Identification of Highly Sensitive Pleural Effusion Protein Biomarkers for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma by Affinity-Based Quantitative Proteomics
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Patient Samples
2.2. Sample Processing
2.3. Isobaric Labelling of Tryptic Peptides
2.4. Proteome Analysis
2.4.1. Off-Line Fractionation
2.4.2. Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry
2.4.3. Targeted Analysis of Mesothelin and Fibulin-3 by Multiple-Reaction-Monitoring Mass Spectrometry
2.4.4. Raw Data Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
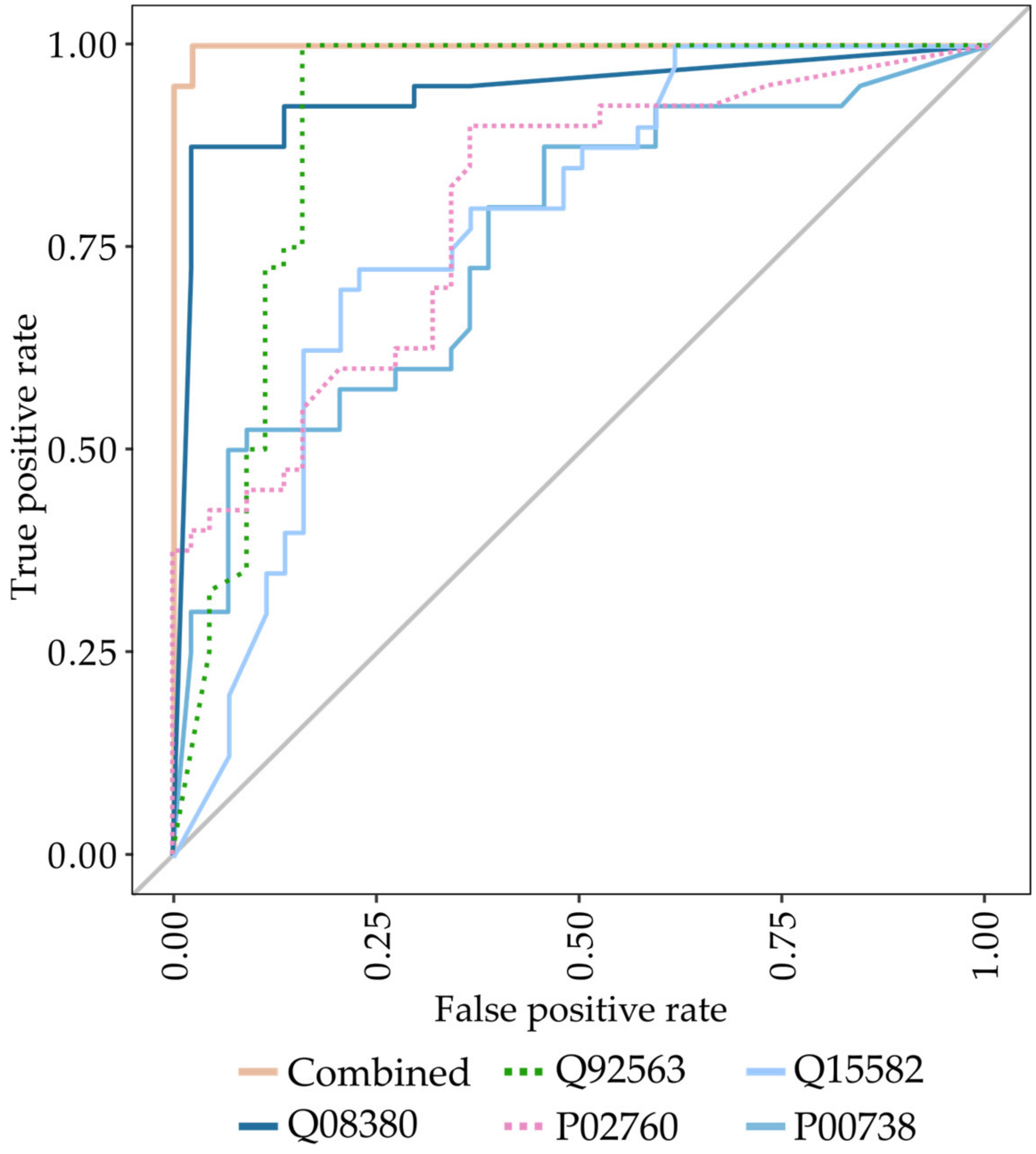
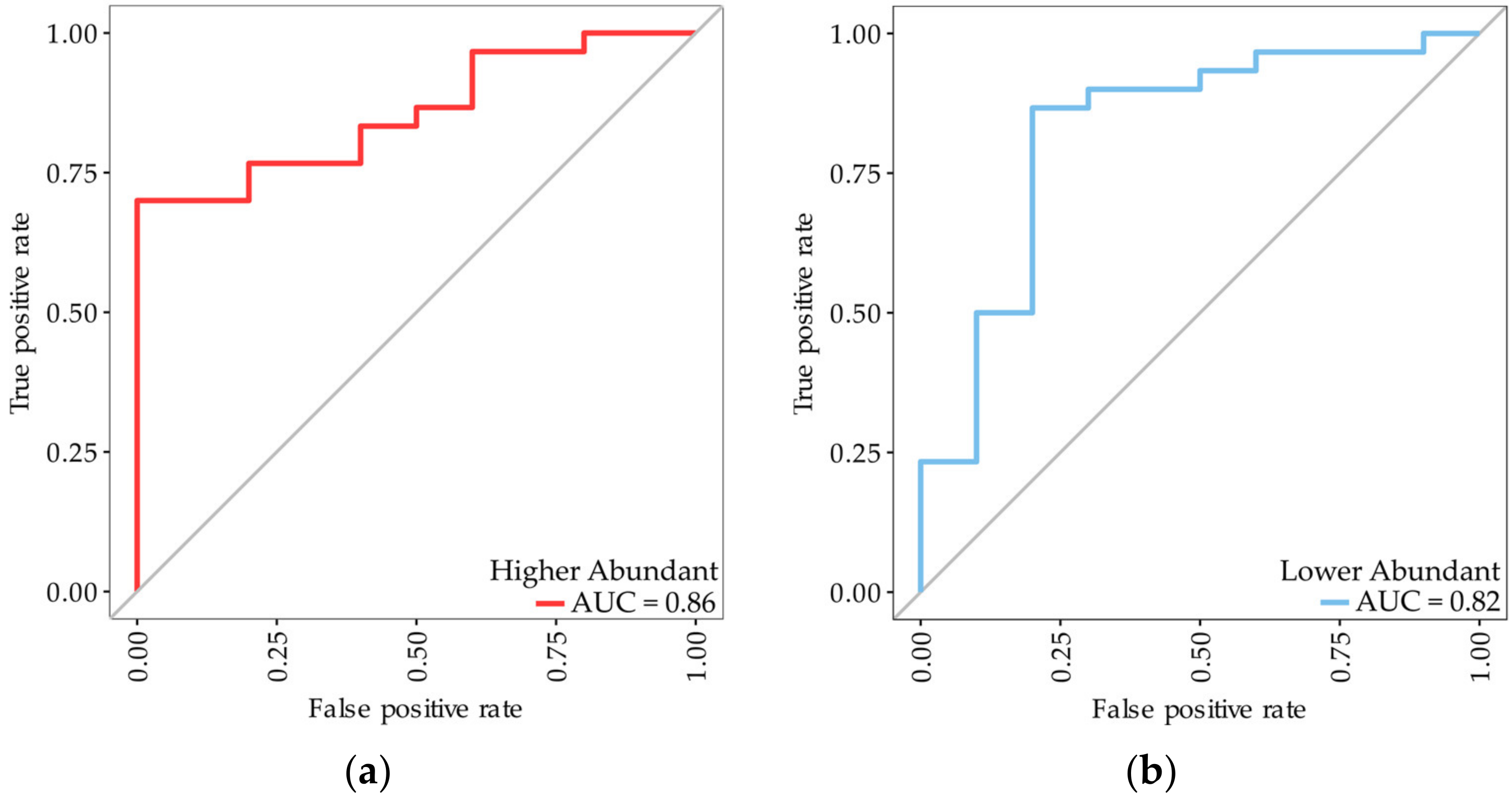
3.1. Identification of Biomarkers for Malignant Mesothelioma
3.2. Analysis of the Previously Identified MPM Protein Biomarkers Fibulin-3 and Mesothelin
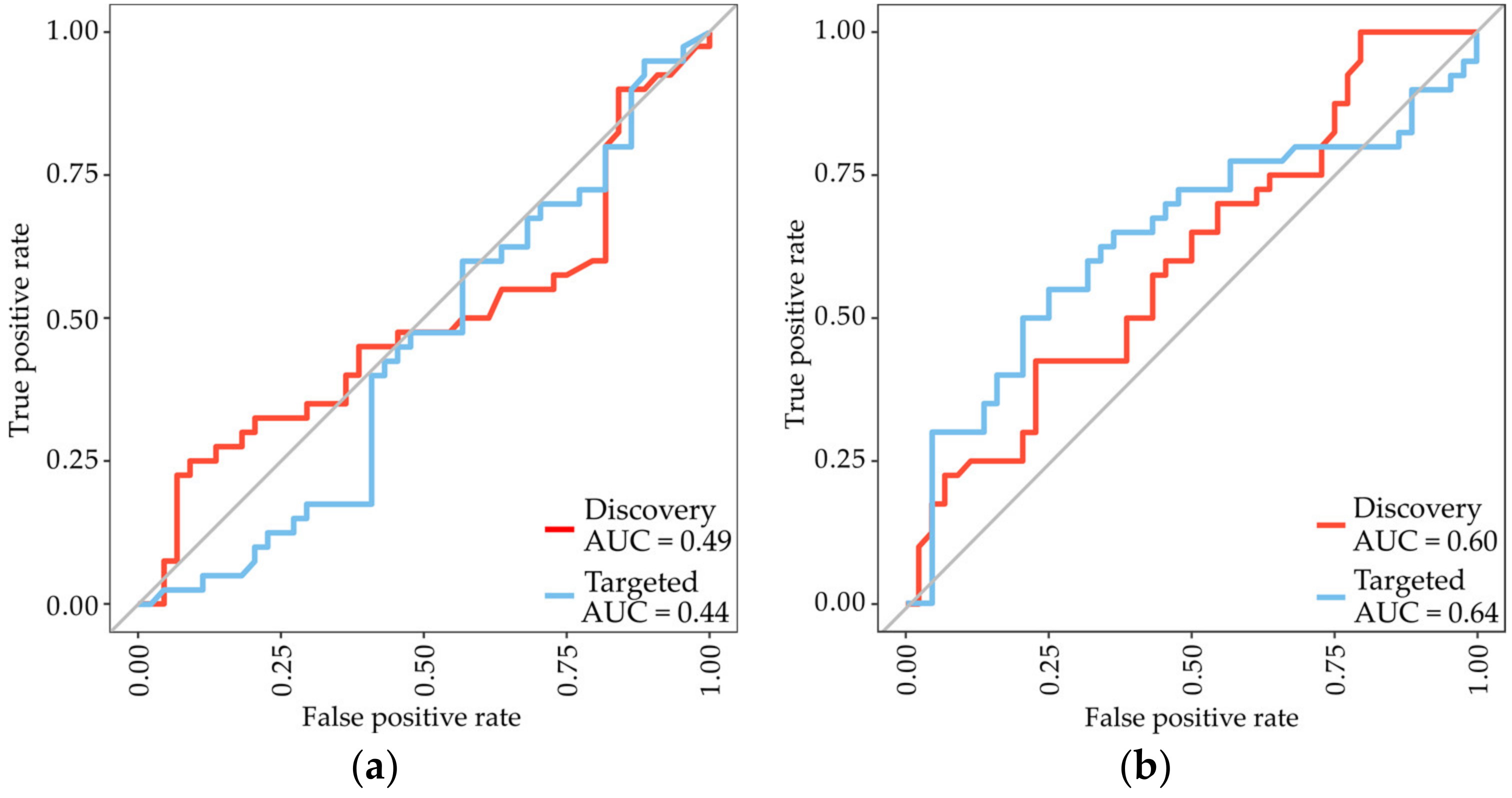
3.3. Identification of Subtype-Specific Proteins for Differentiating MPM Subtypes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson, B.M. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: An epidemiological perspective. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2012, 1, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Cheresh, P.; Kamp, D.W. Molecular basis of asbestos-induced lung disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2013, 8, 161–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.K.; Westbom, C.M.; Shukla, A. Malignant mesothelioma: Development to therapy. J. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 115, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, B.W.; Musk, A.W.; Lake, R.A. Malignant mesothelioma. Lancet 2005, 366, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creaney, J.; Segal, A.; Olsen, N.; Dick, I.M.; Musk, A.W.; Skates, S.J.; Robinson, B.W. Pleural fluid mesothelin as an adjunct to the diagnosis of pleural malignant mesothelioma. Dis. Markers 2014, 2014, 413946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollevoet, K.; Reitsma, J.B.; Creaney, J.; Grigoriu, B.D.; Robinson, B.W.; Scherpereel, A.; Cristaudo, A.; Pass, H.I.; Nackaerts, K.; Rodriguez Portal, J.A.; et al. Serum mesothelin for diagnosing malignant pleural mesothelioma: An individual patient data meta-analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, H.I.; Levin, S.M.; Harbut, M.R.; Melamed, J.; Chiriboga, L.; Donington, J.; Huflejt, M.; Carbone, M.; Chia, D.; Goodglick, L.; et