Clinical Experience with Abemaciclib in Patients Previously Treated with Another CDK 4/6 Inhibitor in a Tertiary Hospital: A Case Series Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patients
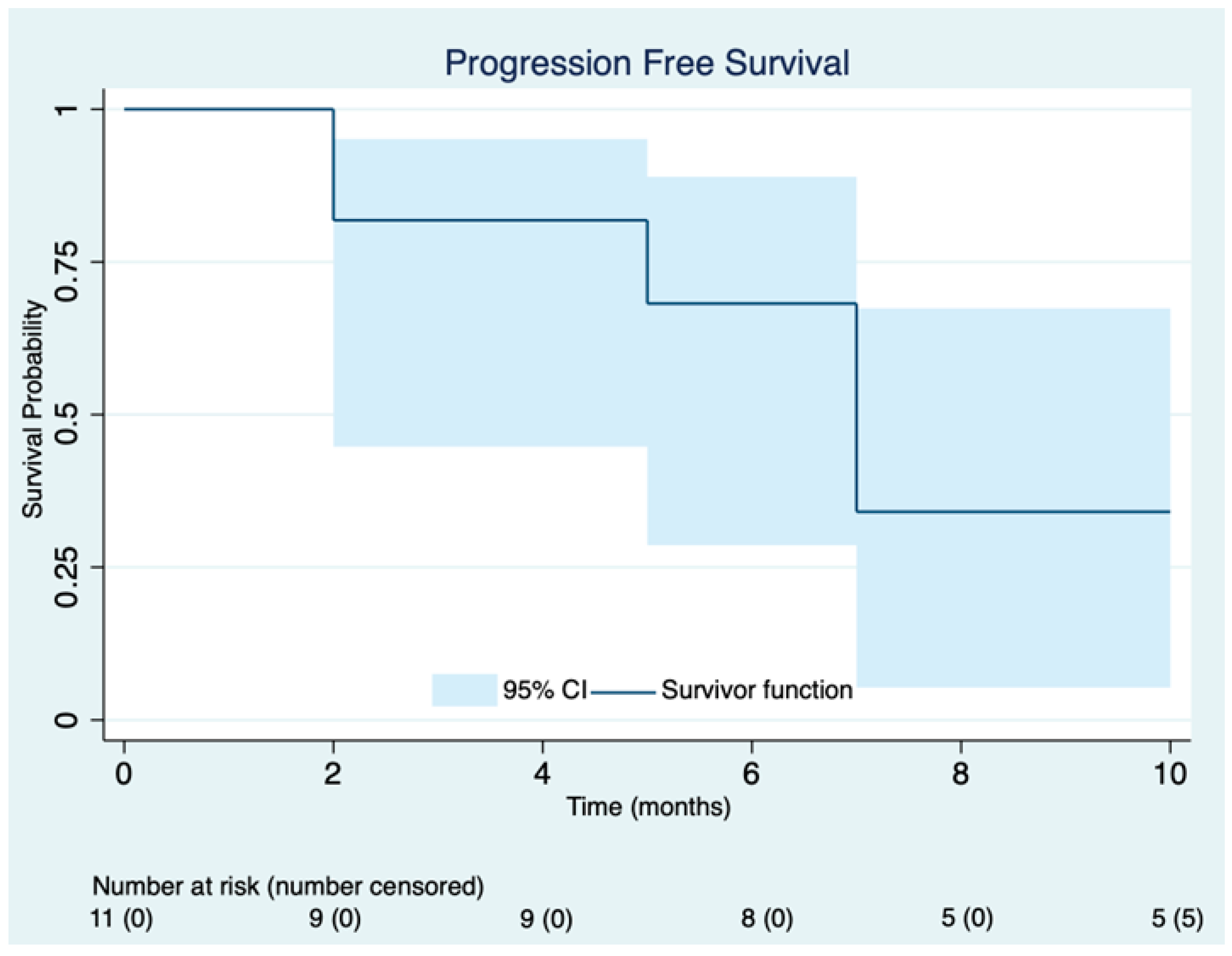
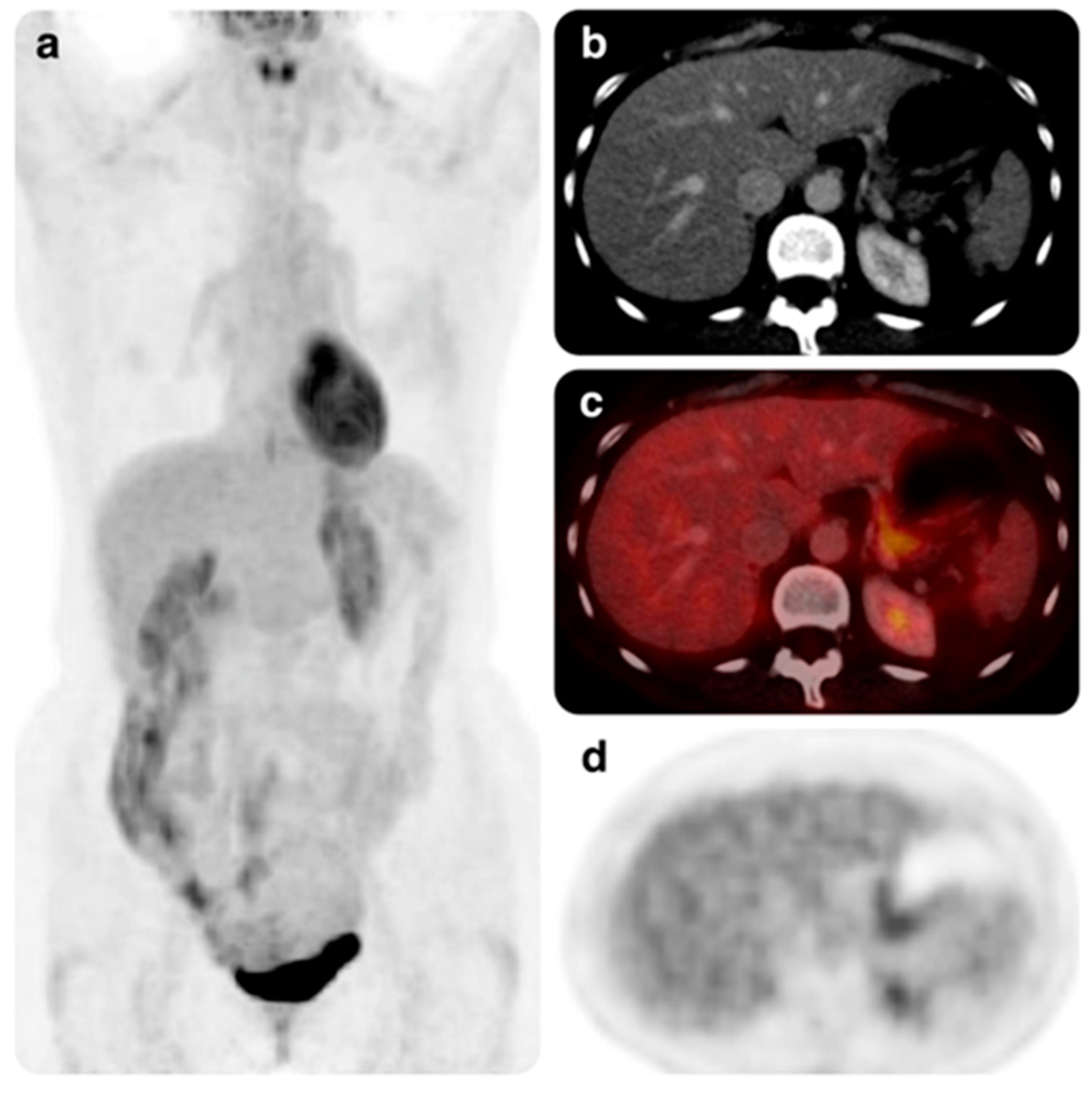
3.2. Efficacy
3.3. Safety
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, N.; Altekruse, S.F.; Li, C.I.; Chen, V.W.; Clarke, C.A.; Ries, L.A.; Cronin, K.A. US Incidence of Breast Cancer Subtypes Defined by Joint Hormone Receptor and HER2 Status. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Groot, A.; Kuijpers, C.; Kroep, J. CDK4/6 inhibition in early and metastatic breast cancer: A review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 60, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafner, M.; Mills, C.E.; Subramanian, K.; Chen, C.; Chung, M.; Boswell, S.A.; Everley, R.A.; Liu, C.; Walmsley, C.S.; Juric, D.; et al. Multiomics Profiling Establishes the Polypharmacology of FDA-Approved CDK4/6 Inhibitors and the Potential for Differential Clinical Activity. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 1067–1080.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickler, M.N.; Tolaney, S.M.; Rugo, H.S.; Cortés, J.; Diéras, V.; Patt, D.; Wildiers, H.; Hudis, C.A.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Zamora, E.; et al. MONARCH 1, A Phase II Study of Abemaciclib, a CDK4 and CDK6 Inhibitor, as a Single Agent, in Patients with Refractory HR+/HER2- Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5218–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, E.; Cortes, J.; Ozyilkan, O.; Chen, S.-C.; Petrakova, K.; Manikhas, A.; Jerusalem, G.; Hegg, R.; Huober, J.; Chapman, S.C.; et al. nextMONARCH: Abemaciclib Monotherapy or Combined With Tamoxifen for Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2020, 21, 181–190.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Abreu, M.T.; Palafox, M.; Asghar, U.; Rivas, M.A.; Cutts, R.J.; Garcia-Murillas, I.; Pearson, A.; Guzman, M.; Rodriguez, O.; Grueso, J.; et al. Early Adaptation and Acquired Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibition in Estrogen Receptor–Positive Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2301–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condorelli, R.; Spring, L.; O’shaughnessy, J.; Lacroix, L.; Bailleux, C.; Scott, V.; Dubois, J.; Nagy, R.; Lanman, R.; Iafrate, A.; et al. Polyclonal RB1 mutations and acquired resistance to CDK 4/6 inhibitors in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 29, 640–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, Z.; Bhatt, T.; Dickler, M.; Giri, D.; Scaltriti, M.; Baselga, J.; Rosen, N.; Chandarlapaty, S. Acquired CDK6 amplification promotes breast cancer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors and loss of ER signaling and dependence. Oncogene 2016, 36, 2255–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldon, C.E.; Sergio, C.M.; Kang, J.; Muthukaruppan, A.; Boersma, M.N.; Stone, A.; Barraclough, J.; Lee, C.S.; Black, M.A.; Miller, L.D.; et al. Cyclin E2 overexpression is associated with endocrine resistance but not insensitivity to CDK2 inhibition in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1488–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.C.