Regulation of EWSR1-FLI1 Function by Post-Transcriptional and Post-Translational Modifications
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Pathology of Ewing Sarcoma
3. Therapies in Ewing Sarcoma
4. Oncogenic Mechanisms of EWSR1-FLI1 in Ewing Sarcoma
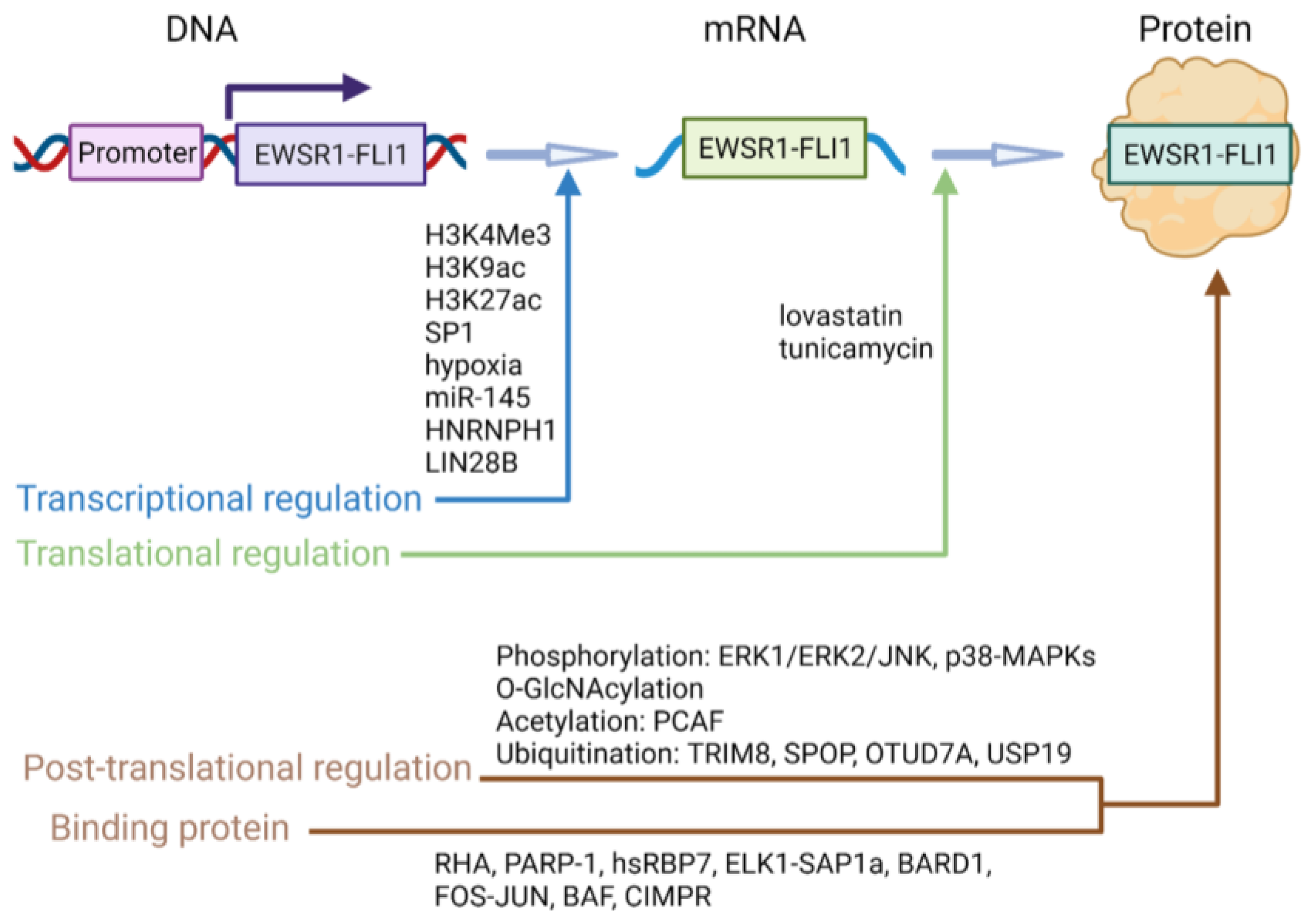
5. EWSR1-FLI1 Regulatory Mechanisms
5.1. Transcriptional Regulation
5.2. Translational Regulation
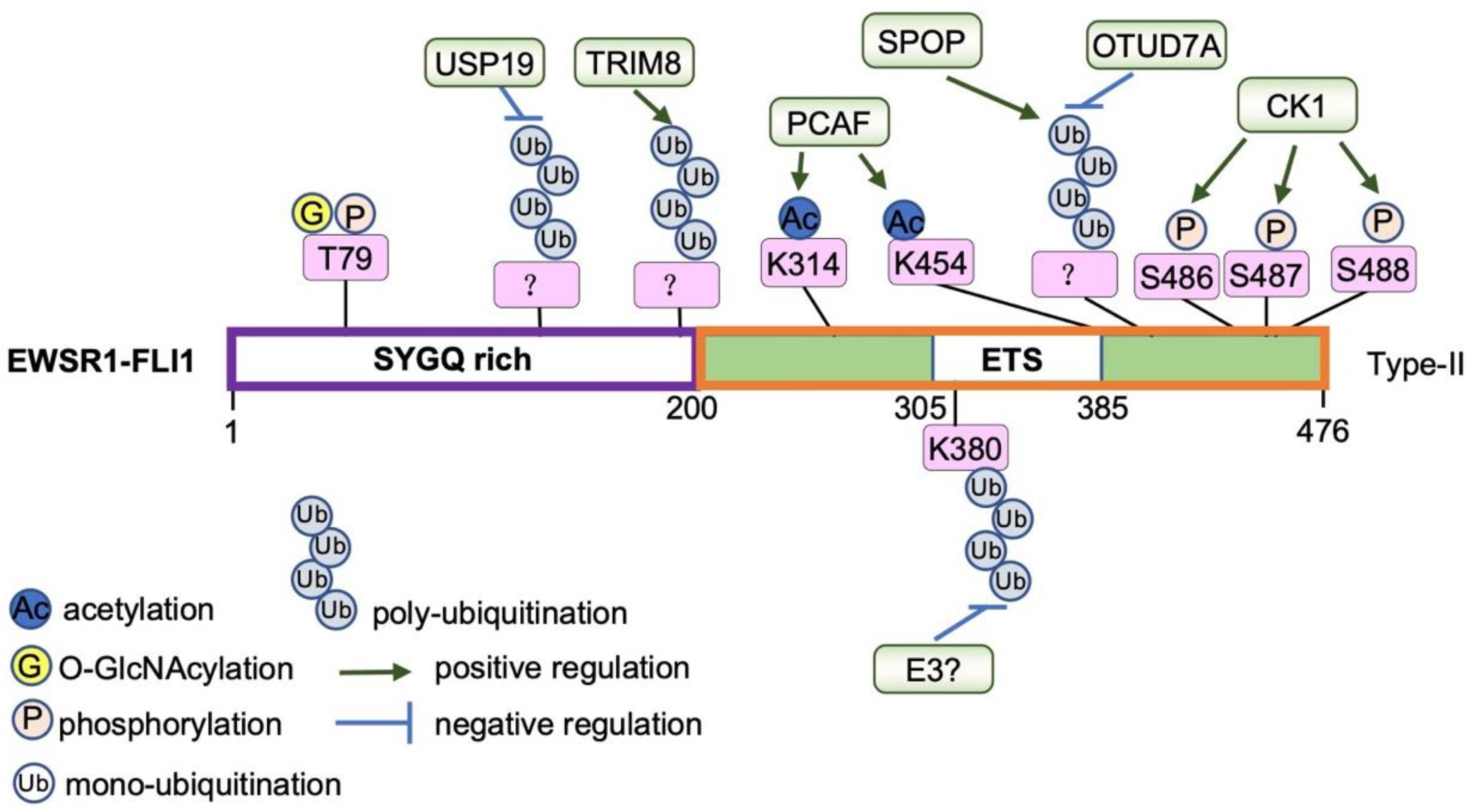
5.3. Protein-Level Regulation
6. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grunewald, T.G.P.; Cidre-Aranaz, F.; Surdez, D.; Tomazou, E.M.; de Alava, E.; Kovar, H.; Sorensen, P.H.; Delattre, O.; Dirksen, U. Ewing sarcoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2018, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zöllner, S.; Amatruda, J.; Bauer, S.; Collaud, S.; de Álava, E.; DuBois, S.; Hardes, J.; Hartmann, W.; Kovar, H.; Metzler, M.; et al. Ewing Sarcoma—Diagnosis, Treatment, Clinical Challenges and Future Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotterill, S.; Ahrens, S.; Paulussen, M.; Jürgens, H.; Voûte, P.; Gadner, H.; Craft, A. Prognostic Factors in Ewing’s Tumor of Bone: Analysis of 975 Patients From the European Intergroup Cooperative Ewing’s Sarcoma Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 3108–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahl, M.; Ranft, A.; Paulussen, M.; Bölling, T.; Vieth, V.; Bielack, S.; Görtitz, I.; Braun-Munzinger, G.; Hardes, J.; Jürgens, H.; et al. Risk of recurrence and survival after relapse in patients with Ewing sarcoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2011, 57, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desmaze, C.; Brizard, F.; Turc-Carel, C.; Melot, T.; Delattre, O.; Thomas, G.; Aurias, A. Multiple chromosomal mechanisms generate an EWS/FLI1 or an EWS/ERG fusion gene in Ewing tumors. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 1997, 97, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forscher, C.; Figlin, R.; Mita, M. Targeted therapy for sarcomas. Biol. Targets Ther. 2014, 8, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauer, M.; Ban, J.; Kofler, R.; Walker, B.; Davis, S.; Meltzer, P.; Kovar, H. A molecular function map of Ewing’s sarcoma. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuna, D.; de Alava, E. Molecular pathology of sarcomas. Rev. Recent Clin. Trials 2009, 4, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delattre, O.; Zucman, J.; Plougastel, B.; Desmaze, C.; Melot, T.; Peter, M.; Kovar, H.; Joubert, I.; De Jong, P.; Rouleau, G.; et al. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature 1992, 359, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovar, H.; Aryee, D.N.; Jug, G.; Henöckl, C.; Schemper, M.; Delattre, O.; Thomas, G.; Gadner, H. EWS/FLI-1 antagonists induce growth inhibition of Ewing tumor cells in vitro. Cell Growth Differ. 1996, 7, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shing, D.C.; McMullan, D.J.; Roberts, P.; Smith, K.; Chin, S.F.; Nicholson, J.; Tillman, R.M.; Ramani, P.; Cullinane, C.; Coleman, N. FUS/ERG gene fusions in Ewing’s tumors. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 4568–4576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elzi, D.J.; Song, M.; Houghton, P.J.; Chen, Y.; Shiio, Y. The role of FLI-1-EWS, a fusion gene reciprocal to EWS-FLI-1, in Ewing sarcoma. Genes Cancer 2015, 6, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.P.; Wang, Y.; Lozano, G. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and the Origin of Ewing’s Sarcoma. Sarcoma 2011, 2011, 276463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Levetzow, C.; Jiang, X.; Gwye, Y.; von Levetzow, G.; Hung, L.; Cooper, A.; Hsu, J.H.; Lawlor, E.R. Modeling initiation of Ewing sarcoma in human neural crest cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Yamazaki, Y.; Kanno, Y.; Igarashi, K.; Aisaki, K.-I.; Kanno, J.; Nakamura, T. Ewing’s sarcoma precursors are highly enriched in embryonic osteochondrogenic progenitors. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3061–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünewald, T.G.P.; Bernard, V.; Gilardi-Hebenstreit, P.; Raynal, V.; Surdez, D.; Aynaud, M.-M.; Mirabeau, O.; Cidre-Aranaz, F.; Tirode, F.; Zaidi, S.; et al. Chimeric EWSR1-FLI1 regulates the Ewing sarcoma susceptibility gene EGR2 via a GGAA microsatellite. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, K.; Smyth, N.A.; Murawski, C.D.; Kennedy, J.G. The Biology of Ewing Sarcoma. ISRN Oncol. 2013, 2013, 759725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcilla, D.; Machado, I.; Grünewald, T.G.P.; Llombart-Bosch, A.; de Álava, E. (Immuno)histological Analysis of Ewing Sarcoma. