Pleiotropic Devitalization of Renal Cancer Cells by Non-Invasive Physical Plasma: Characterization of Molecular and Cellular Efficacy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. NIPP Treatment Inhibits Cell Proliferation by Reducing Cell Number and Growth Rate
2.2. Incubation of Untreated Cells with NIPP-Treated Cell Culture Medium also Results in Cell Growth Inhibition
2.3. Treatment with NIPP Induces Apoptosis in Cells
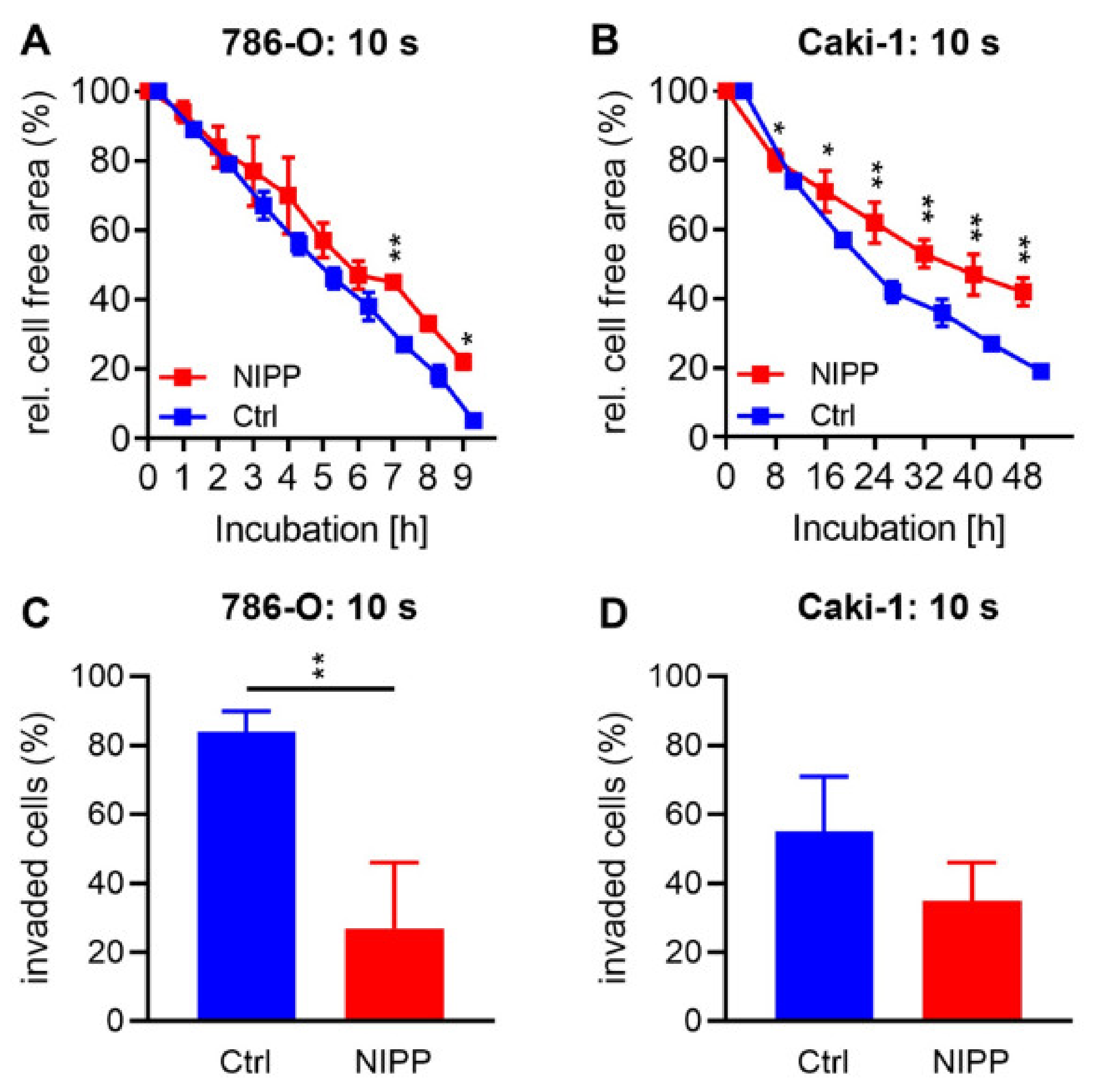
2.4. Treatment with NIPP Reduces Cell Motility and Invasiveness
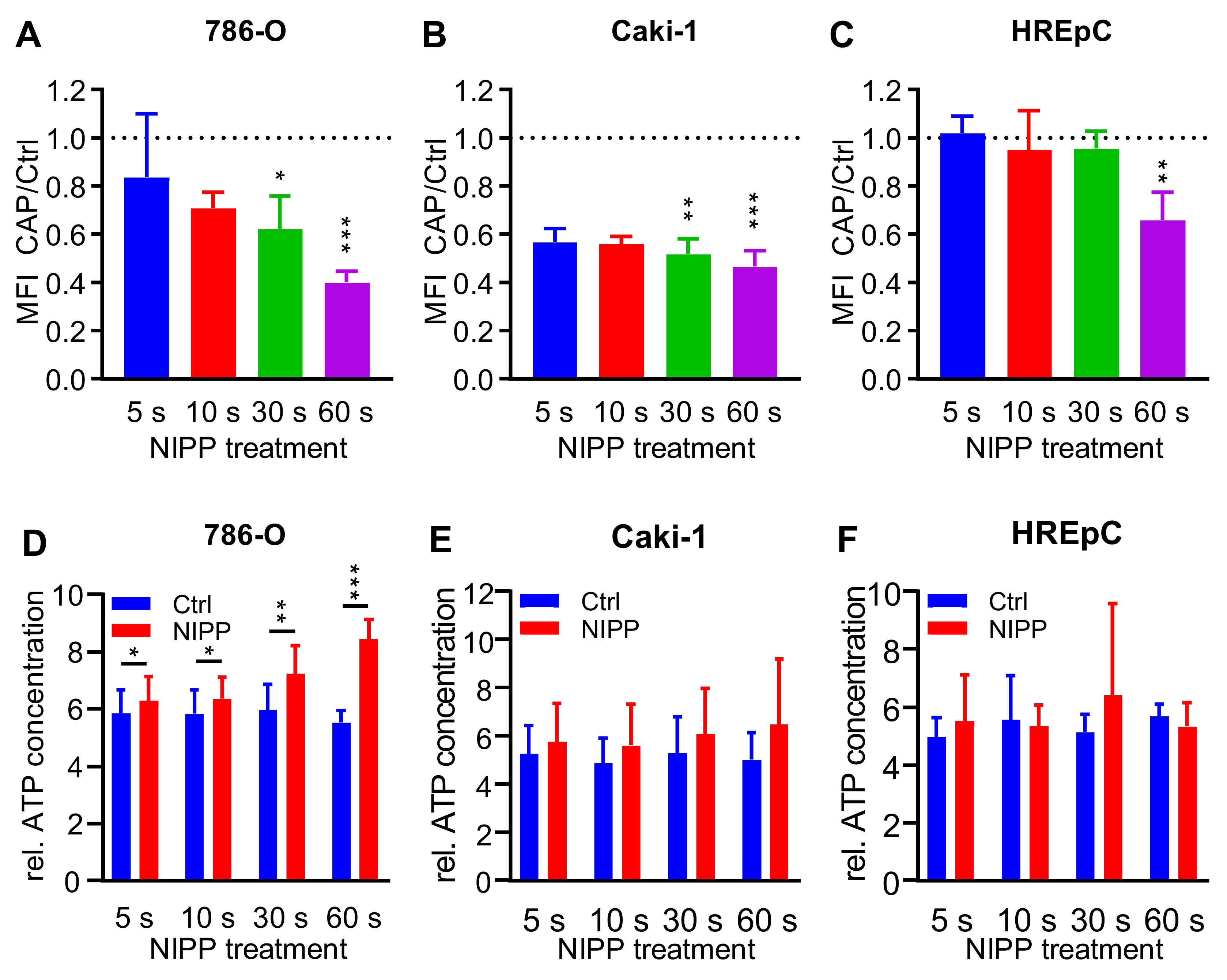
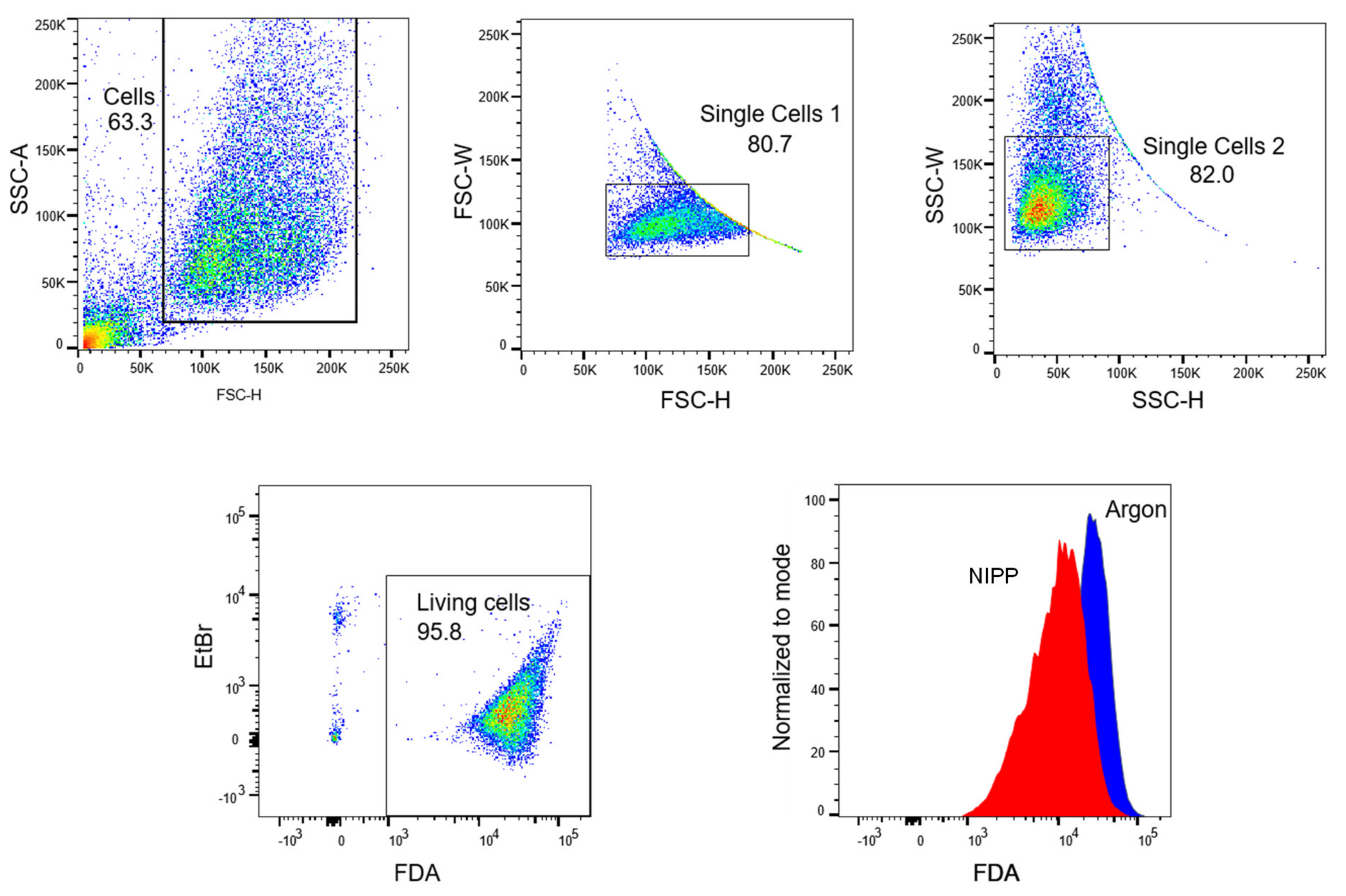
2.5. Treatment with NIPP Impairs the Functionality of the Cytoplasmic Membrane
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Direct NIPP Treatment
4.3. Indirect NIPP Treatment
4.4. Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Formation Assay
4.5. Calculation of Growth Rate and the Nummber of Cell at the Time Immediatley after the Treatment
4.6. TUNEL-Assay
4.7. Caspase-3/7-Assay
4.8. Scratch-Assay
4.9. Invasion-Assay
4.10. Loss of Dye Assay
4.11. ATP Release Assay
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Europäische Union. ECIS—European Cancer Information System. Available online: https://ecis.jrc.ec.europa.eu (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, J.R.; Finelli, A. Landmarks in the diagnosis and treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2014, 11, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basappa, N.S.; Basiuk, J.; Canil, C.; Al-Asaaed, S.; Heng, D.Y.; Wood, L.; Stacey, D.; Kollmannsberger, C.; Jewett, M.A. Setting research priorities for kidney cancer. Eur. Urol. 2017, 72, 861–864. [Google Scholar]
- Fiebig, J.; Kraywinkel, K. Epidemiologie des Nierenzellkarzinoms in Deutschland. Der Onkol. 2019, 25, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doehn, C.; Grünwald, V.; Steiner, T.; Follmann, M.; Rexer, H.; Krege, S. Diagnostik, Therapie und Nachsorge des Nierenzellkarzinoms. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2016, 113, 590–596. [Google Scholar]
- Capitanio, U.; Bensalah, K.; Bex, A.; Boorjian, S.A.; Bray, F.; Coleman, J.; Gore, J.L.; Sun, M.; Wood, C.; Russo, P. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.H.; Klatte, T.; Usher-Smith, J.; Stewart, G.D. Epidemiology and screening for renal cancer. World J. Urol. 2018, 36, 1341–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitlinienprogramm Onkologie. Diagnostik, Therapie und Nachsorge des Nierenzellkarzinoms. Available online: http://leitlinienprogramm-onkologie.de/Nierenzellkarzinom.85.0.html (accessed on 25 January 2020).