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Loi, S.; Colleoni, M.; Loibl, S.; DeMichele, A.; Harbeck, N.; André, F.; Bayar, M.A.; et al. Cyclin E1 Expression and Palbociclib Efficacy in Previously Treated Hormone Receptor–Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formisano, L.; Lu, Y.; Servetto, A.; Hanker, A.B.; Jansen, V.M.; Bauer, J.A.; Sudhan, D.R.; Guerrero-Zotano, A.L.; Croessmann, S.; Guo, Y.; et al. Aberrant FGFR signaling mediates resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in ER+ breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarducci, C.; Bonechi, M.; Benelli, M.; Biagioni, C.; Boccalini, G.; Romagnoli, D.; Verardo, R.; Schiff, R.; Osborne, C.K.; De Angelis, C.; et al. Cyclin E1 and Rb modulation as common events at time of resistance to palbociclib in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. npj Breast Cancer 2018, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risi, E.; Grilli, A.; Migliaccio, I.; Biagioni, C.; McCartney, A.; Guarducci, C.; Bonechi, M.; Benelli, M.; Vitale, S.; Biganzoli, L.; et al. A gene expression signature of Retinoblastoma loss-of-function predicts resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in ER-positive/HER2-positive breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 170, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Bhardwaj, V.; Das, P.; Purohit, R. Natural analogues inhibiting selective cyclin-dependent kinase protein isoforms: A computational perspective. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 38, 5126–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Bhardwaj, V.K.; Sharma, J.; Das, P.; Purohit, R. Identification of selective cyclin-dependent kinase 2 inhibitor from the library of pyrrolone-fused benzosuberene compounds: An in silico exploration. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 40, 7693–7701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Health and Human Studies Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE). Version 5.0. 27 November 2017. Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_5x7.pdf (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Cardoso, F.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Senkus, E.; Curigliano, G.; Aapro, M.S.; André, F.; Barrios, C.H.; Bergh, J.; Bhattacharyya, G.S.; Biganzoli, L.; et al. 5th ESO-ESMO international consensus guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC 5). Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 1623–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rugo, H.S.; Rumble, R.B.; Macrae, E.; Barton, D.L.; Connolly, H.K.; Dickler, M.N.; Fallowfield, L.; Fowble, B.; Ingle, J.N.; Jahanzeb, M.; et al. Endocrine Therapy for Hormone Receptor–Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3069–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Martin, M.; Rugo, H.S.; Jones, S.; Im, S.-A.; Gelmon, K.; Harbeck, N.; Lipatov, O.N.; Walshe, J.M.; Moulder, S.; et al. Palbociclib and Letrozole in Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1925–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Turner, N.C.; Bondarenko, I.; Ro, J.; Im, S.