A Breast Cancer Polygenic Risk Score Is Feasible for Risk Stratification in the Norwegian Population
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Data
2.2. Imputation
2.3. PRS Model
2.4. Hazard Ratio Calculation
2.5. Absolute Risk Estimation
3. Results
3.1. Study Population and Genotypes
3.2. PRS Values
3.3. Hazard Ratio Values
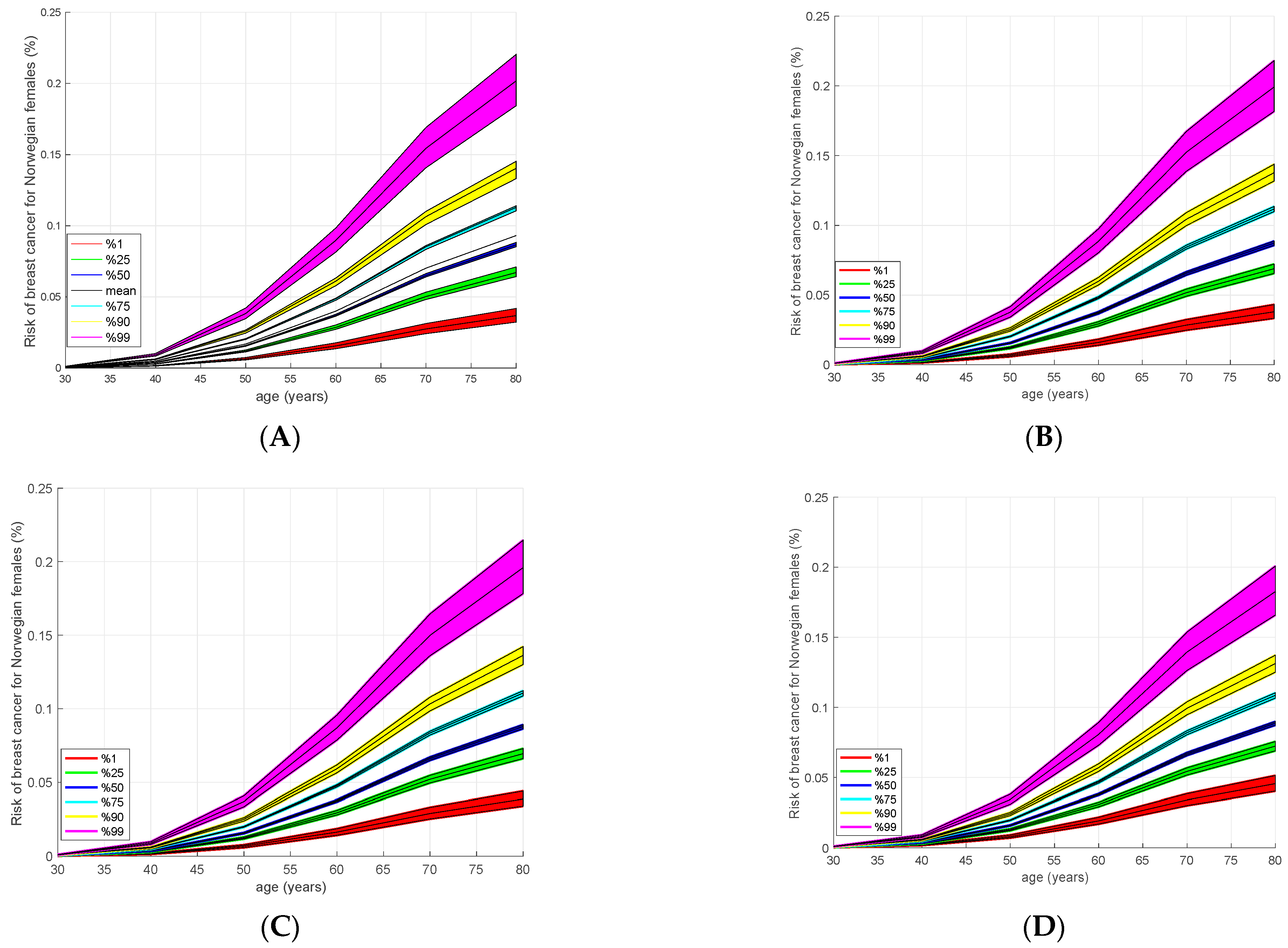
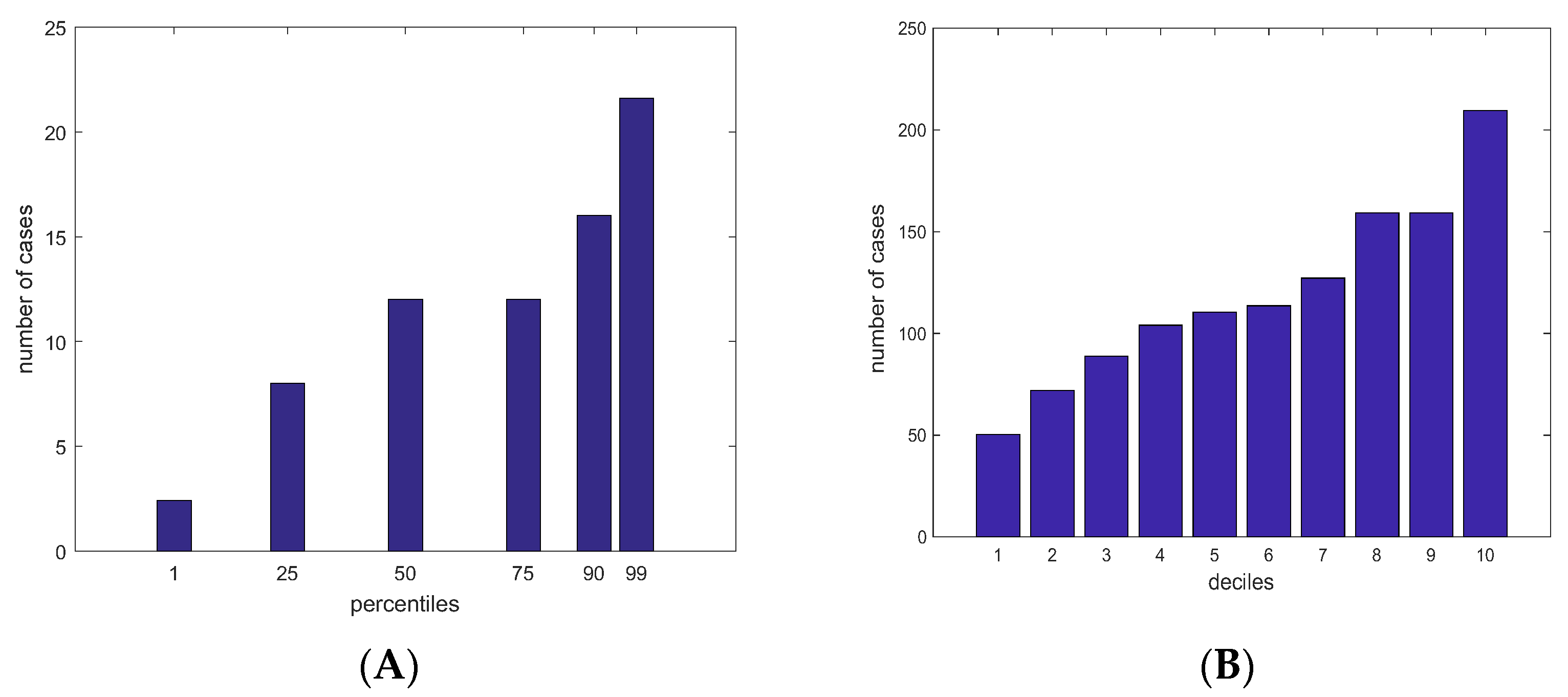
3.4. Absolute Risk Model
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD/European Union. Health at a Glance Europe 2022, State of Health in the EU Cycle; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucci, L.A.; Hjelmborg, J.B.; Harris, J.R.; Czene, K.; Havelick, D.J.; Scheike, T.; Graff, R.E.; Holst, K.; Möller, S.; Unger, R.H.; et al. Familial Risk and Heritability of Cancer among Twins in Nordic Countries. JAMA 2016, 315, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavaddat, N.; Michailidou, K.; Dennis, J.; Lush, M.; Fachal, L.; Lee, A.; Tyrer, J.P.; Chen, T.H.; Wang, Q.; Bolla, M.K.; et al. Polygenic risk scores for prediction of breast cancer and breast cancer subtypes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 104, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfson, M.; Gribble, S.; Pashayan, N.; Easton, D.F.; Antoniou, A.C.; Lee, A.; van Katwyk, S.; Simard, J. Potential of polygenic risk scores for improving population estimates of women’s breast cancer genetic risks. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 2114–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Mavaddat, N.; Wilcox, A.N.; Cunningham, A.P.; Carver, T.; Hartley, S.; de Villiers, C.B.; Izquierdo, A.; Simard, J.; Schmidt, M.K.; et al. BOADICEA: A comprehensive breast cancer risk prediction model incorporating genetic and nongenetic risk factors. