Amivantamab Compared with Real-World Physician’s Choice after Platinum-Based Therapy from a Pan-European Chart Review of Patients with Lung Cancer and Activating EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Amivantamab Cohort
2.2. CATERPILLAR-RWE Cohort
2.3. Endpoint Definitions
2.4. Adjustment for Differences between Patient Cohorts
2.4.1. Inverse Probability Weighting
2.4.2. Multivariable Regression
2.5. Imputation Method
- If information on metastatic locations was available from both the previous and subsequent LOT (as was the case for three LOTs) and if there was no change in the presence/absence of metastases between prior and subsequent LOT, then the available information was imputed for each metastatic location. If a change in metastatic locations between prior and subsequent LOT was present (e.g., the prior LOT did not have a metastatic location and the subsequent LOT did have a metastatic location), then the presence of metastasis was imputed.
- If information only from the prior LOT was available (four LOTs), then the last observation was carried forward.
- If information only from the subsequent LOT was available (two LOTs), then its values were imputed.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Patient and Disease Characteristics
3.2. Treatments Received as Part of RWPC
3.3. Inverse Probability Weighting
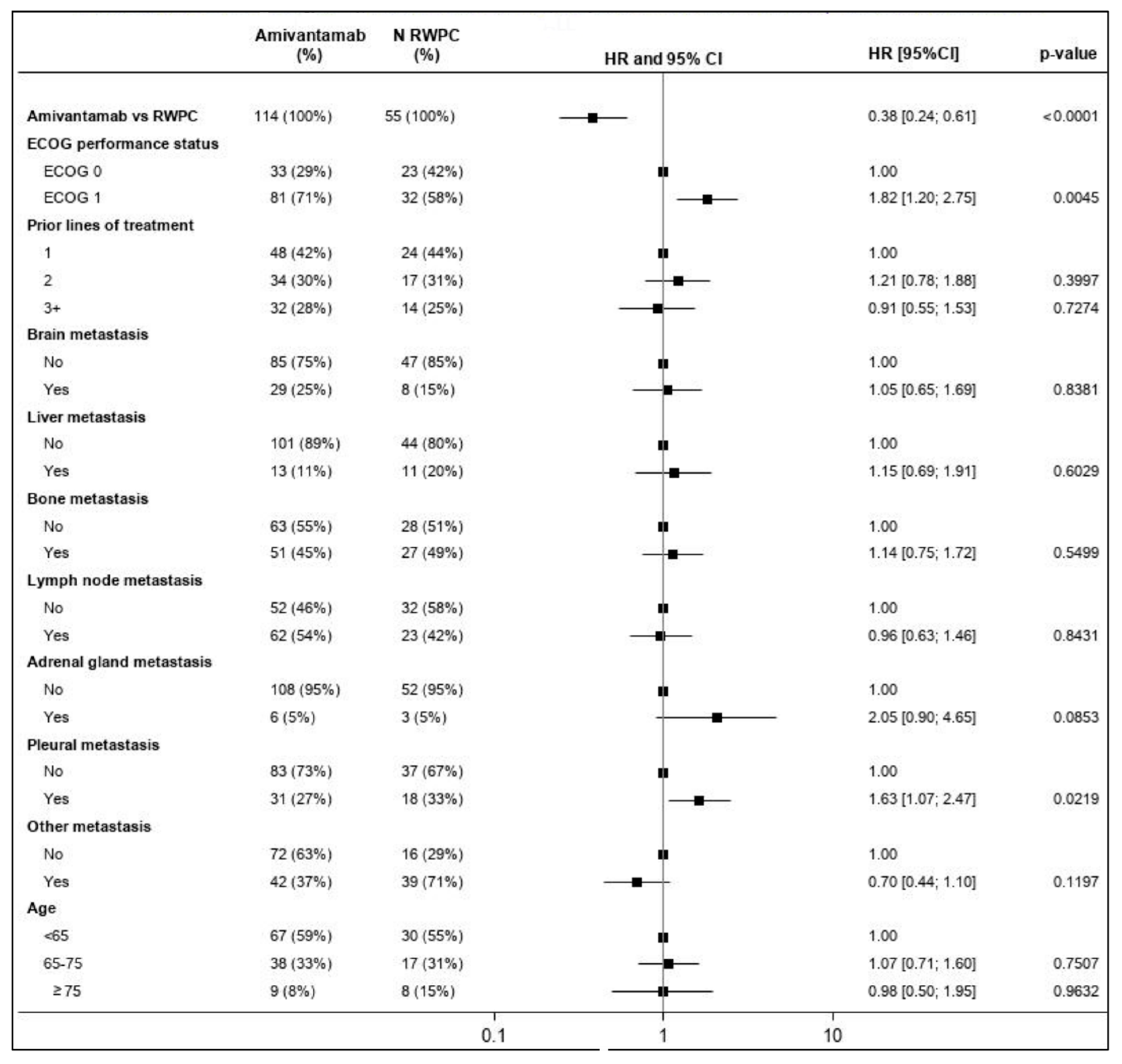
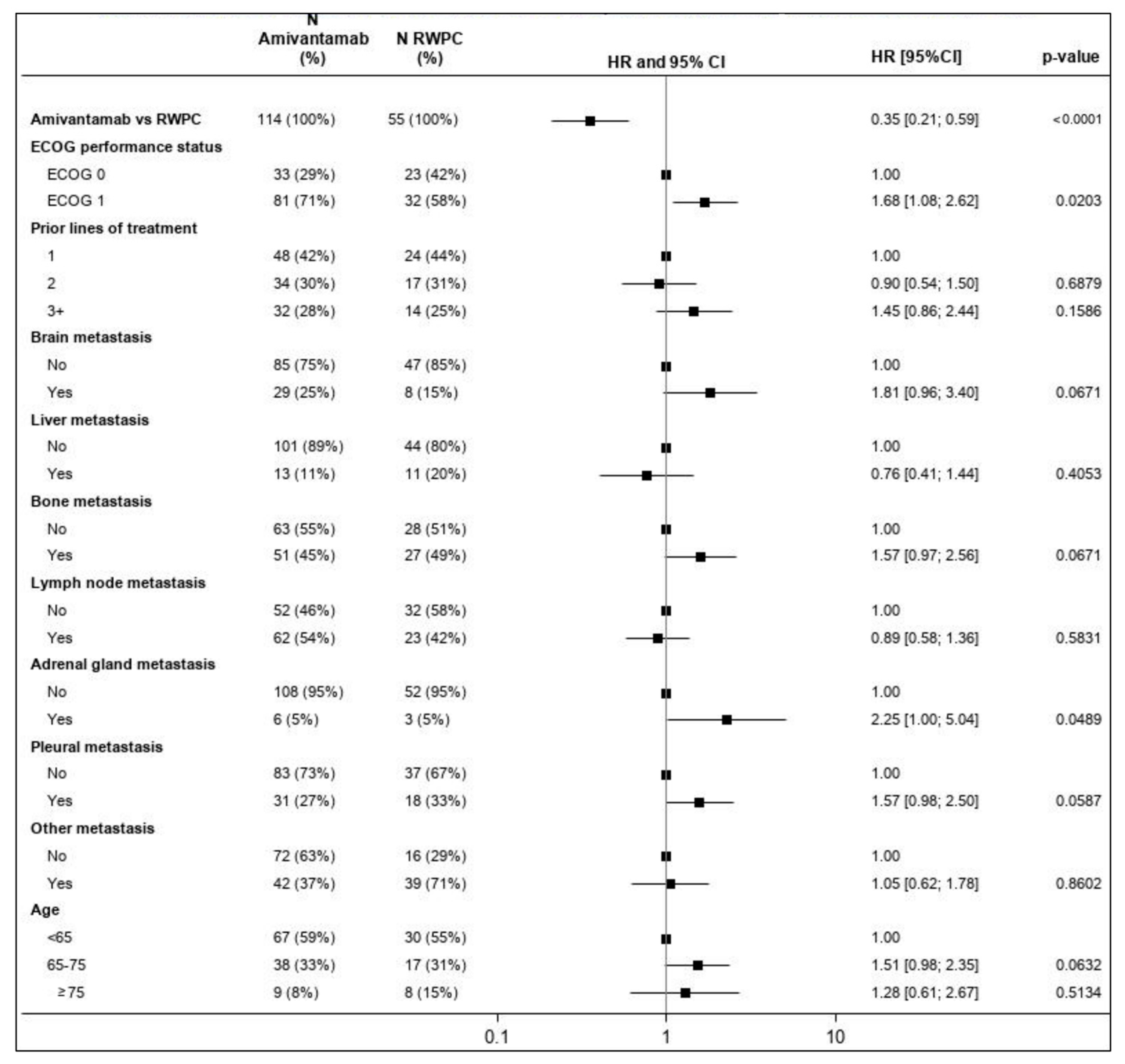
3.4. Efficacy Assessments
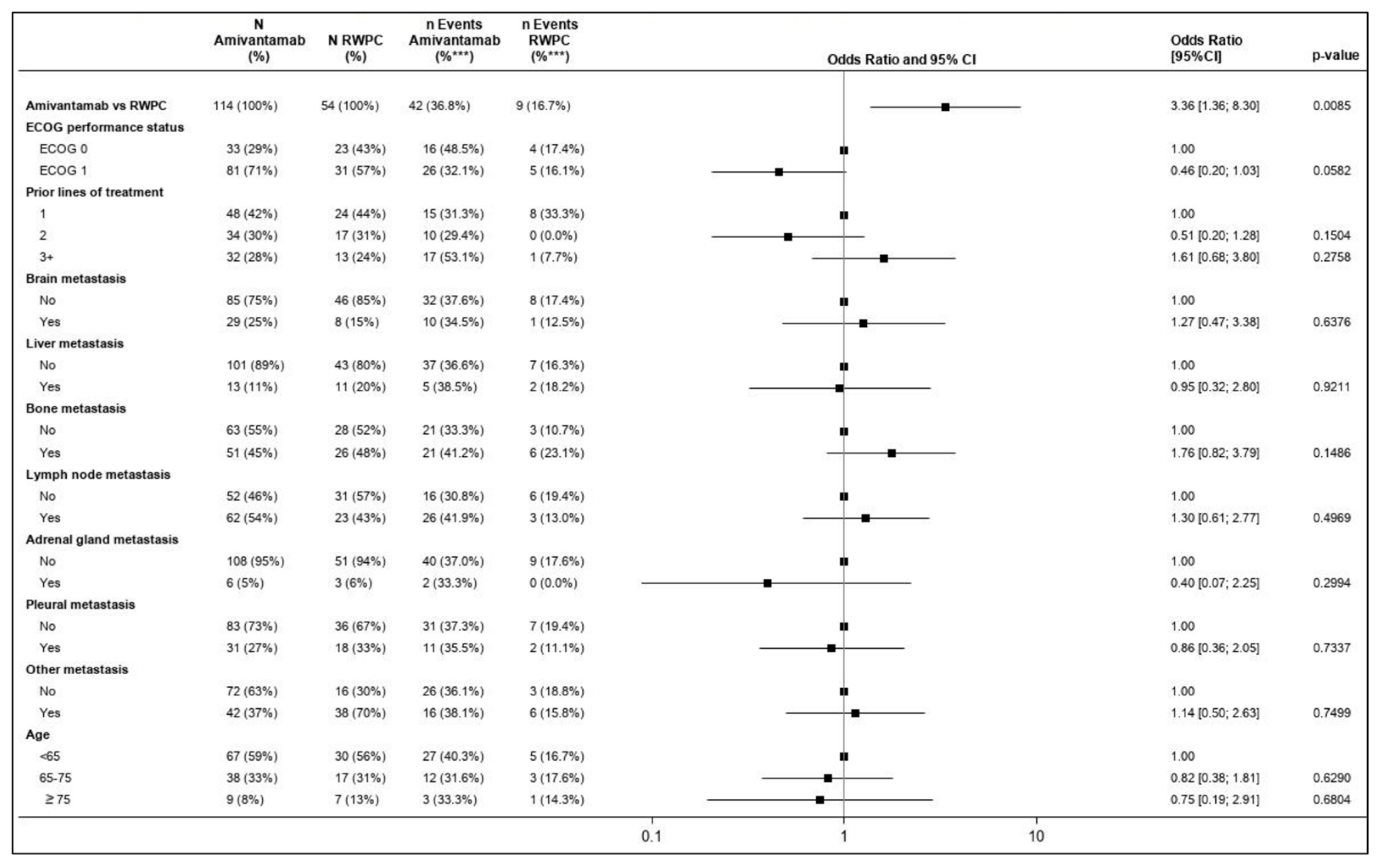
3.4.1. Overall Response Rate
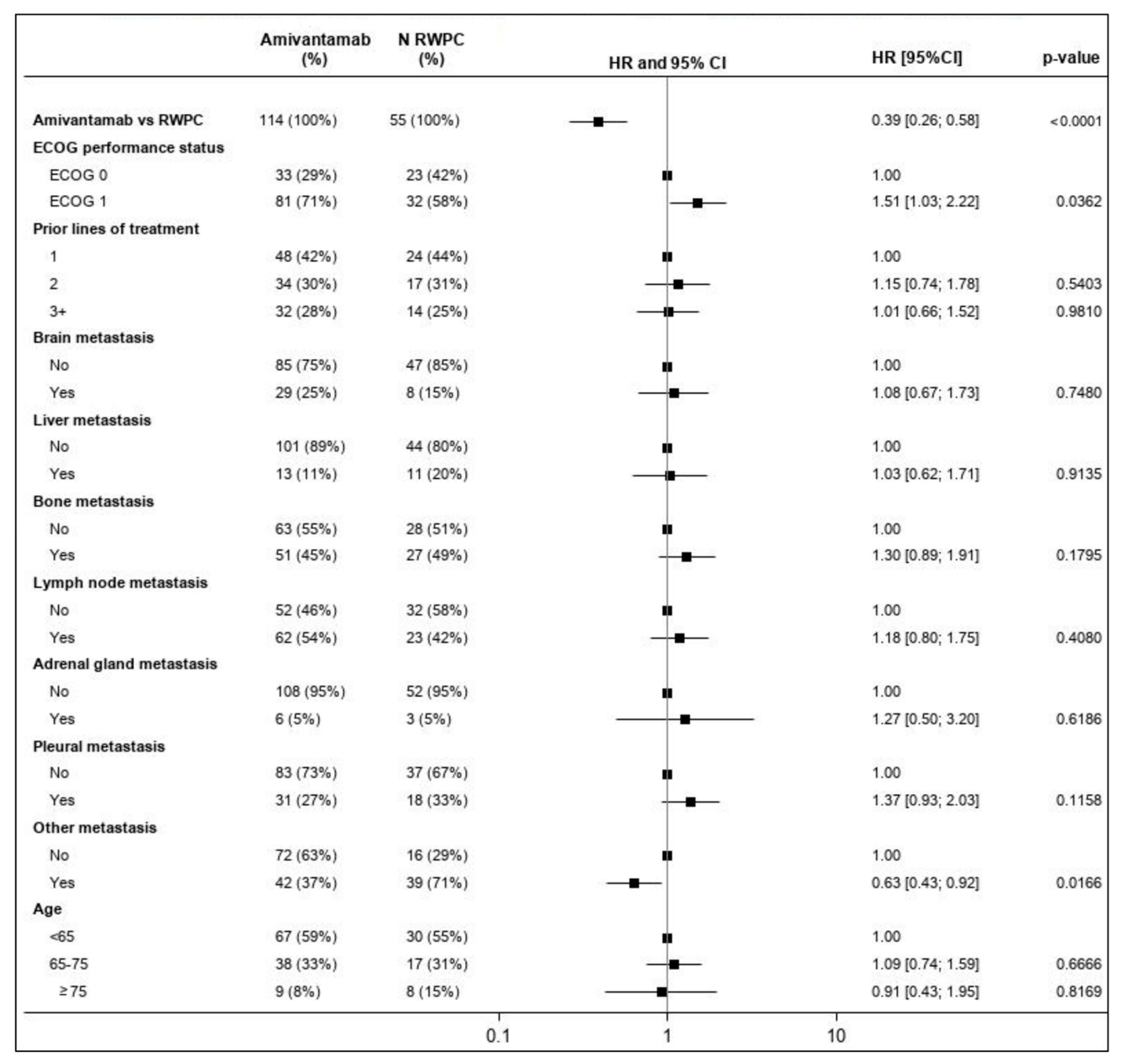
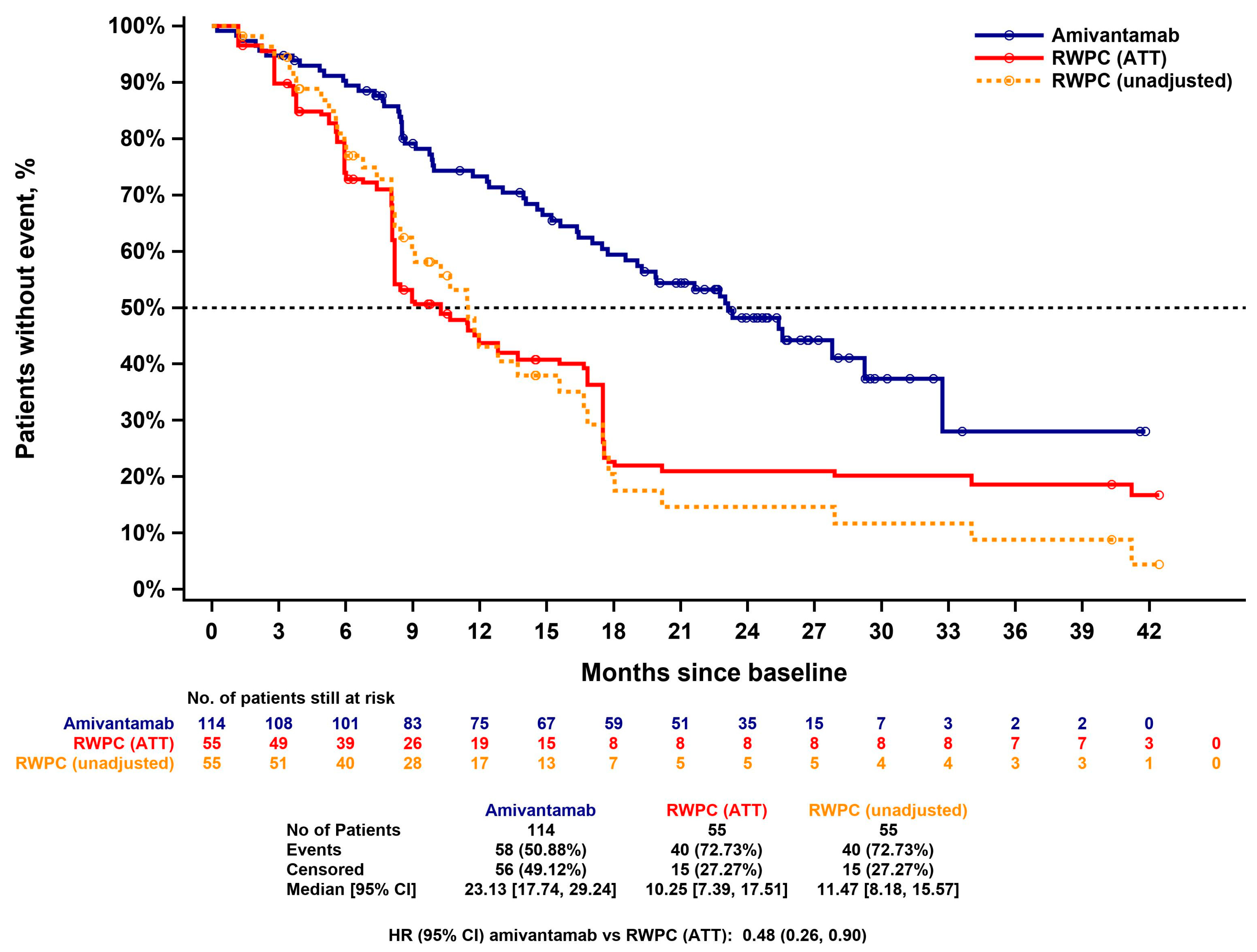
3.4.2. Progression Free Survival
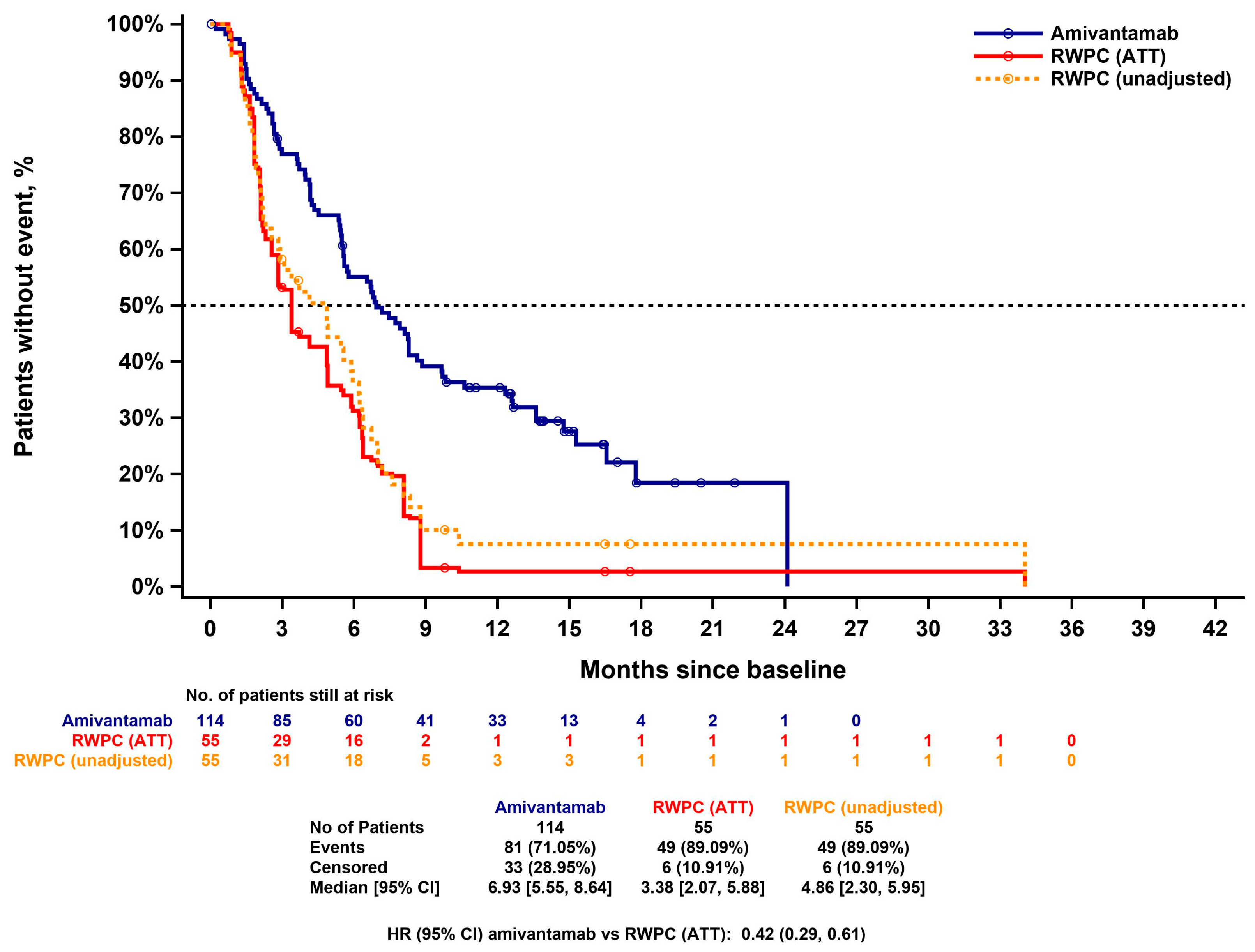
3.4.3. Time-to-Next-Treatment
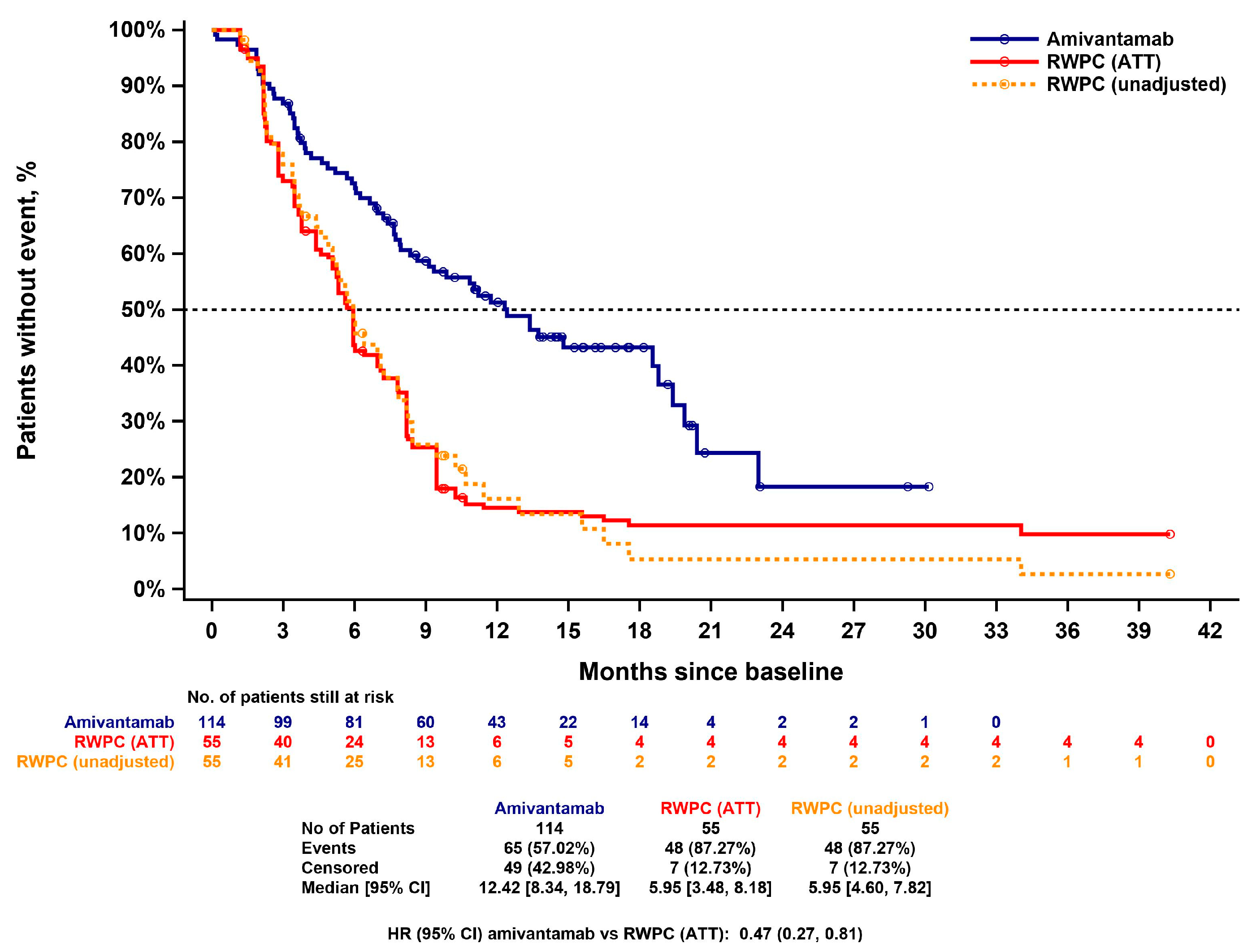
3.4.4. Overall Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; He, Z.; Yang, S.; Hao, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Z.; Han, J.; Wang, L.; et al. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Current status and perspectives. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasuda, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Costa, D.B. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer: Preclinical data and clinical implications. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, e23–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, P.T.; Vyse, S.; Huang, P.H. Rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 61, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, J.W.; Gandara, D.R.; Frampton, G.M.; Madison, R.; Peled, N.; Bufill, J.A.; Dy, G.K.; Ou, S.I.; Stephens, P.J.; McPherson, J.D.; et al. Diverse EGFR Exon 20 Insertions and Co-Occurring Molecular Alterations Identified by Comprehensive Genomic Profiling of NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Lo, P.C.; Nishino, M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Lindeman, N.I.; Butaney, M.; Jackman, D.M.; Johnson, B.E.; Jänne, P.A. Natural history and molecular characteristics of lung cancers harboring EGFR exon 20 insertions. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazhenova, L.; Minchom, A.; Viteri, S.; Bauml, J.M.; Ou, S.I.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Trigo, J.M.; Backenroth, D.; Li, T.; Londhe, A.; et al. Comparative clinical outcomes for patients with advanced NSCLC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations and common EGFR mutations. Lung Cancer 2021, 162, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, H.; Emich, H.; Carroll, C.; Stapleton, N.; Mahadevia, P.; Li, T. Epidemiological and clinical burden of EGFR Exon 20 insertion in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic literature review. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, C.S.; Lin, H.M.; Crossland, V.; Churchill, E.N.; Curran, E.; Forsythe, A.; Tomaras, D.; Ou, S.I. Non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of patient outcomes. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2022, 38, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Sequist, L.V.; Geater, S.L.; Tsai, C.M.; Mok, T.S.; Schuler, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Yu, C.J.; Ou, S.H.; Zhou, C.; et al. Clinical activity of afatinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring uncommon EGFR mutations: A combined post-hoc analysis of LUX-Lung 2, LUX-Lung 3, and LUX-Lung 6. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, Z.; Wang, Y.; Sequist, L.V.; Ramalingam, S.S. ECOG-ACRIN 5162: A phase II study of osimertinib 160 mg in NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertions. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwierenga, F.; van Veggel, B.; Hendriks, L.E.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Hiddinga, B.I.; Kappelle, L.B.H.; Ter Elst, A.; Hashemi, S.M.; Dingemans, A.-M.C.; van der Leest, C. High dose osimertinib in patients with advanced stage EGFR exon 20 mutation-positive NSCLC: Results from the phase 2 multicenter POSITION20 trial. Lung Cancer 2022, 170, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, N.; Wolf, J.; Kim, T.M.; Leighl, N.; Knott, C.; Li, T.; Cabrieto, J.; Diels, J.; Sermon, J.; Mahadevia, P.; et al. Amivantamab Versus Alternative Real-World Anti-Cancer Therapies in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Exon 20 Insertion Mutations in the US and Europe. In Proceedings of the European Lung Cancer Congress, Copenhagen, Denmark, 29 March–1 April 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chouaid, C.; Bosquet, L.; Girard, N.; Kron, A.; Scheffler, M.; Griesinger, F.; Sebastian, M.; Trigo, J.; Viteri, S.; Knott, C.; et al. An Adjusted Treatment Comparison Comparing Amivantamab Versus Real-World Clinical Practice in Europe and the United States for Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with Activating Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 1187–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). European Public Assessment Report: Rybrevant. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/rybrevant-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2023).