-A.; Masuda, N.; Colleoni, M.; DeMichele, A.; Loi, S.; Verma, S.; et al. Fulvestrant plus palbociclib versus fulvestrant plus placebo for treatment of hormone-receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer that progressed on previous endocrine therapy (PALOMA-3): Final analysis of the multicentre, double-blind, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.-S.; Sonke, G.S.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Campone, M.; Blackwell, K.L.; André, F.; Winer, E.P.; et al. Ribociclib as First-Line Therapy for HR-Positive, Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1738–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.S.; Sonke, G.S.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; O’shaughnessy, J. Updated results from MONALEESA-2, a phase 3 trial of first-line ribociclib plus letrozole in hormone receptor-positive (HR+), HER2- negative (HER2-), advanced breast cancer (ABC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, S.-A.; Lu, Y.-S.; Bardia, A.; Harbeck, N.; Colleoni, M.; Franke, F.; Chow, L.; Sohn, J.; Lee, K.-S.; Campos-Gomez, S.; et al. Overall Survival with Ribociclib plus Endocrine Therapy in Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sledge, G.W., Jr.; Toi, M.; Neven, P.; Sohn, J.; Inoue, K.; Pivot, X.; Burdaeva, O.; Okera, M.; Masuda, N.; Kaufman, P.A.; et al. MONARCH 2: Abemaciclib in Combination with Fulvestrant in Women With HR+/HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer Who Had Progressed While Receiving Endocrine Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2875–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sledge, G.W.; Toi, M.; Neven, P.; Sohn, J.; Inoue, K.; Pivot, X.; Burdaeva, O.; Okera, M.; Masuda, N.; Kaufman, P.A.; et al. The effect of abemaciclib plus fulvestrant on overall survival in hormone receptor-positive, ERBB2-negative breast cancer that progressed on endocrine therapy-MONARCH 2: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, M.P.; Toi, M.; Campone, M.; Sohn, J.; Paluch-Shimon, S.; Huober, J.; Park, I.H.; Trédan, O.; Chen, S.-C.; Manso, L.; et al. MONARCH 3: Abemaciclib As Initial Therapy for Advanced Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3638–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wander, S.A.; Cohen, O.; Gong, X.; Johnson, G.N.; Buendia-Buendia, J.E.; Lloyd, M.R.; Kim, D.; Luo, F.; Mao, P.; Helvie, K.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of Intrinsic and Acquired Resistance to Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitors in Patients with Hormone Receptor–Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1174–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wander, S.A.; Spring, L.M.; Stein, C.R.; Yuen, M.; Zangardi, M.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Bardia, A. Abstract P-06-18-39: Abemaciclib after prior palbociclib exposure in patients with metastatic hormone-receptor positive (HR?)