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 1708–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharoah, P.D.; Day, N.E.; Duffy, S.; Easton, D.F.; Ponder, B.A. Family history and the risk of breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 71, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cybulski, C.; Wokołorczyk, D.; Jakubowska, A.; Huzarski, T.; Byrski, T.; Gronwald, J.; Masojć, B.; Dębniak, T.; Górski, B.; Blecharz, P.; et al. Risk of Breast Cancer in Women with a CHEK2 Mutation with and without a Family History of Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3747–3752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kast, K.; Rhiem, K.; Wappenschmidt, B.; Hahnen, E.; Hauke, J.; Bluemcke, B.; Zarghooni, V.; Herold, N.; Ditsch, N.; Kiechle, M.; et al. Prevalence of BRCA1/2 germline mutations in 21 401 families with breast and ovarian cancer. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 53, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breast Cancer Association Consortium. Breast cancer risk genes—association analysis in more than 113,000 women. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanes, T.; Young, M.-A.; Meiser, B.; James, P.A. Clinical applications of polygenic breast cancer risk: A critical review and perspectives of an emerging field. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavaddat, N.; Pharoah, P.D.P.; Michailidou, K.; Tyrer, J.; Brook, M.N.; Bolla, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Dennis, J.; Dunning, A.M.; Shah, M.; et al. Prediction of breast cancer risk based on profiling with common genetic variants. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieh, W.; Rothstein, J.H.; McGuire, V.; Whittemore, A.S. The Role of Genome Sequencing in Personalized Breast Cancer PreventionCan Sequence Data Help Prevent Breast Cancer? Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 2322–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Läll, K.; Lepamets, M.; Palover, M.; Esko, T.; Metspalu, A.; Tõnisson, N.; Padrik, P.; Mägi, R.; Fischer, K. Polygenic prediction of breast cancer: Comparison of genetic predictors and implications for risk stratification. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, S.; Hughes, E.; Wagner, S.; Tshiaba, P.; Rosenthal, E.; Roa, B.B.; Kurian, A.W.; Domchek, S.M.; Garber, J.; Lancaster, J.; et al. Association of a Polygenic Risk Score with Breast Cancer Among Women Carriers of High- and Moderate-Risk Breast Cancer Genes. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e208501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasa, T.; Puustusmaa, M.; Tõnisson, N.; Kolk, B.; Padrik, P. Precision Breast Cancer Screening with a Polygenic Risk Score. medRxiv 2020. medRxiv:2020.08.17.20176263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.R. Regression models and life tables. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1972, 34, 187–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, P.P.; Maas, P.; Wilcox, A.; Wheeler, W.; Brook, M.; Check, D.; Garcia-Closas, M.; Chatterjee, N. iCARE: An R package to build, validate and apply absolute risk models. PloS ONE 2020, 15, e0228198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.G.R.; van Veen, E.M.; Harkness, E.F.; Brentnall, A.R.; Astley, S.M.; Byers, H.; Woodward, E.R.; Sampson, S.; Southworth, J.; Howell, S.J.; et al. Breast cancer risk stratification in women of screening age: Incremental effects of adding mammographic density, polygenic risk, and a gene panel. Genet. Med. 2022, 24, 1485–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinomar, N.; Chung, W.K. Cases in Precision Medicine: The Role of Polygenic Risk Scores in Breast Cancer Risk Assessment. Ann. Intern. Med. 2021, 174, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havdahl, A.; Hannigan, L.; Askeland, R.B.; Ask, H.; Tesli, M.; Corfield, E.; Øyen, A.S.; Andreassen, O.; Smith, G.D.; Reichborn-Kjennerud, T. 75 polygenic risk for adhd and exposures during pregnancy in the norwegian mother and child cohort study (moba). Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2019, 29, S102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, M.C.F.; Wirgenes, K.V.; Haram, M.; Bettella, F.; Lunding, S.H.; Rødevand, L.; Hjell, G.; Agartz, I.; Djurovic, S.; Melle, I.; et al. Indicated association between polygenic risk score and treatment-resistance in a naturalistic sample of patients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Schizophr. Res. 2020, 218, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Næss, M.; Sund, E.R.; Vie, G.