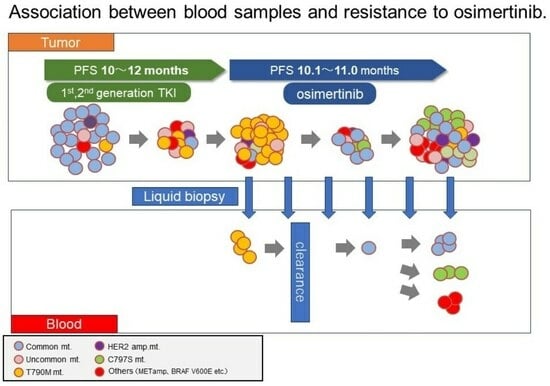
Monitoring of Plasma EGFR Mutations during Osimertinib Treatment for NSCLC Patients with Acquired T790M Mutation
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Study Design
2.2. Plasma Sample Collection and EGFR Mutation Analysis
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
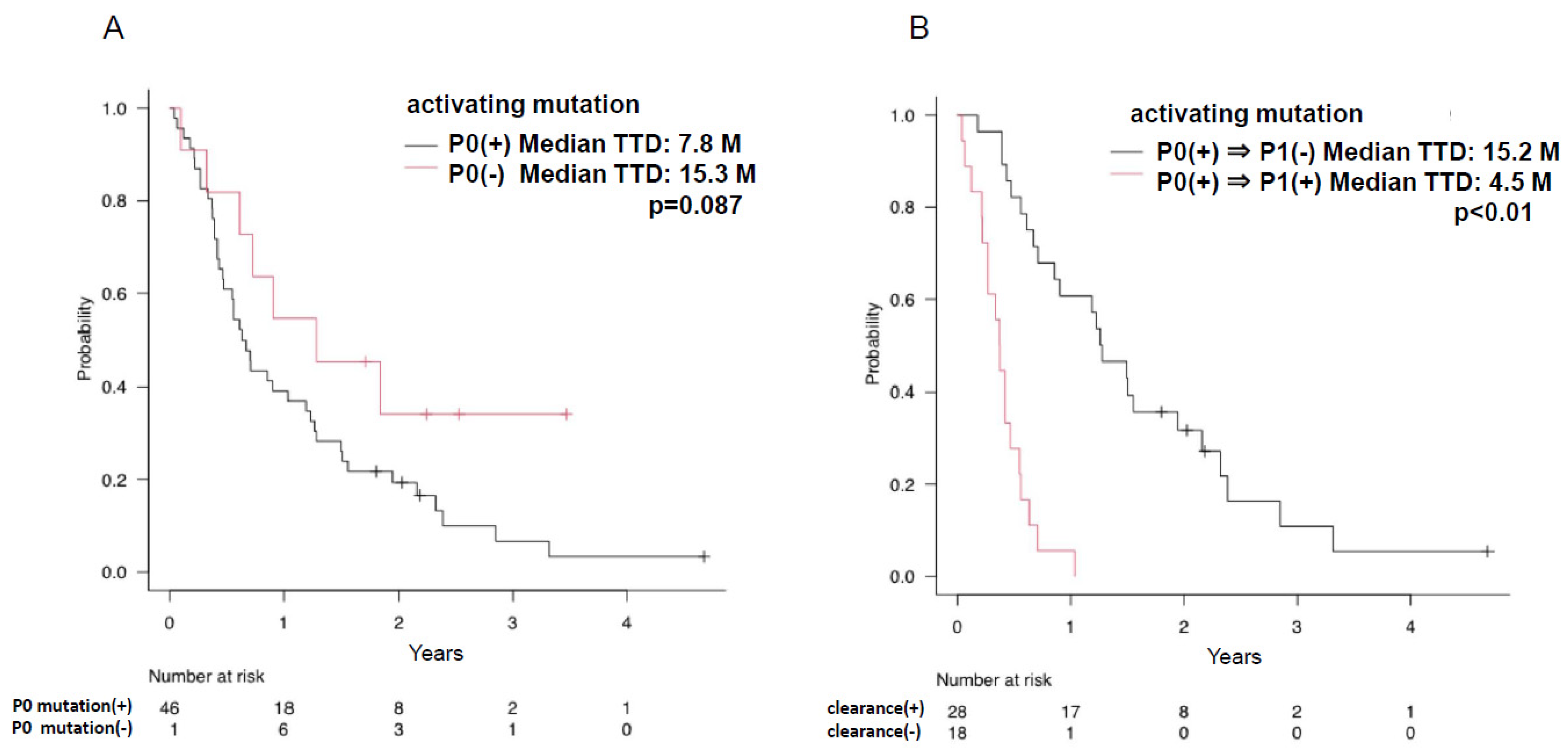
3.2. Plasma EGFR Mutations during Osimertinib Treatment and at Progression
3.3. Efficacy and Plasma EGFR Mutation Status of Osimertinib Treatment in Patients with EGFR T790M Mutation
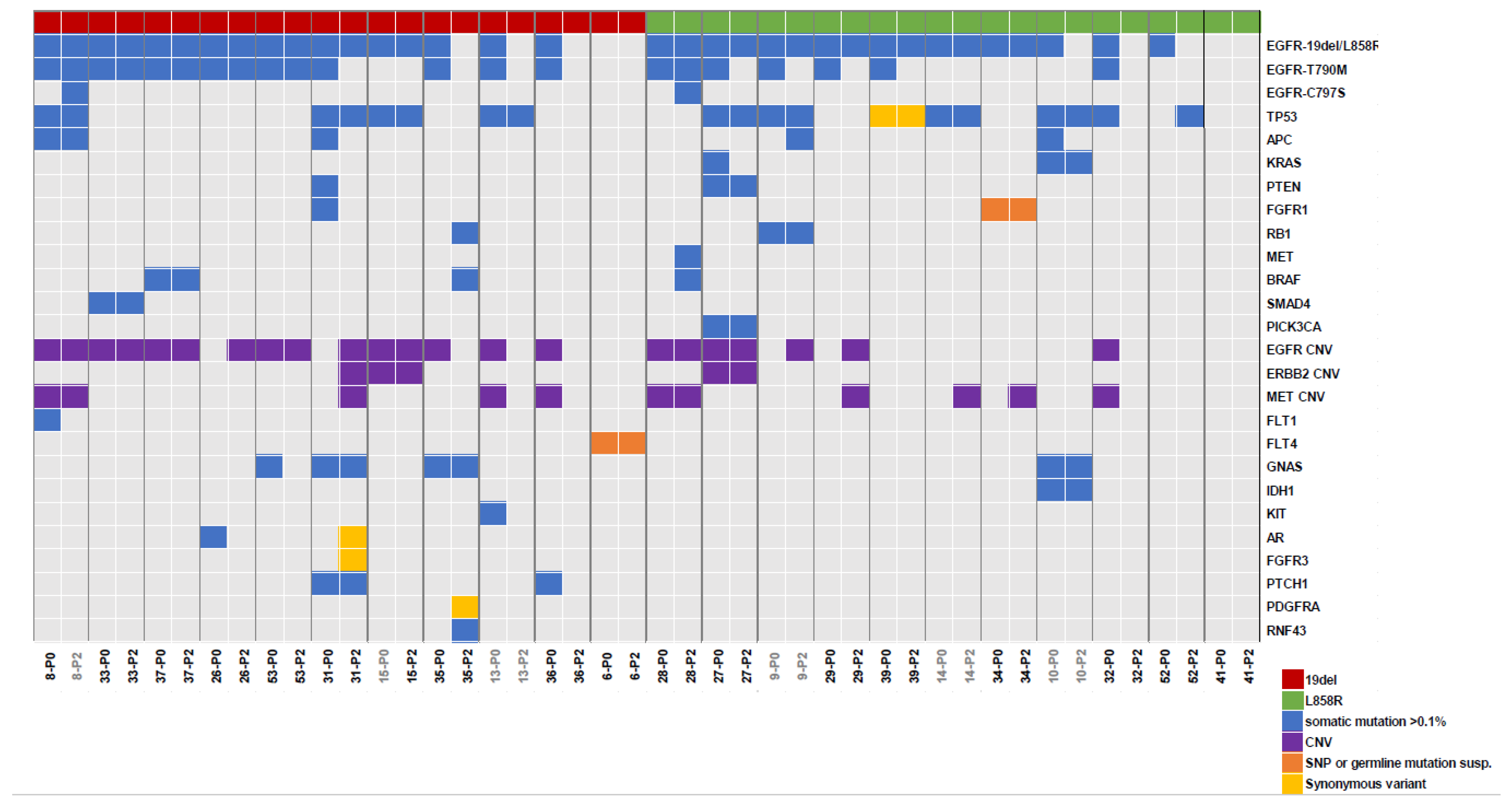
3.4. NGS Analysis of Plasma before and after Osimertinib Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cross, D.A.; Ashton, S.E.; Ghiorghiu, S.; Eberlein, C.; Nebhan, C.A.; Spitzler, P.J.; Orme, J.P.; Finlay, M.R.; Ward, R.A.; Mellor, M.J.; et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1046–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Arcila, M.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Sima, C.S.; Zakowski, M.F.; Pao, W.; Kris, M.G.; Miller, V.A.; Ladanyi, M.; Riely, G.J. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänne, P.A.; Yang, J.C.; Kim, D.W.; Planchard, D.; Ohe, Y.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, S.W.; Su, W.C.; Horn, L.; et al. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Ahn, M.J.; Kim, D.W.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Sequist, L.V.; Su, W.C.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Planchard, D.; Felip, E.; et al. Osimertinib in Pretreated T790M-Positive Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: AURA Study Phase II Extension Component. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1288–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, G.; Tsai, C.M.; Shepherd, F.A.; Bazhenova, L.; Lee, J.S.; Chang, G.C.; Crino, L.; Satouchi, M.; Chu, Q.; Hida, T.; et al. Osimertinib for pretreated EGFR Thr790Met-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (AURA2): A multicenter, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.-L.; Ahn, M.-J.; Garassino, M.C.; Kim, H.R.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Shepherd, F.A.; He, Y.; Akamatsu, H.; Theelen, W.S.; et al. Osimertinib or Platinum–Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M–Positive Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.C.; Shih, J.Y.; Yu, C.J.; Ho, C.C.; Liao, W.