Predictive Biomarkers for Immune-Related Endocrinopathies following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Treatment
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Thyroiditis
2.1. Pre-Treatment
2.2. During-Treatment
3. Hypopituitarism
3.1. Pre-Treatment
3.2. During Treatment
4. Type-1 Diabetes Mellitus
5. Endocrine irAEs
5.1. Pre-Treatment
5.2. During-Treatment
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Debela, D.T.; Muzazu, S.G.; Heraro, K.D.; Ndalama, M.T.; Mesele, B.W.; Haile, D.C.; Kitui, S.K.; Manyazewal, T. New Approaches and Procedures for Cancer Treatment: Current Perspectives. SAGE Open Med. 2021, 9, 205031212110343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albandar, H.J.; Fuqua, J.; Albandar, J.M.; Safi, S.; Merrill, S.A.; Ma, P.C. Immune-Related Adverse Events (Irae) in Cancer Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (Ici) and Survival Outcomes Correlation: To Rechallenge or Not? Cancers 2021, 13, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koustas, E.; Sarantis, P.; Papavassiliou, A.G.; Karamouzis, M.V. The Resistance Mechanisms of Checkpoint Inhibitors in Solid Tumors. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, W.; Li, N.; Neri, S.; Sharma, A.; Jiang, W.; Lin, S.H. Combining Immunotherapy and Radiotherapy for Cancer Treatment: Current Challenges and Future Directions. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Bondarenko, I.; Luft, A.; Serwatowski, P.; Barlesi, F.; Chacko, R.; Sebastian, M.; Lu, H.; Cuillerot, J.M.; Lynch, T.J. Ipilimumab in Combination with Paclitaxel and Carboplatin as First-Line Therapy in Extensivedisease-Small-Cell Lungcancer: Results from a Randomized, Double-Blind, Multicenter Phase 2 Trial. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Kumar, A.B.; Finnes, H.; Markovic, S.N.; Park, S.; Dronca, R.S.; Dong, H. Combining Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors With Conventional Cancer Therapy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, B.J.; Naidoo, J.; Santomasso, B.D.; Lacchetti, C.; Adkins, S.; Anadkat, M.; Atkins, M.B.; Brassil, K.J.; Caterino, J.M.; Chau, I.; et al. Management of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Patients Treated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy: ASCO Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 4073–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, E.P.; Mooradian, M.J.; Baruch, E.N.; Yilmaz, M.; Reynolds, K.L. Immune-Related Adverse Events (IrAEs): Diagnosis, Management, and Clinical Pearls. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 22, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. 2009; pp. 1–78. Available online: Https://Evs.Nci.Nih.Gov/Ftp1/CTCAE/CTCAE_4.03/Archive/CTCAE_4.0_2009-05-29_QuickReference_8.5x11.Pdf (accessed on 22 October 2022).
- Zhou, X.; Yao, Z.; Yang, H.; Liang, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F. Are Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated with the Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients with Cancer? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.S.; Fernandez, C.J.; Eapen, D.; Pappachan, J.M. Organ-Specific Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy, with Special Reference to Endocrinopathies. Eur. Endocrinol. 2021, 1, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kichenadasse, G.; Miners, J.O.; Mangoni, A.A.; Rowland, A.; Hopkins, A.M.; Sorich, M.J. Multiorgan Immune-Related Adverse Events During Treatment With Atezolizumab. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoest, J. Clinical Features, Predictive Correlates, and Pathophysiology of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatments in Cancer: A Short Review. ImmunoTargets Ther. 2017, 6, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parakh, S.; Cebon, J.; Klein, O. Delayed Autoimmune Toxicity Occurring Several Months After Cessation of Anti-PD-1 Therapy. Oncologist 2018, 23, 849–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spain, L.; Diem, S.; Larkin, J. Management of Toxicities of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 44, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoja, L.; Day, D.; Wei-Wu Chen, T.; Siu, L.L.; Hansen, A.R. Tumour- and Class-Specific Patterns of Immune-Related Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michot, J.M.; Bigenwald, C.; Champiat, S.; Collins, M.; Carbonnel, F.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Berdelou, A.; Varga, A.; Bahleda, R.; Hollebecque, A.; et al. Immune-Related Adverse Events with Immune Checkpoint Blockade: A Comprehensive Review. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 54, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Chaudhary, N.; Garg, M.; Floudas, C.S.; Soni, P.; Chandra, A.B. Current Diagnosis and Management of Immune Related Adverse Events (IrAEs) Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmann, G.; Nguyen, V.A.; Plaickner, J.; Jaschke, W. Imaging Features of Toxicities by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Curr. Radiol. Rep. 2016, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso-Sousa, R.; Barry, W.T.; Garrido-Castro, A.C.; Hodi, F.S.; Min, L.; Krop, I.E.; Tolaney, S.M. Incidence of Endocrine Dysfunction Following the Use of Different Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Regimens: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Rodríguez, E.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Review and Management of Endocrine Adverse Events. Oncologist 2016, 21, 804–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filette, J.; Andreescu, C.E.; Cools, F.; Bravenboer, B.; Velkeniers, B. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Endocrine-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Horm. Metab. Res. 2019, 51, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattersley, R.; Nana, M.; Lansdown, A.J. Endocrine Complications of Immunotherapies: A Review. Clin. Med. 2021, 21, E212–E222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.S.; Barroso-Sousa, R.; Tolaney, S.M.; Hodi, F.S.; Kaiser, U.B.; Min, L. Endocrine Toxicity of Cancer Immunotherapy Targeting Immune Checkpoints. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 17–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA-NIH Biomarker Working Group. BEST (Biomarkers, EndpointS, and Other Tools) Resource; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA; National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Califf, R.M. Minireview Biomarker Definitions and Their Applications. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 243, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strimbu, K.; Tavel, J.A. What Are Biomarkers? Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2010, 5, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimbara, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Iwama, S.; Ohashi, K.; Kuchiba, A.; Arima, H.; Yamazaki, N.; Kitano, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Ohe, Y. Association of Antithyroglobulin Antibodies with the Development of Thyroid Dysfunction Induced by Nivolumab. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 3583–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luongo, C.; Morra, R.; Gambale, C.; Porcelli, T.; Sessa, F.; Matano, E.; Damiano, V.; Klain, M.; Schlumberger, M.; Salvatore, D. Higher Baseline TSH Levels Predict Early Hypothyroidism during Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 1927–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollack, R.M.; Kagan, M.; Lotem, M.; Dresner-Pollak, R. Baseline TSH Level Is Associated with Risk of Anti–PD-1–Induced Thyroid Dysfunction. Endocr. Pract. 2019, 25, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilli, L.; Danielli, R.; Campanile, M.; Secchi, C.; Ciuoli, C.; Calabrò, L.; Pilli, T.; Cartocci, A.; Pacini, F.