A Retrospective Multicenter Italian Analysis of Epidemiological, Clinical and Histopathological Features in a Sample of Patients with Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Parotid Gland
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Objectives
2.2. Patient Population
2.3. Pathology
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Population
3.2. Treatment Characteristics
3.3. Staging
3.4. Survival Outcomes
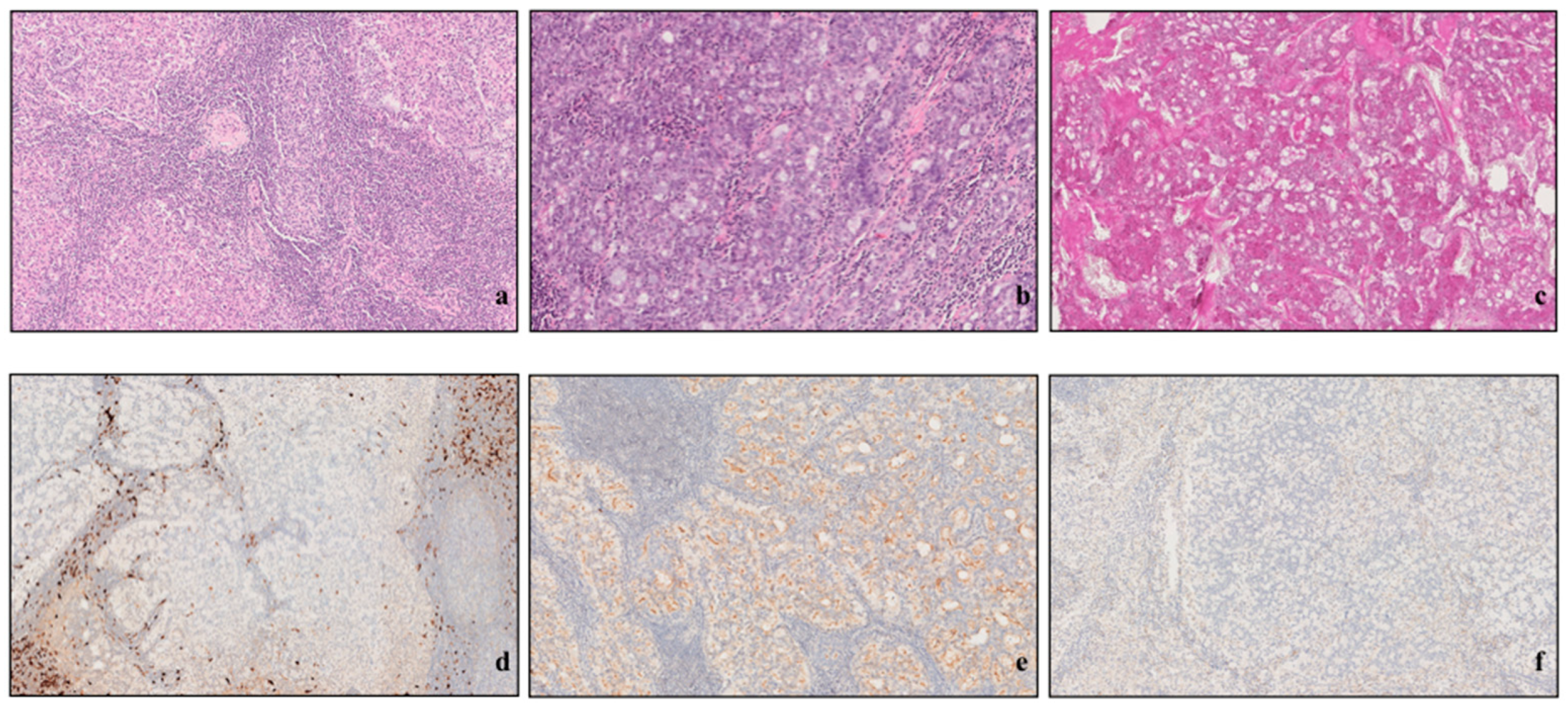
3.5. Histopathological Analysis
3.6. Prognostic Factors for Survival
3.6.1. Clinical Parameters
3.6.2. Histological Characteristics of the Tumor
4. Discussion
Limits of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cavaliere, M.; De Luca, P.; Scarpa, A.; Savignano, L.; Cassandro, C.; Cassandro, E.; Iemma, M. Acinic cell carcinoma of the parotid gland: From pathogenesis to management: A literature review. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2020, 277, 2673–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skálová, A.; Hyrcza, M.D.; Leivo, I. Update from the 5th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Head and Neck Tumors: Salivary Glands. Head Neck Pathol. 2022, 16, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godwin, J.T.; Foote, F.W.; Frazell, E.L. Acinic cell adenocarcinoma of the parotid gland; report of twenty-seven cases. Am. J. Pathol. 1954, 30, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buxton, R.W.; Maxwell, J.H.; French, A.J. Surgical treatment of epithelial tumors of the parotid gland. Surg. Gynecol. Obstet. 1954, 97, 401–416. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, R.J.; Weiland, L.H.; Olsen, K.D.; Pearson, B.W. Dedifferentiated acinic cell (acinous) carcinoma of the parotid gland. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1988, 98, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skálová, A.; Sima, R.; Vanecek, T.; Muller, S.; Korabecna, M.; Nemcova, J.; Elmberger, G.; Leivo, I.; Passador-Santos, F.; Walter, J.; et al. Acinic cell carcinoma with high-grade transformation: A report of 9 cases with immunohisto- chemical study and analysis of TP53 and HER-2/neu genes. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2009, 33, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiosea, S.I.; Griffith, C.; Assaad, A.; Seethala, R.R. The profile of acinic cell carcinoma after recognition of mammary analog secretory carcino-ma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintakuntlawar, A.V.; Shon, W.; Erickson-Johnson, M.; Bilodeau, E.; Jenkins, S.M.; Davidson, J.A.; Keeney, M.G.; Rivera, M.; Price, D.L.; Moore, E.J.; et al. High-grade transformation of acinic cell carcinoma: An inadequately treated entity? Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2016, 121, 542.e1–549.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, P.; de Campora, L.; Tassone, D.; Atturo, F.; Colangeli, R.; Petruzzi, G.; Fermi, M.; Molinari, G.; Abeshi, A.; Cintoli, G.; et al. Acinic cell carcinoma of the parotid gland: Timeo Danaos et dona ferentes? A multicenter retrospective analysis focusing on survival outcome. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2022, 279, 5821–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.D.; Aslam, M.N.; Stall, J.N.; Udager, A.M.; Chiosea, S.; McHugh, J.B. Clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic characterization of 25 cases of acinic cell carcinoma with high-grade transformation. Head Neck Pathol. 2016, 10, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.E.; Samankan, S.; Liu, X.; Sharif, K.F.; Everest, S.; Singh, T.; Dhorajiya, P.; Baik, F.M.; Khorsandi, A.; Stevens, T.M.; et al. Ten patients with high-grade transformation of acinic cell carcinomas: Expression profiling of beta-catenin and cyclin D1 is useful. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.B.; Greene, F.L.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. (Eds.) AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; American Joint Commission on Cancer; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Classification of Tumours Editorial Board. Head and Neck Tumours, 5th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hermanek, P.; Wittekind, C. The pathologist and the residual tumor (R) classification. Pathol. Res. Pract. 1994, 190, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Saliba, M.; Ho, A.; Viswanathan, K.; Alzumaili, B.; Dogan, S.; Ghossein, R.; Katabi, N. Head and Neck Acinic Cell Carcinoma: A New Grading System Proposal and Diagnostic Utility of NR4A3 Immunohistochemistry. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2022, 46, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacchi-Suzzi, M.; Bocciolini, C.; Bertarelli, C.; Dall’Olio, D. Ki-67 proliferation rate as a prognostic marker in major salivary gland carcinomas. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2010, 119, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, R.; Denkert, C.; Demaria, S.; Sirtaine, N.; Klauschen, F.; Pruneri, G.; Wienert, S.; Van den Eynden, G.; Baehner, F.L.; Pénault-Llorca, F.; et al. The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: Recommendations by an International TILs Working Group 2014. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quer, M.; Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Marchal, F.; Poorten, V.V.; Chevalier, D.; León, X.; Eisele, D.; Dulguerov, P. Classification of parotidectomies: A proposal of the European Salivary Gland Society. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2016, 273, 3307–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, D.R.; Katabi, N.; Zhung, J.; Wolden, S.L.; Zelefsky, M.J.; Kraus, D.H.; Shah, J.P.; Wong, R.J.; Ghossein, R.A.; Lee, N.Y. Clinical and pathologic prognostic features in acinic cell carcinoma of the parotid gland. Cancer 2009, 115, 2128–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, H.T.; Karnell, L.H.; Robinson, R.A.; Pinkston, J.A.; Menck, H.R. National Cancer Data Base report on cancer of the head and neck: Acinic cell carcinoma. Head Neck 1999, 21, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Weert, S.; Valstar, M.; Lissenberg-Witte, B.; Bloemena, E.; Smit, L.; van der Wal, J.; Vergeer, M.; Smeele, L.; Leemans, C. Prognostic factors in acinic cell carcinoma of the head and neck: The Amsterdam experience. Oral Oncol. 