Integrative Transcriptomic Profiling of the Wilms Tumor
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Whole-Exome Sequencing Analysis for Exclusion of Germline Variants Associated with the WT
2.3. miRNA Expression in Wilms Tumor Fresh Frozen Kidney Tissue
2.4. miRNA Expression in Wilms Tumor Formaldehyde-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue
2.5. mRNA in Wilms Tumor Fresh Frozen Kidney Tissue
2.6. Bioinformatic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients and Epidemiological Data
3.2. Whole-Exome Sequencing Analysis for Exclusion of Germline Variants Associated with the Wilms Tumor
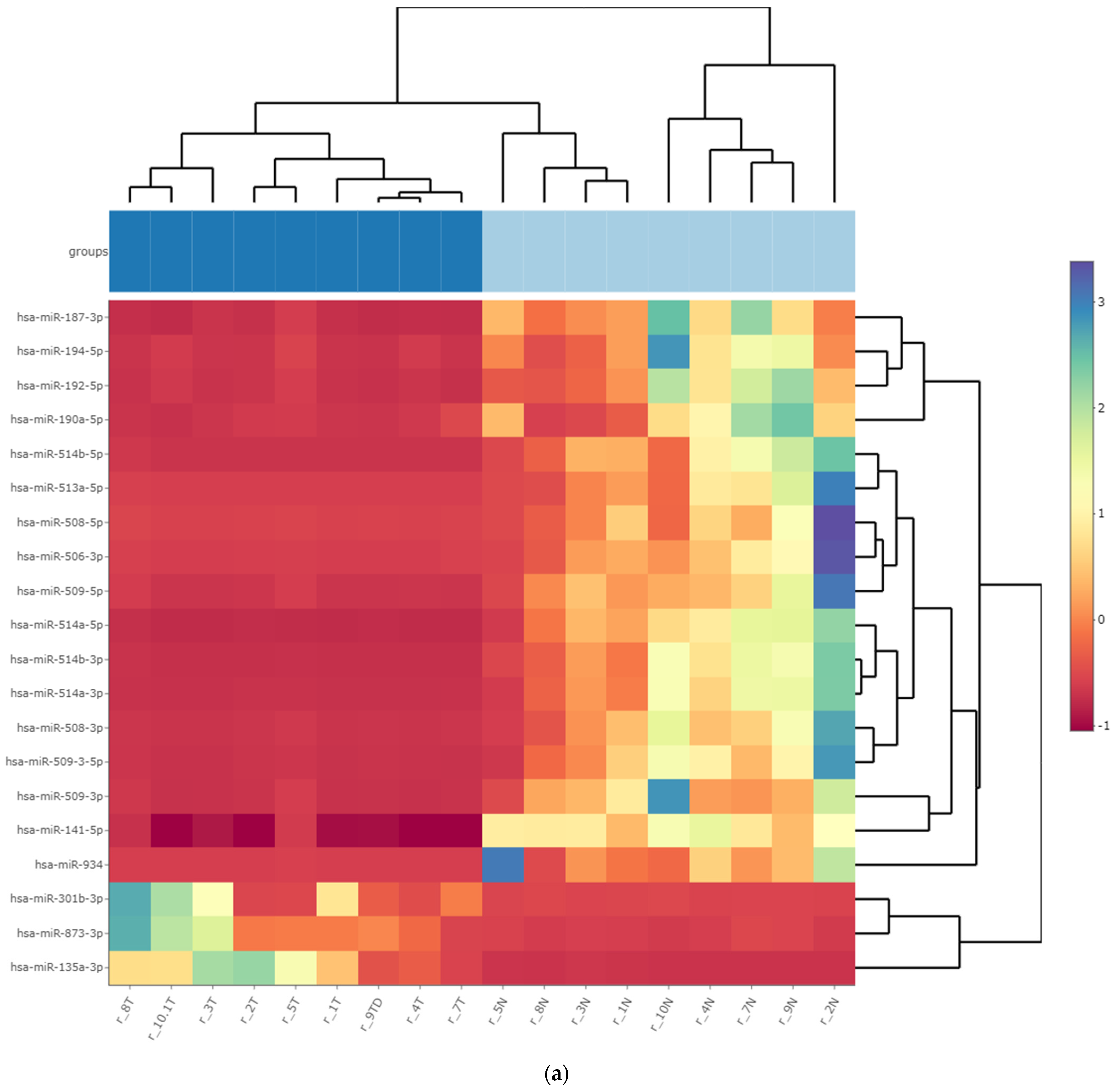
3.3. Differentially Expressed miRNA in Fresh Frozen Tissue WT Samples
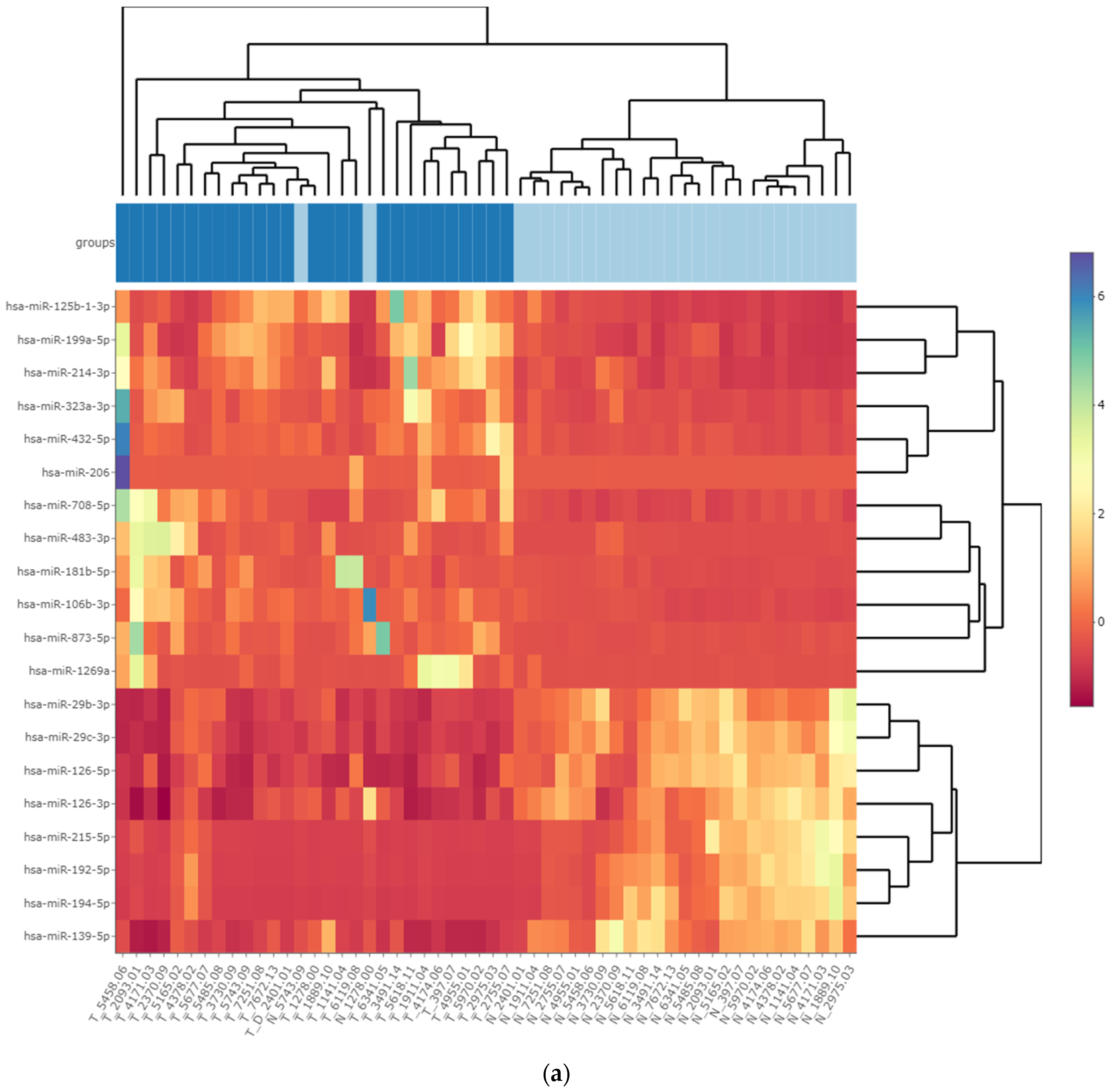
3.4. Differentially Expressed miRNA in Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Wilms Tumor Tissue Samples
3.5. Differentially Expressed miRNAs in the Wilms Tumor Irrespective of Tumor Histological Type and Stage
3.6. Differentially Expressed miRNAs in the High-Risk Wilms Tumor
3.7. Cellular Processes Regulated by Differentially Expressed miRNA in the Wilms Tumor
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leichter, A.L.; Sullivan, M.J.; Eccles, M.R.; Chatterjee, A. MicroRNA Expression Patterns and Signalling Pathways in the Development and Progression of Childhood Solid Tumours. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Treger, T.D.; Chowdhury, T.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; Behjati, S. The Genetic Changes of Wilms Tumour. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciaszek, J.L.; Oak, N.; Nichols, K.E. Recent Advances in Wilms’ Tumor Predisposition. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, R138–R149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolarz, B.; Durczyński, A.; Romanowicz, H.; Szyłło, K.; Hogendorf, P. MiRNAs in Cancer (Review of Literature). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, D.M.; Tayeb, M.; Ho, J. MicroRNAs in Kidney Development and Disease. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e158277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, T.; Zamore, P.D. MicroPrimer: The Biogenesis and Function of MicroRNA. Development 2005, 132, 4645–4652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohtsuka, M.; Ling, H.; Doki, Y.; Mori, M.