Development and Validation of Pretreatment Serum Total Bilirubin as a Biomarker to Predict the Clinical Outcomes in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Multicenter Cohort Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Diagnostic Criteria
2.3. Follow-Up and Treatment
- (1)
- By the deadline for this study, the endpoint event had yet to occur, and the study subjects were still alive.
- (2)
- The study subject lost contact due to relocation, change of phone number, and other reasons, resulting in a loss of follow-up. It is not possible to clearly observe whether the study subject had an endpoint event and the specific time of occurrence.
- (3)
- Due to other reasons, including lack of cooperation from the research subjects or changes in treatment plans by doctors, the study subjects withdrew from this study midway and were unable to continue follow-up observation.
2.4. Laboratory Measurement of STB
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
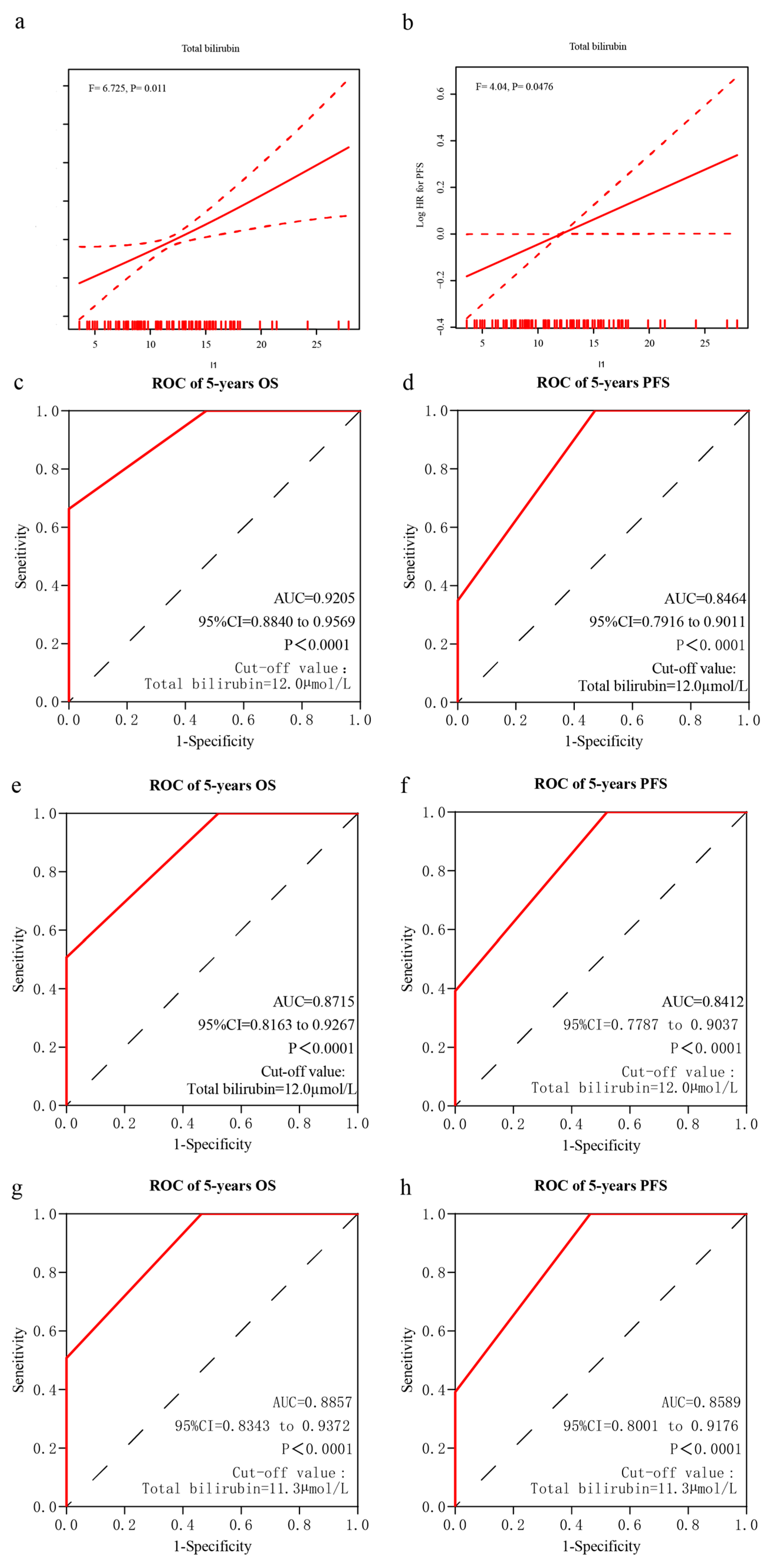
3.2. Determination of Pretreatment STB and Prognosis of Patients with PCNSL
3.3. Comparison of Baseline Characteristics between Patients with STB Levels of <12.0 and ≥12.0 μmol/L in the Discovery Cohort
3.4. Median STB Level as the Cutoff Value
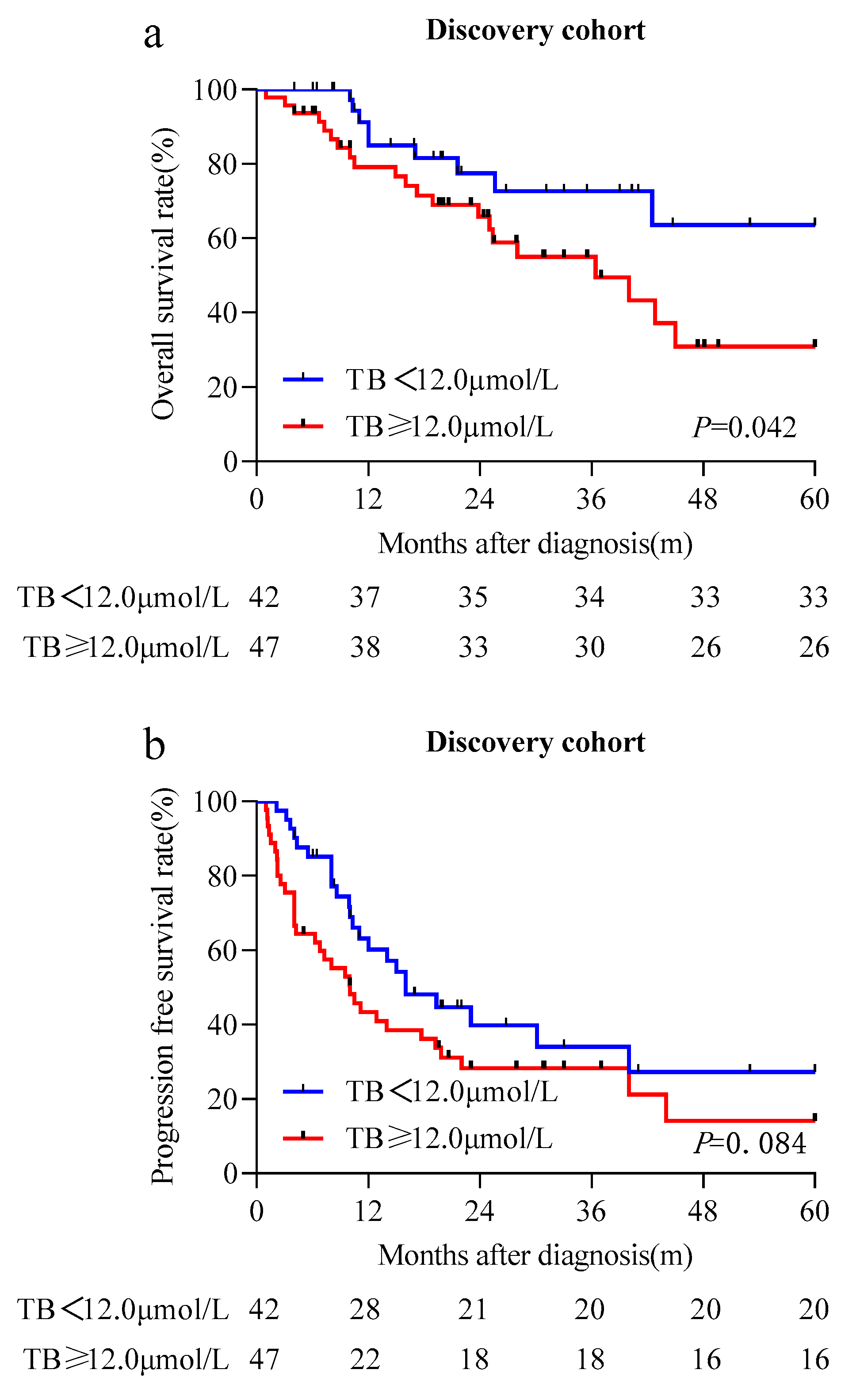
3.5. Prognostic Significance of STB in the Discovery Cohort
3.6. Validation of the Prognostic Value of STB in an Independent Cohort
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Löw, S.; Han, C.H.; Batchelor, T.T. Primary central nervous system lymphoma. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2018, 11, 1756286418793562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Ding, T.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Mao, Y.; Chen, T. Current and emerging therapies for primary central nervous system lymphoma. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langner-Lemercier, S.; Houillier, C.; Soussain, C.; Ghesquières, H.; Chinot, O.; Taillandier, L.; Soubeyran, P.; Lamy, T.; Morschhauser, F.; Benouaich-Amiel, A.; et al. Primary CNS lymphoma at first relapse/progression: Characteristics, management, and outcome of 256 patients from the French LOC network. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calimeri, T.; Steffanoni, S.; Gagliardi, F.; Chiara, A.; Ferreri, A.J.M. How we treat primary central nervous system lymphoma. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaff, L.R.; Grommes, C. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Blood 2022, 140, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, A.J.; Blay, J.Y.; Reni, M.; Pasini, F.; Spina, M.; Ambrosetti, A.; Calderoni, A.; Rossi, A.; Vavassori, V.; Conconi, A.; et al. Prognostic scoring system for primary CNS lymphomas: The International Extranoda Lymphoma Study Group experience. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrey, L.E.; Ben-Porat, L.; Panageas, K.S.; Yahalom, J.; Berkey, B.; Curran, W.; Schultz, C.; Leibel, S.; Nelson, D.; Mehta, M.; et al. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: The Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center prognostic model. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5711–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fevery, J. Bilirubin in clinical practice: A review. Liver Int. 2008, 28, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sticova, E.; Jirsa, M. New insights in bilirubin metabolism and their clinical implications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 6398–6407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čvorovic, J.; Passamonti, S. Membrane Transporters for Bilirubin and Its Conjugates: A Systematic Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, A.F. Bile acids, cholesterol, gallstone calcification, and the enterohepatic circulation of bilirubin. Gastroenterology 1999, 116, 1276–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocker, R.; Yamamoto, Y.; McDonagh, A.F.; Glazer, A.N.; Ames, B.N. Bilirubin is an antioxidant of possible physiological importance. Science 1987, 235, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najib, F. Defensive Role of BilirubinÆ Mia in Pneumococcal Infection. Lancet 1937, 229, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, M.; Marculescu, R.; Doberer, D.; Wolzt, M.; Wagner, O.; Vitek, L.; Bulmer, A.C.; Wagner, K.H. Protection from age-related increase in lipid biomarkers and inflammation contributes to cardiovascular protection in Gilbert’s syndrome. Clin. Sci. 2013, 125, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Li, H.; Si, S.; Yu, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Yan, R.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; et al. Exploring the causal pathway from bilirubin to CVD and diabetes in the UK biobank cohort study: Observational findings and Mendelian randomization studies. Atherosclerosis 2021, 320, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, B.J.; Hong, K.W.; Jung, D.H. Total serum bilirubin and 8-year incident type 2 diabetes mellitus: The Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Diabetes Metab. 2018, 44, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Tiribelli, C.; Bellarosa, C. Translational Approach to the Protective Effect of Bilirubin in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.H.; Wallner, M.; Mölzer, C.; Gazzin, S.; Bulmer, A.C.; Tiribelli, C.; Vitek, L. Looking to the horizon: The role of bilirubin in the development and prevention of age-related chronic diseases. Clin. Sci. 2015, 129, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adin, C.A. Bilirubin as a Therapeutic Molecule: Challenges and Opportunities. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyed Khoei, N.; Jenab, M.; Murphy, N.; Banbury, B.L.; Carreras-Torres, R.; Viallon, V.; Kühn, T.