- Food and Drug Administration. Mobocertinib (EXKIVITY™) Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/215310s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Park, K.; Haura, E.B.; Leighl, N.B.; Mitchell, P.; Shu, C.A.; Girard, N.; Viteri, S.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, C.K.; et al. Amivantamab in EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Progressing on Platinum Chemotherapy: Initial Results From the CHRYSALIS Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Drug Administration. Amivantamab (RYBREVANT™) Prescribing Information. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/761210s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. Rybrevant 50 mg/mL Concentrate for Solution for Infusion SmPC. 2021. Available online: https://mhraproducts4853.blob.core.windows.net/docs/431ad859be20738a20096b590eb779bd4e939c67 (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Zhou, C.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Riely, G.J.; Mekhail, T.; Nguyen, D.; Campelo, M.R.G.; Felip, E. Treatment outcomes and safety of mobocertinib in platinum-pretreated patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion–positive metastatic non–small cell lung cancer: A phase 1/2 open-label nonrandomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, e214761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency. EXKIVITY 40 mg Hard Capsules SmPC. 2021. Available online: https://mhraproducts4853.blob.core.windows.net/docs/5180220753ab1fe3d10b9be546baba0b7f665fa9 (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Takeda. Takeda Provides Update on EXKIVITY® (Mobocertinib). Available online: https://www.takeda.com/newsroom/newsreleases/2023/Takeda-Provides-Update-on-EXKIVITY-mobocertinib/ (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. TAK-788 as First-Line Treatment Versus Platinum-Based Chemotherapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04129502 (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Exkivity: Withdrawal of the Marketing Authorisation Application. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/withdrawn-applications/exkivity (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Hendriks, L.E.; Kerr, K.M.; Menis, J.; Mok, T.S.; Nestle, U.; Passaro, A.; Peters, S.; Planchard, D.; Smit, E.F.; Solomon, B.J.; et al. Oncogene-addicted metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.-H.I.; Hong, J.-L.; Christopoulos, P.; Lin, H.M.; Vincent, S.; Churchill, E.N.; Soeda, J.; Kazdal, D.; Stenzinger, A.; Thomas, M. Distribution and Detectability of EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Variants in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, 744–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makady, A.; Ham, R.T.; de Boer, A.; Hillege, H.; Klungel, O.; Goettsch, W.; on behalf of GetReal Workpackage. Policies for Use of Real-World Data in Health Technology Assessment (HTA): A Comparative Study of Six HTA Agencies. Value Health 2017, 20, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Talvey Assessment Report. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/assessment-report/talvey-epar-public-assessment-report_en.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Carvykti Assessment Report. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/assessment-report/carvykti-epar-public-assessment-report_en.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2023).
- Minchom, A.; Viteri, S.; Bazhenova, L.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Trigo, J.; Bauml, J.M.; Backenroth, D.; Bhattacharya, A.; Li, T.; et al. Amivantamab compared with real-world therapies in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations who progressed after platinum-based chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 2022, 168, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernán, M.A.; Robins, J.M. Using Big Data to Emulate a Target Trial When a Randomized Trial Is not Available. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 183, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernán, M.A.; Alonso, A.; Logan, R.; Grodstein, F.; Michels, K.B.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C.; Manson, J.E.; Robins, J.M. Observational studies analyzed like randomized experiments: An application to postmenopausal hormone therapy and coronary heart disease. Epidemiology 2008, 19, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backenroth, D. How to choose a time zero for patients in external control arms. Pharm. Stat. 2021, 20, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatswell, A.J.; Deighton, K.; Snider, J.T.; Brookhart, M.A.; Faghmous, I.; Patel, A.R. Approaches to selecting “time zero” in external control arms with multiple potential entry points: A simulation study of 8 approaches. Med. Decis. Mak. 2022, 42, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Morgan, K.L.; Zaslavsky, A.M. Balancing covariates via propensity score weighting. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2018, 113, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liu, C. Adjusted Kaplan–Meier estimator and log-rank test with inverse probability of treatment weighting for survival data. Stat. Med. 2005, 24, 3089–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Study of Amivantamab, a Human Bispecific EGFR and cMet Antibody, in Participants with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (CHRYSALIS). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02609776 (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Popat, S.; Liu, S.V.; Scheuer, N.; Hsu, G.G.; Lockhart, A.; Ramagopalan, S.V.; Griesinger, F.; Subbiah, V. Addressing challenges with real-world synthetic control arms to demonstrate the comparative effectiveness of Pralsetinib in non-small cell lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haneuse, S.; VanderWeele, T.J.; Arterburn, D. Using the E-Value to Assess the Potential Effect of Unmeasured Confounding in Observational Studies. JAMA 2019, 321, 602–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopoulos, P.; Kluck, K.; Kirchner, M.; Lüders, H.; Roeper, J.; Falkenstern-Ge, R.-F.; Szewczyk, M.; Sticht, F.; Saalfeld, F.C.; Wesseler, C. The impact of TP53 co-mutations and immunologic microenvironment on outcome of lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertions. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 170, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. A Study of Combination Amivantamab and Carboplatin-Pemetrexed Therapy, Compared with Carboplatin-Pemetrexed, in Participants with Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Characterized by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Exon 20 Insertions (PAPILLON). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04538664 (accessed on 1 March 2023).