/HER2- breast cancer. In Proceedings of the 2018 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, San Antonio, TX, USA, 4–8 December 2018; Available online: https://www.abstracts2view.com/sabcs/view.php?nu=SABCS18L_1832 (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Wander, S.A.; Zangardi, M.; Niemierko, A.; Kambadakone, A.; Kim, L.S.; Xi, J.; Pandey, A.K.; Spring, L.; Stein, C.; Juric, D.; et al. A multicenter analysis of abemaciclib after progression on palbociclib in patients (pts) with hormone receptor-positive (HR?)/HER2- metastatic breast cancer (MBC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. S15), 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, V.; Khong, H.T.; Soliman, H.H.; Costa, R.L.; Fisher, S.; Boulware, D.; Han, H.S. Efficacy of abemaciclib (abema) after palbociclib (palbo) in patients (pts) with metastatic breast cancer (MBC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, e12521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, S.; Makino, T.; Umetsu, R.; Tanaka, T. A Case of Palbociclib plus Fulvestrant‒Resistant Metastatic Breast Cancer That Responded to Abemaciclib plus Fulvestrant. Gan Kagaku Ryoho. Cancer Chemother. 2021, 48, 519–521. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro, A.; Tanimoto, A.; Ito, K.; Ohigashi, A.; Kato, H.; Abe, M.; Kubota, R.; Chiba, R.; Matsunami, O.; Narita, Y. A Case of Hormone Receptor‒Positive HER2‒Negative Advanced/Recurrent Breast Cancer with 1.5 Years Withdrawal Period of Palbociclib Showed a Good Response Treated by Abemaciclib and Fulvestrant. Gan kagaku ryoho. Cancer Chemother. 2021, 48, 697–699. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Wender, I.O.; Haines, K.; Jahanzeb, M. Response to Abemaciclib After 10 Lines of Therapy Including Palbociclib in Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Case Report with Literature Review. Oncol. Ther. 2020, 8, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov Web Page. Bethesda (MD): National Library of Medicine (US). Identifier: NCT05169567, Study of Abemaciclib (LY2835219) Plus Fulvestrant Compared to Placebo Plus Fulvestrant in Previously Treated Breast Cancer (postMONARCH). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05169567?term=postmonarch&draw=2&rank=1 (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Kalinsky, K.; Layman, R.M.; Kaufman, P.A.; Graff, S.L.; Bianchini, G.; Martin, M.; Zhou, Y.; Knoderer, H.; Litchfield, L.; Wander, S.A. postMONARCH: A phase 3 study of abemaciclib plus fulvestrant versus placebo plus fulvestrant in patients with HR+, HER2-, metastatic breast cancer following progression on a CDK4 & 6 inhibitor and endocrine therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S16), TPS1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, E.; Brufsky, A.; Rugo, H.S.; Vogel, C.L.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Getzenberg, R.H.; Barnette, K.G.; Rodriguez, D.; Bird, G.; Steiner, M.S.; et al. Phase 3 ENABLAR-2 study to evaluate enobosarm and abemaciclib combination compared to estrogen-blocking agent for the second-line treatment of AR+, ER+, HER2- metastatic breast cancer in patients who previously received palbociclib and estrogen-blocking agent combination therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S16), TPS1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, S.; Plourde, P.V.; Moore, H.C.F.; Anderson, I.C.; Portman, D.J. Open-label, phase 