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2226, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, G.; Wang, M.; Wejde, J.; Kreicbergs, A.; Larsson, O. Detection of EWS/FLI-1 by Immunostaining. An Adjunctive Tool in Diagnosis of Ewing’s Sarcoma and Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumour on Cytological Samples and Paraffin-Embedded Archival Material. Sarcoma 1999, 3, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbaraglia, M.; Bellan, E.; Tos, A.P.D. The 2020 WHO Classification of Soft Tissue Tumours: News and perspectives. Pathologica 2020, 113, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.S.; Yoon, H.K.; Choi, J.B.; Eum, J.W. Extraskeletal Ewing’s sarcoma of the hard palate. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2005, 20, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collini, P.; Mezzelani, A.; Modena, P.; Dagrada, P.; Tamborini, E.; Luksch, R.; Gronchi, A.; Navarria, P.; Sozzi, G.; Pilotti, S. Evidence of Neural Differentiation in a Case of Post-therapy Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor/Ewing Sarcoma of Bone. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2003, 27, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amann, G.; Zoubek, A.; Salzer-Kuntschik, M.; Windhager, R.; Kovar, H. Relation of neurological marker expression and EWS gene fusion types in MIC2/CD99-positive tumors of the Ewing family. Hum. Pathol. 1999, 30, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, B.; Yang, W.; Li, L.; Ding, L.; Huang, M.; Gery, S.; Lin, D.-C.; et al. EWS-FLI1 regulates and cooperates with core regulatory circuitry in Ewing sarcoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 11434–11451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulay, G.; Volorio, A.; Iyer, S.; Broye, L.C.; Stamenkovic, I.; Riggi, N.; Rivera, M.N. Epigenome editing of microsatellite repeats defines tumor-specific enhancer functions and dependencies. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boro, A.; Pretre, K.; Rechfeld, F.; Thalhammer, V.; Oesch, S.; Wachtel, M.; Schafer, B.W.; Niggli, F.K. Small-molecule screen identifies modulators of EWS/FLI1 target gene expression and cell survival in Ewing’s sarcoma. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 2153–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jully, B.; Vijayalakshmi, R.; Gopal, G.; Sabitha, K.; Rajkumar, T. Junction region of EWS-FLI1 fusion protein has a dominant negative effect in Ewing’s Sarcoma in vitro. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-R.; Jung, W.-W.; Kim, H.-S.; Park, Y.-K. Microarray-based DNA methylation study of Ewing’s sarcoma of the bone. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 8, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liebner, D.A. The indications and efficacy of conventional chemotherapy in primary and recurrent sarcoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 111, 622–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, S.J.; Frezza, A.M.; Abecassis, N.; Bajpai, J.; Bauer, S.; Biagini, R.; Bielack, S.; Blay, J.Y.; Bolle, S.; Bonvalot, S.; et al. Bone sarcomas: ESMO-EURACAN-GENTURIS-ERN PaedCan Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1520–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Dirksen, U.; Bielack, S. Sarcomas of Soft Tissue and Bone. Prog Tumor Res. 2016, 43, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzetti, G.-A.; Laud-Duval, K.; van der Ent, W.; Brisac, A.; Irondelle, M.; Aubert, S.; Dirksen, U.; Bouvier, C.; De Pinieux, G.; Snaar-Jagalska, E.; et al. Cell-to-cell heterogeneity of EWSR1-FLI1 activity determines proliferation/migration choices in Ewing sarcoma cells. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3505–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katschnig, A.M.; Kauer, M.O.; Schwentner, R.; Tomazou, E.M.; Mutz, C.N.; Linder, M.; Sibilia, M.; Alonso, J.; Aryee, D.N.T.; Kovar, H. EWS-FLI1 perturbs MRTFB/YAP-1/TEAD target gene regulation inhibiting cytoskeletal autoregulatory feedback in Ewing sarcoma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5995–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkizan, H.V.; Kong, Y.; Merchant, M.; Schlottmann, S.; Barber-Rotenberg, J.S.; Yuan, L.; Abaan, O.D.; Chou, T.H.; Dakshanamurthy, S.; Brown, M.L.; et al. A small molecule blocking oncogenic protein EWS-FLI1 interaction with RNA helicase A inhibits growth of Ewing’s sarcoma. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povedano, J.M.; Li, V.; Lake, K.E.; Bai, X.; Rallabandi, R.; Kim, J.; Xie, Y.; De Brabander, J.K.; McFadden, D.G. TK216 targets microtubules in Ewing sarcoma cells. Cell Chem. Biol. 2022, 29, 1325–1332.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukowinski, A.; Chang, B.; Reid, J.M.; Liu, X.; Minard, C.G.; Trepel, J.B.; Lee, M.J.; Fox, E.; Weigel, B.J. A phase 1 study of entinostat in children and adolescents with recurrent or refractory solid tumors, including CNS tumors: Trial ADVL1513, Pediatric Early Phase-Clinical Trial Network (PEP-CTN). Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e28892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, B.K.; da Costa Lopez, P.L.; Menegotto, P.R.; Vieira, I.A.; Kersting, N.; Abujamra, A.L.; Brunetto, A.T.; Brunetto, A.L.; Gregianin, L.; de Farias, C.B.; et al. Targeting Histone Deacetylase Activity to Arrest Cell Growth and Promote Neural Differentiation in Ewing Sarcoma. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 7242–7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Dominguez, D.J.; Hontecillas-Prieto, L.; Rodriguez-Nunez, P.; Pascual-Pasto, G.; Vila-Ubach, M.; Garcia-Mejias, R.; Robles, M.J.; Tirado, O.M.; Mora, J.; Carcaboso, A.M.; et al. The combination of epigenetic drugs SAHA and HCI-2509 synergistically inhibits EWS-FLI1 and tumor growth in Ewing sarcoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 31397–31410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattenden, S.G.; Simon, J.M.; Wali, A.; Jayakody, C.N.; Troutman, J.; McFadden, A.W.; Wooten, J.; Wood, C.C.; Frye, S.V.; Janzen, W.P.; et al. High-throughput small molecule screen identifies inhibitors of aberrant chromatin accessibility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3018–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorzi, A.P.; Bernstein, M.; Samson, Y.; Wall, D.A.; Desai, S.; Nicksy, D.; Wainman, N.; Eisenhauer, E.; Baruchel, S. A phase I study of histone deacetylase inhibitor, pracinostat (SB939), in pediatric patients with refractory solid tumors: IND203 a trial of the NCIC IND program/C17 pediatric phase I consortium. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1868–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witt, O.; Milde, T.; Deubzer, H.E.; Oehme, I.; Witt, R.; Kulozik, A.; Eisenmenger, A.; Abel, U.; Karapanagiotou-Schenkel, I. Phase I/II intra-patient dose escalation study of vorinostat in children with relapsed solid tumor, lymphoma or leukemia. Klin Padiatr. 2012, 224, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, L.A.; Kowalewski, A.A.; Lessnick, S.L. EWS/FLI mediates transcriptional repression via NKX2.2 during oncogenic transformation in Ewing’s sarcoma. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnemann, J.; Dreyer, L.; Hartwig, M.; Palani, C.D.; Hong, L.T.T.; Klier, U.; Bröker, B.; Völker, U.; Beck, J.F. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce cell death and enhance the apoptosis-inducing activity of TRAIL in Ewing’s sarcoma cells. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 133, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakimura, R.; Tanaka, K.; Nakatani, F.; Matsunobu, T.; Li, X.; Hanada, M.; Okada, T.; Nakamura, T.; Matsumoto, Y.; Iwamoto, Y. Antitumor effects of histone deacetylase inhibitor on Ewing’s family tumors. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 116, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pishas, K.I.; Drenberg, C.D.; Taslim, C.; Theisen, E.R.; Johnson, K.M.; Saund, R.S.; Pop, I.L.; Crompton, B.D.; Lawlor, E.R.; Tirode, F.; et al. Therapeutic Targeting of KDM1A/LSD1 in Ewing Sarcoma with SP-2509 Engages the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1902–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Lan, F.; Matson, C.; Mulligan, P.; Whetstine, J.R.; Cole, P.A.; Casero, R.A.; Shi, Y. Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell 2004, 119, 941–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majello, B.; Gorini, F.; Saccà, C.D.; Amente, S. Expanding the Role of the Histone Lysine-Specific Demethylase LSD1 in Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, S.; Bell, R.; Stephens, B.; Zhuo, R.; Sharma, S.; Bearss, D.; Lessnick, S.L. Mechanism and relevance of EWS/FLI-mediated transcriptional repression in Ewing sarcoma. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5089–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, S.M.; Pappo, A.S.; Sahr, N.; Sykes, A.; Campagne, O.; Stewart, C.F.; Clay, M.R.; Bahrami, A.; McCarville, M.B.; Kaste, S.C.; et al. A phase I trial of talazoparib and irinotecan with and without temozolomide in children and young adults with recurrent or refractory solid malignancies. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 137, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, D.E.; Collins, J.M.; Dawahare, J.H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Lin, Y.; Voytik-Harbin, S.L.; Zorlutuna, P.; Yoder, M.C.; Boerckel, J.D. YAP and TAZ limit cytoskeletal and focal adhesion maturation to enable persistent cell motility. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 1369–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Taouk, G.M. A Potential Role of YAP/TAZ in the Interplay Between Metastasis and Metabolic Alterations. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, B.K.A.; Dharia, N.V.; Lin, S.; Donovan, K.A.; Chong, S.; Robichaud, A.; Conway, A.; Hamze, A.; Ross, L.; Alexe, G.; et al. TRIM8 modulates the EWS/FLI oncoprotein to promote survival in Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1262–1278.