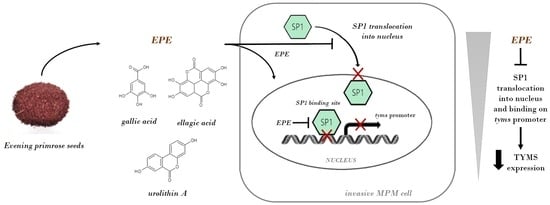
Evening Primrose Extract Modulates TYMS Expression via SP1 Transcription Factor in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extract Preparation and Compound Analysis
2.2. Bioinformatic Analysis of MPM Patient Samples
2.3. Cell Culture and Treatment Conditions
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. Confocal Microscopy
2.7. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
2.8. Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.9. Point Mutation Introduction
2.10. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and Re-ChIP Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
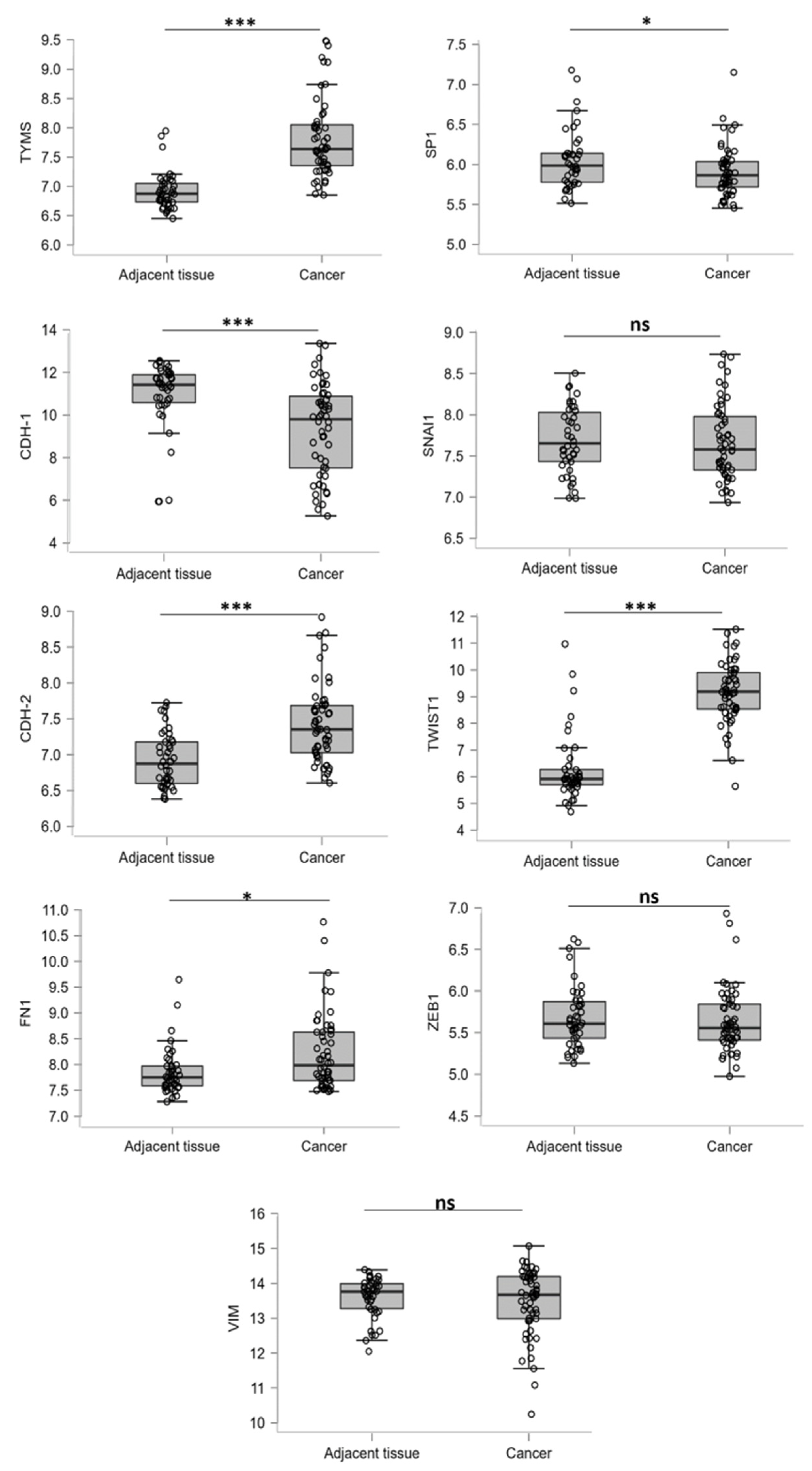
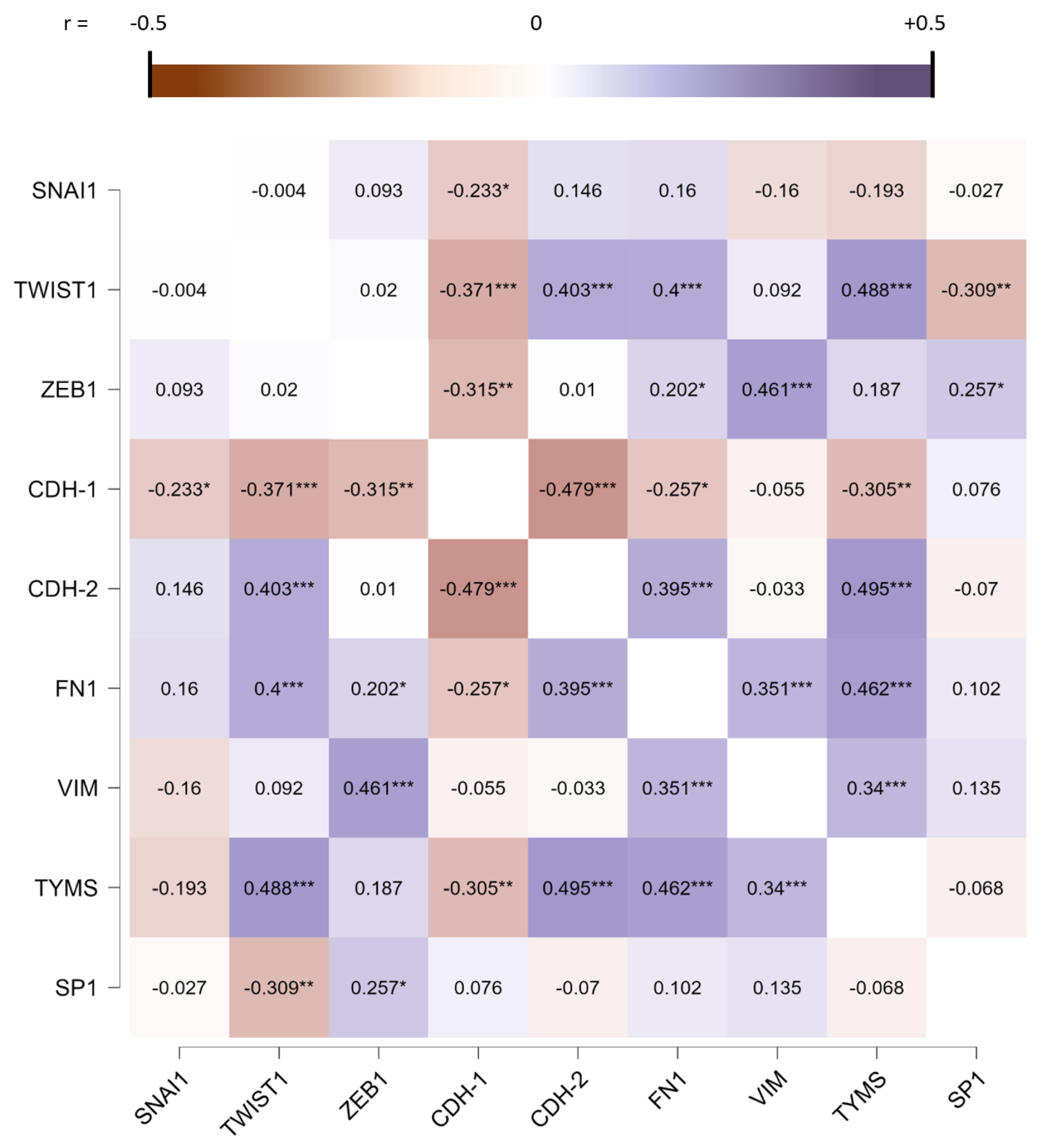
3.1. EMT Regulator Expression Is Modulated in MPM Patients
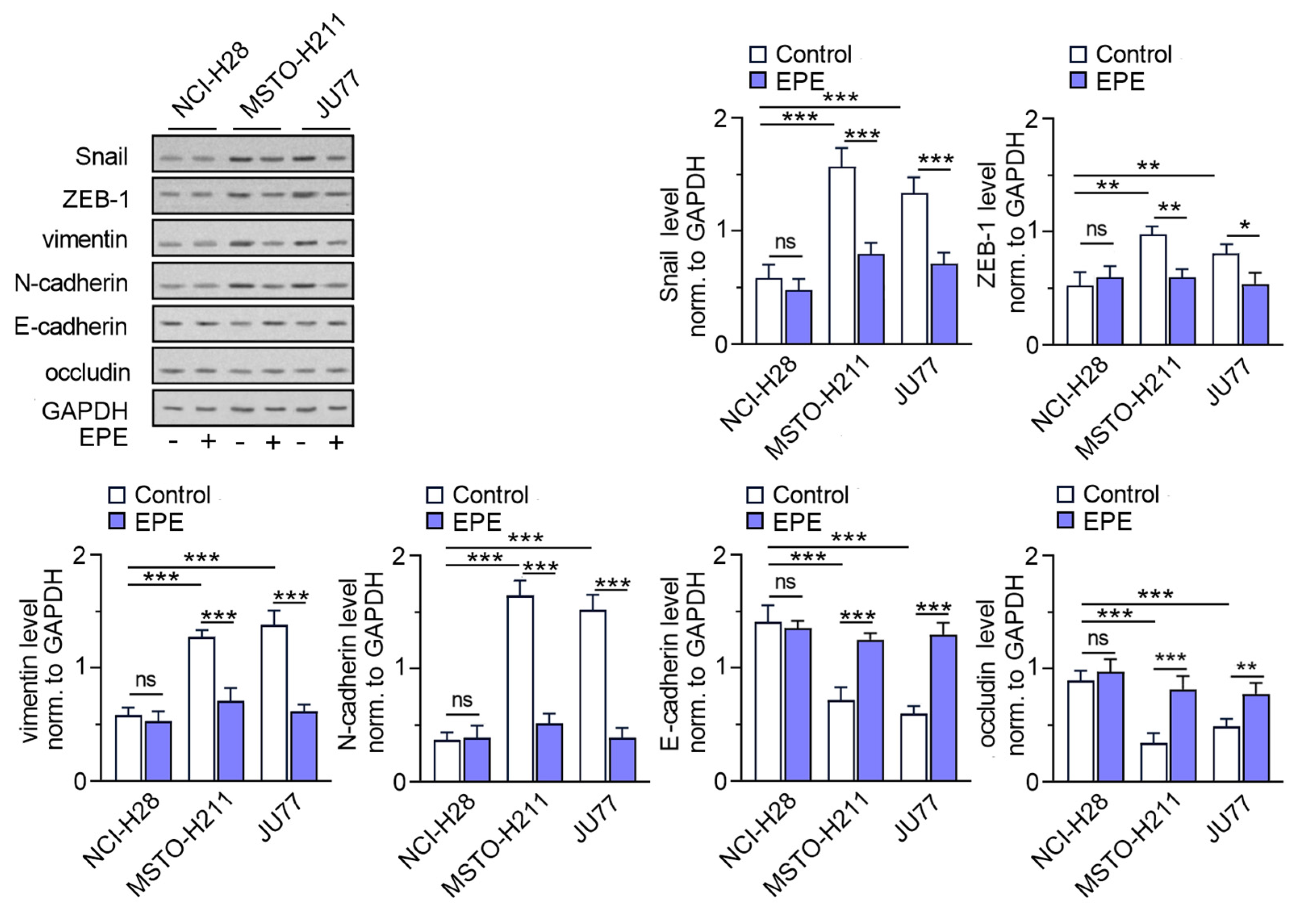
3.2. EPE Reverse Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in MPM Cell Lines
3.3. The TYMS Expression Profile in MPM Cells Is Dependent on Its Invasion Ability and Downregulated by EPE Treatment
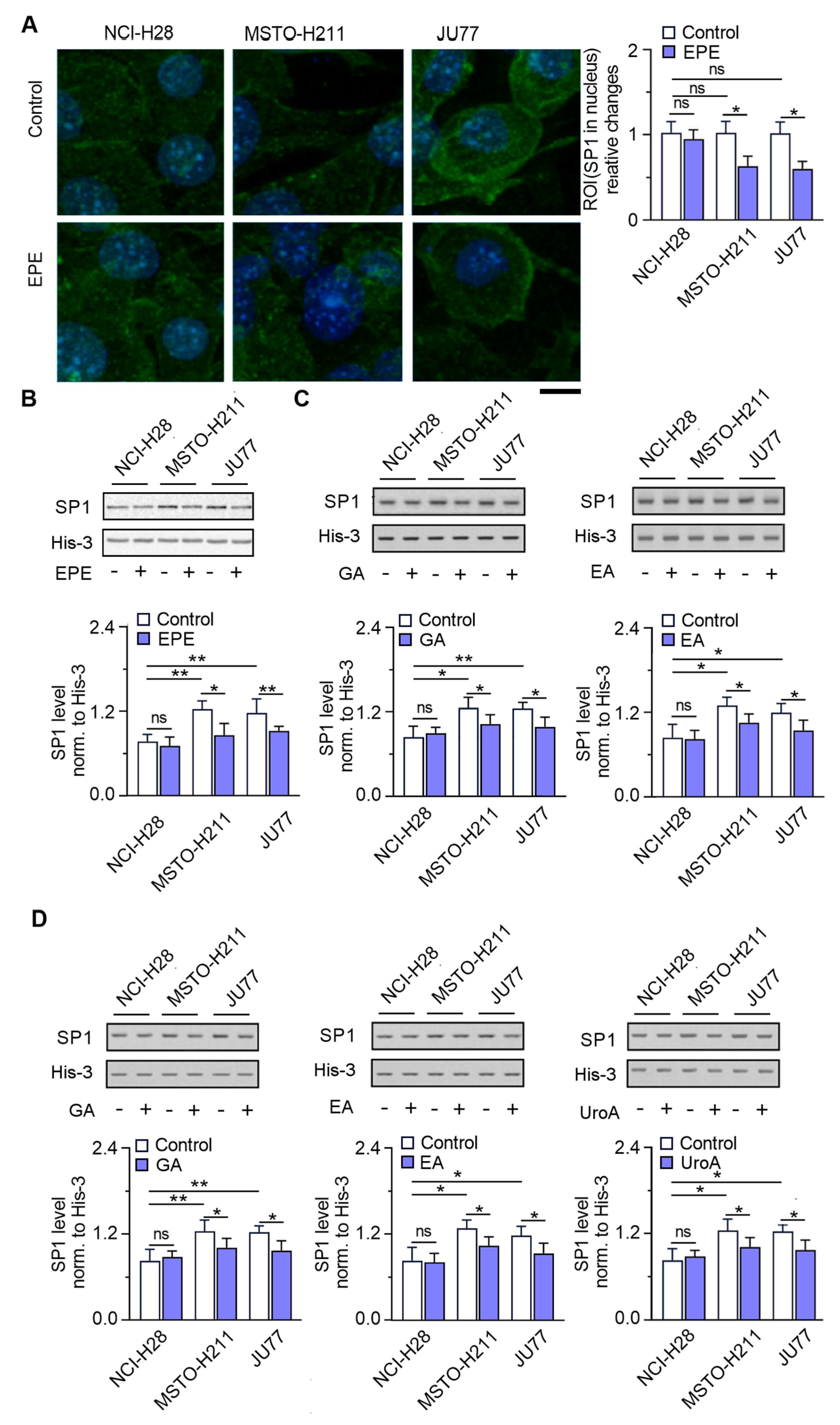
3.4. SP1 Localization in Nucleus Is Significantly Reduced in the EPE-Treated Cells
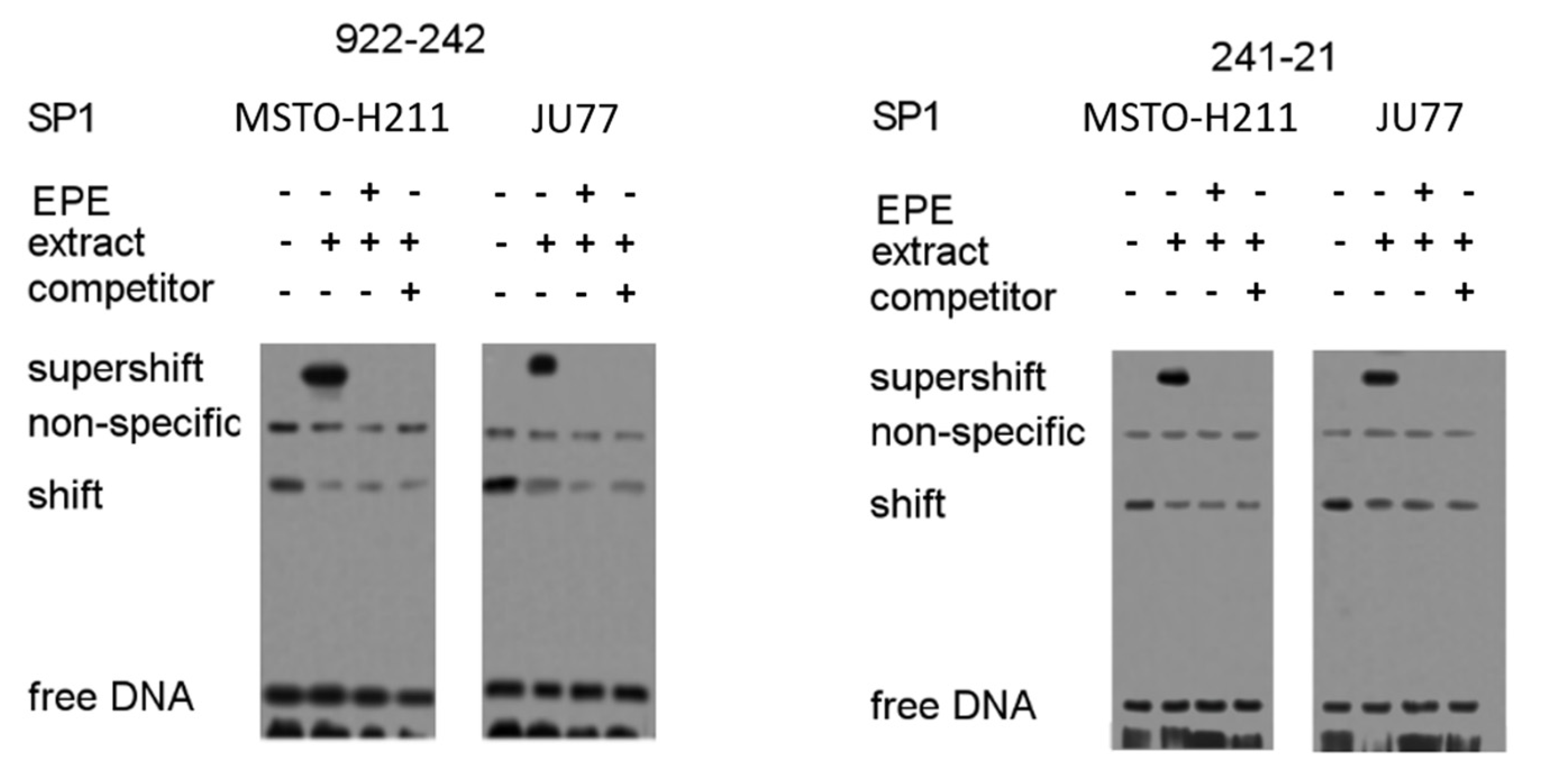
3.5. Identification of Regulatory SP1 Motifs in the Tyms Promoter Region
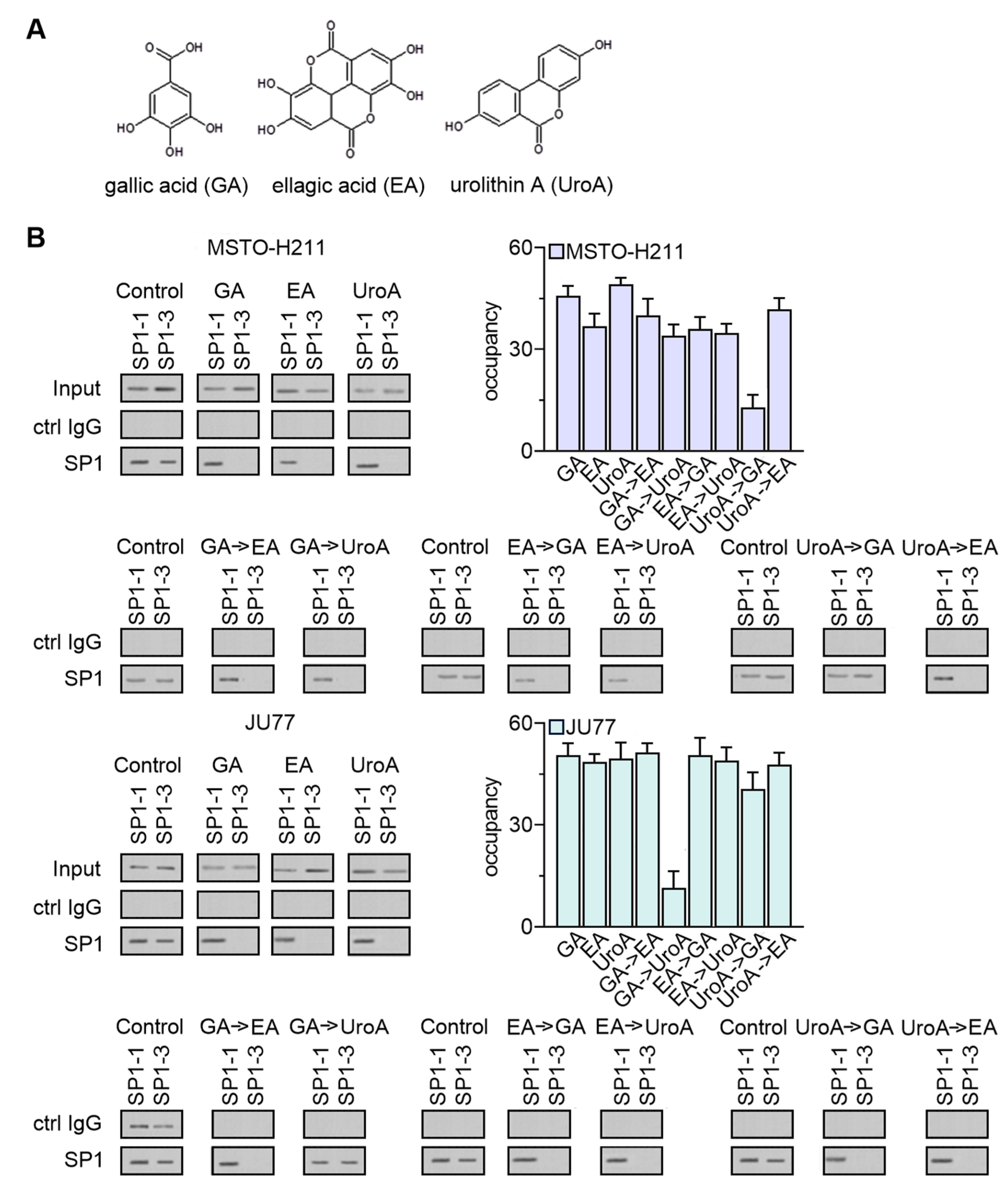
3.6. EPE Components Diminish TYMS Expression via SP1-Specific Motifs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjei, A.A. Pharmacology and mechanism of action of pemetrexed. Clin. Lung Cancer 2004, 5 (Suppl. 2), S51–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, A.L.; Drake, J.C.; Gress, R.E.; Schwartz, G.; Steinberg, S.M.; Allegra, C.J. 5-fluorouracil-mediated thymidylate synthase induction in malignant and nonmalignant human cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1998, 56, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciszewski, W.M.; Chmielewska-Kassassir, M.; Wozniak, L.A.; Sobierajska, K. Thymidylate Synthase Overexpression Drives the Invasive Phenotype in Colon Cancer Cells. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Tomita, M.; Soga, T.; Ochiai, A.; Makinoshima, H. Upregulation of Thymidylate Synthase Induces Pemetrexed Resistance in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 718675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, D.P.