2, multicenter study of lasofoxifene (LAS) combined with abemaciclib (Abema) for treating pre- and postmenopausal women with locally advanced or metastatic ER+/HER2- breast cancer and an ESR1 mutation after progression on prior therapies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40 (Suppl. S16), 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinsky, K.; Accordino, M.K.; Chiuzan, C.; Mundi, P.S.; Sakach, E.; Sathe, C.; Ahn, H.; Trivedi, M.S.; Novik, Y.; Tiersten, A.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Endocrine Therapy with or Without Ribociclib After Progression on Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibition in Hormone Receptor–Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: MAINTAIN Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, JCO2202392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.L.; Ren, Y.; Wagle, N.; Ma, C.; DeMichele, A.; Cristofanilli, M.; Meisel, J. Palbociclib after CDK4/6i and endocrine therapy (PACE): A randomized phase II study of fulvestrant, palbociclib, and avelumab for endocrine pre-treated ER+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer. In Proceedings of the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, San Antonio, TX, USA, 6–10 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Llombart-Cussac, A.; Harper-Wynne, C.; Perello, A.; Hennequin, A.; Fernandez, A.; Colleoni, M.; Carañana, V.; Quiroga, V.; Medioni, J.; Iranzo, V.; et al. Second-line endocrine therapy (ET) with or without palbociclib (P) maintenance in patients (pts) with hormone receptor-positive (HR[+])/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2[−]) advanced breast cancer (ABC): PALMIRA trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Patients Included (n = 11) |
|---|---|
| Age in years, median (range) | 69 (42–84) |
| Sex, n (%) | |
| Female | 11 (100) |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |
| Caucasian | 10 (90.9) |
| Hispanic | 1 (9.1) |
| Median number of previous lines (range) | 3 (1–7) |
| Previous treatment modalities, n (%) | |
| Endocrine therapy | 11 (100) |
| Chemoendocrine therapy | 6 (54.4) |
| Prior CDK4/6 inhibitors | |
| Palbociclib | 7 (63.6) |
| Ribociclib | 4 (36.4) |
| Median time from metastatic diagnosis to treatment with abemaciclib in months, median (range) | 50 (21–71) |
| Median time until treatment with abemaciclib in months since previous CDK4/6 inhibitors (range) | 17.5 (3–41) |
| Median number of endocrine therapies until treatment with abemaciclib since previous CDK4/6 inhibitors (range) | 1 (0–2) |
| Median number of chemotherapies until treatment with abemaciclib since previous CDK4/6 inhibitors (range) | 2 (0–6) |
| Combined therapy, n (%) | |
| Monotherapy | 1 (9.1) |
| Tamoxifen | 9 (81.8) |
| Aromatase inhibitor | 1 (9.1) |
| Visceral involvement, n (%) | |
| Yes | 8 (72.7) |
| No | 3 (27.3) |
| Patient ID | Prior CDK4/6 Inhibitor | Best Response | Calculated PFS (Months) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ribociclib | PR | 6 |
| 2 | Ribociclib | PD | 4 |
| 3 | Palbociclib | PR | 10 |
