Genome-Wide Extrachromosomal Circular DNA Profiling of Paired Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Adjacent Liver Tissues
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introductory Statement
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Tissues
2.2. Tissue DNA Preparation and eccDNA Sequencing
2.3. Circular DNA Identification and Visualization
2.4. RNA Sequencing (RNA-seq) and Transcriptome Data Analyses
2.5. Validation of eccDNA
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
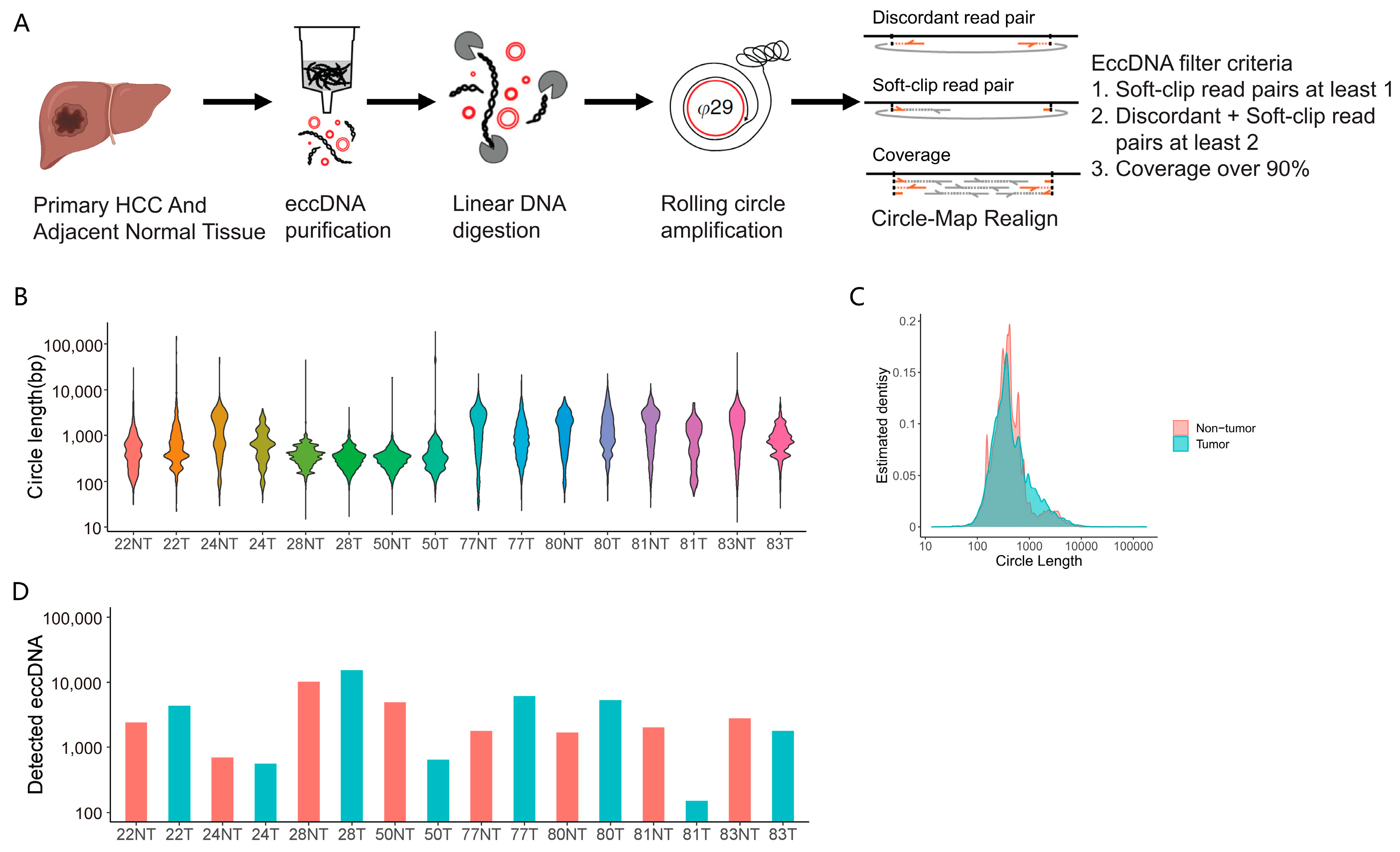
3.1. Genome-Wide eccDNAs Profiling by Circle-seq in Paired HCC and Adjacent Tissue Samples
3.2. Genomic Distribution of eccDNAs in the HCC and Adjacent Tissue Samples
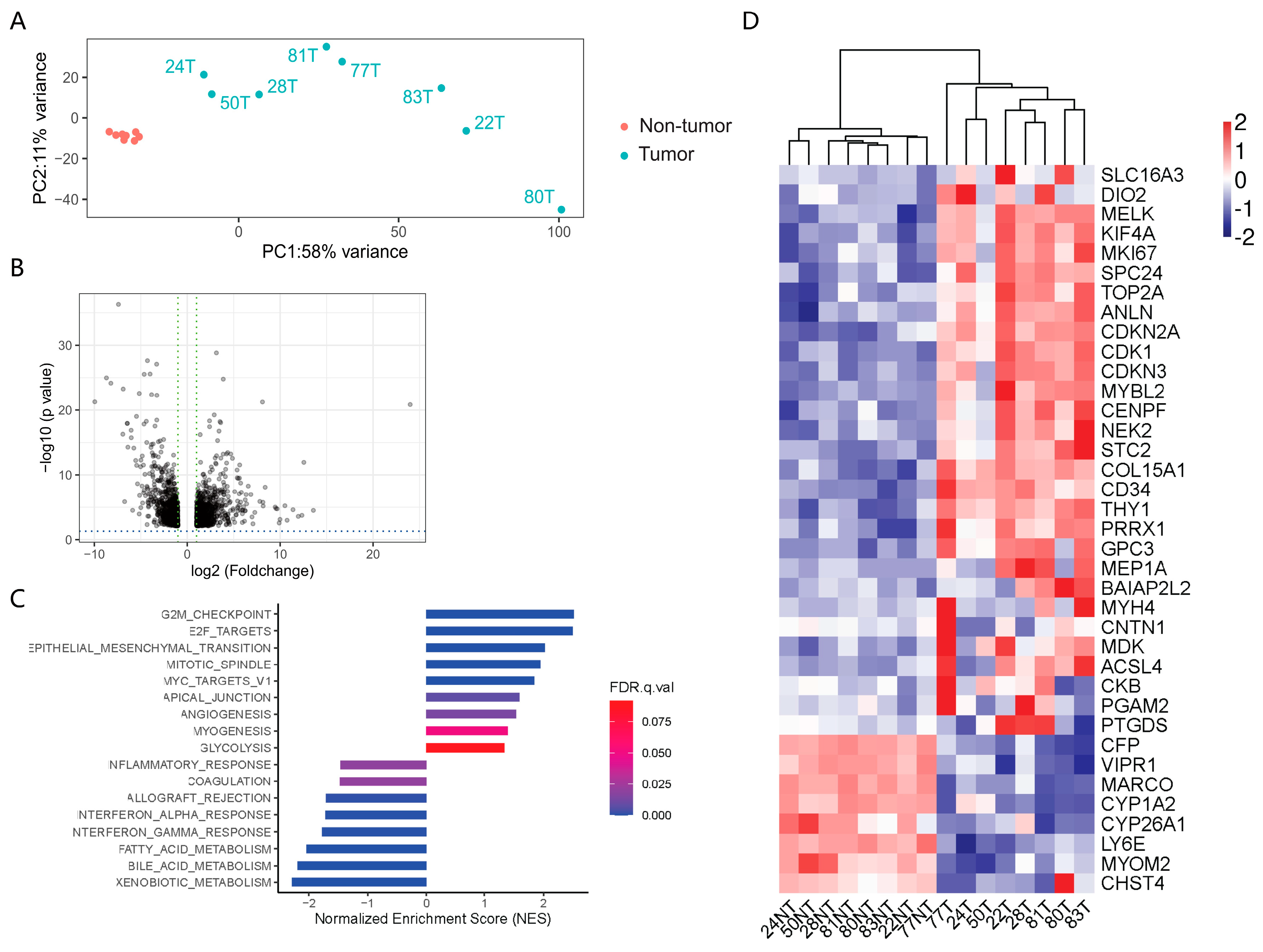
3.3. Transcriptomic Profiling of the Paired HCC and Adjacent Tissue Samples
3.4. Cross-Analysis of the Circle-seq Data with the Transcriptomic Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| eccDNA | extrachromosomal circular DNA |
| ecDNA | extrachromosomal DNA |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| Mb | million bases |
| PCA | principal components analysis |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| BAIAP2L2 | BAR/IMD domain containing adaptor protein 2 like 2 |
| SLC16A3 | Solute carrier family 16 member 3 |
| SMD | standardized mean difference |
References
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ramadori, P.; Pfister, D.; Seehawer, M.; Zender, L.; Heikenwalder, M. The immunological and metabolic landscape in primary and metastatic liver cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 541–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandio, R.C.; Pestana, R.C.; Miyamura, B.V.; Kaseb, A.O. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immunotherapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, Y.; Bassel, A. Molecular size and circularity of DNA in cells of mammals and higher plants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1965, 53, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moller, H.D.; Mohiyuddin, M.; Prada-Luengo, I.; Sailani, M.R.; Halling, J.F.; Plomgaard, P.; Maretty, L.; Hansen, A.J.; Snyder, M.P.; Pilegaard, H.; et al. Circular DNA elements of chromosomal origin are common in healthy human somatic tissue. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, T.; Kumar, P.; Koseoglu, M.M.; Dutta, A. Discoveries of Extrachromosomal Circles of DNA in Normal and Tumor Cells. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaak, R.G.W.; Bafna, V.; Mischel, P.S. Extrachromosomal oncogene amplification in tumour pathogenesis and evolution. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, L.W.; Kumar, P.; Shibata, Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Willcox, S.; Griffith, J.D.; Pommier, Y.; Takeda, S.; Dutta, A. Production of Extrachromosomal MicroDNAs Is Linked to Mismatch Repair Pathways and Transcriptional Activity. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1749–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, T.; Shibata, Y.; Kumar, P.; Dillon, L.; Dutta, A. Small extrachromosomal circular DNAs, microDNA, produce short regulatory RNAs that suppress gene expression independent of canonical promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 4586–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Nguyen, N.P.; Turner, K.; Wu, S.; Gujar, A.D.; Luebeck, J.; Liu, J.; Deshpande, V.; Rajkumar, U.; Namburi, S.; et al. Extrachromosomal DNA is associated with oncogene amplification and poor outcome across multiple cancers. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Jang, M.; Park, Y.N. Histopathological Variants of Hepatocellular Carcinomas: An Update According to the 5th Edition of the WHO Classification of Digestive System Tumors. J. Liver Cancer 2020, 20, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada-Luengo, I.; Krogh, A.; Maretty, L.; Regenberg, B. Sensitive detection of circular DNAs at single-nucleotide resolution using guided realignment of partially aligned reads. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; He, Q.-Y. ChIPseeker: An R/Bioconductor package for ChIP peak annotation, comparison and visualization. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2382–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gel, B.; Serra, E. karyoploteR: An R/Bioconductor package to plot customizable genomes displaying arbitrary data. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3088–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.-G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.-Y. clusterProfiler: An R Package for Comparing Biological Themes Among Gene Clusters. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon provides fast and bias-aware quantification of transcript expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, H.D.; Parsons, L.; Jorgensen, T.S.; Botstein, D.; Regenberg, B. Extrachromosomal circular DNA is common in yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3114–E3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhu, H.; Dong, L.; Shi, W.; Chen, R.; Song, Z.; Huang, C.; Fan, J. Integrated Proteogenomic Characterization of HBV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell 2019, 179, 561–577.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, Y.; Kumar, P.; Layer, R.; Willcox, S.; Gagan, J.R.; Griffith, J.D.; Dutta, A. Extrachromosomal MicroDNAs and Chromosomal Microdeletions in Normal Tissues. Science 2012, 336, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Djekidel, M.N.; Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Alt, F.W.; Zhang, Y. eccDNAs are apoptotic products with high innate immunostimulatory activity. Nature 2021, 599, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, D.J.; Miretti, M.; Rajan, D.; Fiegler, H.; Carter, N.P.; Blayney, M.L.; Beck, S.; Hurles, M.E. Germline rates of de novo meiotic deletions and duplications causing several genomic disorders. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skourti-Stathaki, K.; Proudfoot, N.J. A double-edged sword: R loops as threats to genome integrity and powerful regulators of gene expression. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 1384–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoshani, O.; Brunner, S.F.; Yaeger, R.; Ly, P.; Nechemia-Arbely, Y.; Kim, D.H.; Fang, R.; Castillon, G.A.; Yu, M.; Li, J.S.Z.; et al. Chromothripsis drives the evolution of gene amplification in cancer. Nature 2021, 591, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, R.M.; King, M.; Pizza, G.; Krueger, F.; Vergara, X.; Houseley, J. Transcription-induced formation of extrachromosomal DNA during yeast ageingY. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaubatz, J.W. Extrachromosomal circular dnas and genomic sequence plasticity in eukaryotic cells. Mutat. Res. 1990, 237, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.M.; Deshpande, V.; Beyter, D.; Koga, T.; Rusert, J.; Lee, C.; Li, B.; Arden, K.; Ren, B.; Nathanson, D.A.; et al. Extrachromosomal oncogene amplification drives tumour evolution and genetic heterogeneity. Nature 2017, 543, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanson, D.A.; Gini, B.; Mottahedeh, J.; Visnyei, K.; Koga, T.; Gomez, G.; Eskin, A.; Hwang, K.; Wang, J.; Masuiet, K.; et al. Targeted therapy resistance mediated by dynamic regulation of extrachromosomal mutant EGFR DNA. Science 2014, 343, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttler, F.; Mai, S. Formation of non-random extrachromosomal elements during development, differentiation and oncogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2007, 17, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; He, J.; Huang, S.; Yang, H.; Yi, Q.; Tao, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Qi, H. Identification and Characterization of Extrachromosomal Circular DNA in Human Placentas With Fetal Growth Restriction. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 780779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodfine, K.; Fiegler, H.; Beare, D.M.; Collins, J.E.; McCann, O.T.; Young, B.D.; Debernardi, S.; Mott, R.; Dunham, I.; Carter, N.P. Replication timing of the human genome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2004, 13, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Kudo, J.; Ishibashi, H.; Hirata, Y.; Niho, Y. Frequent loss of heterozygosity on chromosome 22 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 1993, 17, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Chen, S.; Rao, G.; Zhang, G.; Ma, M.; Peng, B.; Du, X.; Huang, W.; Lin, W.; Tian, Y.; et al. Extrachromosomal circular MiR-17-92 amplicon promotes hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, K.L.; Yost, K.E.; Xie, L.; Shi, Q.; Helmsauer, K.; Luebeck, J.; Schopflin, R.; Lange, J.T.; González, R.C.; Weiser, N.E.; et al. ecDNA hubs drive cooperative intermolecular oncogene expression. Nature 2021, 600, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Lu, D.; Chen, R.