Antiangiogenics in Malignant Granular Cell Tumors: Review of the Literature
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
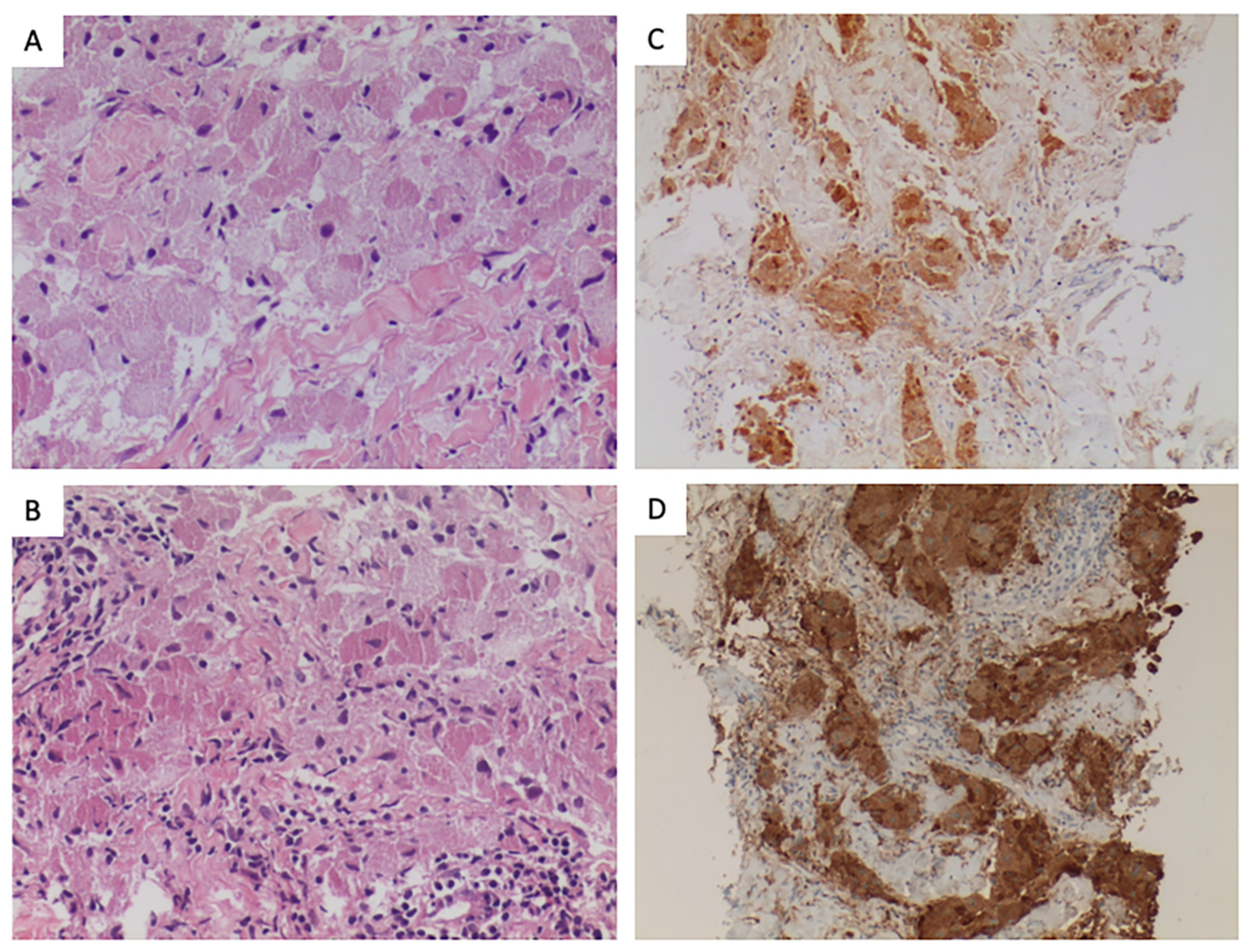
2. Histopathology
3. Molecular Biology
4. Review of the Literature of Systemic Teraphy
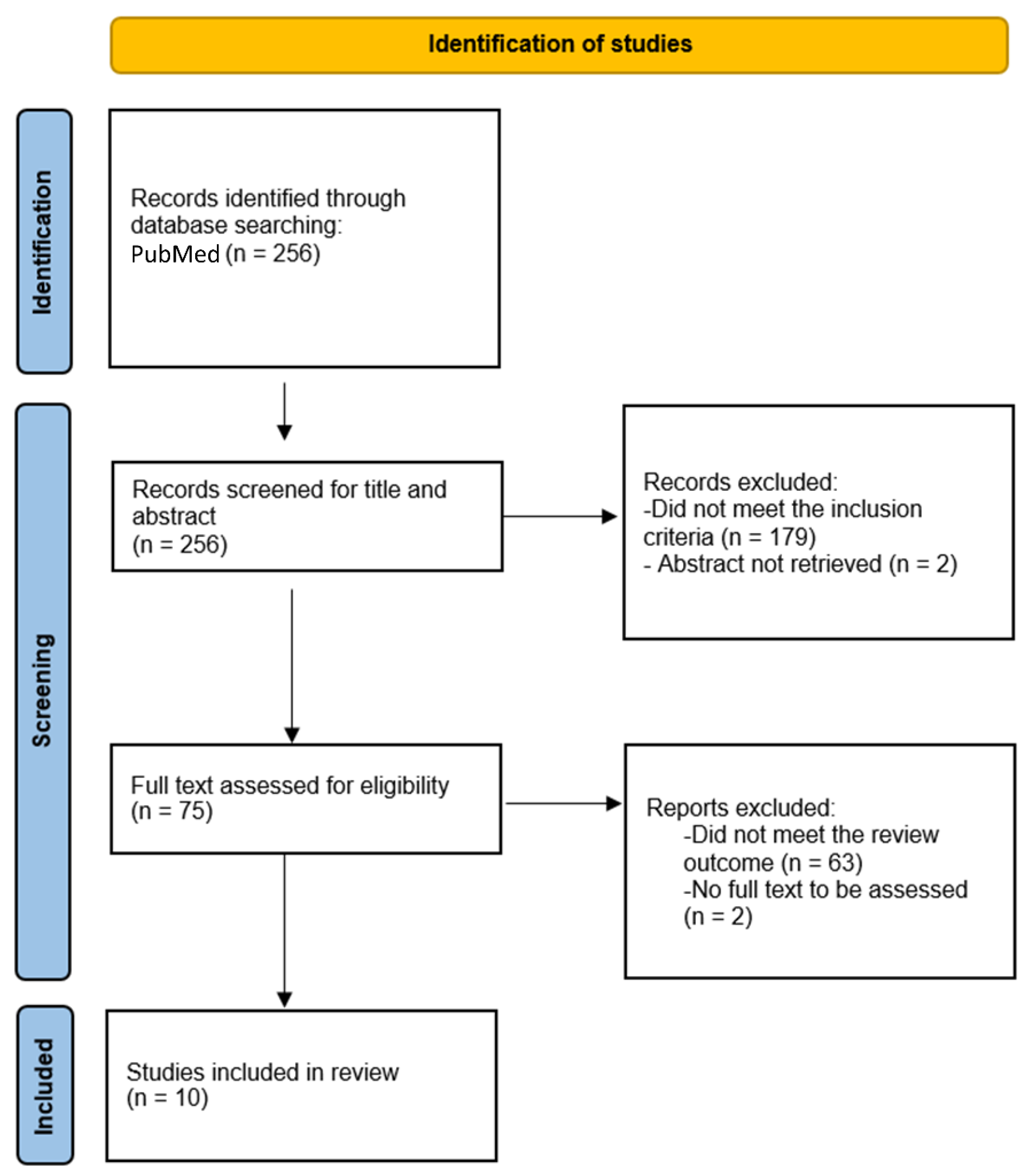
Methods
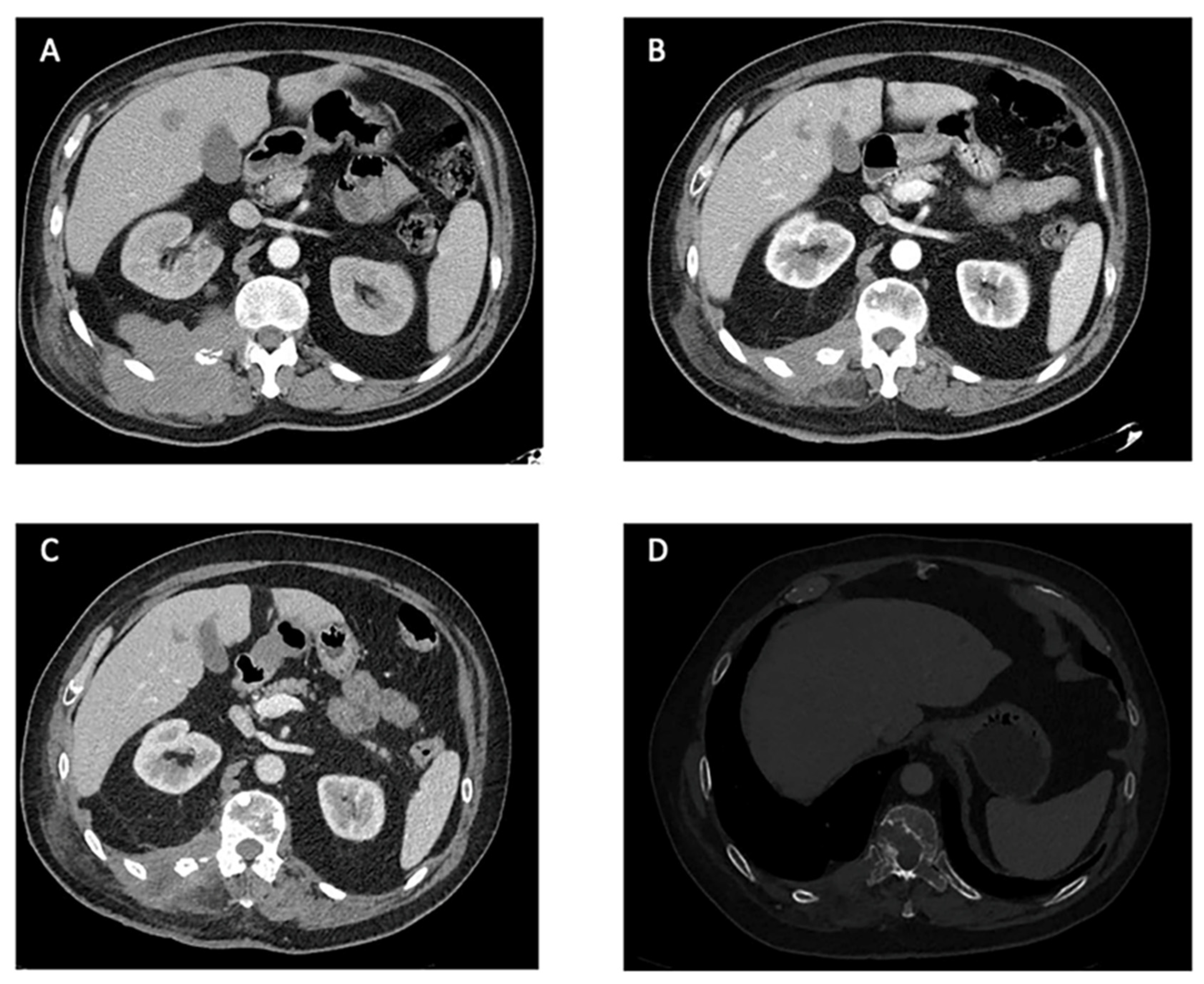
5. Results
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
8. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fletcher, C.; Hogendoorn, P.; Mertens, F. WHO Classification of Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone, 5th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Abrikossoff, A. Virchows Archiv für pathologische Anatomie und Physiologie und für klinische Medizin. Über Myome 1926, 206, 215–233. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida, T.; Okada, K.; Itoi, E.; Sato, T.; Sato, K. Intramuscular malignant granular cell tumor. Skelet. Radiol. 1997, 2, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobarki, M.; Dumollard, J.; Col, P.D.; Camy, F.; Peoc’h, M.; Karpathiou, G. Granular cell tumor a study of 42 cases and systemic review of the literature. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanburg-Smith, J.; Meis-Kindblom, J.; Fante, R.; Kindblom, L. Malignant granular cell tumor of soft tissue: Diagnostic criteria and clinicopathologic correlation. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1998, 22, 779–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, I.; Cruz, J.; Lavernia, J.; Llombart-Bosch, A. Solitary, multiple, benign, atypical, or malignant: The “Granular Cell Tumor” puzzle. Virchows Arch. Int. J. Pathol. 2016, 468, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekimizu, M.; Yoshida, A.; Mitani, S.; Asano, N.; Hirata, M.; Kubo, T.; Yamazaki, F.; Sakamoto, H.; Kato, M.; Makise, N.; et al. Frequent mutations of genes encoding vacuolar H(+)-ATPase components in granular cell tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2019, 58, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareja, F.; Brandes, A.H.; Basili, T.; Selenica, P.; Geyer, F.C.; Fan, D.; Da Cruz Paula, A.; Kumar, R.; Brown, D.N.; Gularte-Mérida, R.; et al. Loss-of-function mutations in ATP6AP1 and ATP6AP2 in granular cell tumors. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, H.; Ahmed, Y.; Szpunar, S.; Kowalski, P. Malignant granular cell tumor: A look into the diagnostic criteria. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2011, 207, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moten, A.S.; Movva, S.; von Mehren, M.; Wu, H.; Esnaola, N.F.; Reddy, S.S.; Farma, J.M. Granular cell tumor experience at a comprehensive cancer center. J. Surg. Res. 2018, 226, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.M.; Hong, S.G.; Kang, S.M.; Chae, B.G.; Kim, S.J.; Park, P.K.; Park, H.S. A case of malignant granular cell tumor in the sigmoid colon. Clin. Endosc. 