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, H.B. Natural Polyphenols for Prevention and Treatment of Cancer. Nutrients 2016, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewska-Kassassir, M.; Wozniak, L.A. Phytochemicals in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Treatment-Review on the Current Trends of Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantini, M.; Benvenuto, M.; Masuelli, L.; Frajese, G.V.; Tresoldi, I.; Modesti, A.; Bei, R. In vitro and in vivo antitumoral effects of combinations of polyphenols, or polyphenols and anticancer drugs: Perspectives on cancer treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9236–9282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciszewski, W.M.; Włodarczyk, J.; Chmielewska-Kassassir, M.; Fichna, J.; Wozniak, L.A.; Sobierajska, K. Evening primrose seed extract rich in polyphenols modulates the invasiveness of colon cancer cells by regulating the tyms expression. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 10994–11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amawi, H.; Ashby, C.R.; Samuel, T.; Peraman, R.; Tiwari, A.K. Polyphenolic Nutrients in Cancer Chemoprevention and Metastasis: Role of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal (EMT) Pathway. Nutrients 2017, 9, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-K.; Choi, E.-J.; Debnath, T. Role of phytochemicals in the inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3677–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorlach, S.; Wagner, W.; Podsedek, A.; Sosnowska, D.; Dastych, J.; Koziołkiewicz, M. Polyphenols from evening primrose (Oenothera paradoxa) defatted seeds induce apoptosis in human colon cancer Caco-2 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6985–6997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowska, U.; Owczarek, K.; Szewczyk, K.; Podsędek, A.; Koziołkiewicz, M.; Hrabec, E. Influence of polyphenol extract from evening primrose (Oenothera paradoxa) seeds on human prostate and breast cancer cell lines. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2014, 68, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewska-Kassassir, M.; Sobierajska, K.; Ciszewski, W.M.; Bukowiecka-Matusiak, M.; Szczesna, D.; Burzynska-Pedziwiatr, I.; Wiczkowski, W.; Wagner, W.; Wozniak, L.A. Polyphenol Extract from Evening Primrose (Oenothera paradoxa) Inhibits Invasion Properties of Human Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewandowska, U.; Szewczyk, K.; Owczarek, K.; Hrabec, Z.; Podsędek, A.; Sosnowska, D.; Hrabec, E. Procyanidins from evening primrose (Oenothera paradoxa) defatted seeds inhibit invasiveness of breast cancer cells and modulate the expression of selected genes involved in angiogenesis, metastasis, and apoptosis. Nutr. Cancer 2013, 65, 1219–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owczarek, K.; Hrabec, E.; Fichna, J.; Sosnowska, D.; Koziołkiewicz, M.; Szymański, J.; Lewandowska, U. Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB, cyclooxygenase-2, and metalloproteinase-9 expression by flavanols from evening primrose (Oenothera paradoxa) in human colon cancer SW-480 cells. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 37, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, N.; Takeishi, K. Identification of functional elements in the promoter region of the human gene for thymidylate synthase and nuclear factors that regulate the expression of the gene. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 18375–18381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Davie, J.R. The role of Sp1 and Sp3 in normal and cancer cell biology. Ann. Anat. 2010, 192, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlosarek, P.W.; Phillips, M.M.; Pavlyk, I.; Steele, J.; Shamash, J.; Spicer, J.; Kumar, S.; Pacey, S.; Feng, X.; Johnston, A.; et al. Expansion Phase 1 Study of Pegargiminase Plus Pemetrexed and Cisplatin in Patients With Argininosuccinate Synthetase 1–Deficient Mesothelioma: Safety, Efficacy, and Resistance Mechanisms. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2020, 1, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryczka, J.; Sochacka, E.; Papiewska-Pająk, I.; Boncela, J. Implications of ABCC4-Mediated cAMP Eflux for CRC Migration. Cancers 2020, 12, 3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobierajska, K.; Wawro, M.E.; Ciszewski, W.M.; Niewiarowska, J. Transforming Growth Factor-β Receptor Internalization via Caveolae Is Regulated by Tubulin-β2 and Tubulin-β3 during Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 2531–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobierajska, K.; Ciszewski, W.M.; Macierzynska-Piotrowska, E.; Klopocka, W.; Przygodzka, P.; Karakula, M.; Pestka, K.; Wawro, M.E.; Niewiarowska, J. The New Model of Snail Expression Regulation: The Role of MRTFs in Fast and Slow Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisberg, J.V. Quantitative sequential chromatin immunoprecipitation, a method for analyzing co-occupancy of proteins at genomic regions in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beasley, M.B.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Dacic, S. Pleural mesothelioma classification update. Virchows Arch. 2021, 478, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwanami, T.; Uramoto, H.; Nakagawa, M.; Shimokawa, H.; Yamada, S.; Kohno, K.; Tanaka, F. Clinical significance of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated markers in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncology 2014, 86, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Chew, S.H.; Nagai, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Ohara, H.; Jiang, L.; Akatsuka, S.; Takahashi, T.; Toyokuni, S. Overexpression of miR-199/214 is a distinctive feature of iron-induced and asbestos-induced sarcomatoid mesothelioma in rats. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2016–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merikallio, H.; Pääkkö, P.; Salmenkivi, K.; Kinnula, V.; Harju, T.; Soini, Y. Expression of snail, twist, and Zeb1 in malignant mesothelioma. Apmis 2013, 121, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espín, J.C.; Larrosa, M.; García-Conesa, M.T.; Tomás-Barberán, F. Biological significance of urolithins, the gut microbial ellagic Acid-derived metabolites: The evidence so far. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 270418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cai, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, L.; Gong, Y.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Huang, W.; Zhou, H. Protective Effect of Spironolactone on Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in HUVECs via Notch Pathway. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 36, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, A.; Gollavilli, P.N.; Schwab, A.; Vazakidou, M.E.; Ersan, P.G.; Ramakrishnan, M.; Pluim, D.; Coggins, S.A.; Saatci, O.; Annaratone, L.; et al. Thymidylate synthase maintains the de-differentiated state of triple negative breast cancers. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 2223–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Fujita, Y.; Hanada, T.; Mimata, H.; Nomura, Y. Clinical significance of thymidylate synthase expression in bladder cancer. Int. J. Urol. 2002, 9, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamoshida, S.; Matsuoka, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Maeda, K.; Shimomura, R.; Inada, K.; Tsutsumi, Y. Immunohistochemical evaluation of thymidylate synthase (TS) and p16INK4a in advanced colorectal cancer: Implication of TS expression in 5-FU-based adjuvant chemotherapy. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 34, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucali, P.A.; Giovannetti, E.; Destro, A.; Mencoboni, M.; Ceresoli, G.L.; Gianoncelli, L.; Lorenzi, E.; De Vincenzo, F.; Simonelli, M.; Perrino, M.; et al. Thymidylate synthase and excision repair cross-complementing group-1 as predictors of responsiveness in mesothelioma patients treated with pemetrexed/carboplatin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2581–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Tian, B.; Zhang, M.; Gao, X.; Jie, L.; Liu, P.; Li, J. Diagnostic and prognostic value of thymidylate synthase expression in breast cancer. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 48, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Lv, L.; Dong, D. Identification and Validation of tyms as a Potential Biomarker for Risk of Metastasis Development in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 762821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Li, B.; Wang, F.; Ma, C.; Hao, T. Expression of ERCC1 and tyms in colorectal cancer patients and the predictive value of chemotherapy efficacy. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Jiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Ji, B.; Jia, B.; Liu, B. tyms presents a novel biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer. Medicine 2019, 98, e18487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhuo, C.; Cui, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, P.; Wang, B. tyms serves as a prognostic indicator to predict the lymph node metastasis in Chinese patients with colorectal cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 1478–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, L.; Papotti, M.; Ceppi, P.; Billè, A.; Bacillo, E.; Molinaro, L.; Ruffini, E.; Scagliotti, G.; Selvaggi, G. Thymidylate Synthase But Not Excision Repair Cross-Complementation Group 1 Tumor Expression Predicts Outcome in Patients With Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Treated With Pemetrexed-Based Chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1534–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairinger, F.; Vollbrecht, C.; Halbwedl, I.; Hatz, M.; Stacher, E.; Gülly, C.; Quehenberger, F.; Stephan-Falkenau, S.; Kollmeier, J.; Roth, A.; et al. Reduced folate carrier and folylpolyglutamate synthetase, but not thymidylate synthase predict survival in pemetrexed-treated patients suffering from malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2013, 8, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoph, D.C.; Asuncion, B.R.; Mascaux, C.; Tran, C.; Lu, X.; Wynes, M.W.; Gauler, T.C.; Wohlschlaeger, J.; Theegarten, D.; Neumann, V.; et al. Folylpoly-glutamate synthetase expression is associated with tumor response and outcome from pemetrexed-based chemotherapy in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Shi, C.; Yu, J.; Xu, Y. FOXM1-induced tyms upregulation promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, M.A.; Gollavilli, P.N.; Ramesh, V.; Parma, B.; Schwab, A.; Vazakidou, M.E.; Natesan, R.; Saatci, O.; Rapa, I.; Bironzo, P.; et