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Tsai, T.H.; Su, K.Y.; Hsieh, M.S.; Chang, Y.L.; et al. Outcomes in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and acquired Thr790Met mutation treated with osimertinib: A genomic study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Thress, K.S.; Alden, R.S.; Lawrance, R.; Paweletz, C.P.; Cantarini, M.; Yang, J.C.; Barrett, J.C.; Jänne, P.A. Association Between Plasma Genotyping and Outcomes of Treatment with Osimertinib (AZD9291) in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3375–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacher, A.G.; Komatsubara, K.M.; Oxnard, G.R. Application of Plasma Genotyping Technologies in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Practical Review. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1344–1356. [Google Scholar]
- Iwama, E.; Sakai, K.; Hidaka, N.; Inoue, K.; Fujii, A.; Nakagaki, N.; Ota, K.; Toyozawa, R.; Azuma, K.; Nakatomi, K.; et al. Longitudinal monitoring of somatic genetic alterations in circulating cell-free DNA during treatment with epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Cancer 2020, 126, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.B.F.; McCulloch, T.; Hansen, K.H.; Linnet, H.; Sorensen, B.; Meldgaard, P. Clearing of circulating tumor DNA predicts clinical response to first line tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced epidermal growth factor receptor mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2020, 141, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Fukuhara, T.; Tsukita, Y.; Morita, M.; Suzuki, A.; Tanaka, N.; Terasaki, H.; Nukiwa, T.; Maemondo, M. EGFR-mutation analysis of circulating tumor DNA using an improved PNA-LNA PCR clamp method. Can. Respir. J. 2016, 2016, 5297329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuhara, T.; Saito, H.; Furuya, N.; Watanabe, K.; Sugawara, S.; Iwasawa, S.; Tsunezuka, Y.; Yamaguchi, O.; Okada, P.M.; Yoshimori, K.; et al. Evaluation of plasma EGFR mutation as an early predictor of response of erlotinib plus bevacizumab treatment in the NEJ026 study. EBioMedicine 2020, 57, 102861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, Y.; Miyazawa, H.; Huqun; Tanaka, T.; Udagawa, K.; Kato, M.; Fukuyama, S.; Yokote, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Kanazawa, M.; et al. Genetic heterogeneity of the epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines revealed by a rapid and sensitive detection system, the peptide nucleic acid-locked nucleic acid PCR clamp. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7276–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nagai, Y.; Miyazawa, H.; Koyama, N.; Matsuoka, S.; Sutani, A.; Huqun; Udagawa, K.; Murayama, Y.; Nagata, M.; et al. Reliability of the peptide nucleic acid-locked nucleic acid polymerase chain reaction clamp-based test for epidermal growth factor receptor mutations integrated into the clinical practice for non-small cell lung cancers. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Food and Drug Administration, cobas EGFR Mutation Test v2. Available online: www.fda.gov/drugs/resources-information-approved-drugs/cobas-egfr-mutation-test (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Jenkins, S.; Yang, J.C.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Yu, K.; Patel, S.; Weston, S.; Hodge, R.; Cantarini, M.; Jänne, P.A.; Mitsudomi, T.; et al. Plasma ctDNA Analysis for Detection of the EGFR T790M Mutation in Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Katsuhiko, N.; Manabe, T.; Masuzawa, K.; Hasegawa, H.; Yasuda, H.; Kawada, I.; Soejima, K.; Betsuyaku, T. Comparison of detection methods of EGFR T790M mutations using plasma, serum, and tumor tissue in EGFR-TKI-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 3335–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwama, E.; Sakai, K.; Azuma, K.; Harada, T.; Harada, D.; Nosaki, K.; Hotta, K.; Ohyanagi, F.; Kurata, T.; Fukuhara, T.; et al. Monitoring of somatic mutations in circulating cell-free DNA by digital PCR and next-generation sequencing during afatinib treatment in patients with lung adenocarcinoma positive for EGFR activating mutations. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Lee, J.S.; Yu, C.J.; Sriuranpong, V.; Sandoval-Tan, J.; Ladrera, G.; Thongprasert, S.; Srimuninnimit, V.; Liao, M.; et al. Detection and Dynamic Changes of EGFR Mutations from Circulating Tumor DNA as a Predictor of Survival Outcomes in NSCLC Patients Treated with First-line Intercalated Erlotinib and Chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3196–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordi, P.; Re, M.D.; Minari, R.; Rofi, E.; Buti, S.; Restante, G.; Squadrilli, A.; Crucitta, S.; Casartelli, C.; Letizia, G.; et al. From the beginning to resistance: Study of plasma monitoring and resistance mechanisms in a cohort of patients treated with osimertinib for advanced T790M-positive NSCLC. Lung Cancer 2019, 131, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Hu, Y.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, N.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Dynamic cfDNA Analysis by NGS in EGFR T790M-Positive Advanced NSCLC Patients Failed to the First-Generation EGFR-TKIs. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 643199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, E.B.F.; McCulloch, T.; Hansen, K.H.; Linnet, H.; Sorensen, B.; Meldgaard, P. Clearing of circulating tumour DNA predicts clinical response to osimertinib in EGFR mutated lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 2020, 143, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Hu, Y.; Mileham, K.F.; Husain, H.; Costa, D.B.; Tracy, P.; Feeney, N.; Sholl, L.M.