Å.; Bjørngaard, J.H.; Åsvold, B.O.; Holmen, T.L.; Kvaløy, K. Intergenerational polygenic obesity risk throughout adolescence in a cross-sectional study design: The HUNT study, Norway. Obesity 2021, 29, 1916–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BreastScreen Norway. Available online: https://www.kreftregisteret.no/en/screening/BreastScreen_Norway/breastscreen-norway/ (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Mattingsdal, M.; Ebenesersdóttir, S.S.; Moore, K.H.; Andreassen, O.A.; Hansen, T.F.; Werge, T.; Kockum, I.; Olsson, T.; Alfredsson, L.; Helgason, A.; et al. The genetic structure of Norway. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 29, 1710–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DRAGEN-GATK. Available online: https://gatk.broadinstitute.org/hc/en-us/articles/360045944831-DRAGEN-GATK (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Corfield, E.; Shadrin, A.; Frei, O.; Rahman, Z.; Lin, A.; Athanasiu, L.; Akdeniz, B.C.; Hannigan, L.; Wootton, R.; Austerberry, C.; et al. Genetic profile of the norwegian mother, father, and child cohort study (moba): Results from the mobapsychgen pipeline. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2022, 63, e292–e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.W.; O’Reilly, P.F. PRSice-2: Polygenic Risk Score software for biobank-scale data. Gigascience 2019, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T.M. A Package for Survival Analysis in R. 2023. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=survival (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- GHO. Available online: https://apps.who.int/gho/data/view.main.61210 (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Nordcan. Available online: https://nordcan.iarc.fr/en/dataviz/tables (accessed on 12 May 2023).