al. Thymidylate synthase drives the phenotypes of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Rahman, M.A.; Chen, Z.G.; Shin, D.M. Multiple biological functions of Twist1 in various cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 20380–20393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraokar, M.B.; Nunez, M.I.; Diao, L.; Chow, C.W.; Kim, D.; Behrens, C.; Lin, H.; Lee, S.; Raso, G.; Moran, C.; et al. Expression profiling stratifies mesothelioma tumors and signifies deregulation of spindle checkpoint pathway and microtubule network with therapeutic implications. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, S.; Pradhan, B.; Nayak, R.; Behera, C.; Das, S.; Patra, S.K.; Efferth, T.; Jena, M.; Bhutia, S.K. Dietary polyphenols in chemoprevention and synergistic effect in cancer: Clinical evidences and molecular mechanisms of action. Phytomedicine 2021, 90, 153554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahfoufi, N.; Alsadi, N.; Jambi, M.; Matar, C. The Immunomodulatory and Anti-Inflammatory Role of Polyphenols. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, E.H.; Lee, Y.; Zhao, X.F.; Park, Y.K.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, S. ZEB2-Sp1 cooperation induces invasion by upregulating cadherin-11 and integrin α5 expression. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierstra, I. Sp1: Emerging roles--beyond constitutive activation of TATA-less housekeeping genes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 372, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, H.S.; Dong, S.M.; Park, J.S.; Yoon, D.S. Specific protein 1(SP1) regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via lysyl oxidase-like 2(LOXL2) in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Yoon, D.S. Modulation of specificity protein 1 (SP1) is a novel therapeutic strategy for pancreatic cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, vi40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-J.; Baek, H.-S.; Ye, D.-J.; Shin, S.; Kim, D.; Chun, Y.-J. CYP1B1 Enhances Cell Proliferation and Metastasis through Induction of EMT and Activation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling via Sp1 Upregulation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, K.; He, M.; Fan, G.; Lu, H. Overexpression of Glypican 5 (GPC5) Inhibits Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion via Suppressing Sp1-Mediated EMT and Activation of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2018, 26, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.-S.; Lee, E.