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Redig, A.J. Assessment of resistance mechanisms and clinical implications in patients with EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer and acquired resistance to osimertinib. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, B.; Kim, H.K.; Sun, J.M.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.J.; Park, K.; Lee, S.H. Genomic landscape of acquired resistance to third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR T790M-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer 2020, 126, 2704–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbosh, C.; Birkbak, N.J.; Wilson, G.A.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Constantin, T.; Salari, R.; Le Quesne, J.; Moore, D.A.; Veeriah, S.; Rosenthal, R.; et al. Phylogenetic ctDNA analysis depicts early-stage lung cancer evolution. Nature 2017, 545, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.A.; Chabon, J.J.; Lovejoy, A.F.; Newman, A.M.; Stehr, H.; Azad, T.D.; Khodadoust, M.S.; Esfahani, M.S.; Liu, C.L.; Zhou, L.; et al. Early Detection of Molecular Residual Disease in Localized Lung Cancer by Circulating Tumor DNA Profiling. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tie, J.; Wang, Y.; Tomasetti, C.; Li, L.; Springer, S.; Kinde, I.; Silliman, N.; Tacey, M.; Wong, H.L.; Christie, M.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA analysis detects minimal residual disease and predicts recurrence in patients with stage II colon cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 346ra92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielecki, J.; Mok, T.S.; Wu, Y.L.; Han, J.Y.; Ahn, M.J.; Ramalingam, S.S.; John, T.; Okamoto, I.; Yang, J.C.H.; Shepherd, F.A.; et al. Analysis of acquired resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer from the AURA3 trial. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Qin, K.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, D.; Jiang, H.; Liu, K.; Zhu, J.; Lv, H.; Li, T.; et al. Concurrent TP53 mutations predict poor outcomes of EGFR-TKI treatments in Chinese patients with advanced NSCLC. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 5665–5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, K.; Hou, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X. Prognostic value of TP53 concurrent mutations for EGFR- TKIs and ALK-TKIs based targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| n | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Median (range) | 68 (43–91) | |
| Gender | Male | 25 | 43 |
| Female | 33 | 57 | |
| EGFR mutation at daignosis | Del19 | 32 | 55 |
| L858R | 25 | 43 | |
| L858R + de novo T790M | 1 | 2 | |
| Disease stage | IIIB/IV | 48 | 83 |
| Postoperative recurrence | 8 | 14 | |
| Post-chemoradiotherapy recurrence | 2 | 3 | |