2021, 125, 105698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yibulayin, F.; Feng, L.; Wang, M.; Lu, M.M.; Luo, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z.C.; Wushou, A. Head & neck acinar cell carcinoma: A population-based study using the seer registry. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasl, S.; Janik, S.; Grasl, M.C.; Pammer, J.; Formanek, M.; Weinreb, I.; Perez-Ordonez, B.; Hope, A.; Hosni, A.; de Almeida, J.R.; et al. Nodal Metastases in Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Parotid Gland. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.M.; Yoon, S.O.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, M.S.; Kim, D.H.; Koh, Y.W.; Kim, S.-H.; Lim, J.-Y.; Choi, E.C. Comprehensive Analysis of Clinicopathologic Factors Predictive of an Unfavorable Prognosis in Patients With Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Parotid Gland. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 14, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenga, J.; Parikh, A.S.; Emerick, K.S.; Lin, D.T.; Faquin, W.C.; Deschler, D.G. Close Margins and Adjuvant Radiotherapy in Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Parotid Gland. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 144, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakely, P.E., Jr.; Lott-Limbach, A.A. Cytopathology of acinic cell carcinoma: A study of 50 cases, including 9 with high-grade transformation. Cancer Cytopathol. 2021, 129, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschnick, L.B.; Silveira, F.M.; Schuch, L.F.; Vasconcelos, A.C.U.; Gomes, A.P.; dos Santos, J.N.; Santana, D.A.; Fonseca, F.P.; Mesquita, R.A.; de Mendonça, E.F.; et al. Acinic cell carcinoma of the oral and maxillofacial region: An international multicenter study. Braz. Oral Res. 2023, 37, e050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, P.; Calvanese, M.; Camaioni, A.; Iaconetta, G.; Iemma, M. Recurrent acinic cell carcinoma of the parotid gland with lateral skull base invasion: Case report and discussion of the literature. Clin. Case Rep. 2023, 11, e7512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.A.; Seethala, R.R. Squamoglandular Variant of Acinic Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report of a Novel Variant. Head Neck Pathol. 2021, 16, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almangush, A.; De Keukeleire, S.; Rottey, S.; Ferdinande, L.; Vermassen, T.; Leivo, I.; Mäkitie, A.A. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Head and Neck Cancer: Ready for Prime Time? Cancers 2022, 14, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Virgilio, A.; Veneroni, M.V.; Costantino, A.; Festa, B.M.; Fiamengo, B.; Sebastiani, D.; Spriano, G.; Di Tommaso, L. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and tumor-associated macrophages as potential predictors of lymph node metastases in major salivary gland cancers. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1163565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, F.; Bieg, M.; Will, R.; Körner, C.; Weichenhan, D.; Bott, A.; Ishaque, N.; Lutsik, P.; Moskalev, E.A.; Mueller, S.K.; et al. Enhancer hijacking activates oncogenic transcription factor NR4A3 in acinic cell carcinomas of the salivary glands. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | n | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Participants | 77 | ||