- Uk, B.; Cancer, I. The benefits and harms of breast cancer screening: An independent review. Lancet 2012, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, E.R.; Moorman, P.; Gierisch, J.M.; Havrilesky, L.J.; Grimm, L.J.; Ghate, S.; Davidson, B.; Mongtomery, R.C.; Crowley, M.J.; McCrory, D.C.; et al. Benefits and harms of breast cancer screening: A systematic review. JAMA 2015, 314, 1615–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabár, L.; Dean, P.B.; Chen, T.H.; Yen, A.M.; Chen, S.L.; Fann, J.C.; Chiu, S.Y.; Ku, M.M.; Wu, W.Y.; Hsu, C.Y.; et al. The incidence of fatal breast cancer measures the increased effectiveness of therapy in women participating in mammography screening. Cancer 2019, 125, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.G.R.; Harkness, E.F.; Brentnall, A.R.; van Veen, E.M.; Astley, S.M.; Byers, H.; Sampson, S.; Southworth, J.; Stavrinos, P.; Howell, S.J.; et al. Breast cancer pathology and stage are better predicted by risk stratification models that include mammographic density and common genetic variants. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 176, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brentnall, A.R.; Veen, E.M.; Harkness, E.F.; Rafiq, S.; Byers, H.; Astley, S.M.; Sampson, S.; Howell, A.; Newman, W.G.; Cuzick, J.; et al. A case–control evaluation of 143 single nucleotide polymorphisms for breast cancer risk stratification with classical factors and mammographic density. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 146, 2122–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurson, A.N.; Choudhury, P.P.; Gao, C.; Hüsing, A.; Eriksson, M.; Shi, M.; Jones, M.E.; Evans, D.G.; Milne, R.L.; Gaudet, M.M.; et al. Prospective evaluation of a breast-cancer risk model integrating classical risk factors and polygenic risk in 15 cohorts from six countries. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 50, 1897–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desikan, R.S.; Fan, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Schork, A.J.; Cabral, H.J.; Cupples, L.A.; Thompson, W.K.; Besser, L.; Kukull, W.A.; Holland, D.; et al. Genetic assessment of age-associated Alzheimer disease risk: Development and validation of a polygenic hazard score. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlstrøm, L.; Fan, C.C.; Frei, O.; Tan, M.; Karunamuni, R.A.; Blauwendraat, C.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Gan-Or, Z.; Grosset, D.G. Genetic stratification of age-dependent Parkinson’s disease risk by polygenic hazard score. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seibert, T.M.; Fan, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Zuber, V.; Karunamuni, R.; Parsons, J.K.; A Eeles, R.; Easton, D.F.; Kote-Jarai, Z.; Al Olama, A.A.; et al. Polygenic hazard score to guide screening for aggressive prostate cancer: Development and validation in large scale cohorts. BMJ 2018, 360, j5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunamuni, R.A.; Huynh-Le, M.-P.; Fan, C.C.; Thompson, W.; Lui, A.; Martinez, M.E.; Rose, B.S.; Mahal, B.; Eeles, R.A.; Kote-Jarai, Z.; et al. Performance of African-ancestry-specific polygenic hazard score varies according to local ancestry in 8q24. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motazedi, E.; Cheng, W.; Thomassen, J.Q.; Frei, O.; Rongve, A.; Athanasiu, L.; Bahrami, S.; Shadrin, A.; Ulstein, I.; Stordal, E.; et al. Using Polygenic Hazard Scores to Predict Age at Onset of Alzheimer’s Disease in Nordic Populations. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 88, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manichaikul, A.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; Rich, S.S.; Daly, K.; Sale, M.; Chen, W.-M. Robust relationship inference in genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2867–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, J.; Gurdasani, D.; Delaneau, O.; Pirastu, N.; Ulivi, S.; Cocca, M.; Traglia, M.; Huang, J.; Huffman, J.E.; Rudan, I.; et al. A General Approach for Haplotype Phasing across the Full Spectrum of Relatedness. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, B.L.; Zhou, Y.; Browning, S.R. A One-Penny Imputed Genome from Next-Generation Reference Panels. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinacci, S.; Delaneau, O.; Marchini, J. Genotype imputation using the Positional Burrows Wheeler Transform. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1009049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
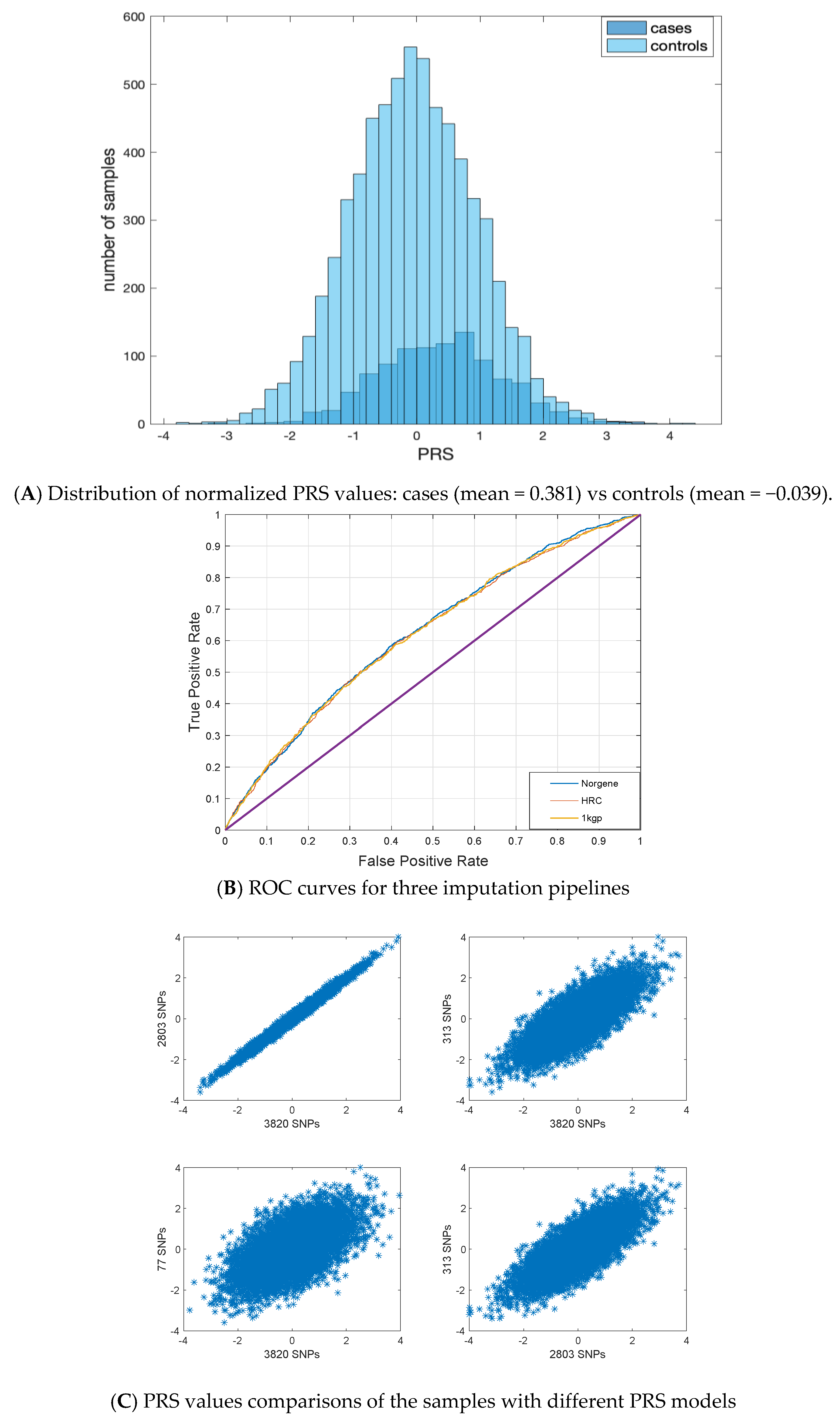

| Metrics | SNPSET | Antegenes Pipeline (1 kgp) | MoBa (HRC) | Norgene (Norwegian Reference Panel) | EstBB (Estonian Reference Panel) | UKB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC (number of SNPs used) | 77 SNPs | 0.582 (66) | 0.584 (66) | 0.600 (66) | 0.591 (73) | 0.607 (73) |
| 313 SNPs | 0.605 (232) | 0.605 (210) | 0.617 (228) | 0.604 (257) | 0.625 (257) | |
| 2803 SNPs | 0.616 (2511) | 0.617 (2379) | 0.618(2474) | 0.615(2803) | 0.632 (2803) | |
| 3820 SNPs | 0.621 (2706) | 0.620 (2482) | 0.625 (2698) | 0.611(3081) | 0.632 (2803) | |
| OR (SE) | 77 SNPs | 1.460 (0.034) | 1.465 (0.034) | 1.503 (0.033) | 1.369 (0.061) | 1.485 (0.012) |
| 313 SNPs | 1.465 (0.034) | 1.475 (0.034) | 1.534 (0.034) | 1.426 (0.060) | 1.556 (0.012) | |
| 2803 SNPs | 1.526 (0.034) | 1.538 (0.034) | 1.534 (0.034) | 1.479 (0.061) | 1.616 (0.012) | |
| 3820 SNPs | 1.546 (0.034) | 1.528 (0.034) | 1.567 (0.034) | 1.474 (0.060) | 1.617 (0.012) |