-O. Sp1 Plays a Key Role in Vasculogenic Mimicry of Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suraokar, M.B.; Lin, H.; He, D.; Llansa, N.; Mendoza, G.; Woods, D.; Prudkin, L.; Lee, J.J.; Wistuba, I.I.; Tsao, A.S. High expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) markers in malignant mesothelioma and possible therapeutic intervention using an N-cadherin antagonist. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 8067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.L.; Zhuang, L.; Rath, E.M.; Yu, T.; Johnson, B.; Sarun, K.H.; Wang, Y.; Kao, S.; Linton, A.; Clarke, C.J.; et al. The Role of E-Cadherin and microRNA on FAK Inhibitor Response in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma (MPM). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition—Activating transcription factors—Multifunctional regulators in cancer. World J. Stem Cells 2013, 5, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, F.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, S. The number of polyploid giant cancer cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related proteins are associated with invasion and metastasis in human breast cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakrim, S.; El Omari, N.; El Hachlafi, N.; Bakri, Y.; Lee, L.-H.; Bouyahya, A. Dietary Phenolic Compounds as Anticancer Natural Drugs: Recent Update on Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Trials. Foods 2022, 11, 3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Atay, S.M.; Shukla, V.; Hong, Y.; Upham, T.; Ripley, R.T.; Hong, J.A.; Zhang, M.; Reardon, E.; Fetsch, P.; et al. Mithramycin Depletes Specificity Protein 1 and Activates p53 to Mediate Senescence and Apoptosis of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Kitamura, H.; Uwatoko, C.; Azumano, M.; Itoh, K.; Kuwahara, J. Interaction of Sp1 zinc finger with transport factor in the nuclear localization of transcription factor Sp1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 403, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizume, S.; Miyagi, Y. Diverse Mechanisms of Sp1-Dependent Transcriptional Regulation Potentially Involved in the Adaptive Response of Cancer Cells to Oxygen-Deficient Conditions. Cancers 2015, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Duan, R.; Chen, I.; Samudio, I.; Safe, S. Transcriptional Activation of Thymidylate Synthase by 17β-Estradiol in MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 2439–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudge, T.L.; Johnson, L.F. Synergistic Activation of the TATA-less Mouse Thymidylate Synthase Promoter by the Ets Transcription Factor GABP and Sp1. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 274, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cykowiak, M.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Kleszcz, R.; Kucińska, M.; Szaefer, H.; Piotrowska-Kempisty, H.; Plewiński, A.; Murias, M.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Comparison of the Impact of Xanthohumol and Phenethyl Isothiocyanate and Their Combination on Nrf2 and NF-κB Pathways in HepG2 Cells In Vitro and Tumor Burden In Vivo. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cykowiak, M.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Combinations of Phytochemicals More Efficiently than Single Components Activate Nrf2 and Induce the Expression of Antioxidant Enzymes in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Nutr. Cancer 2022, 74, 996–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Gene | Primers 5′-3′ | Amplicon Length | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | ||
| TYMS | CGCTACAGCCTGAGAGATGAA | CACTCCCTTGGAAGACAGCTC | 129 bp |
| SP1 | AGTGTATGGCAAGACCTCTCAC | TCTTCTCACCTGTGTGTGTACG | 149 bp |
| GAPDH * | GGTGGTCTCCTCTGACTTCAACA | GTTGCTGTAGCCAAATTCGTTGT | 127 bp |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chmielewska-Kassassir, M.; Sobierajska, K.; Ciszewski, W.M.; Kryczka, J.; Zieleniak, A.; Wozniak, L.A. Evening Primrose Extract Modulates TYMS Expression via SP1 Transcription Factor in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers 2023, 15, 5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15205003
Chmielewska-Kassassir M, Sobierajska K, Ciszewski WM, Kryczka J, Zieleniak A, Wozniak LA. Evening Primrose Extract Modulates TYMS Expression via SP1 Transcription Factor in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers. 2023; 15(20):5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15205003
Chicago/Turabian StyleChmielewska-Kassassir, Małgorzata, Katarzyna Sobierajska, Wojciech M. Ciszewski, Jakub Kryczka, Andrzej Zieleniak, and Lucyna A. Wozniak. 2023. "Evening Primrose Extract Modulates TYMS Expression via SP1 Transcription Factor in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma" Cancers 15, no. 20: 5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15205003
APA StyleChmielewska-Kassassir, M., Sobierajska, K., Ciszewski, W. M., Kryczka, J., Zieleniak, A., & Wozniak, L. A. (2023). Evening Primrose Extract Modulates TYMS Expression via SP1 Transcription Factor in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers, 15(20), 5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15205003