Studies to Assess the Utility of Serum Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Standard Protocol Approvals, Registrations, and Patient Consents
2.3. Study Design
2.4. Biomarker
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patients
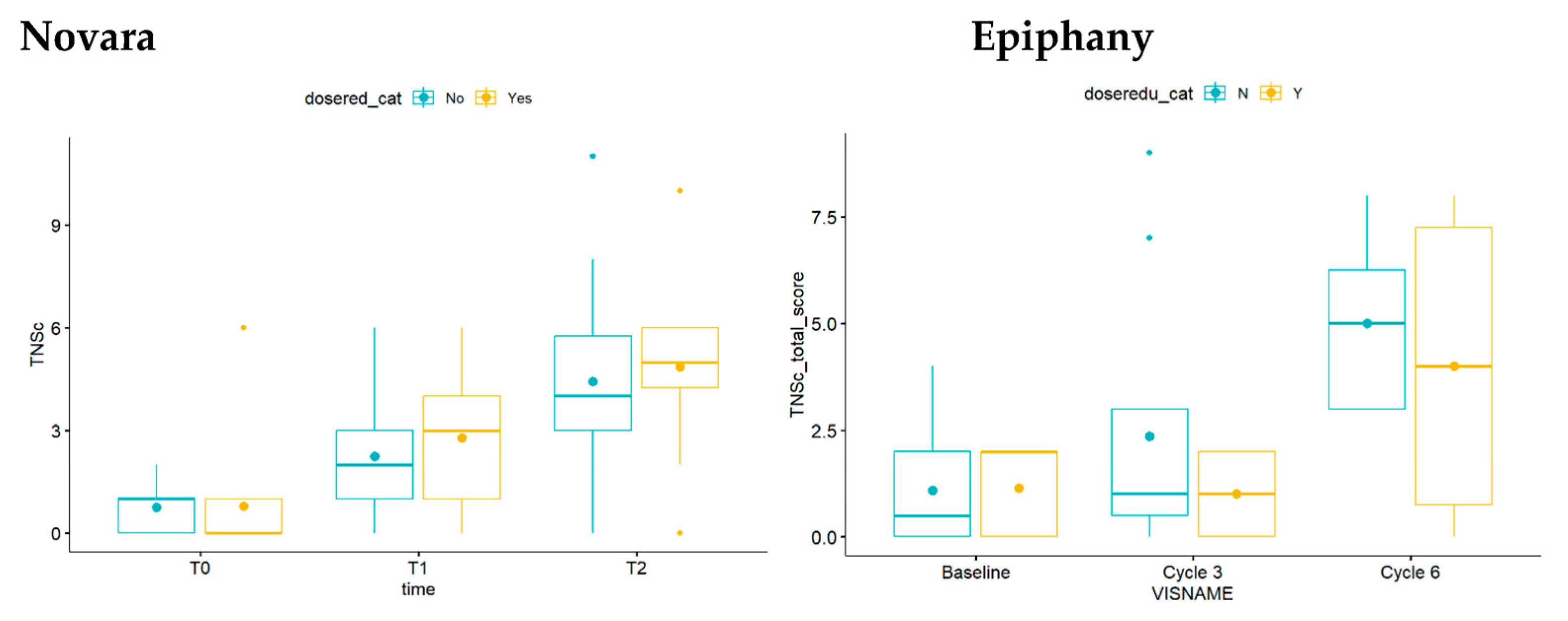
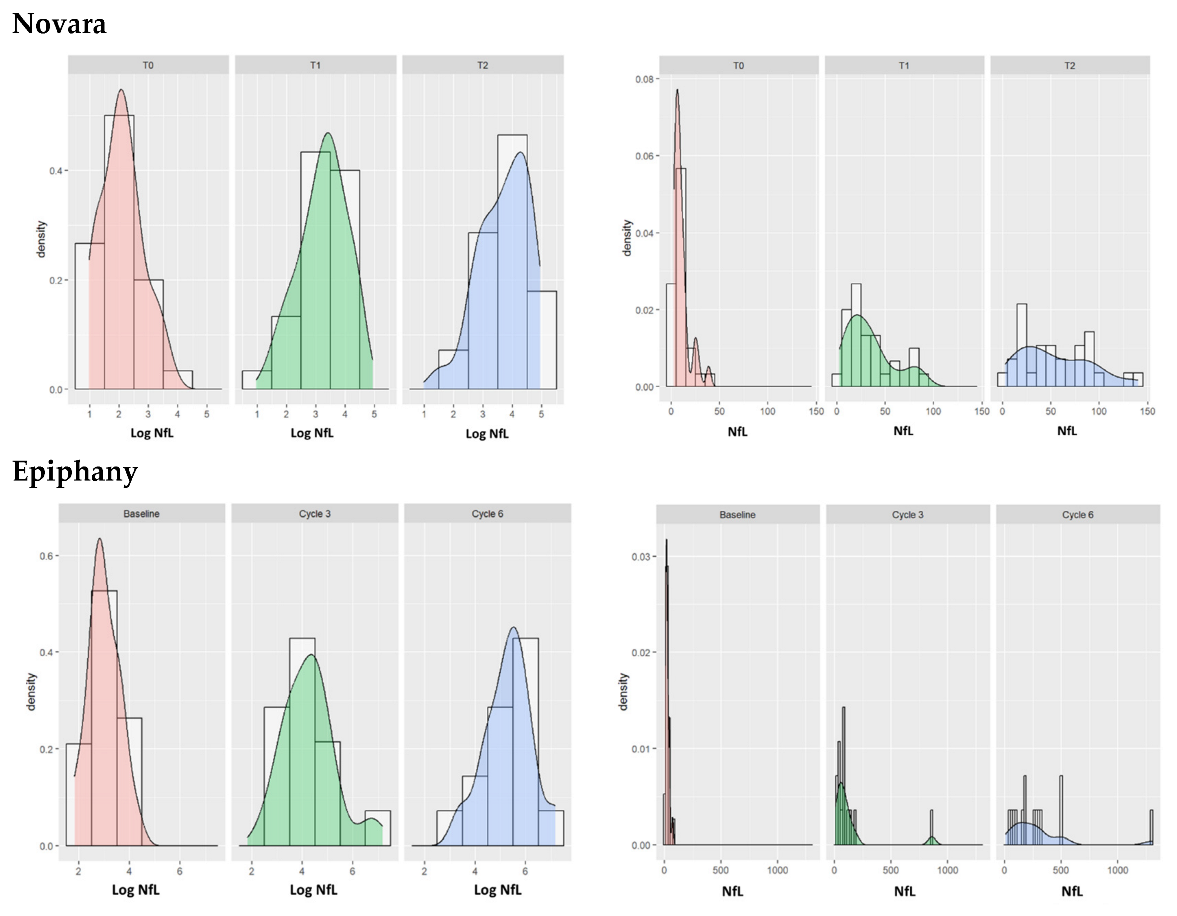
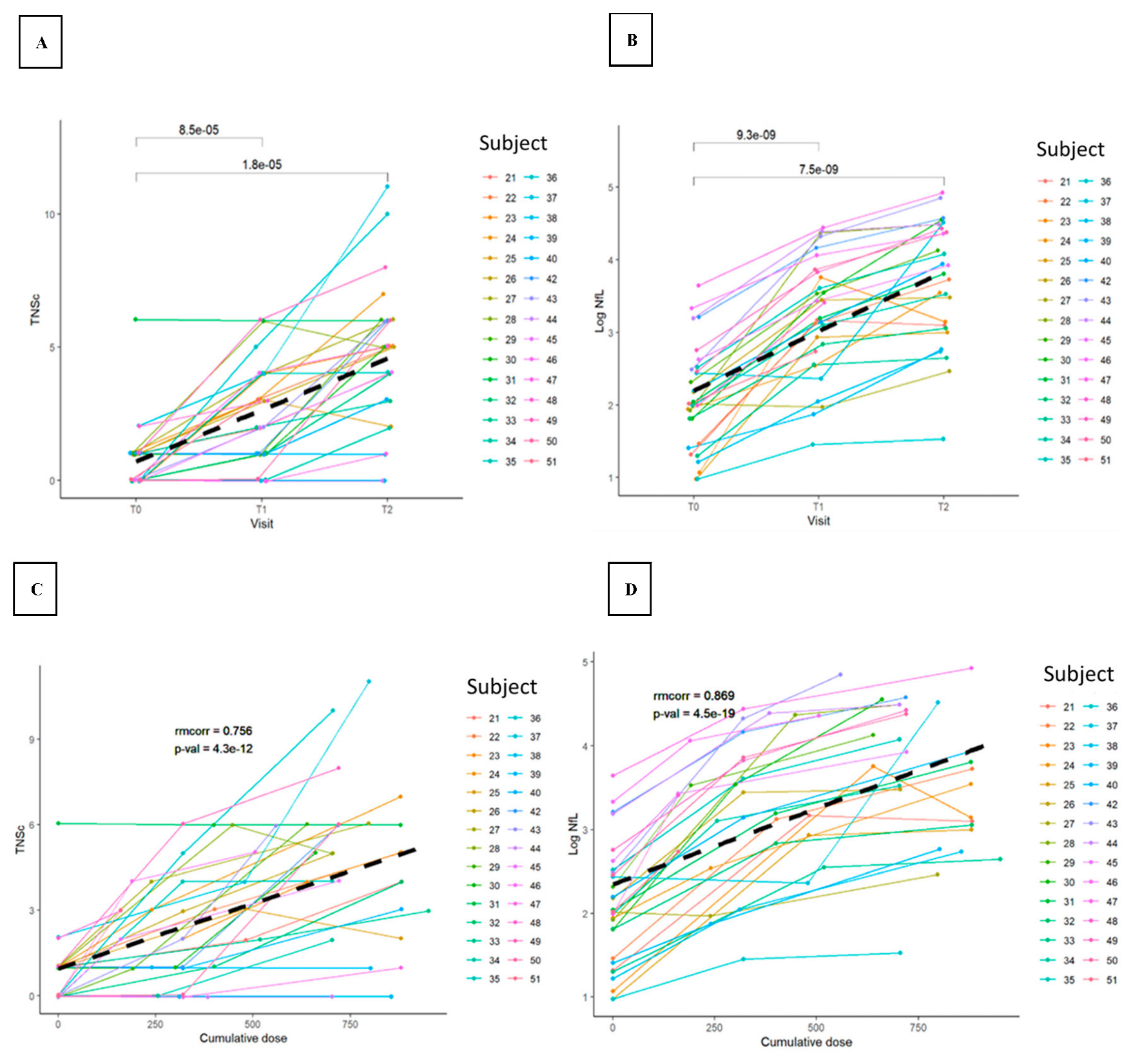
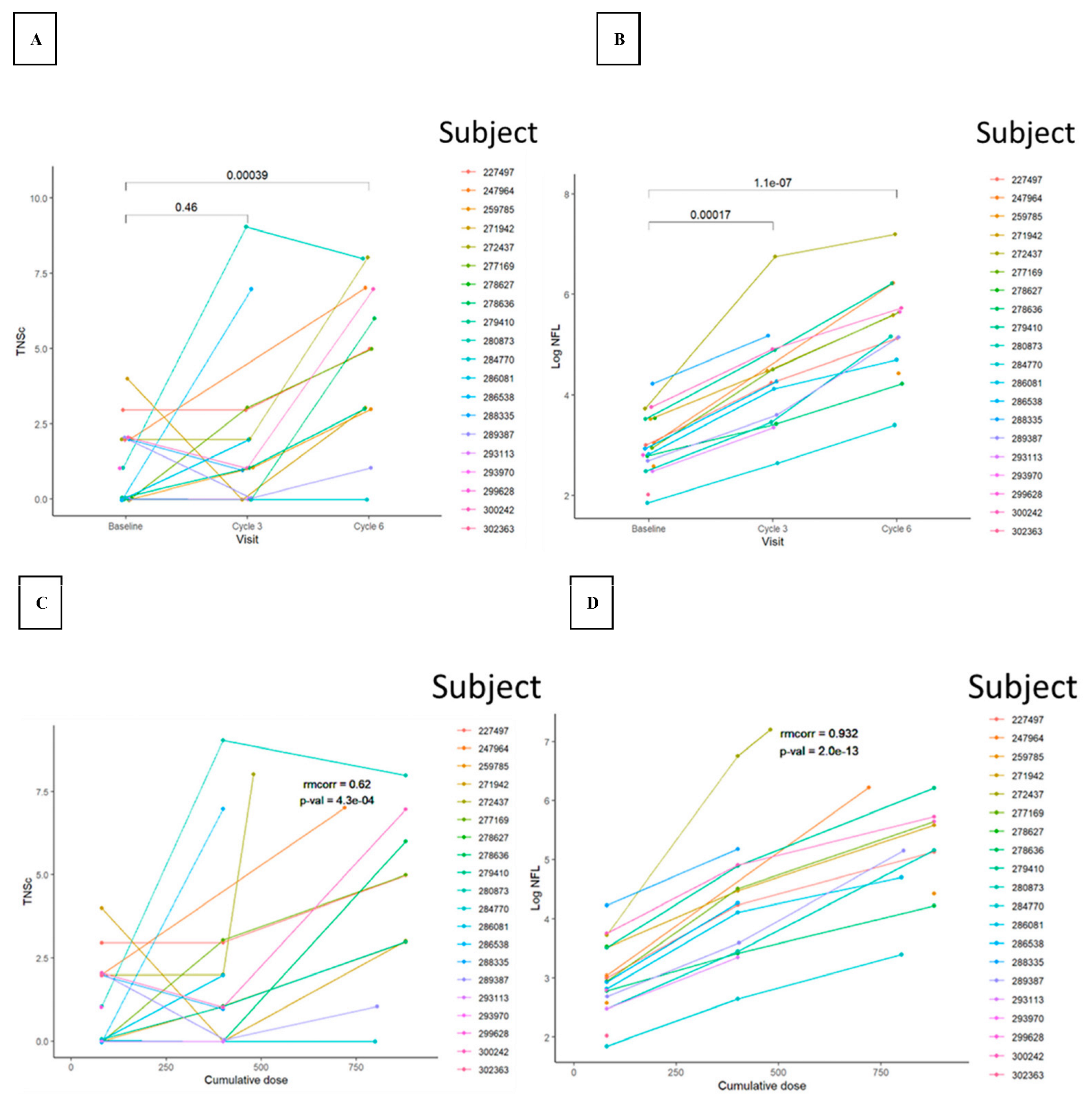
3.2. TNSc, NfL, and CIPN20 Sensory, Motor, and Autonomic Subscore Changes during Chemotherapy in Novara and Epiphany Studies
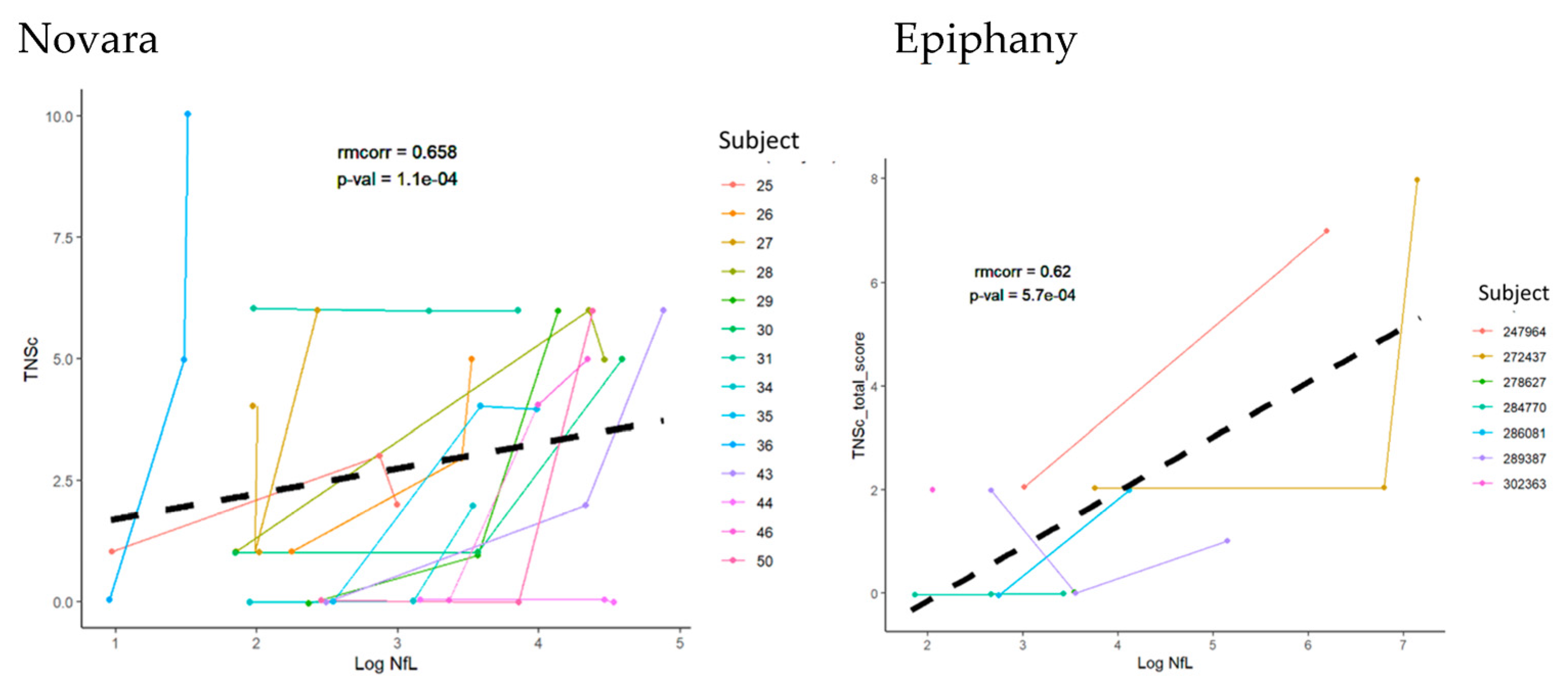
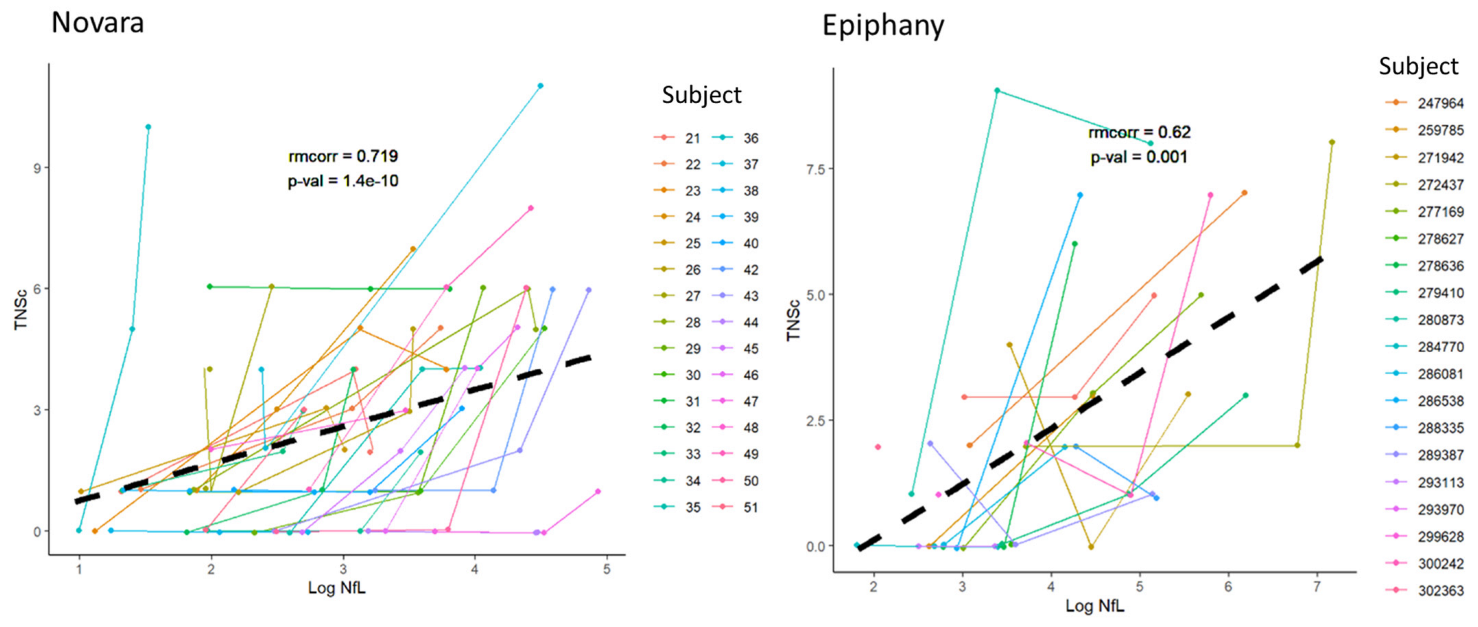
3.3. Repeated Measures Correlation between TNSc, NfL, and CIPN20 Sensory, Motor, and Autonomic Changes in Novara and Epiphany Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Bao, T.; Basal, C.; Seluzicki, C.; Li, S.Q.; Seidman, A.D.; Mao, J.J. Long-term chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy among breast cancer survivors: Prevalence, risk factors, and fall risk. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 159, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerckhove, N.; Collin, A.; Condé, S.; Chaleteix, C.; Pezet, D.; Balayssac, D. Long-term effects, pathophysiological mechanisms, and risk factors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathies: A comprehensive literature review. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, J.R.; Morrison, G.; Dolan, M.E.; Fleming, G.F. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Current status and progress. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 140, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, B.; Gilmore, S.; Goloubeva, O.; Pelser, C.; Medeiros, M.; Chumsri, S.; Tkaczuk, K.; Edelman, M.; Bao, T. Chemotherapy dose reduction due to chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy in breast cancer patients receiving chemotherapy in the neoadjuvant or adjuvant settings: A single-center experience. Springerplus 