2014, 47, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Takeda, M.; Honoki, K.; Omokawa, S.; Tanaka, Y. Malignant granular cell tumor of the median nerve: A case report with a literature review of 157 cases. Skelet. Radiol. 2019, 48, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöffski, P.; Sufliarsky, J.; Gelderblom, H.; Blay, J.-Y.; Strauss, S.J.; Stacchiotti, S.; Rutkowski, P.; Lindner, L.H.; Leahy, M.G.; Italiano, A.; et al. Crizotinib in patients with advanced, inoperable inflammatory myofibroblastic tumours with and without anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene alterations (European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer 90101 CREATE): A multicentre, single-drug, prospective, non-randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kim, T.M.; Keam, B.; Kim, Y.J.; Paeng, J.C.; Moon, K.C.; Kim, D.-W.; Heo, D.S. A Phase II Trial of Pazopanib in Patients with Metastatic Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma. Oncologist 2019, 24, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judson, I.; Morden, J.P.; Kilburn, L.; Leahy, M.; Benson, C.; Bhadri, V.; Campbell-Hewson, Q.; Cubedo, R.; Dangoor, A.; Fox, L.; et al. Cediranib in patients with alveolar soft-part sarcoma (CASPS): A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöffski, P.; Wozniak, A.; Stacchiotti, S.; Rutkowski, P.; Blay, J.-Y.; Lindner, L.; Strauss, S.; Anthoney, A.; Duffaud, F.; Richter, S.; et al. Activity and safety of crizotinib in patients with advanced clear-cell sarcoma with MET alterations: European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer phase II trial 90101 ‘CREATE’. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelderblom, H.; Wagner, A. Long-term outcomes of pexidartinib in tenosynovial giant cell tumors. Cancer 2021, 127, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tap, W.D.; Gelderblom, H.; Palmerini, E.; Desai, J.; Bauer, S.; Blay, J.-Y.; Alcindor, T.; Ganjoo, K.; Martín-Broto, J.; Ryan, C.W.; et al. Pexidartinib versus placebo for advanced tenosynovial giant cell tumour (ENLIVEN): A randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flechter, E.; Zohar, Y.; Guralnik, L.; Passhak, M.; Sela, G. Long-lasting stable disease with mTOR inhibitor treatment in a patient with a perivascular epithelioid cell tumor: A case report and literature review. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4739–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, L.; Yakoub, D. Malignant granular cell tumor of the back: A case report and review of the literature. Case Rep. Med. 2014, 2014, 794648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, A.; Koplin, S.; Caracciollo, J.; Reed, D.; Webber, N.; Attia, S. Dramatic response to pazopanib in a patient with metastatic malignant granular cell tumor. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, S.; Hiramatsu, M.; Sugishita, M.; Gyawali, B.; Shibata, T.; Shimokata, T.; Urakawa, H.; Mitsuma, A.; Moritani, S.; Kubota, T.; et al. Pazopanib monotherapy in a patient with a malignant granular cell tumor originating from the right orbit: A case report. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 972–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Liu, S.; Conroy, J.; Wang, J.; Papanicolau-Sengos, A.; Glenn, S.T.; Murakami, M.; Liu, L.; Hu, Q.; Conroy, J.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of a malignant granular cell tumor with metabolic response to pazopanib. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2015, 1, a000380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katiyar, V.; Vohra, I.; Uprety, A.; Yin, W.; Gupta, S. Recurrent Unresectable Malignant Granular Cell Tumor With Response to Pazopanib. Cureus 2020, 12, e8287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Fox, E.; Drabick, J.; Pameijer, C. Isolated limb infusion as a treatment option for malignant granular cell tumour. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr-2018224618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Graaf, W.T.; Blay, J.-Y.; Chawla, S.P.; Kim, D.-W.; Bui-Nguyen, B.; Casali, P.G.; Schöffski, P.; Aglietta, M.; Staddon, A.P.; Beppu, Y.; et al. Pazopanib for metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma (PALETTE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2012, 379, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, D.; Pashaei, S.; Hunt, E.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Golitz, L. Pustulo-ovoid bodies of Milian in granular cell tumors. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2007, 34, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stemm, M.; Suster, D.; Wakely, P.; Suster, S. Typical and Atypical Granular Cell Tumors of Soft Tissue: A Clinicopathologic Study of 50 Patients. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 148, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekhi, B.; Jambhekar, N.A. Morphologic spectrum, immunohistochemical analysis, and clinical features of a series of granular cell tumors of soft tissues: A study from a tertiary referral cancer center. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2010, 4, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Jang, J.; Min, K.; Kim, M.S.; Park, H.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.H.; Song, H.J.; Kim, K.-J.; et al. Granular cell tumor of the gastrointestinal tract: Histologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 98 cases. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoolmeester, J.K.; Lastra, R.R. Granular cell tumors overexpress TFE3 without corollary gene rearrangement. Hum. Pathol. 2015, 46, 1242–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Flores, A.; Cassarino, D.; Riveiro-Falkenbach, E.; Rodriguez-Peralto, J.; Fernandez-Figueras, M.; Monteagudo, C. Cutaneous dermal non-neural granular cell tumor is a granular cell dermal root sheath fibroma. J. Cutaneus Pathol. 