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNA Processing and Human Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 1651–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA Expression Profiles Classify Human Cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomão, K.B.; Pezuk, J.A.; de Souza, G.R.; Chagas, P.; Pereira, T.C.; Valera, E.T.; Brassesco, M.S. MicroRNA Dysregulation Interplay with Childhood Abdominal Tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2019, 38, 783–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brok, J.; Treger, T.D.; Gooskens, S.L.; van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M.M.; Pritchard-Jones, K. Biology and Treatment of Renal Tumours in Childhood. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 68, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Tang, H.; Huang, Z.; Qin, H.; Cen, Q.; Meng, F.; Huang, L.; Lin, L.; Pu, J.; Yang, D. Bioinformatics Analysis and Identification of Genes and Pathways Involved in Patients with Wilms Tumor. Transl. Cancer Res. 2022, 11, 2843–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, B.; Kirchner, R.; Pantano, L.; Naumenko, S.; De Smet, M.; Beltrame, L.; Khotiainsteva, T.; Sytchev, I.; Guimera, R.V.; Kern, J.; et al. bcbio/bcbio-nextgen: v1.2.5 (v1.2.5). Zenodo 2021. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/5781867 (accessed on 18 June 2023).
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and Accurate Short Read Alignment with Burrows-Wheeler Transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Desvignes, J.P.; Bartoli, M.; Delague, V.; Krahn, M.; Miltgen, M.; Béroud, C.; Salgado, D. VarAFT: A Variant Annotation and Filtration System for Human next Generation Sequencing Data. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2018, 46, W545–W553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio-Puerta, E.; Gómez-Martín, C.; Giannoukakos, S.; Medina, J.M.; Scheepbouwer, C.; García-Moreno, A.; Carmona-Saez, P.; Fromm, B.; Pegtel, M.; Keller, A.; et al. SRNAbench and SRNAtoolbox 2022 Update: Accurate MiRNA and SncRNA Profiling for Model and Non-Model Organisms. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2022, 50, W710–W717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Xia, J. MicroRNA Regulatory Network Analysis Using MiRNet 2.0. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023, 2594, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, V.; Heyne, S.; Sikora, K.; Rabbani, L.; Rauer, M.; Kilpert, F.; Richter, A.S.; Ryan, D.P.; Manke, T. SnakePipes: Facilitating Flexible, Scalable and Integrative Epigenomic Analysis. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 4757–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences From High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon Provides Fast and Bias-Aware Quantification of Transcript Expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, C.; Peng, M.; Lu, Q. Translating Epigenetics into Clinic: Focus on Lupus. Clin. Epigenetics 2017, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujanić, G.M.; Sandstedt, B. The Pathology of Wilms’ Tumour (Nephroblastoma): The International Society of Paediatric Oncology Approach. J. Clin. Pathol. 2010, 63, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ludwig, N.; Werner, T.V.; Backes, C.; Trampert, P.; Gessler, M.; Keller, A.; Lenhof, H.P.; Graf, N.; Meese, E. Combining MiRNA and MRNA Expression Profiles in Wilms Tumor Subtypes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buglyó, G.; Magyar, Z.; Romicsné Görbe, É.; Bánusz, R.; Csóka, M.; Micsik, T.; Berki, Z.; Varga, P.; Sápi, Z.; Nagy, B. Quantitative RT-PCR-Based MiRNA Profiling of Blastemal Wilms’ Tumors from Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Samples. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 298, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buglyó, G.; Magyar, Z.; Görbe, É.R.; Bánusz, R.; Csóka, M.; Micsik, T.; Mezei, M.; Yani, J.A.S.; Varga, P.; Sápi, Z.; et al. MiRNA Profiling of Hungarian Regressive Wilms’ Tumor Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Samples by Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR). Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e932731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.A.; Bryan, K.; Williams, R.; Popov, S.; Vujanic, G.; Coulomb, A.; Boccon-Gibod, L.; Graf, N.