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, K.; Cost, C.; Davis, I.; Glade-Bender, J.; Grohar, P.; Houghton, P.; Isakoff, M.; Stewart, E.; Laack, N.; Yustein, J.; et al. Emerging novel agents for patients with advanced Ewing sarcoma: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group (COG) New Agents for Ewing Sarcoma Task Force. F1000Research 2019, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggi, N.; Cironi, L.; Provero, P.; Suva, M.L.; Kaloulis, K.; Garcia-Echeverria, C.; Hoffmann, F.; Trumpp, A.; Stamenkovic, I. Development of Ewing’s sarcoma from primary bone marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 11459–11468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggi, N.; Suva, M.L.; Suva, D.; Cironi, L.; Provero, P.; Tercier, S.; Joseph, J.M.; Stehle, J.C.; Baumer, K.; Kindler, V.; et al. EWS-FLI-1 expression triggers a Ewing’s sarcoma initiation program in primary human mesenchymal stem cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2176–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindén, M.; Vannas, C.; Österlund, T.; Andersson, L.; Osman, A.; Escobar, M.; Fagman, H.; Ståhlberg, A.; Åman, P. FET fusion oncoproteins interact with BRD4 and SWI/SNF chromatin remodelling complex subtypes in sarcoma. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 2470–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neckles, C.; Boer, R.; Aboreden, N.; Walker, R.L.; Kim, B.-H.; Kim, S.; Schneekloth, J.S.; Caplen, N.J. HNRNPH1-dependent splicing of a fusion oncogene reveals a targetable RNA G-quadruplex interaction. RNA 2019, 25, 1731–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangwal, K.; Sankar, S.; Hollenhorst, P.C.; Kinsey, M.; Haroldsen, S.C.; Shah, A.A.; Boucher, K.M.; Watkins, W.S.; Jorde, L.B.; Graves, B.J.; et al. Microsatellites as EWS/FLI response elements in Ewing’s sarcoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10149–10154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Simon, J.M.; Iglesia, M.D.; Wu, S.B.; McFadden, A.W.; Lieb, J.D.; Davis, I.J. Tumor-specific retargeting of an oncogenic transcription factor chimera results in dysregulation of chromatin and transcription. Genome Res. 2011, 22, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillon, N.; Tirode, F.; Boeva, V.; Zynovyev, A.; Barillot, E.; Delattre, O. The Oncogenic EWS-FLI1 Protein Binds In Vivo GGAA Microsatellite Sequences with Potential Transcriptional Activation Function. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggi, N.; Knoechel, B.; Gillespie, S.M.; Rheinbay, E.; Boulay, G.; Suvà, M.L.; Rossetti, N.E.; Boonseng, W.E.; Oksuz, O.; Cook, E.B.; et al. EWS-FLI1 Utilizes Divergent Chromatin Remodeling Mechanisms to Directly Activate or Repress Enhancer Elements in Ewing Sarcoma. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cidre-Aranaz, F.; Alonso, J. EWS/FLI1 Target Genes and Therapeutic Opportunities in Ewing Sarcoma. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siligan, C.; Ban, J.; Bachmaier, R.; Spahn, L.; Kreppel, M.; Schaefer, K.L.; Poremba, C.; Aryee, D.N.; Kovar, H. EWS-FLI1 target genes recovered from Ewing’s sarcoma chromatin. Oncogene 2005, 24, 2512–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.; Owen, L.A.; Trem, D.J.; Wong, J.S.; Whangbo, J.S.; Golub, T.R.; Lessnick, S.L. Expression profiling of EWS/FLI identifies NKX2.2 as a critical target gene in Ewing’s sarcoma. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, J.D.; Lessnick, S.L. A transcriptional profiling meta-analysis reveals a core EWS-FLI gene expression signature. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunreiter, C.L.; Hancock, J.D.; Coffin, C.M.; Boucher, K.; Lessnick, S.L. Expression of EWS-ETS Fusions in NIH3T3 Cells Reveals Significant Differences to Ewing’s Sarcoma. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 2753–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deneen, B.; Welford, S.M.; Ho, T.; Hernandez, F.; Kurland, I.; Denny, C.T. PIM3 Proto-Oncogene Kinase Is a Common Transcriptional Target of Divergent EWS/ETS Oncoproteins. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 23, 3897–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessnick, S.L.; Dacwag, C.S.; Golub, T.R. The Ewing’s sarcoma oncoprotein EWS/FLI induces a p53-dependent growth arrest in primary human fibroblasts. Cancer Cell 2002, 1, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirode, F.; Laud-Duval, K.; Prieur, A.; Delorme, B.; Charbord, P.; Delattre, O. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Features of Ewing Tumors. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L.; Shimada, H.; Schofield, D.E.; Triche, T.J. EWS-FLI1 fusion protein up-regulates critical genes in neural crest development and is responsible for the observed phenotype of Ewing’s family of tumors. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4633–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rorie, C.J.; Thomas, V.D.; Chen, P.; Pierce, H.H.; O’Bryan, J.P.; Weissman, B.E. The Ews/Fli-1 Fusion Gene Switches the Differentiation Program of Neuroblastomas to Ewing Sarcoma/Peripheral Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsey, M.; Smith, R.; Lessnick, S.L. NR0B1 is required for the oncogenic phenotype mediated by EWS/FLI in Ewing’s sarcoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2006, 4, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Nakatani, F.; Matsunobu, T.; Matsuda, S.; Iwamoto, Y. Downregulation and forced expression of EWS-Fli1 fusion gene results in changes in the expression of G1regulatory genes. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 84, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Hwang, E.E.; Guha, R.; O’Neill, A.F.; Melong, N.; Veinotte, C.J.; Saur, A.C.; Wuerthele, K.; Shen, M.; McKnight, C.; et al. High-throughput Chemical Screening Identifies Focal Adhesion Kinase and Aurora Kinase B Inhibition as a Synergistic Treatment Combination in Ewing Sarcoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4552–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Turkalo, T.K.; Nelson, K.; Folmsbee, S.S.; Robb, C.; Roper, B.; Azuma, M. Ewing sarcoma EWS protein regulates midzone formation by recruiting Aurora B kinase to the midzone. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G.E.; Rix, U.; Lissat, A.; Stukalov, A.; Mullner, M.K.; Bennett, K.L.; Colinge, J.; Nijman, S.M.; Kubicek, S.; Kovar, H.; et al. An integrated chemical biology approach identifies specific vulnerability of Ewing’s sarcoma to combined inhibition of Aurora kinases A and B. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1846–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakahara, K.; Ohno, T.; Kimura, M.; Masuda, T.; Nozawa, S.; Dohjima, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Nagano, A.; Kawai, G.; Matsuhashi, A.; et al. EWS-Fli1 Up-Regulates Expression of the Aurora A and Aurora B Kinases. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vibert, J.; Saulnier, O.; Collin, C.; Petit, F.; Borgman, K.J.; Vigneau, J.; Gautier, M.; Zaidi, S.; Pierron, G.; Watson, S.; et al. Oncogenic chimeric transcription factors drive tumor-specific transcription, processing, and translation of silent genomic regions. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 2458–2471.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques Howarth, M.; Simpson, D.; Ngok, S.P.; Nieves, B.; Chen, R.; Siprashvili, Z.; Vaka, D.; Breese, M.R.; Crompton, B.D.; Alexe, G.; et al. Long noncoding RNA EWSAT1-mediated gene repression facilitates Ewing sarcoma oncogenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 5275–5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, P.J.; Ju, B.G.; Telese, F.; Wang, X.; Glass, C.K.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Tyrosine dephosphorylation of H2AX modulates apoptosis and survival decisions. Nature 2009, 458, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, J.; Jug, G.; Mestdagh, P.; Schwentner, R.; Kauer, M.; Aryee, D.N.; Schaefer, K.L.; Nakatani, F.; Scotlandi, K.; Reiter, M.; et al. Hsa-mir-145 is the top EWS-FLI1-repressed microRNA involved in a positive feedback loop in Ewing’s sarcoma. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2173–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggi, N.; Suvà, M.-L.; De Vito, C.; Provero, P.; Stehle, J.-C.; Baumer, K.; Cironi, L.; Janiszewska, M.; Petricevic, T.; Suvà, D.; et al. EWS-FLI-1 modulates miRNA145 and SOX2 expression to initiate mesenchymal stem cell reprogramming toward Ewing sarcoma cancer stem cells. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 916–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinsey, E.L.; Parrish, J.K.; Irwin, A.E.; Niemeyer, B.F.; Kern, H.B.; Birks, D.K.; Jedlicka, P. A novel oncogenic mechanism in Ewing sarcoma involving IGF pathway targeting by EWS/Fli1-regulated microRNAs. Oncogene 2011, 30, 4910–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- France, K.A.; Anderson, J.L.; Park, A.; Denny, C.T. Oncogenic Fusion Protein EWS/FLI1 Down-regulates Gene Expression by Both Transcriptional and Posttranscriptional Mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 22750–22757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvanathan, S.P.; Graham, G.T.; Erkizan, H.V.; Dirksen, U.; Natarajan, T.G.; Dakic, A.; Yu, S.; Liu, X.; Paulsen, M.T.; Ljungman, M.E.; et al. Oncogenic fusion protein EWS-FLI1 is a network hub that regulates alternative splicing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1307–E1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorthi, A.; Romero, J.C.; Loranc, E.; Cao, L.; Lawrence, L.A.; Goodale, E.; Iniguez, A.B.; Bernard, X.; Masamsetti, V.P.; Roston, S.; et al. EWS–FLI1 increases transcription to cause R-loops and block BRCA1 repair in Ewing sarcoma. Nature 2018, 555, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.S.; Harrell, L.M.; Wieland, D.R.; Lay, M.A.; Thompson, V.F.; Schwartz, J.C. Fusion protein EWS-FLI1 is incorporated into a protein granule in cells. RNA 2021, 27, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulay, G.; Sandoval, G.J.; Riggi, N.; Iyer, S.; Buisson, R.; Naigles, B.; Awad, M.E.; Rengarajan, S.; Volorio, A.; McBride, M.J.; et al. Cancer-Specific Retargeting of BAF Complexes by a Prion-like Domain. Cell 2017, 171, 163–178.