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; et al. Baseline Serum TSH Levels Predict the Absence of Thyroid Dysfunction in Cancer Patients Treated with Immunotherapy. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, C.A.; Clifton-Bligh, R.J.; Long, G.V.; Scolyer, R.A.; Lo, S.N.; Carlino, M.S.; Tsang, V.H.M.; Menzies, A.M. Thyroid Immune-Related Adverse Events Following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, E3704–E3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, N.; Iwama, S.; Okuji, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Yasuda, Y.; Wada, E.; Onoue, T.; Goto, M.; Sugiyama, M.; Tsunekawa, T.; et al. Anti-Thyroid Antibodies and Thyroid Echo Pattern at Baseline as Risk Factors for Thyroid Dysfunction Induced by Anti-Programmed Cell Death-1 Antibodies: A Pmusicrospective Study. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakida, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Uchino, J.; Chihara, Y.; Komori, S.; Asai, J.; Narukawa, T.; Arai, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Tsunezuka, H.; et al. Clinical Features of Immune-Related Thyroid Dysfunction and Its Association with Outcomes in Patients with Advanced Malignancies Treated by PD-1 Blockade. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 2140–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Iwama, S.; Yasuda, Y.; Okada, N.; Tsunekawa, T.; Onoue, T.; Takagi, H.; Hagiwara, D.; Ito, Y.; Morishita, Y.; et al. Patients with Antithyroid Antibodies Are Prone to Develop Destructive Thyroiditis by Nivolumab: A Prospective Study. J. Endocr. Soc. 2018, 2, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toi, Y.; Sugawara, S.; Sugisaka, J.; Ono, H.; Kawashima, Y.; Aiba, T.; Kawana, S.; Saito, R.; Aso, M.; Tsurumi, K.; et al. Profiling Preexisting Antibodies in Patients Treated with Anti-PD-1 Therapy for Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, J.C.; Ni, A.; Chaft, J.E.; Pollina, R.; Kasler, M.K.; Stephens, D.; Rodriguez, C.; Cambridge, L.; Rizvi, H.; Wolchok, J.D.; et al. Antibody-Mediated Thyroid Dysfunction during T-Cell Checkpoint Blockade in Patients with Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Moel, E.C.; Rozeman, E.A.; Kapiteijn, E.H.; Verdegaal, E.M.E.; Grummels, A.; Bakker, J.A.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Haanen, J.B.; Toes, R.E.M.; Van Der Woude, D. Autoantibody Development under Treatment with Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, C.A.; Wood, C.C.G.; Clifton-Blight, R.J.; Long, G.V.; Scolyer, R.A.; Carlino, M.S.; Menzies, A.M.; Tsang, V.H.M. Association of Antithyroid Antibodies in Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Thyroid Immune-Related Adverse Events. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e1843–e1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurimoto, C.; Inaba, H.; Ariyasu, H.; Iwakura, H.; Ueda, Y.; Uraki, S.; Takeshima, K.; Furukawa, Y.; Morita, S.; Yamamoto, Y.; et al. Predictive and Sensitive Biomarkers for Thyroid Dysfunctions during Treatment with Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Music, M.; Iafolla, M.; Soosaipillai, A.; Batruch, I.; Prassas, I.; Pintilie, M.; Hansen, A.R.; Bedard, P.L.; Lheureux, S.; Spreafico, A.; et al. Predicting Response and Toxicity to PD-1 Inhibition Using Serum Autoantibodies Identified from Immuno-Mass Spectrometry. F1000Research 2020, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, S.; Ashida, K.; Sakamoto, R.; Sakaguchi, C.; Ogata, M.; Maruyama, K.; Sakamoto, S.; Ikeda, M.; Ohe, K.; Akasu, S.; et al. Human Leucocyte Antigen DR15, a Possible Predictive Marker for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor–Induced Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 130, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Iwama, S.; Sugiyama, D.; Yasuda, Y.; Okuji, T.; Ito, M.; Ito, S.; Sugiyama, M.; Onoue, T.; Takagi, H.; et al. Anti-Pituitary Antibodies and Susceptible Human Leukocyte Antigen Alleles as Predictive Biomarkers for Pituitary Dysfunction Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, H.; Ariyasu, H.; Iwakura, H.; Ueda, Y.; Kurimoto, C.; Uraki, S.; Takeshima, K.; Yamaoka, H.; Furukawa, Y.; Morita, S.