| Mean age (min–max; SD) | 53.6 years (12–87–18.22) | ||
| Gender | Female | 53 | 71.4 |
| Male | 24 | 28.6 | |
| Comorbidities | Hypertension | 7 | 9 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 5 | 6.5 | |
| Asthma and/or pulmonary emphysema | 4 | 5.2 | |
| Neurological/mental disease | 1 | 1.3 | |
| Chronic renal disease | 1 | 1.3 | |
| Previous oncological disease (no head and neck region) | 1 | 1.3 | |
| FNAB result | Not diagnostic Other parotid neoplasm Acinic cell carcinoma Not performed | 40 16 13 8 | 58 23.2 18.8 |
| Parotid Surgery (according to European Salivary Gland Society Classification) | I–IV (VII) (Total parotidectomy with facial nerve resection) I–IV (Total parotidectomy) I–II (Superficial parotidectomy) I–II–III (Superficial parotidectomy extended to inferior deep lobe) | 1 33 39 4 | 5.3 37.8 50.6 5.3 |
| Nodal dissection (ND) | No ND performed | 64 | 82.1 |
| ND performed | 13 | 16.9 | |
| − Selective (II–IV) | 8 | 61.5 | |
| − Superselective (II or II–III) | 3 | 23.1 | |
| − mRND/RND (I–V) | 2 | 15.4 | |
| Margin status | R0 | 34 | 44.1 |
| R1 | 22 | 28.6 | |
| Rclose | 21 | 27.3 | |
| Staging | Stage I | 25 | 32.5 |
| Stage II | 37 | 48 | |
| Stage III | 9 | 11.7 | |
| Stage IVA | 6 | 7.8 | |
| Adjuvant treatment | No | 60 | 77.9 |
| Yes (RT) | 17 | 22.1 | |
| Pathologic T classification (according to TNM classification—8th edition) | T1 | 26 | 33.8 |
| T2 | 40 | 51.9 | |
| T3 | 8 | 10.4 | |
| T4a | 3 | 3.9 | |
| Pathologic N classification (according to TNM classification—8th edition) | N0 | 70 | 90.9 |
| N1 | 3 | 3.9 | |
| N2a | 2 | 2.6 | |
| N2b | 2 | 2.6 | |
| Recurrence | Local | 6 | |
| Mean follow-up (min–max; SD), months | 67.4 (1–258; SD 59.39) | ||
| Status at last follow-up | NED | 62 | 80.5 |
| DOOC | 8 | 10.4 | |
| NED II | 2 | 2.6 | |
| DOD | 3 | 3.9 | |
| AWD | 2 | 2.6 |
| Parameter | Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, gender | 84, M | 65, F | 79, F | 74, F | 59, F | 55, F |
| Type of surgery | I–IV | I–IV | I–IV | I–IV | I–II | I–IV |
| Ipsilateral ND | I–V | II–IV | None | None | None | II–IV |
| pTNM staging | pT4aN2aM0—IVa | pT3N2bM0—IVa | pT4aN0M0—IVa | pT2N0M0—II | pT1N0M0—I | pT1N1Mo—III |
| Resection margins | R0 | R0 | R1 | R0 | R1 | Rclose |
| Adjuvant therapy | None | RT | CH | None | None | RT |
| Tumor diameter (mm) | 90 | 45 | 60 | 35 | 59 | 15 |
| Growth pattern/s | Trabecular + cribriform | Solid + cribriform | Solid + microcystic | Solid + microcystic | Cribriform | Microcystic |
| Grade | High grade | High grade | Low grade | Low grade | Low grade | Low grade |
| Necrosis | Microfocal (<1 mm) | Microfocal (<1 mm) | Absent | Macrofocal (>1 mm) | Absent | Absent |
| Perineural invasion | Present | Absent | Absent | Absent | Present | Absent |
| LVI | Focal (<2 figures) | Focal (<2 figures) | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| Extraglandular growth | Present | Present | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| Pleomorphism | Absent | Mild | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| Lymphoid stroma | Negative | Negative | Moderate (11–50%) | Moderate (11–50%) | Moderate (11–50%) | Absent |