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; O’Sullivan, M. MiRNA Profiles as a Predictor of Chemoresponsiveness in Wilms’ Tumor Blastema. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, A.; Lupini, L.; Consiglio, J.; Visone, R.; Ferracin, M.; Fornari, F.; Zanesi, N.; Alder, H.; D’Elia, G.; Gramantieri, L.; et al. Oncogenic Role of MiR-483-3p at the IGF2/483 Locus. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3140–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Roth, A.; Yu, M.; Morris, R.; Bersani, F.; Rivera, M.N.; Lu, J.; Shioda, T.; Vasudevan, S.; Ramaswamy, S.; et al. The IGF2 Intronic MiR-483 Selectively Enhances Transcription from IGF2 Fetal Promoters and Enhances Tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 2543–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, G.; Gao, H.; Tian, J.; Hu, Q.; Xie, H.; Zhang, Y. MicroRNA-483-3p Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion and Induces Chemoresistance of Wilms’ Tumor Cells. Pediatr. Dev. Pathol. 2020, 23, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yan, J. Aberrant Expression and Mechanism of MiR-130b-3p/Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog in Nephroblastoma in Children. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senanayake, U.; Das, S.; Vesely, P.; Alzoughbi, W.; Fröhlich, L.F.; Chowdhury, P.; Leuschner, I.; Hoefler, G.; Guertl, B. MiR-192, MiR-194, MiR-215, MiR-200c and MiR-141 Are Downregulated and Their Common Target ACVR2B Is Strongly Expressed in Renal Childhood Neoplasms. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Zhao, P.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, Y.L.; Gu, Q. MiR-200c-3p Suppresses the Proliferative, Migratory, and Invasive Capacities of Nephroblastoma Cells via Targeting FRS2. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2019, 17, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Liu, G.-S.; Zou, N.-Z.; Zhang, H.; He, X.-X.; Sun, P.-L.; An, H.-J.; Shen, H. MicroRNA-200c-3p Suppresses Proliferation and Invasion of Nephroblastoma Cells by Targeting EP300 and Inactivating the AKT/FOXO1/P27 Pathway. Neoplasma, 2022; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecot, C.V.; Rupaimoole, R.; Yang, D.; Akbani, R.; Ivan, C.; Lu, C.; Wu, S.; Han, H.D.; Shah, M.Y.