Recent Progress in Modulation of WD40-Repeat Domain 5 Protein (WDR5): Inhibitors and Degraders
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
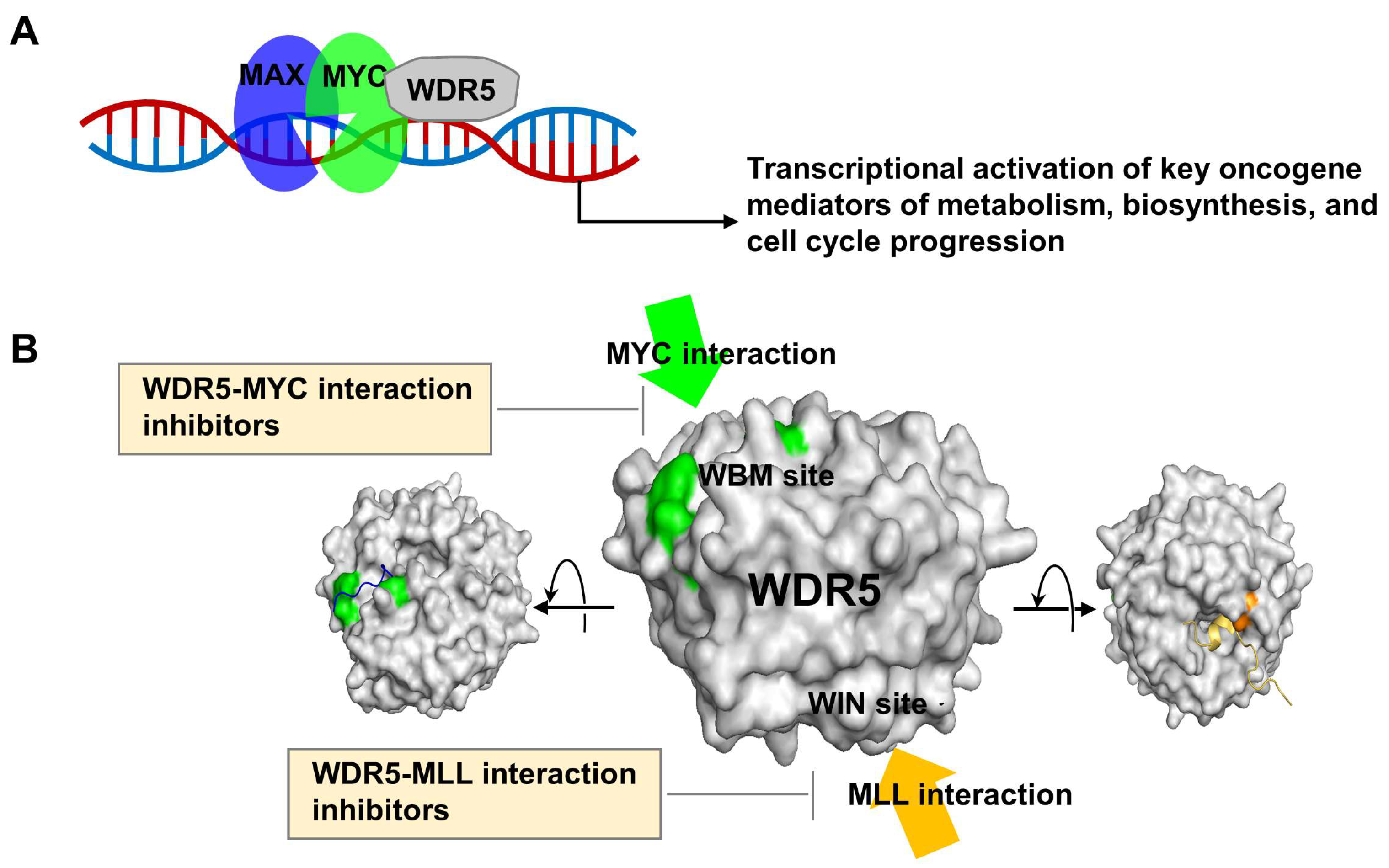
1. Introduction
2. WDR5 Inhibitors
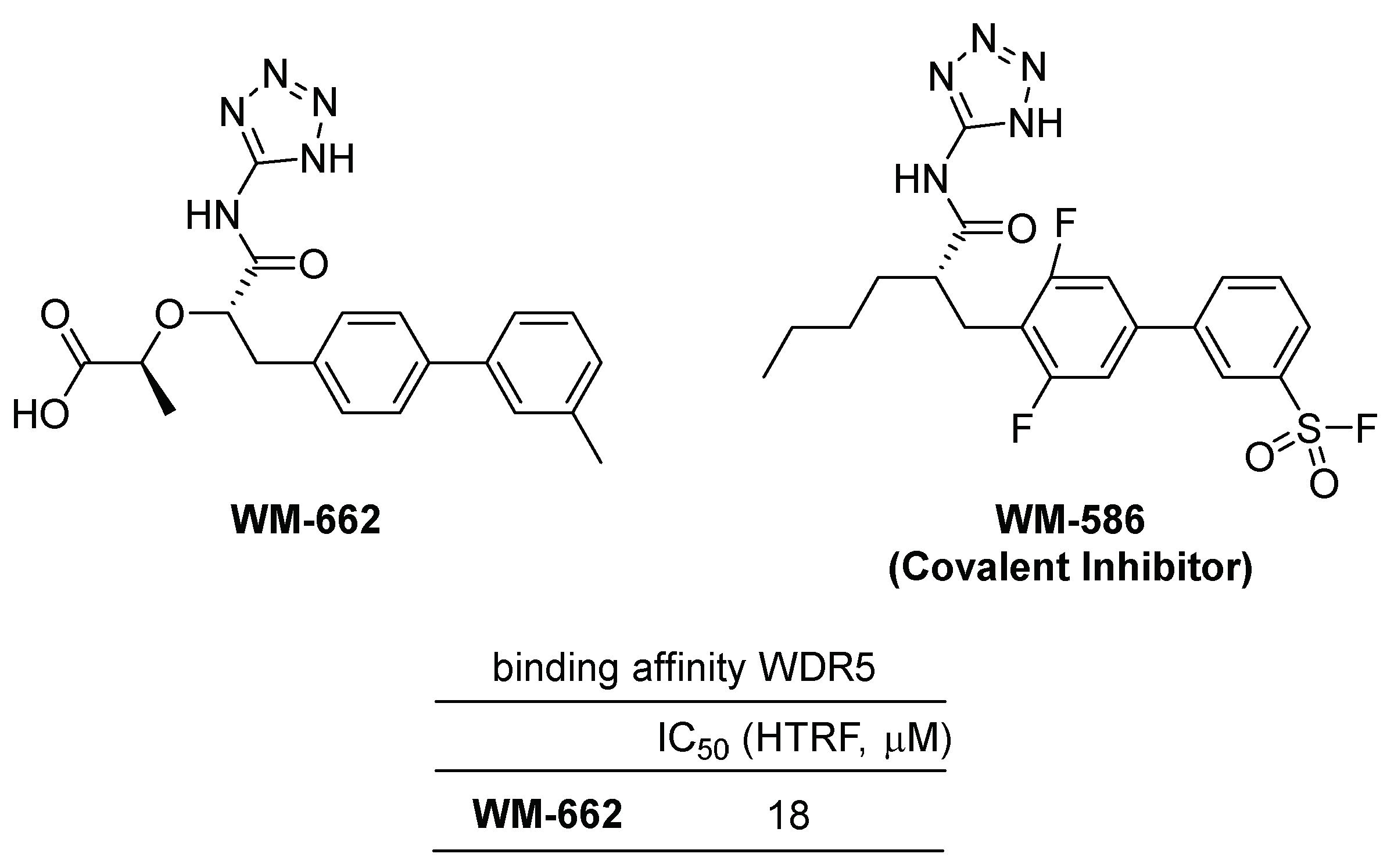
2.1. WDR5-MYC Interaction Inhibitors
2.2. WDR5-MLL1 Protein–Protein Inhibitors
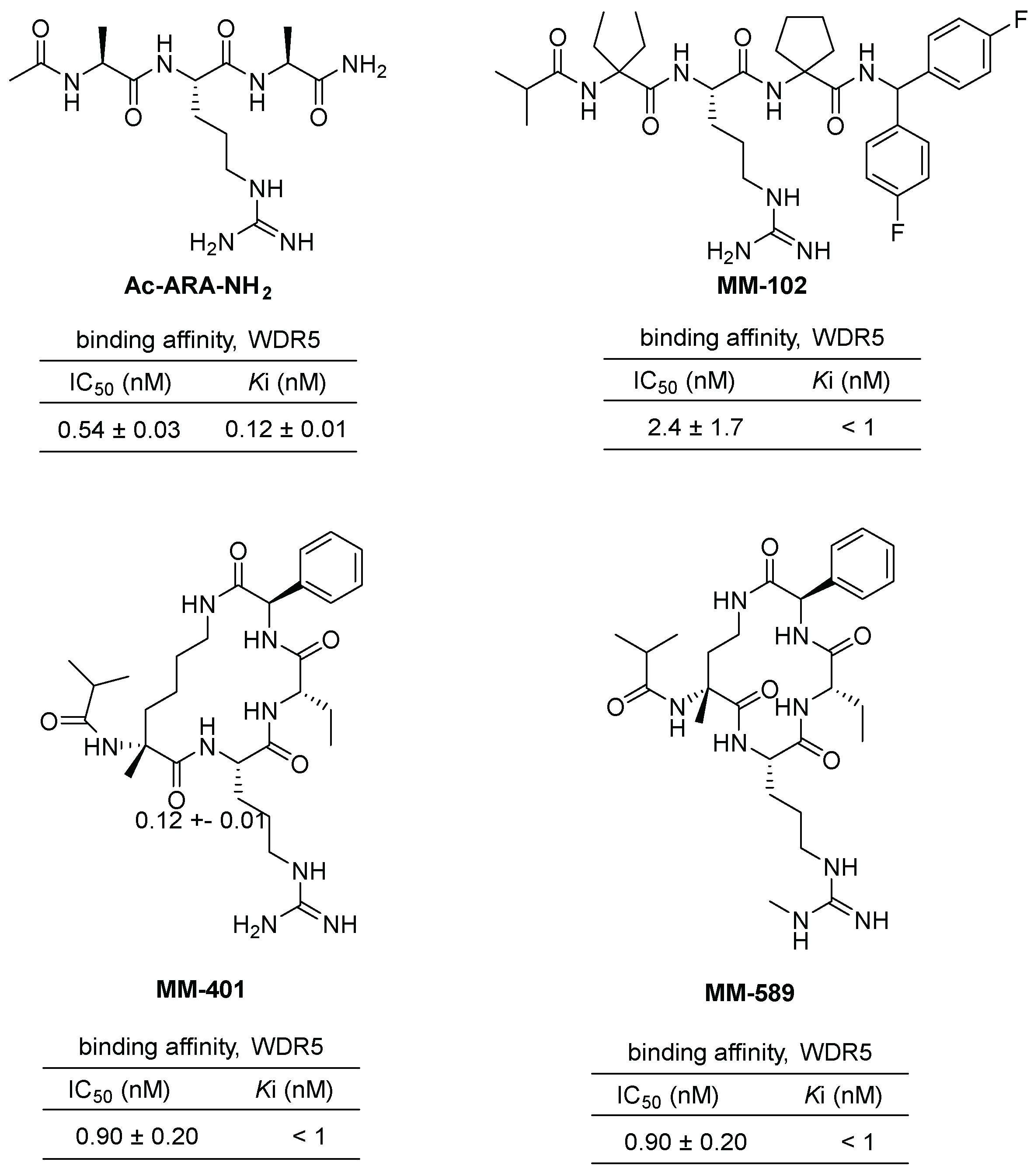
2.2.1. Peptide and Peptidomimetic Inhibitors of WDR5–MLL1 Interactions
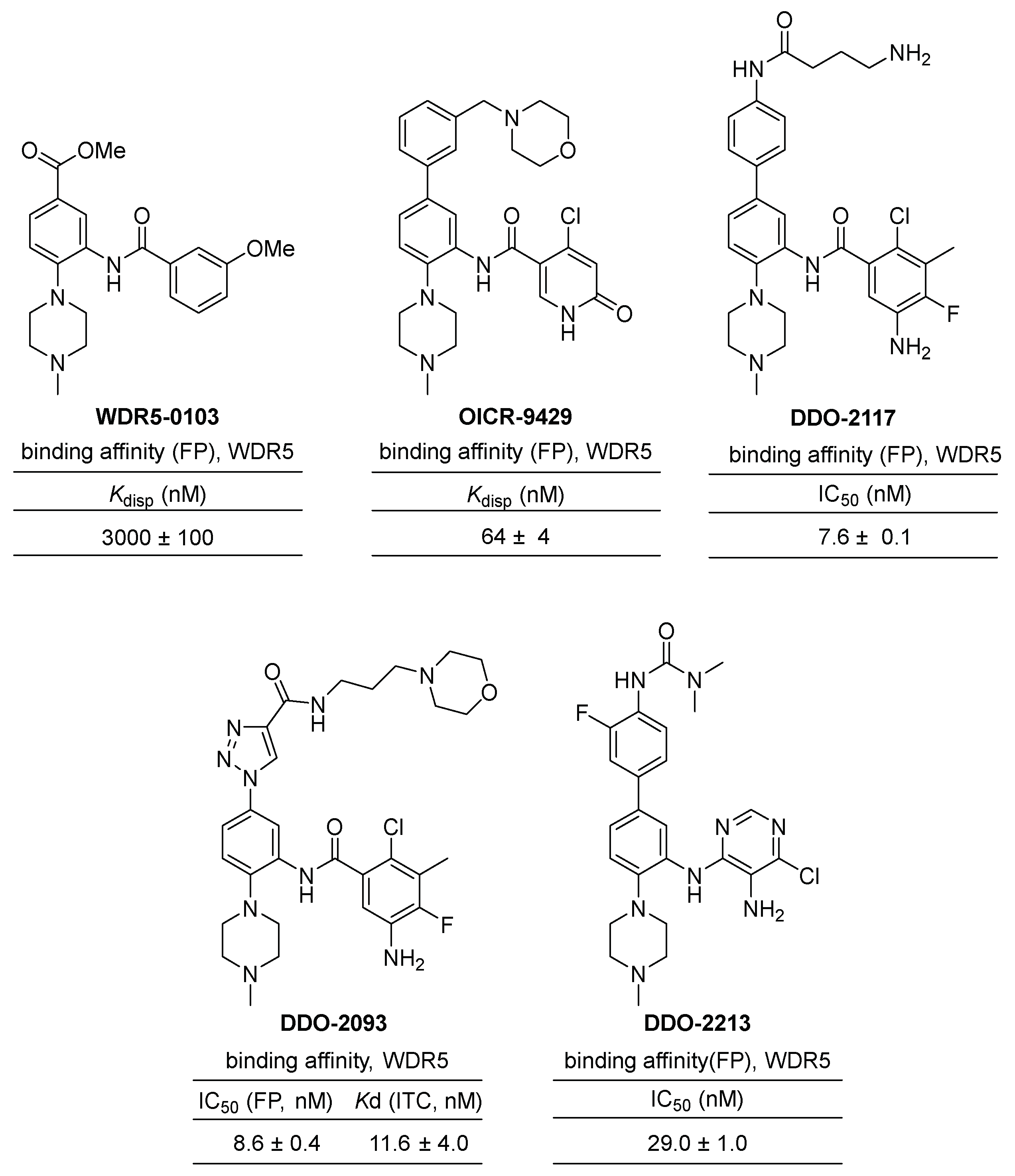
2.2.2. Benzamide Scaffold Small Molecule Inhibitors of WDR5–MLL1 Interactions
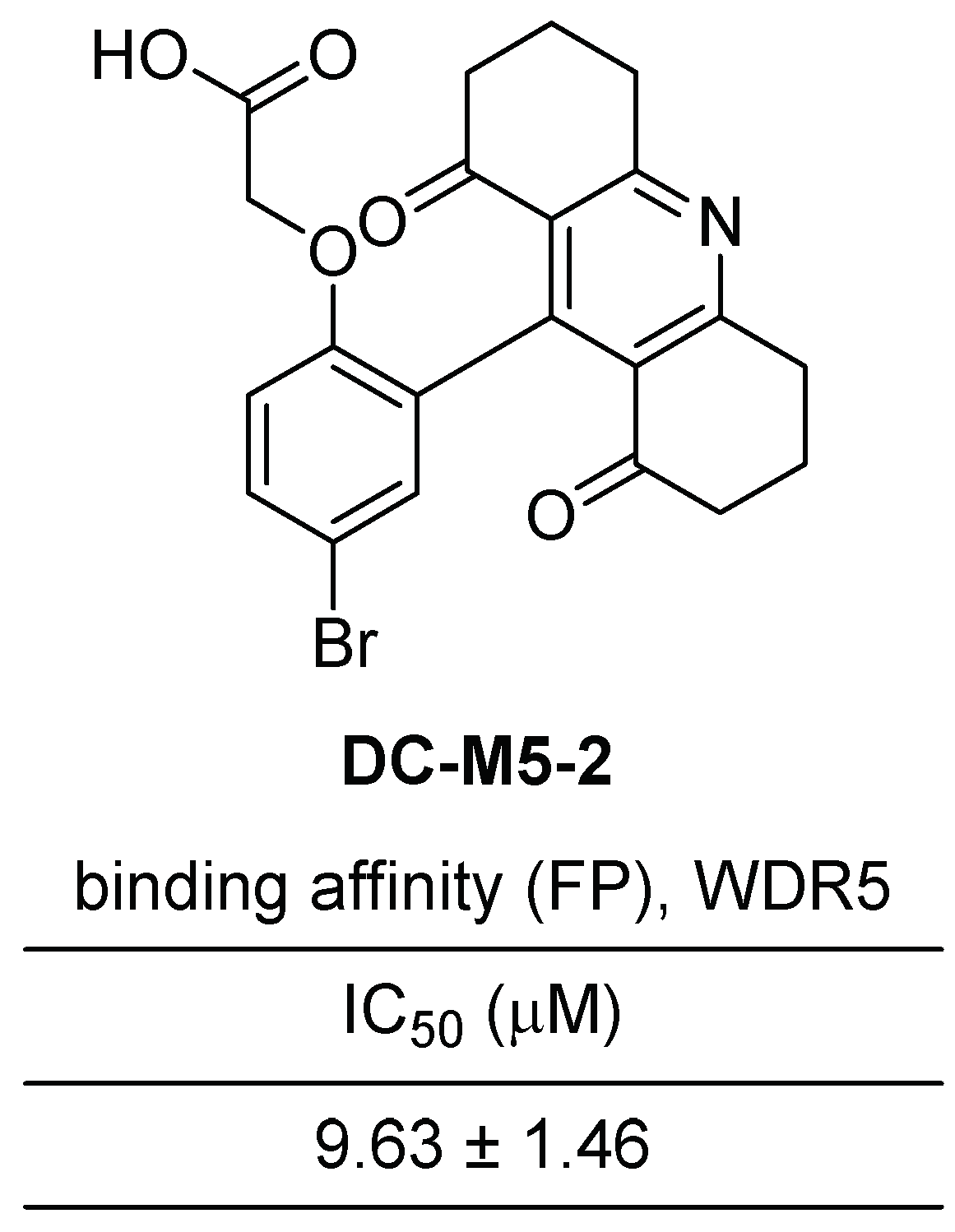
2.2.3. Acridine-1,8-Dione Scaffold Small Molecule Inhibitors of WDR5–MLL1 Interactions
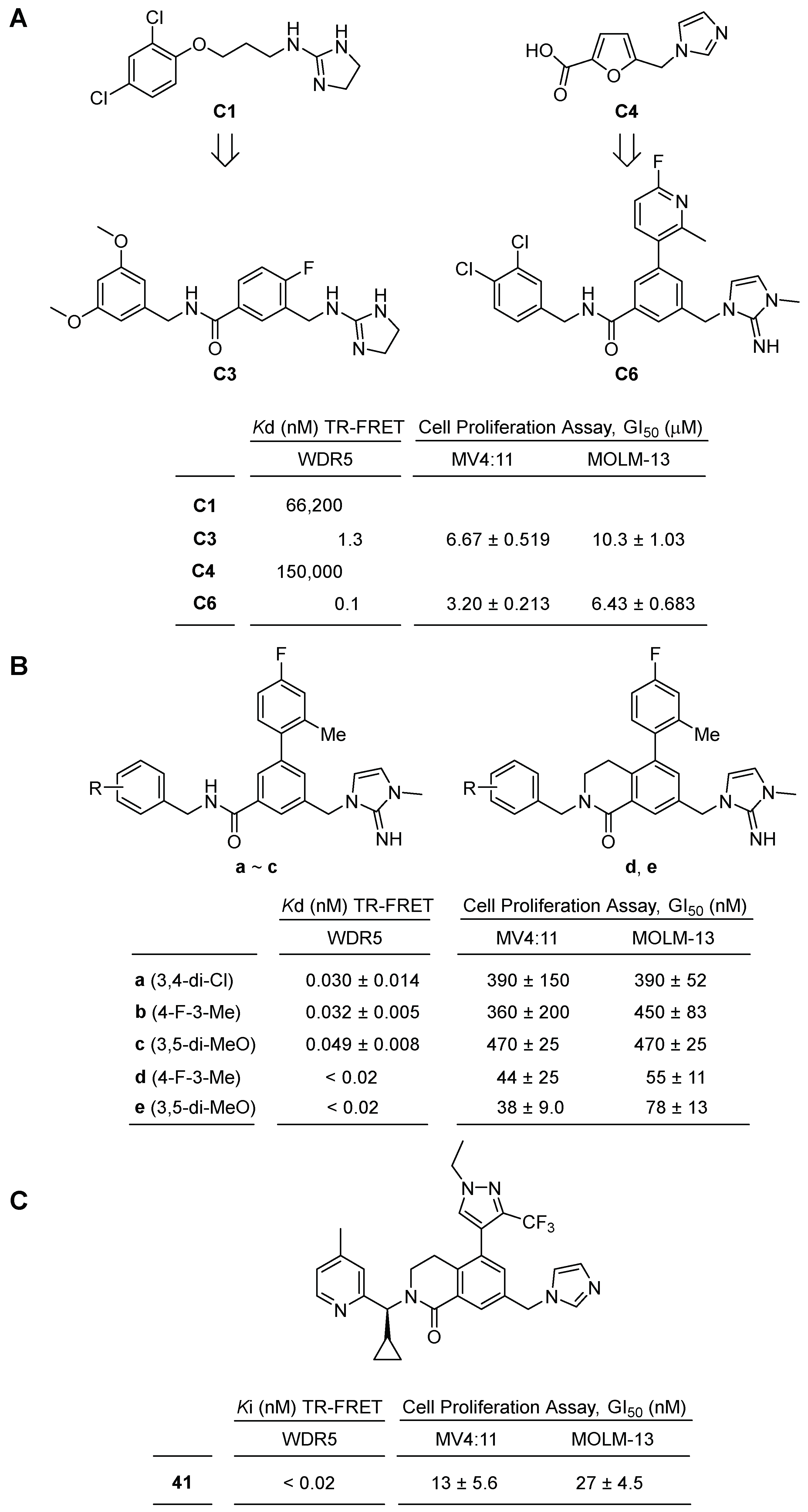
2.2.4. Benzyl Benzamides Scaffold Small Molecule Inhibitors of WDR5–MLL1 Interactions
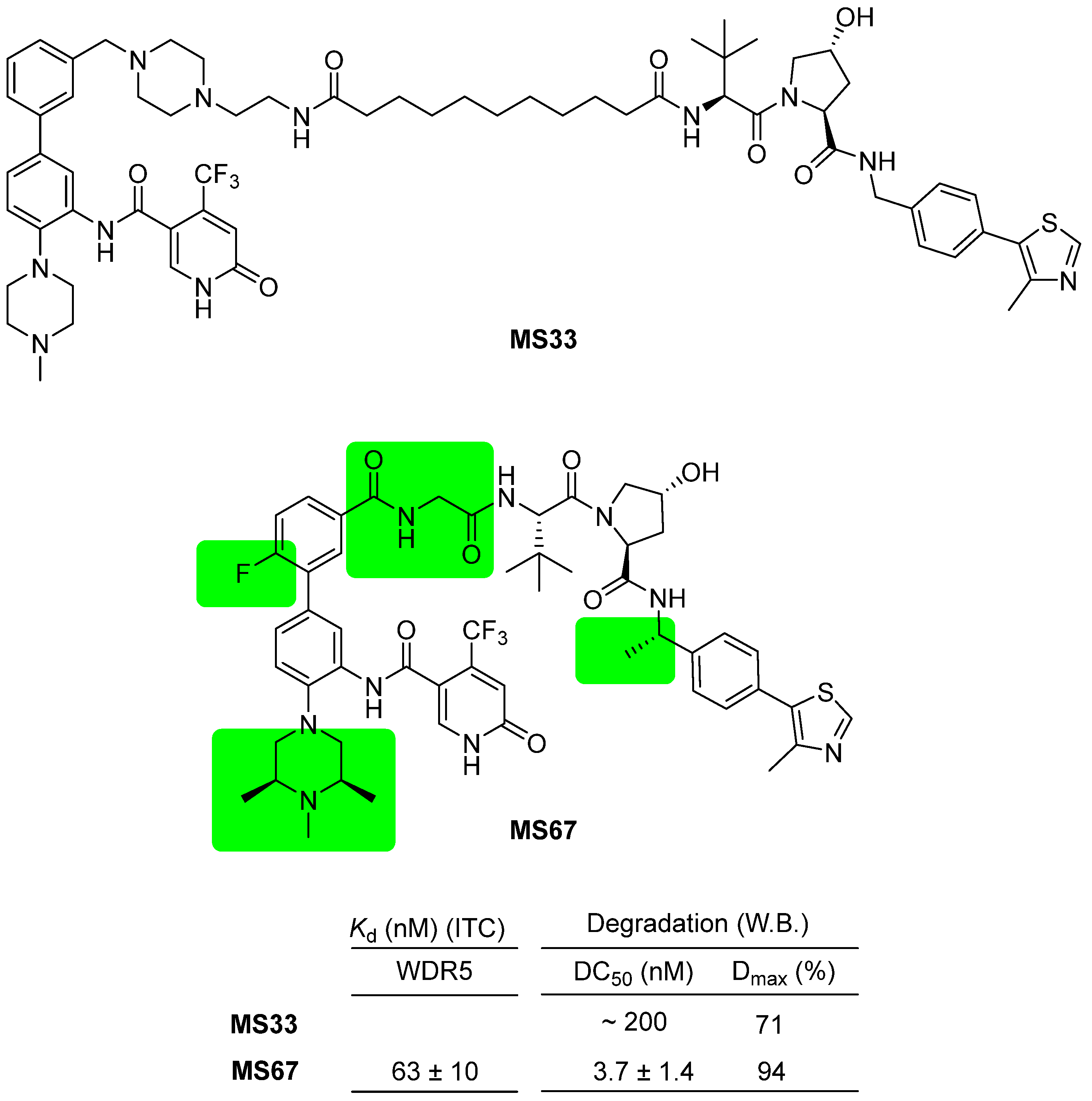
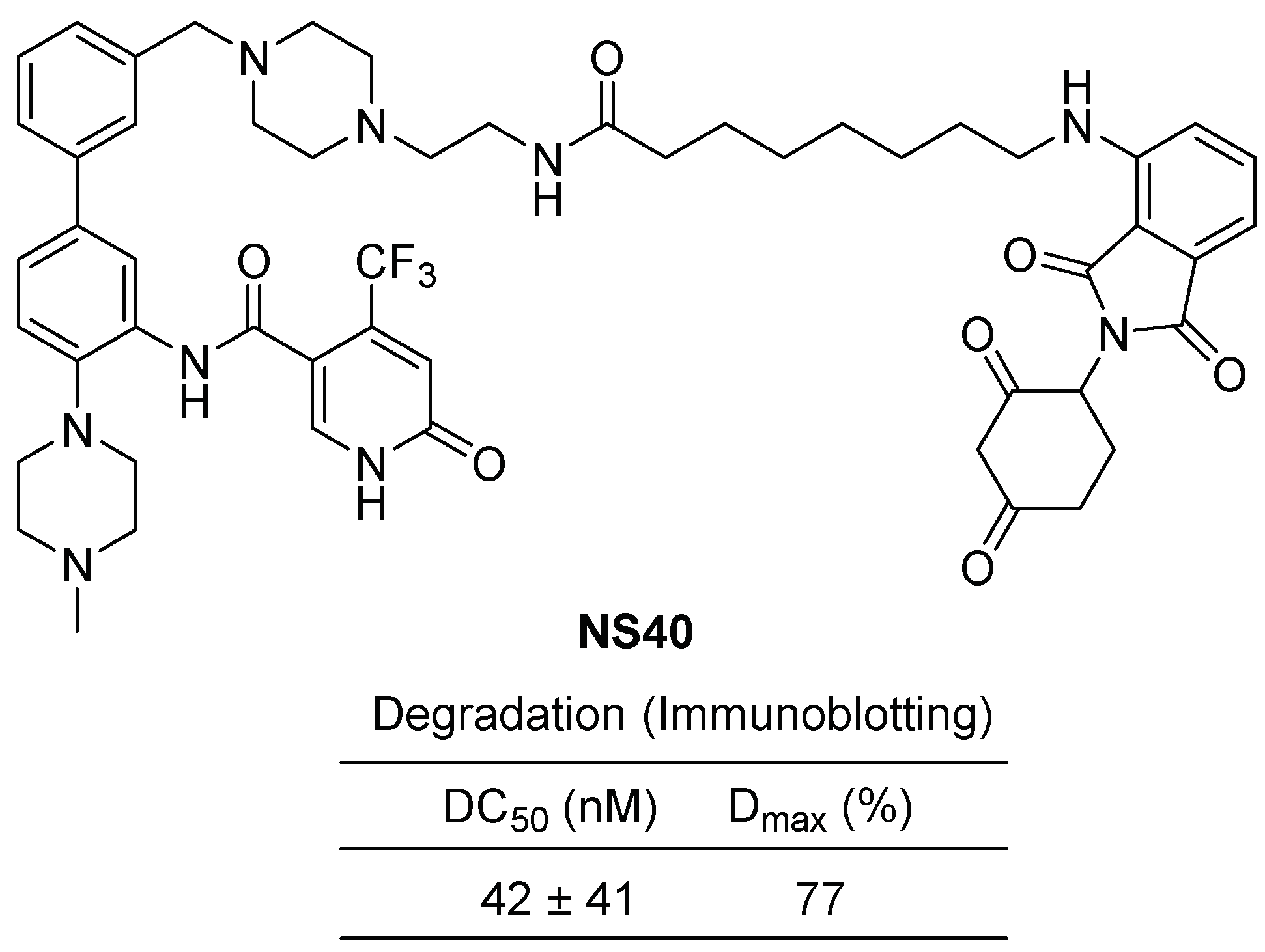
3. WDR5 Degraders
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, D.; Roberts, R. Human Genome and Diseases: WD-repeat proteins: Structure characteristics, biological function, and their involvement in human diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 2085–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, J.J.; Wang, X.H.; Long, G.L.; You, Q.D.; Guo, X.K. Targeting WD Repeat-Containing Protein 5 (WDR5): A Medicinal Chemistry Perspective. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 10537–10556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuscher, K.B.; Chowdhury, S.; Meyers, K.M.; Tian, J.; Sai, J.; Van Meveren, M.; South, T.M.; Sensintaffar, J.L.; Rietz, T.A.; Goswami, S.; et al. Structure-based discovery of potent WD repeat domain 5 inhibitors that demonstrate efficacy and safety in preclinical animal models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2211297120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z.; Song, E.; Li, J.; Dovat, S.; Song, C. Clinical Significance of WDR5 High Expression and Its Effect on Tumorigenesis in Adult Leukemia. Blood 2015, 126, 