| Atypical mitosis | Absent | Present | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| Mitotic index | 2–4 | 2–4 | 0–1 | >5 | 0–1 | 0–1 |
| Neuroendocrine differentiation | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent | Absent |
| Stromal hyalinization | Present | Present | Present | Present | Present | Absent |
| TILs (%) | 5% | 0% | 0% | 30% | 20% | 1 |
| Significant ki67 (>15%) | 20% | DNA | DNA | 30% | DNA | DNA |
| Number of recurrences, sites, and number of months after initial diagnosis | 1; parotid area and external auditory canal; 4 months | 1; parotid area; 5 months | 1; lateral skull base; 1 month | 2; a. parotid area, external auditory canal, tympanic cavity, mastoid, sigmoid sinus, pontocerebellar angle, 11 months; b. site of previous left petrosectomy, foramen lacerum, foramen magnum, 25 months | 1; parotid area, 11 months | 1; parotid area, 26 months |
| Status at last follow-up | 16 months, NEDII | 35, AWD | 2, DOD | 31, DOD | 38, NEDII | 60, DOD |
| Parameter | Categories | Number of Patients (n) |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor diameter | 0–1.9 cm | 36 |
| 2–4.9 cm | 32 | |
| 5–10 cm | 9 | |
| Growth pattern | Solid | 36 |
| Trabecular | 4 | |
| Cribriform | 8 | |
| Microcystic | 12 | |
| Papillary cystic | 8 | |
| Follicular | 9 | |
| Multiple | 39 | |
| Grade | Low | 64 |
| High | 13 | |
| Resection margins | R0 | 32 |
| Rclose | 22 | |
| R1 | 23 | |
| Necrosis | Absent | 54 |
| Microfocal < 1 mm | 7 | |
| Macrofocal > 1 mm | 6 | |
| Diffuse | 10 | |
| Perineural invasion | Absent | 64 |
| Present | 13 | |
| Lymphovascular invasion | Absent | 56 |
| Focal (<2 figures of LVI) | 14 | |
| Diffuse (>2 figures of LVI) | 7 | |
| Extraglandular growth | Absent | 49 |
| Present | 28 | |
| Pleomorphism | Absent | 46 |
| Mild | 11 | |
| Moderate | 10 | |
| Severe | 10 | |
| Lymphoid stroma | Negative (<1%) | 34 |
| Mild (1–10%) | 27 | |
| Moderate (11–50%) | 16 | |
| Severe (>50%) | 0 | |
| Atypical mitosis | Absent | 67 |
| Present | 10 | |
| Mitotic Index (per 10HPFs) | 0–1 | 50 |
| 2–4 | 20 | |
| >5 | 7 | |
| Neuroendocrine differentiation | Absent | 75 |
| Present | 2 | |
| Stromal Hyalinization | Absent | 47 |
| Present | 30 | |
| TILs (%) | 0 | 20 |
| 1–4 | 14 | |
| 5–9 | 12 | |
| 10–19 | 18 | |
| >20 | 13 | |
| Ki67 (%) | 0–4 | 5 |
| 5–9 | 7 | |
| >10 | 13 | |
| DNA | 52 |
| Parameter | Group A (AciCC Patients Who Experienced Recurrence) | Group B (AciCC Patients with no Recurrence) | Two-Tailed p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size of the cohort (n) | 6 | 71 | |
| Age (mean, range, SD), yr | 72.2 | 52.28 | 0.0097 |
| (55–84; SD 9.1) | (72–87; SD 18.11) | ||
| Gender | 5 F; 1 M | 48 F; 23 M | |
| Type of surgery | |||
| I–II | 1 | 38 | |
| I–IV | 5 | 24 | |
| Ipsilateral ND | |||
| No | 3 | 61 | |
| Yes | 3 | 10 | |
| Pathologic T, n | |||
| pT1 | 2 | 24 | |
| pT2 | 1 | 39 | |
| pT3 | 1 | 7 | |
| pT4a | 2 | 1 | |
| Pathologic N, n | |||
| pN0 | 3 | 67 | |
| pN1 | 1 | 2 | |
| pN2(a or b) | 2 | 2 | |
| Staging | |||
| I | 1 | 24 | |
| II | 1 | 36 | |
| III | 1 | 8 | |
| IVa | 3 | 3 | |
| Resection margins | |||
| R0 | 3 | 27 | |
| Rclose | 1 | 30 | |
| R1 | 2 | 22 | |
| Adjuvant RT/CH | |||
| No | 3 | 55 | |
| Yes | 3 | 16 | |