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Human Leucocyte Antigen between Idiopathic and Anti-PD-1 Antibody Induced Isolated Adrenocorticotropic Hormone Deficiency: A Pilot Study. Clin. Endocrinol. 2019, 91, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, S.A.; Gao, J.; Miura, Y.; Blando, J.; Tidwell, R.S.S.; Zhao, H.; Subudhi, S.K.; Tawbi, H.; Keung, E.; Wargo, J.; et al. Autoimmune Antibodies Correlate with Immune Checkpoint Therapy-Induced Toxicities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 22246–22251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanie, K.; Iguchi, G.; Bando, H.; Urai, S.; Shichi, H.; Fujita, Y.; Matsumoto, R.; Suda, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Fukuoka, H.; et al. Mechanistic Insights into Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Related Hypophysitis: A Form of Paraneoplastic Syndrome. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 3669–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, S.M.C.; Sheriff, N.; Tran, C.H.; Menzies, A.M.; Tsang, V.H.M.; Long, G.V.; Tonks, K.T.T. Fall in Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) May Be an Early Marker of Ipilimumab-Induced Hypophysitis. Pituitary 2018, 21, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.S.; Lai, Z.M.; Spain, L.; Greener, V.; Turajlic, S.; Larkin, J.; Morganstein, D.L. Predicting Development of Ipilimumab-Induced Hypophysitis: Utility of T4 and TSH Index but Not TSH. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Washino, S.; Suzuki, D.; Saikawa, R.; Tonezawa, S.; Hagiwara, R.; Funazaki, S.; Yoshida, M.; Konishi, T.; Saito, K.; et al. Hypereosinophilia Is a Predictive Biomarker of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Hypopituitarism in Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayasu, S.; Mizushiri, S.; Watanuki, Y.; Yamagata, S.; Usutani, M.; Nakada, Y.; Asari, Y.; Murasawa, S.; Kageyama, K.; Daimon, M. Eosinophil Counts Can Be a Predictive Marker of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Induced Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Tanaka, R.; Maruyama, H.; Ishitsuka, Y.; Okiyama, N.; Watanabe, R.; Fujimoto, M.; Fujisawa, Y. Correlation between Blood Cell Count and Outcome of Melanoma Patients Treated with Anti-PD-1 Antibodies. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 49, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard-Tessier, A.; Jeanville, P.; Champiat, S.; Lazarovici, J.; Voisin, A.L.; Mateus, C.; Lambotte, O.; Annereau, M.; Michot, J.M. Immune-Related Eosinophilia Induced by Anti-Programmed Death 1 or Death-Ligand 1 Antibodies. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 81, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanvion, Q.; Béné, J.; Gautier, S.; Grandvuillemin, A.; Le Beller, C.; Chenaf, C.; Etienne, N.; Brousseau, S.; Cortot, A.B.; Mortier, L.; et al. Moderate-to-Severe Eosinophilia Induced by Treatment with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: 37 Cases from a National Reference Center for Hypereosinophilic Syndromes and the French Pharmacovigilance Database. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1722022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, A.; Yarchoan, M.; Hopkins, A.; Jaffee, E.; Grossman, S.A. Relationships between Lymphocyte Counts and Treatmentrelated Toxicities and Clinical Responses in Patients with Solid Tumors Treated with PD-1 Checkpoint Inhibitors. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 114268–114280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, T.; Tomita, Y.; Roberts-Thomson, R. A Retrospective Analysis of Eosinophilia as a Predictive Marker of Response and Toxicity to Cancer Immunotherapy. Futur. Sci. OA 2020, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, H.; Kaido, Y.; Ito, S.; Hirobata, T.; Inoue, G.; Sugita, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Jinnin, M.; Kimura, H.; Kobayashi, T.; et al. Human Leukocyte Antigens and Biomarkers in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Induced by Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 37, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatouli, A.M.; Quandt, Z.; Perdigoto, A.L.; Clark, P.L.; Kluger, H.; Weiss, S.A.; Gettinger, S.; Sznol, M.; Young, A.; Rushakoff, R.; et al. Collateral Damage: Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Induced with Checkpoint Inhibitors. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Okamoto, M.; Gotoh, K.; Masaki, T.; Ozeki, Y.; Ando, H.; Anai, M.; Sato, A.; Yoshida, Y.; Ueda, S.; et al. Fulminant Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus with Anti-Programmed Cell Death-1 Therapy. J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.; Shono-Saito, T.; Yamate, T.; Kai, Y.; Sakai, T.; Shimizu, F.; Yamada, Y.; Mori, H.; Noso, S.; Ikegami, H.; et al. A Case of Fulminant Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus, with a Precipitous Decrease in Pancreatic Volume, Induced by Nivolumab for Malignant Melanoma: Analysis of HLA and CTLA-4 Polymorphisms. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2017, 27, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, Y.; Udagawa, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Imai, K.; Ohashi, K.; Ishibashi, M.; Kirita, K.; Umemura, S.; Yoh, K.; Niho, S.; et al. Association of Serum Anti-GAD Antibody and HLA Haplotypes with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Triggered by Nivolumab in Patients with Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, e41–e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishi, A.; Tanaka, I.; Iwama, S.; Sakakibara, T.; Mastui, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Hase, T.; Morise, M.; Sato, M.; Arima, H.; et al. Efficacies of Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand 1 Blockade in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Acquired Resistance to Prior Programmed Cell Death 1 Inhibitor and Development of Diabetic Ketoacidosis Caused by Two Different Etiologies: A Retrospective. Endocr. J. 2021, 68, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Preiato, V.; Salvagni, S.; Ricci, C.; Ardizzoni, A.; Pagotto, U.; Pelusi, C. Diabetes Mellitus Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: Type 1 Diabetes Variant or New Clinical Entity? Review of the Literature. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2021, 22, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchand, L.; Thivolet, A.; Dalle, S.; Chikh, K.; Reffet, S.; Vouillarmet, J.; Fabien, N.; Cugnet-Anceau, C.; Thivolet, C. Diabetes Mellitus Induced by PD-1 and PD-L1 Inhibitors: Description of Pancreatic Endocrine and Exocrine Phenotype. Acta Diabetol. 2019, 56, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheema, A.; Makadia, B.; Karwadia, T.; Bajwa, R.; Hossain, M. Autoimmune Diabetes Associated With Pembrolizumab: A Review of Published Case Reports. World J. Oncol. 2018, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedzior, S.K.; Jacknin, G.; Hudler, A.; Mueller, S.W.; Kiser, T.H. A Severe Case of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Associated with Anti-Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Antibodies Following Immunotherapy with Pembrolizumab. Am. J. Case Rep. 2021, 22, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapke, J.; Shaheen, Z.; Kilari, D.; Knudson, P.; Wong, S. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Case Series, Review of the Literature, and Optimal Management. Case Rep. Oncol. 