3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, W.; Gu, P.; Cai, Q.; Wang, B.; Xie, Y.; Dong, W.; He, W.; Zhong, G.; Lin, T.; et al. Upregulated WDR5 promotes proliferation, self-renewal and chemoresistance in bladder cancer via mediating H3K4 trimethylation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, Q.; Li, Z.; Chen, J. WDR5 positively regulates p53 stability by inhibiting p53 ubiquitination. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 487, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, M.; Dong, W.; Xie, R.H.; Wu, J.L.; Su, Q.; Li, W.G.; Yao, K.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhou, Q.H.; Zhang, Q.; et al. HSF1 facilitates the multistep process of lymphatic metastasis in bladder cancer via a novel PRMT5-WDR5-dependent transcriptional program. Cancer Commun. 2022, 42, 447–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aho, E.R.; Weissmiller, A.M.; Fesik, S.W.; Tansey, W.P. Targeting WDR5: A WINning Anti-Cancer Strategy? Epigenet. Insights 2019, 12, 2516865719865282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Southall, S.M.; Wong, P.-S.; Odho, Z.; Roe, S.M.; Wilson, J.R. Structural Basis for the Requirement of Additional Factors for MLL1 SET Domain Activity and Recognition of Epigenetic Marks. Mol. Cell 2009, 33, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmarajan, V.; Lee, J.-H.; Patel, A.; Skalnik, D.G.; Cosgrove, M.S. Structural Basis for WDR5 Interaction (Win) Motif Recognition in Human SET1 Family Histone Methyltransferases. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 27275–27289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Namitz, K.E.W.; Tan, S.; Cosgrove, M.S. Hierarchical assembly of the MLL1 core complex regulates H3K4 methylation and Hierarchical assembly of the MLL1 core complex regis dependent on temperature and component concentration. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 102874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemin-van der Poel, S.; McCabe, N.R.; Gill, H.J.; Espinosa, R.; Patel, Y.; Harden, A.; Rubinelli, P.; Smith, S.D.; LeBeau, M.M.; Rowley, J.D. Identification of a gene, MLL, that spans the breakpoint in 11q23 translocations associated with human leukemias. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10735–10739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, K.; Sprowls, S.A.; Arora, S.; Shakya, S.; Silver, D.J.; Goins, C.M.; Wallace, L.; Roversi, G.; Schafer, R.E.; Kay, K.; et al. WDR5 represents a therapeutically exploitable target for cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Genes Dev. 2023, 37, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.R.; Adams, C.M.; Wang, J.; Weissmiller, A.M.; Creighton, J.; Lorey, S.L.; Liu, Q.; Fesik, S.W.; Eischen, C.M.; Tansey, W.P. Interaction of the oncoprotein transcription factor MYC with its chromatin cofactor WDR5 is essential for tumor maintenance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 25260–25268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabay, M.; Li, Y.; Felsher, D.W. MYC activation is a hallmark of cancer initiation and maintenance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a014241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dang, C.V. MYC on the Path to Cancer. Cell 2012, 149, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thomas, L.R.; Wang, Q.; Grieb, B.; Phan, J.; Foshage, A.M.; Sun, Q.; Olejniczak, E.T.; Clark, T.; Dey, S.; Lorey, S.; et al. Interaction with WDR5 Promotes Target Gene Recognition and Tumorigenesis by MYC. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, J.; Li, G.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Lin, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhou, G.; Shen, L.; Zhao, M.; Yu, Y.; et al. Discovery of Potent Small-Molecule Inhibitors of WDR5-MYC Interaction. ACS Chem. Biol. 2023, 18, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, J.D.; Simon, S.C.; Han, C.; Wang, F.; Shaw, J.G.; Howes, J.E.; Sai, J.; Yuh, J.P.; Camper, D.; Alicie, B.M.; et al. Discovery and Optimization of Salicylic Acid-Derived Sulfonamide Inhibitors of the WD Repeat-Containing Protein 5–MYC Protein–Protein Interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 