| Tumor diameter (range, mean), mm | 50.7 | 27.3 | 0.0012 |
| (15–90; SD 23.28) | (4–73; SD 15.7) | ||
| Main growth pattern, n | |||
| Solid | 3 | 36 | |
| Trabecular | 1 | 4 | |
| Cribriform | 1 | 7 | |
| Microcystic | 1 | 12 | |
| Papillary cystic | 0 | 3 | |
| Follicular | 0 | 9 | |
| Multiple growth patterns, n | 4 | 35 | |
| Grade, n | |||
| Low grade | 4 | 60 | |
| High grade | 2 | 11 | |
| Necrosis, n | |||
| Absent | 4 | 51 | |
| Present | 2 | 20 | |
| Perineural invasion, n | |||
| Absent | 4 | 60 | |
| Present | 2 | 11 | |
| LVI, n | |||
| Absent | 4 | 52 | |
| Present | 2 | 19 | |
| Extraglandular growth, n | |||
| Absent | 4 | 44 | |
| Present | 2 | 27 | |
| Pleomorphism, n | |||
| Absent | 5 | 43 | |
| Present | 1 | 29 | |
| Lymphoid stroma, n | |||
| Absent | 5 | 31 | |
| Present | 1 | 40 | |
| Atypical mitosis, n | |||
| Absent | 5 | 62 | |
| Present | 1 | 9 | |
| Mitotic index, n | |||
| 0–1 | 3 | 45 | |
| 2–4 | 2 | 21 | |
| >5 | 1 | 8 | |
| Stromal hyalinization, n Absent Present | 1 | 45 | |
| 5 | 26 | ||
| TILs (%), n | |||
| 0 | 2 | 18 | |
| 1–4 | 1 | 12 | |
| 5–9 | 1 | 23 | |
| 10–19 | 0 | 6 | |
| >20 | 2 | 12 | |
| Follow-up (range, mean, SD), months | 30.3 | 67.4 | 0.1338 |
| (2–60; SD 18.11) | (1–258; SD 59.39) |
| Parameter | Group A (Low-Grade AciCC) | Group B (High-Grade AciCC) | Two-Tailed p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size of the cohort (n) | 64 (83%) | 13 (17%) | |
| Age (mean, range, SD), yr | 49.93 (12–87; SD 17.28) | 71.7 (55–84; SD 10.11) | <0.0001 |
| Gender | 45 F (70.3%); 19 M (29.7%) | 8 F (61.5%); 5 M (38.5%) | 0.5 |
| Comorbidities | 4 | 3 | |
| Hypertension | 3 | 2 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 2 | 2 | |
| Asthma and/or pulmonary emphysema | |||
| Neurological/mental disease | 1 | 0 | |
| Chronic renal disease | 1 | 0 | |
| Previous oncological disease (not in the head and neck region) | 1 | 0 | |
| Type of surgery | 0.42 | ||
| I–II | 35 (54.7%) | 4 (31%) | |
| I–IV | 23 (35.9%) | 6 (46%) | |
| Ipsilateral ND | 0.00182 | ||
| No | 57 (89%) | 7 (54%) | |
| Yes | 7 (11%) | 6 (46%) | |
| Pathologic T, n | 0.000093 | ||
| pT1 | 26 (41%) | 0 | |
| pT2 | 32 (50%) | 8 (61%) | |
| pT3 | 5 (8%) | 3 (23%) | |
| pT4a | 1 (1%) | 2 (16%) | |
| Pathologic N, n | 0.00119 | ||
| pN0 | 60 (94%) | 10 (77%) | |
| pN1 | 3 (5%) | 0 | |
| pN2(a or b) | 1 (1%) | 3 (23%) | |
| Staging | |||
| I | 25 (39%) | 0 | |
| II | 29 (45%) | 8 (61.5%) | |
| III | 8 (12.5%) | 1 (8%) | |
| IVa | 2 (3.5%) | 4 (30.5%) | |
| Resection margins | 0.003 | ||
| R0 | 29 (45%) | 3 (23%) | |
| Rclose | 20 (31%) | 1 (8%) | |
| R1 | 15 (24%) | 9 (69%) | |
| Adjuvant RT/CH | 0.0206 | ||
| No | 50 (78%) | 7 (54%) | |
| Yes | 14 (22%) | 6 (46%) | |
| Tumor diameter (range, mean), mm | 25.8 (4–70; SD 15.5) | 42.6 (18–90; SD 20.54) | 0.000751 |
| Main growth pattern, n | 0.33 | ||
| Solid | 31 (48%) | 5 (38%) | |
| Trabecular | 3 (5%) | 1 (8%) | |
| Cribriform | 5 (8%) | 3 (23%) | |
| Microcystic | 9 (14%) | 3 (23%) | |
| Papillary cystic | 7 (11%) | 1 (8%) | |
| Follicular | 9 (14%) | 0 | |
| Multiple growth patterns, n | 32 (50%) | 7 (54%) | 0.8 |
| Necrosis, n | 0.01 | ||
| Absent | 51 (80%) | 3 (23%) | |
| Present | 13 (20%) | 10 (77%) | |
| Perineural invasion, n | 0.1426 | ||