al. Fibulin-3 as a blood and effusion biomarker for pleural mesothelioma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Yan, S.; Guo, X.; Xu, X.; Guo, X. Diagnostic and prognostic utilities of humoral fibulin-3 in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 13030–13038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, S.C.; Kirschner, M.B.; Cooper, W.A.; Tran, T.; Burgers, S.; Wright, C.; Korse, T.; van den Broek, D.; Edelman, J.; Vallely, M.; et al. A proteomics-based approach identifies secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine as a prognostic biomarker in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palstrom, N.B.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Beck, H.C. Affinity Capture Enrichment versus Affinity Depletion: A Comparison of Strategies for Increasing Coverage of Low-Abundant Human Plasma Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.C.; Palstrom, N.B.; Diederichsen, A.; Lindholt, J.S.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Beck, H.C. Determining Plasma Protein Variation Parameters as a Prerequisite for Biomarker Studies-A TMT-Based LC-MSMS Proteome Investigation. Proteomes 2021, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overgaard, M.; Cangemi, C.; Jensen, M.L.; Argraves, W.S.; Rasmussen, L.M. Total and isoform-specific quantitative assessment of circulating fibulin-1 using selected reaction monitoring MS and time-resolved immunofluorometry. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2015, 9, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Pagala, V.R.; Breuer, A.M.; Peng, J.; Bin, M.; Wang, X. Spectral Library Search Improves Assignment of TMT Labeled MS/MS Spectra. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3325–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLean, B.; Tomazela, D.M.; Shulman, N.; Chambers, M.; Finney, G.L.; Frewen, B.; Kern, R.; Tabb, D.L.; Liebler, D.C.; MacCoss, M.J. Skyline: An open source document editor for creating and analyzing targeted proteomics experiments. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 966–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debrabant, B.; Halekoh, U.; Soerensen, M.; Moller, J.E.; Hassager, C.; Frydland, M.; Palstrom, N.; Hjelmborg, J.; Beck, H.C.; Rasmussen, L.M. STEMI, Cardiogenic Shock, and Mortality in Patients Admitted for Acute Angiography: Associations and Predictions from Plasma Proteome Data. Shock 2021, 55, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palstrom, N.B.; Matthiesen, R.; Beck, H.C. Data Imputation in Merged Isobaric Labeling-Based Relative Quantification Datasets. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2051, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.C.; Jensen, L.O.; Gils, C.; Ilondo, A.M.M.; Frydland, M.; Hassager, C.; Moller-Helgestad, O.K.; Moller, J.E.; Rasmussen, L.M. Proteomic Discovery and Validation of the Confounding Effect of Heparin Administration on the Analysis of Candidate Cardiovascular Biomarkers. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creaney, J.; Dick, I.M.; Meniawy, T.M.; Leong, S.L.; Leon, J.S.; Demelker, Y.; Segal, A.; Musk, A.W.; Lee, Y.C.; Skates, S.J.; et al. Comparison of fibulin-3 and mesothelin as markers in malignant mesothelioma. Thorax 2014, 69, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschner, M.B.; Pulford, E.; Hoda, M.A.; Rozsas, A.; Griggs, K.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Edelman, J.J.; Kao, S.C.; Hyland, R.; Dong, Y.; et al. Fibulin-3 levels in malignant pleural mesothelioma are associated with prognosis but not diagnosis. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Ying, Y.; Shan, L.; Feng, J.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y.; Xu, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, C.; Mao, W. Enhanced expression of cohesin loading factor NIPBL confers poor prognosis and chemotherapy resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ween, M.P.; Oehler, M.K.; Ricciardelli, C. Transforming growth Factor-Beta-Induced Protein (TGFBI)/(betaig-H3): A matrix protein with dual functions in ovarian cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 10461–10477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanrıverdi, Z.; Meteroglu, F.; Yüce, H.; Şenyiğit, A.; Işcan, M.; Unüvar, S. The usefulness of biomarkers in diagnosis of asbestos-induced malignant pleural mesothelioma. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusti, L.; Da Valle, Y.; Bonotti, A.; Donadio, E.; Ciregia, F.; Ventroni, T.; Foddis, R.; Giannaccini, G.; Guglielmi, G.; Cristaudo, A.; et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of malignant pleural mesothelioma evidences an altered expression of nuclear lamin and filament-related proteins. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2014, 8, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccellino, M.; Pinto, F.; Ieluzzi, V.; Giovane, A.; Quagliuolo, L.; Fariello, C.; Coppola, M.; Carlucci, A.; Santini, M.; Ferati, K.; et al. Proteomics analysis of human serum of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer reveals proteins as diagnostic biomarker candidates. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 23798–23806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, S.; Wiewrodt, R.; Malden, L.D.; Amin, K.M.; Matzie, K.; Friedberg, J.; Kucharczuk, J.C.; Litzky, L.A.; Johnson, S.W.; Kaiser, L.R.; et al. Gene expression profiling of malignant mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 3080–3097. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.Y.; Yang, C.H.; Chou, H.C.; Cheng, C.M.; Liu, Y.W.; Wang, J.Y.; Huang, L.R.; Tsai, S.F.; Huang, S.F.; Chen, Y.R. EGFR Mutation-Harboring Lung Cancer Cells Produce CLEC11A with Endothelial Trophic and Tumor-Promoting Activities. Cancers 2022, 14, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, Y.G.; Mulder, L.M.; van Zeijl, R.J.M.; Paskoski, L.B.; van Veelen, P.; de Ru, A.; Strefezzi, R.F.; Heijs, B.; Fukumasu, H. Proteomic Analysis Identifies FNDC1, A1BG, and Antigen Processing Proteins Associated with Tumor Heterogeneity and Malignancy in a Canine Model of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappas, A.G.; Magkouta, S.; Pateras, I.S.; Skianis, I.; Moschos, C.; Vazakidou, M.E.; Psarra, K.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Kalomenidis, I. Versican modulates tumor-associated macrophage properties to stimulate mesothelioma growth. Oncoimmunology 2019, 8, e1537427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, H.; Li, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, L. COL11A1 Was Involved in Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis and Migration in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. J. Investig. Surg. 2021, 34, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Wang, W.; Yu, B.; Tan, S. Thrombospondin-2 acts as a bridge between tumor extracellular matrix and immune infiltration in pancreatic and stomach adenocarcinomas: An integrative pan-cancer analysis. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battolla, E.; Canessa, P.A.; Ferro, P.; Franceschini, M.C.; Fontana, V.; Dessanti, P.; Pinelli, V.; Morabito, A.; Fedeli, F.; Pistillo, M.P.; et al. Comparison of the Diagnostic Performance of Fibulin-3 and Mesothelin in Patients with Pleural Effusions from Malignant Mesothelioma. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schillebeeckx, E.; van Meerbeeck, J.P.; Lamote, K. Clinical utility of diagnostic biomarkers in malignant pleural mesothelioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrman, C.; Duche, J.C.; Chouaid, C.; Abd Alsamad, I.; Atassi, K.; Monnet, I.; Tillement, J.P.; Housset, B. Use of tumor markers for differential diagnosis of mesothelioma and secondary pleural malignancies. Clin. Biochem. 2000, 33, 405–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.F.; Wu, Y.H.; Wang, M.S.; Wang, Y.S. CEA, AFP, CA125, CA153 and CA199 in malignant pleural effusions predict the cause. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiberti, R.; Parodi, S.; Libener, R.; Ivaldi, G.P.; Canessa, P.A.; Ugolini, D.; Bobbio, B.; Marroni, P. Diagnostic value of mesothelin in pleural fluids: Comparison with CYFRA 21-1 and CEA. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alatas, F.; Alatas, O.; Metintas, M.; Colak, O.; Harmanci, E.; Demir, S. Diagnostic value of CEA, CA 15-3, CA 19-9, CYFRA 21-1, NSE and TSA assay in pleural effusions. Lung Cancer 2001, 31, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otoshi, T.; Kataoka, Y.; Ikegaki, S.; Saito, E.; Matsumoto, H.; Kaku, S.; Shimada, M.; Hirabayashi, M. Pleural effusion biomarkers and computed tomography findings in diagnosing malignant pleural mesothelioma: A retrospective study in a single center. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0185850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | MPM (n = 40) | Benign (n = 44) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 71.54 ± 8.61 | 68.88 ± 8.82 |
| Gender | ||
| Male (%) | 35 (87.5) | 36 (81.8) |
| Female (%) | 5 (12.5) | 8 (18.2) |
| MM Histology (%) | ||
| Biphasic | 10 (25) | - |
| Epithelioid | 26 (65) | - |
| Unknown | 4 (10) | - |
| Benign Histology (%) | ||
| Fibrosis | 8 (18) | |
| Inflammation | 11 (25) | |
| Nonspecific reactive change | 19 (43) | |
| Others * | 6 (14) |
| SwissProt ID | Protein Name | Gene Name | Fold-Change | p-Value | Importance Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q08380 | Galectin-3-binding protein | LGALS3BP | 1.51 #/1.69 * | 1.44 × 10−5 #/8.22 × 10−12 * | 10.31 #/29.27 * |