11232–11259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, S.C.; Wang, F.; Thomas, L.R.; Phan, J.; Zhao, B.; Olejniczak, E.T.; Macdonald, J.D.; Shaw, J.G.; Schlund, C.; Payne, W.; et al. Discovery of WD Repeat-Containing Protein 5 (WDR5)-MYC Inhibitors Using Fragment-Based Methods and Structure-Based Design. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 4315–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.R.; Adams, C.M.; Fesik, S.W.; Eischen, C.M.; Tansey, W.P. Targeting MYC through WDR5. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2020, 7, 1709388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, L.R.; Foshage, A.M.; Weissmiller, A.M.; Tansey, W.P. The MYC-WDR5 Nexus and Cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4012–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carugo, A.; Genovese, G.; Seth, S.; Nezi, L.; Rose, J.L.; Bossi, D.; Cicalese, A.; Shah, P.K.; Viale, A.; Pettazzoni, P.F.; et al. In Vivo Functional Platform Targeting Patient-Derived Xenografts Identifies WDR5-Myc Association as a Critical Determinant of Pancreatic Cancer. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narayanan, A.; Jones, L.H. Sulfonyl fluorides as privileged warheads in chemical biology. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 2650–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karatas, H.; Townsend, E.C.; Cao, F.; Chen, Y.; Bernard, D.; Liu, L.; Lei, M.; Dou, Y.L.; Wang, S.M. High-Affinity, Small-Molecule Peptidomimetic Inhibitors of MLL1/WDR5 Protein-Protein Interaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, F.; Townsend, E.C.; Karatas, H.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Lee, S.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Ouillette, P.; Zhu, J.D.; et al. Targeting MLL1 H3K4 Methyltransferase Activity in Mixed-Lineage Leukemia. Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karatas, H.; Li, Y.B.; Liu, L.; Ji, J.; Lee, S.