippel-Lindau gene, kidney cancer, and oxygen sensing. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 2703–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, F.; Tory, K.; Gnarra, J.; Yao, M.; Duh, F.M.; Orcutt, M.L.; Stackhouse, T.; Kuzmin, I.; Modi, W.; Geil, L.; et al. Identification of the von Hippel-Lindau disease tumor suppressor gene. Science 1993, 260, 1317–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickerson, M.L.; Jaeger, E.; Shi, Y.; Durocher, J.A.; Mahurkar, S.; Zaridze, D.; Matveev, V.; Janout, V.; Kollarova, H.; Bencko, V.; et al. Improved identification of von Hippel-Lindau gene alterations in clear cell renal tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4726–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudier, B.; Pluzanska, A.; Koralewski, P.; Ravaud, A.; Bracarda, S.; Szczylik, C.; Chevreau, C.; Filipek, M.; Melichar, B.; Bajetta, E.; et al. Bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a for treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A randomised, double-blind phase III trial. Lancet 2007, 370, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parveen, A.; Subedi, L.; Kim, H.W.; Khan, Z.; Zahra, Z.; Farooqi, M.Q.; Kim, S.Y. Phytochemicals Targeting VEGF and VEGF-Related Multifactors as Anticancer Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Tomczak, P.; Michaelson, M.D.; Bukowski, R.M.; Rixe, O.; Oudard, S.; Negrier, S.; Szczylik, C.; Kim, S.T.; et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Cella, D.; Reeves, J.; Hawkins, R.; Guo, J.; Nathan, P.; Staehler, M.; de Souza, P.; Merchan, J.R.; et al. Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zeng, T.; Liang, X.; Chen, D.; Duan, X.; Zeng, G.; Wu, W. Crosstalk between VEGFR and other receptor tyrosine kinases for TKI therapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudier, B.; Eisen, T.; Stadler, W.M.; Szczylik, C.; Oudard, S.; Siebels, M.; Negrier, S.; Chevreau, C.; Solska, E.; Desai, A.A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Glen, H.; Michaelson, M.D.; Molina, A.; Eisen, T.; Jassem, J.; Zolnierek, J.; Maroto, J.P.; Mellado, B.; et al. Lenvatinib, everolimus, and the combination in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A randomised, phase 2, open-label, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Escudier, B.; Powles, T.; Mainwaring, P.N.; Rini, B.I.; Donskov, F.; Hammers, H.; Hutson, T.E.; Lee, J.L.; Peltola, K.; et al. Cabozantinib versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Escudier, B.; Tomczak, P.; Kaprin, A.; Szczylik, C.; Hutson, T.E.; Michaelson, M.D.; Gorbunova, V.A.; Gore, M.E.; Rusakov, I.G.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of axitinib versus sorafenib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (AXIS): A randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2011, 378, 1931–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, C.N.; Davis, I.D.; Mardiak, J.; Szczylik, C.; Lee, E.; Wagstaff, J.; Barrios, C.H.; Salman, P.; Gladkov, O.A.; Kavina, A.; et al. Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Results of a randomized phase III trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rini, B.I.; Pal, S.K.; Escudier, B.J.; Atkins, M.B.; Hutson, T.E.; Porta, C.; Verzoni, E.; Needle, M.N.; McDermott, D.F. Tivozanib versus sorafenib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (TIVO-3): A phase 3, multicentre, randomised, controlled, open-label study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robb, V.A.; Karbowniczek, M.