2014, 3, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denduluri, N.; Lyman, G.H.; Wang, Y.; Morrow, P.K.; Barron, R.; Patt, D.; Bhowmik, D.; Li, X.; Bhor, M.; Fox, P.; et al. Chemotherapy dose intensity and overall survival among patients with advanced breast or ovarian cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2018, 18, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettengell, R.; Schwenkglenks, M.; Bosly, A. Association of reduced relative dose intensity and survival in lymphoma patients receiving CHOP-21 chemotherapy. Ann. Hematol. 2008, 87, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Kavelaars, A.; Dougherty, P.M.; Heijnen, C.J. Beyond symptomatic relief for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Targeting the source. Cancer 2018, 124, 2289–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seretny, M.; Currie, G.L.; Sena, E.S.; Ramnarine, S.; Grant, R.; MacLeod, M.R.; Colvin, L.A.; Fallon, M. Incidence, prevalence, and predictors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 2014, 155, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lema, M.J.; Foley, K.M.; Hausheer, F.H. Types and epidemiology of cancer-related neuropathic pain: The intersection of cancer pain and neuropathic pain. Oncologist 2010, 15 (Suppl. S2), 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Hoffman, E.M.; Mauermann, M.L.; Loprinzi, C.L.; Windebank, A.J.; Klein, C.J.; Staff, N.P. Incidence and disease burden of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in a population-based cohort. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisold, W.; Cavaletti, G.; Windebank, A.J. Peripheral neuropathies from chemotherapeutics and targeted agents: Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14 (Suppl. S4), iv45–iv54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaletti, G.; Marmiroli, P. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2015, 28, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaletti, G.; Frigeni, B.; Lanzani, F.; Piatti, M.; Rota, S.; Briani, C.; Zara, G.; Plasmati, R.; Pastorelli, F.; Caraceni, A.; et al. The total neuropathy score as an assessment tool for grading the course of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity: Comparison with the National Cancer Institute-common toxicity scale. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2007, 12, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaletti, G.; Jann, S.; Pace, A.; Plasmati, R.; Siciliano, G.; Briani, C.; Cocito, D.; Padua, L.; Ghiglione, E.; Manicone, M.; et al. Multi-center assessment of the total neuropathy score for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2006, 11, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postma, T.J.; Aaronson, N.K.; Heimans, J.J.; Muller, M.; Hildebrand, J.G.; Delattre, J.Y.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Lantéri-Minet, M.; Grant, R.; Huddart, R.; et al. The development of an EORTC quality of life questionnaire to assess chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: The QLQ-CIPN20. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, T.R.; Wang, X.S.; Williams, L.A.; Shi, Q.; Vichaya, E.G.; Dougherty, P.M.; Thomas, S.K.; Yucel, E.; Bastida, C.C.; Woodruff, J.F.; et al. Measuring therapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Preliminary development and validation of the treatment-induced neuropathy assessment scale. J. Pain 2015, 16, 1032–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.A.; Garcia-Gonzalez, A.; Mendoza, T.R.; Haq, S.; Cleeland, C.S. Concept domain validation and item generation for the treatment-induced neuropathy assessment scale (TNAS). Support. Care Cancer 2019, 27, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajączkowska, R.; Kocot-Kępska, M.; Leppert, W.; Wrzosek, A.; Mika, J.; Wordliczek, J. Mechanisms of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benatar, M.