| SNPSET | Metrics | Antegenes Pipeline (1 kgp) | MoBa (HRC) | Norgene (Norwegian Reference Panel) | EstBB (Estonian Reference Panel) | UKB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 77 SNPs | HR (%95 confidence interval) | 1.273 (1.211–1.339) | 1.276 (1.214–1.342) | 1.373 (1.307–1.443) | 1.580 (1.428–1.747) | 1.440 (1.406–1.476) |
| c-index | 0.563 (se = 0.008) | 0.563 (se = 0.008) | 0.581 (se = 0.008) | 0.638 (se = 0.015) | 0.600 (se = 0.004) | |
| 313 SNPs | HR (%95 confidence interval) | 1.373 (1.305–1.444) | 1.355 (1.288–1.425) | 1.439 (1.368–1.513) | 1.615 (1.457–1.789) | 1.551 (1.515–1.588) |
| c-index | 0.58 (se = 0.010) | 0.578 (se = 0.008) | 0.593 (se = 0.008) | 0.642 (se = 0.015) | 0.622 (se = 0.004) | |
| 2803 SNPs | HR (%95 confidence interval) | 1.421 (1.351–1.494) | 1.442 (1.370–1.517) | 1.455 (1.384–1.531) | 1.660 (1.500–1.837) | 1.562 (1.526–1.588) |
| c-index | 0.593 (se = 0.008) | 0.596 (se = 0.008) | 0.598 (se = 0.008) | 0.656 (se = 0.015) | 0.625 (se = 0.003) | |
| 3820 SNPs | HR (%95 confidence interval) | 1.462 (1.375–1.554) | 1.458 (1.371–1.55) | 1.494 (1.406–1.588) | 1.654 (1.494–1.830) | 1.562 (1.526–1.600) |
| c-index | 0.602 (se = 0.010) | 0.601 (se = 0.010) | 0.607 (se = 0.010) | 0.654 (se = 0.015) | 0.625 (se = 0.003) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akdeniz, B.C.; Mattingsdal, M.; Dominguez-Valentin, M.; Frei, O.; Shadrin, A.; Puustusmaa, M.; Saar, R.; Sõber, S.; Møller, P.; Andreassen, O.A.; et al. A Breast Cancer Polygenic Risk Score Is Feasible for Risk Stratification in the Norwegian Population. Cancers 2023, 15, 4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164124
Akdeniz BC, Mattingsdal M, Dominguez-Valentin M, Frei O, Shadrin A, Puustusmaa M, Saar R, Sõber S, Møller P, Andreassen OA, et al. A Breast Cancer Polygenic Risk Score Is Feasible for Risk Stratification in the Norwegian Population. Cancers. 2023; 15(16):4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164124
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkdeniz, Bayram Cevdet, Morten Mattingsdal, Mev Dominguez-Valentin, Oleksandr Frei, Alexey Shadrin, Mikk Puustusmaa, Regina Saar, Siim Sõber, Pål Møller, Ole A. Andreassen, and et al. 2023. "A Breast Cancer Polygenic Risk Score Is Feasible for Risk Stratification in the Norwegian Population" Cancers 15, no. 16: 4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164124
APA StyleAkdeniz, B. C., Mattingsdal, M., Dominguez-Valentin, M., Frei, O., Shadrin, A., Puustusmaa, M., Saar, R., Sõber, S., Møller, P., Andreassen, O. A., Padrik, P., & Hovig, E. (2023). A Breast Cancer Polygenic Risk Score Is Feasible for Risk Stratification in the Norwegian Population. Cancers, 15(16), 4124. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15164124






