Single-Stage Immediate Breast Reconstruction with Acellular Dermal Matrix after Breast Cancer: Comparative Study and Evaluation of Breast Reconstruction Outcomes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
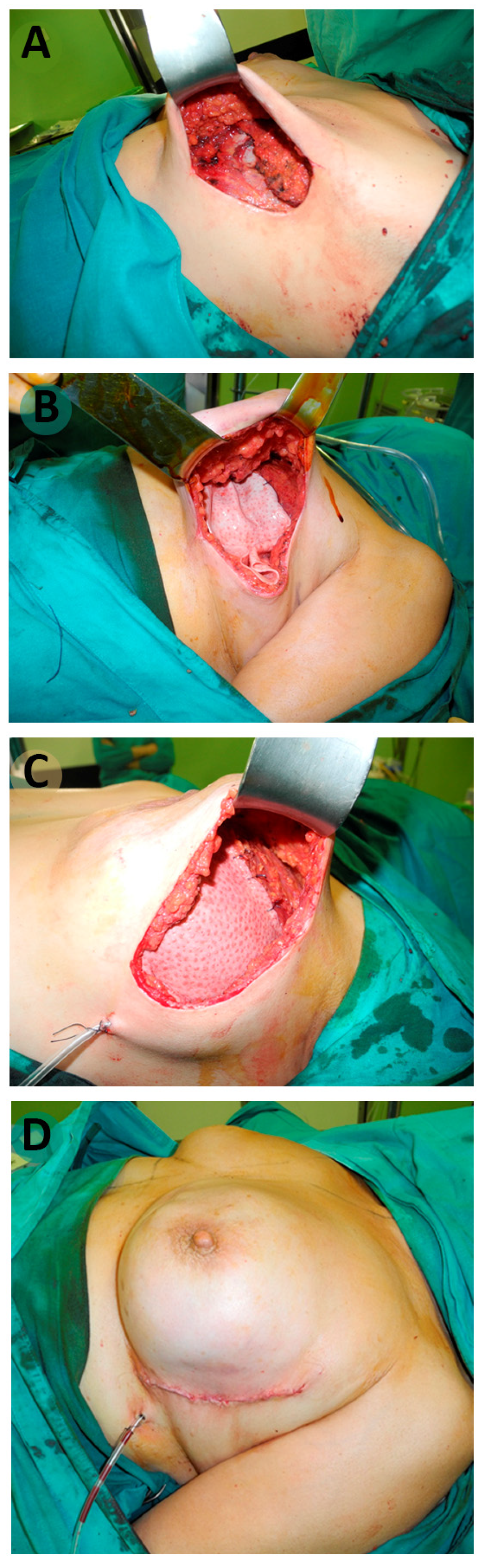
2.3. Surgical Technique
2.4. Study of Complications
2.5. Patient-Reported Outcome Measure
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Study Design
3.3. Between-Groups Complication Comparison
3.4. Measuring Patient Outcomes
4. Discussion
4.1. Suitable Mesh
4.2. Complications after Radiotherapy
4.3. Analysis of Results
4.4. Lower Rate of Loss Implant with ADM Use
4.5. Higher Level of Satisfaction with ADM Breast Reconstruction
4.6. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaidar-Person, O.; Offersen, B.V.; Boersma, L.J.; de Ruysscher, D.; Tramm, T.; Kuhn, T.; Gentilini, O.; Matrai, Z.; Poortmans, P. A multidisciplinary view of mastectomy and breast reconstruction: Understanding the challenges. Breast 2021, 56, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wan, H.; Zuo, W.; Sun, W.; Owens, R.T.; Harper, J.R.; Ayares, D.L.; McQuillan, D.J. A Porcine-Derived Acellular Dermal Scaffold That Supports Soft Tissue Regeneration: Removal of Terminal Galactose-alpha-(1,3)-Galactose and Retention of Matrix Structure. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connor, J.; McQuillan, D.; Sandor, M.; Wan, H.; Lombardi, J.; Bachrach, N.; Harper, J.; Xu, H. Retention of structural and biochemical integrity in a biological mesh supports tissue remodeling in a primate abdominal wall model. Regen. Med. 2009, 4, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanlik, H.; Bayrak, S.; Fayda, M.; Ozgur, I.; Kurul, S. Comparison of implant-based immediate breast reconstruction with and without vicryl mesh. Breast 2015, 24, S132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebril, B.A.; Novoa, A.G.; Jimenez, L.G.; Carballada, C.D.; Alejandro, A.B.; Iglesias, C.C. Reconstruccion mamaria inmediata mediante implante prepectoral de poliuretano. Resultados preliminares del estudio prospectivo PreQ-20. Cir. Esp. 2023, 101, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzberg, C.A. Nonexpansive immediate breast reconstruction using human acellular tissue matrix graft (AlloDerm). Ann. Plast. Surg. 2006, 57, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganske, I.; Verma, K.; Rosen, H.; Eriksson, E.; Chun, Y.S. Minimizing Complications With the Use of Acellular Dermal Matrix for Immediate Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2013, 71, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spear, S.L.; Seruya, M.; Clemens, M.W.; Teitelbaum, S.; Nahabedian, M.Y. Acellular Dermal Matrix for the Treatment and Prevention of Implant-Associated Breast Deformities. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuing, K.H.; Colwell, A.S. Inferolateral AlloDerm hammock for implant coverage in breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2007, 59, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namnoum, J.D. Expander/Implant Reconstruction with AlloDerm: Recent Experience. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, S.L.; Parikh, P.M.; Reisin, E.; Menon, N.G. Acellular dermis-assisted breast reconstruction. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2008, 32, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardanian, A.J.; Clayton, J.L.; Roostaeian, J.; Shirvanian, V.; Da Lio, A.; Lipa, J.E.; Crisera, C.; Festekjian, J.H. Comparison of Implant-Based Immediate Breast Reconstruction with and without Acellular Dermal Matrix. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 128, 403e–410e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zienowicz, R.J.; Karacaoglu, E. Implant-based breast reconstruction with allograft. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 120, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, R.V.; Vucicevic, A.; Barrett, E.; Highton, L.; Johnson, R.; Kirwan, C.C.; Harvey, J.R.; Murphy, J. Risk factors for complications and implant loss after prepectoral implant-based immediate breast reconstruction: Medium-term outcomes in a prospective cohort. Br. J. Surg. 2021, 108, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negenborn, V.L.; Young-Afat, D.A.; Dikmans, R.E.G.; Smit, J.M.; Winters, H.A.H.; Griot, J.P.W.D.; Twisk, J.W.R.; Ruhe, P.Q.; Mureau, M.A.M.; Lapid, O.; et al. Quality of life and patient satisfaction after one-stage implant-based breast reconstruction with an acellular dermal matrix versus two-stage breast reconstruction (BRIOS): Primary outcome of a randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, Y.S.; Verma, K.; Rosen, H.; Lipsitz, S.; Morris, D.; Kenney, P.; Eriksson, E. Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction Using Acellular Dermal Matrix and the Risk of Postoperative Complications. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 125, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikmans, R.E.G.; El Morabit, F.; Ottenhof, M.J.; Tuinder, S.M.H.; Twisk, J.W.R.; Moues, C.; Bouman, M.B.; Mullender, M.G. Single-stage breast reconstruction using Strattice (TM): A retrospective study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic 2016, 69, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasberg, S.B.; Light, D. AlloDerm and Strattice in Breast Reconstruction: A Comparison and Techniques for Optimizing Outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preminger, B.A.; McCarthy, C.M.; Hu, Q.Y.; Mehrara, B.J.; Disa, J.J. The influence of AlloDerm on expander dynamics and complications in the setting of immediate tissue expander/implant reconstruction—A matched-cohort study. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2008, 60, 510–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whisker, L.; Barber, M.; Egbeare, D.; Gandhi, A.; Gilmour, A.; Harvey, J.; Martin, L.; Tillett, R.; Potter, S. Biological and synthetic mesh assisted breast reconstruction procedures: Joint guidelines from the Association of Breast Surgery and the British Association of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgeons. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 2807–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.; O’Donnell, J.P.; Ryan, E.J.; Lane O’Neill, B.; Boland, M.R.; Lowery, A.J.; Kerin, M.J.; McInerney, N.M. Immediate Breast Cancer Reconstruction with or without Dermal Matrix or Synthetic Mesh Support: A Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 151, 563e–574e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logan Ellis, H.; Asaolu, O.; Nebo, V.; Kasem, A. Biological and synthetic mesh use in breast reconstructive surgery: A literature review. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallberg, H.; Rafnsdottir, S.; Selvaggi, G.; Strandell, A.; Samuelsson, O.; Stadig, I.; Svanberg, T.; Hansson, E.; Lewin, R. Benefits and risks with acellular dermal matrix (ADM) and mesh support in immediate breast reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2018, 52, 130–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, E.A.; Wilkins, E.G.; Strawderman, M.; Cederna, P.; Goldfarb, S.; Vicini, F.A.; Pierce, L.J. Complications and patient satisfaction following expander/implant breast reconstruction with and without radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2001, 49, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, P.G.; McCarthy, C.M. A single surgeon’s 12-year experience with tissue expander/implant breast reconstruction: Part I: A prospective analysis of early complications. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danino, M.A.; Giaccone, D.; El Khatib, A.; Dimitropoulos, G.; Doucet, O.; Gagnon, A.; Retchkiman, M.; Bou-Merhi, J.; Bernier, C. Immediate breast reconstruction surgery with expander/direct implant and use of acellular dermal matrix: Does hormone therapy increases the risk of infection? Ann. Chir. Plast. Esthétique 2020, 65, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahabedian, M.Y. AlloDerm Performance in the Setting of Prosthetic Breast Surgery, Infection, and Irradiation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 1743–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sbitany, H.; Sandeen, S.N.; Amalfi, A.N.; Davenport, M.S.; Langstein, H.N. Acellular Dermis-Assisted Prosthetic Breast Reconstruction versus Complete Submuscular Coverage: A Head-to-Head Comparison of Outcomes. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 1735–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzberg, C.A.; Dunavant, C.; Nocera, N. Immediate breast reconstruction using porcine acellular dermal matrix (Strattice (TM)): Long-term outcomes and complications. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic 2013, 66, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillberg, N.S.; Hogenboom, J.; Hommes, J.; Van Kuijk, S.M.J.; Keuter, X.H.A.; van der Hulst, R. Risk of major postoperative complications in breast reconstructive surgery with and without an acellular dermal matrix: A development of a prognostic prediction model. JPRAS Open 2022, 33, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movassaghi, K.; Gilson, A.; Stewart, C.N.; Cusic, J.; Movassaghi, A. Prepectoral Two Stage Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction with Poly-4-Hydroxybutyrate (P4HB) for Pocket Control without the use of Acellular Dermal Matrix (ADM): A 4-Year Review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 10, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polotto, S.; Pedrazzi, G.; Bergamini, M.; D’Abbiero, N.; Cattelani, L. ADM-Assisted Direct-to-Implant Prepectoral Breast Reconstruction in Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy Setting: Long-Term Results. Clin. Breast Cancer 2023, 23, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, M.D.; Williams, L.; Anderson, E.D.C.; Neades, G.T.; Raine, C.; Young, O.; Kulkarni, D.; Young, I.; Dixon, J.M. Outcome of the use of acellular-dermal matrix to assist implant-based breast reconstruction in a single centre. Ejso-Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 41, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelotti, B.F.; Brooke, S.; Mesa, J.; Wilson, M.Z.; Moyer, K.; Mackay, D.R.; Neves, R.I.; Potochny, J. Analysis of Clinically Significant Seroma Formation in Breast Reconstruction Using Acellular Dermal Grafts. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2013, 71, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, S.; Chambers, A.; Govindajulu, S.; Sahu, A.; Warr, R.; Cawthorn, S. Early complications and implant loss in implant-based breast reconstruction with and without acellular dermal matrix (Tecnoss Protexa(R)): A comparative study. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 41, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisa, A.; Carbonaro, R.; Bottoni, M.; Ostapenko, E.; Rietjens, M. Bovine Acellular Dermal Matrix-Based Breast Reconstruction in Previously Irradiated Breasts: Complications and Outcomes From a Single-Center Experience. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2023, 10, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.L.; Barbosa, R.F.; Guerreiro, F.C.; Andresen, C.; Pereira, M.J.; Pinho, C.J.; Rebelo, M.A.; Ribeiro, M.M. A Two-Year Retrospective Analysis of the Clinical Outcomes of Immediate Submuscular Breast Reconstructions With Native(R) Acellular Dermal Matrix. Cureus 2023, 15, e41343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledwon, J.K.; Applebaum, S.A.; Progri, B.; Han, T.; Vignesh, O.; Gutowski, K.S.; Chang, A.B.; Reddy, N.K.; Tepole, A.B.; Gosain, A.K. Acellular dermal matrix cover improves skin growth during tissue expansion by affecting distribution of mechanical forces. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 10, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tellarini, A.; Garutti, L.; Corno, M.; Tamborini, F.; Paganini, F.; Fasoli, V.; Di Giovanna, D.; Valdatta, L. Immediate post-mastectomy prepectoral breast reconstruction with animal derived acellular dermal matrices: A systematic review. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2023, 86, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Ye, J.; Tian, T. Implant Based Breast Reconstruction Using a Titanium-Coated Polypropylene Mesh (TiLOOP(R) Bra): A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezienski, M.A.; Jarrell, J.A.t.; Mooty, R.C. Classification and management of seromas in immediate breast reconstruction using the tissue expander and acellular dermal matrix technique. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2013, 70, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.S.; Davila, A.A.; Persing, S.; Connor, C.M.; Jovanovic, B.; Khan, S.A.; Fine, N.; Rawlani, V. A Meta-Analysis of Human Acellular Dermis and Submuscular Tissue Expander Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, G.; Nguyen, T.J.; Shahabi, A.; Hwang, B.H.; Chan, L.S.; Wong, A.K. A systematic review and meta-analysis of complications associated with acellular dermal matrix-assisted breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2012, 68, 346–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbitany, H.; Serletti, J.M. Acellular dermis-assisted prosthetic breast reconstruction: A systematic and critical review of efficacy and associated morbidity. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 128, 1162–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, A.; Walsh, M.; Chandrasekharan, S.; Chakravorty, A. Single-stage immediate breast reconstruction with acellular dermal matrix: Experience gained and lessons learnt from patient reported outcome measures. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 42, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mesh (n = 51) | No Mesh (n = 38) | p-Value | Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 49.50 (1.49) | 47.93 (1.89) | 0.521 | Student’s t-test |