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Granit, V.; Statland, J.; Barohn, R.; Swenson, A.; Ravits, J.; Jackson, C.; Burns, T.M.; et al. Validation of serum neurofilaments as prognostic and potential pharmacodynamic biomarkers for ALS. Neurology 2020, 95, e59–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disanto, G.; Barro, C.; Benkert, P.; Naegelin, Y.; Schädelin, S.; Giardiello, A.; Zecca, C.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Leppert, D.; et al. Serum neurofilament light: A biomarker of neuronal damage in multiple sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilotto, A.; Imarisio, A.; Conforti, F.; Scalvini, A.; Masciocchi, S.; Nocivelli, S.; Turrone, R.; Gipponi, S.; Cottini, E.; Borroni, B.; et al. Plasma NfL, clinical subtypes and motor progression in Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2021, 87, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahim, P.; Politis, A.; van der Merwe, A.; Moore, B.; Chou, Y.-Y.; Pham, D.L.; Butman, J.A.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; Gill, J.M.; Brody, D.L.; et al. Neurofilament light as a biomarker in traumatic brain injury. Neurology 2020, 95, e610–e622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Choi, M.K.; Park, N.Y.; Hyun, J.-W.; Lee, M.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, S.K.; Cha, Y. Serum neurofilament light chain levels as a biomarker of neuroaxonal injury and severity of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huehnchen, P.; Schinke, C.; Bangemann, N.; Dordevic, A.D.; Kern, J.; Maierhof, S.K.; Hew, L.; Nolte, L.; Körtvelyessy, P.; Göpfert, J.C.; et al. Neurofilament proteins as a potential biomarker in chemotherapy-induced polyneuropathy. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e54395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzamiglio, C.; Ripellino, P.; Prandi, P.; Clemente, N.; Saggia, C.; Rossi, V.; Strigaro, G.; Bonda, P.L.F.; Comi, C.; Cantello, R. Nerve conduction, circulating osteopontin and taxane-induced neuropathy in breast cancer patients. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2020, 50, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakdash, J.Z.; Marusich, L.R. Repeated measures correlation. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bland, J.M.; Altman, D.G. Calculating correlation coefficients with repeated observations: Part 1–correlation within subjects. BMJ 1995, 310, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.H.; Macdonald-Wallis, C.; Gray, E.; Pearce, N.; Petzold, A.; Norgren, N.; Giovannoni, G.; Fratta, P.; Sidle, K.; Fish, M.; et al. Neurofilament light chain: A prognostic biomarker in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 2015, 84, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhle, J.; Kropshofer, H.; Haering, D.A.; Kundu, U.; Meinert, R.; Barro, C.; Dahlke, F.; Tomic, D.; Leppert, D.; Kappos, L. Blood neurofilament light chain as a biomarker of MS disease activity and treatment response. Neurology 2019, 92, e1007–e1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaletti, G.; Marmiroli, P. Pharmacotherapy options for managing chemotherapy-induced peripheral neurotoxicity. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2018, 19, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascella, M. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Limitations in current prophylactic strategies and directions for future research. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2017, 33, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petzold, A.; Mondria, T.; Kuhle, J.; Rocca, M.A.; Cornelissen, J.; Boekhorst, P.T.; Lowenberg, B.; Giovannoni, G.; Filippi, M.; Kappos, L.; et al. Evidence for acute neurotoxicity after chemotherapy. Ann. Neurol. 2010, 68, 806–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewandter, J.S.; Freeman, R.; Kitt, R.A.; Cavaletti, G.; Gauthier, L.R.; McDermott, M.P.; Mohile, N.A.; Mohlie, S.G.; Smith, A.G.; Tejani, M.A.; et al. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy clinical trials: Review and recommendations. Neurology 2017, 89, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meregalli, C.; Fumagalli, G.; Alberti, P.; Canta, A.; Carozzi, V.A.; Chiorazzi, A.; Monza, L.; Pozzi, E.; Sandelius, Å.; Blennow, K.; et al. Neurofilament light chain as disease biomarker in a rodent model of chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 307, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.V.; Houseweart, M.K.; Williamson, T.L.; Crawford, T.O.; Folmer, J.; Cleveland, D.W. Neurofilament-dependent radial growth of motor axons and axonal organization of neurofilaments does not require the neurofilament heavy subunit (NF-H) or its phosphorylation. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soylu-Kucharz, R.; Sandelius, Å.; Sjögren, M.; Blennow, K.; Wild, E.J.; Zetterberg, H.; Björkqvist, M. Neurofilament light protein in CSF and blood is associated with neurodegeneration and disease severity in Huntington’s disease R6/2 mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaetani, L.; Blennow, K.; Calabresi, P.; Di Filippo, M.; Parnetti, L.; Zetterberg, H. Neurofilament light chain as a biomarker in neurological disorders. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, M.; Malmeström, C.; Axelsson, M.; Sundström, P.; Dahle, C.; Vrethem, M.; Olsson, T.; Piehl, F.; Norgren, N.; Rosengren, L.; et al. Axonal damage in relapsing multiple sclerosis is markedly reduced by natalizumab. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosengren, L.E.; Karlsson, J.E.; Karlsson, J.O.; Persson, L.I.; Wikkelsø, C. Patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other neurodegenerative diseases have increased levels of neurofilament protein in CSF. J. Neurochem. 