- Siva, S.; Pham, D.; Gill, S.; Corcoran, N.M.; Foroudi, F. A systematic review of stereotactic radiotherapy ablation for primary renal cell carcinoma. BJU Int. 2012, 110, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Dib, R.; Touma, N.J.; Kapoor, A. Cryoablation vs radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of renal cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis of case series studies. BJU Int. 2012, 110, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, S.; Imamura, M.; Lapitan, M.C.; Omar, M.I.; Lam, T.B.L.; Hilvano-Cabungcal, A.M.; Royle, P.; Stewart, F.; MacLennan, G.; MacLennan, S.J.; et al. Systematic review of oncological outcomes following surgical management of localised renal cancer. Eur. Urol. 2012, 61, 972–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungberg, B.; Albiges, L.; Abu-Ghanem, Y.; Bensalah, K.; Dabestani, S.; Fernández-Pello, S.; Giles, R.H.; Hofmann, F.; Hora, M.; Kuczyk, M.A.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2019 Update. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggener, S.E.; Yossepowitch, O.; Kundu, S.; Motzer, R.J.; Russo, P. Risk score and metastasectomy independently impact prognosis of patients with recurrent renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2008, 180, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alt, A.L.; Boorjian, S.A.; Lohse, C.M.; Costello, B.A.; Leibovich, B.C.; Blute, M.L. Survival after complete surgical resection of multiple metastases from renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 2011, 117, 2873–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Bander, N.H.; Nanus, D.M. Renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 335, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, J.T.; Bokemeyer, C. Chemotherapy for renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 1999, 19, 1541–1543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Minasian, L.M.; Motzer, R.J.; Gluck, L.; Mazumdar, M.; Vlamis, V.; Krown, S.E. Interferon alfa-2a in advanced renal cell carcinoma: Treatment results and survival in 159 patients with long-term follow-up. J. Clin. Oncol. 1993, 11, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Sherry, R.M.; Steinberg, S.M.; Topalian, S.L.; Schwartzentruber, D.J.; Hwu, P.; Seipp, C.A.; Rogers-Freezer, L.; Morton, K.E.; White, D.E.; et al. Randomized study of high-dose and low-dose interleukin-2 in patients with metastatic renal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 3127–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Tomczak, P.; Michaelson, M.D.; Bukowski, R.M.; Rixe, O.; Oudard, S.; Negrier, S.; Szczylik, C.; Kim, S.T.; et al. Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Hutson, T.E.; Tomczak, P.; Michaelson, M.D.; Bukowski, R.M.; Oudard, S.; Negrier, S.; Szczylik, C.; Pili, R.; Bjarnason, G.A.; et al. Overall survival and updated results for sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3584–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaatsch, P.; Spix, C.; Katalinic, A.; Hentschel, S.; Luttmann, S.; Waldeyer-Sauerland, M.; Waldmann, A.; Christ, M.; Folkerts, J.; Hansmann, J.; et al. Niere. In Krebs in Deutschland für 2015/2016; Robert Koch-Institut: Berlin, Germany, 2019; pp. 