2017, 44, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corso, G.; Di Nubila, B.; Ciccia, A.; De Camilli, E.; Vicini, E.; Trentin, C.; Lissidini, G.; Cairns, L.; Veronesi, P.; Galimberti, V. Granular cell tumor of the breast: Molecular pathology and clinical management. Breast J. 2018, 24, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehner, C.; Moon, T.; Lyu, T.; Zhang, X.; Yang, K.; Chrisinger, J.; Griffin, A.; Wunder, J.; Dickson, B.; Hirbe, A. Mutations involving TGFB and MAPK may be associated with malignancy in granular cell tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2023, 62, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bavi, P.; Rosenberg, A.; Yamani, F.; Stickle, N.; Virtanen, C.; Winegarden, N.; Wang, J.; Roehrl, M.H. Whole Exome Sequencing of Benign and Malignant Granular Cell Tumors. Lab. Investig. 2015, 95, 14A–15A. [Google Scholar]
- Rogala, B.; Khan, Z.; Jackson-Boeters, L.; Darling, R. Investigation of the Molecular Profile of Granular Cell Tumours and Schwannomas of the Oral Cavity. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.; Alassiri, A.; Ng, T.; Mallinson, P.; Munk, P. Malignant granular cell tumor of the foot-multimodality imaging findings and literature review. Clin. Imaging 2015, 39, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imanishi, J.; Yazawa, Y.; Saito, T.; Shimizu, M.; Kawashima, H.; Ae, K.; Matsumine, A.; Torigoe, T.; Sugiura, H.; Joyama, S. Atypical and malignant granular cell tumors in Japan: A Japanese Musculoskeletal Oncology Group (JMOG) study. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 21, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, O.; Fleckenstein, G.; Gunawan, B.; Füzesi, L.; Emons, G. Recurrence and rapid metastasis formation of a granular cell tumor of the vulva. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2003, 106, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foteini, K.; Konstantinos, E.; Grigorios, K.; Athanasios, K.; Stella, K.; de Paz Anna, T.; Vassilios, T. A rare case of granular cell tumor of the urethra provoking urinary retention. Archiv. Nephrol. Urol. 2021, 4, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Broto, J.; Cruz, J.; Penel, N.; Le Cesne, A.; Hindi, N.; Luna, P.; Moura, D.S.; Bernabeu, D.; de Alava, E.; Lopez-Guerrero, J.A.; et al. Pazopanib for treatment of typical solitary fibrous tumours: A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Broto, J.; Stacchiotti, S.; Lopez-Pousa, A.; Redondo, A.; Bernabeu, D.; de Alava, E.; Casali, P.G.; Italiano, A.; Gutierrez, A.; Moura, D.S.; et al. Pazopanib for treatment of advanced malignant and dedifferentiated solitary fibrous tumour: A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stacchiotti, S.; Ferrari, S.; Redondo, A.; Hindi, N.; Palmerini, E.; Salgado, M.A.V.; Frezza, A.M.; Casali, P.G.; Gutierrez, A.; Lopez-Pousa, A.; et