Predictive Risk Score for Acute Kidney Injury in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Population, and Data Collection
2.2. Definitions
2.3. Statistical Methods
3. Results
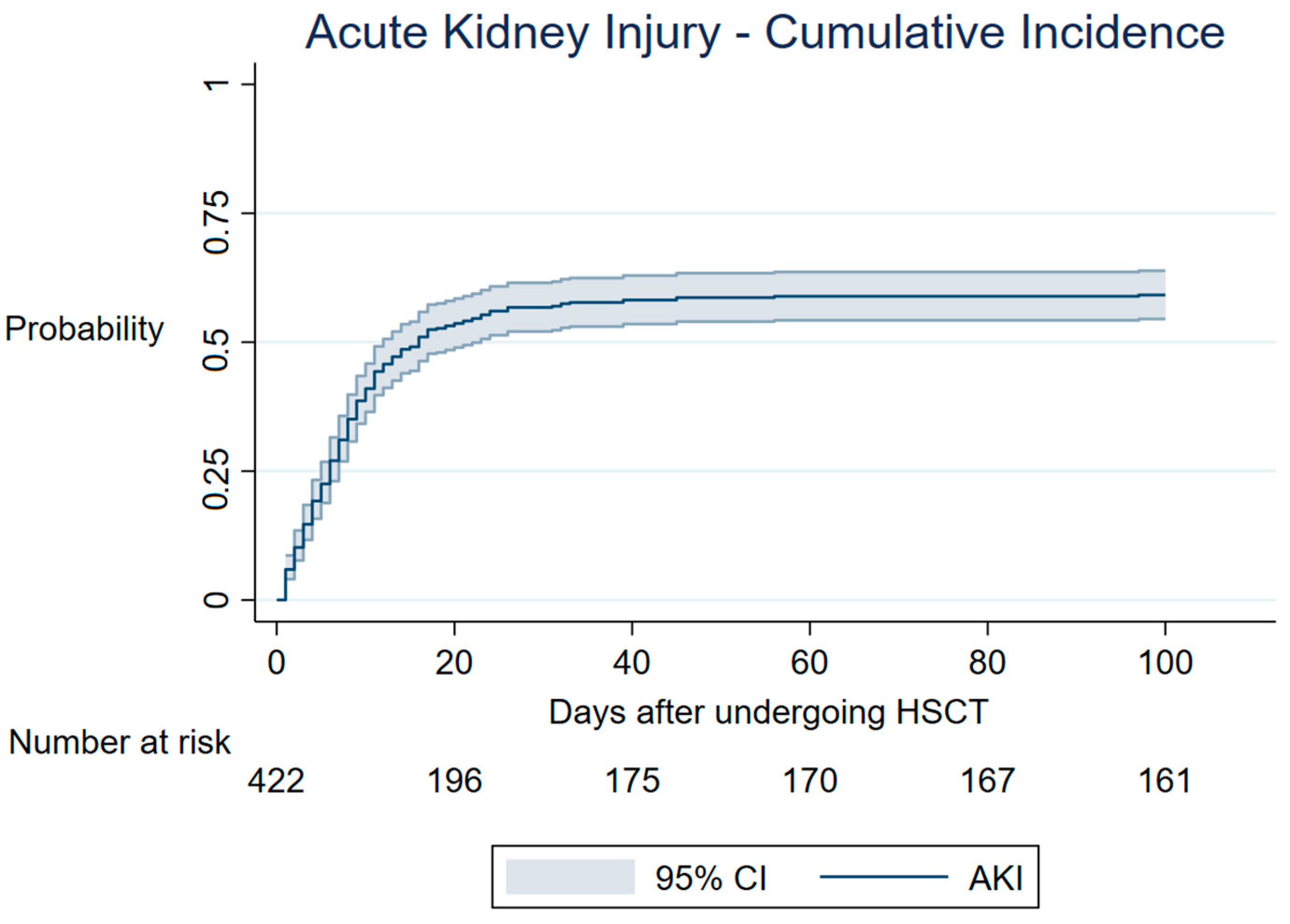
3.1. AKI—Cumulative Incidence
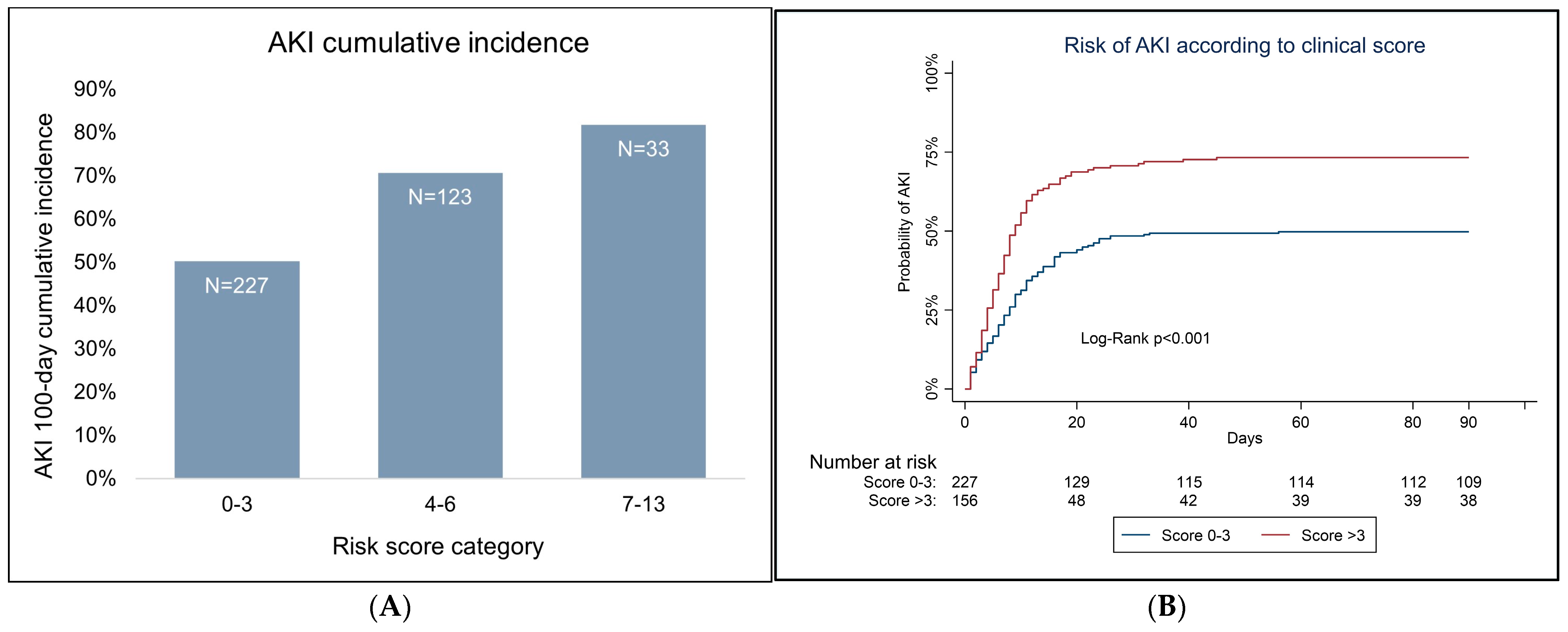
3.2. Variable Analysis and Predictive Score for AKI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Burden of Disease 2019 Cancer Collaboration. Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived with Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life Years for 29 Cancer Groups From 2010 to 2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 420–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chan, S.C.; Lok, V.; Zhang, L.; Lucero-Prisno, D.E.; Xu, W.; Zheng, Z.-J.; Elcarte, E.; Withers, M.; Wong, M.C.S. The epidemiological landscape of multiple myeloma: A global cancer registry estimate of disease burden, risk factors, and temporal trends. Lancet Haematol. 2022, 9, e670–e677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Yue, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhang, Y. Immunosenescence: A key player in cancer development. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- HAEMACARE Working Group. Incidence of hematologic malignancies in Europe by morphologic subtype: Results of the HAEMACARE project. Blood 2010, 116, 3724–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNerney, M.E.; Godley, L.A.; Le Beau, M.M. Therapy-related myeloid neoplasms: When genetics and environment collide. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 513–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowden, J.A.; Sánchez-Ortega, I.; Corbacioglu, S.; Basak, G.W.; Chabannon, C.; de la Camara, R.; Dolstra, H.; Duarte, R.F.; Glass, B.; Greco, R.; et al. Indications for haematopoietic cell transplantation for haematological diseases, solid tumours and immune disorders: Current practice in Europe, 2022. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2022, 57, 1217–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkumar, S.V. Multiple myeloma: 2022 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 1086–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, T.; Guglielmi, C.; Hagenbeek, A.; Somers, R.; Lelie, H.; Bron, D. Autologous Bone Marrow Transplantation as Compared with Salvage Chemotherapy in Relapses of Chemotherapy-Sensitive Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 1540–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, S.; Fanale, M.; DeVos, S.; Engert, A.; Illidge, T.; Borchmann, P.; Younes, A.; Morschhauser, F.; McMillan, A.; Horning, S.J. Defining a Hodgkin lymphoma population for novel therapeutics after relapse from autologous hematopoietic cell transplant. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 2531–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederwieser, D.; Baldomero, H.; Atsuta, Y.; Aljurf, M.; Seber, A.; Greinix, H.T.; Koh, M.; Worel, N.; Galeano, S.; Jaimovich, G.; et al. One and Half Million Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplants (HSCT). Dissemination, Trends and Potential to Improve Activity by Telemedicine from the Worldwide Network for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (WBMT). Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanduri, S.R.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Thongprayoon, C.; Kovvuro, K.; Garla, V.; Medaura, J.; Vaitla, P.; Kashani, K.B. Incidence and mortality of acute kidney injury in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. QJM 2020, 113, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-García, G.; Villarreal, J.; Garrote, M.; Rovira, M.; Blasco, M.; Suárez-Lledó, M.; Rodríguez-Lobato, L.G.; Charry, P.; Rosiñol, L.; Marín, P.; et al. Impact of severe acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease on allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant recipients: A retrospective single center analysis. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2020, 55, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, N.; Costa, C.; Branco, C.; Marques, F.; Vasconcelos, P.; Martins, C.; Papoila, A.L.; Pinto, I.; Neves, M.; Lopes, J.A. Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Leukaemia Submitted to Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant—KDIGO Classification with Creatinine and Urinary Output Criteria: Cohort Analysis. Clin. Onco. 2023, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, N.; Branco, C.; Costa, C.; Marques, F.; Neves, M.; Vasconcelos, P.; Martins, C.; Lopes, J.A. Acute kidney injury in autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant for patients with lymphoma—KDIGO classification with creatinine and urinary output criteria: A cohort analysis. Ren. Fail. 2023, 45, 2183044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanchoo, R.; Stotter, B.R.; Bayer, R.L.; Jhaveri, K.D. Acute kidney injury in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2019, 25, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andronesi, A.; Sorohan, B.; Burcea, A.; Lipan, L.; Stanescu, C.; Cracium, O.; Stefan, L.; Ranete, A.; Varady, Z.; Ungureanu, O.; et al. Incidence and Risk Factors for Acute Kidney Injury after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Prospective Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Eckardt, K.U.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Levin, A.; Coresh, J.; Rossert, J.; Zeeuw, D.D.; Hostetter, T.H.; Lameire, N.; Eknoyan, G. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: A position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorror, M.L.; Maris, M.B.; Storb, R.; Baron, F.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Maloney, D.G.; Storer, B. Hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT)-specific comorbidity index: A new tool for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT. Blood 2005, 106, 2912–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Stevens, L.A.; Schmid, C.