| Diabetes | 2 (3.92%) | 0 (0%) | 0.505 | Fisher’s exact test |
| Smoking | 6 (11.76%) | 1 (2.63%) | 0.231 | Fisher’s exact test |
| Radiotherapy RT | 16 (31.4%) | 10 (27.0%) | 0.838 | Chi-square with Yates correction |
| Pre-operative | 5 (31.3%) | 3 (30.0%) | 1.000 | Fisher’s exact test * |
| Post-operative | 11 (68.8%) | 7 (70.0%) | ||
| Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy | 29 (56.9%) | 18 (48.6%) | 0.585 | Chi-square with Yates correction |
| Adjuvant Chemotherapy | 15 (29.4%) | 7 (18.9%) | 0.383 | Chi-square with Yates correction |
| BRCA1 | 7 (13.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0.020 | Fisher’s exact test |
| BRCA2 | 2 (3.9%) | 1 (2.7%) | 1 | Fisher’s exact test |
| Mesh (n = 62) | No Mesh (n = 41) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skin necrosis | 11 (21.6%) | 5 (12.2%) | 0.367 (Chi-square with Yates correction) |
| Seroma | 5 (8.1%) | 5 (12.2%) | 0.514 (Fisher’s exact test) |
| Extrusion of the implant | 3 (5.9%) | 9 (24.3%) | 0.030 (Fisher’s exact test) |
| Total or partial loss of NAC | 3 (4.8%) | 4 (9.8%) | 0.432 (Fisher’s exact test) |
| Infection | 3 (4.8%) | 3 (7.3%) | 0.680 (Fisher’s exact test) |
| Hematoma | 5 (8.1%) | 3 (7.3%) | 1.000 (Fisher’s exact test) |
| Variable | Group | N | Average | SD | Typical Error | Minimum | Maximum | Rank | Median |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satisfaction with Breasts pre | No Mesh | 29 | 58.66 | 22.283 | 4.138 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 63.00 |
| Mesh | 42 | 63.26 | 21.226 | 3.275 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 63.00 | |
| Total | 71 | 61.38 | 21.626 | 2.567 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 63.00 | |
| PsychoSocial Wellbeing pre | No Mesh | 29 | 67.66 | 16.715 | 3.104 | 37 | 100 | 63 | 67.00 |
| Mesh | 42 | 74.60 | 17.576 | 2.712 | 36 | 100 | 64 | 77.50 | |
| Total | 71 | 71.76 | 17.450 | 2.071 | 36 | 100 | 64 | 70.00 | |
| Physical Wellbeing Chest pre | No Mesh | 29 | 61.86 | 16.803 | 3.120 | 31 | 100 | 69 | 60.00 |
| Mesh | 41 | 64.34 | 15.244 | 2.381 | 25 | 100 | 75 | 63.00 | |
| Total | 70 | 63.31 | 15.837 | 1.893 | 25 | 100 | 75 | 62.00 | |
| Physical Wellbeing Abdomen pre | No Mesh | 28 | 68.07 | 21.022 | 3.973 | 25 | 100 | 75 | 72.00 |
| Mesh | 40 | 75.70 | 22.869 | 3.616 | 14 | 100 | 86 | 83.00 | |
| Total | 68 | 72.56 | 22.289 | 2.703 | 14 | 100 | 86 | 77.50 | |
| Sexual Wellbeing pre | No Mesh | 26 | 48.58 | 20.379 | 3.997 | 16 | 100 | 84 | 46.00 |
| Mesh | 41 | 62.73 | 22.808 | 3.562 | 16 | 100 | 84 | 60.00 | |
| Total | 67 | 57.24 | 22.823 | 2.788 | 16 | 100 | 84 | 54.00 | |
| Satisfaction with Breasts post | No Mesh | 26 | 54.46 | 17.591 | 3.450 | 20 | 78 | 58 | 56.00 |
| Mesh | 41 | 66.22 | 16.044 | 2.506 | 40 | 100 | 60 | 65.00 | |
| Total | 67 | 61.66 | 17.509 | 2.139 | 20 | 100 | 80 | 62.00 | |
| Satisfaction with Outcome post | No Mesh | 25 | 77.96 | 21.532 | 4.306 | 35 | 100 | 65 | 75.00 |
| Mesh | 40 | 82.90 | 17.666 | 2.793 | 35 | 100 | 65 | 80.50 | |
| Total | 65 | 81.00 | 19.233 | 2.386 | 35 | 100 | 65 | 75.00 | |
| PsychoSocial Wellbeing post | No Mesh | 26 | 71.54 | 18.862 | 3.699 | 41 | 100 | 59 | 70.00 |
| Mesh | 39 | 79.26 | 18.113 | 2.900 | 26 | 100 | 74 | 49.00 | |
| Total | 65 | 76.17 | 18.663 | 2.315 | 26 | 100 | 74 | 76.00 | |