al. Pazopanib for treatment of advanced extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma: A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1252–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauro, S.; Trasatti, L.; Bria, E.; Gelibter, A.; Larosa, G.; Vecchione, A. Malignant bronchial Abrikossoff’s tumor and small cell lung cancer: A case report and review. Anticancer. Res. 2001, 21, 563–565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.; Shayahi, S. Pazopanib: Approval for soft-tissue sarcoma. J. Adv. Pract. Oncol. 2013, 4, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Akaike, K.; Kurisaki-Arakawa, A.; Toda-Ishii, M.; Mukaihara, K.; Suehara, Y.; Takagi, T.; Kaneko, K.; Yao, T. TERT promoter mutations are rare in bone and soft tissue sarcomas of Japanese patients. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 4, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zenker, M. Clinical manifestations of mutations in RAS and related intracellular signal transduction factors. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2011, 23, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamps, S.; Oyen, T.; Legius, E.; Vandenoord, J.; Stas, M. Multiple granular cell tumors in a child with Noonan syndrome. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. Off. J. Austrian Assoc. Pediatr. Surg. [Et Al] = Z. Fur Kinderchir. 2013, 23, 257–259. [Google Scholar]
- Ramaswamy, P.; Storm, C.; Filiano, J.; Dinulos, J. Multiple granular cell tumors in a child with Noonan syndrome. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2010, 27, 209–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagna, J.; Clerc, J.; Dupond, A.; Laresche, C. Multiple granular cell tumours in a patient with Noonan’s syndrome and juvenile myelomonocytic leukaemia. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 144, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.; Neldner, K.; Boyd, A.; Coates, P. Multiple cutaneous granular cell tumors and neurofibromatosis in childhood. A case report and review of the literature. Arch. Dermatol. 1990, 126, 1051–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, M.A.; Biggs, W.H., III; Treiber, D.K.; Atteridge, C.E.; Azimioara, M.D.; Benedetti, M.G.; Carter, T.A.; Ciceri, P.; Edeen, P.T.; Floyd, M.; et al. A small molecule-kinase interaction map for clinical kinase inhibitors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Govindharajulu, J.P.; Park, S.R.; Navas, T.; Ferry-Galow, K.V.; Kinders, R.J.; Lee, Y.H.; Bottaro, D.P.; Wright, J.J.; Hollingshead, M.G.; et al. Pazopanib to suppress MET signaling in patients with refractory advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Knick, V.B.; Rudolph, S.K.; Johnson, J.H.; Crosby, R.M.; Crouthamel, M.-C.; Hopper, T.M.; Miller, C.G.; Harrington, L.E.; Onori, J.A.; et al. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic correlation from mouse to human with pazopanib, a multikinase angiogenesis inhibitor with potent antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 2012–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Meyer, C.; Zinner, R.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Zahurak, M.L.; O’Connor, A.; Roszik, J.; Shaw, K.; Ludwig, J.A.; Kurzrock, R.; et al. Phase Ib/II Study of the Safety and Efficacy of Combination Therapy with Multikinase VEGF Inhibitor Pazopanib and MEK Inhibitor Trametinib In Advanced Soft Tissue Sarcoma. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4027–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, R.; Thomas, S.; Pawlowska, N.; Bartelink, I.; Grabowsky, J.; Jahan, T.; Cripps, A.; Harb, A.; Leng, J.; Reinert, A.; et al. Inhibiting Histone Deacetylase as a Means to Reverse Resistance to Angiogenesis Inhibitors: Phase I Study of Abexinostat Plus Pazopanib in Advanced Solid Tumor Malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahn, E.; Dunlavey, E.; Parsons, J. Multiple cutaneous granular cell tumors in a child with possible neurofibromatosis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1997, 36, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.L.; Zhang, Q.H.; Yang, Y.X.; Xiong, W.; Shen, S.R.; Li, X.L.; et al. The transcriptional regulation role of BRD7 by binding to acetylated histone through bromodomain. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 97, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kapur, P.; Rakheja, D.; Balani, J.; Roy, L.; Amirkhan, R.; Hoang, M. Phosphorylated histone H3, Ki-67, p21, fatty acid synthase, and cleaved caspase-3 expression in benign and atypical granular cell tumors. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2007, 131, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Broto, J.; Hindi, N.; Grignani, G.; Martinez-Trufero, J.; Redondo, A.; Valverde, C.; Stacchiotti, S.; Lopez-Pousa, A.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Gutierrez, A.; et al. Nivolumab and sunitinib combination in advanced soft tissue sarcomas: A multicenter, single-arm, phase Ib/II trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilky, B.; Trucco, M.; Subhawong, T.; Florou, V.; Park, W.; Kwon, D. Axitinib plus pembrolizumab in patients with advanced sarcomas including alveolar soft-part sarcoma: A single-centre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Ming, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Cho, W.C.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; et al. Granular cell tumors overexpress TFE3 without gene rearrangement: Evaluation of immunohistochemistry and break-apart FISH in 45 cases. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 6355–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, B.; McClain, C.; Gonzalez, R.; Coffin, C.; Cates, J. Alveolar soft part sarcoma and granular cell tumor: An immunohistochemical comparison study. Hum. Pathol. 