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, S.; Dugast-Darzacq, C.; Liu, Z.; Dong, P.; Dailey, G.M.; Cattoglio, C.; Heckert, A.; Banala, S.; Lavis, L.; Darzacq, X.; et al. Imaging dynamic and selective low-complexity domain interactions that control gene transcription. Science 2018, 361, eaar2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, S.; Graham, T.G.; Dugast-Darzacq, C.; Dailey, G.M.; Darzacq, X.; Tjian, R. Tuning levels of low-complexity domain interactions to modulate endogenous oncogenic transcription. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 2084–2097.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwentner, R.; Papamarkou, T.; Kauer, M.O.; Stathopoulos, V.; Yang, F.; Bilke, S.; Meltzer, P.S.; Girolami, M.; Kovar, H. EWS-FLI1 employs an E2F switch to drive target gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 2780–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, R.; Tanaka, M.; Tsutsumi, S.; Aburatani, H.; Yamazaki, Y.; Homme, M.; Kitagawa, Y.; Nakamura, T. EWS-FLI 1 regulates a transcriptional program in cooperation with Foxq1 in mouse Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2907–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, C.; Rey, L.; Rodriguez, J.; Fernandez, M.J.; Troncoso, D.; Canas, A.; Moreno, O.; Henriquez, B.; Rojas, A. Epigenetic control of the EWSFLI1 promoter in Ewing’s sarcoma. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi, C.; Boro, A.; Rechfeld, F.; Lopez-Garcia, L.A.; Gierisch, M.E.; Schafer, B.W.; Niggli, F.K. PI3K/AKT signaling modulates transcriptional expression of EWS/FLI1 through specificity protein 1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 28895–28910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryee, D.N.; Niedan, S.; Kauer, M.; Schwentner, R.; Bennani-Baiti, I.M.; Ban, J.; Muehlbacher, K.; Kreppel, M.; Walker, R.L.; Meltzer, P.; et al. Hypoxia modulates EWS-FLI1 transcriptional signature and enhances the malignant properties of Ewing’s sarcoma cells in vitro. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4015–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grohar, P.J.; Kim, S.; Rivera, G.O.R.; Sen, N.; Haddock, S.; Harlow, M.L.; Maloney, N.K.; Zhu, J.; O’Neill, M.; Jones, T.L.; et al. Functional Genomic Screening Reveals Splicing of the EWS-FLI1 Fusion Transcript as a Vulnerability in Ewing Sarcoma. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, T.; Bakaric, A.; Waszyk, P.; Boulay, G.; Torsello, M.; Cornaz-Buros, S.; Chevalier, N.; Geiser, T.; Martin, P.; Volorio, A.; et al. LIN28B Underlies the Pathogenesis of a Subclass of Ewing Sarcoma LIN28B Control of EWS-FLI1 Stability. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 4567–4583.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Lin, D.-C.; Cao, Q.; Guo, X.; Marijon, H.; Zhao, Z.; Gery, S.; Xu, L.; Yang, H.; Pang, B.; et al. CRM1 Inhibition Promotes Cytotoxicity in Ewing Sarcoma Cells by Repressing EWS-FLI1–Dependent IGF-1 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2687–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xie, Y.; Girnita, L.; Nilsson, G.; Dricu, A.; Wejde, J.; Larsson, O. Regulatory role of mevalonate and N-linked glycosylation in proliferation and expression of the EWS/FLI-1 fusion protein in Ewing’s sarcoma cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 246, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girnita, L.; Wang, M.; Xie, Y.; Nilsson, G.; Dricu, A.; Wejde, J.; Larsson, O. Inhibition of N-linked glycosylation down-regulates insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor at the cell surface and kills Ewing’s sarcoma cells: Therapeutic implications. Anticancer Drug Des. 2000, 15, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Klevernic, I.V.; Morton, S.; Davis, R.J.; Cohen, P. Phosphorylation of Ewing’s sarcoma protein (EWS) and EWS-Fli1 in response to DNA damage. Biochem. J. 2009, 418, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmaier, R.; Aryee, D.N.; Jug, G.; Kauer, M.; Kreppel, M.; Lee, K.A.; Kovar, H. O-GlcNAcylation is involved in the transcriptional activity of EWS-FLI1 in Ewing’s sarcoma. Oncogene 2009, 28, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlottmann, S.; Erkizan, H.V.; Barber-Rotenberg, J.S.; Knights, C.; Cheema, A.; Üren, A.; Avantaggiati, M.L.; Toretsky, J.A. Acetylation Increases EWS-FLI1 DNA Binding and Transcriptional Activity. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierisch, M.E.; Pfistner, F.; Lopez-Garcia, L.A.; Harder, L.; Schäfer, B.W.; Niggli, F.K. Proteasomal Degradation of the EWS-FLI1 Fusion Protein Is Regulated by a Single Lysine Residue. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 26922–26933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzi, D.J.; Song, M.; Hakala, K.; Weintraub, S.T.; Shiio, Y. Proteomic Analysis of the EWS-Fli-1 Interactome Reveals the Role of the Lysosome in EWS-Fli-1 Turnover. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 3783–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Vital, T.; Zhang, J.; Laggner, C.; Nguyen, K.T.; Zhu, Z.; Prevatte, A.W.; et al. SPOP and OTUD7A Control EWS-FLI1 Protein Stability to Govern Ewing Sarcoma Growth. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2004846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierisch, M.E.; Pedot, G.; Walser, F.; Lopez-Garcia, L.A.; Jaaks, P.; Niggli, F.K.; Schäfer, B.W. USP19 deubiquitinates EWS-FLI1 to regulate Ewing sarcoma growth. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toretsky, J.A.; Erkizan, V.; Levenson, A.; Abaan, O.D.; Parvin, J.D.; Cripe, T.P.; Rice, A.M.; Lee, S.B.; Üren, A. Oncoprotein EWS-FLI1 Activity Is Enhanced by RNA Helicase A. Cancer Res 2006, 66, 5574–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, J.C.; Feng, F.Y.; Han, S.; Patel, S.; Goyal, S.V.; Bou-Maroun, L.M.; Liu, M.; Lonigro, R.; Prensner, J.R.; Tomlins, S.A.; et al. PARP-1 inhibition as a targeted strategy to treat Ewing’s sarcoma. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1608–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolotti, A.; Melot, T.; Acker, J.; Vigneron, M.; Delattre, O.; Tora, L. EWS, but Not EWS-FLI-1, Is Associated with Both TFIID and RNA Polymerase II: Interactions between Two Members of the TET Family, EWS and hTAF II 68, and Subunits of TFIID and RNA Polymerase II Complexes. Mol. Cell Biol. 1998, 18, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.K.; Robinson, L.; Hodge, D.R.; Kola, I.; Papas, T.S.; Seth, A. FLI1 and EWS-FLI1 function as ternary complex factors and ELK1 and SAP1a function as ternary and quaternary complex factors on the Egr1 promoter serum response elements. Oncogene 1997, 14, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spahn, L.; Petermann, R.; Siligan, C.; Schmid, J.A.; Aryee, D.N.; Kovar, H. Interaction of the EWS NH2 terminus with BARD1 links the Ewing’s sarcoma gene to a common tumor suppressor pathway. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 4583–4587. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Denny, C.T.; Wisdom, R. Cooperative DNA Binding with AP-1 Proteins Is Required for Transformation by EWS-Ets Fusion Proteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 2467–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Nataraj, N.B.; Sekar, A.; Ghosh, S.; Bornstein, C.; Drago-Garcia, D.; Roth, L.; Romaniello, D.; Marrocco, I.; David, E.; et al. ETS Proteins Bind with Glucocorticoid Receptors: Relevance for Treatment of Ewing Sarcoma. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 104–117.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileva, E.; Warren, M.; Triche, T.J.; Amatruda, J.F. Dysregulated heparan sulfate proteoglycan metabolism promotes Ewing sarcoma tumor growth. Elife 2022, 11, e69734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, C.; Reina, J.; Herrero, A.; Heinen, J.P.; Méndiz, V.; Bonnal, S.; Irimia, M.; Sánchez-Jiménez, M.; Sánchez-Molina, S.; Mora, J.; et al. Human EWS-FLI protein recapitulates in Drosophila the neomorphic functions that induce Ewing sarcoma tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. Nexus 2022, 1, pgac222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedlicka, P. Ewing Sarcoma, an enigmatic malignancy of likely progenitor cell origin, driven by transcription factor oncogenic fusions. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2010, 3, 338–347. [Google Scholar]
- Toomey, E.C.; Schiffman, J.D.; Lessnick, S.L. Recent advances in the molecular pathogenesis of Ewing’s sarcoma. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4504–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackintosh, C.; Madoz-Gurpide, J.; Ordonez, J.L.; Osuna, D.; Herrero-Martin, D. The molecular pathogenesis of Ewing’s sarcoma. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 9, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirode, F.; Surdez, D.; Ma, X.; Parker, M.; Le Deley, M.C.; Bahrami, A.; Zhang, Z.; Lapouble, E.; Grossetête-Lalami, S.; Rusch, M.; et al. Genomic Landscape of Ewing Sarcoma Defines an Aggressive Subtype with Co-Association of STAG2 and TP53 Mutations. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1342–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aynaud, M.