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; et al. Tumour Angiogenesis Regulation by the MiR-200 Family. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Linares, F.J.; Pérezpeña-Diazconti, M.; García-Quintana, J.; Baay-Guzmán, G.; Cabrera-Muñoz, L.; Sadowinski-Pine, S.; Serrano-Bello, C.; Murillo-Maldonado, M.; Contreras-Ramos, A.; Eguía-Aguilar, P. MicroRNA Profiling in Wilms Tumor: Identification of Potential Biomarkers. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Rong, Z.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, Z.; Huang, C. The Novel GINS4 Axis Promotes Gastric Cancer Growth and Progression by Activating Rac1 and CDC42. Theranostics 2019, 9, 8294–8311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.-J.; Wang, J.-Y.; Zhang, T.-J.; An, G.-S.; Ni, J.-H.; Li, S.-Y.; Jia, H.-T. MiR-509-3-5p-NONHSAT112228.2 Axis Regulates P21 and Suppresses Proliferation and Migration of Lung Cancer Cells. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moch, H.; Lukamowicz-Rajska, M. MiR-30c-2-3p and MiR-30a-3p: New Pieces of the Jigsaw Puzzle in HIF2α Regulation. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sukocheva, O.A.; Liu, J.; Neganova, M.E.; Beeraka, N.M.; Aleksandrova, Y.R.; Manogaran, P.; Grigorevskikh, E.M.; Chubarev, V.N.; Fan, R. Perspectives of Using MicroRNA-Loaded Nanocarriers for Epigenetic Reprogramming of Drug Resistant Colorectal Cancers. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86 Pt 2, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Khoshbakht, T.; Hussen, B.M.; Taheri, M.; Samadian, M. A Review on the Role of MCM3AP-AS1 in the Carcinogenesis and Tumor Progression. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Huo, C.; Jiang, S.; Huang, Y.; Fang, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, M.; Ren, J.; Xu, B.; Liu, Y. Exostosin1 as a Novel Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker for Squamous Cell Lung Carcinoma: A Study Based on Bioinformatics Analysis. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 2787–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Dashti, S.; Farsi, M.; Hussen, B.M.; Taheri, M. A Review on the Role of Oncogenic LncRNA OIP5-AS1 in Human Malignancies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111366:1–1113661:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungormez, C.; Gumushan Aktas, H.; Dilsiz, N.; Borazan, E. Novel MiRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Stage II Colon Cancer: Microarray Analysis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 4175–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Xie, H.; Zhu, B.; Sun, Z.; Huang, Y. MiR-455-5p Suppresses the Progression of Prostate Cancer by Targeting CCR5. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 6394784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, J.; Guo, X.; Sun, L.; Wang, K.; Yao, H. Networks Analysis of Genes and MicroRNAs in Human Wilms’ Tumors. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 3579–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.; Zhuang, J.; Gong, L.; Dai, Y.; Diao, H. Investigating the Dysfunctional Pathogenesis of Wilms’ Tumor through a Multidimensional Integration Strategy. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado, M.; Robles-Valero, J. VAV Proteins as Double Agents in Cancer: Oncogenes with Tumor Suppressor Roles. Biology 2021, 10, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, S.; Schäfer, P.; Nojszewski, J.; Meyer, F.; Windhorst, S. DIAPH1 Regulates Chromosomal Instability of Cancer Cells by Controlling Microtubule Dynamics. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 100, 151156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idossa, D.; Borrero, M.; Blaes, A. ERBB2-Low (Also Known as HER2-Low) Breast Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 576:1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Zhou, X.; Qin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Tang, M.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W. Identification of Key Genes and MicroRNAs Involved in Kidney Wilms Tumor by Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 2554–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juracek, J.; Madrzyk, M.; Stanik, M.; Slaby, O. Urinary MicroRNAs and Their Significance in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: A 5-Year Update. Cancers 2022, 14, 