Dual Targeting of EZH2 Degradation and EGFR/HER2 Inhibition for Enhanced Efficacy against Burkitt’s Lymphoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.2. Drug Preparations
2.3. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) Assay
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.6. Real-Time Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-PCR)
2.7. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
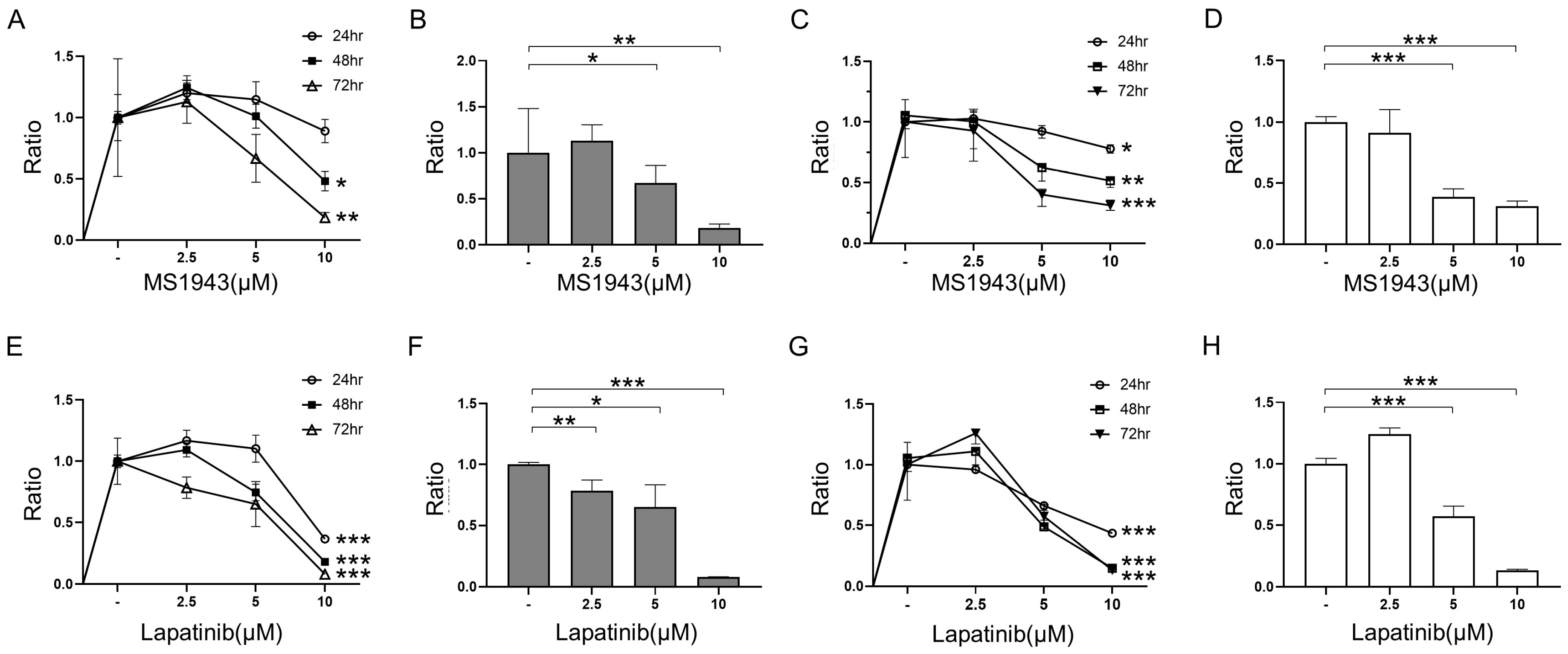
3.1. MS1943 (EZH2 Degrader) and Lapatinib (EGFR/HER2 Inhibitor) Inhibit Cell Growth in BL Cells
3.2. MS1943 Synergizes with Lapatinib Drugs in BL Cell Lines, Resulting in Significant BL Proliferation Inhibition
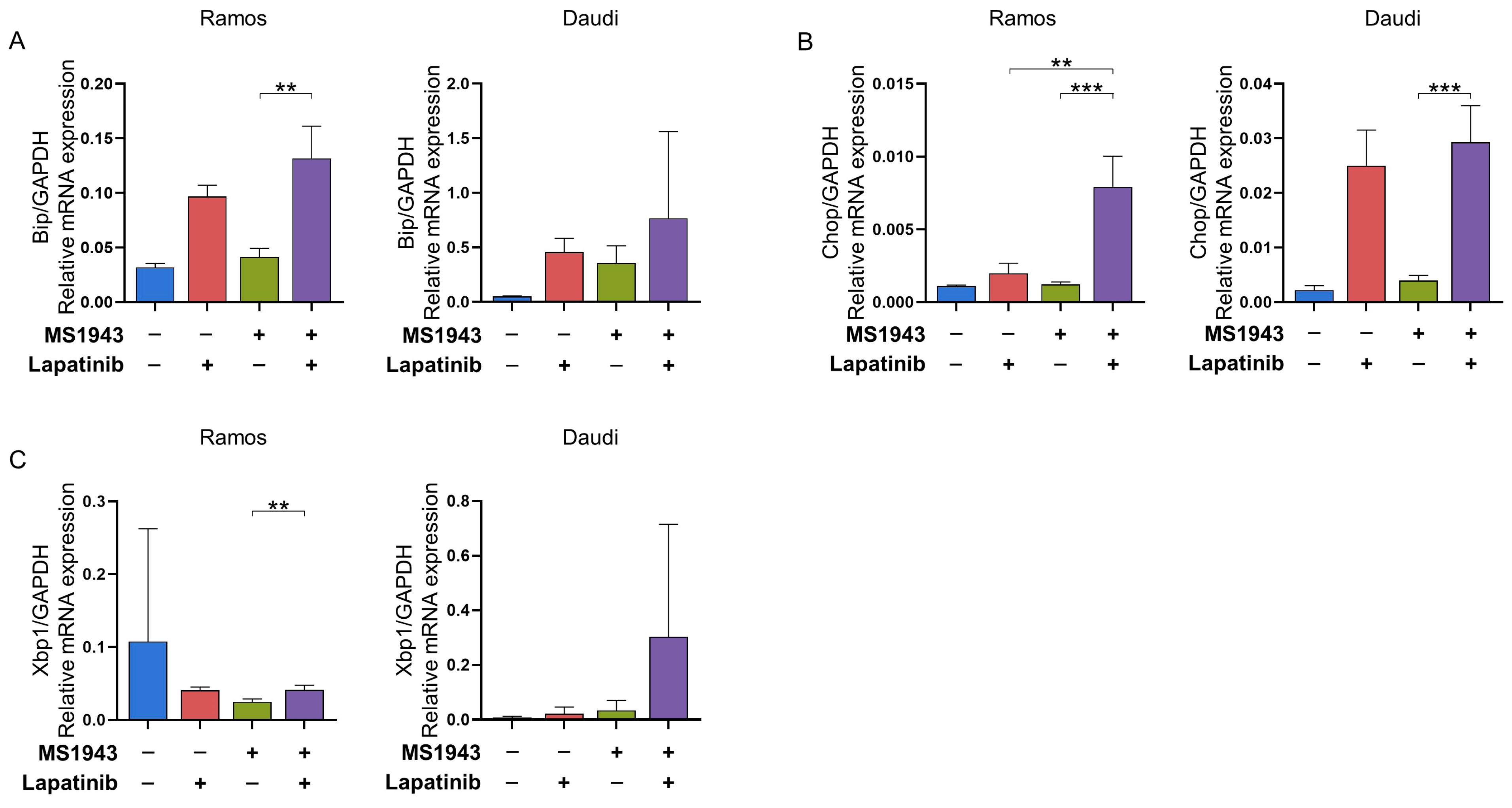
3.3. Combination of MS1943 and Lapatinib Therapy Induces Prolonged Activation of the UPR Pathway in BL Cells
3.4. Combination of MS1943 and Lapatinib Leads to BL Cell Cycle Arrest
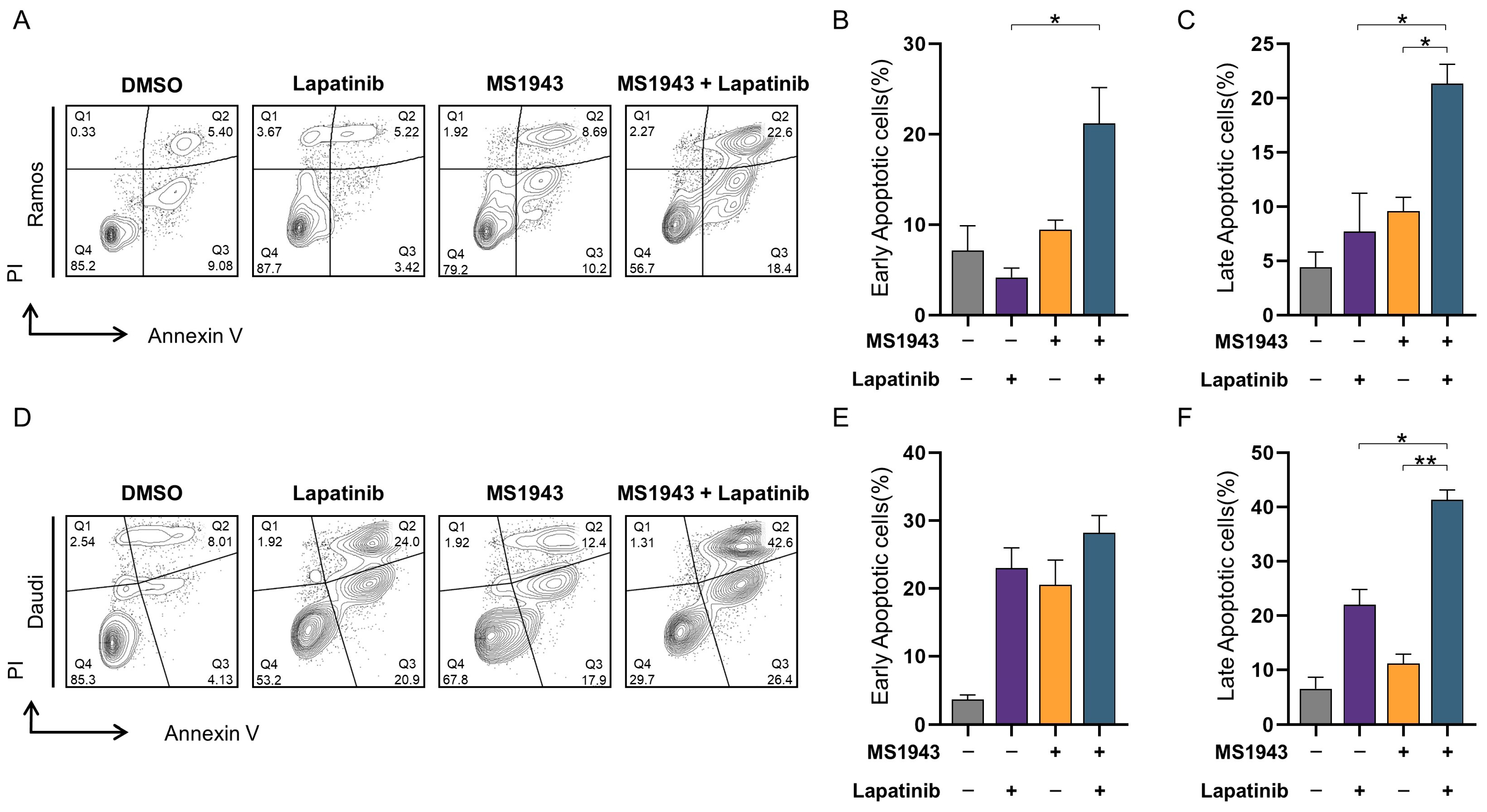
3.5. Synergistic Effects of MS1943 and Lapatinib Promote Apoptotic Cell Death
3.6. Combination of MS1943 and Lapatinib Induces Apoptosis through Caspase Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmitz, R.; Ceribelli, M.; Pittaluga, S.; Wright, G.; Staudt, L.M. Oncogenic mechanisms in Burkitt lymphoma. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.; Young, R.M.; Ceribelli, M.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, M.; Wright, G.; Shaffer, A.L.; Hodson, D.J.; Buras, E.; et al. Burkitt lymphoma pathogenesis and therapeutic targets from structural and functional genomics. Nature 2012, 490, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.A. Burkitt’s lymphoma: Clinicopathologic features and differential diagnosis. Oncologist 2006, 11, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teras, L.R.; DeSantis, C.E.; Cerhan, J.R.; Morton, L.M.; Jemal, A.; Flowers, C.R. 2016 US lymphoid malignancy statistics by World Health Organization subtypes. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roschewski, M.; Dunleavy, K.; Abramson, J.S.; Powell, B.L.; Link, B.K.; Patel, P.; Bierman, P.J.; Jagadeesh, D.; Mitsuyasu, R.T.; Peace, D.; et al. Multicenter Study of Risk-Adapted Therapy with Dose-Adjusted EPOCH-R in Adults with Untreated Burkitt Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2519–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evens, A.M.; Danilov, A.; Jagadeesh, D.; Sperling, A.; Kim, S.H.; Vaca, R.; Wei, C.; Rector, D.; Sundaram, S.; Reddy, N.; et al. Burkitt lymphoma in the modern era: Real-world outcomes and prognostication across 30 US cancer centers. Blood 2021, 137, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crombie, J.; LaCasce, A. The treatment of Burkitt lymphoma in adults. Blood 2021, 137, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Burkhardt, B.; Chan, J.K.C.; Leoncini, L.; Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Ogwang, M.D.; Orem, J.; Rochford, R.; Roschewski, M.; Siebert, R. Burkitt lymphoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2022, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, J.K.; Amengual, J.E. Emerging EZH2 Inhibitors and Their Application in Lymphoma. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2018, 13, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, R.; Du, W.; Guo, W. EZH2: A novel target for cancer treatment. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Ren, C.; Banerjee, S.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, Y. Targeting EZH2 for cancer therapy: From current progress to novel strategies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 238, 114419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Hu, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, W.; Su, X.; He, H.; Zhou, S.; Hu, R.; et al. Design and Synthesis of EZH2-Based PROTACs to Degrade the PRC2 Complex for Targeting the Noncatalytic Activity of EZH2. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 2829–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, A.; Stratikopoulos, E.; Park, K.S.; Wei, J.; Martin, T.C.; Yang, X.; Schwarz, M.; Leshchenko, V.; Rialdi, A.; Dale, B.; et al. Discovery of a first-in-class EZH2 selective degrader. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cell Proliferation Signaling Pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, R.; Roden, D.L.; Teo, W.S.; McFarland, A.; Junankar, S.; Ye, S.; Nguyen, A.; Yang, J.; Nikolic, I.; Hui, M.; et al. c-Myc and Her2 cooperate to drive a stem-like phenotype with poor prognosis in breast cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3992–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Pu, T.; Chen, S.; Qiu, Y.; Zhong, X.; Zheng, H.; Chen, L.; Bu, H.; Ye, F. Breast cancers with EGFR and HER2 co-amplification favor distant metastasis and poor clinical outcome. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 6562–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lv, Y.; Sui, F.; Ma, J.; Ren, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, H.; Shi, B.; Hou, P.; Ji, M. Increased expression of EHF contributes to thyroid tumorigenesis through transcriptionally regulating HER2 and HER3. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57978–57990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranic, S.; Beslija, S.; Gatalica, Z. Targeting HER2 expression in cancer: New drugs and new indications. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2021, 21, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.R.; Railkar, R.; Sanford, T.; Crooks, D.R.; Eckhaus, M.A.; Haines, D.; Choyke, P.L.; Kobayashi, H.; Agarwal, P.K. Targeting Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) Expressing Bladder Cancer Using Combination Photoimmunotherapy (PIT). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanezi, F.; Carvalho, S.; Schmitt, F.C. EGFR/HER2 in breast cancer: A biological approach for molecular diagnosis and therapy. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2008, 8, 417–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, P.J.; Goodin, S. Lapatinib: A dual inhibitor of human epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Clin. Ther. 2008, 30, 1426–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Dhadda, A.S.; Shehata, M.; Chan, S. Lapatinib: A tyrosine kinase inhibitor with a clinical role in breast cancer. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2007, 8, 2189–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.H.; Iwakoshi, N.N.; Glimcher, L.H. XBP-1 regulates a subset of endoplasmic reticulum resident chaperone genes in the unfolded protein response. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 23, 7448–7459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieger, A.M.; Nelson, K.L.; Konowalchuk, J.D.; Barreda, D.R. Modified annexin V/propidium iodide apoptosis assay for accurate assessment of cell death. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 2011, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.J.; Hong, Y.K.; Kim, K.H.; Han, C.H.; Cho, S.H.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, B.W. Methanolic extract of Pterocarpus santalinus induces apoptosis in HeLa cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 105, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, A.G.; Janicke, R.U. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villunger, A.; Michalak, E.M.; Coultas, L.; Mullauer, F.; Bock, G.; Ausserlechner, M.J.; Adams, J.M.; Strasser, A. p53- and drug-induced apoptotic responses mediated by BH3-only proteins puma and noxa. Science 2003, 302, 1036–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, M.T.; Ott, H.M.; Ganji, G.; Korenchuk, S.; Thompson, C.; Van Aller, G.S.; Liu, Y.; Graves, A.P.; Della Pietra, A., 3rd; Diaz, E.; et al. EZH2 inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for lymphoma with EZH2-activating mutations. Nature 2012, 492, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chng, W.J. EZH2 abnormalities in lymphoid malignancies: Underlying mechanisms and therapeutic implications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eich, M.L.; Athar, M.; Ferguson, J.E., 3rd; Varambally, S. EZH2-Targeted Therapies in Cancer: Hype or a Reality. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 5449–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.B.; Yang, C.-E.; Jeong, Y.; Yu, M.; Choi, W.-S.; Lim, J.-Y.; Jeon, Y. Dual Targeting of EZH2 Degradation and EGFR/HER2 Inhibition for Enhanced Efficacy against Burkitt’s Lymphoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 4472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184472
Kim SB, Yang C-E, Jeong Y, Yu M, Choi W-S, Lim J-Y, Jeon Y. Dual Targeting of EZH2 Degradation and EGFR/HER2 Inhibition for Enhanced Efficacy against Burkitt’s Lymphoma. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184472
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Se Been, Chae-Eun Yang, Yurim Jeong, Minseo Yu, Wan-Su Choi, Jung-Yeon Lim, and Youngwoo Jeon. 2023. "Dual Targeting of EZH2 Degradation and EGFR/HER2 Inhibition for Enhanced Efficacy against Burkitt’s Lymphoma" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184472
APA StyleKim, S. B., Yang, C.-E., Jeong, Y., Yu, M., Choi, W.-S., Lim, J.-Y., & Jeon, Y. (2023). Dual Targeting of EZH2 Degradation and EGFR/HER2 Inhibition for Enhanced Efficacy against Burkitt’s Lymphoma. Cancers, 15(18), 4472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184472