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Castro, A.F., 3rd; Feldman, H.I.; Kusek, J.W.; Eggers, P.; Van Lente, F.; Greene, T.; et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 150, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobelli, S.; Committee, E.S. Suggestions on the use of statistical methodologies in studies of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, S1–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, J.P.; Gray, R.J. A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1999, 94, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clajus, C.; Hanke, N.; Gottlieb, J.; Stadler, M.; Weismüller, T.J.; Strassburg, C.P.; Bröcker, V.; Bara, C.; Lehner, F.; Drube, J.; et al. Renal Comorbidity After Solid Organ and Stem Cell Transplantation: Renal Comorbidity After Transplantation. Am. J. Transpl. 2012, 12, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellomo, R.; Ronco, C.; Kellum, J.A.; Mehta, R.L.; Palevsky, P. Acute renal failure—Definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: The Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit. Care 2004, 8, R204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, R.L.; Kellum, J.A.; Shah, S.V.; Molitoris, B.A.; Ronco, C.; Warnock, D.G.; Levin, A. Acute Kidney Injury Network: Report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit. Care 2007, 11, R31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishani, A.; Xue, J.L.; Himmelfarb, J.; Eggers, P.W.; Kimmel, P.L.; Molitoris, B.A.; Collins, A.J. Acute kidney injury increases risk of ESRD among elderly. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.L.; Daniels, F.; Star, R.A.; Kimmel, P.L.; Eggers, P.W.; Molitoris, B.A.; Himmelfarb, J.; Collins, A.J. Incidence and mortality of acute renal failure in Medicare beneficiaries, 1992 to 2001. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, M.T.; Grams, M.E.; Woodward, M.; Elley, C.R.; Green, J.A.; Wheeler, D.C.; James, M.T.; Grams, M.E.; Woodward, M.; Elley, C.R.; et al. A Meta-analysis of the Association of Estimated GFR, Albuminuria, Diabetes Mellitus, and Hypertension with Acute Kidney Injury. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 602–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferenbach, D.A.; Bonventre, J.V. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease: From the laboratory to the clinic. Nephrol. Ther. 2016, 12 (Suppl. 1), S41–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.J.; Ace, O.; McNamara, M.G.; Al-Mubarak, M.; Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Hermanns, T.; Seruga, B.; Ocaña, A.; Tannock, I.F.; Amir, E. Prognostic role of platelet to lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2014, 23, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.L.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Yin, T.-T.; Meng, Q.-H.; Wei, H.-Q.; Zhou, Q.