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, B.; Aleksandrova, K.; Cross, A.J. Circulating bilirubin levels and risk of colorectal cancer: Serological and Mendelian randomization analyses. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, G.N.; Liou, I.W.; Weiss, N.S. Serum bilirubin and colorectal cancer risk: A population-based cohort study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 23, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy-Iglesias, M.J.; Moss, C.; Beckmann, K.; Hammar, N.; Walldius, G.; Bosco, C.; Van Hemelrijck, M.; Santaolalla, A. Serum Total Bilirubin and Risk of Cancer: A Swedish Cohort Study and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2021, 13, 5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Li, S.; Xia, Z.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, W.; Fang, J.; Liu, Q.; et al. Prognostic significance of pretreatment red blood cell distribution width in primary diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the central nervous system for 3P medical approaches in multiple cohorts. EPMA J. 2022, 13, 499–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Xia, Z.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Chen, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, W.; Li, D.; Hua, W.; et al. Proposed new prognostic model using the systemic immune-inflammation index for primary central nervous system lymphoma: A prospective-retrospective multicohort analysis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1039862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Ma, J.; Ma, Y.; Lin, Z.; Kang, H.; Chen, B. Improvement of outcomes of an escalated high-dose methotrexate-based regimen for patients with newly diagnosed primary central nervous system lymphoma: A real-world cohort study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 6115–6122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Generalized additive modelsfor medical research. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1995, 4, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S.N. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R, 2nd ed.; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Lou, Y.; Hu, S.; Yu, K.; Li, R.; Zhang, X.; Jin, B.; Han, B. Pretreatment direct bilirubin and total cholesterol are significant predictors of overall survival in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients with EGFR mutations. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Fang, L.; Li, J.T.; Zhao, H.C. Significance and prognostic value of increased serum direct bilirubin level for lymph node metastasis in Chinese rectal cancer patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2576–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ding, J.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. The prognostic value of serum bilirubin in colorectal cancer patients with surgical resection. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2021, 36, 17246008211036128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Deng, S.; Yan, L.; Gu, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, M.; Liu, L.; Cai, K. A nomogram based on pretreatment levels of serum bilirubin and total bile acid levels predicts survival in colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyed Khoei, N.; Wagner, K.H.; Carreras-Torres, R.; Gunter, M.J.; Murphy, N.; Freisling, H. Associations between Prediagnostic Circulating Bilirubin Levels and Risk of Gastrointestinal Cancers in the UK Biobank. Cancers 2021, 13, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyed Khoei, N.; Carreras-Torres, R.; Murphy, N.; Gunter, M.J.; Brennan, P.; Smith-Byrne, K.; Mariosa, D.; Mckay, J.; O’Mara, T.A.; Jarrett, R. Genetically Raised Circulating Bilirubin Levels and Risk of Ten Cancers: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Cells 2021, 10, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, K.H.; Shiels, R.G.; Lang, C.A.; Seyed Khoei, N.; Bulmer, A.C. Diagnostic criteria and contributors to Gilbert’s syndrome. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2018, 55, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruo, Y.; Nakahara, S.; Yanagi, T.; Nomura, A.; Mimura, Y.; Matsui, K.; Sato, H.; Takeuchi, Y. Genotype of UGT1A1 and phenotype correlation between Crigler-Najar syndrome type II and Gilbert syndrome. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, A.; Lawlor, M.W.; Mazariegos, G.V.; McKiernan, P.; Squires, J.E.; Strauss, K.A.; Gupta, D.; James, E.; Prasad, S. Disease burden of Crigler-Najar syndrome: Systematic review and future perspectives. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, M.; Sugiyama, T. UGT1A1 polymorphisms in cancer: Impact on irinotecan treatment. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2017, 10, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R.S.; Seligson, N.D.; Bottiglieri, S.; Carballido, E.; Cueto, A.D.; Imanirad, I.; Levine, R.; Parker, A.S.; Swain, S.M.; Tillman, E.M. UGT1A1 Guided Cancer Therapy: Review of the Evidence and Considerations for Clinical Implementation. Cancers 2021, 13, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, N.; Weinberger, B.I.; Hegyi, T.; Aleksunes, L.M. Inherited disorders of bilirubin clearance. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 79, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFino, C.E.; Barreto, J.N.; Pawlenty, A.G.; Ruff, M.W.; Carabenciov, I.D.; Mara, K.C.; Thompson, C.A. Lack of drug interaction between levetiracetam and high-dose methotrexate in patients with lymphoma. Pharmacotherapy 2021, 41, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.R.; Chowdhary, S.; Lombardi, K.M.; Chalmers, L.M.; Chamberlain, M. Clinical utility and pharmacology of high-dose methotrexate in the treatment of primary CNS lymphoma. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2006, 6, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, K.; Korfel, A.; Martus, P.; Weller, M.; Herrlinger, U.; Schmittel, A.; Fischer, L.; Thiel, E.; German Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma Study Group (G-PCNSL-SG). High-dose methotrexate toxicity in elderly patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | All | Huashan Cohort | Shanghai Cancer Center Cohort | Renji Cohort | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 158 | % | N = 44% | N = 45% | N = 69 | % | |||
| Median age (IQR), y | 57 (49, 65) | 49 (44.5, 57) | 58 (52, 71) | 59 (52, 66) | ||||
| <60 | 98 | 62.0 | 37 | 84.0 | 23 | 51.1 | 38 | 55.1 |
| ≥60 | 60 | 38.0 | 7 | 16.0 | 22 | 48.9 | 31 | 44.9 |
| Sex | ||||||||
| Male | 98 | 62.0 | 31 | 70.0 | 26 | 57.8 | 41 | 59.4 |
| Female | 60 | 38.0 | 13 | 30.0 | 19 | 42.2 | 28 | 40.6 |
| Diabetes | ||||||||
| Yes | 8 | 5.1 | 1 | 2.3 | 5 | 11.1 | 2 | 2.9 |
| None | 150 | 94.9 | 43 | 97.7 | 40 | 88.9 | 67 | 97.1 |
| Hypertension | ||||||||
| Yes | 44 | 27.8 | 6 | 13.6 | 14 | 31.1 | 24 | 34.8 |
| No | 114 | 72.2 | 38 | 86.4 | 31 | 68.9 | 45 | 65.2 |
| BMI (IQR), kg/m2 | 23.8 (21.5, 25.8) | 23.9 (22.4, 25.4) | ||||||
| Missing | 19 | 12.0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4.4 | 17 | 24.6 |
| <18.0 | 4 | 2.5 | 2 | 4.6 | 1 | 2.2 | 1 | 1.4 |
| 18.0–24.0 | 67 | 42.4 | 18 | 40.9 | 24 | 53.3 | 25 | 36.2 |
| >24.0 | 68 | 43.0 | 24 | 54.5 | 18 | 40.0 | 26 | 37.7 |
| Median Total bilirubin (IQR), µmol/L | 11.9 (8.8, 15.1) | 12.0 (8.9, 15.2) | 10.6 (8.6, 14.4) | 11.3 (9.2, 15.2) | ||||
| <12.0 | 78 | 49.4 | 17 | 28.6 | 25 | 55.6 | 36 | 52.2 |
| ≥12.0 | 80 | 50.6 | 27 | 61.4 | 20 | 44.4 | 33 | 47.8 |
| ALT (IQR), U/L | 23.0 (16.0, 28.0) | 20.0 (15.0, 25.0) | 16.0 (12.0, 25.5) | 26.0 (22.0, 33.0) | ||||
| AST (IQR), U/L | 21.0 (17.0, 31.0) | 21.0 (20.0, 25.0) | 18.5 (16.0, 30.0) | 26.0 (14.0, 36.0) | ||||
| Gamma-GT (IQR), U/L | 21.0 (15.0, 33.0) | 21.0 (15.0, 37.0) | 18.5 (15.0, 25.5) | 23.0 (16.0, 34.0) | ||||
| Variables | All | Discovery Cohort | Validation Cohort | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 158 | % | N = 89 | % | N = 69 | % | |
| Median Age (IQR), y | 57 (49, 65) | 55 (48, 62) | 59 (52, 66) | |||
| <60 | 98 | 62.0 | 60 | 67.4 | 38 | 55.1 |
| ≥60 | 60 | 38.0 | 29 | 32.6 | 31 | 44.9 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Male | 98 | 62.0 | 57 | 64.0 | 41 | 59.4 |
| Female | 60 | 38.0 | 32 | 36.0 | 28 | 40.6 |
| Diabetes | ||||||
| Yes | 8 | 5.1 | 6 | 6.7 | 2 | 2.9 |
| None | 150 | 94.9 | 83 | 93.3 | 67 | 97.1 |
| Hypertension | ||||||
| Yes | 44 | 27.8 | 20 | 22.5 | 24 | 34.8 |
| No | 114 | 72.2 | 69 | 77.5 | 45 | 65.2 |
| BMI(IQR), kg/m2 | 23.8 (21.5, 25.8) | 23.5 (21.6, 26.1) | 23.9 (22.4, 25.4) | |||
| Missing | 19 | 12.0 | 2 | 2.2 | 17 | 24.6 |