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ahrend, H.; Kaul, A.; Ziegler, S.; Brandenburg, L.O.; Zimmermann, U.; Mustea, A.; Burchardt, M.; Ziegler, P.; Stope, M.B. MicroRNA-1 and MicroRNA-21 Individually Regulate Cellular Growth of Non-malignant and Malignant Renal Cells. In Vivo 2017, 31, 625–630. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, T.O.; Dao, V.T.; Nguyen, V.T.; Feugeas, J.P.; Pamoukdjian, F.; Bousquet, G. Genomics of Clear-cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. 2022, 81, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelbrich, N.; Ahrend, H.; Kaul, A.; Brandenburg, L.O.; Zimmermann, U.; Mustea, A.; Burchardt, M.; Gümbel, D.; Stope, M.B. Different Cytokine and Chemokine Expression Patterns in Malignant Compared to Those in Nonmalignant Renal Cells. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2017, 2017, 7190546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beksac, A.T.; Paulucci, D.J.; Blum, K.A.; Yadav, S.S.; Sfakianos, J.P.; Badani, K.K. Heterogeneity in renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezest, M.; Chavatte, L.; Bourdens, M.; Quinton, D.; Camus, M.; Garrigues, L.; Descargues, P.; Arbault, S.; Burlet-Schiltz, O.; Casteilla, L.; et al. Mechanistic insights into the impact of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma on human epithelial cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keidar, M.; Shashurin, A.; Volotskova, O.; Stepp, M.; Srinivasan, P.; Sandler, A.; Trink, B. Cold Atmospheric Plasma in Cancer Therapy. Phys. Plasmas 2012, 20, 057101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. Cold atmospheric plasma, a novel promising anti-cancer treatment modality. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15977–15995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zeng, W.; Xia, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, D.; Liu, D.; Kong, M.G.; Dong, Y. Cold atmospheric plasma induces apoptosis of melanoma cells via Sestrin2-mediated nitric oxide synthase signaling. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Chung, T.H.; Bae, S.H.; Leem, S.H. Induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by a pulsed atmospheric pressure plasma jet. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 023702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koensgen, D.; Besic, I.; Gumbel, D.; Kaul, A.; Weiss, M.; Diesing, K.; Kramer, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Mustea, A.; Stope, M.B. Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP) and CAP-Stimulated Cell Culture Media Suppress Ovarian Cancer Cell Growth—A Putative Treatment Option in Ovarian Cancer Therapy. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 6739–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Ballato, J.; Foy, P.; Hawkins, T.; Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Kim, S.