Interaction between Macrophages and Adipose Stromal Cells Increases the Angiogenic and Proliferative Potential of Pregnancy-Associated Breast Cancers
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
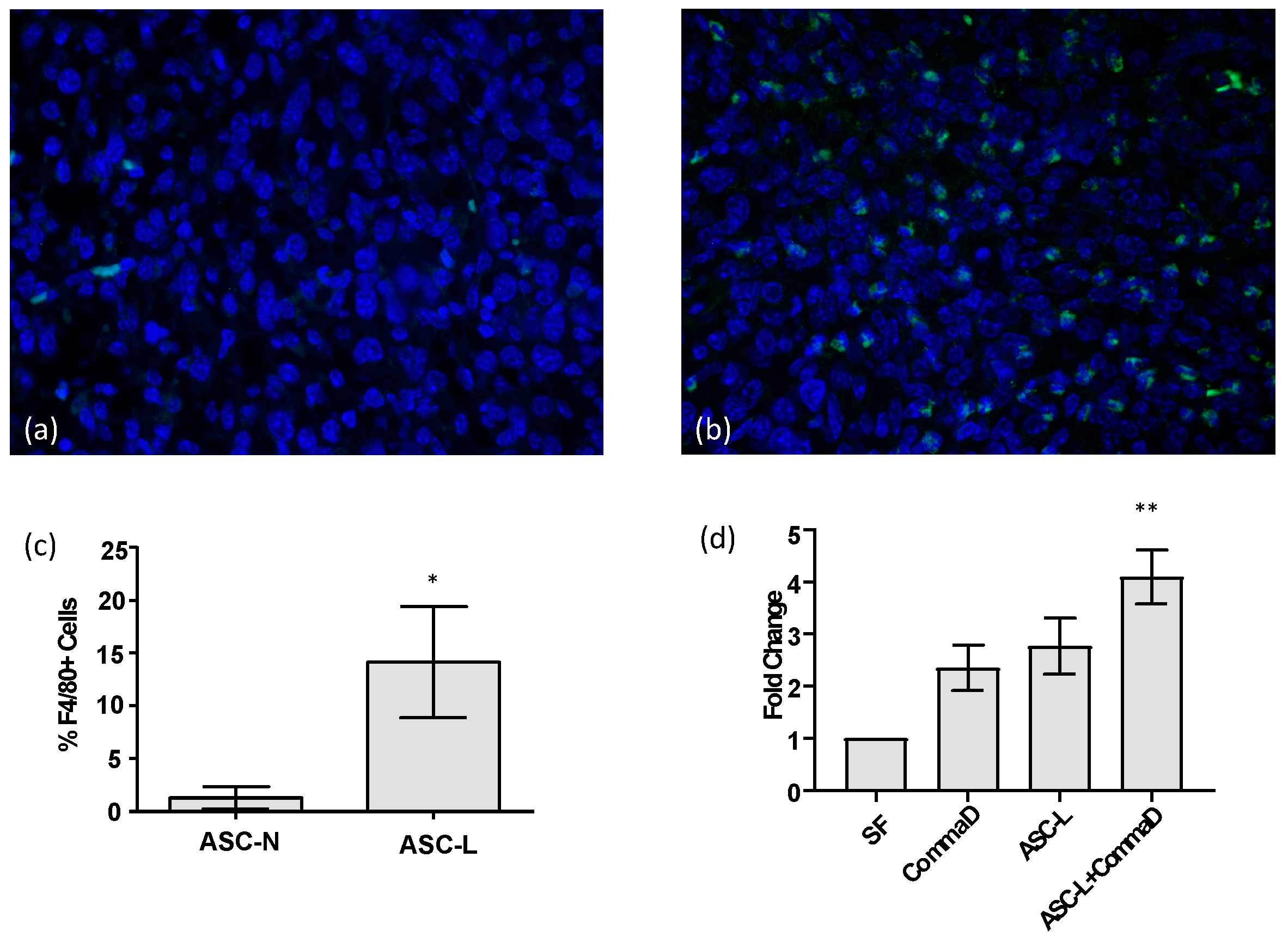
3.1. ASC-Ls Recruit Macrophages into the Tumor Microenvironment
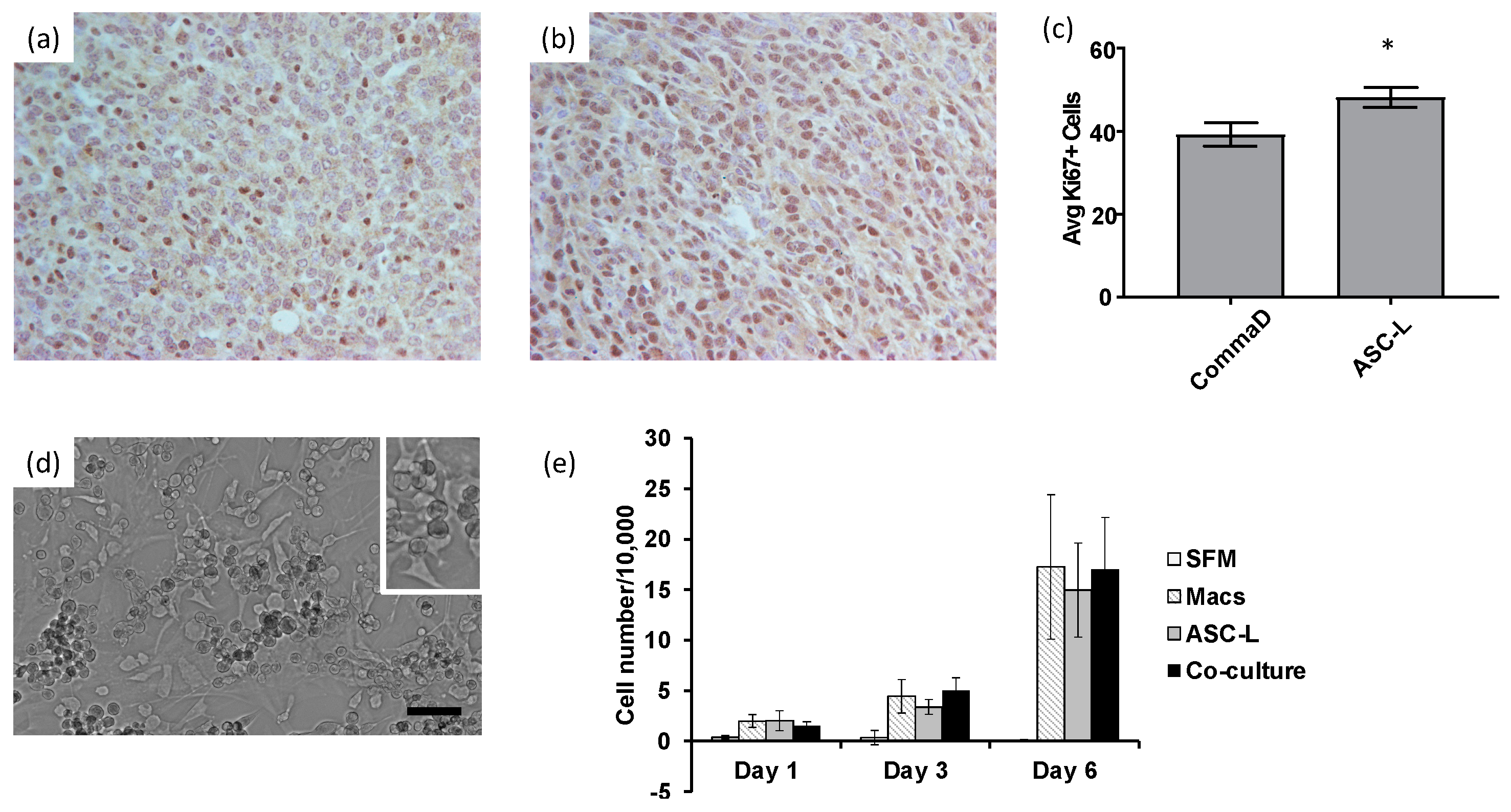
3.2. ASC-Ls and Macrophages Increase Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation
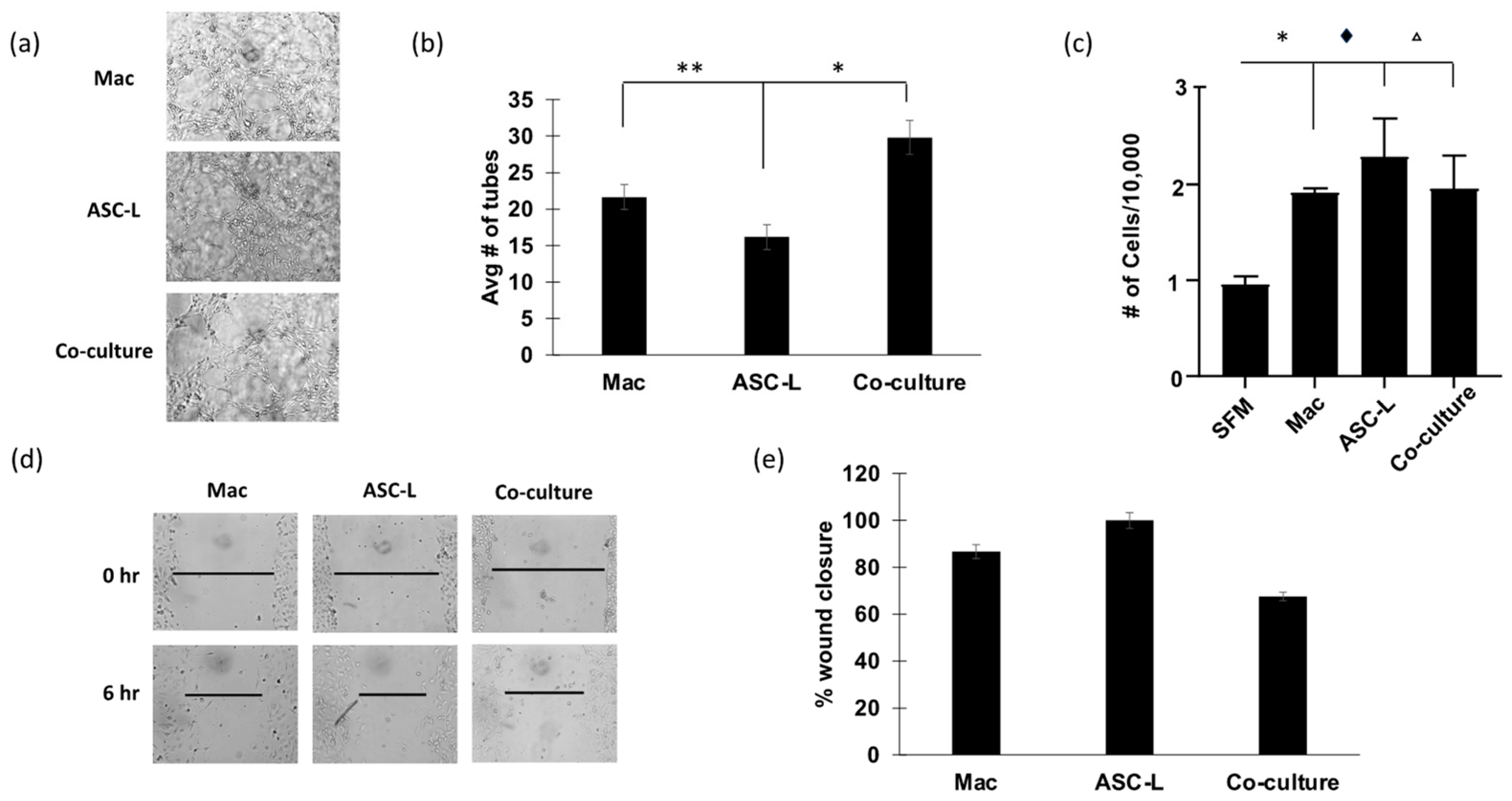
3.3. Co-Culture of ASC-Ls and Macrophages Increases Angiogenesis
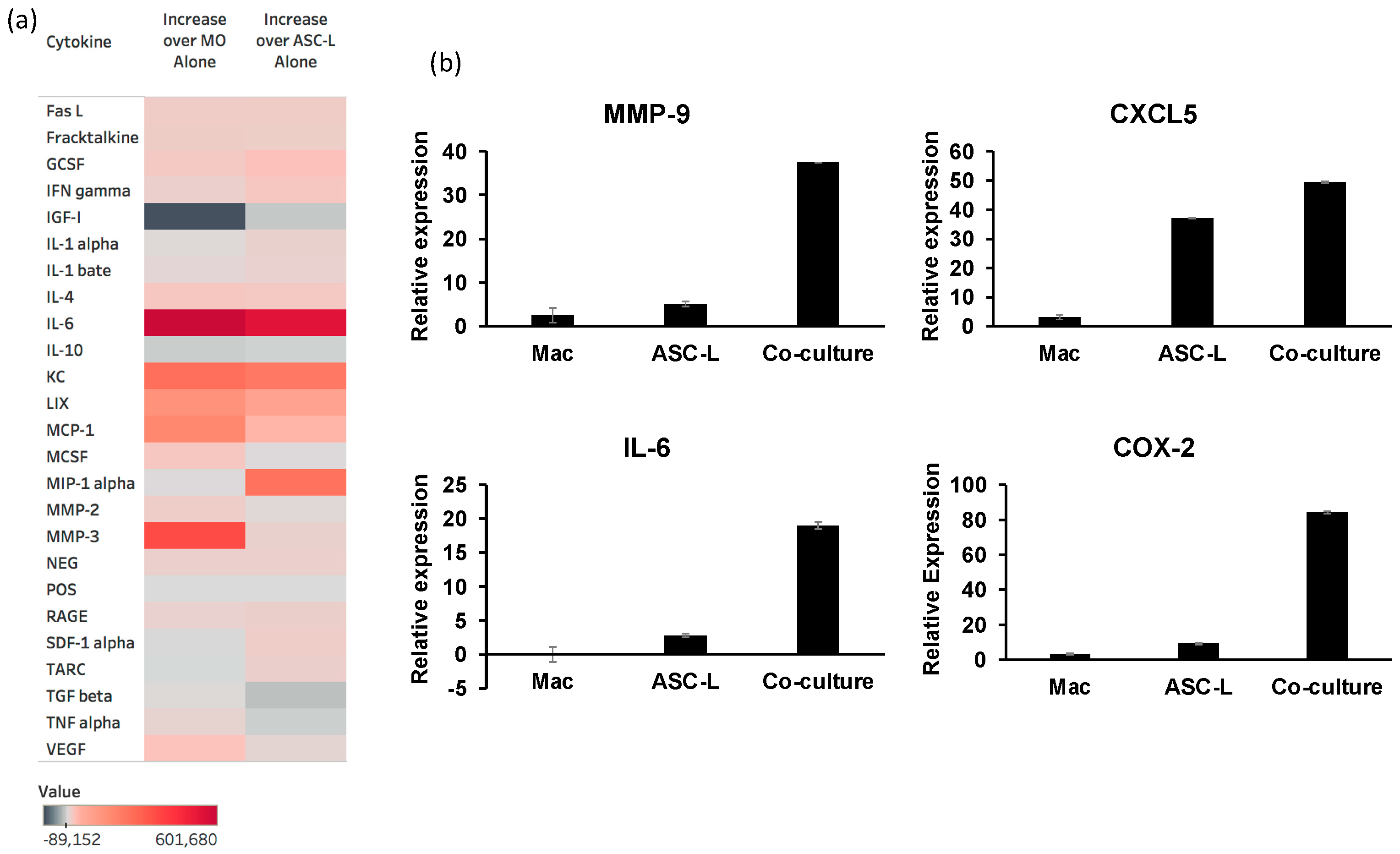
3.4. The Interaction of ASC-Ls and Macrophages Increases Cytokine Secretion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schedin, P. Pregnancy-associated breast cancer and metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannan, F.M.; Elajnaf, T.; Vandenberg, L.N.; Kennedy, S.H.; Thakker, R.V. Hormonal regulation of mammary gland development and lacation. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCready, J.; Arendt, L.M.; Glover, E.; Briendel, J.L.; Lyle, S.R.; Naber, S.P.; Jay, D.G.; Kuperwasser, C. Pregnancy-associated breast cancers are driven by differences in adipose stromal cells present during lactation. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, R2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inman, J.L.; Robertson, C.; Mott, J.D.; Bissell, M.J. Mammary gland development: Cell fate specification, stem cells and the microenvironment. Development 2015, 142, 1028–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Schedin, P. Macrophages in breast cancer: Do involution macrophages account for the poor prognosis of pregnancy-associated breast cancer? J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2009, 14, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, P.M.; Davison, R.S.; Bliss, E.; McGee, J.O. Macrophages in human breast disease: A quantitative immunohistochemical study. Br. J. Cancer 1988, 57, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, S.; Brion, R.; Lintunen, M.; Kronqvist, P.; Sandholm, J.; Monkkonen, J.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.-L.; Lauttia, S.; Tynninen, O.; Joensuu, H.; et al. Human breast cancer cells educate macrophages toward the M2 activation status. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carron, E.C.; Homra, S.; Rosenberg, J.; Coffelt, S.B.; Kittrell, F.; Zhang, Y.; Creighton, C.J.; Fuqua, S.A.; Medina, D.; Machado, H.L. Macrophages promote the progression of premalignant mammary lesions to invasive cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 50731–50746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.P.; Tang, B.; Wang, Y.; Duran, C.L.; Karagiannis, G.S.; Xue, E.A.; Entenberg, D.; Borriello, L.; Coste, A.; Eddy, R.J.; et al. Live tumor imaging shows macrophage induction and TMEM-mediated enrichment of cancer stem cells during metastatic dissemination. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornetti, J.; Martinson, H.; Borges, V.; Schedin, P. Emerging targets for the prevention of pregnancy-associated breast cancer. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 639–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Lv, W.; Zhao, C.; Xia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q. The pleiotropic roles of adipocyte secretome in remodeling breast cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, A.L.; Pei, D.T.; Hurst, C.G.; Gimble, J.M.; Burow, M.E.; Bunnell, B.A. Obesity enhances the conversion of adipose-derived stromal/stem cells into carcinoma-associated fibroblast leading to cancer cell proliferation and progression to an invasive phenotype. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 9216502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Sun, S.; Sun, S. Cancer-associated adipocytes: Key players in breast cancer progression. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, T.A.; Hughes, K.; Hume, D.A.; Davis, F.M. Developmental Stage-Specific Distribution of Macrophages in Mouse Mammary Gland. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, K.; Fang, M.; Alroy, J.; Sahagian, G.G. Imageable 4T1 model for the study of late-stage breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2008, 9, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerry, D.J.; Medina, D.; Butel, J.S. p53 mutations in CommaD cells. Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 1994, 30, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, Y.S.; Tseng, H.Y.; Chen, Y.A.; Shen, P.C.; Al Haq, A.T.; Chen, L.M.; Tung, Y.C.; Hsu, H.L. MCT-1/mir-34a/IL-6/IL-6R signaling axis promotes EMT progression, cancer stemness and M2 macrophage polarization in triple negative breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, R.J.; Allam, A.H.; Yeo, B.; Deb, S.; Murone, C.; Lim, E.; Johnstone, C.N.; Ernst, M. Paracrine IL-6 Signaling Confers Proliferation between Heterogenous Inflammatory Breast Cancer Sub-Clones. Cancers 2022, 14, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strieter, R.M.; Burdick, M.D.; Gomperts, B.N.; Belperio, J.A.; Keane, M.P. CXC chemokines in angiogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Hung, A.C.; Wu, Y.