- Good Publication Practice (GPP) Guidelines for Company-Sponsored Biomedical Research: 2022 Update. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, 1298–1304. [CrossRef]
| Amivantamab | RWPC (Observed) | RWPC (with Imputation) | ATT-Adjusted RWPC | SMD (after ATT Adjustment) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECOG performance status | |||||
| N | 114 | 55 | 55 | 55 | −0.060 |
| 0 | 33 (28.9%) | 23 (41.8%) | 23 (41.8%) | 14 (26.3%) | |
| 1 | 81 (71.1%) | 32 (58.2%) | 32 (58.2%) | 41 (73.7%) | |
| Prior lines of treatment | |||||
| N | 114 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 0.024 |
| 1 | 48 (42.1%) | 24 (43.6%) | 24 (43.6%) | 24 (43.2%) | |
| 2 | 34 (29.8%) | 17 (30.9%) | 17 (30.9%) | 16 (29.4%) | |
| 3+ | 32 (28.1%) | 14 (25.5%) | 14 (25.5%) | 15 (27.3%) | |
| Brain metastasis | |||||
| N | 114 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 0.068 |
| No | 85 (74.6%) | 39 (70.9%) | 47 (85.5%) | 43 (77.5%) | |
| Yes | 29 (25.4%) | 7 (12.7%) | 8 (14.5%) | 12 (22.5%) | |
| Missing | 0 | 9 (16.4%) | 0 | 0 | |
| Liver metastasis | |||||
| N | 114 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 0.061 |
| No | 101 (88.6%) | 37 (67.3%) | 44 (80.0%) | 50 (90.5%) | |
| Yes | 13 (11.4%) | 9 (16.4%) | 11 (20.0%) | 5 (9.5%) | |
| Missing | 0 | 9 (16.4%) | 0 | 0 | |
| Bone metastasis | |||||
| N | 114 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 0.058 |
| No | 63 (55.3%) | 24 (43.6%) | 28 (50.9%) | 32 (58.1%) | |
| Yes | 51 (44.7%) | 22 (40.0%) | 27 (49.1%) | 23 (41.9%) | |
| Missing | 0 | 9 (16.4%) | 0 | 0 | |
| Lymph node metastasis | |||||
| N | 114 | 55 | 55 | 55 | −0.159 |
| No | 52 (45.6%) | 27 (49.1%) | 32 (58.2%) | 21 (37.8%) | |
| Yes | 62 (54.4%) | 19 (34.5%) | 23 (41.8%) | 34 (62.2%) | |
| Missing | 0 | 9 (16.4%) | 0 | 0 | |
| Adrenal gland metastasis | |||||
| N | 114 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 0.179 |
| No | 108 (94.7%) | 43 (78.2%) | 52 (94.5%) | 54 (98.1%) | |
| Yes | 6 (5.3%) | 3 (5.5%) | 3 (5.5%) | 1 (1.9%) | |
| Missing | 0 | 9 (16.4%) | 0 | 0 | |
| Pleural metastasis | |||||
| N | 114 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 0.006 |
| No | 83 (72.8%) | 31 (56.4%) | 37 (67.3%) | 40 (73.1%) | |
| Yes | 31 (27.2%) | 15 (27.3%) | 18 (32.7%) | 15 (26.9%) | |
| Missing | 0 | 9 (16.4%) | 0 | 0 | |
| Other metastasis | |||||
| N | 114 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 0.043 |
| No | 72 (63.2%) | 10 (18.2%) | 16 (29.1%) | 36 (65.2%) | |
| Yes | 42 (36.8%) | 36 (65.5%) | 39 (70.9%) | 19 (34.8%) | |
| Missing | 0 | 9 (16.4%) | 0 | 0 | |
| Age | |||||
| N | 114 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 0.136 |
| <65 | 67 (58.8%) | 30 (54.5%) | 30 (54.5%) | 30 (54.9%) | |
| 65–75 | 38 (33.3%) | 17 (30.9%) | 17 (30.9%) | 21 (39.1%) | |
| ≥75 | 9 (7.9%) | 8 (14.5%) | 8 (14.5%) | 3 (6.1%) | |
| Treatment Class | Number of LOTs (%) |
|---|---|
| IO | 7 (12.7) |
| EGFR TKI | 9 (16.4) |
| Non-platinum-based chemotherapy | 15 (27.3) |
| VEGFi + chemotherapy | 3 (5.5) |
| Other 1 | 21 (38.2) |
| Method | ORR | OR (95% CI) | p Value | Response Rate Ratio (95% CI) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amivantamab | RWPC | |||||
| Unadjusted comparison | 36.8% | 16.7% | 2.92 (1.30, 6.56) | 0.0096 | 2.21 (1.16, 4.20) | 0.0156 |
| IPW–ATT approach | 36.8% | 17.2% | 2.80 (1.26, 6.22) | 0.0116 | 2.14 (1.14, 4.01) | 0.0181 |
| Multivariable regression | 29.7% | 11.1% | 3.36 (1.36, 8.30) | 0.0085 | 2.37 (1.23, 4.58) | 0.0103 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christopoulos, P.; Girard, N.; Proto, C.; Soares, M.; Lopez, P.G.; van der Wekken, A.J.; Popat, S.; Diels, J.; Schioppa, C.A.; Sermon, J.; et al. Amivantamab Compared with Real-World Physician’s Choice after Platinum-Based Therapy from a Pan-European Chart Review of Patients with Lung Cancer and Activating EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. Cancers 2023, 15, 5326. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225326
Christopoulos P, Girard N, Proto C, Soares M, Lopez PG, van der Wekken AJ, Popat S, Diels J, Schioppa CA, Sermon J, et al. Amivantamab Compared with Real-World Physician’s Choice after Platinum-Based Therapy from a Pan-European Chart Review of Patients with Lung Cancer and Activating EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. Cancers. 2023; 15(22):5326. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225326
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristopoulos, Petros, Nicolas Girard, Claudia Proto, Marta Soares, Pilar Garrido Lopez, Anthonie J. van der Wekken, Sanjay Popat, Joris Diels, Claudio A. Schioppa, Jan Sermon, and et al. 2023. "Amivantamab Compared with Real-World Physician’s Choice after Platinum-Based Therapy from a Pan-European Chart Review of Patients with Lung Cancer and Activating EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations" Cancers 15, no. 22: 5326. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225326
APA StyleChristopoulos, P., Girard, N., Proto, C., Soares, M., Lopez, P. G., van der Wekken, A. J., Popat, S., Diels, J., Schioppa, C. A., Sermon, J., Rahhali, N., Pick-Lauer, C., Adamczyk, A., Penton, J., & Wislez, M. (2023). Amivantamab Compared with Real-World Physician’s Choice after Platinum-Based Therapy from a Pan-European Chart Review of Patients with Lung Cancer and Activating EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. Cancers, 15(22), 5326. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225326