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Henske, E.P. Activation of the mTOR signaling pathway in renal clear cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2007, 177, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.V.; Tran, C.; Mellinghoff, I.K.; Welsbie, D.S.; Chan, E.; Fueger, B.; Czernin, J.; Sawyers, C.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor determines sensitivity to inhibitors of mTOR in kidney cancer. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; Oudard, S.; Hutson, T.E.; Porta, C.; Bracarda, S.; Grunwald, V.; Thompson, J.A.; Figlin, R.A.; Hollaender, N.; et al. Efficacy of everolimus in advanced renal cell carcinoma: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled phase III trial. Lancet 2008, 372, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudes, G.; Carducci, M.; Tomczak, P.; Dutcher, J.; Figlin, R.; Kapoor, A.; Staroslawska, E.; Sosman, J.; McDermott, D.; Bodrogi, I.; et al. Temsirolimus, interferon alfa, or both for advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2271–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovelli, R.; Sternberg, C.N.; Porta, C.; Verzoni, E.; de Braud, F.; Escudier, B.; Procopio, G. Inhibition of the VEGF/VEGFR pathway improves survival in advanced kidney cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macleod, L.C.; Tykodi, S.S.; Holt, S.K.; Wright, J.L.; Lin, D.W.; Tretiakova, M.S.; True, L.D.; Gore, J.L. Trends in Metastatic Kidney Cancer Survival From the Cytokine to the Targeted Therapy Era. Urology 2015, 86, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, D.Y.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Warren, M.A.; Golshayan, A.R.; Sahi, C.; Eigl, B.J.; Ruether, J.D.; Cheng, T.; North, S.; et al. Prognostic factors for overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted agents: Results from a large, multicenter study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5794–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, D.Y.; Xie, W.; Regan, M.M.; Harshman, L.C.; Bjarnason, G.A.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; Mackenzie, M.; Wood, L.; Donskov, F.; Tan, M.H.; et al. External validation and comparison with other models of the International Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium prognostic model: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankenstein, T.; Coulie, P.G.; Gilboa, E.; Jaffee, E.M. The determinants of tumour immunogenicity. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2012, 12, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcherding, N.; Vishwakarma, A.; Voigt, A.P.; Bellizzi, A.; Kaplan, J.; Nepple, K.; Salem, A.K.; Jenkins, R.W.; Zakharia, Y.; Zhang, W. Mapping the immune environment in clear cell renal carcinoma by single-cell genomics. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Xia, Y.; Lin, Z.; Qu, Y.; Qi, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zeng, H.; Wang, J.; Chang, Y.; et al. Tumor-infiltrating CD39+CD8+ T cells determine poor prognosis and immune evasion in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2020, 69, 1565–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wherry, E.J.; Kurachi, M. Molecular and cellular insights into T cell exhaustion. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, E.; Long, J.; Hu, Z.; Peng, J.; Liu, L.; Tang, F.; Li, L.; Ouyang, Y.; Zeng, Z. Immune infiltration in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreiber, R.D.; Old, L.J.; Smyth, M.J. Cancer immunoediting: Integrating immunity’s roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science 2011, 331, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyman, O.; Sprent, J. The role of interleukin-2 during homeostasis and activation of the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, V.; Sarkar, S. Regulation of Effector and Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation by IL-2-A Balancing Act. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, J.M.; McDermott, D.F. The High-Dose Aldesleukin (IL-2) “Select” Trial: A Trial Designed to Prospectively Validate Predictive Models of Response to High-Dose IL-2 Treatment in Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2009, 7, E7–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyfe, G.; Fisher, R.I.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Sznol, M.; Parkinson, D.R.; Louie, A.C. Results of treatment of 255 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 13, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, M.P.; Parker, R.A.; Youmans, A.; McDermott, D.F.; Atkins, M.B. Histologic Predictors of Renal Cell Carcinoma Response to Interleukin-2-Based Therapy. J. Immunother. 2005, 28, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borden, E.C. Interferons α and β in cancer: Therapeutic opportunities from new insights. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Bander, N.H.; Nanus, D.M. Renal-Cell Carcinoma. New Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escudier, B.; Bellmunt, J.; Négrier, S.; Bajetta, E.; Melichar, B.; Bracarda, S.; Ravaud, A.; Golding, S.; Jethwa, S.; Sneller, V. Phase III trial of bevacizumab plus interferon alfa-2a in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (AVOREN): Final analysis of overall survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2144–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevrier, S.; Levine, J.H.; Zanotelli, V.R.T.; Silina, K.; Schulz, D.; Bacac, M.; Ries, C.H.; Ailles, L.; Jewett, M.A.S.; Moch, H.; et al. An Immune Atlas of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell 2017, 169, 736–749.e718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speiser, D.E.; Ho, P.-C.; Verdeil, G. Regulatory circuits of T cell function in cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, X. PD-1 and its ligands are important immune checkpoints in cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 2171–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; George, S.; Hammers, H.J.; Srinivas, S.; Tykodi, S.S.; Sosman, J.A.; Procopio, G.; Plimack, E.R.; et al. Nivolumab versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Arén Frontera, O.; Melichar, B.; Choueiri, T.K.; Plimack, E.R.; Barthélémy, P.; Porta, C.; George, S.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1277–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Tannir, N.M.; McDermott, D.F.; Burotto, M.; Choueiri, T.K.; Hammers, H.J.; Plimack, E.R.; Porta, C.G.; George, S.; Powles, T.B.; et al. 661P Conditional survival and 5-year follow-up in CheckMate 214: First-line nivolumab + ipilimumab (N+I) versus sunitinib (S) in advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC). Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S685–S687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, C.L.; Lynn, K.D.; Toombs, J.E.; Dineen, S.P.; Udugamasooriya, D.G.; Brekken, R.A. Cytokine levels correlate with immune cell infiltration after anti-VEGF therapy in preclinical mouse models of breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Bronte, V. Coordinated regulation of myeloid cells by tumours. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Plimack, E.R.; Stus, V.; Gafanov, R.; Hawkins, R.; Nosov, D.; Pouliot, F.; Alekseev, B.; Soulières, D.; Melichar, B.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rini, B.I.; Plimack, E.R.; Stus, V.; Waddell, T.; Gafanov, R.; Pouliot, F.; Nosov, D.; Melichar, B.; Soulieres, D.; Borchiellini, D.; et al. Pembrolizumab (pembro) plus axitinib (axi) versus sunitinib as first-line therapy for advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC): Results from 42-month follow-up of KEYNOTE-426. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Powles, T.; Burotto, M.; Escudier, B.; Bourlon, M.T.; Zurawski, B.; Oyervides Juárez, V.M.; Hsieh, J.J.; Basso, U.; Shah, A.Y.; et al. Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.; Alekseev, B.; Rha, S.-Y.; Porta, C.; Eto, M.; Powles, T.; Grünwald, V.; Hutson, T.E.; Kopyltsov, E.; Méndez-Vidal, M.J.; et al. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab or Everolimus for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Tomczak, P.; Park, S.H.; Venugopal, B.; Ferguson, T.; Chang, Y.-H.; Hajek, J.; Symeonides, S.N.; Lee, J.L.; Sarwar, N.; et al. Adjuvant Pembrolizumab after Nephrectomy in Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 683–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Tomczak, P.; Park, S.H.; Venugopal, B.; Ferguson, T.; Symeonides, S.N.; Hajek, J.; Chang, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-L.; Sarwar, N.; et al. Pembrolizumab as post nephrectomy adjuvant therapy for patients with renal cell carcinoma: Results from 30-month follow-up of KEYNOTE-564. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minasian, L.M.; Motzer, R.J.; Gluck, L.; Mazumdar, M.; Vlamis, V.; Krown, S.E. Interferon alfa-2a in advanced renal cell carcinoma: Treatment results and survival in 159 patients with long-term follow-up. J. Clin. Oncol. 1993, 11, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, Y.; Motzer, R.J.; Choueiri, T.K.; Rini, B.I.; Miyake, H.; Uemura, H.; Albiges, L.; Fujii, Y.; Umeyama, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of avelumab plus axitinib (A + Ax) versus sunitinib (S) in elderly patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC): Extended follow-up results from JAVELIN Renal 101. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Penkov, K.; Haanen, J.; Rini, B.; Albiges, L.; Campbell, M.T.; Venugopal, B.; Kollmannsberger, C.; Negrier, S.; Uemura, M.; et al. Avelumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markewitz, M.; Taylor, D.A.; Veenema, R.J. Spontaneous regression of pulmonary metastases following palliative nephrectomy. Case report. Cancer 1967, 20, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonick, P.; Jackiw, N.M. Regression of pulmonary metastases from renal adenocarcinoma. J. Urol. 1964, 92, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakula, A. Spontaneous regression of pulmonary metastases secondary to carcinoma of kidney. Br. J. Dis. Chest. 