-C.; Lo, S.; Chen, H.-D.; Chen, Y.-K.; Hsieh, Y.-C.; Hu, S.C.-S.; Hou, M.-F.; Yuan, S.-S. ADSCs stimulated by resistin promote breast cancer cell malignancy via CXCL5 in a breast cancer coculture model. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, P.; Sarkissyan, M.; Paico, K.; Wu, Y.; Vadgama, J.V. MCP-1 is overexpressed in triple-negative breast cancers and drives cancer invasiveness and metastasis. Cancer Med. 2018, 170, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquivel-Velazquez, M.; Ostoa-Saloma, P.; Palacios-Arreola, M.I.; Nava-Castro, K.E.; Castro, J.I.; Morales-Montor, J. The Role of Cytokines in Breast Cancer Development and Progression. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2015, 35, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radisky, E.S.; Radisky, D.C. Matrix metalloproteinases as breast cancer drivers and therapeutic targets. Front. Biosci. 2015, 20, 1143–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergers, G.; Brekken, R.; McMahon, G.; Vu, T.H.; Itoh, T.; Tamaki, K.; Tanzawa, K.; Thorpe, P.; Itohara, S.; Werb, Z.; et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, T.R.; O’Brien, J.; Borges, V.F.; Conklin, M.W.; Keely, P.J.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Marusyk, A.; Tan, A.C.; Schedin, P. Postpartum mammary gland involution drives progression of ductal carcinoma in situ through collagen and COX-2. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.A.; Li, W.; Walker, T.M.; Silvers, C.; Arendt, L.M.; Hernandez, L.L. Investigating the complex interplay between genotype and high-fat-diet feeding in the lactating mammary gland using the Tph1 and Ldlr knockout models. Transl. Physiol. 