Inducing Mitotic Catastrophe as a Therapeutic Approach to Improve Outcomes in Ewing Sarcoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DepMap Portal Gene Expression Analysis
2.2. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.3. Drugs
2.4. Cell Viability and Drug Synergy Assay
2.5. Colony Formation Assay
2.6. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.7. Capillary Western Blot (Wes) Analysis
2.8. Tumor Xenograft and Drug Treatment Studies
2.9. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. In Silico Bioinformatics Screen Identifies Mitotic Proteins Essential for EWS Growth
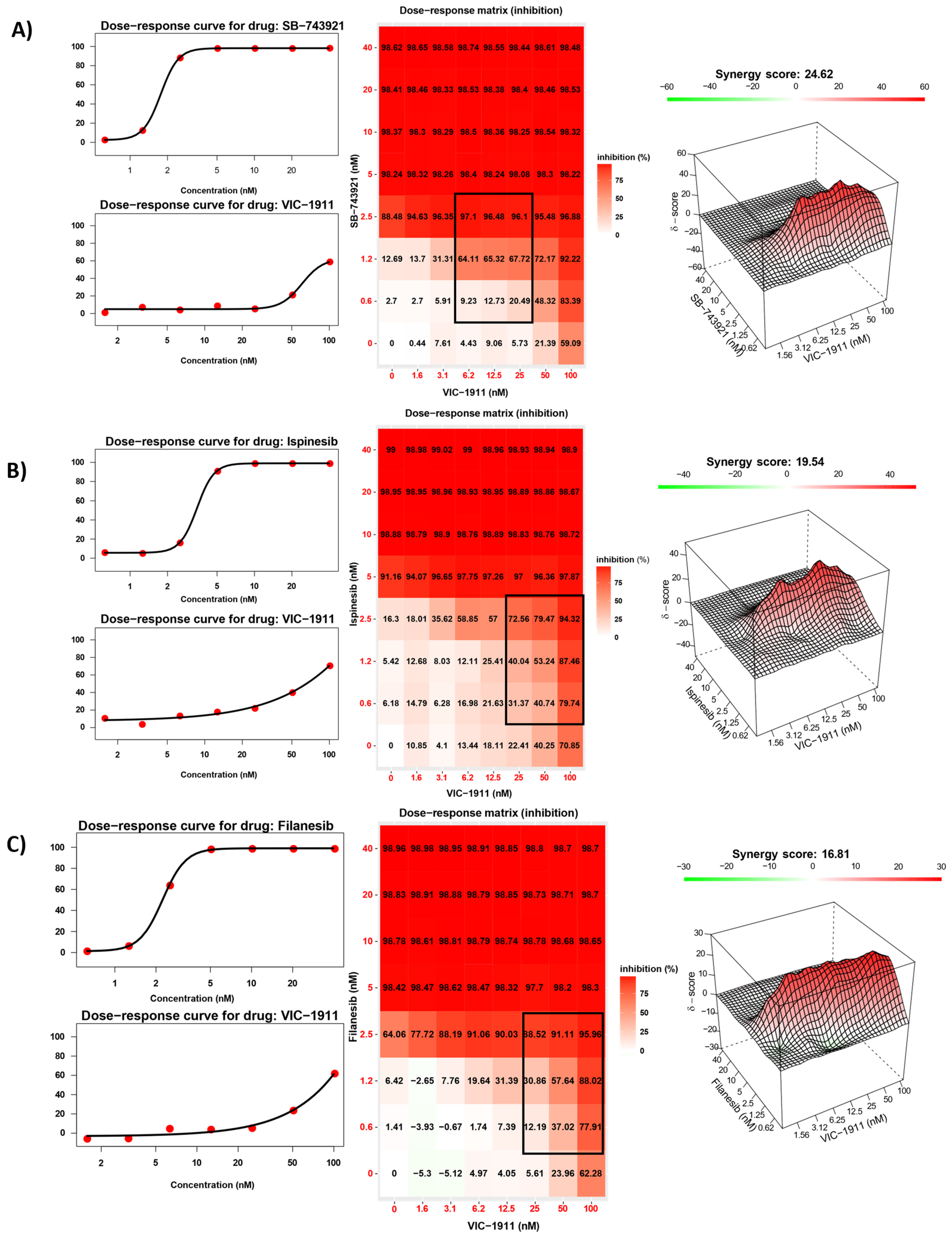
3.2. Synergistic Inhibition of EWS Growth In Vitro by KIF11 and AURKA Inhibitors
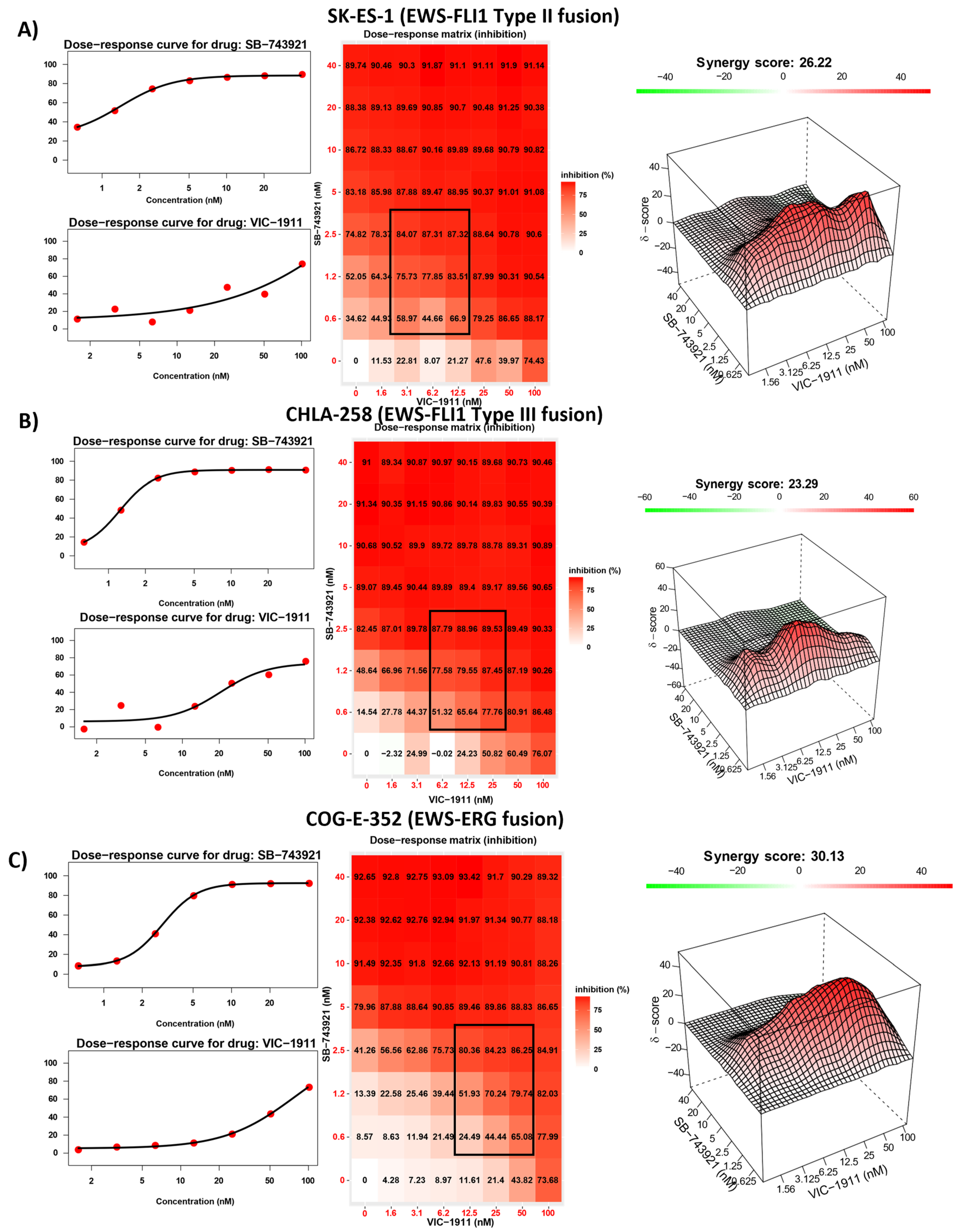
3.3. Drug Synergy Is Observed in Different EWS Fusion Type Cell Lines
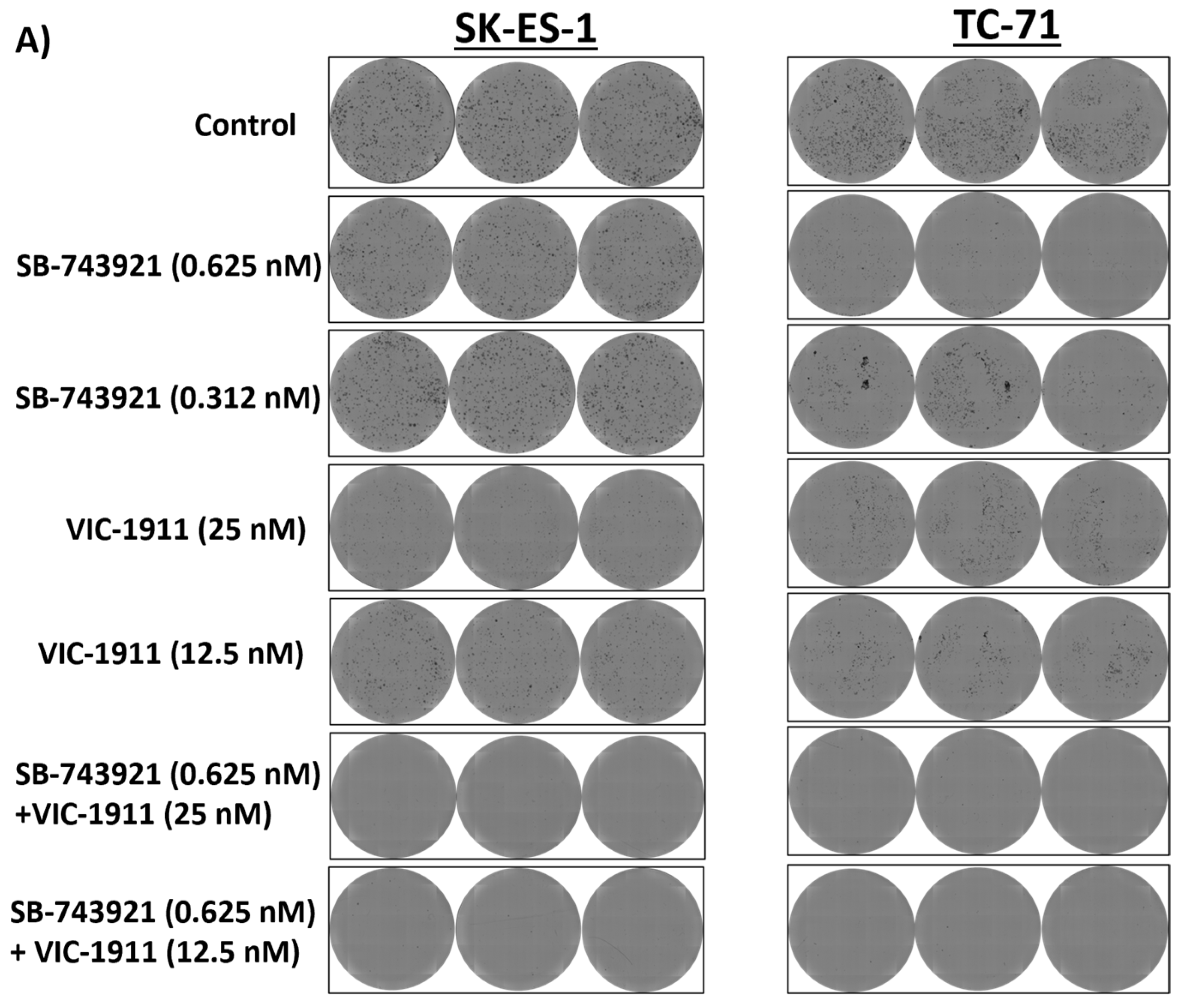
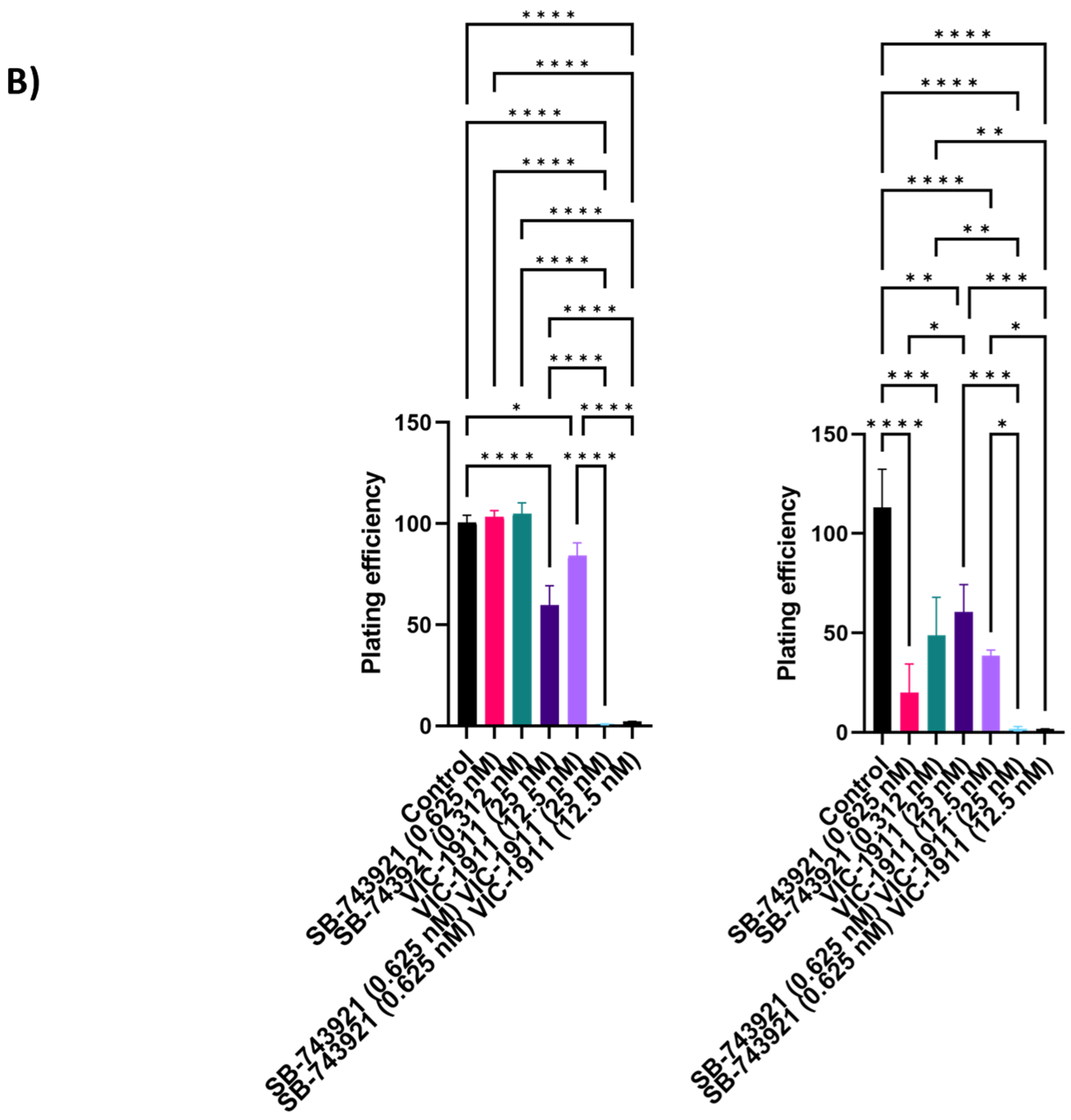
3.4. Combination Treatment with SB-743921 and VIC-1911 Reduces Colony Formation In Vitro
3.5. Cell Cycle Analysis Indicates Combination Treatment Arrests the Cells in G2/M Phase
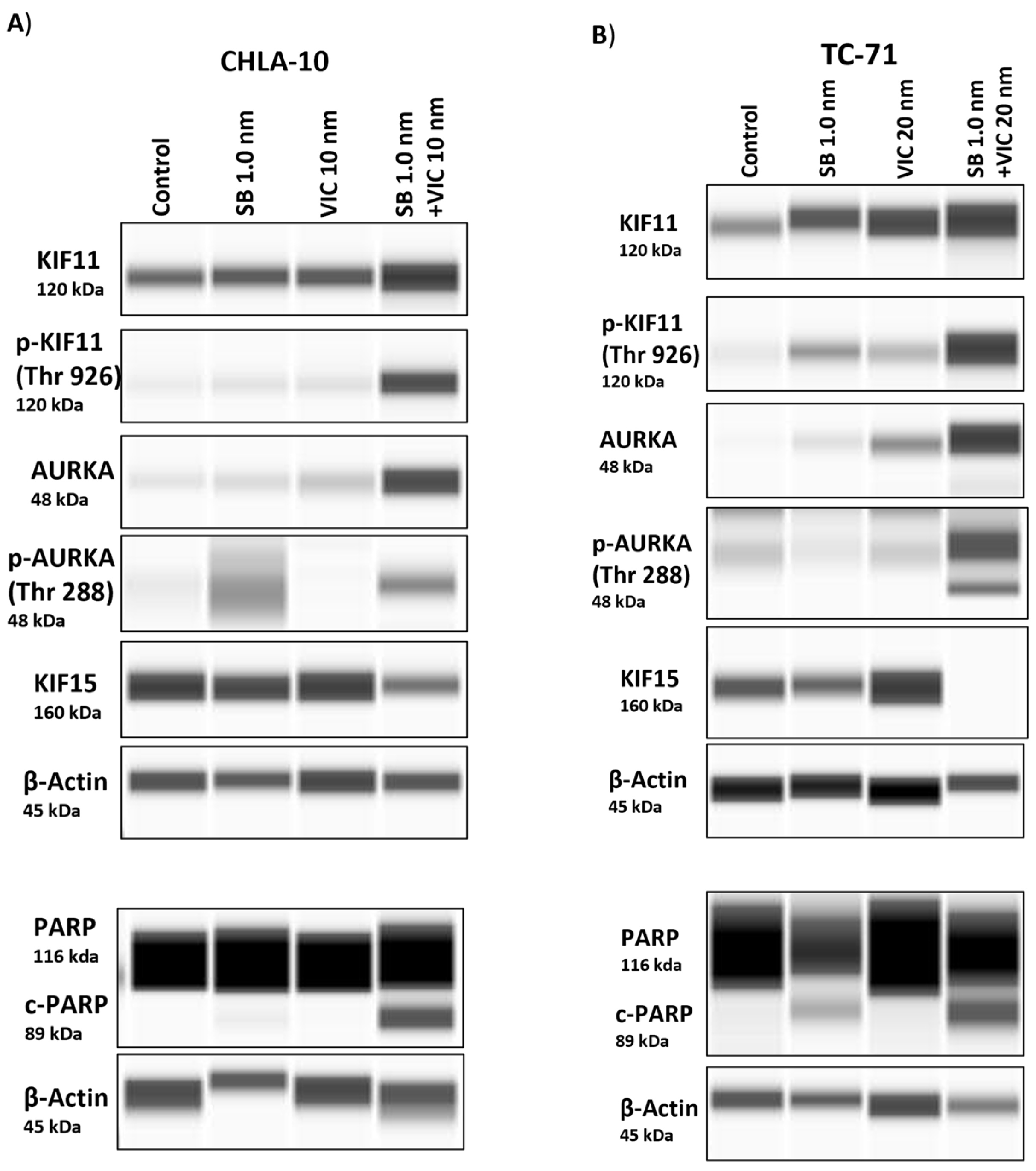
3.6. Protein Expression Post-Combination Treatment Indicates an Increase in Expression of KIF11 and AURKA
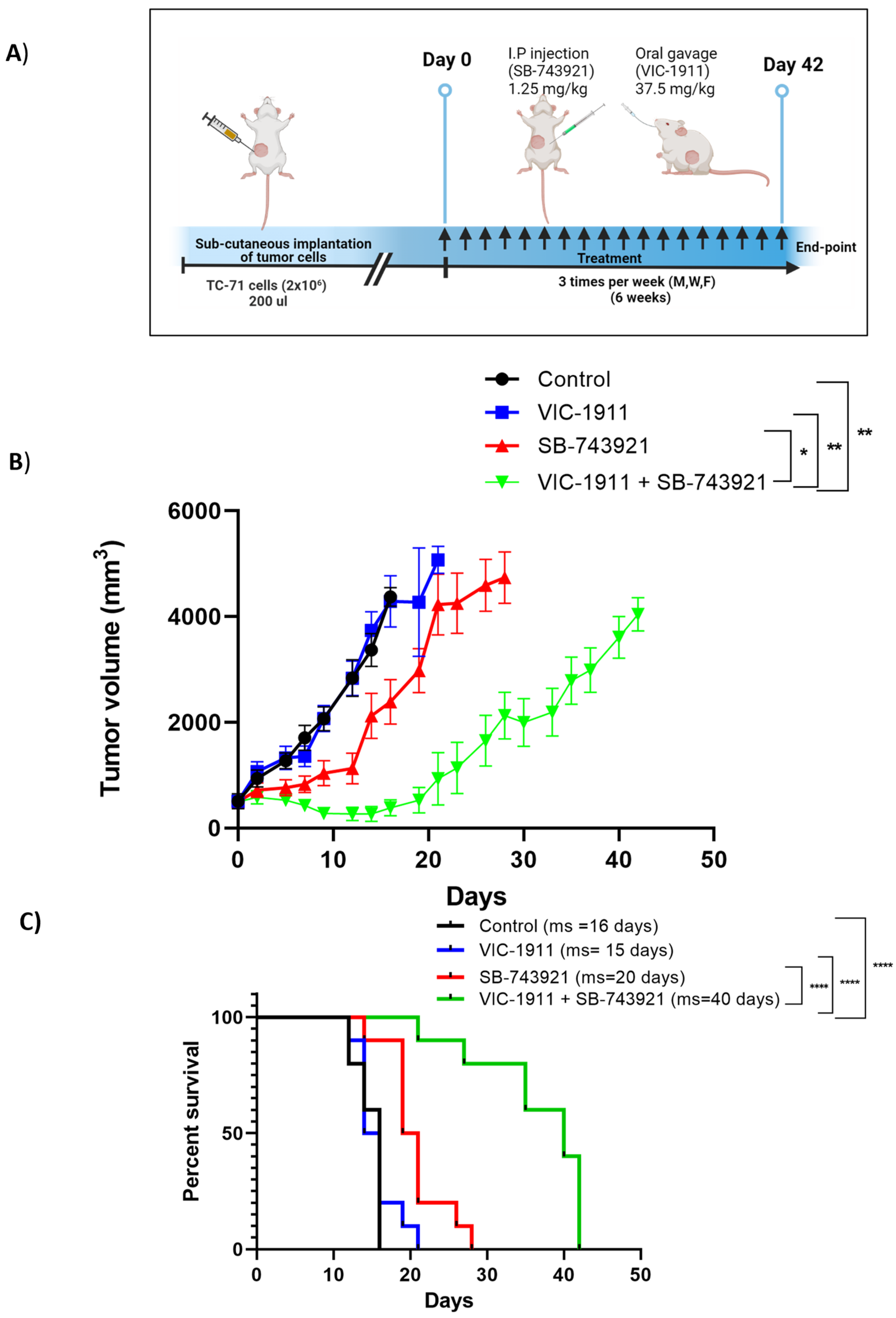
3.7. Combination Treatment Synergistically Leads to Tumor Regression in EWS Xenograft Mouse Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esiashvili, N.; Goodman, M.; Marcus, R.B., Jr. Changes in incidence and survival of Ewing sarcoma patients over the past 3 decades: Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results data. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2008, 30, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamuth, N.J.; Womer, R.B. Ewing’s sarcoma. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessetto, Z.Y.; Chen, B.; Alturkmani, H.; Hyter, S.; Flynn, C.A.; Baltezor, M.; Ma, Y.; Rosenthal, H.G.; Neville, K.A.; Weir, S.J.; et al. In silico and in vitro drug screening identifies new therapeutic approaches for Ewing sarcoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 4079–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Baltezor, M.; Rajewski, L.; Crow, J.; Samuel, G.; Staggs, V.S.; Chastain, K.M.; Toretsky, J.A.; Weir, S.J.; Godwin, A.K. Targeted inhibition of histone deacetylase leads to suppression of Ewing sarcoma tumor growth through an unappreciated EWS-FLI1/HDAC3/HSP90 signaling axis. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, B.J.; Balchand, S.K.; Wadsworth, P. Regulation of Kif15 localization and motility by the C-terminus of TPX2 and microtubule dynamics. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouwers, N.; Mallol Martinez, N.; Vernos, I. Role of Kif15 and its novel mitotic partner KBP in K-fiber dynamics and chromosome alignment. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raaijmakers, J.A.; van Heesbeen, R.G.; Meaders, J.L.; Geers, E.F.; Fernandez-Garcia, B.; Medema, R.H.; Tanenbaum, M.E. Nuclear envelope-associated dynein drives prophase centrosome separation and enables Eg5-independent bipolar spindle formation. Embo J. 2012, 31, 4179–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanneste, D.; Takagi, M.; Imamoto, N.; Vernos, I. The role of Hklp2 in the stabilization and maintenance of spindle bipolarity. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 1712–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanenbaum, M.E.; Macurek, L.; Janssen, A.; Geers, E.F.; Alvarez-Fernandez, M.; Medema, R.H. Kif15 cooperates with eg5 to promote bipolar spindle assembly. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sethi, G.; Pathak, H.B.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Einarson, M.B.; Vathipadiekal, V.; Gunewardena, S.; Birrer, M.J.; Godwin, A.K. An RNA interference lethality screen of the human druggable genome to identify molecular vulnerabilities in epithelial ovarian cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.; Gao, K.; Chu, L.; Zhang, R.; Yang, J.; Zheng, J. Aurora kinases: Novel therapy targets in cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23937–23954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.; Huang, C.; Liu, K.; Li, X.; Dong, Z. Targeting AURKA in Cancer: Molecular mechanisms and opportunities for Cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, P.K.; Yang, E.J.; Shi, C.; Ren, G.; Tao, S.; Shim, J.S. Aurora kinase A, a synthetic lethal target for precision cancer medicine. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 835–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Heesbeen, R.G.H.P.; Raaijmakers, J.A.; Tanenbaum, M.E.; Halim, V.A.; Lelieveld, D.; Lieftink, C.; Heck, A.J.R.; Egan, D.A.; Medema, R.H. Aurora A, MCAK, and Kif18b promote Eg5-independent spindle formation. Chromosoma 2017, 126, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.T.; Erdal, S.; Huang, S.; Poon, R.Y. Synergism between inhibitors of Aurora A and KIF11 overcomes KIF15-dependent drug resistance. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 1404–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sootome, H.; Miura, A.; Masuko, N.; Suzuki, T.; Uto, Y.; Hirai, H. Aurora A Inhibitor TAS-119 Enhances Antitumor Efficacy of Taxanes In Vitro and In Vivo: Preclinical Studies as Guidance for Clinical Development and Trial Design. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, A.; Sootome, H.; Fujita, N.; Suzuki, T.; Fukushima, H.; Mizuarai, S.; Masuko, N.; Ito, K.; Hashimoto, A.; Uto, Y.; et al. TAS-119, a novel selective Aurora A and TRK inhibitor, exhibits antitumor efficacy in preclinical models with deregulated activation of the Myc, β-Catenin, and TRK pathways. Investig. New Drugs 2021, 39, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbrecht, D.G.J.; Lopez, J.; Calvo, E.; He, X.; Hiroshi, H.; Soni, N.; Cook, N.; Dowlati, A.; Fasolo, A.; Moreno, V.; et al. A first-in-human phase 1 and pharmacological study of TAS-119, a novel selective Aurora A kinase inhibitor in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, O.; Kozielski, F. Kinesins and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carol, H.; Lock, R.; Houghton, P.J.; Morton, C.L.; Kolb, E.A.; Gorlick, R.; Reynolds, C.P.; Maris, J.M.; Keir, S.T.; Billups, C.A.; et al. Initial testing (stage 1) of the kinesin spindle protein inhibitor ispinesib by the pediatric preclinical testing program. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2009, 53, 1255–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lad, L.; Luo, L.; Carson, J.D.; Wood, K.W.; Hartman, J.J.; Copeland, R.A.; Sakowicz, R. Mechanism of inhibition of human KSP by ispinesib. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 3576–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souid, A.K.; Dubowy, R.L.; Ingle, A.M.; Conlan, M.G.; Sun, J.; Blaney, S.M.; Adamson, P.C. A pediatric phase I trial and pharmacokinetic study of ispinesib: A Children’s Oncology Group phase I consortium study. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2010, 55, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Saez, I.; Skoufias, D.A. Eg5 targeting agents: From new anti-mitotic based inhibitor discovery to cancer therapy and resistance. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 184, 114364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.W.; Bélanger, K.; Rao, S.C.; Petrella, T.M.; Tozer, R.G.; Wood, L.; Savage, K.J.; Eisenhauer, E.A.; Synold, T.W.; Wainman, N.; et al. A phase II study of ispinesib (SB-715992) in patients with metastatic or recurrent malignant melanoma: A National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group trial. Investig. New Drugs 2008, 26, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holen, K.D.; Belani, C.P.; Wilding, G.; Ramalingam, S.; Volkman, J.L.; Ramanathan, R.K.; Vasist, L.S.; Bowen, C.J.; Hodge, J.P.; Dar, M.M.; et al. A first in human study of SB-743921, a kinesin spindle protein inhibitor, to determine pharmacokinetics, biologic effects and establish a recommended phase II dose. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xiao, F.; Yu, Y.; Wang, H.; Fang, M.; Yang, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, L.; Sheng, Y. KSP inhibitor SB743921 inhibits growth and induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells by regulating p53, Bcl-2, and DTL. Anticancer. Drugs 2016, 27, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchook, G.S.; Bastida, C.C.; Kurzrock, R. Aurora Kinase Inhibitors in Oncology Clinical Trials: Current State of the Progress. Semin. Oncol. 2015, 42, 832–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahin, R.; Aljamal, S. Kinesin spindle protein inhibitors in cancer: From high throughput screening to novel therapeutic strategies. Future Sci. OA 2022, 8, Fso778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandi, M.; Huang, F.W.; Jané-Valbuena, J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Lo, C.C.; McDonald, E.R.; Barretina, J.; Gelfand, E.T.; Bielski, C.M.; Li, H.; et al. Next-generation characterization of the Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. Nature 2019, 569, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, G.; Crow, J.; Klein, J.B.; Merchant, M.L.; Nissen, E.; Koestler, D.C.; Laurence, K.; Liang, X.; Neville, K.; Staggs, V.; et al. Ewing sarcoma family of tumors-derived small extracellular vesicle proteomics identify potential clinical biomarkers. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 2995–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 3.0: An interactive analysis and consensus interpretation of multi-drug synergies across multiple samples. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W739–W743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Jin, X.; Tsueng, G.; Afrasiabi, C.; Su, A.I. BioGPS: Building your own mash-up of gene annotations and expression profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D313–D316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonsdale, J.; Thomas, J.; Salvatore, M.; Phillips, R.; Lo, E.; Shad, S.; Hasz, R.; Walters, G.; Garcia, F.; Young, N.; et al. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, M.E.; Chen, G.Y.; Kendrick, N.D.; Xu, G.; Larsen, S.D.; Jana, S.; Waterson, A.G.; Bauer, J.A.; Hancock, W.; Sulikowski, G.A.; et al. Dual inhibition of Kif15 by oxindole and quinazolinedione chemical probes. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milic, B.; Chakraborty, A.; Han, K.; Bassik, M.C.; Block, S.M. KIF15 nanomechanics and kinesin inhibitors, with implications for cancer chemotherapeutics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4613–E4622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirode, F.; Laud-Duval, K.; Prieur, A.; Delorme, B.; Charbord, P.; Delattre, O. Mesenchymal stem cell features of Ewing tumors. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigo, K.; Takano, A.; Thang, P.M.; Yoshitake, Y.; Shinohara, M.; Tohnai, I.; Murakami, Y.; Maegawa, J.; Daigo, Y. Characterization of KIF11 as a novel prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target for oral cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, L.; Zhou, Q.; Fen, L.; Cao, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, A. Silencing of AURKA augments the antitumor efficacy of the AURKA inhibitor MLN8237 on neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vuuren, R.J.; Visagie, M.H.; Theron, A.E.; Joubert, A.M. Antimitotic drugs in the treatment of cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2015, 76, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paier, C.R.K.; Maranhão, S.S.; Carneiro, T.R.; Lima, L.M.; Rocha, D.D.; Santos, R.D.S.; Farias, K.M.; Moraes-Filho, M.O.; Pessoa, C. Natural products as new antimitotic compounds for anticancer drug development. Clinics 2018, 73 (Suppl. S1), e813s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womer, R.B.; West, D.C.; Krailo, M.D.; Dickman, P.S.; Pawel, B.R.; Grier, H.E.; Marcus, K.; Sailer, S.; Healey, J.H.; Dormans, J.P.