Novel Non-Cyclooxygenase Inhibitory Derivative of Sulindac Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Growth In Vitro and Reduces Mammary Tumorigenesis in Rats
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Data Analysis
2.2. Molecular Modeling
2.3. Biochemical Assays
2.4. Cell-Based Assays
2.5. Western Blotting
2.6. In Vivo Efficacy
2.7. Immunohistochemistry
3. Results
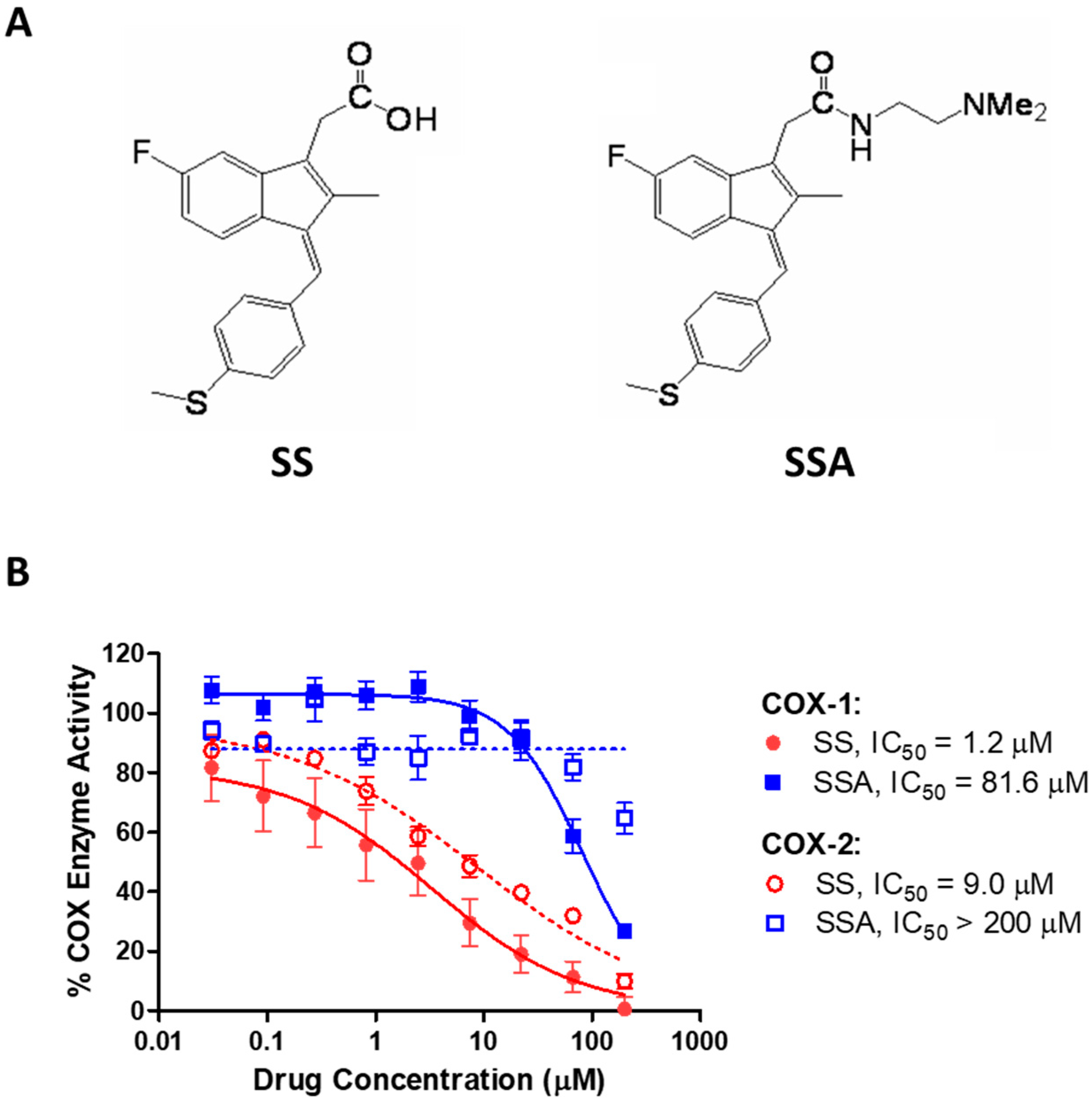
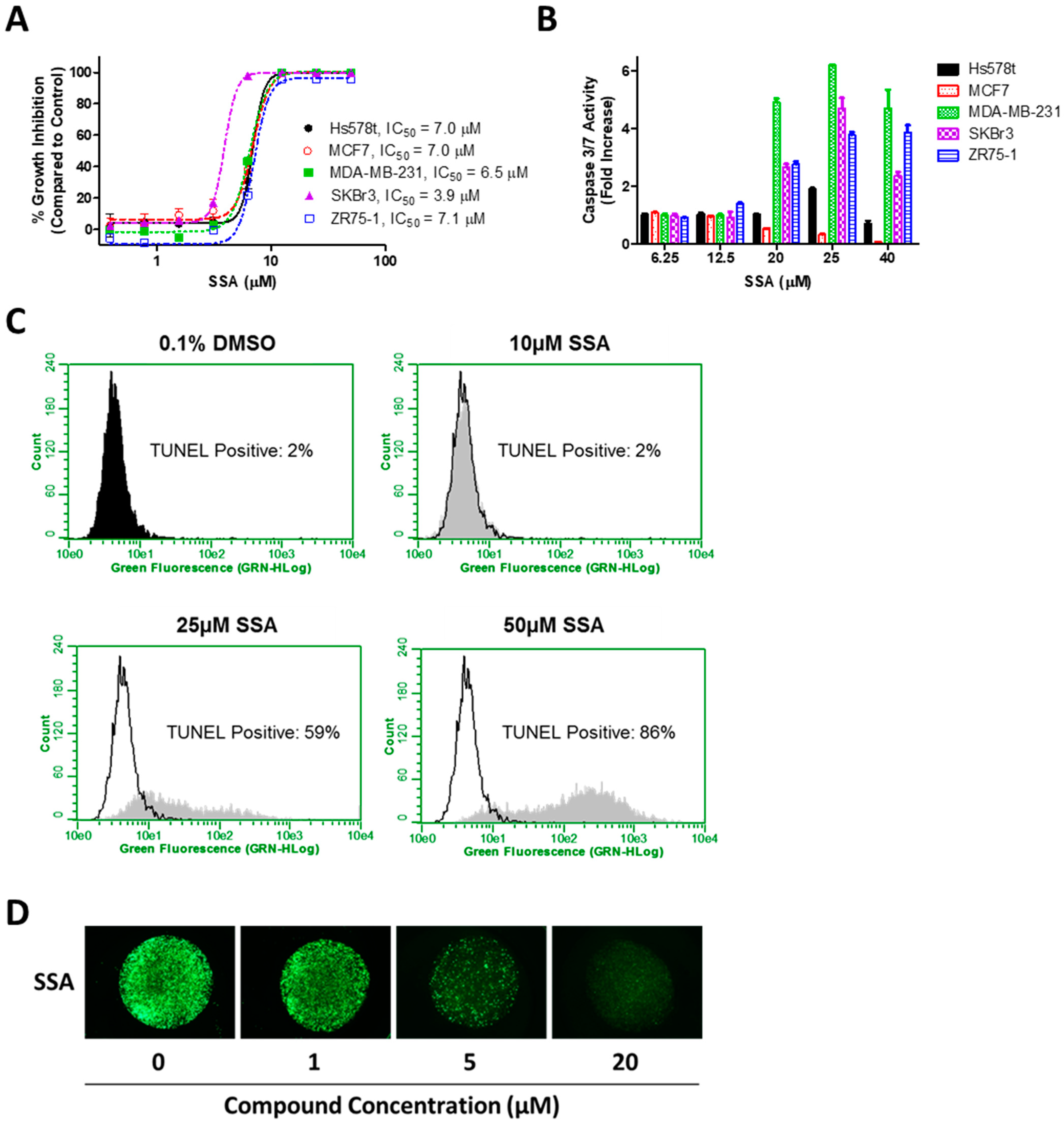
3.1. SSA Lacks COX-Inhibitory Activity but Inhibits Breast Tumor Cell Growth In Vitro
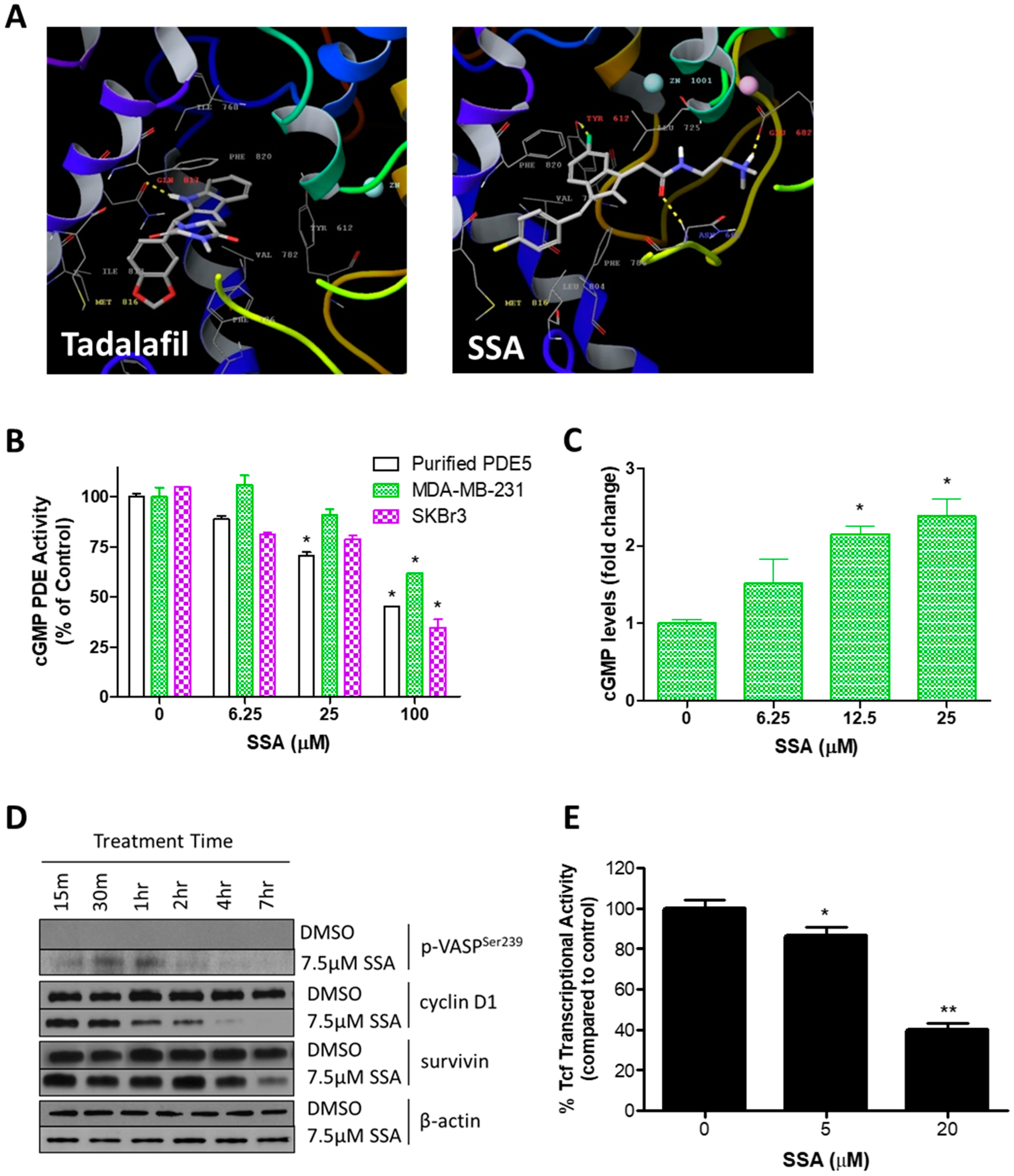
3.2. SSA Activates cGMP/PKG Signaling and Attenuates Wnt/β-Catenin Transcriptional Activity
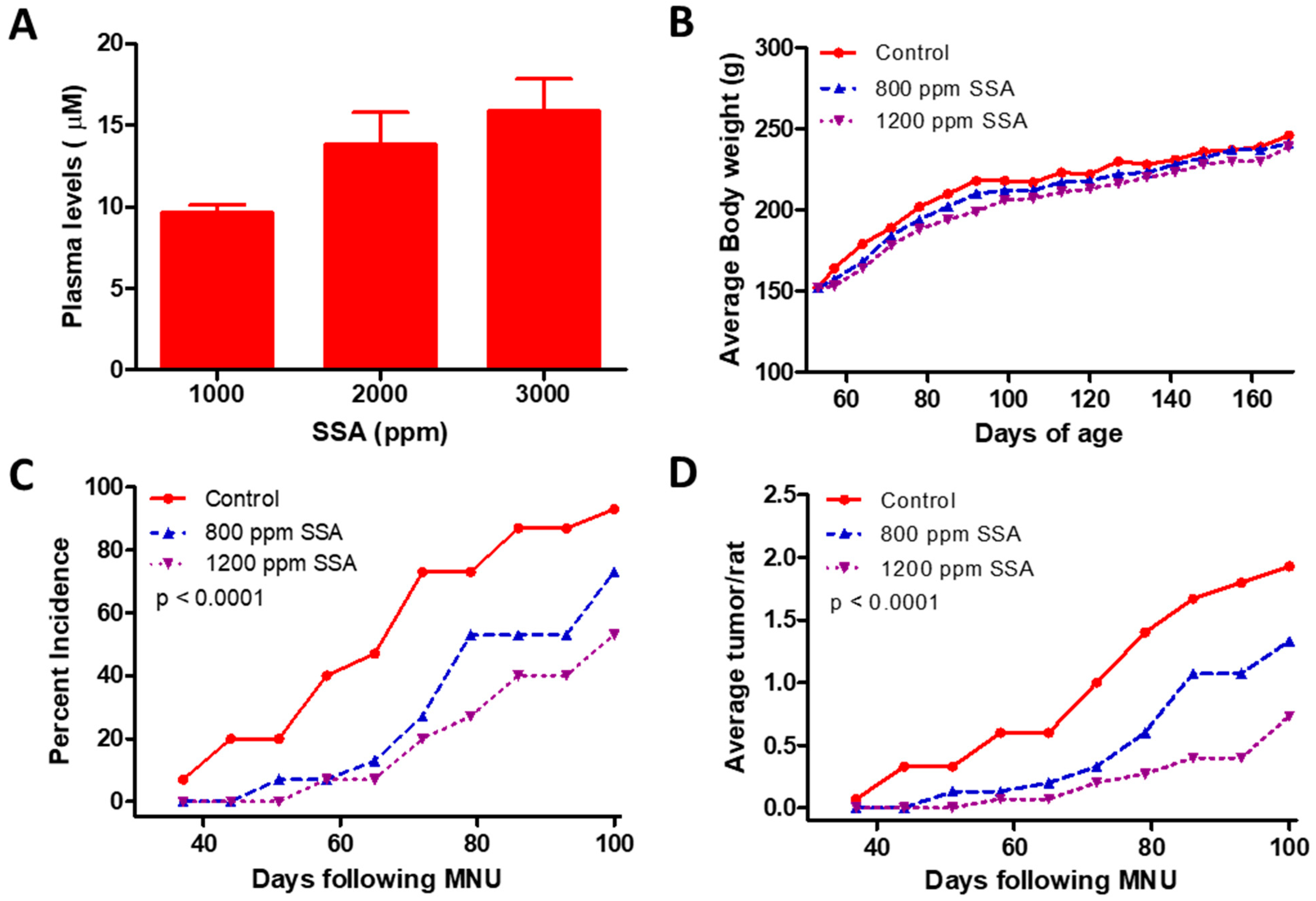
3.3. SSA Inhibits Tumor Formation in the MNU Rat Model of Mammary Carcinogenesis
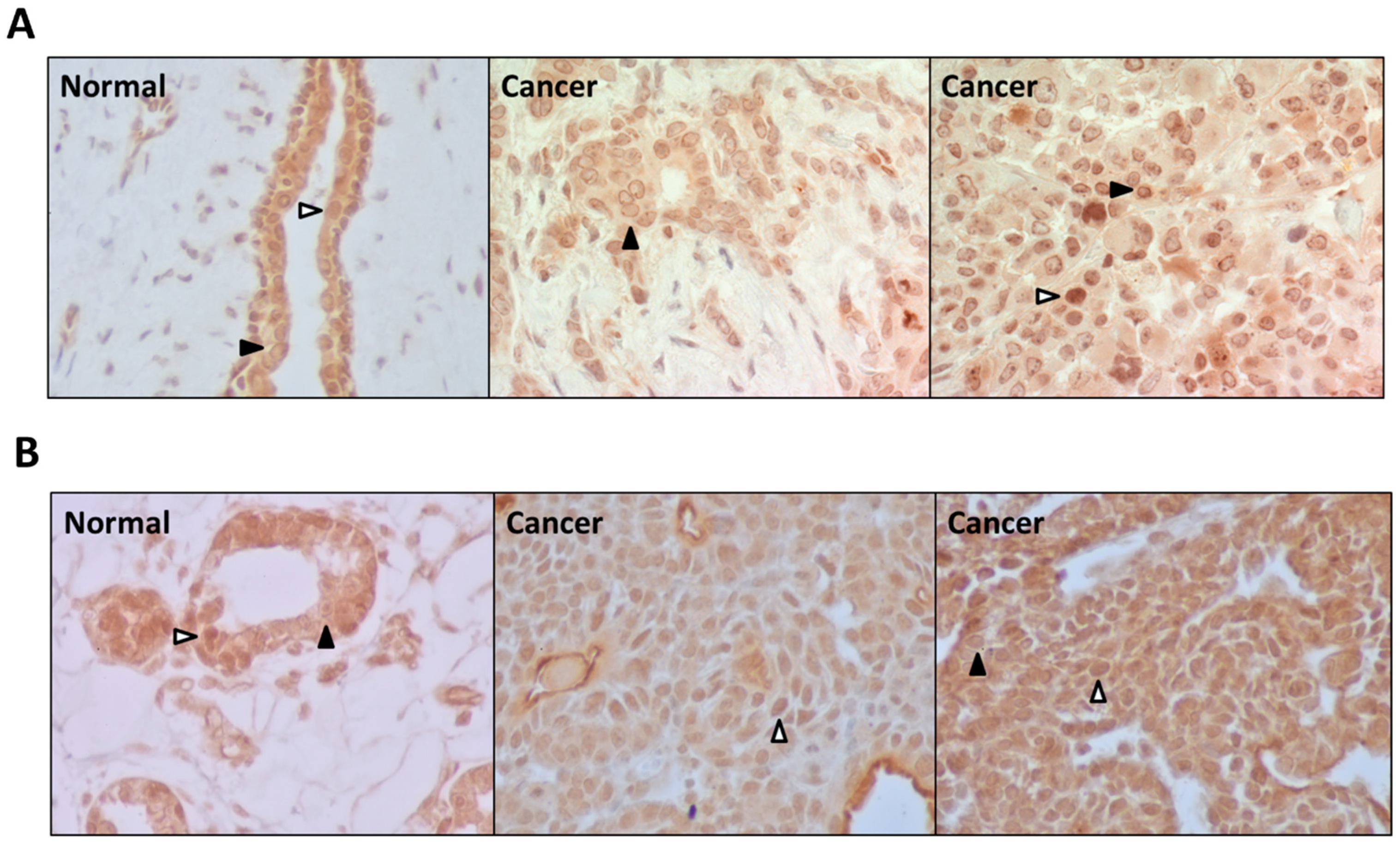
3.4. PDE5 Is Differentially Expressed in Normal and Cancerous Breast Tissues
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2019. Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, K.A.; Scott, S.; Firth, A.U.; Sung, H.; Henley, S.J.; Sherman, R.L.; Siegel, R.L.; Anderson, R.N.; Kohler, B.A.; Benard, V.B.; et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, Part 1: National Cancer Statistics. Cancer 2022, 128, 4251–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.A.; Cronin, K.A.; Plevritis, S.K.; Fryback, D.G.; Clarke, L.; Zelen, M.; Mandelblatt, J.S.; Yakovlev, A.Y.; Habbema, J.D.F.; Feuer, E.J.; et al. Effect of Screening and Adjuvant Therapy on Mortality from Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, H.B.; Stürmer, T.; Lee, V.S.; Anderson, C.; Lee, J.S.; Roh, J.M.; Visvanathan, K.; Muss, H.; Kushi, L.H. Breast Cancer Chemoprevention in an Integrated Health Care Setting. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2017, 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colditz, G.A.; Bohlke, K. Priorities for the Primary Prevention of Breast Cancer. CA. Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, N.M.L.; Smith, I.E. Preventing Late Recurrence in Hormone Receptor-Positive Early Breast Cancer: A Review. Eur. J. Cancer Oxf. Engl. 1990 2022, 172, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visvanathan, K.; Hurley, P.; Bantug, E.; Brown, P.; Col, N.F.; Cuzick, J.; Davidson, N.E.; Decensi, A.; Fabian, C.; Ford, L.; et al. Use of Pharmacologic Interventions for Breast Cancer Risk Reduction: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2942–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Preventive Services Task