2017, 10, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, A.; Sugiyama, K.; Yamada, T. A Case of Nivolumab-Induced Fulminant Type 1 Diabetes with Steroids and Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Administration during the Early Onset. J. Clin. Case Rep. 2016, 6, 11–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Casals, M.; Brahmer, J.R.; Callahan, M.K.; Flores-Chávez, A.; Keegan, N.; Khamashta, M.A.; Lambotte, O.; Mariette, X.; Prat, A.; Suárez-Almazor, M.E. Immune-Related Adverse Events of Checkpoint Inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2020, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elia, G.; Ferrari, S.M.; Galdiero, M.R.; Ragusa, F.; Paparo, S.R.; Ruffilli, I.; Varricchi, G.; Fallahi, P.; Antonelli, A. New Insight in Endocrine-Related Adverse Events Associated to Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 34, 101370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Johnson, D.B. Immune-Related Adverse Events and Anti-Tumor Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haratani, K.; Hayashi, H.; Chiba, Y.; Kudo, K.; Yonesaka, K.; Kato, R.; Kaneda, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Takeda, M.; et al. Association of Immune-Related Adverse Events with Nivolumab Efficacy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, B.; Zhang, J.; Naqash, A.R.; Forde, P.M.; Feliciano, J.L.; Marrone, K.A.; Ettinger, D.S.; Hann, C.L.; Brahmer, J.R.; Ricciuti, B.; et al. Multisystem Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors for Treatment of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1952–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Keany, M.P.; Dong, H.; Al-Alem, L.F.; Pandya, U.M.; Lazo, S.; Boehnke, K.; Lynch, K.N.; Xu, R.; Zarrella, D.T.; et al. Enhanced Efficacy of Simultaneous PD-1 and PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Blockade in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 158–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes-Lima, C.J.; Kwagyan, J.; King, F.; Fernandez, S.J.; Burman, K.D.; Veytsman, I. A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Endocrine Immune-Related Adverse Events of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Outcomes in Head and Neck Cancer and Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, e14096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ma, F.; Sun, B.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Luo, J.; Chen, H.; Luo, Z. Intestinal Microbiome Associated With Immune-Related Adverse Events for Patients Treated With Anti-PD-1 Inhibitors, a Real-World Study. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 756872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCulloch, J.A.; Davar, D.; Rodrigues, R.R.; Badger, J.H.; Fang, J.R.; Cole, A.M.; Balaji, A.K.; Vetizou, M.; Prescott, S.M.; Fernandes, M.R.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota Signatures of Clinical Response and Immune-Related Adverse Events in Melanoma Patients Treated with Anti-PD-1. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hribernik, N.; Huff, D.T.; Studen, A.; Zevnik, K.; Klaneček, Ž.; Emamekhoo, H.; Škalic, K.; Jeraj, R.; Reberšek, M. Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers of Immune-Related Adverse Events in Immune-Checkpoint Blockade-Treated Metastatic Melanoma Patients: A Pilot Study. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 49, 1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribas, A.; Kefford, R.; Marshall, M.A.; Punt, C.J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Marmol, M.; Garbe, C.; Gogas, H.; Schachter, J.; Linette, G.; et al. Phase III Randomized Clinical Trial Comparing Tremelimumab with Standard-of-Care Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved Survival with Ipilimumab in Patients with Metastatic Melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
