Overview of Risk Factors for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in China
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
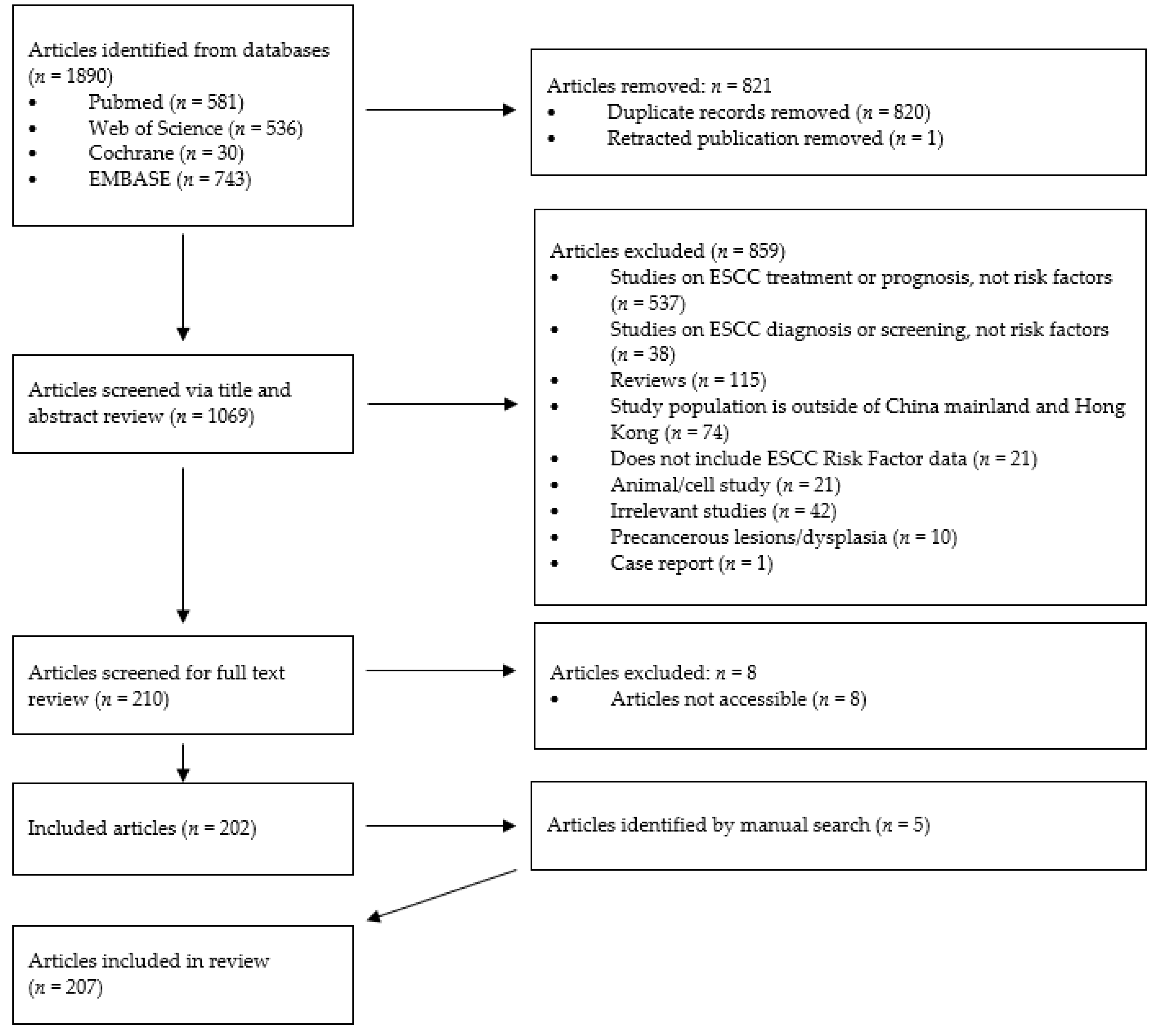
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
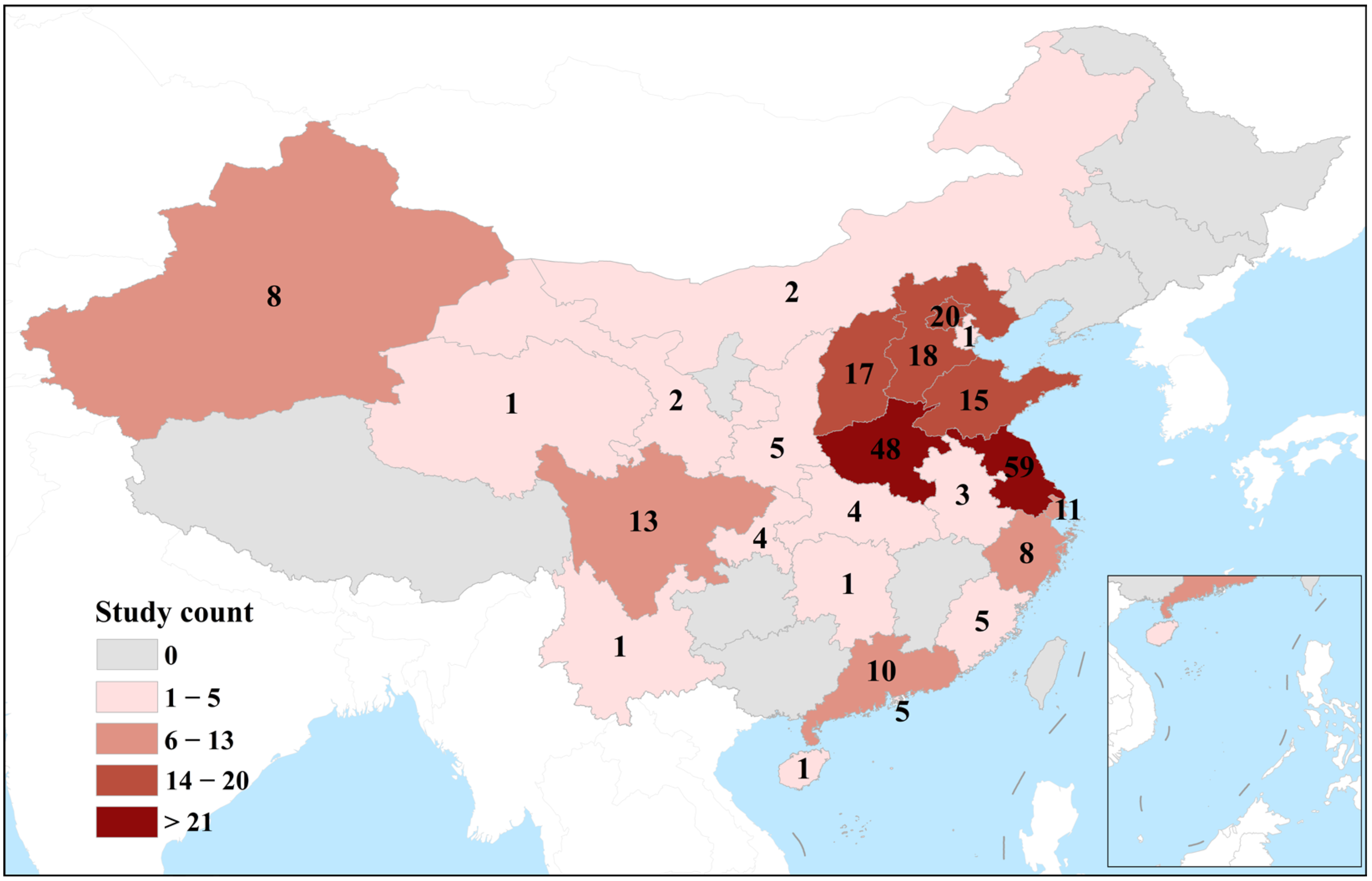
3.1. Study Characteristics
3.2. Study Type
3.2.1. Genetic
3.2.2. Gene–Environment Interactions
3.2.3. Family History
3.2.4. HPV
3.2.5. Helicobacter pylori
3.2.6. Alcohol and Smoking
3.2.7. Pickled Vegetable Consumption
3.2.8. Salted Meat Consumption
3.2.9. Tea Type Consumption
3.2.10. Fresh Fruit and Vegetable Consumption
3.2.11. Other Dietary Factors
3.2.12. Dietary Behavior
3.2.13. Oral Health
3.2.14. Environmental Factors
3.2.15. Socioeconomic Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allemani, C.; Matsuda, T.; Di Carlo, V.; Harewood, R.; Matz, M.; Nikšić, M.; Bonaventure, A.; Valkov, M.; Johnson, C.J.; Estève, J.; et al. Global Surveillance of Trends in Cancer Survival 2000–14 (CONCORD-3): Analysis of Individual Records for 37 513 025 Patients Diagnosed with One of 18 Cancers from 322 Population-Based Registries in 71 Countries. Lancet 2018, 391, 1023–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, N.; Kelly, R.J. The Management of Localized Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Western Approach. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkin, D.M.; Ferlay, J.; Curado, M.-P.; Bray, F.; Edwards, B.; Shin, H.-R.; Forman, D. Fifty Years of Cancer Incidence: CI5 I–IX. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2918–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Zeng, X.; Yin, P.; Zhu, J.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Mortality, Morbidity, and Risk Factors in China and Its Provinces, 1990-2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 394, 1145–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Totsuka, Y.; Shan, B.; Wang, C.; Wei, W.; Qiao, Y.; Kikuchi, S.; Inoue, M.; Tanaka, H.; He, Y. Esophageal Cancer in High-Risk Areas of China: Research Progress and Challenges. Ann. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, K.; Zeng, H.; Li, L.; Wei, W.; He, J. Patterns and Trends in Esophageal Cancer Incidence and Mortality in China: An Analysis Based on Cancer Registry Data. J. Natl. Cancer Cent. 2023, 3, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A Web and Mobile App for Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, B.; Li, W.; Xiong, H.; Qiu, H.; Fu, Q.; Chen, B.; Hu, G.; Yuan, X. Association of P53 and MDM2 Polymorphisms with Risk of Human Papillomavirus (HPV)-Related Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC). Cancer Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Ning, T.; Ke, Y. P53 Codon 72 Polymorphism and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2008, 47, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Q.; Hu, N.; Hyland, P.L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.M.; Yu, K.; Su, H.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, L.M.; Chanock, S.J.; et al. Genetic Variants in DNA Repair Pathway Genes and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Gastric Adenocarcinoma in a Chinese Population. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; Tan, W.; Zhang, S. P53 Gene Codon 72 Polymorphism and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case/Control Study in a Chinese Population. Esophagus 2008, 21, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Yang, J.; Liu, B.; Li, W.; Hu, G.; Qiu, H.; Huang, L.; Xiong, H.; Yuan, X. Combined Effects of Leukocyte Telomere Length, P53 Polymorphism and Human Papillomavirus Infection on Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Han Chinese Population. Cancer Epidemiol. 2014, 38, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Sun, G.; Song, W.; Zhang, B.; Borjigin, B. Association of TP53 Codon 72 Genotype Polymorphism and Environmental Factors with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Mongolian Population of the Chinese Region of Inner Mongolia. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cai, L.; Mu, L.N.; Lu, H.; Lu, Q.Y.; You, N.C.Y.; Yu, S.Z.; Le, A.D.; Zhao, J.; Zhou, X.F.; Marshall, J.; et al. Dietary Selenium Intake and Genetic Polymorphisms of the GSTP1 and P53 Genes on the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Ning, T.; Chen, Z.; Xu, C. Association of Genetic Polymorphisms in MDM2, PTEN and P53 with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 57, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Tong, L.; Wei, J.; Pan, W.; Li, L.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, Q.; Zhou, C.; Yang, M. The ALDH7A1 Genetic Polymorphisms Contribute to Development of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Tumor. Biol. 2014, 35, 12665–12670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Runli, J.; Wei, X.; Lili, G.; Linyan, C.; Yamei, R.; Ruitao, W.; Zhengyun, Z.; Baiqing, L.; Xia, S. Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and ALDH2 and ADH1B Polymorphisms in Chinese Females. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2011, 12, 2065–2068. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; You, N.C.; Lu, H.; Mu, L.N.; Lu, Q.Y.; Yu, S.Z.; Le, A.D.; Marshall, J.; Heber, D.; Zhang, Z.F. Dietary Selenium Intake, Aldehyde Dehydrogenase-2 and X-Ray Repair Cross-Complementing 1 Genetic Polymorphisms, and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer 2006, 106, 2345–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.M.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.Z.; Chen, H.M.; Qi, Z.; Guo, Q.H. Genetic Polymorphisms in Cytochrome P4502E1, Alcohol and Aldehyde Dehydrogenases and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Gansu Chinese Males. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, C.; Yang, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, T.; Yang, X.; Qing, T.; Gao, P.; Shi, L.; Fan, M.; Cheng, H.; et al. Alcohol Intake Interacts with Functional Genetic Polymorphisms of Aldehyde Dehydrogenase (ALDH2) and Alcohol Dehydrogenase (ADH) to Increase Esophageal Squamous Cell Cancer Risk. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, B.; Wang, H.; Zhou, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, Y.; Miao, X.; Tan, W.; Wei, Q.; et al. Identification of Genetic Variants in Base Excision Repair Pathway and Their Associations with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 4378–4384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Zhou, R.M.; Wan, L.L.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Dong, X.J. Polymorphisms of the DNA Repair Gene Xeroderma Pigmentosum Groups A and C and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Population of High Incidence Region of North China. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 134, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Fu, C.; Wang, J.; Xue, H.; Xu, B. Interaction between XRCC1 Polymorphisms and Intake of Long-Term Stored Rice in the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case-Control Study. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2011, 24, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, Y.X.; Dai, L.P.; Wang, P.; Wang, K.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xie, W. Association of Polymorphisms in X-Ray Repair Cross Complementing 1 Gene and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 509215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Du, J.; Shi, M.; Jin, G.; Yang, M. Short Leukocyte Telomere Length, Alone and in Combination with Smoking, Contributes to Increased Risk of Gastric Cancer or Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Miao, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, C.; Xiong, P.; Liang, G.; Sun, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; et al. Significant Increase in Risk of Gastroesophageal Cancer Is Associated with Interaction between Promoter Polymorphisms in Thymidylate Synthase and Serum Folate Status. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 1430–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Luo, G.J.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Zhang, D.Q.; Chen, J.M.; Chen, X.B.; Li, Z.D.; Zhao, Q. Interaction between Alcohol Consumption and CYP 2C19 Gene Polymorphism in Relation to Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Cheng, H.; Chen, X.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhuang, M.; Lu, M.; Jin, L.; Ye, W. Family History of Esophageal Cancer Increases the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, J.B.; Zhang, J.Y.; Fan, J.H.; Qiao, Y.L.; Taylor, P.R. Family History and Risk of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer in the Linxian General Population. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 605106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, N.; Wen, X.D.; Zhang, N.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.W.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, N.; Wen, D.G. Younger Age of Onset and Multiple Primary Lesions Associated with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cases with a Positive Family History of the Cancer Suggests Genetic Predisposition. Chin. Med. J. 2014, 127, 2779–2783. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, H.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J. The Absence of Human Papillomavirus in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in East China. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 4184–4193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Liu, Q.; Liang, M.; Zheng, S.; Li, X.L.; Lu, X.; Sheyhidin, I. Viral Load of HPV 16/18 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Three Ethnic Groups Living in Xinjiang Autonomous Region, China. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; He, Z.; Weiss, N.S.; Madeleine, M.M.; Liu, F.; Tian, X.; Song, Y.; Pan, Y.; et al. Human Papillomavirus Infection and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case-Control Study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2012, 21, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.; Zhang, D.K.; Lam, K.Y.; Ma, L.; Ngan, H.Y.; Liu, S.S.; Tsao, S.W. Prevalence of HPV Infection in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Patients and Its Relationship to the P53 Gene Mutation. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 72, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, H.; Huang, L.; Hu, G.; Yuan, X. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Dis. Esophagus 2013, 26, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehryar, M.M.; Li, S.Y.; Liu, H.W.; Li, F.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Y.B.; Zeng, Y.; Li, J.T. Prevalence of Human Papillomavirus in Esophageal Carcinoma in Tangshan, China. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 2905–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.Y.; Hu, S.P.; Lu, L.C.; Tang, C.Z.; Kuang, Z.S.; Zhong, S.P.; Zeng, Y. Detection of Human Papillomavirus in Esophageal Carcinoma. J. Med. Virol. 2002, 68, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, H.X.; Tsao, S.W.; Poon, C.S.P.; Wang, L.D.; Wong, Y.C.; Cheung, A.L.M. Viral Load of HPV in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 103, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.F.; Roth, M.J.; Wei, W.Q.; Abnet, C.C.; Chen, F.; Lu, N.; Zhao, F.H.; Li, X.Q.; Wang, G.Q.; Taylor, P.R.; et al. No Association between HPV Infection and the Neoplastic Progression of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Result from a Cross-Sectional Study in a High-Risk Region of China. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuyama, K.; Castillo, A.; Aguayo, F.; Sun, Q.; Khan, N.; Koriyama, C.; Akiba, S. Human Papillomavirus in High- and Low-Risk Areas of Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in China. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wu, H.; Wei, S.; Xiong, H.; Fu, X.; Qi, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Li, W.; Hu, G.; Yuan, X.; et al. HPV Seropositivity Joints with Susceptibility Loci Identified in GWASs at Apoptosis Associated Genes to Increase the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC). BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Xu, Z.; Hang, D.; Guo, F.; Abliz, A.; Weiss, N.S.; Xi, L.; Liu, F.; Ning, T.; Pan, Y.; et al. Anti-HPV-E7 Seropositivity and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a High-Risk Population in China. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kamangar, F.; Qiao, Y.L.; Schiller, J.T.; Dawsey, S.M.; Fears, T.; Sun, X.D.; Abnet, C.C.; Zhao, P.; Taylor, P.R.; Mark, S.D. Human Papillomavirus Serology and the Risk of Esophageal and Gastric Cancers: Results from a Cohort in a High-Risk Region in China. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 579–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.S.; Tian, D.P.; Guan, X.Y.; Yun, H.; Wang, H.T.; Xiao, Y.; Bi, C.; Ying, S.; Su, M. Esophageal Intraepithelial Invasion of Helicobacter Pylori Correlates with Atypical Hyperplasia. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 2626–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Xing, L.; Shen, H.; Cui, J.; Mi, J.; Wang, J.; Misumi, J.; Hang, X. Serum Pepsinogens and Helicobacter Pylori Are Not Associated with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a High-Risk Area in China. Tumori 2013, 99, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, L.; Sun, G.; Tang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Gao, W.; Cox, S.B.; Wang, J.S. Etiological Study of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in an Endemic Region: A Population-Based Case Control Study in Huaian, China. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekheden, I.; Yang, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Yuan, Z.; Jin, L.; Lu, M.; Ye, W. Gastric Atrophy and Its Interaction with Poor Oral Health Elevate the Risk for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a High-Risk Region of China: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 189, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.S.; Kamangar, F.; Qiao, Y.L.; Taylor, P.R.; Liang, H.; Dawsey, S.M.; Liu, B.; Fan, J.H.; Abnet, C.C. Serum Pepsinogens and Risk of Gastric and Oesophageal Cancers in the General Population Nutrition Intervention Trial Cohort. Gut 2009, 58, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Mao, B.; Wu, L.; Liu, L.; Rui, J.; Chen, G. A118G Polymorphism in μ-Opioid Receptor Gene and Interactions with Smoking and Drinking on Risk of Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Xu, B.; Rao, J.Y.; Shen, H.B.; Xue, H.C.; Jiang, Q.W. Diet Habits, Alcohol Drinking, Tobacco Smoking, Green Tea Drinking, and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Chinese Population. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 19, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhao, J.-K.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Han, R.-Q.; Yang, J.; Zhou, J.-Y.; Wang, X.-S.; Zhang, X.-F.; Liu, A.-M.; Veer, P.V.; et al. Smoking and Alcohol Drinking Increased the Risk of Esophageal Cancer among Chinese Men but Not Women in a High-Risk Population. Cancer Causes Control 2011, 22, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, D.Y.; Tan, W.; Song, N.; Lin, D.X. Ser326Cys Polymorphism in hOGG1 Gene and Risk of Esophageal Cancer in a Chinese Population. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 95, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, B.; Feng, J.; Pan, X.; Yang, Y.; Ji, C.; Cheng, M.; Cheng, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhao, H. Genetic Variant of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Is Associated with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2014, 18, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, N.; Wakai, T.; Wei, L.; He, Y.; Kumagai, N.; Kitsu, K.; Wang, S.; Akazawa, K. Effect of the Interaction between the Amount and Duration of Alcohol Consumption and Tobacco Smoking on the Risk of Esophageal Cancer: A Case-Control Study. Exp. Ther. Med. 2010, 1, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, N.; Wakai, T.; Akazawa, K.; Ling, Y.; Wang, S.; Shan, B.; Okuhara, Y.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Kataoka, H. Heavy Alcohol Intake Is a Risk Factor for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma among Middle-Aged Men: A Case-Control and Simulation Study. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Hu, A.; Hu, Y.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y. Comparison of Lifestyle and Living Environment among High Risk Immigrant and Low Risk Host Residents: Implications for Esophageal Cancer Etiology. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2010, 11, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.E.; Chen, H.F.; Hu, Z.J.; Shi, X.S. Independent and Combined Effects of Environmental Factors and CYP2C19 Polymorphisms on the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Fujian Province of China. BMC Med. Genet. 2015, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, G.D.; Sun, X.D.; Abnet, C.C.; Fan, J.H.; Dawsey, S.M.; Dong, Z.W.; Mark, S.D.; Qiao, Y.L.; Taylor, P.R. Prospective Study of Risk Factors for Esophageal and Gastric Cancers in the Linxian General Population Trial Cohort in China. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 113, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Huang, C.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Yu, I.T.S.; Christiani, D.C. Consumption of Salted Meat and Its Interactions with Alcohol Drinking and Tobacco Smoking on Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Li, Y.C.; Wu, J.P.; Zhao, Y.J.; Wang, R.B.; Jiang, M.; Song, Q.K. Increased Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Associated with Frequent and Long-Term Consumption of Salted Meat and Salted Fat. J. Int. Med. Res. 2019, 47, 3841–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Ni, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, H.; Plymoth, A.; Jin, L.; Chen, X.; Lu, M.; Ye, W. Very Hot Tea Drinking Increases Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk in a High-Risk Area of China: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Clin. Epidemiol. 2018, 10, 1307–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Xu, G.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Ma, L.; Wang, X. Tea Drinking and the Risk of Esophageal Cancer: Focus on Tea Type and Drinking Temperature. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2020, 29, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, N.; Han, X.; Giffen, C.; Ding, T.; Goldstein, A.M.; Taylor, P.R. Jasmine Tea Consumption and Upper Gastrointestinal Cancer in China. Cancer Causes Control 2009, 20, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, N.; Han, X.Y.; Ding, T.; Giffen, C.; Goldstein, A.M.; Taylor, P.R. Risk Factors for Esophageal and Gastric Cancers in Shanxi Province, China: A Case-Control Study. Cancer Epidemiol. 2011, 35, e91–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Lin, S.; Lao, X.; Zhao, J.; Song, Q.; Su, X.; Yu, I.T.-S. Dietary Patterns and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Population-Based Case-Control Study in a Rural Population. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Z.; Tang, X.; Song, J.; Lin, J.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Z. Dietary Fatty Acid Patterns and Risk of Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.X.; Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Xie, P.; Wang, S.; Yan, L.; Xing, X.; Lu, J.; Tse, L.A.; Wang, H.H.X.; et al. Dietary Intake of Monounsaturated and Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Is Related to the Reduced Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.L.; Yang, L.; Su, M.; Wang, S.K.; Yin, H.; Wang, J.S.; Sun, G.J. Vitamin D3 and Beta-Carotene Deficiency Is Associated with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma—Results of a Case-Control Study in China. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, W.; Li, J.; Tse, L.A.; Xing, X.; Lin, S.; Zhao, J.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, C.X.; Liu, X. Dietary Flavonoid Intake and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Nutrition 2021, 89, 111235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Z.; Wu, J.; Li, J.; Qu, C.; He, Y.; Song, Q. Peanut Consumption Associated with a Reduced Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case-Control Study in a High-Risk Area in China. Thorac. Cancer 2018, 9, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Ye, J.; Lin, Z.; Lin, Z.; Tang, X.; Rao, W.; Hu, Z. Dietary Inflammatory Nutrients and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk: A Case-Control Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, K.S.; Tang, L.; Sun, G.; Wang, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, J.S. Mycotoxin Exposure Is Associated with Increased Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Huaian Area, China. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Jia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, N.; Tan, B.; Guan, S.; An, D.; Cheng, Y. Dinner-to-Bed Time and Post-Dinner Walk: New Potential Independent Factors in Esophageal Cancer Development. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 140, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, C.L.; Song, Q.K.; Deng, Y.M.; Qu, C.X.; Li, J. Association between Dietary Behavior and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Yanting. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 8657–8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tai, W.P.; Nie, G.J.; Chen, M.J.; Yaz, T.Y.; Guli, A.; Wuxur, A.; Huang, Q.Q.; Lin, Z.G.; Wu, J. Hot Food and Beverage Consumption and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case-Control Study in a Northwest Area in China. Medicine 2017, 96, e9325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Yang, A.; Xing, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, K.; Lu, H.; Han, J. Association of Alcohol Consumption before a Meal with the Risk of Gastric Adenocarcinoma and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case-Control Study. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2019, 12, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yuan, Z.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Ye, W. Poor Oral Health Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma—A Population-Based Case-Control Study in China. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Winckler, B.; Lu, M.; Cheng, H.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jin, L.; Ye, W. Oral Microbiota and Risk for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a High-Risk Area of China. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Li, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Lu, M.; Ye, W.; Jin, L.; Suo, C.; Chen, X. Association of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma With the Interaction Between Poor Oral Health and Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Regulating Cell Cycles and Angiogenesis: A Case-Control Study in High-Incidence Chinese. Cancer Control 2022, 29, 10732748221075811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Xie, S.; Li, W.; Ran, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, Z.; Zuo, X.; Tian, L. Association of Wheat Chaff Derived Silica Fiber and Esophageal Cancer in North China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 178, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, C.; Zuo, X.; Tian, L. A Possible Role of Biogenic Silica in Esophageal Cancer in North China? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 8340–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhou, J.; Gu, Y.; Pan, E.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, R.; et al. Urinary Exposure of N-Nitrosamines and Associated Risk of Esophageal Cancer in a High Incidence Area in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Yang, X.; Suo, C.; Yuan, Z.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Lu, M.; Chen, X.; Ye, W. Socioeconomic Status Is Inversely Associated with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk: Results from a Population-Based Case-Control Study in China. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 6911–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubrey, B.J.; Strasser, A.; Kelly, G.L. Tumor-Suppressor Functions of the TP53 Pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivier, M.; Hollstein, M.; Hainaut, P. TP53 Mutations in Human Cancers: Origins, Consequences, and Clinical Use. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, T.; Nakagawara, A. Role of P53 in Cell Death and Human Cancers. Cancers 2011, 3, 994–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Cao, J.; Topatana, W.; Juengpanich, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Shen, J.; Cai, L.; Cai, X.; Chen, M. Targeting Mutant P53 for Cancer Therapy: Direct and Indirect Strategies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marei, H.E.; Althani, A.; Afifi, N.; Hasan, A.; Caceci, T.; Pozzoli, G.; Morrione, A.; Giordano, A.; Cenciarelli, C. P53 Signaling in Cancer Progression and Therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Ke, Y. Precision Screening for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in China. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 32, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Ershow, A.G.; Chen, Z.J.; Wacholder, S.; Li, G.Y.; Guo, W.; Li, B.; Blot, W.J. A Case-Control Study of Cancer of the Esophagus and Gastric Cardia in Linxian. Int. J. Cancer 1989, 43, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricker, A.R.; Preussmann, R. Carcinogenic N-Nitrosamines in the Diet: Occurrence, Formation, Mechanisms and Carcinogenic Potential. Mutat. Res. 1991, 259, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Drinking Coffee, Mate, and Very Hot Beverages; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2018; Volume 116, pp. 33–34. [Google Scholar]
- Claeys, L.; Romano, C.; De Ruyck, K.; Wilson, H.; Fervers, B.; Korenjak, M.; Zavadil, J.; Gunter, M.J.; De Saeger, S.; De Boevre, M.; et al. Mycotoxin Exposure and Human Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review of Epidemiological Studies. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1449–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burd, E.M. Human Papillomavirus and Cervical Cancer. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervical Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cervical-cancer (accessed on 9 August 2023).