Force; Owens, D.K.; Davidson, K.W.; Krist, A.H.; Barry, M.J.; Cabana, M.; Caughey, A.B.; Doubeni, C.A.; Epling, J.W.; Kubik, M.; et al. Medication Use to Reduce Risk of Breast Cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. JAMA 2019, 322, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, G.A.; Keeton, A.B.; Tinsley, H.N.; Whitt, J.D.; Gary, B.D.; Mathew, B.; Singh, R.; Grizzle, W.E.; Reynolds, R.C. NSAIDs: Old Drugs Reveal New Anticancer Targets. Pharm. Basel Switz. 2010, 3, 1652–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Deming-Halverson, S.L.; Shrubsole, M.J.; Beeghly-Fadiel, A.; Cai, H.; Fair, A.M.; Shu, X.-O.; Zheng, W. Use of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Reduced Breast Cancer Risk among Overweight Women. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 146, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.A.; Canchola, A.J.; Moy, L.M.; Neuhausen, S.L.; Chung, N.T.; Lacey, J.V.; Bernstein, L. Regular and Low-Dose Aspirin, Other Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Medications and Prospective Risk of HER2-Defined Breast Cancer: The California Teachers Study. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2017, 19, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehm, R.D.; Hopper, J.L.; John, E.M.; Phillips, K.-A.; MacInnis, R.J.; Dite, G.S.; Milne, R.L.; Liao, Y.; Zeinomar, N.; Knight, J.A.; et al. Regular Use of Aspirin and Other Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Breast Cancer Risk for Women at Familial or Genetic Risk: A Cohort Study. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2019, 21, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadi, V.; Shetty, S. Potential of Anti-Inflammatory Molecules in the Chemoprevention of Breast Cancer. Recent Adv. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists’ (CNT) Collaboration; Bhala, N.; Emberson, J.; Merhi, A.; Abramson, S.; Arber, N.; Baron, J.A.; Bombardier, C.; Cannon, C.; Farkouh, M.E.; et al. Vascular and Upper Gastrointestinal Effects of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: Meta-Analyses of Individual Participant Data from Randomised Trials. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2013, 382, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, H.N.; Gary, B.D.; Keeton, A.B.; Zhang, W.; Abadi, A.H.; Reynolds, R.C.; Piazza, G.A. Sulindac Sulfide Selectively Inhibits Growth and Induces Apoptosis of Human Breast Tumor Cells by Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibition, Elevation of Cyclic GMP, and Activation of Protein Kinase G. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 3331–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xi, Y.; Tinsley, H.N.; Gurpinar, E.; Gary, B.D.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Keeton, A.B.; Abadi, A.H.; et al. Sulindac Selectively Inhibits Colon Tumor Cell Growth by Activating the CGMP/PKG Pathway to Suppress Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1848–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, H.N.; Grizzle, W.E.; Abadi, A.; Keeton, A.; Zhu, B.; Xi, Y.; Piazza, G.A. New NSAID Targets and Derivatives for Colorectal Cancer Chemoprevention. Recent Results Cancer Res. Fortschritte Krebsforsch. Progres Dans Rech. Sur Cancer 2013, 191, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, H.-H.; Zhou, Y.-J.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Cao, M.; Huang, J.-J. Effects of Sulindac Sulfide on Proliferation and Apoptosis of Human Breast Cancer Cell. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 7981–7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Omo, G.; Crescenti, D.; Vantaggiato, C.; Parravicini, C.; Borroni, A.P.; Rizzi, N.; Garofalo, M.; Pinto, A.; Recordati, C.; Scanziani, E.; et al. Inhibition of SIRT1 Deacetylase and P53 Activation Uncouples the Anti-Inflammatory and Chemopreventive Actions of NSAIDs. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, H.N.; Gary, B.D.; Thaiparambil, J.; Li, N.; Lu, W.; Li, Y.; Maxuitenko, Y.Y.; Keeton, A.B.; Piazza, G.A. Colon Tumor Cell Growth-Inhibitory Activity of Sulindac Sulfide and Other Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Is Associated with Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibition. Cancer Prev. Res. Phila. Pa 2010, 3, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, H.N.; Gary, B.D.; Keeton, A.B.; Lu, W.; Li, Y.; Piazza, G.A. Inhibition of PDE5 by Sulindac Sulfide Selectively Induces Apoptosis and Attenuates Oncogenic Wnt/β-Catenin Mediated Transcription in Human Breast Tumor Cells. Cancer Prev. Res. Phila. Pa 2011, 4, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, G.A.; Ward, A.; Chen, X.; Maxuitenko, Y.; Coley, A.; Aboelella, N.S.; Buchsbaum, D.J.; Boyd, M.R.; Keeton, A.B.; Zhou, G. PDE5 and PDE10 Inhibition Activates CGMP/PKG Signaling to Block Wnt/β-Catenin Transcription, Cancer Cell Growth, and Tumor Immunity. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Chen, X.; Zhu, B.; Ramírez-Alcántara, V.; Canzoneri, J.C.; Lee, K.; Sigler, S.; Gary, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Suppression of β-Catenin/TCF Transcriptional Activity and Colon Tumor Cell Growth by Dual Inhibition of PDE5 and 10. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27403–27415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.J.; Piazza, G.A.; Li, H.; Liu, L.; Fetter, J.; Zhu, B.; Sperl, G.; Ahnen, D.; Pamukcu, R. Exisulind Induction of Apoptosis Involves Guanosine 3′,5′-Cyclic Monophosphate Phosphodiesterase Inhibition, Protein Kinase G Activation, and Attenuated Beta-Catenin. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3338–3342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piazza, G.A.; Thompson, W.J.; Pamukcu, R.; Alila, H.W.; Whitehead, C.M.; Liu, L.; Fetter, J.R.; Gresh, W.E.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Farnell, D.R.; et al. Exisulind, a Novel Proapoptotic Drug, Inhibits Rat Urinary Bladder Tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3961–3968. [Google Scholar]
- F. Windham, P.; S. Rodriguez, P.; J. Rivers, N.; N. Tinsley, H. PKGI Mediates the Growth Inhibitory Effects of CGMP Signaling in Human Breast Cancer Cells Independent of β-Catenin. Integr. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Lindsey, A.; Li, N.; Lee, K.; Ramirez-Alcantara, V.; Canzoneri, J.C.; Fajardo, A.; Madeira da Silva, L.; Thomas, M.; Piazza, J.T.; et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A Is Overexpressed in Lung Tumor Cells and Inhibitors Selectively Suppress Growth by Blocking β-Catenin and MAPK Signaling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 69264–69280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lee, K.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, B.; Gary, B.D.; Ramírez-Alcántara, V.; Gurpinar, E.; Canzoneri, J.C.; Fajardo, A.; Sigler, S.; et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A: A Novel Target for Selective Inhibition of Colon Tumor Cell Growth and β-Catenin-Dependent TCF Transcriptional Activity. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, B.; Hobrath, J.V.; Connelly, M.C.; Kiplin Guy, R.; Reynolds, R.C. Diverse Amide Analogs of Sulindac for Cancer Treatment and Prevention. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 4614–4621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, B.; Hobrath, J.V.; Connelly, M.C.; Guy, R.K.; Reynolds, R.C. Amine Containing Analogs of Sulindac for Cancer Prevention. Open Med. Chem. J. 2018, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, G.A.; Keeton, A.B.; Tinsley, H.N.; Gary, B.D.; Whitt, J.D.; Mathew, B.; Thaiparambil, J.; Coward, L.; Gorman, G.; Li, Y.; et al. A Novel Sulindac Derivative That Does Not Inhibit Cyclooxygenases but Potently Inhibits Colon Tumor Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis with Antitumor