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of interval-compressed chemotherapy for the treatment of localized Ewing sarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 4148–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marina, N.M.; Liu, Q.; Donaldson, S.S.; Sklar, C.A.; Armstrong, G.T.; Oeffinger, K.C.; Leisenring, W.M.; Ginsberg, J.P.; Henderson, T.O.; Neglia, J.P.; et al. Longitudinal follow-up of adult survivors of Ewing sarcoma: A report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study. Cancer 2017, 123, 2551–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D.N.; Chastain, K.; Chou, J.F.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Adsuar, R.; Wexler, L.H.; Chou, A.J.; DeRosa, A.; Candela, J.; Magnan, H.; et al. Morbidity and mortality after treatment of Ewing sarcoma: A single-institution experience. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspar, N.; Hawkins, D.S.; Dirksen, U.; Lewis, I.J.; Ferrari, S.; Le Deley, M.C.; Kovar, H.; Grimer, R.; Whelan, J.; Claude, L.; et al. Ewing Sarcoma: Current Management and Future Approaches Through Collaboration. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3036–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Was, H.; Borkowska, A.; Bagues, A.; Tu, L.; Liu, J.Y.H.; Lu, Z.; Rudd, J.A.; Nurgali, K.; Abalo, R. Mechanisms of Chemotherapy-Induced Neurotoxicity. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 750507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartrell, J.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C. Ewing sarcoma: Investigational mono- and combination therapies in clinical trials. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2021, 30, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felix, A.; Berlanga, P.; Toulmonde, M.; Landman-Parker, J.; Dumont, S.; Vassal, G.; Le Deley, M.C.; Gaspar, N. Systematic review of phase-I/II trials enrolling refractory and recurrent Ewing sarcoma: Actual knowledge and future directions to optimize the research. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 1589–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, K.; Cost, C.; Davis, I.; Glade-Bender, J.; Grohar, P.; Houghton, P.; Isakoff, M.; Stewart, E.; Laack, N.; Yustein, J.; et al. Emerging novel agents for patients with advanced Ewing sarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) New Agents for Ewing Sarcoma Task Force. F1000Research 2019, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, G.; Agarwal, R. New combination therapies with cell-cycle agents. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 9, 591–604. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, V.C.; Butterfield, H.E.; Poral, A.H.; Yan, M.J.; Yang, K.L.; Pham, C.D.; Muller, F.L. Why Great Mitotic Inhibitors Make Poor Cancer Drugs. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 924–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, D.; Duijf, P.H.G.; Khanna, K.K. Mitotic slippage: An old tale with a new twist. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, J. KIF11 As a Potential Pan-Cancer Immunological Biomarker Encompassing the Disease Staging, Prognoses, Tumor Microenvironment, and Therapeutic Responses. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 2764940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novais, P.; Silva, P.M.A.; Amorim, I.; Bousbaa, H. Second-Generation Antimitotics in Cancer Clinical Trials. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mossé, Y.P.; Fox, E.; Teachey, D.T.; Reid, J.M.; Safgren, S.L.; Carol, H.; Lock, R.B.; Houghton, P.J.; Smith, M.A.; Hall, D.; et al. A Phase II Study of Alisertib in Children with Recurrent/Refractory Solid Tumors or Leukemia: Children’s Oncology Group Phase I and Pilot Consortium (ADVL0921). Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3229–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, R.P.; Roesler, R.; Gregianin, L.; Brunetto, A.T.; da Cunha Jaeger, M.; Lunardi Brunetto, A.; de Farias, C.B. Cancer Stem Cells and Chemoresistance in Ewing Sarcoma. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2023, 18, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.I.; Williams, R.T.; Henderson, M.J.; Norris, M.D.; Haber, M. ABC transporters as mediators of drug resistance and contributors to cancer cell biology. Drug Resist. Updates 2016, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Rank | Gene ID | Gene Symbol | Name | Pathway |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56992 | KIF15 | Kinesin family member 15 | Motor proteins |
| 2 | 1058 | CENPA | Centromere protein A | Mitosis, chromosome segregation, and cytokinesis |
| 3 | 7153 | TOP2A | DNA topoisomerase II alpha | Platinum drug resistance |
| 4 | 5502 | PPP1R1A | Protein phosphatase 1, regulatory (inhibitor) subunit 1A | Adrenergic signaling |