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.L.; Huang, L.Y.; Bernard, D.; Xu, J.; et al. Discovery of a Highly Potent, Cell-Permeable Macrocyclic Peptidomimetic (MM-589) Targeting the WD Repeat Domain 5 Protein (WDR5)-Mixed Lineage Leukemia (MLL) Protein-Protein Interaction. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4818–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senisterra, G.; Wu, H.; Allali-Hassani, A.; Wasney, G.A.; Barsyte-Loyejoy, D.; Dombrovski, L.; Dong, A.P.; Nguyen, K.T.; Smil, D.; Bolshan, Y.; et al. Small-molecule inhibition of MLL activity by disruption of its interaction with WDR5. Biochem. J. 2013, 449, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.D.; Wang, Z.H.; Chen, W.L.; Xie, Y.Y.; You, Q.D.; Guo, X.K. Structure-based design of ester compounds to inhibit MLL complex catalytic activity by targeting mixed lineage leukemia 1 (MLL1)-WDR5 interaction. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 6109–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolshan, Y.; Getlik, M.; Kuznetsova, E.; Wasney, G.A.; Hajian, T.; Poda, G.; Nguyen, K.T.; Wu, H.; Dombrovski, L.; Dong, A.; et al. Synthesis, Optimization, and Evaluation of Novel Small Molecules as Antagonists of WDR5-MLL Interaction. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.D.; Chen, W.L.; Xu, X.L.; Jiang, F.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Guo, X.K.; You, Q.D.; Sun, H.P. Structure-based design and synthesis of small molecular inhibitors disturbing the interaction of MLL1-WDR5. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 118, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grebien, F.; Vedadi, M.; Getlik, M.; Giambruno, R.; Grover, A.; Avellino, R.; Skucha, A.; Vittori, S.; Kuznetsova, E.; Smil, D.; et al. Pharmacological targeting of the Wdr5-MLL interaction in C/EBPα N-terminal leukemia. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Sammons, M.A.; Donahue, G.; Dou, Z.; Vedadi, M.; Getlik, M.; Barsyte-Lovejoy, D.; Al-awar, R.; Katona, B.W.; Shilatifard, A.; et al. Gain-of-function p53 mutants co-opt chromatin pathways to drive cancer growth. Nature 2015, 525, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.T.; Zhou, Q.H.; Xie, K.J.; Cheng, L.; Peng, S.M.; Xie, R.H.; Liu, L.X.; Zhang, Y.J.; Dong, W.; Han, J.L.; et al. Targeting WD repeat domain 5 enhances chemosensitivity and inhibits proliferation and programmed death-ligand 1 expression in bladder cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, X.; He, H.; Peng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, L.; Liu, S.; Huang, M.; Xie, R.; et al. WD repeat domain 5 promotes chemoresistance and Programmed Death-Ligand 1 expression in prostate cancer. Theranostics 2021, 11, 4809–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Bell, J.L.; Carter, D.; Gherardi, S.; Poulos, R.C.; Milazzo, G.; Wong, J.W.H.; Al-Awar, R.; Tee, A.E.; Liu, P.Y.; et al. WDR5 Supports an N-Myc Transcriptional Complex That Drives a Protumorigenic Gene Expression Signature in Neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 5143–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Getlik, M.; Smil, D.; Zepeda-Velazquez, C.; Bolshan, Y.; Poda, G.; Wu, H.; Dong, A.P.; Kuznetsova, E.; Marcellus, R.; Senisterra, G.; et al. Structure-Based Optimization of a Small Molecule Antagonist of the Interaction Between WD Repeat-Containing Protein 5 (WDR5) and Mixed-Lineage Leukemia 1 (MLL1). J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2478–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.D.; Chen, W.L.; Wang, Z.H.; Xie, Y.Y.; Xu, X.L.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; You, Q.D.; Guo, X.K. High-affinity small molecular blockers of mixed lineage leukemia 1 (MLL1)-WDR5 interaction inhibit MLL1 complex H3K4 methyltransferase activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.L.; Chen, X.; Li, D.D.; Wang, X.H.; Long, G.L.; Jiang, Z.Y.; You, Q.D.; Guo, X.K. Discovery of a potent MLL1 and WDR5 protein-protein interaction inhibitor with in vivo antitumor activity. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 223, 113677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.L.; Chen, X.; Li, D.D.; Zhou, J.R.; Jiang, Z.Y.; You, Q.D.; Guo, X.K. Discovery of DDO-2213 as a Potent and Orally Bioavailable Inhibitor of the WDR5-Mixed Lineage Leukemia 1 Protein-Protein Interaction for the Treatment of MLL Fusion Leukemia. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 8221–8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.Q.; Zhang, R.K.; Lian, F.L.; Zhang, W.Y.; Lu, W.C.; Han, J.; Zhang, N.X.; Jin, J.; Luo, C.; Chen, K.X.; et al. The identification of novel small-molecule inhibitors targeting WDR5-MLL1 interaction through fluorescence polarization based high-throughput screening. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aho, E.R.; Wang, J.; Gogliotti, R.D.; Howard, G.C.; Phan, J.; Acharya, P.; Macdonald, J.D.; Cheng, K.; Lorey, S.L.; Lu, B.; et al. Displacement of WDR5 from Chromatin by a WIN Site Inhibitor with Picomolar Affinity. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 2916–2928.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, J.; Teuscher, K.B.; Aho, E.R.; Alvarado, J.R.; Mills, J.J.; Meyers, K.M.; Gogliotti, R.D.; Han, C.H.; Macdonald, J.D.; Sai, J.Q.; et al. Discovery and Structure-Based Optimization of Potent and Selective WD Repeat Domain 5 (WDR5) Inhibitors Containing a Dihydroisoquinolinone Bicyclic Core. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 656–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuscher, K.B.; Meyers, K.M.; Wei, Q.Q.; Mills, J.J.; Tian, J.H.; Alvarado, J.; Sai, J.Q.; Van Meveren, M.; South, T.M.; Rietz, T.A.; et al. Discovery of Potent Orally Bioavailable WD Repeat Domain 5(WDR5) Inhibitors Using a Pharmacophore-Based Optimization. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 6287–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Békés, M.; Langley, D.R.; Crews, C.M. PROTAC targeted protein degraders: The past is prologue. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 181–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.F.; Li, D.X.; Kottur, J.; Shen, Y.D.; Kim, H.S.; Park, K.S.; Tsai, Y.H.; Gong, W.D.; Wang, J.; Suzuki, K.; et al. A selective WDR5 degrader inhibits acute myeloid leukemia in patient-derived mouse models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabj1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dölle, A.; Adhikari, B.; Krämer, A.; Weckesser, J.; Berner, N.; Berger, L.