-M.; Mirabeau, O.; Gruel, N.; Grossetête, S.; Boeva, V.; Durand, S.; Surdez, D.; Saulnier, O.; Zaïdi, S.; Gribkova, S.; et al. Transcriptional Programs Define Intratumoral Heterogeneity of Ewing Sarcoma at Single-Cell Resolution. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1767–1779.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagodzińska-Mucha, P.; Sobczuk, P.; Mikuła, M.; Raciborska, A.; Dawidowska, A.; Kulecka, M.; Bilska, K.; Szumera-Ciećkiewicz, A.; Kluska, A.; Piątkowska, M.; et al. Mutational landscape of primary and recurrent Ewing sarcoma. Contemp. Oncol. 2021, 25, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brohl, A.S.; Ms, R.P.; Turner, C.E.; Wen, X.; Song, Y.K.; Wei, J.S.; Calzone, K.A.; Khan, J. Frequent inactivating germline mutations in DNA repair genes in patients with Ewing sarcoma. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 19, 955–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompton, B.; Stewart, C.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Alexa, G.; Kurek, K.; Calicchio, M.; Kiezun, A.; Carter, S.; Shukla, S.; Mehta, S.; et al. Abstract 999: The genomic landscape of pediatric Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1326–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillani, R.; Camp, S.Y.; Han, S.; Jones, J.K.; Chu, H.; O’Brien, S.; Young, E.L.; Hayes, L.; Mitchell, G.; Fowler, T.; et al. Germline predisposition to pediatric Ewing sarcoma is characterized by inherited pathogenic variants in DNA damage repair genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 1026–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, G.; Surdez, D.; Tirode, F.; Laud, K.; Barillot, E.; Zinovyev, A.; Delattre, O. Systems biology of Ewing sarcoma: A network model of EWS-FLI1 effect on proliferation and apoptosis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 8853–8871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, E.J.; Li, H.; Reidy, K.; Beers, L.F.; Christensen, B.L.; Lee, S.B. EWS/FLI1 Oncogene Activates Caspase 3 Transcription and Triggers Apoptosis In vivo. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Ent, W.; Jochemsen, A.G.; Teunisse, A.F.; Krens, S.F.; Szuhai, K.; Spaink, H.P.; Hogendoorn, P.C.; Snaar-Jagalska, B.E. Ewing sarcoma inhibition by disruption of EWSR1-FLI1 transcriptional activity and reactivation of p53. J. Pathol. 2014, 233, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Glasgow, E.; Agarwal, S. Zebrafish Xenografts for Drug Discovery and Personalized Medicine. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, S.; Vaeteewoottacharn, K.; Kariya, R. Application of Highly Immunocompromised Mice for the Establishment of Patient-Derived Xenograft (PDX) Models. Cells 2019, 8, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Neumann, C.A.; LeDuc, P.R. Tumor-on-a-chip for integrating a 3D tumor microenvironment: Chemical and mechanical factors. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, R.M. Patient-derived orthotopic xenografts: Better mimic of metastasis than subcutaneous xenografts. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, E.; Federico, S.M.; Chen, X.; Shelat, A.A.; Bradley, C.; Gordon, B.; Karlstrom, A.; Twarog, N.R.; Clay, M.R.; Bahrami, A.; et al. Orthotopic patient-derived xenografts of paediatric solid tumours. Nature 2017, 549, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| FET | ETS | Fusion Gene | Frequency | Translocation |
| EWSR1 | FLI1 | EWSR1-FLI1 | 85% | t(11; 22)(q24; q12) |
| EWSR1 | ERG | EWSR1-ERG | 10% | t(21; 12)(q22; q12) |
| EWSR1 | FEV | EWSR1-FEV | <1% | t(2; 22)(q33; q12) |
| EWSR1 | ETV1 | EWSR1-ETV1 | <1% | t(7; 22)(p22; q12) |
| EWSR1 | E1AF | EWSR1-E1AF | <1% | t(17; 22)(q21; q12 |
| FUS | FEV | FUS-FEV | <1% | t(2; 16)(q35; p11) |
| FUS | ERG | FUS-ERG | <1% | t(16; 21)(p11; q22) |
| ETS | FET | Fusion gene | Frequency | Translocation |
| FLI1 | EWSR1 | FLI1-EWSR1 | TBD | t(22; 11)(q12; q24) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Davis, I.J.; Liu, P. Regulation of EWSR1-FLI1 Function by Post-Transcriptional and Post-Translational Modifications. Cancers 2023, 15, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020382
Yu L, Davis IJ, Liu P. Regulation of EWSR1-FLI1 Function by Post-Transcriptional and Post-Translational Modifications. Cancers. 2023; 15(2):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020382
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Le, Ian J. Davis, and Pengda Liu. 2023. "Regulation of EWSR1-FLI1 Function by Post-Transcriptional and Post-Translational Modifications" Cancers 15, no. 2: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020382
APA StyleYu, L., Davis, I. J., & Liu, P. (2023). Regulation of EWSR1-FLI1 Function by Post-Transcriptional and Post-Translational Modifications. Cancers, 15(2), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020382