1996, 67, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Teunissen, C.E.; Otto, M.; Piehl, F.; Sormani, M.P.; Gattringer, T.; Barro, C.; Kappos, L.; Comabella, M.; Fazekas, F.; et al. Neurofilaments as biomarkers in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karteri, S.; Bruna, J.; Argyriou, A.A.; Mariotto, S.; Velasco, R.; Alemany, M.; Kalofonou, F.; Alberti, P.; Dinoto, A.; Velissaris, D.; et al. Prospectively assessing serum neurofilament light chain levels as a biomarker of paclitaxel-induced peripheral neurotoxicity in breast cancer patients. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2022, 27, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaletti, G.; Cornblath, D.R.; Merkies, I.S.J.; Postma, T.J.; Rossi, E.; Frigeni, B.; Alberti, P.; Bruna, J.; Velasco, R.; Argyriou, A.A.; et al. The chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy outcome measures standardization study: From consensus to the first validity and reliability findings. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, S.L.; Barton, D.L.; Qin, R.; Wos, E.J.; Sloan, J.A.; Liu, H.; Aaronson, N.K.; Satele, D.V.; Mattar, B.I.; Green, N.B.; et al. The relationship between numbness, tingling, and shooting/burning pain in patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) as measured by the EORTC QLQ-CIPN20 instrument, N06CA. Support. Care Cancer 2012, 20, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie Smith, E.M.; Barton, D.L.; Qin, R.; Steen, P.D.; Aaronson, N.K.; Loprinzi, C.L. Assessing patient-reported peripheral neuropathy: The reliability and validity of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-CIPN20 Questionnaire. Qual. Life Res. 2013, 22, 2787–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, B.L.; Cho, E.; Honigberg, L. Neurofilament light as a predictive biomarker of unresolved chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in subjects receiving paclitaxel and carboplatin. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 15593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fundaun, J.; Kolski, M.; Molina-Álvarez, M.; Baskozos, G.; Schmid, A.B. Types and concentrations of blood-based biomarkers in adults with peripheral neuropathies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2248593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Epiphany | Novara | |