3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, M.; Poojary, S.S.; Seshan, V.; Kumar, S.; Agarwal, P.; Tandon, S.; Zutshi, V.; Das, B.C. Urine MiRNA Signature as a Potential Non-Invasive Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Cervical Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, A.; Kajau, H.; Margolis, E.; Tutrone, R.; Grimm, T.; Trottmann, M.; Stief, C.; Stoll, G.; Fischer, C.A.; Flinspach, C.; et al. Validation of a CE-IVD, Urine Exosomal RNA Expression Assay for Risk Assessment of Prostate Cancer Prior to Biopsy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, J.; Hossain, G.S.; Kocerha, J. The Potential for MicroRNA Therapeutics and Clinical Research. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
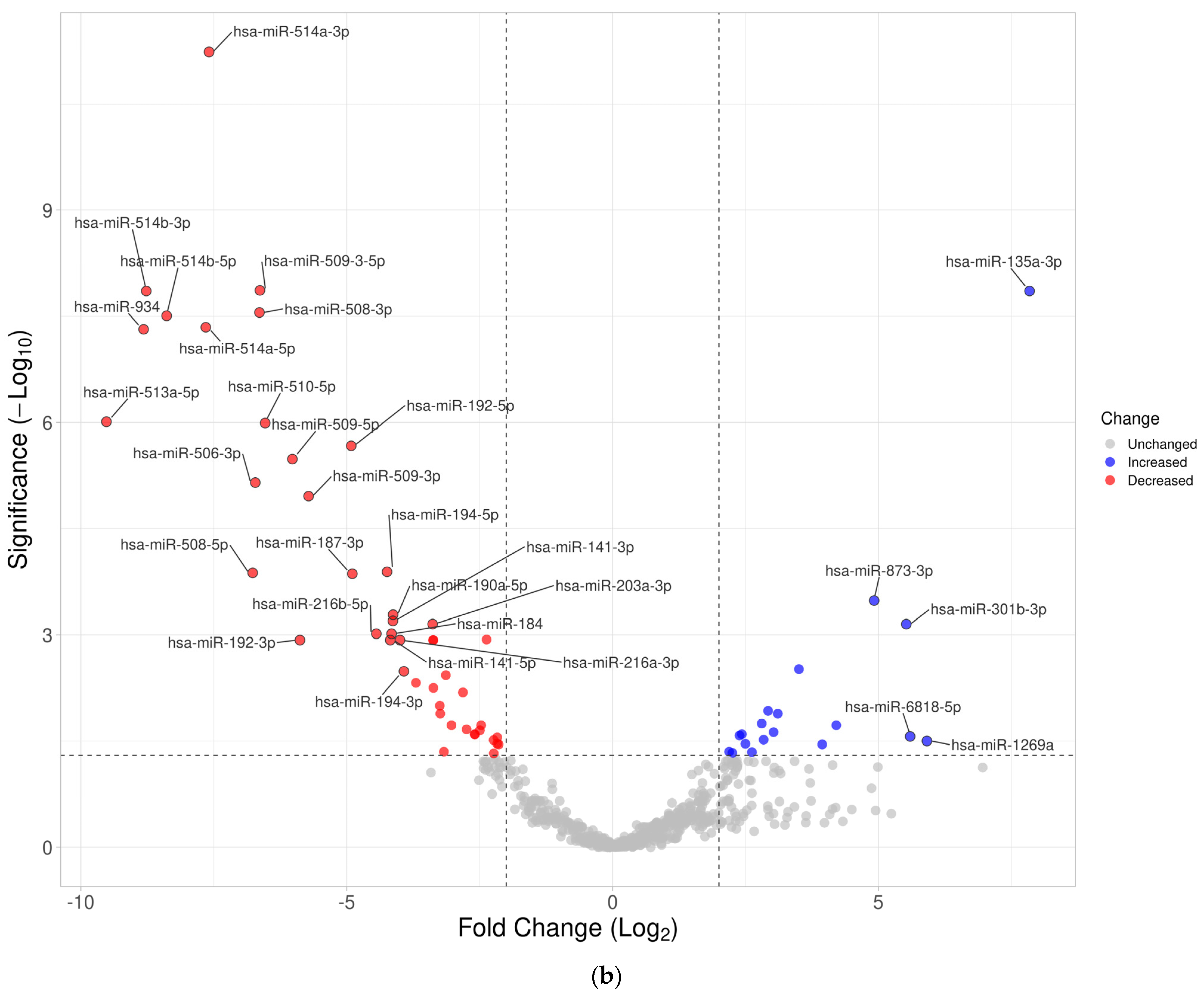
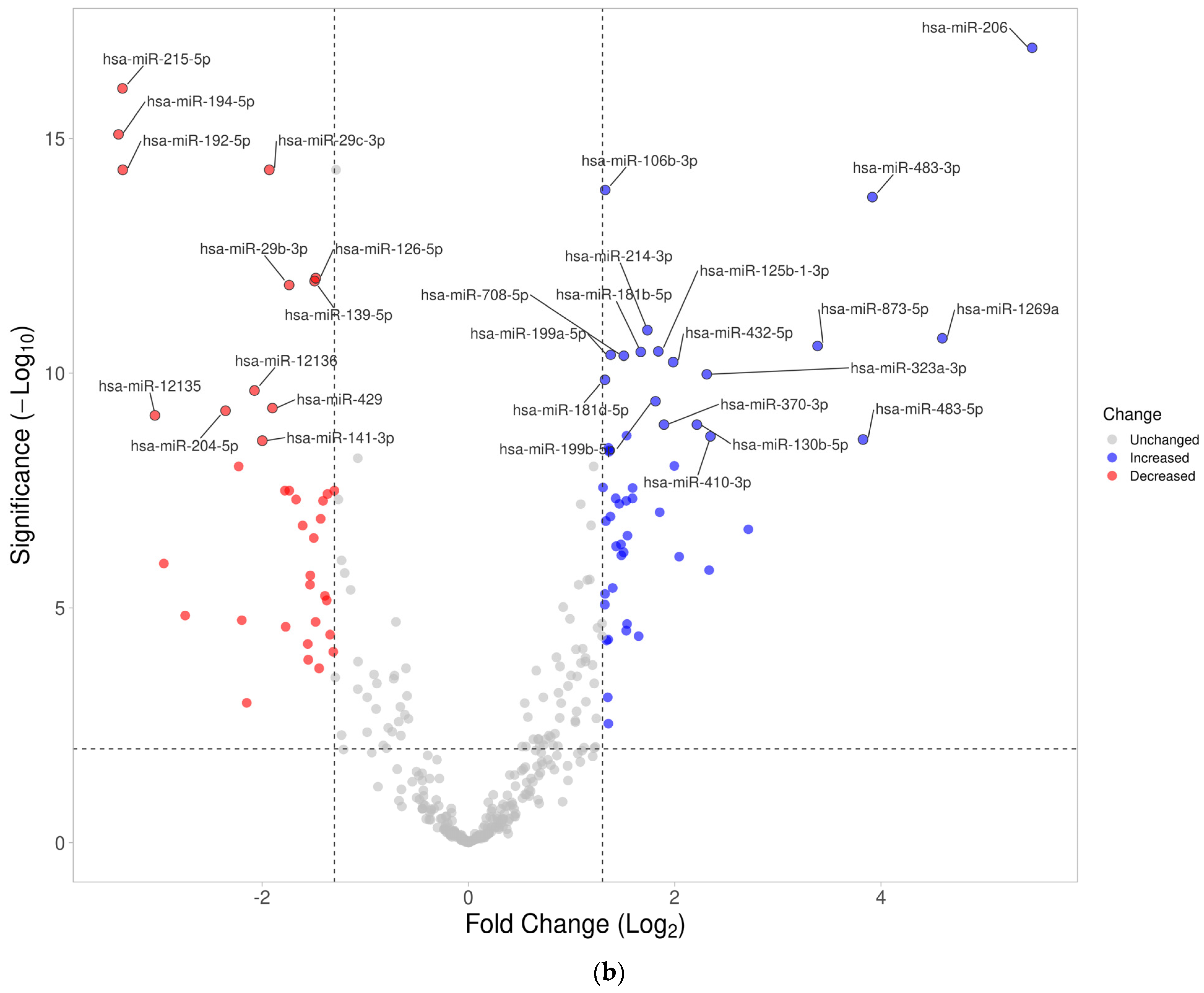



| Decreased Expression in WT Tissue | Increased Expression in WT Tissue |
|---|---|
| hsa-miR-9-5p | hsa-miR-34a-5p |
| hsa-miR-30a-5p | hsa-miR-106b-3p |
| hsa-miR-30b-5p | hsa-miR-130b-3p |
| hsa-miR-30c-2-3p | hsa-miR-130b-5p |
| hsa-miR-138-5p | hsa-miR-181a-2-3p |
| hsa-miR-139-5p | hsa-miR-199b-5p |
| hsa-miR-141-3p | hsa-miR-206 |
| hsa-miR-184 | hsa-miR-323a-3p |
| hsa-miR-190a-5p | hsa-miR-335-3p |
| hsa-miR-192-5p | hsa-miR-335-5p |
| hsa-miR-194-5p | hsa-miR-483-3p |
| hsa-miR-200a-3p | hsa-miR-483-5p |
| hsa-miR-200a-5p | hsa-miR-873-5p |
| hsa-miR-200b-3p | hsa-miR-1269a |
| hsa-miR-200c-3p | |
| hsa-miR-204-5p | |
| hsa-miR-215-5p | |
| hsa-miR-378a-3p | |
| hsa-miR-378c | |
| hsa-miR-378d | |
| hsa-miR-378f | |
| hsa-miR-422a | |
| hsa-miR-429 | |
| hsa-miR-455-5p | |
| hsa-miR-509-3-5p | |
| hsa-miR-514a-3p | |
| hsa-miR-12135 |
| Name | Hits | p Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prostate cancer | 7 | 0.00000394 | 0.000394 |
| Focal adhesion | 9 | 0.0000174 | 0.00087 |
| Pathways in cancer | 10 | 0.0000981 | 0.00327 |
| Bladder cancer | 3 | 0.00144 | 0.0269 |
| Glioma | 4 | 0.00159 | 0.0269 |
| p53 signaling pathway | 4 | 0.00188 | 0.0269 |
| Melanoma | 4 | 0.00188 | 0.0269 |
| Chronic myeloid leukemia | 4 | 0.00244 | 0.0305 |
| Small cell lung cancer | 4 | 0.00341 | 0.0379 |
| Apoptosis | 4 | 0.00389 | 0.0389 |
| Name | Hits (mRNA/Genes) | p Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | 54/66 | 1.96 × 10−16 | 6.2 × 10−14 |