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, S.; Cui, P.; Song, G.; Rao, D.; et al. Proteogenomic characterization identifies clinically relevant subgroups of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shangguan, Y.; Sun, J.; Cong, W.; Xie, Y. BAIAP2L2 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via AKT/mTOR and Wnt3a/beta-catenin signaling pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Peng, J.; Hu, J.; Chang, S.; Liu, H.; Luo, H.; Chen, X.; Tang, H.; Chen, Y. BAIAP2L2 promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of osteosarcoma associated with the Wnt/b-catenin pathway. J. Bone Oncol. 2021, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhuang, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, M. BAIAP2L2 facilitates the malignancy of prostate cancer (PCa) via VEGF and apoptosis signaling pathways. Genes Genom. 2021, 43, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Du, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Yan, L.; Tian, G.; Fu, X. BAI1-associated protein 2-like 2 is a potential biomarker in lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 41, 1304–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, J.; Huang, P.; Ma, K.; Zhao, Z.; Hua, T.; Zai, W.; Chen, J.; Fu, X. Genome-Wide Extrachromosomal Circular DNA Profiling of Paired Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Adjacent Liver Tissues. Cancers 2023, 15, 5309. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225309
Ye J, Huang P, Ma K, Zhao Z, Hua T, Zai W, Chen J, Fu X. Genome-Wide Extrachromosomal Circular DNA Profiling of Paired Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Adjacent Liver Tissues. Cancers. 2023; 15(22):5309. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225309
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Jianyu, Peixin Huang, Kewei Ma, Zixin Zhao, Ting Hua, Wenjing Zai, Jieliang Chen, and Xiutao Fu. 2023. "Genome-Wide Extrachromosomal Circular DNA Profiling of Paired Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Adjacent Liver Tissues" Cancers 15, no. 22: 5309. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225309
APA StyleYe, J., Huang, P., Ma, K., Zhao, Z., Hua, T., Zai, W., Chen, J., & Fu, X. (2023). Genome-Wide Extrachromosomal Circular DNA Profiling of Paired Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Adjacent Liver Tissues. Cancers, 15(22), 5309. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15225309




