RETRACTED: Precision Isolation of Circulating Leukemia Cells in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Patients Using a Novel Microfluidic Device and Its Clinical Applications
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Cultivation of Leukemia Cancer Cell Line
2.2. Clinical Sample Collection
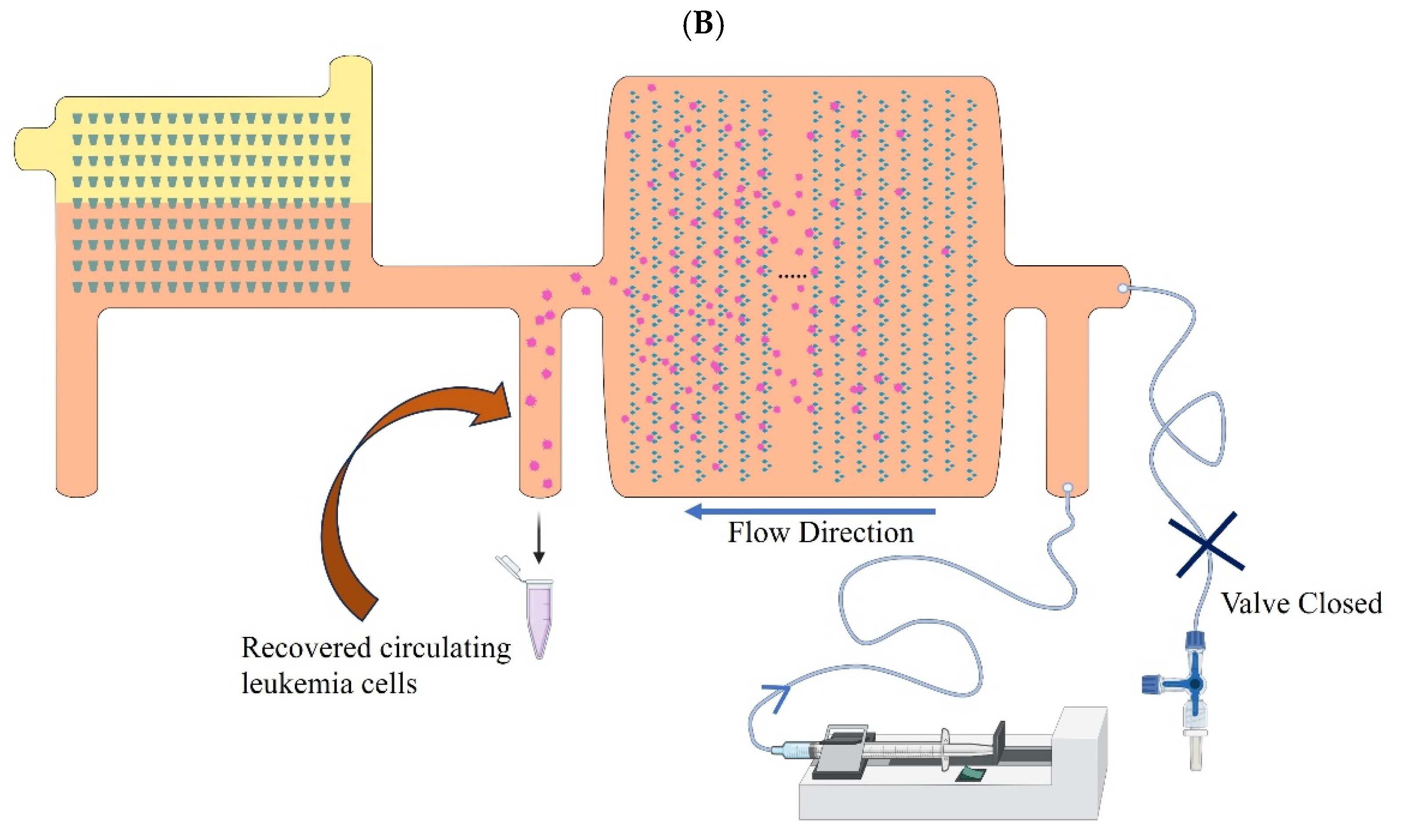
2.3. Microfluidic Device Design Principle to Separate CLCs from Blood
2.4. Microfluidic Assay for CLCs Separation, Enumeration, and Retrieval
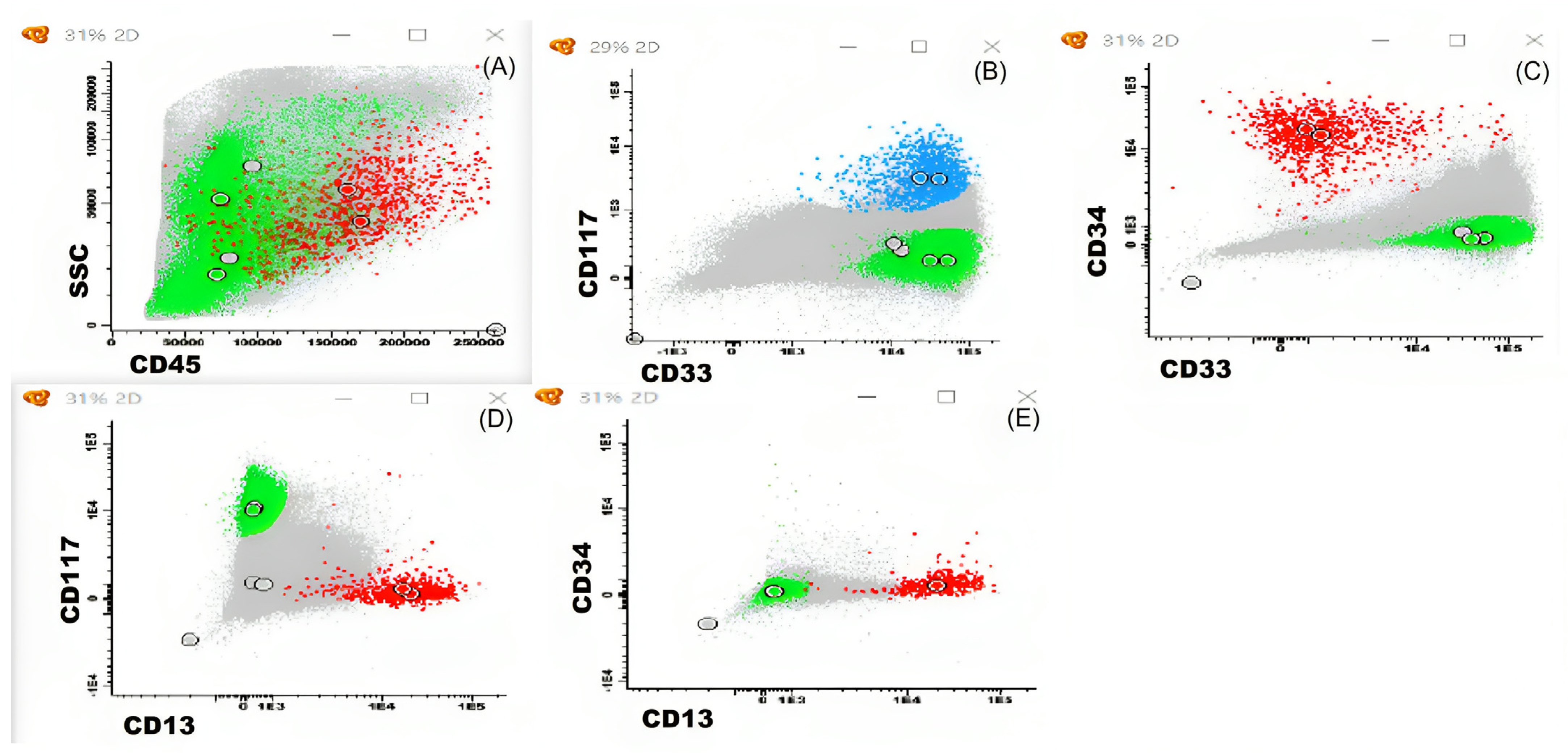
2.5. Bone Marrow Aspiration Sample Accessed by Multi-Parameter Flow Cytometry (MFC)
2.6. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) Assay
3. Results
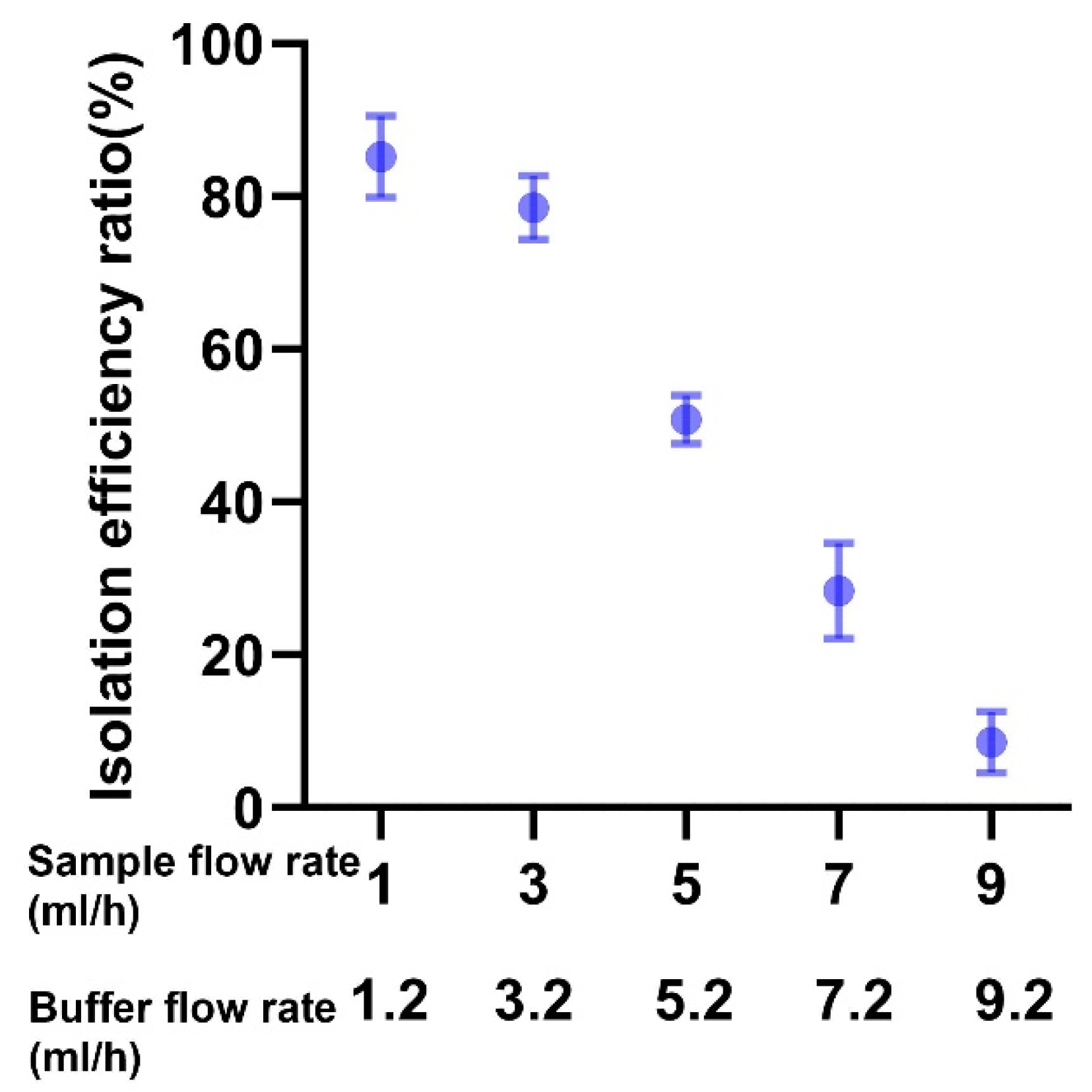
3.1. Microfluidics Device Efficacy in Isolating CLCs across Different Flow Rates
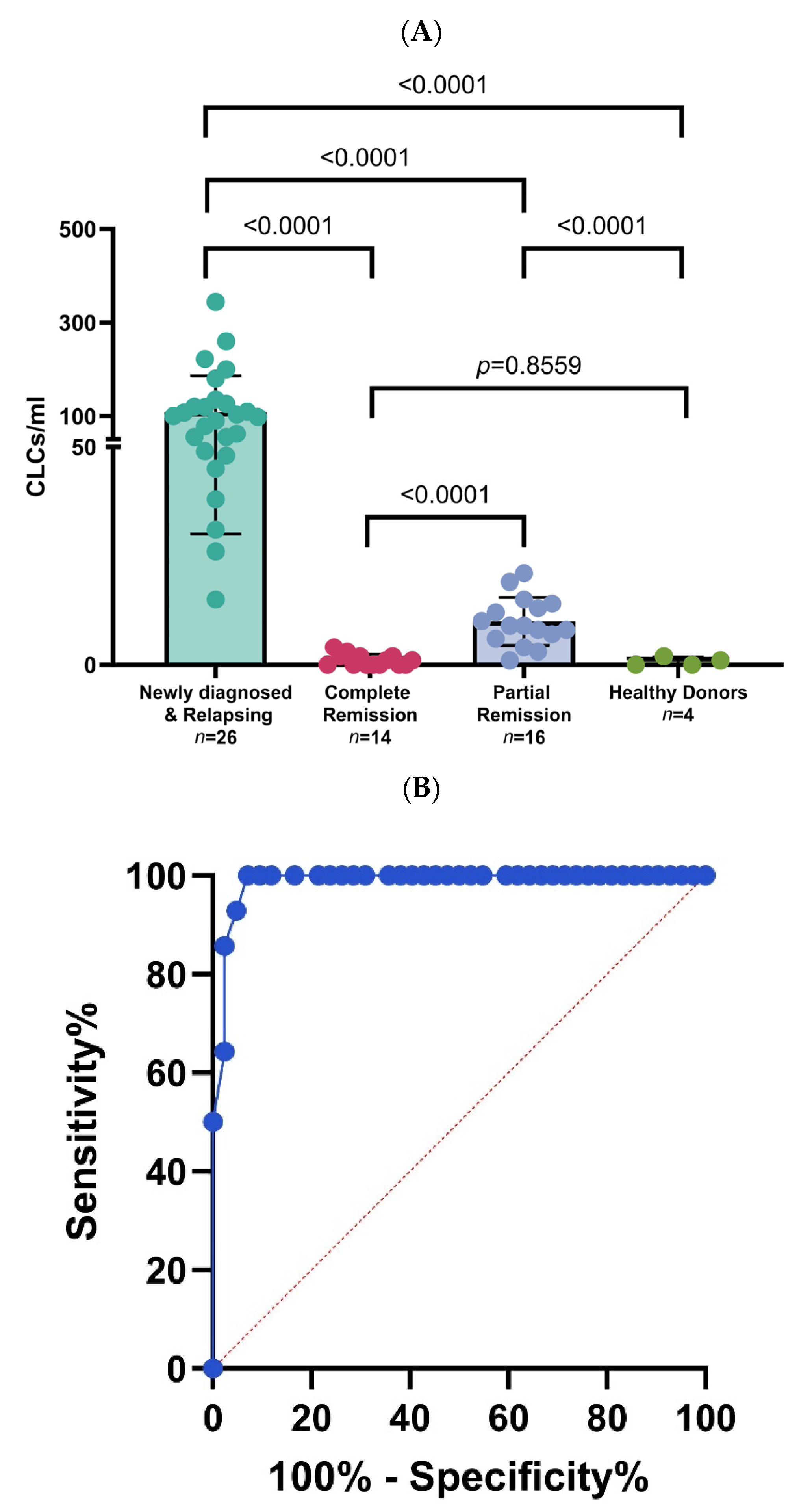
3.2. Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Patient Samples Processing in Microfluidic Device through Different Disease Stages
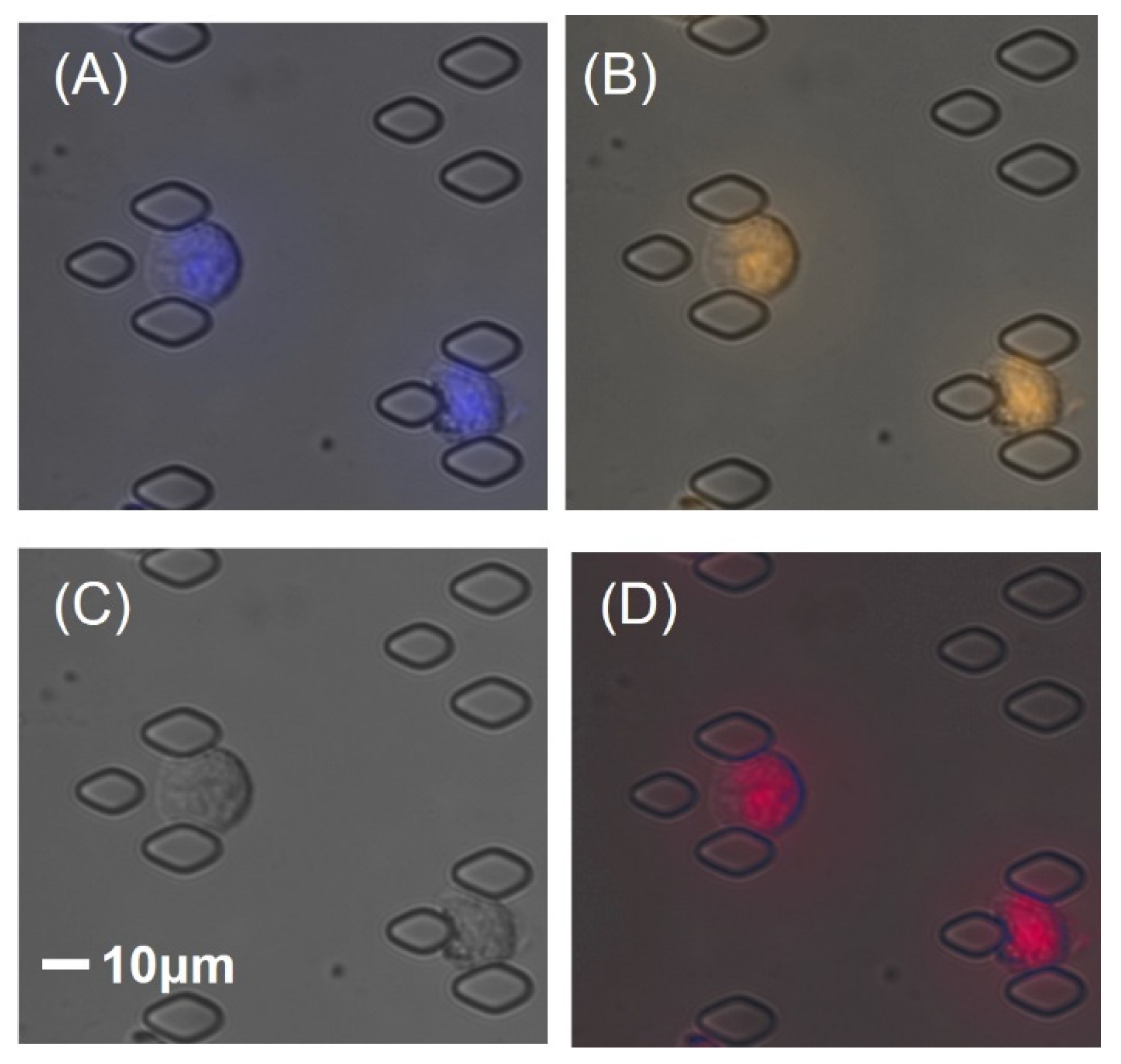
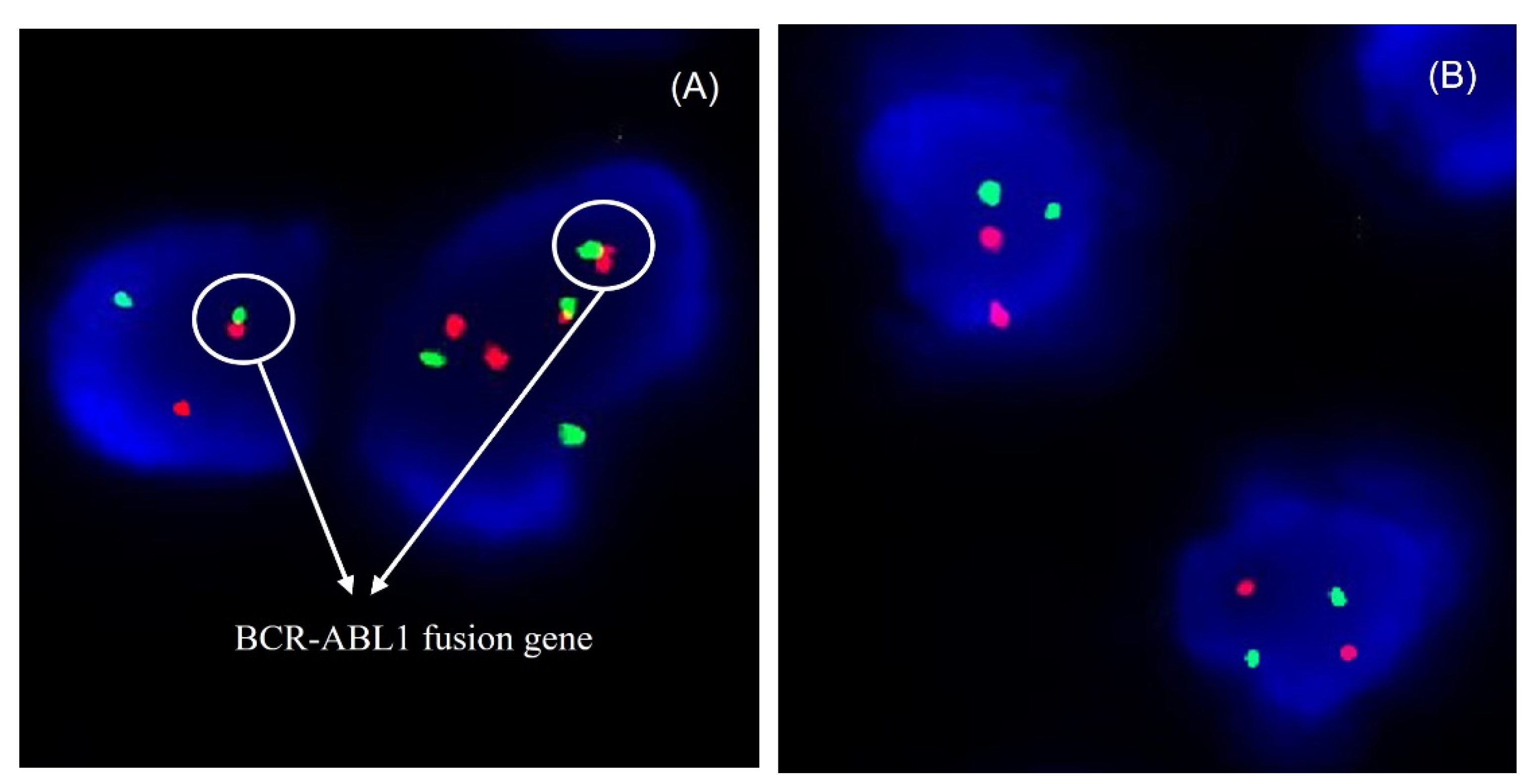
3.3. Cytogenetic Analysis of Circulating Leukemia Cells by FISH Assay
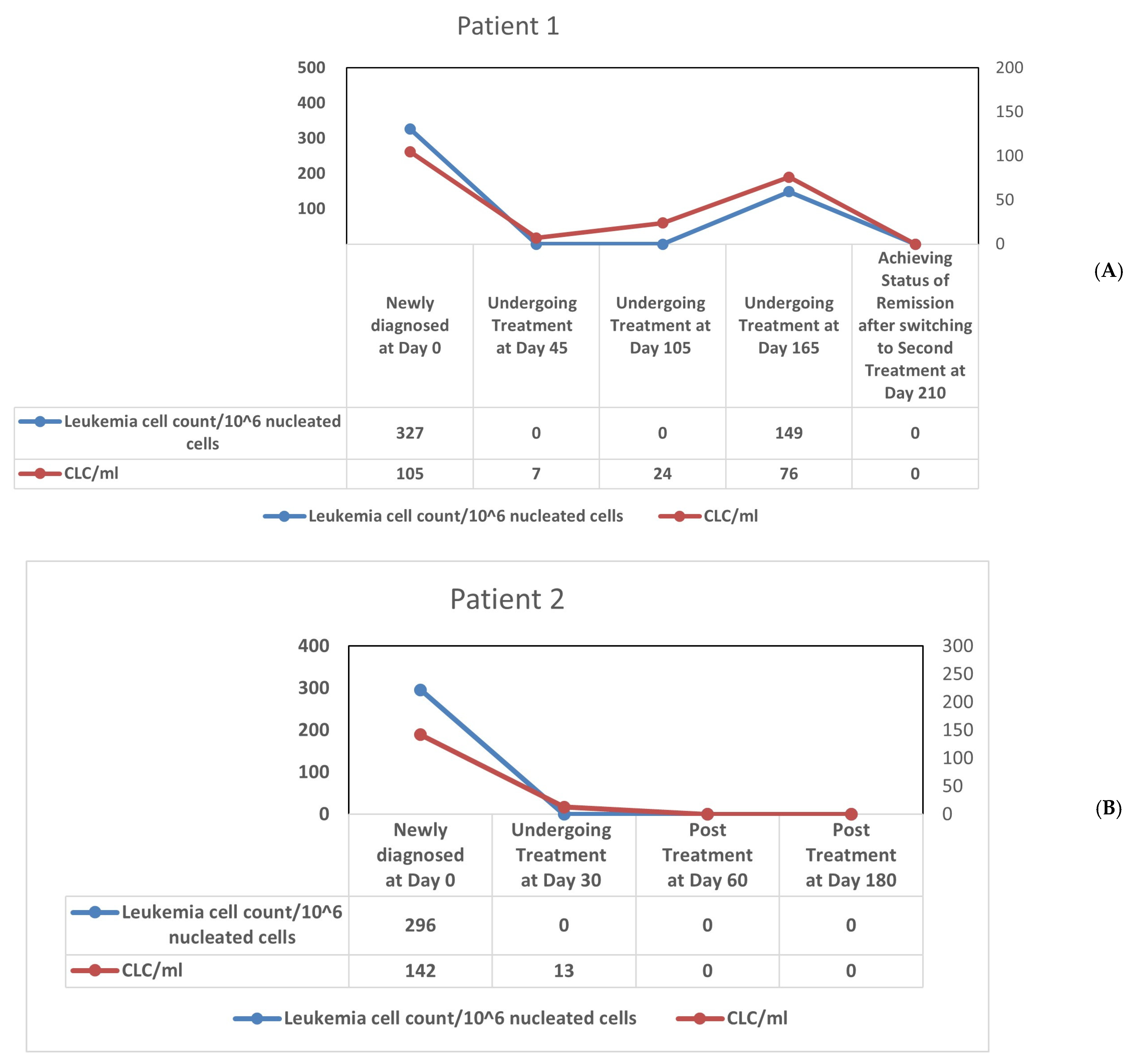
3.4. Longitudinal Monitoring of Leukemic Cell Levels in CML Using Microfluidic Platform and Multiparameter Flow Cytometry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia—Cancer Stat Facts. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/cmyl.html (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- Gyurkocza, B.; Rezvani, A.; Storb, R.F. Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: The State of the Art. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2014, 3, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittencourt, M.C.B.; Ciurea, S.O. Recent Advances in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, e215–e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Tang, G.; Lei, X.; Huang, H.; Peng, J.P. The Progress of Small Molecule Targeting BCR-ABL in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2023, 23, 642–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faderl, S.; Hochhaus, A.; Hughes, T. Monitoring of Minimal Residual Disease in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 18, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hourigan, C.S.; Karp, J.E. Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landstrom, A.P.; Tefferi, A. Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization in the Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment Monitoring of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Leuk. Lymphoma 2006, 47, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, R.; Holtz, M.; Niu, N.; Gray, R.; Snyder, D.S.; Sawyers, C.L.; Arber, D.A.; Slovak, M.L.; Forman, S.J. Persistence of Malignant Hematopoietic Progenitors in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Patients in Complete Cytogenetic Remission Following Imatinib Mesylate Treatment. Blood 2003, 101, 4701–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, E.H.; Earle, J.D.; Goris, M.L.; Kaplan, H.S.; Kriss, J.P. 111Indium bone marrow scintigraphy as an aid in selecting marrow biopsy sites for the evaluation of marrow elements in patients with lymphoma. Cancer 1976, 32, 1560–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulk, B.; Schaffer, M.; Gross, S.; Rao, C.; Smirnov, D.; Connelly, M.C.; Chaturvedi, S.; Reddy, M.; Brittingham, G.; Mata, M.; et al. Enumeration and Characterization of Circulating Multiple Myeloma Cells in Patients with Plasma Cell Disorders. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, C.A.; Wiernik, P.H. Functional Evaluation of Circulating Leukemic Cells in Acute Non-Lymphocytic Leukemia. Leuk. Res. 1977, 1, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oran, B.; De Lima, M. Prevention and Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Relapse after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2011, 18, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, H.M.; Feinstein, D.M.; Kirsch, A.S.; Christenson, L. Multistation Multiparameter Flow Cytometry: Some Influences of Instrumental Factors on System Performance. Cytometry 1983, 4, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earhart, C.M.; Hughes, C.E.; Gaster, R.S.; Ooi, C.C.; Wilson, R.J.; Zhou, L.Y.; Humke, E.W.; Xu, L.; Wong, D.J.; Willingham, S.B.; et al. Isolation and Mutational Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells from Lung Cancer Patients with Magnetic Sifters and Biochips. Lab Chip 2013, 14, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.J.; Kozminsky, M.; Nagrath, S. Emerging Role of Nanomaterials in Circulating Tumor Cell Isolation and Analysis. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 1995–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, J.; Yu, V.; Dhar, M.; Renier, C.; Matsumoto, M.; Heirich, K.; Garon, E.B.; Goldman, J.; Rao, J.; Sledge, G.W.; et al. Classification of Large Circulating Tumor Cells Isolated with Ultra-High Throughput Microfluidic Vortex Technology. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 12748–12760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Li, J.; Sun, Y. Microfluidic Approaches for Cancer Cell Detection, Characterization, and Separation. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1753–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Bessette, P.H.; Qian, J.; Meinhart, C.D.; Daugherty, P.S.; Soh, H.T. Marker-Specific Sorting of Rare Cells Using Dielectrophoresis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15757–15761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baret, J.C.; Miller, O.J.; Taly, V.; Ryckelynck, M.; El-Harrak, A.; Frenz, L.; Rick, C.; Samuels, M.L.; Hutchison, J.B.; Agresti, J.J.; et al. Fluorescence-Activated Droplet Sorting (FADS): Efficient Microfluidic Cell Sorting Based on Enzymatic Activity. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 1850–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.M.; Taylor, J.B.; Witek, M.A.; Hunsucker, S.A.; Waugh, J.P.; Fedoriw, Y.; Shea, T.C.; Soper, S.A.; Armistead, P.M. Microfluidics for the Detection of Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients Using Circulating Leukemic Cells Selected from Blood. Analyst 2016, 141, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.D.; Cantatore, C.; Ohl, D.A. Microfluidic Systems for Isolation of Spermatozoa from Testicular Specimens of Non-Obstructive Azoospermic Men: Does/Can It Improve Sperm Yield? J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; White, A.; Ou, W.; Van Belleghem, S.; Stewart, S.; Shamul, J.G.; Rahaman, S.O.; Fisher, J.P.; He, X. Noncovalent Reversible Binding-Enabled Facile Fabrication of Leak-Free PDMS Microfluidic Devices without Plasma Treatment for Convenient Cell Loading and Retrieval. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 16, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Li, W.; Pappas, D. Recent Advances in Microfluidic Cell Separations. Analyst 2013, 138, 4714–4721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, J.; Yu, V.; Garon, E.B.; Goldman, J.W.; Di Carlo, D. Biophysical Isolation and Identification of Circulating Tumor Cells. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 1452–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyatt Shields Iv, C.; Reyes, C.D.; López, G.P. Microfluidic Cell Sorting: A Review of the Advances in the Separation of Cells from Debulking to Rare Cell Isolation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1230–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Cai, L.; Chang, J.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Li, T.; Sun, J. Label-Free Isolation of Rare Tumor Cells from Untreated Whole Blood by Interfacial Viscoelastic Microfluidics. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 3436–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, D.; Li, Y.; He, W.; Lin, W.; Hu, L.; Wang, C.; Xu, L.; Park, J.; You, L. Mechanical Segregation and Capturing of Clonal Circulating Plasma Cells in Multiple Myeloma Using Micropillar-Integrated Microfluidic Device. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 64114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fachin, F.; Spuhler, P.; Martel-Foley, J.M.; Edd, J.F.; Barber, T.A.; Walsh, J.; Karabacak, M.; Pai, V.; Yu, M.; Smith, K.; et al. Monolithic Chip for High-Throughput Blood Cell Depletion to Sort Rare Circulating Tumor Cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.L.; Hui, T.H.; Tang, B.; Ngan, A.H.W. Accurate Measurement of Stiffness of Leukemia Cells and Leukocytes Using an Optical Trap by a Rate-Jump Method. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 8453–8460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoji, T. Immunophenotypes on Blast Cells of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Nihon Rinsho 2001, 59, 2342–2347. [Google Scholar]
- Carulli, G.; Cannizzo, E.; Ottaviano, V.; Cervetti, G.; Buda, G.; Galimberti, S.; Baratè, C.; Marini, A.; Petrini, M. Abnormal Phenotype of Bone Marrow Plasma Cells in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Undergoing Therapy with Imatinib. Leuk. Res. 2010, 34, 1336–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastogi, P.; Sachdeva, M.U.S. Flow Cytometric Minimal Residual Disease Analysis in Acute Leukemia: Current Status. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2020, 36, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagler, A.; Condiotti, R.; Rabinowitz, R.; Schlesinger, M.; Nguyen, M.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Detection of Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) after Bone Marrow Transplantation (BMT) by Multi-Parameter Flow Cytometry (MPFC). Med. Oncol. 1999, 16, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, H.F.L.; Sokolic, R.A.; Mark, Y. Conventional Cytogenetics and FISH in the Detection of BCR/ABL Fusion in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2006, 81, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkenburg, J.H.F.; Wafelman, A.R.; Joosten, P.; Smit, W.M.; Van Bergen, C.A.M.; Bongaerts, R.; Lurvink, E.; Van Der Hoorn, M.; Kluck, P.; Landegent, J.E.; et al. Complete Remission of Accelerated Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia by Treatment With Leukemia-Reactive Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes. Blood 1999, 94, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochhaus, A.; Weisser, A.; La Rosée, P.; Emig, M.; Müller, M.C.; Saußele, S.; Reiter, A.; Kuhn, C.; Berger, U.; Hehlmann, R.; et al. Detection and Quantification of Residual Disease in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Leukemia 2000, 14, 998–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R.S.; Williams, D.; Ross, M.; Zhao, S.; Chesney, A.; Clark, B.D.; Ben-Ezra, J.M. Bone Marrow Aspirate and Biopsy: A Pathologist’s Perspective. II. Interpretation of the Bone Marrow Aspirate and Biopsy. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2009, 23, 259–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouyang, D.; Ye, N.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Hu, L.; Chao, S.; Li, Y. RETRACTED: Precision Isolation of Circulating Leukemia Cells in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Patients Using a Novel Microfluidic Device and Its Clinical Applications. Cancers 2023, 15, 5696. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235696
Ouyang D, Ye N, Yang K, Wang Y, Hu L, Chao S, Li Y. RETRACTED: Precision Isolation of Circulating Leukemia Cells in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Patients Using a Novel Microfluidic Device and Its Clinical Applications. Cancers. 2023; 15(23):5696. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235696
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuyang, Dongfang, Ningxin Ye, Kun Yang, Yiyang Wang, Lina Hu, Shuen Chao, and Yonghua Li. 2023. "RETRACTED: Precision Isolation of Circulating Leukemia Cells in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Patients Using a Novel Microfluidic Device and Its Clinical Applications" Cancers 15, no. 23: 5696. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235696
APA StyleOuyang, D., Ye, N., Yang, K., Wang, Y., Hu, L., Chao, S., & Li, Y. (2023). RETRACTED: Precision Isolation of Circulating Leukemia Cells in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Patients Using a Novel Microfluidic Device and Its Clinical Applications. Cancers, 15(23), 5696. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235696