-H. The prognostic role of platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with acute heart failure: A cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, W. Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic predictor of mortality for sepsis: Interaction effect with disease severity—A retrospective study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e022896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparyan, A.Y.; Ayvazyan, L.; Mukanova, U.; Yessirkepov, M.; Kitas, G.D. The Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as an Inflammatory Marker in Rheumatic Diseases. Ann. Lab. Med. 2019, 39, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, F.; Li, M.; Yuan, J.J.; Chang, X.N.; Wei, B.H.; Du, H.; Dong, C.-M. Relationship between platelet/lymphocyte ratio and prognosis of patients with septic acute kidney injury: A pilot study. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2020, 83, 1004–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Patients Characteristics | Category | n (%) | P50 | P25 | P75 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age at transplant (years) | 50.2 | 36.0 | 59.5 | ||
| Gender | Male | 236 (55.9) | |||
| Female | 186 (44.1) | ||||
| Race | Caucasian | 385 (91.4) | |||
| Non-Caucasian | 37 (8.6) | ||||
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 24.6 | 21.9 | 27.8 | ||
| HCT-CI | 0–1 | 353 (84.3) | |||
| ≥2 | 66 (15.8) | ||||
| Hypertension | 88 (20.9) | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 26 (6.2) | ||||
| Congestive heart failure | 23 (5.5) | ||||
| Chronic kidney disease | 27 (6.4) | ||||
| Hematologic diagnosis | Leukaemia | 164 (38.8) | |||
| Lymphoma | 115 (27.3) | ||||
| Multiple myeloma | 143 (33.9) | ||||
| Type of HSCT | Autologous | 258 (61.1) | |||
| Allogeneic | 164 (38.9) | ||||
| Type of donor | Self | 258 (61.1) | |||
| Related | 92 (21.8) | ||||
| Not related | 72 (17.1) | ||||
| Previous radiotherapy | yes | 82 (19.5) | |||
| basal eGFR (ml/min/1.73 m2) | 107.3 | 94.3 | 122.1 | ||
| Conditioning regimen | Myeloablative | 305 (72.2) | |||
| Non-myeloablative | 117 (27.8) | ||||
| Graft source | Peripheral blood | 389 (92.2) | |||
| Bone marrow | 33 (7.8) | ||||
| GVHD prophylaxis | CsA + MMF | 117 (27.7) | |||
| CsA + MTX | 47 (11.1) | ||||
| None | 258 (61.1) | ||||
| At hospital admission day: | |||||
| Hemoglobin (gr/dL) | 11.6 | 10.2 | 12.6 | ||
| Leukocytes (cells/mm3) | 4920 | 3500 | 6860 | ||
| Neutrophils (cells/mm3) | 2960 | 1850 | 4420 | ||
| Platelets (/μL) | 179,000 | 127,000 | 245,000 | ||
| Urea (mg/dL) | 33 | 27 | 41 | ||
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 5 | 4 | 6 | ||
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 9 | 8.8 | 10 | ||
| Phosphate (mg/dL) | 4 | 3.2 | 4.1 | ||
| Reactive C protein (mg/dL) | 0.49 | 0.15 | 2 | ||
| Lactate dehydrogenase (U/L) | 339 | 291 | 426 | ||
| Albumin (mg/dL) | 4 | 3.7 | 4.5 | ||
| Alanine transaminase (U/L) | 22 | 15 | 37 | ||