| 4 | Palbociclib | PD | 2 |
| 5 | Palbociclib | PR | 7 (ongoing) |
| 6 | Ribociclib | CR | 7 (ongoing) |
| 7 | Ribociclib | SD | 8 |
| 8 | Palbociclib | PD | 3 |
| 9 | Palbociclib | PR | 5 (ongoing) |
| 10 | Ribociclib | SD | 2 (ongoing) |
| 11 | Palbociclib | PR | 2 (ongoing) |
| Name of Study | Phase of Study | Drug | Prior CDK4/6 Inhibitors Used | Arms of Treatment | Primary Outcome Measures | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| postMONARCH [36] | III | Abemaciclib | Palbociclib, abemaciclib, ribociclib | Abemaciclib plus fulvestrant vs. placebo plus fulvestrant | PFS | Pending |
| MAINTAIN [40] | II | Ribociclib | Palbociclib, abemaciclib, ribociclib | Ribociclib plus fulvestrant/exemestane vs. placebo plus fulvestrant/exemestane | PFS Percentage of patients free of progression at 24 weeks from the start of the study | Positive |
| PACE [41] | II | Palbociclib | Palbociclib, abemaciclib, ribociclib | Fulvestrant vs. fulvestrant with palbociclib vs. fulvestrant with palbociclib and avelumab | PFS | Negative |
| PALMIRA [42] | II | Palbociclib | Palbociclib Must have achieved clinical benefit criteria in response to a first-line palbociclib-based endocrine regimen | Palbociclib plus letrozole/fulvestrant vs. letrozole/fulvestrant | PFS | Negative |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Luna Aguilar, A.M.; Fuentes, J.D.B.; Ortega Anselmi, J.; Olalla Inoa, J.; Flores Navarro, P.; Lopez de Sá, A.; Fuentes Antras, J.; Rodríguez Rey, C.; Ortega Candil, A.; Moreno Antón, F.; et al. Clinical Experience with Abemaciclib in Patients Previously Treated with Another CDK 4/6 Inhibitor in a Tertiary Hospital: A Case Series Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 4452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184452
de Luna Aguilar AM, Fuentes JDB, Ortega Anselmi J, Olalla Inoa J, Flores Navarro P, Lopez de Sá A, Fuentes Antras J, Rodríguez Rey C, Ortega Candil A, Moreno Antón F, et al. Clinical Experience with Abemaciclib in Patients Previously Treated with Another CDK 4/6 Inhibitor in a Tertiary Hospital: A Case Series Study. Cancers. 2023; 15(18):4452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184452
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Luna Aguilar, Alicia Milagros, Javier David Benitez Fuentes, Justo Ortega Anselmi, Jennifer Olalla Inoa, Paloma Flores Navarro, Alfonso Lopez de Sá, Jesus Fuentes Antras, Cristina Rodríguez Rey, Aída Ortega Candil, Fernando Moreno Antón, and et al. 2023. "Clinical Experience with Abemaciclib in Patients Previously Treated with Another CDK 4/6 Inhibitor in a Tertiary Hospital: A Case Series Study" Cancers 15, no. 18: 4452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184452
APA Stylede Luna Aguilar, A. M., Fuentes, J. D. B., Ortega Anselmi, J., Olalla Inoa, J., Flores Navarro, P., Lopez de Sá, A., Fuentes Antras, J., Rodríguez Rey, C., Ortega Candil, A., Moreno Antón, F., & García Sáenz, J. Á. (2023). Clinical Experience with Abemaciclib in Patients Previously Treated with Another CDK 4/6 Inhibitor in a Tertiary Hospital: A Case Series Study. Cancers, 15(18), 4452. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15184452