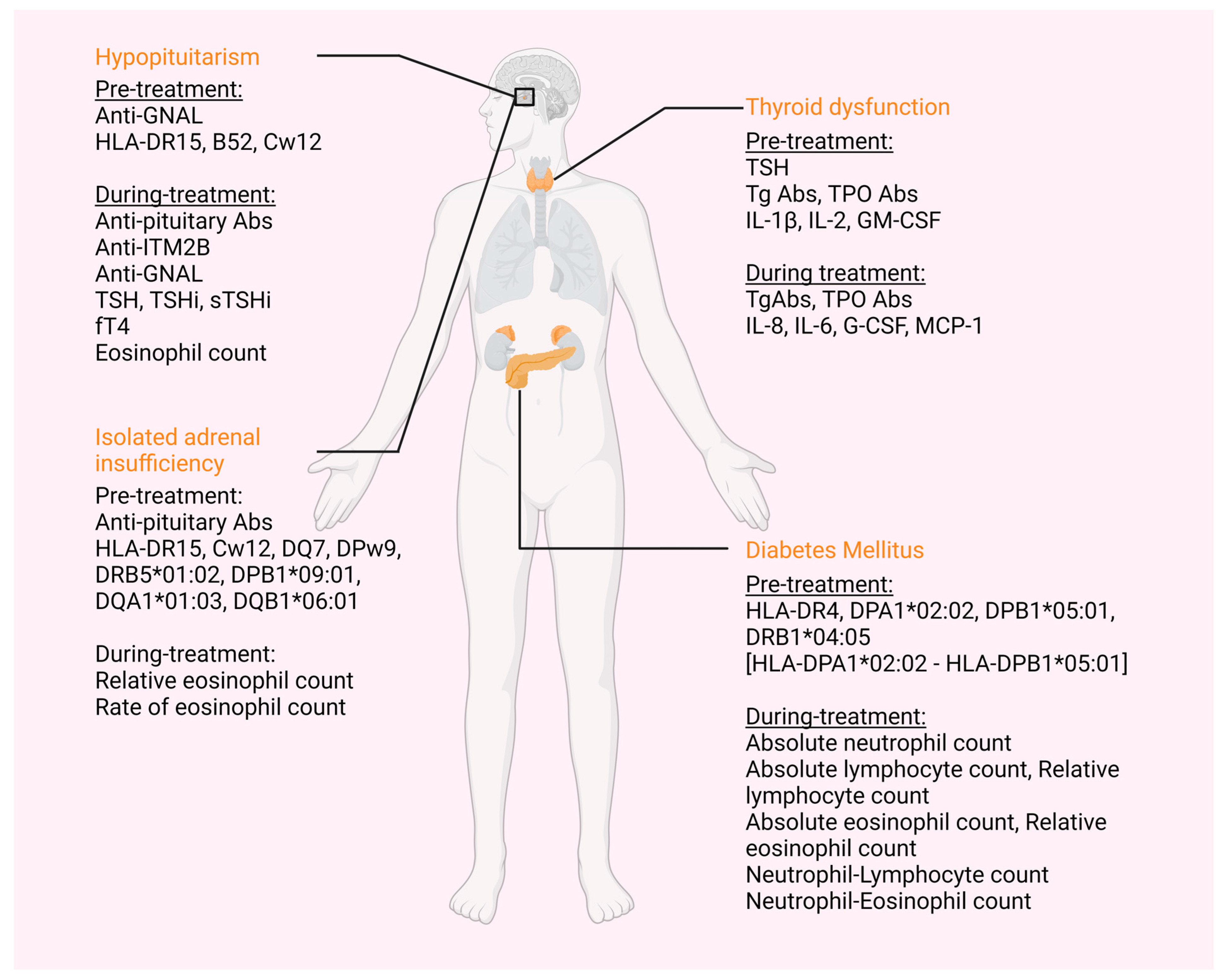

| irAE | Biomarker | Biomarker Assessment | No of Papers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thyroid | TSH | Higher levels | 5 [28,29,30,31,32] |
| TgAbs and/or TPOAbs | Presence | 10 [28,29,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38] | |
| IL-1β | Higher levels | 1 [40] | |
| IL-2 | Higher levels | 1 [40] | |
| GM-CSF | Increase | 1 [40] | |
| Pituitary | |||
| Hypopituitarism | Anti-GNAL Abs | Presence | 1 [45] |
| HLA-DR15 | Presence | 2 [42,43] | |
| HLA-B52 | Presence | 1 [42] | |
| HLA-Cw12 | Presence | 2 [42,43] | |
| Isolated ACTH deficiency | Anti-pituitary Abs | Presence | 1 [43] |
| HLA-DR15 | Presence | 1 [43] | |
| HLA-Cw12 | Presence | 1 [43] | |
| HLA-DQ7 | Presence | 1 [43] | |
| HLA-DPw9 | Presence | 1 [43] | |
| HLA-DRB5*01:02 | Presence | 1 [44] | |
| HLA-DPB1*09:01 | Presence | 1 [44] | |
| HLA-DQA1*01:03 | Presence | 1 [44] | |
| HLA-DQB1*06:01 | Presence | 1 [44] | |
| Diabetes Mellitus | HLA-DR4 | Presence | 1 [57] |
| HLA-DPA1*02:02 | Presence | 1 [56] | |
| DPB1*05:01 | Presence | 1 [56] | |
| HLA-DRB1*04:05 | Presence | 5 [44,58,59,60,61] | |
| HLA-DPA1*02: 02-DPB1*05:01 | Presence | 1 [44] | |
| Endocrine | Absolute Eosinophilic count | Higher levels | 1 [51] |
| irAE | Biomarker | Biomarker Assessment | No of Research |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thyroid | TgAbs and/or TPOAbs | Increase | 3 [39,40,41] |
| Thyroglobulin (Tg) | Elevation before third ICI treatment | 1 [40] | |
| IL-8 | Decrease | 1 [40] | |
| IL-6 | Increase | 1 [39] | |
| G-CSF | Decrease | 1 [40] | |
| MCP-1 | Decrease | 1 [40] | |
| Pituitary | |||
| Hypopituitarism | Anti-pituitary Abs | From negative pre-treatment to positive | 2 [43,46] |
| Anti-ITM2B | Increase | 1 [45] | |
| Anti-GNAL Abs | Increase | 1 [45] | |
| TSH | Decrease | 1 [47] | |
| TSHi, sTSHi | Decrease | 1 [48] | |
| fT4 | Decrease | 1 [48] | |
| Eosinophil count (/μL) | Increase | 1 [49] | |
| Isolated ACTH deficiency | Relative eosinophil count | Increase | 1 [50] |
| Rate of eosinophil count | Higher levels | 1 [50] | |
| Diabetes Mellitus | Absolute neutrophil count | Increase | 1 [56] |
| Relative neutrophil count | Increase | 1 [56] | |
| Absolute lymphocyte count | Decrease | 1 [56] | |
| Absolute eosinophil count | Decrease | 1 [56] | |
| Relative eosinophil count | Decrease | 1 [56] | |
| Neutrophil–Lymphocyte count | Increase | 1 [56] | |
| Neutrophil–Eosinophil count | Increase | 1 [56] | |
| Endocrine | Relative Eosinophilic count | Higher levels | 1 [51] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shalit, A.; Sarantis, P.; Koustas, E.; Trifylli, E.-M.; Matthaios, D.; Karamouzis, M.V. Predictive Biomarkers for Immune-Related Endocrinopathies following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Treatment. Cancers 2023, 15, 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020375
Shalit A, Sarantis P, Koustas E, Trifylli E-M, Matthaios D, Karamouzis MV. Predictive Biomarkers for Immune-Related Endocrinopathies following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Treatment. Cancers. 2023; 15(2):375. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020375
Chicago/Turabian StyleShalit, Almog, Panagiotis Sarantis, Evangelos Koustas, Eleni-Myrto Trifylli, Dimitris Matthaios, and Michalis V. Karamouzis. 2023. "Predictive Biomarkers for Immune-Related Endocrinopathies following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Treatment" Cancers 15, no. 2: 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020375
APA StyleShalit, A., Sarantis, P., Koustas, E., Trifylli, E.-M., Matthaios, D., & Karamouzis, M. V. (2023). Predictive Biomarkers for Immune-Related Endocrinopathies following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Treatment. Cancers, 15(2), 375. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15020375