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.48 | 0.36 | 0.61 | ||
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio | 159.9 | 94.1 | 265.4 |
| Patient’s Characteristics | HR Estimate | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
| Age at transplant (years) | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.01 | 0.830 |
| Gender (female versus male) | 1.05 | 0.83 | 1.35 | 0.654 |
| Race (Caucasian versus non-Caucasian) | 0.90 | 0.58 | 1.40 | 0.634 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 1.02 | 1.00 | 1.05 | 0.105 |
| HCT-CI (score < 2 versus score ≥ 2) | 1.69 | 1.27 | 2.25 | <0.001 |
| Hypertension | 1.15 | 0.86 | 1.54 | 0.335 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.29 | 0.82 | 2.02 | 0.269 |
| Congestive heart failure | 1.41 | 0.91 | 2.20 | 0.128 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 2.11 | 1.36 | 3.27 | 0.001 |
| Hematologic diagnosis: | ||||
| Multiple myeloma versus lymphoma | 1.51 | 1.10 | 2.08 | 0.011 |
| Multiple myeloma versus leukemia | 1.44 | 1.07 | 1.92 | 0.015 |
| Leukemia versus lymphoma | 1.05 | 0.78 | 1.41 | 0.728 |
| Multiple myeloma versus (lymphoma + leukemia) | 1.46 | 1.12 | 1.90 | 0.005 |
| Type of HSCT (allogeneic versus autologous) | 0.84 | 0.66 | 1.08 | 0.169 |
| Type of donor (related versus unrelated) | 1.14 | 0.86 | 1.52 | 0.368 |
| Previous radiotherapy | 1.09 | 0.81 | 1.47 | 0.573 |
| Conditioning regimen (non-myeloablative versus myeloablative) | 1.27 | 0.84 | 1.95 | 0.260 |
| basal eGFR (ml/min/1.73 m2) | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.012 |
| Graft source (peripheral blood versus bone marrow) | 1.36 | 0.88 | 2.12 | 0.170 |
| GVHD prophylaxis (methotrexate versus others) | 1.03 | 0.73 | 1.46 | 0.849 |
| At hospital admission day: | ||||
| Hemoglobin (gr/dL) | 1.01 | 0.94 | 1.09 | 0.752 |
| Leukocytes * (cells/mm3) | 1.07 | 1.04 | 1.09 | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils * (cells/mm3) | 1.06 | 0.88 | 1.26 | 0.547 |
| Lymphocytes * (cells/mm3) | 1.23 | 1.13 | 1.34 | <0.001 |
| Platelets * (/μL) | 1.01 | 0.99 | 1.02 | 0.841 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 1.01 | 1.00 | 1.02 | 0.019 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | 1.01 | 0.97 | 1.04 | 0.662 |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 1.06 | 0.85 | 1.31 | 0.598 |
| Phosphate (mg/dL) | 0.92 | 0.77 | 1.10 | 0.367 |
| Reactive C protein ** (mg/dL) | 1.02 | 1.01 | 1.03 | <0.001 |
| Lactate dehydrogenase ** (U/L) | 1.05 | 1.03 | 1.07 | <0.001 |
| Albumin (mg/dL) | 1.00 | 0.96 | 1.04 | 0.847 |
| Alanine transaminase (U/L) | 1.00 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.081 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.91 | 0.62 | 1.32 | 0.611 |
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | <0.001 |
| Patient’s Characteristics | HR Estimate | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | |||
| BMI (>24.5 Kg/m2) | 1.20 | 0.94 | 1.53 | 0.147 |