| <18.0 | 4 | 2.5 | 3 | 3.4 | 1 | 1.4 |
| 18.0–24.0 | 67 | 42.4 | 42 | 47.2 | 25 | 36.2 |
| >24.0 | 68 | 43.0 | 42 | 47.2 | 26 | 37.7 |
| Median Total bilirubin (IQR), µmol/L | 11.9 (8.8, 15.1) | 12.0 (8.8, 14.5) | 11.3 (9.2, 15.2) | |||
| <12.0 | 78 | 49.4 | 42 | 28.6 | 47.2 | 52.2 |
| ≥12.0 | 80 | 50.6 | 47 | 61.4 | 52.8 | 47.8 |
| ALT (IQR), U/L | 23.0 (16.0, 28.0) | 18.0 (14.0, 25.0) | 26.0 (22.0, 33.0) | |||
| AST (IQR), U/L | 21.0 (17.0, 31.0) | 20.0 (17.0, 26.0) | 26.0 (14.0, 36.0) | |||
| Gamma-GT (IQR), U/L | 21.0 (15.0, 33.0) | 20.0 (15.0, 30.0) | 23.0 (16.0, 34.0) | |||
| Variables | All | Total Bilirubin < 12.0 | Total Bilirubin ≥ 12.0 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 89 | % | N = 44 | % | N = 45 | % | p | |
| Discovery cohort Median age (IQR), y | 55 (48, 62) | 49 (44.5, 57) | 58 (52, 71) | ||||
| <60 | 60 | 67.4 | 37 | 84.0 | 23 | 51.1 | 0.887 |
| ≥60 | 29 | 32.6 | 7 | 16.0 | 22 | 48.9 | |
| Sex | |||||||
| Male | 57 | 64.0 | 31 | 70.0 | 26 | 57.8 | 0.009 |
| Female | 32 | 36.0 | 13 | 30.0 | 19 | 42.2 | |
| Diabetes | |||||||
| Yes | 6 | 6.7 | 1 | 2.3 | 5 | 11.1 | 0.571 |
| None | 83 | 93.3 | 43 | 97.7 | 40 | 88.9 | |
| Hypertension | |||||||
| Yes | 20 | 22.5 | 6 | 13.6 | 14 | 31.1 | 0.215 |
| No | 69 | 77.5 | 38 | 86.4 | 31 | 68.9 | |
| BMI, kg/ m2 | 23.5 (21.6, 26.1) | ||||||
| Missing | 2 | 2.2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 4.4 | 0.0243 |
| <18.0 | 3 | 3.4 | 2 | 4.6 | 1 | 2.2 | |
| 18.0–24.0 | 42 | 47.2 | 18 | 40.9 | 24 | 53.3 | |
| >24.0 | 42 | 47.2 | 24 | 54.5 | 18 | 40.0 | |
| Death | |||||||
| Yes | 30 | 33.7 | 9 | 21.4 | 21 | 44.7 | 0.002 |
| None | 59 | 66.3 | 33 | 78.6 | 26 | 55.3 | |
| Progression | |||||||
| Yes | 56 | 62.9 | 23 | 54.8 | 33 | 70.2 | 0.132 |
| None | 30 | 37.1 | 19 | 45.2 | 14 | 29.8 | |
| ALT (IQR), U/L | 18.0 (14.0, 25.0) | 16.0 (11.5, 27.0) | 19.0 (15.0, 24.0) | 0.241 | |||
| AST (IQR), U/L | 20.0 (17.0, 26.0) | 19.0 (15.5, 31.0) | 20.5 (20.0, 25.0) | 0.182 | |||
| Gamma-GT (IQR), U/L | 20.0 (15.0, 30.0) | 20.0 (14.5, 28.0) | 20.0 (15.0, 34.0) | 0.511 | |||
| OS | PFS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| Univariate analysis | ||||
| Age, y | 1.061 (1.024, 1.100) | 0.001 | 1.015 (0.991, 1.039) | 0.221 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 1.053 (0.487, 2.276) | 0.895 | 1.158 (0.663, 2.022) | 0.606 |
| Diabetes (yes vs. no) | 2.148 (0.492, 9.378) | 0.309 | 1.849 (0.731, 4.680) | 0.194 |
| Hypertension (yes vs. no) | 1.215 (0.515, 2.865) | 0.657 | 1.089 (0.580, 2.046) | 0.790 |
| BMI, kg/ m2 | 1.011 (0.901, 1.133) | 0.858 | 1.050 (0.969, 1.138) | 0.230 |
| ALT, U/L | 1.022 (0.993, 1.053) | 0.138 | 1.009 (0.989, 1.029) | 0.391 |
| AST, U/L | 1.026 (0.992, 1.062) | 0.138 | 1.011 (0.988, 1.036) | 0.351 |
| Gamma-GT, U/L | 0.148 (0.995, 1.030) | 1.030 | 1.005 (0.993, 1.018) | 0.412 |