| Q15063 | Periostin | POSTN | 1.31 | 0.018 | 8.09 |
| P00738 | Haptoglobin | HP | 1.22 | 0.0011 | 6.90 |
| P02774 | Vitamin D-binding protein | GC | 1.08 | 0.0036 | 6.54 |
| Q12805 | Fibulin-3 | EFEMP1 | 1.12 | 0.004 | 6.46 |
| Q92563 | Testican-2 | SPOCK2 | 2.78 | 1.33 × 10−11 | 23.67 |
| Q15582 | Beta ig-h3 | TGFBI | 1.56 | 6.44 × 10−7 | 15.16 |
| P02760 | Protein AMBP | AMBP | 1.35 | 5.28 × 10−10 | 12.79 |
| Q6KC79 | Nipped-B-like protein | NIPBL | 1.64 | 0.00037 | 7.26 |
| P21741 | Midkine | MDK | 1.63 | 0.0013 | 7.21 |
| Q96GQ7 | DEAD box protein 27 | DDX27 | 1.40 | 0.01 | 6.94 |
| Q6ZRQ5 | Protein MMS22-like | MMS22L | 1.80 | 0.0015 | 6.94 |
| Q99715 | Collagen alpha-1(XII) chain | COL12A1 | 1.42 | 0.00290 | 6.31 |
| Q8WWA0 | Intelectin-1 | ITLN1 | 2.26 | 0.0049 | 5.70 |
| O00468-6 | Agrin | AGRN | 1.56 | 0.00051 | 5.21 |
| Variables | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Accuracy | AUC (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Higher abundant proteins Protein accession (gene name) Q08380 (LGALS3BP), P00738 (HP), Q15063 (POSTN) | 0.97 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.99 (0.98–1.00) |
| Lower abundant proteins Q92563 (SPOCK2), Q6KC79 (NIPBL), Q15582 (TGFBI), P02760 (AMBP) | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.97 (0.94–1.00) |
| Combined Q92563 (SPOCK2), P00738 (HP), Q15582 (TGFBI), P02760 (AMBP), Q08380 (LGALS3BP) | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) |
| SwissProt ID | Protein Name | Gene | Fold-Change (Biphasic/Epithelioid) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Higher abundant proteins | ||||
| Q9HC84 | Mucin-5B | MUC5B | 1.49 | 0.00068 |
| P23381 | Tryptophan-tRNA ligase | WARS1 | 1.42 | 0.0023 |
| Q15582 | Beta ig-h3 | TGFBI | 1.31 | 0.0025 |
| P04217 | Alpha-1B-glycoprotein | A1BG | 1.10 | 0.0043 |
| Q9Y240 | C-type lectin domain F11A | CLEC11A | 1.62 | 0.0054 |
| Lower abundant proteins | ||||
| Q4ZHG4 | Fibronectin type III protein 1 | FNDC1 | 2.23 | 2.47 × 10−5 |
| P13611 | Versican core protein | VCAN | 2.12 | 0.00064 |
| P12107 | Collagen alpha-1(XI) chain | COL11A1 | 1.83 | 0.00075 |
| P35442 | Thrombospondin-2 | THBS2 | 1.67 | 0.0017 |
| Q16363 | Laminin subunit alpha-4 | LAMA4 | 1.62 | 0.0018 |
| SwissProt ID | Protein ID | Gene | Cancer-Related | Biological Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q08380 | Galectin-3-binding protein | LGALS3BP | Yes [25] | cell adhesion |