-O. Apoptosis of lung carcinoma cells induced by a flexible optical fiber-based cold microplasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralambiev, L.; Wien, L.; Gelbrich, N.; Kramer, A.; Mustea, A.; Burchardt, M.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Stope, M.B.; Gümbel, D. Effects of Cold Atmospheric Plasma on the Expression of Chemokines, Growth Factors, TNF Superfamily Members, Interleukins, and Cytokines in Human Osteosarcoma Cells. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralambiev, L.; Nitsch, A.; Jacoby, J.M.; Strakeljahn, S.; Bekeschus, S.; Mustea, A.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Stope, M.B. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment of Chondrosarcoma Cells Affects Proliferation and Cell Membrane Permeability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Talbot, A.; Nourmohammadi, N.; Cheng, X.; Canady, J.; Sherman, J.; Keidar, M. Principles of using Cold Atmospheric Plasma Stimulated Media for Cancer Treatment. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sensenig, R.; Kalghatgi, S.; Cerchar, E.; Fridman, G.; Shereshevsky, A.; Torabi, B.; Arjunan, K.P.; Podolsky, E.; Fridman, A.; Friedman, G.; et al. Non-thermal plasma induces apoptosis in melanoma cells via production of intracellular reactive oxygen species. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 39, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partecke, L.I.; Evert, K.; Haugk, J.; Doering, F.; Normann, L.; Diedrich, S.; Weiss, F.-U.; Evert, M.; Huebner, N.O.; Guenther, C.; et al. Tissue tolerable plasma (TTP) induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishaq, M.; Evans, M.D.M.; Ostrikov, K.K. Atmospheric pressure gas plasma-induced colorectal cancer cell death is mediated by Nox2-ASK1 apoptosis pathways and oxidative stress is mitigated by Srx-Nrf2 anti-oxidant system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2827–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiazi, R.; Akbari, M.E.; Norozi, A.; Etedadialiabadi, M. Application of Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP) in Cancer Therapy: A Review. Int. J. Cancer Manag. 2017, 10, e8728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuc, A.; Monsarrat, P.; Virard, F.; Merbahi, N.; Sarrette, J.-P.; Laurencin-Dalicieux, S.; Cousty, S. Use of cold-atmospheric plasma in oncology: A concise systematic review. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1758835918786475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gümbel, D.; Bekeschus, S.; Gelbrich, N.; Napp, M.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Kramer, A.; Stope, M.B. Cold Atmospheric Plasma in the Treatment of Osteosarcoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Rödder, K.; Fregin, B.; Otto, O.; Lippert, M.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Wende, K.; Schmidt, A.; Gandhirajan, R.K. Toxicity and Immunogenicity in Murine Melanoma following Exposure to Physical Plasma-Derived Oxidants. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4396467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privat-Maldonado, A.; Schmidt, A.; Lin, A.; Weltmann, K.D.; Wende, K.; Bogaerts, A.; Bekeschus, S. ROS from Physical Plasmas: Redox Chemistry for Biomedical Therapy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 9062098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wende, K.; von Woedtke, T.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Bekeschus, S. Chemistry and biochemistry of cold physical plasma derived reactive species in liquids. Biol. Chem. 2018, 400, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralambiev, L.; Nitsch, A.; Einenkel, R.; Muzzio, D.O.; Gelbrich, N.; Burchardt, M.; Zygmunt, M.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Stope, M.B.; Gümbel, D. The Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma on the Membrane Permeability of Human Osteosarcoma Cells. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 841–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggers, B.; Marciniak, J.; Memmert, S.; Wagner, G.; Deschner, J.; Kramer, F.J.; Nokhbehsaim, M. Influences of cold atmospheric plasma on apoptosis related molecules in osteoblast-like cells in vitro. Head Face Med. 2021, 17, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitsch, A.; Strakeljahn, S.; Jacoby, J.M.; Sieb, K.F.; Mustea, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Stope, M.B.; Haralambiev, L. New Approach against Chondrosoma Cells—Cold Plasma Treatment Inhibits Cell Motility and Metabolism, and Leads to Apoptosis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gümbel, D.; Daeschlein, G.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Kramer, A.; Stope, M.B. Cold atmospheric plasma in orthopaedic and urologic tumor therapy. GMS Hyg. Infect Control 2017, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbrich, N.; Stope, M.; Burchardt, M. Kaltes atmosphärisches Plasma für die urologische Tumortherapie. Der. Urol. 2019, 58, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Holmes, B.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, W.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, L.G. Cold atmospheric plasma for selectively ablating metastatic breast cancer cells. PloS ONE 2013, 8, e73741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, D.B. The emerging role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in redox biology and some implications for plasma applications to medicine and biology. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 263001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Woedtke, T.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Wende, K.; Weltmann, K.-D. Plasma Medicine: A Field of Applied Redox Biology. In Vivo 2019, 33, 1011–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, G.