| Total bilirubin, µmol/L (≥12.0 vs. <12.0) | 2.458 (1.087, 5.555) | 0.031 | 1.637 (0.954, 2.810) | 0.074 |
| Multivariate analysis | ||||
| Age, y | 1.082 (1.037, 1.128) | <0.001 | 1.015 (0.989, 1.042) | 0.266 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 0.978 (0.405, 2.361) | 0.960 | 1.193 (0.642, 2.217) | 0.577 |
| Diabetes (yes vs. no) | 1.505 (0.271, 8.371) | 0.640 | 1.701 (0.577, 5.020) | 0.336 |
| Hypertension (yes vs. no) | 0.804 (0.311, 2.078) | 0.652 | 0.991 (0.487, 2.014) | 0.980 |
| BMI, kg/ m2 | 1.059 (0.937, 1.196) | 0.362 | 1.053 (0.965, 1.149) | 0.249 |
| ALT, U/L | 0.961 (0.891, 1.036) | 0.295 | 0.992 (0.942, 1.044) | 0.744 |
| AST, U/L | 1.029 (0.943, 1.124) | 0.516 | 1.017 (0.960, 1.077) | 0.567 |
| Gamma-GT, U/L | 1.021 (0.995, 1.047) | 0.119 | 1.002 (0.986, 1.019) | 0.796 |
| Total bilirubin, µmol/L (≥12.0 vs. <12.0) | 3.912 (1.332, 11.493) | 0.013 | 1.957 (1.042, 3.675) | 0.037 |
| Variables | OS | PFS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| Univariate analysis | ||||
| Age, y | 1.039 (1.004, 1.074) | 0.026 | 1.028 (0.998, 1.059) | 0.064 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 0.959 (0.483, 1.902) | 0.904 | 0.594 (0.322, 1.096) | 0.095 |
| Diabetes (yes vs. no) | 0.698 (0.095, 5.125) | 0.724 | 0.555 (0.076, 4.046) | 0.561 |
| Hypertension (yes vs. no) | 1.260 (0.636, 2.496) | 0.508 | 1.114 (0.600,2.070) | 0.732 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 1.073 (0.954, 1.207) | 0.240 | 1.065 (0.956, 1.188) | 0.253 |
| ALT, U/L | 0.991 (0.950, 1.034) | 0.684 | 1.011 (0.975, 1.049) | 0.545 |
| AST, U/L | 0.991 (0.975, 1.007) | 0.275 | 0.997 (0.986, 1.008) | 0.602 |
| Gamma-GT, U/L | 0.999 (0.977, 1.022) | 0.933 | 1.006 (0.987, 1.025) | 0.537 |
| Total bilirubin, µmol/L (≥12.0 vs. <12.0) | 1.039 (1.004, 1.074) | 0.041 | 1.028 (0.998, 1.059) | 0.137 |
| Multivariate analysis | ||||
| Age, y | 1.030 (0.980, 1.082) | 0.249 | 1.019 (0.974, 1.066) | 0.414 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 1.302 (0.389, 4.354) | 0.669 | 0.650 (0.225, 1.875) | 0.425 |
| Diabetes (yes vs. no) | 0.273 (0.016, 4.754) | 0.374 | 0.515 (0.037, 7.178) | 0.621 |
| Hypertension (yes vs. no) | 1.704 (0.559, 5.198) | 0.349 | 1.214 (0.425, 3.464) | 0.718 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 1.142 (0.937, 1.392) | 0.189 | 1.102 (0.921, 1.320) | 0.289 |
| ALT, U/L | 1.060 (0.958, 1.173) | 0.258 | 1.053 (0.968, 1.147) | 0.230 |
| AST, U/L | 1.002 (0.957, 1.049) | 0.934 | 0.995 (0.958, 1.033) | 0.786 |
| Gamma-GT, U/L | 0.984 (0.925, 1.047) | 0.607 | 1.002 (0.950, 1.057) | 0.938 |
| Total bilirubin, µmol/L (≥12.0 vs. <12.0) | 3.671 (1.255, 10.734) | 0.018 | 2.627 (1.048, 6.584) | 0.039 |
| Variables | OS | PFS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p | HR (95% CI) | p | |
| Univariate analysis | ||||
| Age, y | 1.039 (1.004, 1.074) | 0.026 | 1.028 (0.998, 1.059) | 0.064 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 0.959 (0.483, 1.902) | 0.904 | 0.594 (0.322, 1.096) | 0.095 |