Activity. Cancer Prev. Res. Phila. Pa 2009, 2, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Quealy, E.; Gary, B.D.; Reynolds, R.C.; Piazza, G.A.; Lü, J. A Novel Sulindac Derivative Lacking Cyclooxygenase-Inhibitory Activities Suppresses Carcinogenesis in the Transgenic Adenocarcinoma of Mouse Prostate Model. Cancer Prev. Res. Phila. Pa 2010, 3, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurpinar, E.; Grizzle, W.E.; Shacka, J.J.; Mader, B.J.; Li, N.; Piazza, N.A.; Russo, S.; Keeton, A.B.; Piazza, G.A. A Novel Sulindac Derivative Inhibits Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Growth through Suppression of Akt/MTOR Signaling and Induction of Autophagy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitt, J.D.; Li, N.; Tinsley, H.N.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Gary, B.D.; Keeton, A.B.; Xi, Y.; Abadi, A.H.; et al. A Novel Sulindac Derivative That Potently Suppresses Colon Tumor Cell Growth by Inhibiting CGMP Phosphodiesterase and β-Catenin Transcriptional Activity. Cancer Prev. Res. Phila. Pa 2012, 5, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubet, R.A.; Steele, V.E.; DeCoster, R.; Bowden, C.; You, M.; Juliana, M.M.; Eto, I.; Kelloff, G.J.; Grubbs, C.J. Chemopreventive Effects of the Aromatase Inhibitor Vorozole (R 83842) in the Methylnitrosourea-Induced Mammary Cancer Model. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jänicke, R.U. MCF-7 Breast Carcinoma Cells Do Not Express Caspase-3. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2009, 117, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.-L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J.-M.; Qiu, J.-G.; Zhang, W.-J.; Jiang, Q.-W.; Xue, Y.-Q.; Zheng, D.-W.; et al. Sildenafil Inhibits the Growth of Human Colorectal Cancer in Vitro and in Vivo. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 3311–3324. [Google Scholar]
- Fallahian, F.; Karami-Tehrani, F.; Salami, S.; Aghaei, M. Cyclic GMP Induced Apoptosis via Protein Kinase G in Oestrogen Receptor-Positive and -Negative Breast Cancer Cell Lines. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 3360–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, K.; Donnenwirth, R.; Mills, K.; Tinsley, H.N. Cyclic GMP Signaling during Human Lactation and Breast Cancer: Implications for Breast Cancer Prevention. Breast J. 2019, 25, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Cheng, K.