-Y.; Storz, P. Reactive oxygen species in cancer. Free Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 479–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. On the history of oxidative stress: Concept and some aspects of current development. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Wende, K.; Vollmar, B.; von Woedtke, T. A cold plasma jet accelerates wound healing in a murine model of full-thickness skin wounds. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attri, P.; Park, J.H.; Ali, A.; Choi, E.H. How Does Plasma Activated Media Treatment Differ From Direct Cold Plasma Treatment? Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Xu, W.; Yao, X.; Lin, L.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. The Cell Activation Phenomena in the Cold Atmospheric Plasma Cancer Treatment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeschus, S.; Schütz, C.S.; Nießner, F.; Wende, K.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Gelbrich, N.; von Woedtke, T.; Schmidt, A.; Stope, M.B. Elevated H2AX Phosphorylation Observed with kINPen Plasma Treatment Is Not Caused by ROS-Mediated DNA Damage but Is the Consequence of Apoptosis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 8535163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzariti, A.; Iacobazzi, R.M.; Di Fonte, R.; Porcelli, L.; Gristina, R.; Favia, P.; Fracassi, F.; Trizio, I.; Silvestris, N.; Guida, G.; et al. Plasma-activated medium triggers cell death and the presentation of immune activating danger signals in melanoma and pancreatic cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepp, O.; Senovilla, L.; Vitale, I.; Vacchelli, E.; Adjemian, S.; Agostinis, P.; Apetoh, L.; Aranda, F.; Barnaba, V.; Bloy, N.; et al. Consensus guidelines for the detection of immunogenic cell death. Oncoimmunology 2014, 3, e955691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Truong, B.; Patel, S.; Kaushik, N.; Choi, H.E.; Fridman, G.; Fridman, A.; Miller, V. Nanosecond-Pulsed DBD Plasma-Generated Reactive Oxygen Species Trigger Immunogenic Cell Death in A549 Lung Carcinoma Cells through Intracellular Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volotskova, O.; Stepp, M.A.; Keidar, M. Integrin activation by a cold atmospheric plasma jet. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 053019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, Z.; Chen, C.; Xu, R.; Tian, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Kong, M.G. Cold atmospheric-pressure plasma induces DNA-protein crosslinks through protein oxidation. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 783–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Attri, P.; Yadav, D.K.; Choi, J.; Choi, E.H.; Uhm, H.S. Induced apoptosis in melanocytes cancer cell and oxidation in biomolecules through deuterium oxide generated from atmospheric pressure non-thermal plasma jet. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volotskova, O.; Shashurin, A.; Stepp, M.A.; Pal-Ghosh, S.; Keidar, M. Plasma-Controlled Cell Migration: Localization of Cold Plasma-Cell Interaction Region. Plasma Med. 2011, 1, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Kwon, S.; Bahn, J.H.; Lee, K.; Jun, S.I.; Rack, P.D.; Baek, S.J. Effects of atmospheric nonthermal plasma on invasion of colorectal cancer cells. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 243701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasaki, S.; Horiguchi, A.; Asano, T.; Ito, K.; Asano, T.; Asakura, H. Docosahexaenoic acid inhibits the phosphorylation of STAT3 and the growth and invasion of renal cancer cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.H. Mechanisms of a novel anticancer therapeutic strategy involving atmospheric pressure plasma-mediated apoptosis and DNA strand break formation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrini, E.; Laurita, R.; Stancampiano, A.; Catanzaro, E.; Calcabrini, C.; Maffei, F.; Gherardi, M.; Colombo, V.; Fimognari, C. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Induces Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress Pathway Regulation in T-Lymphoblastoid Leukemia Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4271065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Jarick, K.; Hasse, S.; von Woedtke, T.; Wende, K. Cold Physical Plasma Modulates p53 and Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling in Keratinocytes. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 7017363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.; Berganza, C.; Zhang, J. Cold Atmospheric Plasma: Methods of production and application in dentistry and oncology. Med. Gas Res. 2013, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralambiev, L.; Bandyophadyay, A.; Suchy, B.; Weiss, M.; Kramer, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Mustea, A.; Kaderali, L.; Stope, M.B. Determination of Immediate vs. Kinetic Growth Retardation in Physically Plasma-treated Cells by Experimental and Modelling Data. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 3743–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C. Boyden chamber assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2005, 294, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
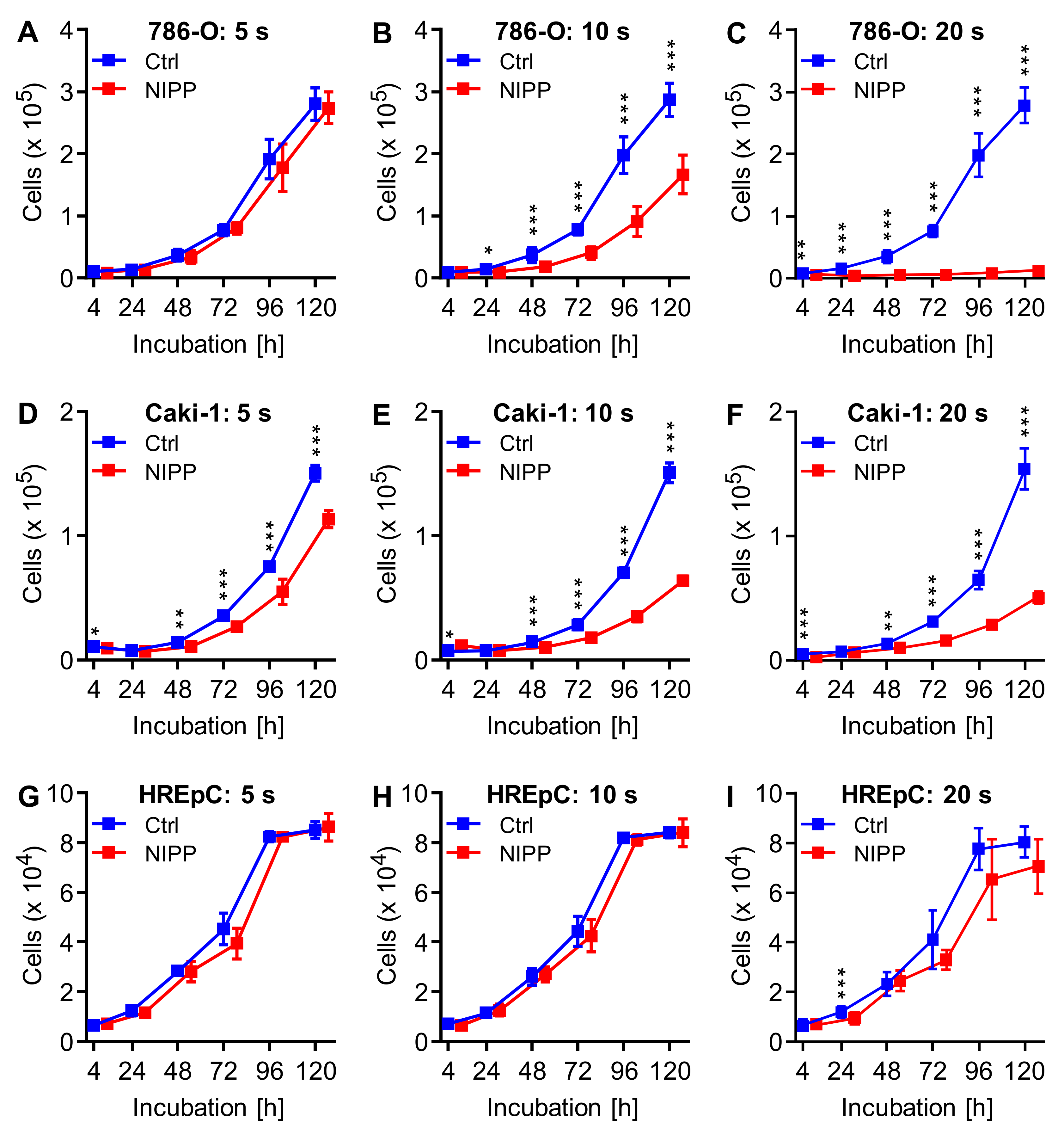
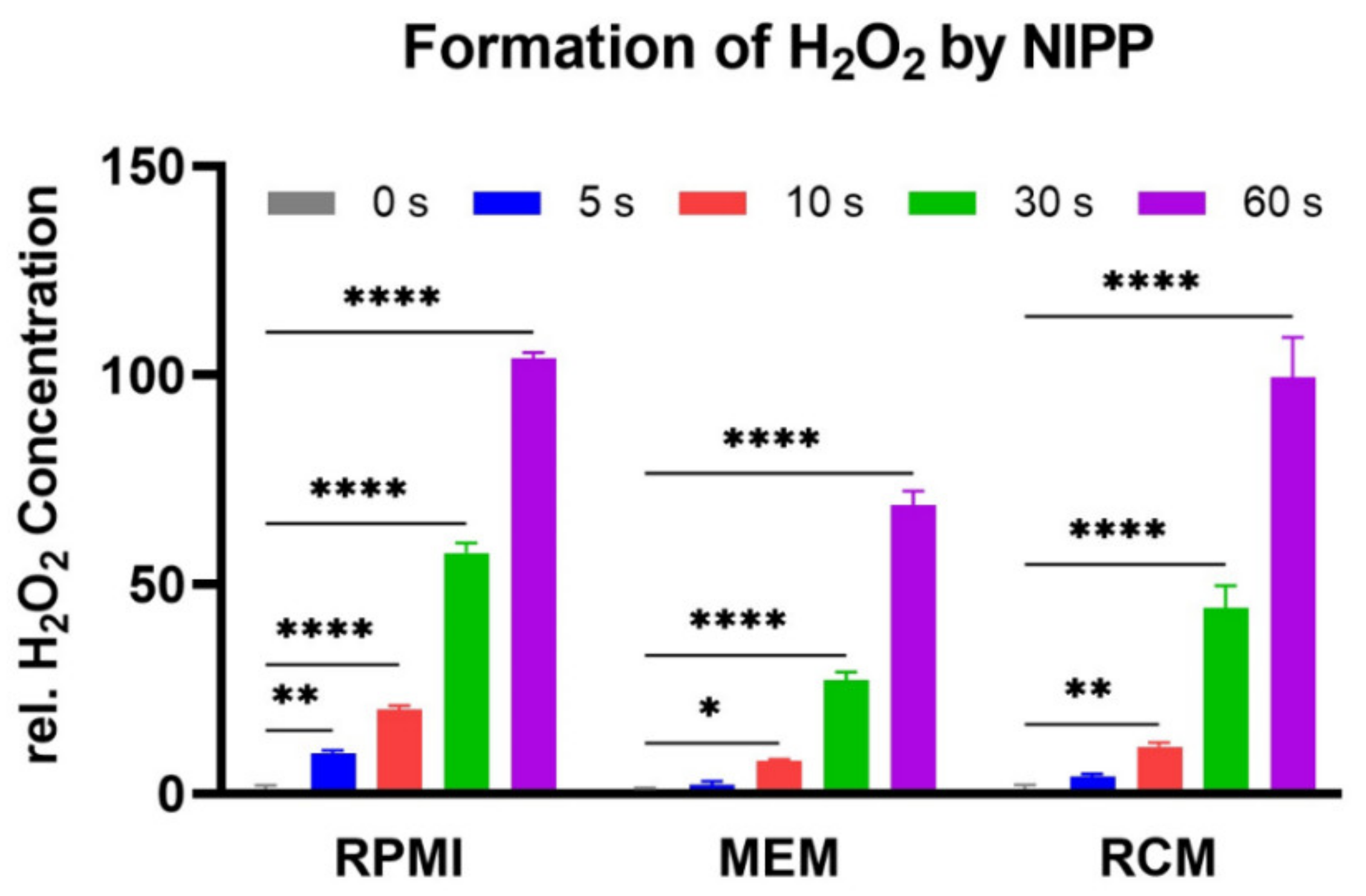
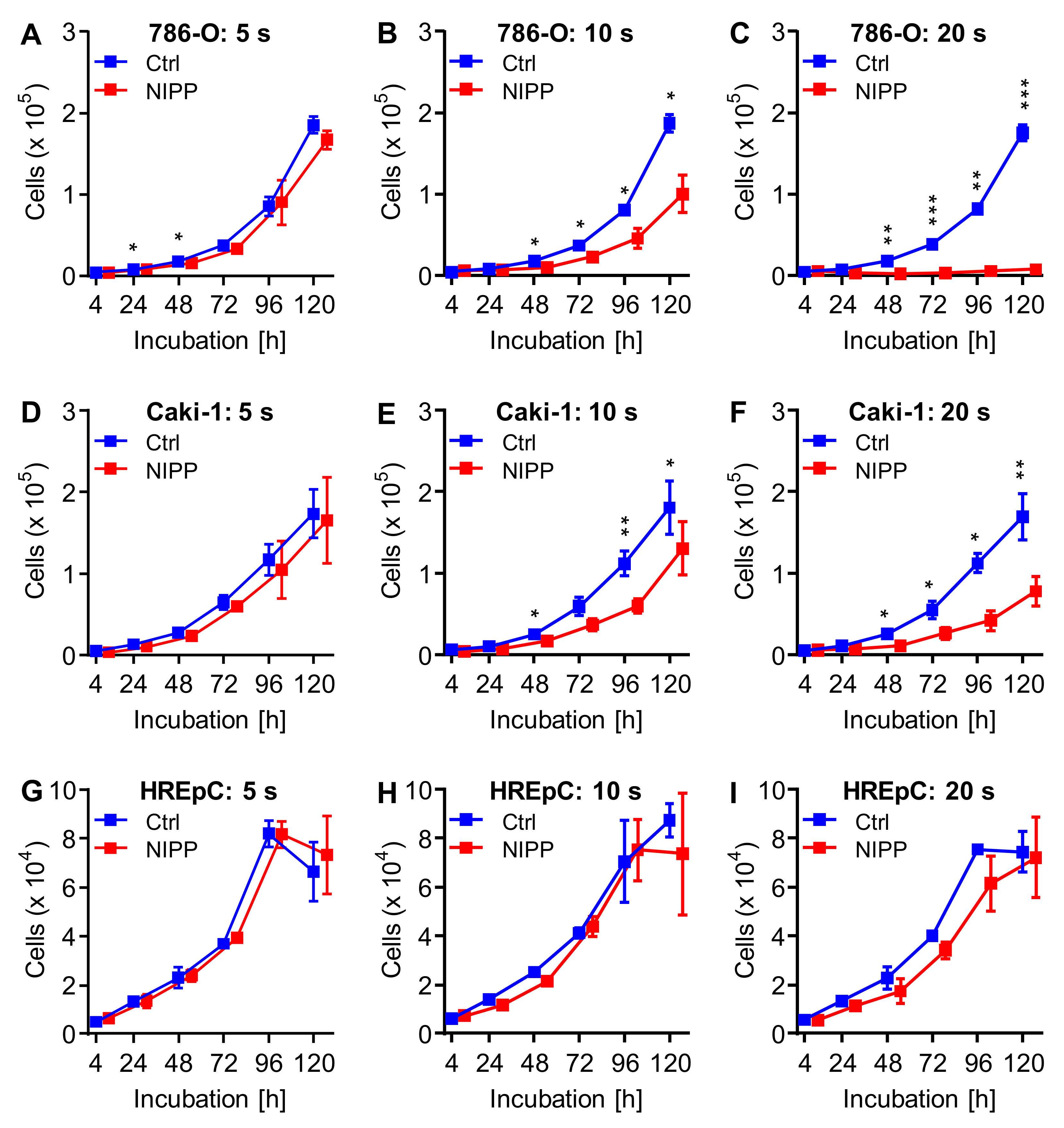
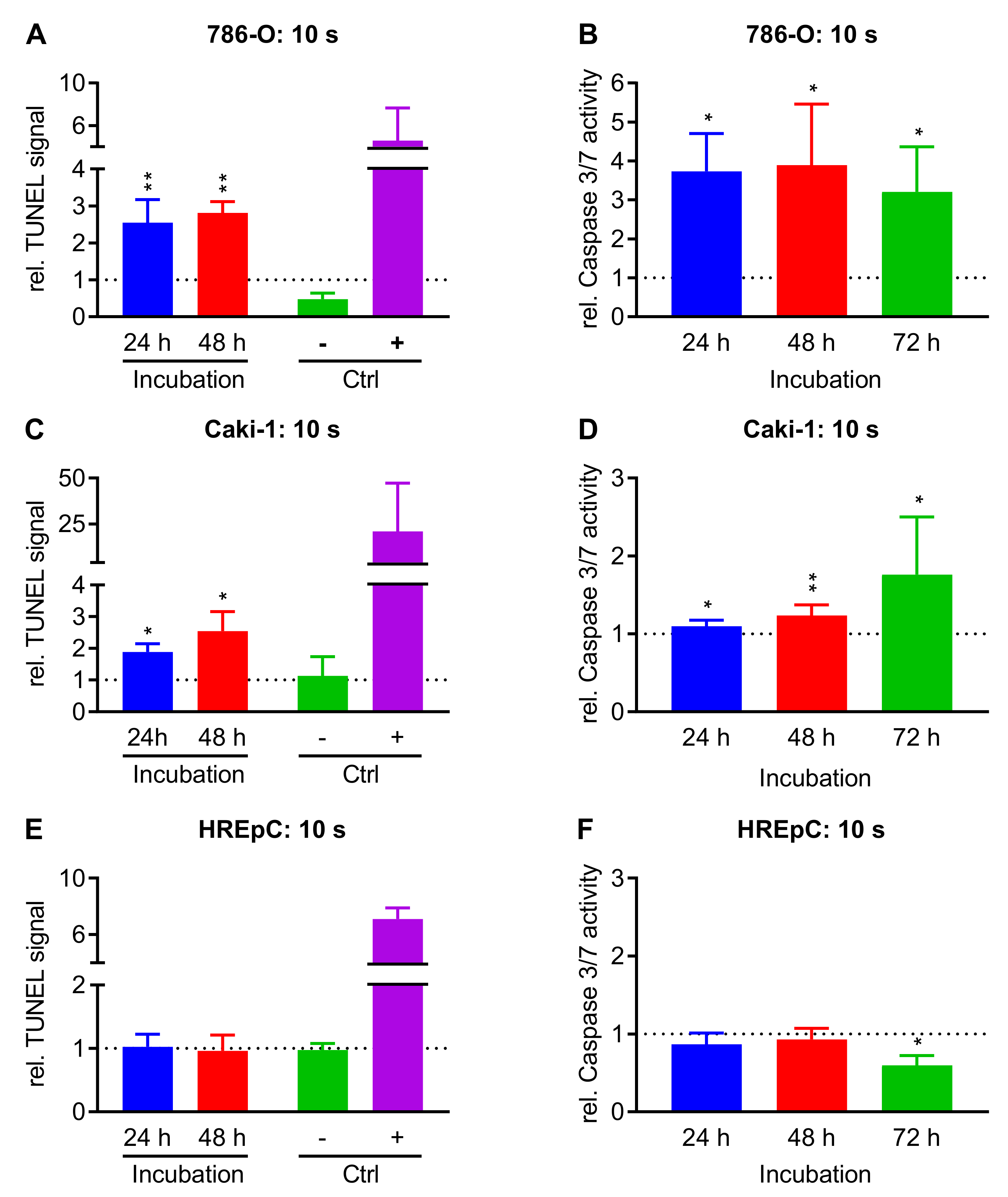

| Cell | Treatment | Cells at t = 0 | Growth Rate | Doubling Time (h) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line | Ctrl | NIPP | Ctrl | NIPP | Ctrl | NIPP | |
| 786-O | 5 s | 10,626 (±1074) | 9866 (±1098) | 0.02757 (±0.00089) | 0.02789 (±0.00098) | 25.1 | 24.8 |
| 10 s | 10,8921 (±1229) | 5537 (±698) | 0.02760 (±0.00010) | 0.02907 (±0.00111) | 25.1 | 23.8 | |
| 20 s | 9294 (±757) | 3518 (±623) | 0.02888 (±0.00072) | 0.00995 (±0.00185) | 24.0 | 69.6 | |
| Caki-1 | 5 s | 4133 (±278) | 3094 (±364) | 0.02995 (±0.00059) | 0.02997 (±0.00104) | 23.1 | 23.1 |