| Source of T790M | Tissue | 26 | 45 |
| Pleural effusion | 6 | 10 | |
| Blood | 26 | 45 | |
| T790M analysis methods | Cobas | 35 | 60 |
| PNA-LNA PCR Clamp | 23 | 40 | |
| Treatment line | 2nd | 30 | 52 |
| 3rd | 11 | 19 | |
| 4th+ | 17 | 29 | |
| First EGFR-TKI | Gefitinib | 25 | 43 |
| Erlotinib | 11 | 19 | |
| Afatinib | 22 | 38 |
| P0 | P1-1 | P1-2 | P1-3 | P1-4 | P1-5 | P1-6 | P2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 58 | 57 | 46 | 36 | 28 | 24 | 20 | 37 |
| Activating mutations | 47 | 27 | 14 | 9 | 6 | 7 | 3 | 30 |
| (%) | 81.0 | 47.4 | 30.4 | 25.0 | 21.4 | 29.2 | 15.0 | 81.1 |
| T790M | 44 | 10 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 13 |
| (%) | 75.9 | 17.5 | 10.9 | 8.3 | 10.7 | 8.3 | 5.0 | 35.1 |
| C797S | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Total | Activating Mutation | T790M | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 58 | P0(+) n = 47 | P0(−) n = 11 | P0(+) n = 44 | P0(−) n = 14 | |
| CR | 1 (1.7) | 1 (2.1) | 0 | 1 (2.3) | 0 |
| PR | 30 (51.5) | 21 (44.7) | 9 (81.8) | 23 (52.3) | 7 (50.0) |
| SD | 23 (39.7) | 21 (44.7) | 2 (18.2) | 16 (36.4) | 7 (50.0) |
| PD | 2 (3.4) | 2 (4.2) | 0 | 2 (4.5) | 0 |
| NE | 2 (3.4) | 2 (4.2) | 0 | 2 (4.5) | 0 |
| ORR (%) | 53.4 | 46.8 | 81.8 | 54.5 | 50.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watanabe, K.; Saito, R.; Miyauchi, E.; Nagashima, H.; Nakamura, A.; Sugawara, S.; Tanaka, N.; Terasaki, H.; Fukuhara, T.; Maemondo, M. Monitoring of Plasma EGFR Mutations during Osimertinib Treatment for NSCLC Patients with Acquired T790M Mutation. Cancers 2023, 15, 4231. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174231
Watanabe K, Saito R, Miyauchi E, Nagashima H, Nakamura A, Sugawara S, Tanaka N, Terasaki H, Fukuhara T, Maemondo M. Monitoring of Plasma EGFR Mutations during Osimertinib Treatment for NSCLC Patients with Acquired T790M Mutation. Cancers. 2023; 15(17):4231. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174231
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatanabe, Kana, Ryota Saito, Eisaku Miyauchi, Hiromi Nagashima, Atsushi Nakamura, Shunichi Sugawara, Nobuyuki Tanaka, Hiroshi Terasaki, Tatsuro Fukuhara, and Makoto Maemondo. 2023. "Monitoring of Plasma EGFR Mutations during Osimertinib Treatment for NSCLC Patients with Acquired T790M Mutation" Cancers 15, no. 17: 4231. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174231
APA StyleWatanabe, K., Saito, R., Miyauchi, E., Nagashima, H., Nakamura, A., Sugawara, S., Tanaka, N., Terasaki, H., Fukuhara, T., & Maemondo, M. (2023). Monitoring of Plasma EGFR Mutations during Osimertinib Treatment for NSCLC Patients with Acquired T790M Mutation. Cancers, 15(17), 4231. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174231