| Diabetes (yes vs. no) | 0.698 (0.095, 5.125) | 0.724 | 0.555 (0.076, 4.046) | 0.561 |
| Hypertension (yes vs. no) | 1.260 (0.636, 2.496) | 0.508 | 1. 114 (0.600, 2.070) | 0.732 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 1.073 (0.954, 1.207) | 0.240 | 1.065 (0.956, 1.188) | 0.253 |
| ALT, U/L | 0.991 (0.950, 1.034) | 0.684 | 1.011 (0.975, 1.049) | 0.545 |
| AST, U/L | 0.991 (0.975, 1.007) | 0.275 | 0.997 (0.986, 1.008) | 0.602 |
| Gamma-GT, U/L | 0.999 (0.977, 1.022) | 0.933 | 1.006 (0.987, 1.025) | 0.537 |
| Total bilirubin, µmol/L (≥ 11.3 vs. <11.3) | 2.525 (1.245, 5.121) | 0.010 | 1.855 (1.003, 3.432) | 0.049 |
| Multivariate analysis | ||||
| Age, y | 1.024 (0.975, 1.076) | 0.335 | 1.022 (0.976, 1.070) | 0.364 |
| Sex (male vs. female) | 1.493 (0.425, 5.251) | 0.532 | 0.596 (0.209, 1.703) | 0.334 |
| Diabetes (yes vs. no) | 0.257 (0.014, 4.662) | 0.257 | 0.518 (0.037, 7.239) | 0.625 |
| Hypertension (yes vs. no) | 2.039 (0.642, 6.478) | 0.227 | 1.084 (0.386, 3.045) | 0.878 |
| BMI, kg/ m2 | 1.168 (0.954, 1.430) | 0.134 | 1.085 (0.905, 1.299) | 0.378 |
| ALT, U/L | 1.068 (0.963, 1.183) | 0.211 | 1.052 (0.966, 1.145) | 0.246 |
| AST, U/L | 1.005 (0.960, 1.052) | 0.834 | 0.994 (0.956, 1.033) | 0.753 |
| Gamma-GT, U/L | 0.978 (0.919, 1.041) | 0.482 | 1.005 (0.953, 1.060) | 0.844 |
| Total bilirubin, µmol/L (≥11.3 vs. <11.3) | 3.061 (1.086, 8.625) | 0.034 | 3.174 (1.226, 8.215) | 0.017 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, J.; Li, S.; Li, D.; Hua, W.; Guo, L.; Xia, Z. Development and Validation of Pretreatment Serum Total Bilirubin as a Biomarker to Predict the Clinical Outcomes in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 4584. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184584
Cao J, Li S, Li D, Hua W, Guo L, Xia Z. Development and Validation of Pretreatment Serum Total Bilirubin as a Biomarker to Predict the Clinical Outcomes in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4584. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184584
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Jiazhen, Shengjie Li, Danhui Li, Wei Hua, Lin Guo, and Zuguang Xia. 2023. "Development and Validation of Pretreatment Serum Total Bilirubin as a Biomarker to Predict the Clinical Outcomes in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Multicenter Cohort Study" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4584. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184584
APA StyleCao, J., Li, S., Li, D., Hua, W., Guo, L., & Xia, Z. (2023). Development and Validation of Pretreatment Serum Total Bilirubin as a Biomarker to Predict the Clinical Outcomes in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: A Multicenter Cohort Study. Cancers, 15(18), 4584. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184584