| 10 s | 3001 (±12) | 3610 (±413) | 0.03253 (±0.00062) | 0.02380 (±0.00103) | 21.3 | 29.1 | |
| 20 s | 2975 (±160) | 3173 (±268) | 0.03256 (±0.00047) | 0.02284 (±0.00077) | 21.3 | 30.4 | |
| HREpC | 5 s | 7715 (±748) | 6626 (±898) | 0.02469 (±0.00111) | 0.02612 (±0.00156) | 28.1 | 26.5 |
| 10 s | 7079 (±645) | 7154 (±753) | 0.02553 (±0.00103) | 0.02526 (±0.00119) | 27.2 | 27.4 | |
| 20 s | 6455 (±1267) | 6333 (±1645) | 0.02590 (±0.00222) | 0.02419 (±0.002970) | 26.8 | 28.7 | |
| Cell | Treatment | Cells at t = 0 | Growth Rate | Doubling Time (h) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line | Ctrl | NIPP | Ctrl | NIPP | Ctrl | NIPP | |
| 786-O | 5 s | 3850 ±127 | 3426 ±163 | 0.03203 ±0.00029 | 0.03205 ±0.00041 | 21.6 | 21.6 |
| 10 s | 3302 ±156 | 2679 ±329 | 0.03365 ±0.00051 | 0.02888 ±0.00110 | 20.6 | 24.0 | |
| 20 s | 3666 ±241 | 2766 ±621 | 0.03246 ±0.00059 | 0.00686 ±0.00251 | 21.4 | 101.1 | |
| Caki-1 | 5 s | 10,339 ±1629 | 7553 ±1830 | 0.22453 ±0.00146 | 0.02722 ±0.00221 | 28.3 | 25.5 |
| 10 s | 8250 ±1169 | 3713 ±664 | 0.02669 ±0.00129 | 0.02982 ±0.00168 | 26.0 | 23.3 | |
| 20 s | 8591 ±1222 | 3969 ±1250 | 0.02585 ±0.00130 | 0.02481 ±0.00283 | 26.8 | 28.0 | |
| HREpC | 5 s | 5296 ±717 | 6117 ±660 | 0.02840 ±0.00151 | 0.02688 ±0.00121 | 24.4 | 25.8 |
| 10 s | 7964 ±1618 | 6813 ±1165 | 0.02275 ±0.00234 | 0.02511 ±0.00195 | 30.5 | 27.6 | |
| 20 s | 6499 ±488 | 5518 ±1101 | 0.02551 ±0.00085 | 0.02512 ±0.00227 | 27.2 | 27.6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nitsch, A.; Sander, C.; Eggers, B.; Weiss, M.; Egger, E.; Kramer, F.-J.; Erb, H.H.H.; Mustea, A.; Stope, M.B. Pleiotropic Devitalization of Renal Cancer Cells by Non-Invasive Physical Plasma: Characterization of Molecular and Cellular Efficacy. Cancers 2023, 15, 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020481
Nitsch A, Sander C, Eggers B, Weiss M, Egger E, Kramer F-J, Erb HHH, Mustea A, Stope MB. Pleiotropic Devitalization of Renal Cancer Cells by Non-Invasive Physical Plasma: Characterization of Molecular and Cellular Efficacy. Cancers. 2023; 15(2):481. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020481
Chicago/Turabian StyleNitsch, Andreas, Caroline Sander, Benedikt Eggers, Martin Weiss, Eva Egger, Franz-Josef Kramer, Holger H. H. Erb, Alexander Mustea, and Matthias B. Stope. 2023. "Pleiotropic Devitalization of Renal Cancer Cells by Non-Invasive Physical Plasma: Characterization of Molecular and Cellular Efficacy" Cancers 15, no. 2: 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020481
APA StyleNitsch, A., Sander, C., Eggers, B., Weiss, M., Egger, E., Kramer, F.-J., Erb, H. H. H., Mustea, A., & Stope, M. B. (2023). Pleiotropic Devitalization of Renal Cancer Cells by Non-Invasive Physical Plasma: Characterization of Molecular and Cellular Efficacy. Cancers, 15(2), 481. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020481