2021, 320, E438–E452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, J.P. Lipid metabolism in adipose tissue during lactation: A model of metabolic control system. J. Nutr. 1994, 124, 1383S–1391S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovey, R.C.; Goldhar, A.S.; Baffi, J.; Bonderhaar, B.K. Transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in epithelial and stomal cells during mouse mammary gland development. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Martinson, H.; Durand-Rougely, C.; Schedin, P. Macrophages are crucial for epithelial cell death and adipocyte repopulation during mammary gland involution. Development 2012, 139, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q. CXCL5 secreted from adipose tissue-derived stem cells promotes cancer cell proliferation. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, N.; Sun, D.; Lan, Y.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Feng, L.; Zhang, B.; Jin, L.; et al. Andrographolide inhibits breast cancer through suppressing COX-2 expression and angiogenesis via inactivation of p300 signaling and VEGF pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, H. Prognostic values of tumoral MMP2 and MMP9 overexpression in breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wu, M.; Zeng, N.; Xiong, M.; Hu, W.; Lv, W.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y. Cancer-associated adipocytes: Emerging supporters in breast cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, N.M.; Zhou, X.K.; Gucalp, A.; Morris, P.G.; Howe, L.R.; Giri, D.D.; Morrow, M.; Wang, H.; Pollak, M.; Jones, L.W.; et al. Systemic Correlates of White Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Early-Stage Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2283–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggiani, F.; Labanca, V.; Mancuso, P.; Rabascio, C.; Talarico, G.; Orecchioni, S.; Manconi, A.; Bertolini, F. Adipose Progenitor Cell Secretion of GM-CSF and MMP-9 Promoters a Stromal and Immunological Microenvironment That Supports Breast Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5169–5182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doyle, M.; Kwami, N.; Joshi, J.; Arendt, L.M.; McCready, J. Interaction between Macrophages and Adipose Stromal Cells Increases the Angiogenic and Proliferative Potential of Pregnancy-Associated Breast Cancers. Cancers 2023, 15, 4500. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184500
Doyle M, Kwami N, Joshi J, Arendt LM, McCready J. Interaction between Macrophages and Adipose Stromal Cells Increases the Angiogenic and Proliferative Potential of Pregnancy-Associated Breast Cancers. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4500. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184500
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoyle, Michael, Noor Kwami, Jaitri Joshi, Lisa M. Arendt, and Jessica McCready. 2023. "Interaction between Macrophages and Adipose Stromal Cells Increases the Angiogenic and Proliferative Potential of Pregnancy-Associated Breast Cancers" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4500. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184500
APA StyleDoyle, M., Kwami, N., Joshi, J., Arendt, L. M., & McCready, J. (2023). Interaction between Macrophages and Adipose Stromal Cells Increases the Angiogenic and Proliferative Potential of Pregnancy-Associated Breast Cancers. Cancers, 15(18), 4500. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184500