| 5 | 51361 | HOOK1 | Hook microtubule-tethering protein 1 | Vesicle trafficking |
| 6 | 6790 | AURKA | Aurora kinase A | Oocyte meiosis |
| 7 | 5733 | PTGER3 | Prostaglandin E receptor 3 (subtype EP3) | Calcium signaling |
| 8 | 2619 | GAS1 | Growth arrest-specific 1 | Membrane trafficking |
| 9 | 23306 | TMEM194A | Transmembrane protein 194A | Nuclear envelope stiffness |
| 10 | 1612 | DAPK1 | Death-associated protein kinase 1 | Autophagy |
| 11 | 29028 | ATAD2 | ATPase family, AAA domain-containing 2 | Transcriptional activator |
| 12 | 783 | CACNB2 | Calcium channel, voltage dependent beta 2 subunit | MAPK-signaling pathway |
| 13 | 9787 | DLGAP5 | Discs, large (Drosophila) homolog-associated protein 5 | Centrosome and spindle formation |
| 14 | 22974 | TPX2 | TPX2, microtubule-associated homolog (Xenopus laevis) | Regulation of kinetochore-microtubule interactions |
| 15 | 2956 | MSH6 | Muts homolog 6 | Mismatch repair |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turaga, S.M.; Vishwakarma, V.; Hembruff, S.L.; Gibbs, B.K.; Sabu, P.; Puri, R.V.; Pathak, H.B.; Samuel, G.; Godwin, A.K. Inducing Mitotic Catastrophe as a Therapeutic Approach to Improve Outcomes in Ewing Sarcoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 4911. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15204911
Turaga SM, Vishwakarma V, Hembruff SL, Gibbs BK, Sabu P, Puri RV, Pathak HB, Samuel G, Godwin AK. Inducing Mitotic Catastrophe as a Therapeutic Approach to Improve Outcomes in Ewing Sarcoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(20):4911. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15204911
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuraga, Soumya M., Vikalp Vishwakarma, Stacey L. Hembruff, Benjamin K. Gibbs, Priya Sabu, Rajni V. Puri, Harsh B. Pathak, Glenson Samuel, and Andrew K. Godwin. 2023. "Inducing Mitotic Catastrophe as a Therapeutic Approach to Improve Outcomes in Ewing Sarcoma" Cancers 15, no. 20: 4911. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15204911
APA StyleTuraga, S. M., Vishwakarma, V., Hembruff, S. L., Gibbs, B. K., Sabu, P., Puri, R. V., Pathak, H. B., Samuel, G., & Godwin, A. K. (2023). Inducing Mitotic Catastrophe as a Therapeutic Approach to Improve Outcomes in Ewing Sarcoma. Cancers, 15(20), 4911. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15204911