-W.; Ouyang, N.; Huang, L.; Sun, Y.; Constantinides, P.; Rigas, B. Phosphosulindac (OXT-328) Selectively Targets Breast Cancer Stem Cells in Vitro and in Human Breast Cancer Xenografts. Stem Cells Dayt. Ohio 2012, 30, 2065–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borneman, R.M.; Gavin, E.; Musiyenko, A.; Richter, W.; Lee, K.J.; Crossman, D.K.; Andrews, J.F.; Wilhite, A.M.; McClellan, S.; Aragon, I.; et al. Phosphodiesterase 10A (PDE10A) as a Novel Target to Suppress β-Catenin and RAS Signaling in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 2022, 15, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.J.; Chang, W.-C.L.; Chen, X.; Valiyaveettil, J.; Ramirez-Alcantara, V.; Gavin, E.; Musiyenko, A.; Madeira da Silva, L.; Annamdevula, N.S.; Leavesley, S.J.; et al. Suppression of Colon Tumorigenesis in Mutant Apc Mice by a Novel PDE10 Inhibitor That Reduces Oncogenic β-Catenin. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila. Pa.) 2021, 14, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallahian, F.; Karami-Tehrani, F.; Salami, S. Induction of Apoptosis by Type Iβ Protein Kinase G in the Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-468. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2012, 30, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravani, R.; Karami-Tehrani, F.; Hashemi, M.; Aghaei, M.; Edalat, R. Inhibition of Phosphodiestrase 9 Induces CGMP Accumulation and Apoptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines, MCF-7 and MDA-MB-468. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.-C.; Chuu, C.-P.; Chen, C.-Y.; Shiah, S.-G.; Kung, H.-J.; King, K.-L.; Su, L.-C.; Chang, S.-C.; Chang, C.-H. Elevation of Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Suppresses Proliferation and Survival of Human Breast Cancer Cells. PloS ONE 2015, 10, e0125518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, S.; Campana, A.; Giordano, C.; Győrffy, B.; Tarallo, R.; Rinaldi, A.; Bruno, G.; Ferraro, A.; Romeo, F.; Lanzino, M.; et al. Expression and Function of Phosphodiesterase Type 5 in Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines and Tissues: Implications for Targeted Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2271–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klutzny, S.; Anurin, A.; Nicke, B.; Regan, J.L.; Lange, M.; Schulze, L.; Parczyk, K.; Steigemann, P. PDE5 Inhibition Eliminates Cancer Stem Cells via Induction of PKA Signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfian Sargazi, M.; Saravani, R.; Shahraki, A. Hydroalcoholic Extract of Levisticum Officinale Increases CGMP Signaling Pathway by Down-Regulating PDE5 Expression and Induction of Apoptosis in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-468 Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Iran. Biomed. J. 2019, 23, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, S.; Panza, S.; Augimeri, G.; Giordano, C.; Malivindi, R.; Gelsomino, L.; Marsico, S.; Giordano, F.; Győrffy, B.; Bonofiglio, D.; et al. Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) Is Highly Expressed in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts and Enhances Breast Tumor Progression. Cancers 2019, 11, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Sundquist, J.; Sundquist, K.; Ji, J. Use of Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors Is Associated With Lower Risk of Colorectal Cancer in Men With Benign Colorectal Neoplasms. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 672–681.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, I.; Giordano, C.; Bonofiglio, D.; Andò, S.; Catalano, S. Phosphodiesterase Type 5 and Cancers: Progress and Challenges. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 99179–99202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.-R.; Tiwari, A.K.; Ohnuma, S.; Lee, J.W.K.K.; An, X.; Dai, C.-L.; Lu, Q.-S.; Singh, S.; Yang, D.-H.; Talele, T.T.; et al. The Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitor Vardenafil Is a Potent Inhibitor of ABCB1/P-Glycoprotein Transporter. PloS ONE 2011, 6, e19329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.K.; Chen, Z.-S. Repurposing Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitors as Chemoadjuvants. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, G.A. Validation of PDE5 as a Chemoprevention Target. Cancer Prev. Res. Phila. Pa 2017, 10, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dolci, S.; Belmonte, A.; Santone, R.; Giorgi, M.; Pellegrini, M.; Carosa, E.; Piccione, E.; Lenzi, A.; Jannini, E.A. Subcellular Localization and Regulation of Type-1C and Type-5 Phosphodiesterases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 341, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Cheng, H.; Bai, Z.; Li, J. Breast Cancer Cell Line Classification and Its Relevance with Breast Tumor Subtyping. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 3131–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.E.; Mellor, P.; Ward, A.K.; Kendall, S.; McDonald, M.; Vizeacoumar, F.S.; Vizeacoumar, F.J.; Napper, S.; Anderson, D.H. Molecular Characterization of Breast Cancer Cell Lines through Multiple Omic Approaches. Breast Cancer Res. 2017, 19, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Wang, P.-W.; Huang, C.-H.; Yang, P.-M.; Pan, T.