- Farhadi, M.; Tahmasebi, Z.; Merat, S.; Kamangar, F.; Nasrollahzadeh, D.; Malekzadeh, R. Human Papillomavirus in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Esophagus in a High-Risk Population. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 1200–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abnet, C.C.; Qiao, Y.L.; Mark, S.D.; Dong, Z.W.; Taylor, P.R.; Dawsey, S.M. Prospective Study of Tooth Loss and Incident Esophageal and Gastric Cancers in China. Cancer Causes Control 2001, 12, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Wang, X.; Zheng, L.; Tang, W.; Dong, C.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Shao, A.; Ding, G.; Liu, C.; et al. Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphisms and Esophageal Cancer Risk in a Chinese Population: A Negative Study. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.F.; Yue, W.B.; Zhou, F.Y.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, X.K.; Jin, Y.; Song, X.; Li, B.; Han, X.N.; Tang, S.; et al. Variations in the MHC Region Confer Risk to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma on the Subjects from High-Incidence Area in Northern China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Sang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, L.; Yuan, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Shao, A.; Ding, G.; et al. Uracil-DNA Glycosylase (UNG) Rs246079 G/A Polymorphism Is Associated with Decreased Risk of Esophageal Cancer in a Chinese Population. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Xue, W.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, X.; Gu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, C.; Gao, Y.; Dai, J.; Ma, H.; et al. U-Shaped Association between Telomere Length and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk: A Case-Control Study in Chinese Population. Front. Med. 2015, 9, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Wei, L.; Miao, X.; Yu, D.; Tan, W.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Lin, D. Two Novel Variants on 13q22.1 Are Associated with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 1774–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Shi, M.; Xia, J.; Xing, H.; Yang, W.; Xiong, X.; Pan, W.; Han, S.; Shang, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, L.; et al. The Sp1-Mediaded Allelic Regulation of MMP13 Expression by an ESCC Susceptibility SNP Rs2252070. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, F.; Fang, Y.; Yu, J.; Jiang, T.; Lin, S.; Zhang, S.; Lv, L.; Long, T.; Pan, H.; Qi, J.; et al. The Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms of AP1S1 Are Associated with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Population. Pharmacogenomics Pers. Med. 2022, 15, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, C.; Sun, C.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Yu, H. The Impact of Pri-MiR-218 Rs11134527 on the Risk and Prognosis of Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 6206–6212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Fu, G.; Wei, J.; Shi, J.; Pan, W.; Ren, Y.; Xiong, X.; Xia, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, H.; et al. The Identification of Two Regulatory ESCC Susceptibility Genetic Variants in the TERT-CLPTM1L Loci. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 5495–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, L.; Fu, G.; Sun, F.; Shi, J.; Wei, J.; Lu, C.; Zhou, C.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, M. The Identification of an ESCC Susceptibility SNP Rs920778 That Regulates the Expression of LncRNA HOTAIR via a Novel Intronic Enhancer. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2062–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Shao, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Xiao, D.; Huang, F. The Functional Variant in the 3′UTR of PTPRT with the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, L.G.; Wang, X.Z.; Liu, A.J. The Correlation between XIAP Gene Polymorphisms and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Susceptibility and Prognosis in a Chinese Population. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2017, 213, 1482–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Wang, L.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Shao, A.; Ding, G.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Tang, W.; et al. TERT-CLPTM1L Rs401681 C>T Polymorphism Was Associated with a Decreased Risk of Esophageal Cancer in a Chinese Population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Song, Q.; Han, J.; Xu, H.; Chen, T.; Xu, J.; Cheng, Y. Sitting Time and Occupational and Recreational Physical Activity in Relation to the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 4787–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Qu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Song, C.; Wang, P.; Ye, H.; Zhang, J.; Dai, L. Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in MicroRNA-Binding Site of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Pathway and Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Dig. Dis. 2020, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, C.M.; Bi, M.X.; Tan, W.; Deng, D.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Guo, L.P.; Lin, D.X.; Lu, S.H. Short Tandem Repeat Polymorphism in a Novel Esophageal Cancer-Related Gene (ECRG2) Implicates Susceptibility to Esophageal Cancer in Chinese Population. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 108, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.W.; Fan, J.H.; Dawsey, S.M.; Taylor, P.R.; Qiao, Y.L.; Abnet, C.C. Serum Thyroglobulin, a Biomarker for Iodine Deficiency, Is Not Associated with Increased Risk of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancers in a Large Chinese Cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2284–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wei, J.; Xu, X.; Pan, W.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, C.; Liu, C.; Gao, J.; Yang, M.; Mao, W. Replication Study of ESCC Susceptibility Genetic Polymorphisms Locating in the ADH1B-ADH1C-ADH7 Cluster Identified by GWAS. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, D.; Hu, N.; Hu, Y.; Wang, C.; Giffen, C.; Tang, Z.Z.; Han, X.Y.; Yang, H.H.; Lee, M.P.; Goldstein, A.M.; et al. Replication of a Genome-Wide Case-Control Study of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 1610–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.C.; Yang, J.M.; Sun, Y.H.; Yang, Y.J.; Qian, J.; Jin, L.; Wang, M.Y.; Bi, R.; Zhang, R.X.; Zhu, M.L.; et al. Putatively Functional PLCE1 Variants and Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC): A Case-Control Study in Eastern Chinese Populations. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, H.; Cao, Y.Y.; Chen, L.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; Chen, Z.F.; Wen, D.G.; Zhang, X.F.; Guo, W.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; et al. PTEN Polymorphisms and the Risk of Esophageal Carcinoma and Gastric Cardiac Carcinoma in a High Incidence Region of China. Dis. Esophagus 2008, 21, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, G.; Fan, J.H.; Mark, S.D.; Dawsey, S.M.; Selhub, J.; Wang, J.; Taylor, P.R.; Qiao, Y.L.; Abnet, C.C. Prospective Study of Serum Cysteine Levels and Oesophageal and Gastric Cancers in China. Gut 2011, 60, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Zhao, J.Q.; Zang, B. PRKAA1 Rs13361707 C/T Polymorphism Confers Decreased Susceptibility to Esophageal Cancer: A Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Xiao, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, M.; Qiu, L.; et al. Pri-MiR-124 Rs531564 and Pri-MiR-34b/c Rs4938723 Polymorphisms Are Associated with Decreased Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Populations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, T.K.; Freedman, N.D.; Fan, J.H.; Qiao, Y.L.; Dawsey, S.M.; Taylor, P.R.; Abnet, C.C. Prediagnostic Plasma Vitamin C and Risk of Gastric Adenocarcinoma and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 98, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Xiong, G.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, K.; Fu, Y.; Yang, K.; Bai, Y. Polymorphisms of Survivin Promoter Are Associated with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 135, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, D.; Qi, J.; Miao, X.; Lu, W.; Tan, W.; Lin, D. Polymorphisms of DNA Repair Genes XRCC1 and XPD and Their Associations with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 100, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, G.; Guo, H.; Wang, K.; Hu, H.; Wang, D.; Xu, X.; Guan, X.; Yang, K.; Bai, Y. Polymorphisms of Decoy Receptor 3 Are Associated with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Han. Tumour Biol. 2010, 31, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Miao, X.; Zhang, X.; Tan, W.; Xiong, P.; Lin, D. Polymorphisms of Death Pathway Genes FAS and FASL in Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2004, 96, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.L.; Shi, T.Y.; Hu, H.C.; He, J.; Wang, M.; Jin, L.; Yang, Y.J.; Wang, J.C.; Sun, M.H.; Chen, H.; et al. Polymorphisms in the ERCC5 Gene and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) in Eastern Chinese Populations. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.P.; Wang, X.L.; Sun, X.; Su, Y.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Lu, B.; Shi, L.Y.; Xiong, C.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, F.; et al. Polymorphisms in the DNA Repair Gene XPD and Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2004, 154, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; He, J.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J.C.; Jin, L.; Wang, X.F.; Yang, Y.J.; Xiang, J.Q.; Wei, Q. Polymorphisms in the AKT1 and AKT2 Genes and Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk in an Eastern Chinese Population. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.L.; Yu, H.; Shi, T.Y.; He, J.; Wang, M.Y.; Li, Q.X.; Sun, M.H.; Jin, L.; Yang, Y.J.; Wang, J.C.; et al. Polymorphisms in MTORC1 Genes Modulate Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Eastern Chinese Populations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.L.; Cui, J.; Fan, Z.M.; Li, X.M.; Li, J.L.; Liu, B.C.; Zhang, D.Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhao, X.K.; Song, X.; et al. Polymorphism of A133S and Promoter Hypermethylation in Ras Association Domain Family 1A Gene (RASSF1A) Is Associated with Risk of Esophageal and Gastric Cardia Cancers in Chinese Population from High Incidence Area in Northern China. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tan, W.; Miao, X.; Sun, T.; Zhao, D.; Lin, D. Platelet 12-Lipoxygenase Arg261Gln Polymorphism: Functional Characterization and Association with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Combination with COX-2 Polymorphisms. Pharmacogenetics Genom. 2007, 17, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, H.X.; Tsao, S.W.; Poon, C.S.P.; Wong, Y.C.; Cheung, A.L.M. Physical Status of HPV-16 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Virol. 2005, 32, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, F.J.; Xie, W.; Cui, L.H.; Wang, P.; Song, C.H.; Qu, H.H.; Wang, K.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Dai, L.P. Novel Functional Variants Locus in PLCE1 and Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Based on Published Genome-Wide Association Studies in a Central Chinese Population. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Kuang, G.; Wei, L.Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Guo, W.; Wang, N.; Fang, S.M.; Wen, D.G.; Chen, Z.F.; et al. No Association of the Matrix Metalloproteinase 1 Promoter Polymorphism with Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Gastric Cardiac Adenocarcinoma in Northern China. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 2385–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Chen, X.F.; Dai, H.F.; Shen, B.H.; Chu, D.; McAfee, T.; Zhang, Z.F. Mutational Spectra of P53 in Geographically Localized Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Groups in China. Cancer 2004, 101, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moody, S.; Senkin, S.; Islam, S.M.A.; Wang, J.; Nasrollahzadeh, D.; Cortez Cardoso Penha, R.; Fitzgerald, S.; Bergstrom, E.N.; Atkins, J.; He, Y.; et al. Mutational Signatures in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma from Eight Countries with Varying Incidence. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Zheng, L.; Liu, S.; Yin, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Shao, A.; Tang, W.; Ding, G.; et al. MiR-196a2 Rs11614913 T>C Polymorphism and Risk of Esophageal Cancer in a Chinese Population. Human. Immunol. 2013, 74, 1199–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.K.; Guo, S.; Yang, F.; Zhao, L.S.; Wang, L.D. MDM2 and Its Functional Polymorphism SNP309 Contribute to the Development of Esophageal Carcinoma. J. Gene Med. 2019, 21, e3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Wang, X.; Luo, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J. Matrix Metalloproteinase 1, 3, and 9 Polymorphisms and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk. Med. Sci. Monit. 2014, 20, 2269–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, E.P.; Yang, G.Y.; Wang, L.D.; Shi, S.T.; Yang, C.S. Loss of Heterozygosity of the Rb Gene Correlates with PRb Protein Expression and Associates with P53 Alteration in Human Esophageal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.; Tian, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, P.; Ning, T.; Xing, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Shi, X.; Chen, D.; et al. LMP7/TAP2 Gene Polymorphisms and HPV Infection in Esophageal Carcinoma Patients from a High Incidence Area in China. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Cao, R.; Liu, C.; Tang, W.; Kang, M. Investigation of IL-4, IL-10, and HVEM Polymorphisms with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case-Control Study Involving 1,929 Participants. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20193895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.S.; Lan, Y.; Liu, Y.G.; Tang, H.; Tang, R.G.; Wang, J.C. Interleukin-18 Gene Promoter Polymorphisms and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Acta Oncol. 2007, 46, 1090–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Shao, A.; Tang, W.; Wang, X.; Ding, G.; Liu, C.; Chen, S.; Gu, H. Interleukin 17A Rs4711998 A>G Polymorphism Was Associated with a Decreased Risk of Esophageal Cancer in a Chinese Population. Dis. Esophagus 2014, 27, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.M.; Li, Q.; Gu, H.Y.; Chen, Y.J.; Wei, J.S.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, L. Interleukin 10 Rs1800872 T>G Polymorphism Was Associated with an Increased Risk of Esophageal Cancer in a Chinese Population. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 3443–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yang, H.P.; Liu, J.F.; Rao, J.; Zhang, X.M.; Qian, H.L.; Niu, X.Q.; Zhao, Z.L. Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-3 (IGFBP-3) Genetic Variant and the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 4146–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, S.M.; Yang, M.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, A.; Song, Q.; Mao, W. Impact of Alcohol Dehydrogenase Gene 4 Polymorphisms on Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk in a Chinese Population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yin, J.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y.; Shao, A.; Tang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Ding, G.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. IL-15 Receptor Alpha Rs2228059 A>C Polymorphism Was Associated with a Decreased Risk of Esophageal Cancer in a Chinese Population. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 1951–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tang, W.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, H.; Yin, J.; Gu, H. IGFBP3 Polymorphisms and Risk of Esophageal Cancer in a Chinese Population. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 17006–17014. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, N.; Roth, M.J.; Polymeropolous, M.; Tang, Z.Z.; Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Wang, Q.H.; Goldstein, A.M.; Feng, S.S.; Dawsey, S.M.; Ding, T.; et al. Identification of Novel Regions of Allelic Loss from a Genomewide Scan of Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma in a High-Risk Chinese Population. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2000, 27, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, L.; Ou, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, E.; Li, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Identification of Genomic Alterations in Oesophageal Squamous Cell Cancer. Nature 2014, 509, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, G.; Miao, X.; Guo, L.; Lin, D.; Lu, S.H. Identification of a Novel Polymorphism Arg290Gln of Esophageal Cancer Related Gene 1 (ECRG1) and Its Related Risk to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.Y.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Hu, Z.B.; Chen, R.; Zhu, Y.J.; Shen, H.B.; Wei, Q.Y.; Zhou, J.W. Identification and Functional Characterization of JWA Polymorphisms and Their Association with Risk of Gastric Cancer and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2007, 70, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, H.X.; Tsao, S.W.; Poon, C.S.P.; Cheung, A.L.M. Human Papillomavirus Infection and Loss of Heterozygosity in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2004, 213, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.C.; Ren, J.L.; Chang, F.B.; Li, J.L.; Yuan, L.; Song, X.; Zhou, S.L.; Guo, T.; Fan, Z.M.; Zeng, Y.; et al. Human Papillomavirus DNA and P16INK4A Expression in Concurrent Esophageal and Gastric Cardia Cancers. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 5901–5906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Wang, X.; Zheng, L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, L.; Shao, A.; Tang, W.; Ding, G.; Liu, C.; Liu, R.; et al. Hsa-MiR-34b/c Rs4938723 T>C and Hsa-MiR-423 Rs6505162 C>A Polymorphisms Are Associated with the Risk of Esophageal Cancer in a Chinese Population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Hu, N.; Goldstein, A.M.; Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Tang, Z.Z.; Roth, M.J.; Wang, Q.H.; Dawsey, S.M.; Han, X.Y.; Ding, T.; et al. High Frequency Allelic Loss on Chromosome 17p13.3-P11.1 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinomas from a High Incidence Area in Northern China. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, L.D.; Zhou, F.Y.; Sun, L.D.; Song, X.; Jin, Y.; Li, J.M.; Kong, G.Q.; Qi, H.; Cui, J.; Zhang, L.Q.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Subjects Identifies Susceptibility Loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Hu, Z.; He, Z.; Jia, W.; Wang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Three New Susceptibility Loci for Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Populations. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Kraft, P.; Zhai, K.; Chang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; He, Z.; Jia, W.; Abnet, C.C.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analyses of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Identify Multiple Susceptibility Loci and Gene-Environment Interactions. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, H.; Wang, L.; Sun, B.; Yin, J.; Gu, H. Genetic Variations in MTHFR and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Susceptibility in Chinese Han Population. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.S.; Xu, Q.Q.; Wang, C.F.; Pan, Y.; Liang, F.; Long, X.K. Genetic Variation in Transforming Growth Factor-Beta1 Gene Associated with Increased Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Tissue Antigens 2007, 70, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, L.; You, W.; Cui, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Song, X.; Wei, Y.; et al. Genetic Variation in MiR-100 Rs1834306 Is Associated with Decreased Risk for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Kazakh Patients in Northwest China. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 7332–7340. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, X.; Luo, A.; Lin, D.; Tan, W.; Liu, Z. Genetic Variants of C1orf10 and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyland, P.L.; Freedman, N.D.; Hu, N.; Tang, Z.Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Ding, T.; Fan, J.H.; Qiao, Y.L.; Golozar, A.; et al. Genetic Variants in Sex Hormone Metabolic Pathway Genes and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1062–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Chen, J.; Guo, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, D.; et al. Genetic Variants in MiR-196a2 and MiR-499 Are Associated with Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Han Population. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 4777–4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Yan, C.; Gao, Y.; Du, J.; Zhu, X.; Yu, F.; Huang, T.; Dai, J.; Ma, H.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Genetic Variants at 9p21.3 Are Associated with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, N.; Zheng, M.; Wang, C.; Ji, Y.; Du, J.; Zhu, C.; He, Y.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, X.; Sun, M.; et al. Genetic Variants at 8q24 Are Associated with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yu, X.; Guo, Y.; Song, W.; Yu, D.; Zhang, X. Genetic Variant in CASP3 Affects Promoter Activity and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ji, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Wu, F.; Hu, J.; Jiang, J.; Cui, X.; Chen, Y.; Pang, L.; et al. Genetic Variability in LMP2 and LMP7 Is Associated with the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Kazakh Population but Is Not Associated with HPV Infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Li, H.; Tan, W.; Miao, X.; Wang, L. Genetic Polymorphisms in Folate- Metabolizing Enzymes and Risk of Gastroesophageal Cancers: A Potential Nutrient-Gene Interaction in Cancer Development. Forum Nutr. 2007, 60, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, A.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Wei, Z.; Lian, C.; Ma, L.; Chen, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, L.; Wei, W. Functional SNPs in Human C20orf54 Gene Influence Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2011, 12, 3207–3212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ni, B.; Chen, S.; Xie, H.; Ma, H. Functional Polymorphisms in Interleukin-23 Receptor and Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Miao, X.; Xiong, P.; Tan, W.; Lin, D. Functional Haplotypes in the Promoter of Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Predict Risk of the Occurrence and Metastasis of Esophageal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7622–7628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.T.; Yang, J.Y.; Wei, J.Y.; Chen, H.W.; Ge, Y.X.; Zhang, J.F.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhou, C.C.; Yuan, Q.P.; Zhou, L.Q.; et al. Functional BCL-2 Regulatory Genetic Variants Contribute to Susceptibility of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichun, Y.; Tang, C.M.C.; Wai Lau, K.; Lung, M.L. Frequent Loss of Heterozygosity on Chromosome 9 in Chinese Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cancer Lett. 2004, 203, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Huang, J.; Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Tang, Z.Z.; Roth, M.J.; Wang, C.; Dawsey, S.M.; Li, G.; Li, W.J.; Wang, Q.H.; et al. Frequent Inactivation of the TP53 Gene in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma from a High-Risk Population in China. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 883–891. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, L.; Zhu, Z.Z.; Shen, Y.; Sun, G.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, S.; Yin, X.; Zhu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, G. Frequent Germline Mutation in the BRCA2 Gene in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients from a Low-Risk Chinese Population. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2011, 12, 1771–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, W.; Chen, G.F.; Xing, D.Y.; Song, C.Y.; Kadlubar, F.F.; Lin, D.X. Frequency of CYP2A6 Gene Deletion and Its Relation to Risk of Lung and Esophageal Cancer in the Chinese Population. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 95, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Shi, Y.; Tang, W.; Chen, S.; Gu, H.; Yin, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, P. Forkhead Box A1 (FOXA1) Tagging Polymorphisms and Esophageal Cancer Risk in a Chinese Population: A Fine-Mapping Study. Biomarkers 2016, 21, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.; Bo, L.; Gu, H.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y. Flap Endonuclease-1 Rs174538 G>A Polymorphisms Are Associated with the Risk of Esophageal Cancer in a Chinese Population. Thorac. Cancer 2017, 8, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Zheng, L.; Li, X.; Wang, L. FasL Gene -844T/C Mutation of Esophageal Cancer in South China and Its Clinical Significance. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Noffsinger, A.; Stemmermann, G.; Fenoglio-Preiser, C. Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinomas Arising in Patients from a High-Risk Area of North China Lack an Association with Epstein-Barr Virus. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 1999, 8, 1111–1114. [Google Scholar]
- Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Qiao, Y.L.; Abnet, C.C.; Ratnasinghe, D.L.; Dawsey, S.M.; Dong, Z.W.; Taylor, P.R.; Mark, S.D. Esophageal and Gastric Cardia Cancer Risk and Folate- and Vitamin B 12-Related Polymorphisms in Linxian, China. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2003, 12, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.X.; Yang, S.; Xu, C.Q.; Hou, R.P.; Zhang, C.Z.; Xu, C.P. Equivocal Association of RAD51 Polymorphisms with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, Y.; Shi, L.; Wu, Y.; Yang, W.; Gu, H.; Yin, J.; Yuan, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; et al. Epiregulin Rs1460008 A>G Polymorphism Is Associated with Decreased Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 9, 23685–23690. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.X.; Wang, Y.S.; Sheng, J.; Xiang, D.; Huang, T.X.; Tan, B.B.; Zeng, C.M.; Li, H.H.; Yang, J.; Meltzer, S.J.; et al. Epigenetic Alterations of a Novel Antioxidant Gene SLC22A3 Predispose Susceptible Individuals to Increased Risk of Esophageal Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1658–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.J.; Lv, G.D.; Zheng, S.T.; Huang, C.G.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Lin, R.Y.; Sheyhidin, I.; Lu, X.M. DNA Polymorphism and Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Population of North Xinjiang, China. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, C.; Qing, T.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Yang, Y.J.; Fan, M.; Zhang, T.; Lu, M.; Jin, L.; et al. Differential Cumulative Risk of Genetic Polymorphisms in Familial and Nonfamilial Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2019, 28, 2014–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.B.; Guo, M.; Quan, L.P.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Z.M.; Wang, Q.H.; Ke, Y.; Xu, N.Z. Detection of Human Papillomavirus in Chinese Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Its Adjacent Normal Epithelium. World J. Gastroenterol. 2003, 9, 1170–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Tan, W.; Lin, D. Cyclooxygenase-2 Gly587Arg Variant Is Associated with Differential Enzymatic Activity and Risk of Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Hu, L.; Tao, H.; Guan, X.; Zhang, K.; Bai, Y.; Yang, K. Copy Number Loss of Variation_91720 in PIK3CA Predicts Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 14479–14485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Yuan, G.; Hu, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, P.; Chen, Z.; Song, J. Contribution of ZBTB20 Polymorphisms to Esophageal Cancer Risk Among the Chinese Han Population. Pharmacogenomics Pers. Med. 2022, 15, 827–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Xiao, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhou, T.; Yin, Y. Comparison of Tumor-Associated and Nontumor-Associated Esophageal Mucosa Microbiota in Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Medicine 2022, 101, E30483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, L.; Huo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhu, Y. Comparison of Prevalence, Viral Load, Physical Status and Expression of Human Papillomavirus-16, -18 and -58 in Esophageal and Cervical Cancer: A Case-Control Study. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.B.; Dawsey, S.M.; Fan, J.H.; Freedman, N.D.; Tang, Z.Z.; Ding, T.; Hu, N.; Wang, L.M.; Wang, C.Y.; Su, H.; et al. Common Genetic Variants Related to Vitamin D Status Are Not Associated with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk in China. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015, 39, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Li, W.J.; Su, H.; Wang, C.; Goldstein, A.M.; Albert, P.S.; Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Kong, L.H.; Roth, M.J.; Dawsey, S.M.; et al. Common Genetic Variants of TP53 and BRCA2 in Esophageal Cancer Patients and Healthy Individuals from Low and High Risk Areas of Northern China. Cancer Detect. Prev. 2003, 27, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Yang, H.H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Hu, N.; Tang, Z.Z.; Su, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Ding, T.; et al. Common Genetic Variants in Epigenetic Machinery Genes and Risk of Upper Gastrointestinal Cancers. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.M.; Ning, L.; Zhao, X.K.; Chai, A.W.Y.; Lei, L.C.; Choi, S.S.A.; Tao, L.; Law, S.; Kwong, A.; Lee, N.P.; et al. BRCA2 Loss-of-Function Germline Mutations Are Associated with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk in Chinese. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1042–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhu, M.; He, J.; Wang, J.C.; Jin, L.; Wang, X.F.; Xiang, J.Q.; Wei, Q. Associations of PI3KR1 and MTOR Polymorphisms with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk and Gene-Environment Interactions in Eastern Chinese Populations. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, H.; Wang, L.; Qian, C. Association Study of Map3k1 Snps and Risk Factors with Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population: A Case-Control Study. Pharmacogenomics Pers. Med. 2020, 13, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Diao, Y.; Fang, X.; Li, H. Association of the Polymorphisms of MTHFR C677T, VDR C352T, and MPO G463A with Risk for Esophageal Squamous Cell Dysplasia and Carcinoma. Arch. Med. Res. 2008, 39, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Liu, C.; Teng, X.; Yin, J.; Zheng, L.; Wang, L.; Tang, W.; Gu, H.; Gu, B.; Chen, L. Association of the Interleukin-18 Receptor 1 and Interleukin-18 Receptor Accessory Protein Polymorphisms with the Risk of Esophageal Cancer. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 4, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Yin, X.; Yang, H.; Yang, J.; Zhao, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, H. Association of the Genetic Polymorphisms in XRCC6 and XRCC5 with the Risk of ESCC in a High-Incidence Region of North China. Tumori 2015, 101, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wei, W.Q.; Cormier, R.T.; Zhang, S.T.; Qiao, Y.L.; Li, X.Q.; Zhu, S.T.; Zhai, Y.C.; Peng, X.X.; Yan, Y.X.; et al. Association of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in the Prostaglandin-Endoperoxide Synthase 2 (PTGS2) and Phospholipase A(2) Group IIA (PLA2G2A) Genes with Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 1797–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Wang, L.Z.; Wang, P.; Song, C.H.; Wang, K.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Dai, L.P. Association of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms in ERCC2 Gene and Their Haplotypes with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 4225–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Yang, C.; Yang, L.; Qi, C.; Tian, S.; Han, Y.; Dou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tian, D.; Zheng, Y. Association of Roasting Meat Intake with the Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Kazakh Chinese via Affecting Promoter Methylation of P16 Gene. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 23, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.M.; Li, Y.; Wang, N.; Huang, X.; Cao, S.R.; Shan, B.E. Association of Programmed Death-1 Polymorphisms with the Risk and Prognosis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Genet. 2016, 209, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Yu, C.; Wen, D.; Chen, J.; Ling, Y.; Terajima, K.; Akazawa, K.; Shan, B.; Wang, S. Association of Nitrogen Compounds in Drinking Water with Incidence of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Shexian, China. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2012, 226, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Schulz, W.A.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Zotz, R.; Wen, D.; Siegel, D.; Ross, D.; Gabbert, H.E.; Sarbia, M. Association of NAD(P)H: Quinone Oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1) C609T Polymorphism with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a German Caucasian and a Northern Chinese Population. Carcinogenesis 2003, 24, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Luo, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Hou, Y. Association of Matrix Metalloproteinases-9 Gene Polymorphisms with Genetic Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. DNA Cell Biol. 2008, 27, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Wen, D.; Sarbia, M.; Kuang, G.; Wu, M.; Wei, L.; He, M.; Zhang, L.; et al. Association of Cyclin D1 (G870A) Polymorphism with Susceptibility to Esophageal and Gastric Cardiac Carcinoma in a Northern Chinese Population. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 105, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Fu, L.; Wang, H.; Zhu, W.; Fu, W.; Lv, Y.; Wang, S.; et al. Association of CHRNA5-A3-B4 Variation with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk and Smoking Behaviors in a Chinese Population. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.F.; Wang, Y.M.; Ge, H.; Cao, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.F.; Wen, D.G.; Guo, W.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.H. Association of CDH1 Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms with Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Gastric Cardia Carcinomas. Dis. Esophagus 2008, 21, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Tang, W.; Long, T.; Pan, H.; Liu, J.; Lv, L.; Liu, C.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, J.; Sun, Y.; et al. Association of ALDH3B2 Gene Polymorphism and Risk Factors with Susceptibility of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in a Chinese Population: A Case-Control Study Involving 2,358 Subjects. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 110153–110165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, C.; Li, M.; Tang, X.; Lu, C.; Li, H.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, M. Association of a Genetic Variation in a MiR-191 Binding Site in MDM4 with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.Z.; Sun, J. Association between XPD Gene Polymorphisms and Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cao, R.; Tang, W.; Chen, S. Association between BTLA Polymorphisms and Susceptibility to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in the Chinese Population. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Su, H.; Li, W.J.; Giffen, C.; Goldstein, A.M.; Hu, Y.; Wang, C.; Roth, M.J.; Li, G.; Dawsey, S.M.; et al. Allelotyping of Esophageal Squamous-Cell Carcinoma on Chromosome 13 Defines Deletions Related to Family History. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2005, 44, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hu, N.; Goldstein, A.M.; Tang, Z.Z.; Roth, M.J.; Wang, Q.H.; Dawsey, S.M.; Han, X.Y.; Ding, T.; Huang, J.; et al. Allelic Loss on Chromosome Bands 13q11-Q13 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2001, 31, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Roth, M.J.; Emmert-Buck, M.R.; Tang, Z.Z.; Polymeropolous, M.; Wang, Q.H.; Goldstein, A.M.; Han, X.Y.; Dawsey, S.M.; Ding, T.; et al. Allelic Loss in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients with and without Family History of Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 1999, 5, 3476–3482. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Yin, X.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, H.; Plymoth, A.; Jin, L.; Chen, X.; Lu, M.; Ye, W. Adult Height, Body Mass Index Change, and Body Shape Change in Relation to Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Risk: A Population-Based Case-Control Study in China. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 5769–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; You, W.; Zhu, J.; Cui, X.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, L.; Li, S.; Wei, Y.; et al. A Genetic Variant in MiRNA-219-1 Is Associated with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Kazakhs. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 541531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L.; Ma, J.; Chen, E.; Zang, R.; Jia, W.; Tao, X.; Hu, L. A Genetic Variant in CHRNB3-CHRNA6 Increases Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Populations. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Guo, H.; Wang, K.; Xiong, G.; Hu, H.; Wang, D.; Xu, X.; Guan, X.; Yang, K.; Bai, Y. A Functional Varient in MicroRNA-146a Is Associated with Risk of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Chinese Han. Fam. Cancer 2010, 9, 599–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Database | Search Terms |
|---|---|
| Pubmed | (“risk factor” OR “risk factors”) AND (“esophageal squamous cell carcinoma” OR “oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma” OR “esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma” OR “oesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma”) AND (“China” or “Chinese”) Filters: Human, English |
| Web of Science | (“risk factor” OR “risk factors”) AND (“esophageal squamous cell carcinoma” OR “oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma” OR “esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma” OR “oesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma”) AND (“China” or “Chinese”) |
| Cochrane trials | All text: (risk factor OR risk factors) AND (China OR Chinese) AND (esophageal squamous cell carcinoma OR oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma OR oesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma OR esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma) Filters: English, Human |
| Embase | All text: (risk factor OR risk factors) AND (China OR Chinese) AND (esophageal squamous cell carcinoma OR oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma OR oesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma OR esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma) Filters: English, Human, has an abstract, and exported only articles. Selected exclusions: conference abstracts, reviews, articles in press, preprints |
| Study Group | Count (n = 207) |
|---|---|
| Genetic | 129 (62.3%) |
| Diet/dietary habits | 22 (10.6%) |
| HPV | 19 (9.2%) |
| Other | 11 (5.3%) |
| Gene–environ. interaction | 10 * (4.8%) |
| Multiple risk factors | 6 (2.9%) |
| Oral Health | 5 (2.4%) |
| Family history | 3 (1.4%) |
| H. pylori | 2 ** (1.0%) |
| Study Population Ethnicity | Count (n = 207) |
|---|---|
| Not reported | 138 (66.7%) |
| Han | 66 (31.9%) |
| Kazakh | 2 (1%) |
| Uyghur, Kazakh, or Han | 1 (0.5%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conway, E.; Wu, H.; Tian, L. Overview of Risk Factors for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in China. Cancers 2023, 15, 5604. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235604
Conway E, Wu H, Tian L. Overview of Risk Factors for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in China. Cancers. 2023; 15(23):5604. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235604
Chicago/Turabian StyleConway, Erica, Haisheng Wu, and Linwei Tian. 2023. "Overview of Risk Factors for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in China" Cancers 15, no. 23: 5604. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235604
APA StyleConway, E., Wu, H., & Tian, L. (2023). Overview of Risk Factors for Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in China. Cancers, 15(23), 5604. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15235604