1963, 57, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freed, S.Z. Nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma with metastases. Urology 1977, 9, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanigan, R.C. Debulking Nephrectomy in Metastatic Renal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6335S–6341S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahn, M.; Fisch, P.; Köhler, G.; Kunzmann, R.; Hentrich, I.; Jesuiter, H.; Behringer, D.; Muschal, B.; Veelken, H.; Kulmburg, P.; et al. Pro-inflammatory and T cell inhibitory cytokines are secreted at high levels in tumor cell cultures of human renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 1999, 35, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sella, A.; Swanson, D.A.; Ro, J.Y.; Putnam, J.B., Jr.; Amato, R.J.; Markowitz, A.B.; Logothetis, C.J. Surgery following response to interferon-alpha-based therapy for residual renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 1993, 149, 19–21, discussion 21–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palapattu, G.S.; Kristo, B.; Rajfer, J. Paraneoplastic syndromes in urologic malignancy: The many faces of renal cell carcinoma. Rev. Urol. 2002, 4, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Van Praet, C.; Slots, C.; Vasdev, N.; Rottey, S.; Fonteyne, V.; Andras, I.; Albersen, M.; De Meerleer, G.; Bex, A.; Decaestecker, K. Current role of cytoreductive nephrectomy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Turk. J. Urol. 2021, 47, S79–s84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bex, A.; Mulders, P.; Jewett, M.; Wagstaff, J.; van Thienen, J.V.; Blank, C.U.; van Velthoven, R.; Del Pilar Laguna, M.; Wood, L.; van Melick, H.H.E.; et al. Comparison of Immediate vs. Deferred Cytoreductive Nephrectomy in Patients With Synchronous Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Receiving Sunitinib: The SURTIME Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méjean, A.; Ravaud, A.; Thezenas, S.; Colas, S.; Beauval, J.B.; Bensalah, K.; Geoffrois, L.; Thiery-Vuillemin, A.; Cormier, L.; Lang, H.; et al. Sunitinib Alone or after Nephrectomy in Metastatic Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejean, A.; Thezenas, S.; Chevreau, C.; Bensalah, K.; Geoffrois, L.; Thiery-Vuillemin, A.; Cormier, L.; Lang, H.; Guy, L.; Gravis, G.; et al. Cytoreductive nephrectomy (CN) in metastatic renal cancer (mRCC): Update on Carmena trial with focus on intermediate IMDC-risk population. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakouny, Z.; El Zarif, T.; Dudani, S.; Connor Wells, J.; Gan, C.L.; Donskov, F.; Shapiro, J.; Davis, I.D.; Parnis, F.; Ravi, P.; et al. Upfront Cytoreductive Nephrectomy for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors or Targeted Therapy: An Observational Study from the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium. Eur. Urol. 2022, in press. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, M.; Hannan, R. The Emerging Role of Radiation Therapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuodeh, Y.; Venkat, P.; Kim, S. Systematic review of case reports on the abscopal effect. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2016, 40, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, H.B.; Peters, L.J.; Milas, L. Effect of host immune capability on radiocurability and subsequent transplantability of a murine fibrosarcoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1979, 63, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Masini, C.; Iotti, C.; De Giorgi, U.; Bellia, R.S.; Buti, S.; Salaroli, F.; Zampiva, I.; Mazzarotto, R.; Mucciarini, C.; Vitale, M.G.; et al. Nivolumab in Combination with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy in Pretreated Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma. Results of the Phase II NIVES Study. Eur. Urol. 2022, 81, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhuillier, C.; Rudqvist, N.-P.; Elemento, O.; Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Radiation therapy and anti-tumor immunity: Exposing immunogenic mutations to the immune system. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Liang, H.; Burnette, B.; Beckett, M.; Darga, T.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Fu, Y.-X. Irradiation and anti–PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammers, H.J.; Vonmerveldt, D.; Ahn, C.; Nadal, R.M.; Drake, C.G.; Folkert, M.R.; Laine, A.M.; Courtney, K.D.; Brugarolas, J.; Song, D.Y.; et al. Combination of dual immune checkpoint inhibition (ICI) with stereotactic radiation (SBRT) in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) (RADVAX RCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Schoenhals, J.; Christie, A.; Mohamad, O.; Wang, C.; Bowman, I.; Singla, N.; Hammers, H.; Courtney, K.; Bagrodia, A.; et al. Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy (SAbR) Used to Defer Systemic Therapy in Oligometastatic Renal Cell Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenhals, J.E.; Mohamad, O.; Christie, A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Singla, N.; Bowman, I.; Arafat, W.; Hammers, H.; Courtney, K.; et al. Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy for Oligoprogressive Renal Cell Carcinoma. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 6, 100692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonasch, E.; Donskov, F.; Iliopoulos, O.; Rathmell, W.K.; Narayan, V.K.; Maughan, B.L.; Oudard, S.; Else, T.; Maranchie, J.K.; Welsh, S.J.; et al. Belzutifan for Renal Cell Carcinoma in von Hippel–Lindau Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 2036–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varshney, N.; Kebede, A.A.; Owusu-Dapaah, H.; Lather, J.; Kaushik, M.; Bhullar, J.S. A Review of Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome. J. Kidney Cancer VHL 2017, 4, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Tang, B.; Sun, X. Development of Inhibitors Targeting Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 and 2 for Cancer Therapy. Yonsei Med. J. 2017, 58, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W.S.W.; Boland, J.; Lin, J. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2α as a Novel Target in Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Kidney Cancer VHL 2021, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaifel, A.; Xie, W.; Braun, D.A.; Ficial, M.; Bakouny, Z.; Nassar, A.H.; Jennings, R.B.; Escudier, B.; George, D.J.; Motzer, R.J.; et al. PD-L1 Expression and Clinical Outcomes to Cabozantinib, Everolimus, and Sunitinib in Patients with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: Analysis of the Randomized Clinical Trials METEOR and CABOSUN. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6080–6088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovelli, R.; Nolè, F.; Verri, E.; Renne, G.; Paglino, C.; Santoni, M.; Cossu Rocca, M.; Giglione, P.; Aurilio, G.; Cullurà, D.; et al. Prognostic Role of PD-L1 Expression in Renal Cell Carcinoma. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Target. Oncol. 2016, 11, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, A.; Sepe, P.; Zattarin, E.; Mennitto, A.; Stellato, M.; Claps, M.; Guadalupi, V.; Verzoni, E.; de Braud, F.; Procopio, G. Predictive Biomarkers of Response to Immunotherapy in Metastatic Renal Cell Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, J.R.; Kofman, E.; Mo, S.S.; Elmarakeby, H.; Van Allen, E. Genomics of response to immune checkpoint therapies for cancer: Implications for precision medicine. Genome Med. 2018, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Choueiri, T.K.; McDermott, D.F.; Powles, T.; Yao, J.; Ammar, R.; Papillon-Cavanagh, S.; Saggi, S.S.; McHenry, B.M.; Ross-Macdonald, P.; et al. Biomarker analyses from the phase III CheckMate 214 trial of nivolumab plus ipilimumab (N+I) or sunitinib (S) in advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Robbins, P.B.; Powles, T.; Albiges, L.; Haanen, J.B.; Larkin, J.; Mu, X.J.; Ching, K.A.; Uemura, M.; Pal, S.K.; et al. Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in advanced renal cell carcinoma: Biomarker analysis of the phase 3 JAVELIN Renal 101 trial. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1733–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
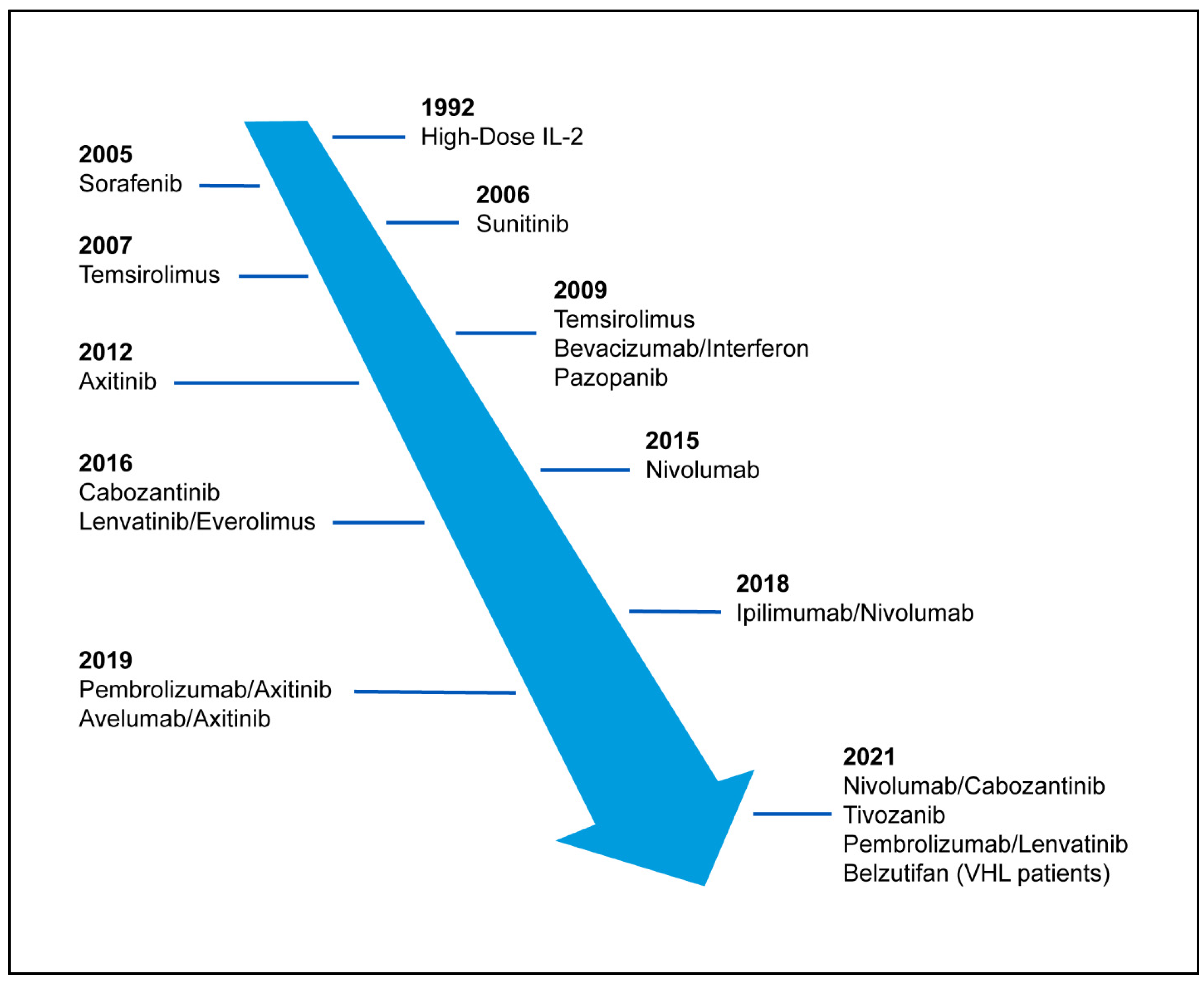
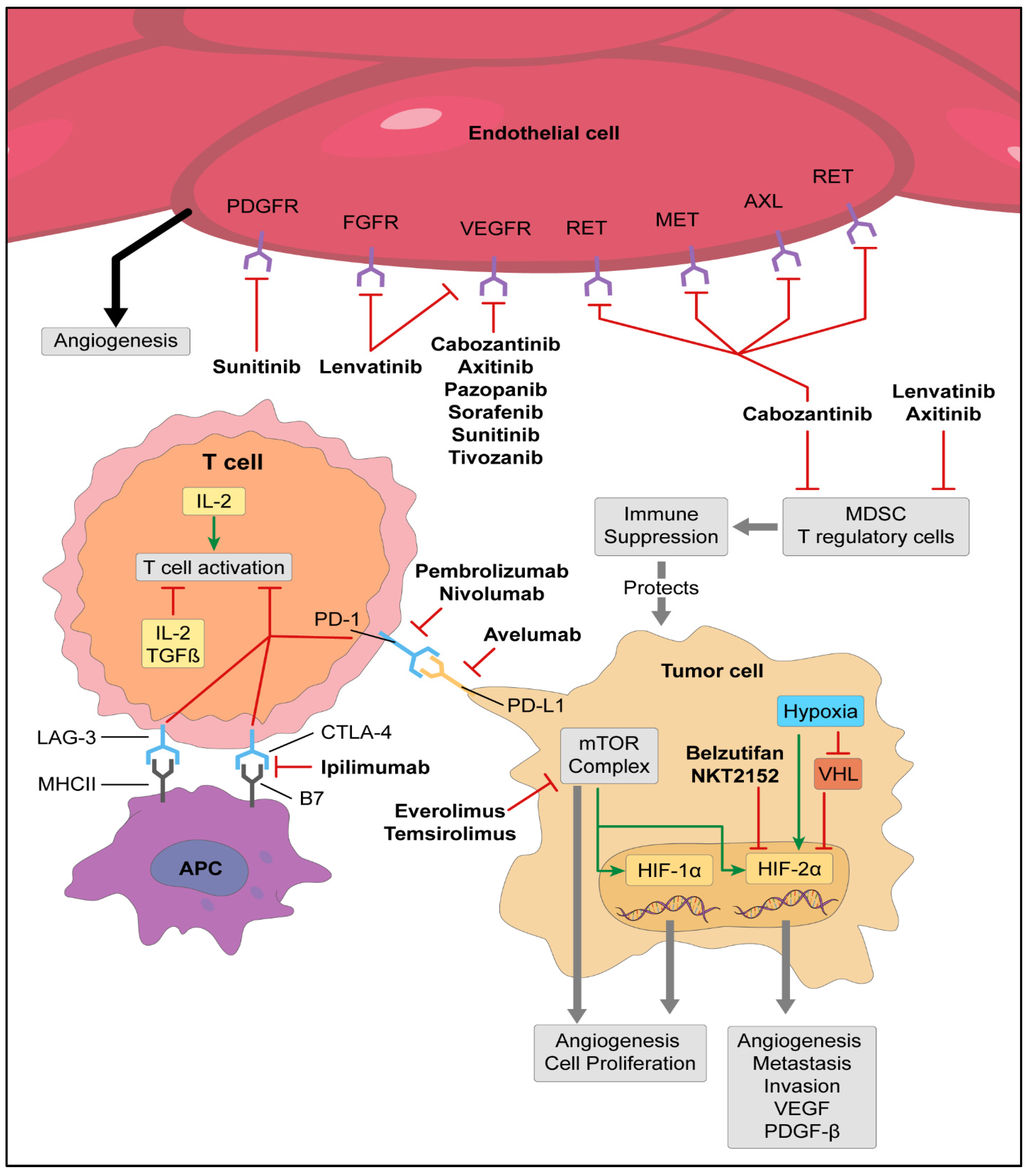
| VEGFR TKI | Receptor | Trial | Efficacy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sorafenib [16] | Raf-1, B-Raf, B-Raf (V599E), VEGFR, PDGFR, c-Kit, RET | Phase III RCT, sorafenib vs. placebo, previously untreated | PFS 5.5 months vs. 2.8 months (HR 0.44, 95% CI 0.35–0.55, p < 0.01) |
| Sunitinib [13] | c-Kit, FLT3, PDGFRβ | Phase III RCT, sunitinib vs. interferon, previously untreated | PFS 11 months vs. 5 months (HR 0.42, 95% CI 0.32–0.54; p < 0.001) |
| Lenvatinib [17] (combined with everolimus) | PDGFRα, PDGFRβ, FGFR1 | Phase II RCT, lenvatinib + everolimus vs. everolimus, previously treated | PFS 14.6 months vs. 5.5 months (HR 0.4, 95% CI 0.24–0.68; p = 0.0005) |
| Cabozantinib [18] | c-MET, AXL, RET, KIT, FLT3, TRKB, Tie-2 | Phase III RCT, cabozantinib vs. everolimus, previously treated | PFS 7.4 months vs. 3.8 months (HR 0.58; 95% CI 0.45–0.75, p < 0.001) |
| Axitinib [19] | PDGFRα, PDGFRβ, Kit, BCR-ABL1 | Phase III RCT, axitinib vs. sorafenib, previously treated | PFS 6.7 months vs. 4.7 months (HR 0.665, 95% CI 0.544–0.812, p < 0.0001) |
| Pazopanib [20] | PDGFR, FGFR, c-Kit | Phase III RCT, pazopanib vs. placebo, previously untreated and cytokine pre-treated | PFS 9.2 months vs. 4.2 months (HR 0.46, 95% CI 0.34–0.62, p < 0.001) |
| Tivozanib [21] | Predominantly VEGFR 1–3 | Phase III, RCT, tivozanib vs. sorafenib, previously treated | PFS 5.6 months vs. 3.9 months (HR 0.73, 95% CI 0.56–0.93, p = 0.016) |
| Immunotherapy | Immunotherapy Target | Study | ORR | PFS | OS (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Dose IL-2 [4,39] | T cells | Phase 2 trial in advanced RCC and retrospective review | 14–20% (8–9% CR) | n/a | 19 |
| IFN-α2a [58] | Immune cells | Prospective trial in advanced RCC | 10% (1% CR) | n/a | 11.4 |