|---|---|---|
| Total, n | 19 | 30 |
| Sex, female (%) | 19 (100.0) | 30 (100.0) |
| Age, years (SD) | 52.8 (12.4) | 54.0 (9.6) |
| Cancer stage, n (%) | ||
| I | NR | 10 (33.3) |
| II | NR | 14 (46.7) |
| III | NR | 6 (20.0) |
| IV | NR | 0 (0) |
| Dose reduction, n (%) | 7 (36.8) | 14 (46.7) |
| Neuropathic pain, n | NR | 6 |
| Hematologic toxicity, n | NR | 4 |
| PAC cumulative dose, mg/m2 (SD) | ||
| T1 | 370.7 (81.0) | 332.1 (115.7) |
| T2 | 835.6 (103.7) | 771.5 (111.1) |
| BMI, average (SD) | 31.6 (7.8) | 22.3 (2.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavaletti, G.; Pizzamiglio, C.; Man, A.; Engber, T.M.; Comi, C.; Wilbraham, D. Studies to Assess the Utility of Serum Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Cancers 2023, 15, 4216. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174216
Cavaletti G, Pizzamiglio C, Man A, Engber TM, Comi C, Wilbraham D. Studies to Assess the Utility of Serum Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Cancers. 2023; 15(17):4216. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174216
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavaletti, Guido, Chiara Pizzamiglio, Albert Man, Thomas M. Engber, Cristoforo Comi, and Darren Wilbraham. 2023. "Studies to Assess the Utility of Serum Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy" Cancers 15, no. 17: 4216. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174216
APA StyleCavaletti, G., Pizzamiglio, C., Man, A., Engber, T. M., Comi, C., & Wilbraham, D. (2023). Studies to Assess the Utility of Serum Neurofilament Light Chain as a Biomarker in Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Cancers, 15(17), 4216. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15174216