2014, 45, 1039–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoluzzi, L.; Maki, R. Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment of Alveolar Soft-Part Sarcoma: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Primary Site | Metastases | Previous Systemic Therapies | Line | Duration of Treatment | Best Response (RECIST) | Cause of Withdrawal | Genes Involved |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| McGuire, 2004 [20] | Upper back | Lung, soft tissues | None | First | >5 months | SD | * | - |
| Conley, 2014 [21] | Peri-scapular | Lungs | Dasatinib | Second | >4 months | PR | * | SRC; MET; VEGFA |
| Tan, 2014 [37] | Foot | Bone | None | ** First | 4 months | - | PD | - |
| Morita, 2015 [22] | Orbicular | Lungs | Smoothened inhibitor, PI3K inhibitor | Third | 7 months | PR | Toxicity (fatigue) | ASXL1 |
| Wei, 2015 [23] | Pharyngeal | Bones, soft tissues | Gemcitabine plus docetaxel | Second | 6 months | PR | PD | BRD7; GFRA2 |
| Imanishi, 2016 (Case 1) [38] | Elbow | Lung, lymph nodes | None | First | - | - | PD | - |
| Imanishi 2016 (Case 2) [38] | C5 root | Lung, lymph nodes | Adriamycin plus Ifosfamide | Second | >12 months | SD | - | - |
| Katiyar, 2020 [24] | Lower lip | # None | Carboplatin plus paclitaxel and cetuximab | Second | 10 months | PR | & Death | - |
| Tian, 2018 [25] | Posterior calf | Lung, colon | None | First | ∆ 48 months | SD | * | - |
| Karasavvidou, 2023 [40] | Urethra | Lung, pelvis | None | First | 10 months | SD | * | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torrado, C.; Camaño, M.; Hindi, N.; Ortega, J.; Sevillano, A.R.; Civantos, G.; Moura, D.S.; Dimino, A.; Martín-Broto, J. Antiangiogenics in Malignant Granular Cell Tumors: Review of the Literature. Cancers 2023, 15, 5187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215187
Torrado C, Camaño M, Hindi N, Ortega J, Sevillano AR, Civantos G, Moura DS, Dimino A, Martín-Broto J. Antiangiogenics in Malignant Granular Cell Tumors: Review of the Literature. Cancers. 2023; 15(21):5187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215187
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorrado, Carlos, Melisa Camaño, Nadia Hindi, Justo Ortega, Alberto R. Sevillano, Gema Civantos, David S. Moura, Alessandra Dimino, and Javier Martín-Broto. 2023. "Antiangiogenics in Malignant Granular Cell Tumors: Review of the Literature" Cancers 15, no. 21: 5187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215187
APA StyleTorrado, C., Camaño, M., Hindi, N., Ortega, J., Sevillano, A. R., Civantos, G., Moura, D. S., Dimino, A., & Martín-Broto, J. (2023). Antiangiogenics in Malignant Granular Cell Tumors: Review of the Literature. Cancers, 15(21), 5187. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15215187