| IFN-α2a plus Bevacizumab [11,43] | Immune cells | Phase 3 trial in untreated mRCC combination vs. IFN-α2a monotherapy | 31% vs. 13% | 10.5 vs. 5.4 (p = 0.0001) | 23.3 vs. 21.3 (ns) |
| Nivolumab [47] | PD-1 | Phase 3 previously treated mRCC vs. everolimus | 25% vs. 5% (1% CR Nivolumab) | 4.6 vs. 4.4 (ns) | 25 vs. 19.6 (HR 0.73, 95% CI 0.57–0.93, p = 0.002) |
| Ipilimumab plus Nivolumab [48,49] | CTLA-4/PD-1 | Phase 3 untreated advanced ccRCC vs. sunitinib | 42% vs. 27% (11% CR Ipilimumab/ Nivolumab) | 11.6 vs. 8.4 (ns) | 47 vs. 26.6 HR 0.68 (95% CI 0.58–0.81) |
| Avelumab plus Axitinib [59,60] | PD-L1 | Phase 3 untreated advanced RCC vs. sunitinib | 55.2% vs. 25.5% (4.4% CR Avelumab/Axitinib) | 13.8 vs. 8.4 (p < 0.001) | 19.3 vs. 19.2 (ns) |
| Pembrolizumab plus Axitinib [52,53] | PD-1 | Phase 3 untreated advanced RCC vs. sunitinib | 59.3% vs. 35.7% (5.8% CR Pembrolizumab/ Axitinib) | 15.1 vs. 11.1 | 45.7 vs. 40.1 (HR, 0.73; 95% CI 0.60–0.88, p < 0.001) |
| Nivolumab plus Cabozantinib [54] | PD-1 | Phase 3 untreated advanced RCC vs. sunitinib | 55.7% vs. 27.1% (8.0% CR Nivolumab/ Cabozantinib) | 16.6 vs. 8.3 | 12-month OS 85.7% vs. 75.6% (HR of 0.60, p = 0.001) |
| Pembrolizumab plus Lenvatinib [55] | PD-1 | Phase 3 untreated advanced RCC vs. sunitinib | 71% vs. 36% (16% CR Pembrolizumab/ Lenvatinib) | 23.9 vs. 9.2 | HR of 0.66 (95% CI 0.49–0.88, p = 0.005) |
| Pembrolizumab [56,57] | PD-1 | Phase 3 adjuvant therapy after nephrectomy in high-risk RCC vs. placebo | n/a | n/a | 2-year DFS 78.3% vs. 67.3% (HR 0.63, p < 0.0001); OS not mature |
| Intervention | Target | Trial Type | Estimated Completion Date | Identifier | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belzutifan (standard dose vs. high dose) | HIF-2α | Phase 2 | October 2025 | NCT04489771 | Active, not recruiting |
| Belzutifan vs. everolimus | HIF-2α | Phase 3 | September 2025 | NCT04195750 | Active, not recruiting |
| Belzutifan plus lenvatinib vs. cabozantinib | HIF-2α | Phase 3 | December 2024 | NCT04586231 | Recruiting |
| Belzutifan + pembrolizumab vs. pembrolizumab + placebo | HIF-2α | Phase 3 | January 2030 | NCT05239728 | Recruiting |
| Pembrolizumab + belzutifan + lenvatinib or pembrolizumab/quavonlimab + lenvatinib vs. pembrolizumab + lenvatinib | HIF-2α | Phase 3 | October 2026 | NCT04736706 | Recruiting |
| NKT2152 | HIF-2α | Phase 1/2 | September 2026 | NCT05119335 | Recruiting |
| Belzutifan + cabozantinib | HIF-2α | Phase 2 | August 2025 | NCT03634540 | Recruiting |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kase, A.M.; George, D.J.; Ramalingam, S. Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: From Biology to Treatment. Cancers 2023, 15, 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030665
Kase AM, George DJ, Ramalingam S. Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: From Biology to Treatment. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):665. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030665
Chicago/Turabian StyleKase, Adam M., Daniel J. George, and Sundhar Ramalingam. 2023. "Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: From Biology to Treatment" Cancers 15, no. 3: 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030665
APA StyleKase, A. M., George, D. J., & Ramalingam, S. (2023). Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: From Biology to Treatment. Cancers, 15(3), 665. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030665