-M.; Diebold, M.; Szewczyk, M.M.; Barsyte-Lovejoy, D.; Arrowsmith, C.H.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation of WD-Repeat-Containing Protein 5 (WDR5) Degraders. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 10682–10710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Jeon, K.O.; Salovich, J.M.; Macdonald, J.D.; Alvarado, J.H.; Gogliotti, R.D.; Phan, J.; Olejniczak, E.T.; Sun, Q.; Wang, S.D.; et al. Discovery of Potent 2-Aryl-6,7-dihydro-5H-pyrrolo 1,2-a imidazoles as WDR5-WIN-Site Inhibitors Using Fragment-Based Methods and Structure-Based Design. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5623–5642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.X.; Yu, X.F.; Kottur, J.; Gong, W.D.; Zhang, Z.; Storey, A.J.; Tsai, Y.H.; Uryu, H.; Shen, Y.D.; Byrum, S.D.; et al. Discovery of a dual WDR5 and Ikaros PROTAC degrader as an anti-cancer therapeutic. Oncogene 2022, 41, 3328–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gurung, R.; Om, D.; Pun, R.; Hyun, S.; Shin, D. Recent Progress in Modulation of WD40-Repeat Domain 5 Protein (WDR5): Inhibitors and Degraders. Cancers 2023, 15, 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153910
Gurung R, Om D, Pun R, Hyun S, Shin D. Recent Progress in Modulation of WD40-Repeat Domain 5 Protein (WDR5): Inhibitors and Degraders. Cancers. 2023; 15(15):3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153910
Chicago/Turabian StyleGurung, Raju, Darlami Om, Rabin Pun, Soonsil Hyun, and Dongyun Shin. 2023. "Recent Progress in Modulation of WD40-Repeat Domain 5 Protein (WDR5): Inhibitors and Degraders" Cancers 15, no. 15: 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153910
APA StyleGurung, R., Om, D., Pun, R., Hyun, S., & Shin, D. (2023). Recent Progress in Modulation of WD40-Repeat Domain 5 Protein (WDR5): Inhibitors and Degraders. Cancers, 15(15), 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153910