| Alcoholism | 59/90 | 1.38 × 10−10 | 2.19 × 10−8 |
| Neuroactive ligand–receptor interaction | 45/71 | 1.1 × 10−7 | 1.17 × 10−5 |
| Drug metabolism–cytochrome P450 | 18/22 | 3.31 × 10−6 | 2.62 × 10−4 |
| Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 13/14 | 5.18 × 10−6 | 3.28 × 10−4 |
| Metabolic pathways | 236/593 | 4.97 × 10−5 | 0.00245 |
| PPAR signaling pathway | 27/43 | 5.42 × 10−5 | 0.00245 |
| Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 | 15/21 | 3.47 × 10−4 | 0.0138 |
| Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 10/12 | 4.91 × 10−4 | 0.0173 |
| Protein digestion and absorption | 23/39 | 7.23 × 10−4 | 0.0229 |
| Arginine and proline metabolism | 18/29 | 0.00121 | 0.0348 |
| Glycine, serine and threonine metabolism | 17/27 | 0.00132 | 0.0348 |
| Mineral absorption | 19/32 | 0.00188 | 0.0459 |
| Drug metabolism–other enzymes | 18/30 | 0.0021 | 0.0476 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avčin, S.L.; Črepinšek, K.; Jenko Bizjan, B.; Šket, R.; Kovač, J.; Vrhovšek, B.; Blazina, J.; Blatnik, O.; Kordič, R.; Kitanovski, L.; et al. Integrative Transcriptomic Profiling of the Wilms Tumor. Cancers 2023, 15, 3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153846
Avčin SL, Črepinšek K, Jenko Bizjan B, Šket R, Kovač J, Vrhovšek B, Blazina J, Blatnik O, Kordič R, Kitanovski L, et al. Integrative Transcriptomic Profiling of the Wilms Tumor. Cancers. 2023; 15(15):3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153846
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvčin, Simona Lucija, Klementina Črepinšek, Barbara Jenko Bizjan, Robert Šket, Jernej Kovač, Blaž Vrhovšek, Jerca Blazina, Olga Blatnik, Robert Kordič, Lidija Kitanovski, and et al. 2023. "Integrative Transcriptomic Profiling of the Wilms Tumor" Cancers 15, no. 15: 3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153846
APA StyleAvčin, S. L., Črepinšek, K., Jenko Bizjan, B., Šket, R., Kovač, J., Vrhovšek, B., Blazina, J., Blatnik, O., Kordič, R., Kitanovski, L., Jazbec, J., Debeljak, M., & Tesovnik, T. (2023). Integrative Transcriptomic Profiling of the Wilms Tumor. Cancers, 15(15), 3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15153846