-L. Characterizing the Relapse Potential in Different Luminal Subtypes of Breast Cancers with Functional Proteomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neve, R.M.; Chin, K.; Fridlyand, J.; Yeh, J.; Baehner, F.L.; Fevr, T.; Clark, L.; Bayani, N.; Coppe, J.-P.; Tong, F.; et al. A Collection of Breast Cancer Cell Lines for the Study of Functionally Distinct Cancer Subtypes. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustino-Rocha, A.I.; Silva, A.; Gabriel, J.; Teixeira-Guedes, C.I.; Lopes, C.; Gil da Costa, R.; Gama, A.; Ferreira, R.; Oliveira, P.A.; Ginja, M. Ultrasonographic, Thermographic and Histologic Evaluation of MNU-Induced Mammary Tumors in Female Sprague-Dawley Rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomedecine Pharmacother. 2013, 67, 771–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, P.; Zhang, A.; Mao, X. Advances in Rodent Models for Breast Cancer Formation, Progression, and Therapeutic Testing. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 593337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tinsley, H.N.; Mathew, B.; Chen, X.; Maxuitenko, Y.Y.; Li, N.; Lowe, W.M.; Whitt, J.D.; Zhang, W.; Gary, B.D.; Keeton, A.B.; et al. Novel Non-Cyclooxygenase Inhibitory Derivative of Sulindac Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Growth In Vitro and Reduces Mammary Tumorigenesis in Rats. Cancers 2023, 15, 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030646
Tinsley HN, Mathew B, Chen X, Maxuitenko YY, Li N, Lowe WM, Whitt JD, Zhang W, Gary BD, Keeton AB, et al. Novel Non-Cyclooxygenase Inhibitory Derivative of Sulindac Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Growth In Vitro and Reduces Mammary Tumorigenesis in Rats. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030646
Chicago/Turabian StyleTinsley, Heather N., Bini Mathew, Xi Chen, Yulia Y. Maxuitenko, Nan Li, Whitney M. Lowe, Jason D. Whitt, Wei Zhang, Bernard D. Gary, Adam B. Keeton, and et al. 2023. "Novel Non-Cyclooxygenase Inhibitory Derivative of Sulindac Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Growth In Vitro and Reduces Mammary Tumorigenesis in Rats" Cancers 15, no. 3: 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030646
APA StyleTinsley, H. N., Mathew, B., Chen, X., Maxuitenko, Y. Y., Li, N., Lowe, W. M., Whitt, J. D., Zhang, W., Gary, B. D., Keeton, A. B., Grizzle, W. E., Grubbs, C. J., Reynolds, R. C., & Piazza, G. A. (2023). Novel Non-Cyclooxygenase Inhibitory Derivative of Sulindac Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Growth In Vitro and Reduces Mammary Tumorigenesis in Rats. Cancers, 15(3), 646. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030646