| Sexual Wellbeing post | No Mesh | 23 | 49.91 | 21.753 | 4.536 | 16 | 100 | 84 | 49.00 |
| Mesh | 38 | 64.50 | 24.380 | 3.955 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 60.00 | |
| Total | 61 | 59.00 | 24.307 | 3.112 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 57.00 | |
| Physical Wellbeing Chest post | No Mesh | 26 | 56.92 | 15.226 | 2.986 | 47 | 100 | 53 | 50.00 |
| Mesh | 35 | 51.29 | 3.777 | 0.639 | 50 | 68 | 18 | 50.00 | |
| Total | 61 | 53.69 | 10.611 | 1.359 | 47 | 100 | 53 | 50.00 | |
| Physical Wellbeing Abdomen post | No Mesh | Not evaluated because they do not apply to operated patients | |||||||
| Mesh | |||||||||
| Total | |||||||||
| Satisfaction with Nipples post | No Mesh | Not evaluated because they do not apply to operated patients | |||||||
| Mesh | |||||||||
| Total | |||||||||
| Satisfaction with Information post | No Mesh | 23 | 65.13 | 19.485 | 4.063 | 25 | 100 | 75 | 60.00 |
| Mesh | 38 | 75.03 | 20.346 | 3.301 | 22 | 100 | 78 | 72.50 | |
| Total | 61 | 71.30 | 20.442 | 2.617 | 22 | 100 | 78 | 69.00 | |
| Surgeon post | No Mesh | 25 | 88.28 | 19.208 | 3.842 | 31 | 100 | 69 | 100.00 |
| Mesh | 38 | 92.34 | 13.869 | 2.250 | 29 | 100 | 71 | 100.00 | |
| Total | 63 | 90.73 | 16.175 | 2.038 | 29 | 100 | 71 | 100.00 | |
| Medical Staff post | No Mesh | 25 | 99.36 | 3.200 | 0.640 | 84 | 100 | 16 | 100.00 |
| Mesh | 40 | 96.20 | 8.489 | 1.342 | 74 | 100 | 26 | 100.00 | |
| Total | 65 | 97.42 | 7.082 | 0.878 | 74 | 100 | 26 | 100.00 | |
| Office Staff post | No Mesh | 24 | 99.00 | 3.502 | 0.715 | 85 | 100 | 15 | 100.00 |
| Mesh | 37 | 95.08 | 12.698 | 2.088 | 43 | 100 | 57 | 100.00 | |
| Total | 61 | 96.62 | 10.255 | 1.313 | 43 | 100 | 57 | 100.00 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dueñas-Rodríguez, B.; Navarro-Cecilia, J.; Luque-López, C.; Sánchez-Andujar, B.; Garcelán-Trigo, J.A.; Ramírez-Expósito, M.J.; Martínez-Martos, J.M. Single-Stage Immediate Breast Reconstruction with Acellular Dermal Matrix after Breast Cancer: Comparative Study and Evaluation of Breast Reconstruction Outcomes. Cancers 2023, 15, 5349. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225349
Dueñas-Rodríguez B, Navarro-Cecilia J, Luque-López C, Sánchez-Andujar B, Garcelán-Trigo JA, Ramírez-Expósito MJ, Martínez-Martos JM. Single-Stage Immediate Breast Reconstruction with Acellular Dermal Matrix after Breast Cancer: Comparative Study and Evaluation of Breast Reconstruction Outcomes. Cancers. 2023; 15(22):5349. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225349
Chicago/Turabian StyleDueñas-Rodríguez, Basilio, Joaquín Navarro-Cecilia, Carolina Luque-López, Belén Sánchez-Andujar, Juan Arsenio Garcelán-Trigo, María Jesús Ramírez-Expósito, and José Manuel Martínez-Martos. 2023. "Single-Stage Immediate Breast Reconstruction with Acellular Dermal Matrix after Breast Cancer: Comparative Study and Evaluation of Breast Reconstruction Outcomes" Cancers 15, no. 22: 5349. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225349
APA StyleDueñas-Rodríguez, B., Navarro-Cecilia, J., Luque-López, C., Sánchez-Andujar, B., Garcelán-Trigo, J. A., Ramírez-Expósito, M. J., & Martínez-Martos, J. M. (2023). Single-Stage Immediate Breast Reconstruction with Acellular Dermal Matrix after Breast Cancer: Comparative Study and Evaluation of Breast Reconstruction Outcomes. Cancers, 15(22), 5349. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225349