| Q15063 | Periostin | POSTN | Yes [22] | cell adhesion |
| P00738 | Haptoglobin | HP | Yes [23] | acute-phase response |
| Q92563 | Testican-2 | SPOCK2 | No | extracellular matrix organization |
| Q15582 | Beta ig-h3 | TGFBI | Yes [21] | angiogenesis |
| P02760 | Protein AMBP | AMBP | Yes [24] | cell adhesion |
| Q6KC79 | Nipped-B-like protein | NIPBL | Yes [20] | cellular response to DNA damage |
| Q9HC84 | Mucin-5B | MUC5B | No | |
| P23381 | Tryptophan--tRNA ligase | WARS1 | No | angiogenesis |
| P04217 | Alpha-1B-glycoprotein | A1BG | No | |
| Q9Y240 | C-type lectin domain F11A | CLEC11A | Yes [26] | ossification |
| Q4ZHG4 | Fibronectin type III protein 1 | FNDC1 | Yes [27] | |
| P13611 | Versican core protein | VCAN | Yes [28] | cell adhesion |
| P12107 | Collagen alpha-1(XI) chain | COL11A1 | Yes [29] | cartilage condensation |
| P35442 | Thrombospondin-2 | THBS2 | Yes [30] | cell adhesion |
| Q16363 | Laminin subunit alpha-4 | LAMA4 | No | cell adhesion |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Palstrøm, N.B.; Overgaard, M.; Licht, P.; Beck, H.C. Identification of Highly Sensitive Pleural Effusion Protein Biomarkers for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma by Affinity-Based Quantitative Proteomics. Cancers 2023, 15, 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030641
Palstrøm NB, Overgaard M, Licht P, Beck HC. Identification of Highly Sensitive Pleural Effusion Protein Biomarkers for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma by Affinity-Based Quantitative Proteomics. Cancers. 2023; 15(3):641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030641
Chicago/Turabian StylePalstrøm, Nicolai B., Martin Overgaard, Peter Licht, and Hans C. Beck. 2023. "Identification of Highly Sensitive Pleural Effusion Protein Biomarkers for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma by Affinity-Based Quantitative Proteomics" Cancers 15, no. 3: 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030641
APA StylePalstrøm, N. B., Overgaard, M., Licht, P., & Beck, H. C. (2023). Identification of Highly Sensitive Pleural Effusion Protein Biomarkers for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma by Affinity-Based Quantitative Proteomics. Cancers, 15(3), 641. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15030641