| Absent | 55 (86%) | 9 (54%) | |
| Present | 9 (14%) | 4 (46%) | |
| LVI, n | 0.006 | ||
| Absent | 51 (80%) | 5 (38%) | |
| Present | 13 (20%) | 8 (62%) | |
| Extraglandular growth, n | 0.00997 | ||
| Absent | 44 (69%) | 4 (46%) | |
| Present | 20 (31%) | 9 (54%) | |
| Pleomorphism, n | 0.00334 | ||
| Absent | 49 (77%) | 3 (23%) | |
| Present | 21 (23%) | 10 (77%) | |
| Lymphoid stroma, n | 0.12 | ||
| Absent | 27 (42%) | 7 (54%) | |
| Present | 37 (58%) | 6 (46%) | |
| Atypical mitosis, n | <0.00001 | ||
| Absent | 61 (95%) | 6 (46%) | |
| Present | 3 (5%) | 7 (54%) | |
| Mitotic index, n | 0.33 | ||
| 0–1 | 48 (75%) | 2 (16%) | |
| 2–4 | 15 (23%) | 5 (38%) | |
| >5 | 1 (2%) | 6 (46%) | |
| Stromal hyalinization, n | 0.6345 | ||
| Absent | 39 (61%) | 7 (54%) | |
| Present | 25 (39%) | 6 (46%) | |
| TILs (%), n | 0.2619 | ||
| 0 | 17 (26%) | 3 (23%) | |
| 1–4 | 14 (22%) | 0 | |
| 5–9 | 7 (11%) | 5 (38%) | |
| 10–19 | 13 (20%) | 2 (16%) | |
| >20 | 13 (20%) | 3 (23%) | |
| Follow-up (range, mean, SD), months | 71.9 (1–258; SD 63.13) | 45 (12–112; SD 25.83) | 0.06 |
| Status at the last follow-up, n | |||
| NED | 54 (84%) | 9 (69%) | |
| NEDII | 1 (2%) | 1 (8%) | |
| AWD | 0 | 1 (8%) | |
| DOD | 3 (5%) | 0 | |
| DOOC | 6 (9%) | 2 (15%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Luca, P.; Di Stadio, A.; de Campora, L.; De Bonis, E.; Fermi, M.; Petruzzi, G.; Atturo, F.; Colangeli, R.; Scarpa, A.; Lo Manto, A.; et al. A Retrospective Multicenter Italian Analysis of Epidemiological, Clinical and Histopathological Features in a Sample of Patients with Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Parotid Gland. Cancers 2023, 15, 5456. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225456
De Luca P, Di Stadio A, de Campora L, De Bonis E, Fermi M, Petruzzi G, Atturo F, Colangeli R, Scarpa A, Lo Manto A, et al. A Retrospective Multicenter Italian Analysis of Epidemiological, Clinical and Histopathological Features in a Sample of Patients with Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Parotid Gland. Cancers. 2023; 15(22):5456. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225456
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Luca, Pietro, Arianna Di Stadio, Luca de Campora, Egidio De Bonis, Matteo Fermi, Gerardo Petruzzi, Francesca Atturo, Roberta Colangeli, Alfonso Scarpa, Alfredo Lo Manto, and et al. 2023. "A Retrospective Multicenter Italian Analysis of Epidemiological, Clinical and Histopathological Features in a Sample of Patients with Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Parotid Gland" Cancers 15, no. 22: 5456. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225456
APA StyleDe Luca, P., Di Stadio, A., de Campora, L., De Bonis, E., Fermi, M., Petruzzi, G., Atturo, F., Colangeli, R., Scarpa, A., Lo Manto, A., Colizza, A., Cintoli, G., Togo, G., Salzano, G., Crescenzi, D., Ralli, M., Abbate, V., Ricciardiello, F., Magaldi, L., ... Camaioni, A. (2023). A Retrospective Multicenter Italian Analysis of Epidemiological, Clinical and Histopathological Features in a Sample of Patients with Acinic Cell Carcinoma of the Parotid Gland. Cancers, 15(22), 5456. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225456