| HCT-CI (socre < 2 versus score ≥ 2) | 1.69 | 1.27 | 2.25 | <0.001 |
| Congestive heart failure | 1.41 | 0.91 | 2.2 | 0.128 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 2.11 | 1.36 | 3.27 | 0.001 |
| Hematologic diagnosis (multiple myeloma versus (lymphoma + leukemia) | 1.46 | 1.12 | 1.91 | 0.005 |
| Type of HSCT (allogeneic versus autologous) | 0.84 | 0.66 | 1.08 | 0.169 |
| basal eGFR (>107.2 mL/min/1.73 m2) | 0.89 | 0.7 | 1.13 | 0.342 |
| Graft source (peripheral blood versus bone marrow) | 1.36 | 0.88 | 2.12 | 0.170 |
| Leukocytes (>5330 cells/mm3) | 1.05 | 0.82 | 1.34 | 0.696 |
| Lymphocytes (>1100 cells/mm3) | 0.89 | 0.7 | 1.13 | 0.334 |
| Urea (>30 mg/dL) | 1.15 | 0.9 | 1.48 | 0.263 |
| Reactive C protein (>0.47 mg/dL) | 1.20 | 0.92 | 1.55 | 0.176 |
| Lactate dehydrogenase (>339 U/L) | 1.26 | 0.98 | 1.61 | 0.066 |
| Alanine transaminase (>22 U/L) | 1.02 | 0.8 | 1.31 | 0.853 |
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (>171.9) | 1.26 | 0.97 | 1.62 | 0.078 |
| Patient’s Characteristics | HR Estimate | 95% CI | p-Value | Score Points | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||||
| HCT-CI (reference category < 2) | 1.47 | 1.08 | 2.00 | 0.013 | 3 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 2.10 | 1.31 | 3.36 | 0.002 | 4 |
| Hematologic diagnosis (reference category multiple myeloma) | 1.69 | 1.26 | 2.25 | <0.001 | 3 |
| Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (reference category < 171.9) | 1.43 | 1.1 | 1.86 | 0.008 | 3 |
| Multivariable model C-Statistic = 0.71 | |||||
| Score C-Statistic = 0.70 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, N.; Fragão-Marques, M.; Costa, C.; Branco, C.; Marques, F.; Vasconcelos, P.; Martins, C.; Leite-Moreira, A.; Lopes, J.A. Predictive Risk Score for Acute Kidney Injury in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Cancers 2023, 15, 3720. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143720
Rodrigues N, Fragão-Marques M, Costa C, Branco C, Marques F, Vasconcelos P, Martins C, Leite-Moreira A, Lopes JA. Predictive Risk Score for Acute Kidney Injury in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Cancers. 2023; 15(14):3720. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143720
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Natacha, Mariana Fragão-Marques, Cláudia Costa, Carolina Branco, Filipe Marques, Pedro Vasconcelos, Carlos Martins, Adelino Leite-Moreira, and José António Lopes. 2023. "Predictive Risk Score for Acute Kidney Injury in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant" Cancers 15, no. 14: 3720. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143720
APA StyleRodrigues, N., Fragão-Marques, M., Costa, C., Branco, C., Marques, F., Vasconcelos, P., Martins, C., Leite-Moreira, A., & Lopes, J. A. (2023). Predictive Risk Score for Acute Kidney Injury in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. Cancers, 15(14), 3720. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15143720







