An Emerging Role for Sigma Receptor 1 in Personalized Treatment of Breast Cancer
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
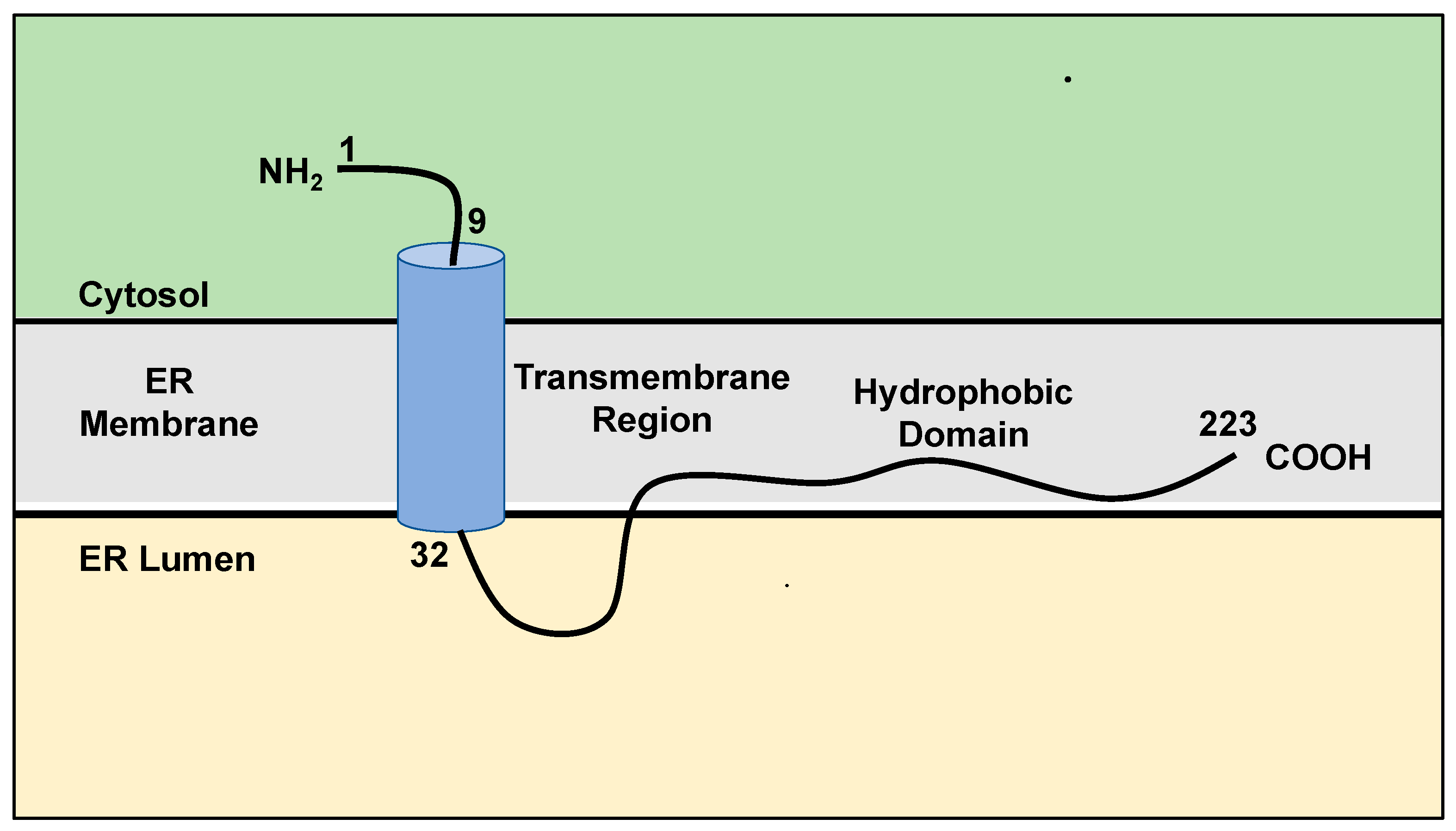
2. Structure, Localization, and Function of SigmaR1
3. The Role of SigmaR1 in Breast Cancer
4. Towards Targeting SigmaR1 in Breast Cancer
5. Perspective: SigmaR1 as an Adaptor Protein in Key Cellular Functions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Łukasiewicz, S.; Czeczelewski, M.; Forma, A.; Baj, J.; Sitarz, R.; Stanisławek, A. Breast Cancer-Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification, Prognostic Markers, and Current Treatment Strategies-An Updated Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbeck, N.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Cortes, J.; Gnant, M.; Houssami, N.; Poortmans, P.; Ruddy, K.; Tsang, J.; Cardoso, F. Breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2021, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aysola, K.; Desai, A.; Welch, C.; Xu, J.; Qin, Y.; Reddy, V.; Matthews, R.; Owens, C.; Okoli, J.; Beech, D.J.; et al. Triple Negative Breast Cancer—An Overview. Hereditary Genet. 2013, 2013 (Suppl. 2), 001. [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi, T.; Su, T.P. Sigma-1 receptor chaperones at the ER-mitochondrion interface regulate Ca (2+) signaling and cell survival. Cell 2007, 131, 596–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.P.; Hayashi, T.; Maurice, T.; Buch, S.; Ruoho, A. The sigma-1 receptor chaperone as an inter-organelle signaling modulator. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, L.; Niu, F.; Liao, K.; Buch, S. Role of sigma-1 receptor in cocaine abuse and neurodegenerative disease. Sigma Recept. Role Dis. Ther. Targets 2017, 964, 163–175. [Google Scholar]
- Couly, S.; Goguadze, N.; Yasui, Y.; Kimura, Y.; Wang, S.M.; Sharikadze, N.; Wu, H.E.; Su, T.P. Knocking Out Sigma-1 Receptors Reveals Diverse Health Problems. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 42, 597–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, W.; Eades, C.G.; Thompson, J.; Huppler, R.E.; Gilbert, P.E. The effects of morphine-and nalorphine-like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1976, 197, 517–532. [Google Scholar]
- Hellewell, S.B.; Bruce, A.; Feinstein, G.; Orringer, J.; Williams, W.; Bowen, W.D. Rat liver and kidney contain high densities of σ1 and σ2 receptors: Characterization by ligand binding and photoaffinity labeling. Eur. J. Pharmacol. Mol. Pharmacol. 1994, 268, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, W.D.; Hellewell, S.B.; McGarry, K.A. Evidence for a multi-site model of the rat brain σ receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1989, 163, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, E.C.; McCracken, K.A.; Liu, Y.; Pouw, B.; Matsumoto, R.R. Involvement of sigma (σ) receptors in the acute actions of methamphetamine: Receptor binding and behavioral studies. Neuropharmacology 2005, 49, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharkey, J.; Glen, K.A.; Wolfe, S.; Kuhar, M.J. Cocaine binding at σ receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 149, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monnet, F.P.; Debonnel, G.; Junien, J.L.; De Montigny, C. N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced neuronal activation is selectively modulated by σ receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 179, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, J.; Pasternak, G.W. ς1 Receptor Modulation of Opioid Analgesia in the Mouse. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 300, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergeron, R.; Debonnel, G.; De Montigny, C. Modification of the N-methyl-D-aspartate response by antidepressant σ receptor ligands. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 240, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villard, V.; Espallergues, J.; Keller, E.; Alkam, T.; Nitta, A.; Yamada, K.; Nabeshima, T.; Vamvakides, A.; Maurice, T. Antiamnesic and neuroprotective effects of the amino tetrahydrofuran derivative ANAVEX1-41 against amyloid β25–35-induced toxicity in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 1552–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmo, C.T., Jr.; Vernon, D.O.; Collier, L.; Pennypacker, K.R.; Cuevas, J. Sigma receptor activation reduces infarct size at 24 hours after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Curr. Neurovascular Res. 2006, 3, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, M.D.; Whittaker, K.M.; Choi, R.; Tashkin, D.P.; Baldwin, G.C. Cocaine and σ-1 receptors modulate HIV infection, chemokine receptors, and the HPA axis in the huPBL-SCID model. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 78, 1198–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Shu, X.; Hovsepyan, H.; Mosteller, R.D.; Broek, D. VEGF receptor expression and signaling in human bladder tumors. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3361–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydar, E.; Palmer, C.P.; Klyachko, V.A.; Jackson, M.B. The sigma receptor as a ligand-regulated auxiliary potassium channel subunit. Neuron 2002, 34, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.R.; Zheng, S.; Gurpinar, E.; Koehl, A.; Manglik, A.; Kruse, A.C. Crystal structure of the human σ1 receptor. Nature 2016, 532, 527–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Patel, C.; Shenkman, M.; Kessel, A.; Ben-Tal, N.; Lederkremer, G.Z. The Sigma-1 receptor is an ER-localized type II membrane protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 101299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabba, M. The essential roles of protein–protein interaction in sigma-1 receptor functions. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobos, E.J.; Entrena, J.M.; Nieto, F.R.; Cendán, C.M.; Pozo, E.D. Pharmacology and therapeutic potential of sigma1 receptor ligands. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2008, 6, 344–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, T.; Hayashi, T.; Hayashi, E.; Su, T.-P. Sigma-1 Receptor Chaperone at the ER-Mitochondrion Interface Mediates the Mitochondrion-ER-Nucleus Signaling for Cellular Survival. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, C.P.; Mahen, R.; Schnell, E.; Djamgoz, M.B.; Aydar, E. Sigma-1 receptors bind cholesterol and remodel lipid rafts in breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11166–11175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, T.; Lei, P.; Zhou, H.; Liang, R.; Zhu, R.; Wang, W.; Zhou, L.; Sun, Y. Sigma-1 receptor protects against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 7349–7359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreser, A.; Vollrath, J.T.; Sechi, A.; Johann, S.; Roos, A.; Yamoah, A.; Katona, I.; Bohlega, S.; Wiemuth, D.; Tian, Y.; et al. The ALS-linked E102Q mutation in Sigma receptor-1 leads to ER stress-mediated defects in protein homeostasis and dysregulation of RNA-binding proteins. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1655–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.; Shajahan, A.N.; Wang, Y.; Tyson, J.J.; Riggins, R.B.; Weiner, L.M.; Bauman, W.T.; Xuan, J.; Zhang, B.; Facey, C.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress, the unfolded protein response, and gene network modeling in antiestrogen resistant breast cancer. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2011, 5, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, R.; Cook, K.L.; Hu, R.; Facey, C.O.; Tavassoly, I.; Schwartz, J.L.; Baumann, W.T.; Tyson, J.J.; Xuan, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress, the unfolded protein response, autophagy, and the integrated regulation of breast cancer cell fate. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.X.; Sharma, S.; Gardner, B.; Escuadro, B.; Atianzar, K.; Tashkin, D.P.; Dubinett, S.M. IL-10 mediates sigma1 receptor-dependent suppression of antitumor immunity. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3585–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebreselassie, D.; Bowen, W.D. Sigma-2 receptors are specifically localized to lipid rafts in rat liver membranes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 493, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Rouzier, R.; Albarracin, C.T.; Şahin, A.; Wagner, P.; Yang, Y.; Smith, T.L.; Bernstam, F.M.; Marcelo, A.C.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; et al. Expression of sigma 1 receptor in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2004, 87, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, B.; Zhu, L.X.; Roth, M.D.; Tashkin, D.P.; Dubinett, S.M.; Sharma, S. Cocaine modulates cytokine and enhances tumor growth through sigma receptors. J. Neuroimmunol. 2004, 147, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mégalizzi, V.; Mathieu, V.; Mijatovic, T.; Gailly, P.; Debeir, O.; De Neve, N.; Van Damme, M.; Bontempi, G.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Decaestecker, C.; et al. 4-IBP, a σ1 receptor agonist, decreases the migration of human cancer cells, including glioblastoma cells, in vitro and sensitizes them in vitro and in vivo to cytotoxic insults of proapoptotic and proautophagic drugs. Neoplasia 2007, 9, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mégalizzi, V.; Decaestecker, C.; Debeir, O.; Spiegl-Kreinecker, S.; Berger, W.; Lefranc, F.; Kast, R.E.; Kiss, R. Screening of anti-glioma effects induced by sigma-1 receptor ligands: Potential new use for old anti-psychiatric medicines. Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 2893–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.T.; Robson, M.J.; Szeszel-Fedorowicz, W.; Patel, D.; Rooney, R.; McCurdy, C.R.; Matsumoto, R.R. CM156, a sigma receptor ligand, reverses cocaine-induced place conditioning and transcriptional responses in the brain. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 101, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riganas, S.; Papanastasiou, I.; Foscolos, G.B.; Tsotinis, A.; Dimas, K.; Kourafalos, V.N.; Andreas, E.; Vassilios, I.M.; Humaira, K.; Prassa, M.; et al. New adamantane derivatives with sigma affinity and antiproliferative activity. Med. Chem. 2012, 8, 569–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simony-Lafontaine, J.; Esslimani, M.; Bribes, E.; Gourgou, S.; Lequeux, N.; Lavail, R.; Grenier, J.; Kramar, A.; Casellas, P. Immunocytochemical assessment of sigma-1 receptor and human sterol isomerase in breast cancer and their relationship with a series of prognostic factors. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 1958–1966. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borde, P.; Cosgrove, N.; Charmsaz, S.; Safrany, S.T.; Young, L. An investigation of Sigma-1 receptor expression and ligand-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in breast cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2023, 30, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueguinou, M.; Crottès, D.; Chantôme, A.; Rapetti-Mauss, R.; Potier-Cartereau, M.; Clarysse, L.; Girault, A.; Fourbon, Y.; Jézéquel, P.; Guérin-Charbonnel, C.; et al. The SigmaR1 chaperone drives breast and colorectal cancer cell migration by tuning SK3-dependent Ca(2+) homeostasis. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3640–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colabufo, N.A.; Berardi, F.; Contino, M.; Niso, M.; Abate, C.; Perrone, R.; Tortorella, V. Antiproliferative and cytotoxic effects of some σ 2 agonists and σ 1 antagonists in tumour cell lines. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2004, 370, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spruce, B.A.; Campbell, L.A.; McTavish, N.; Cooper, M.A.; Appleyard, M.V.L.; O’Neill, M.; Howie, J.; Samson, J.; Watt, S.; Murray, K.; et al. Small molecule antagonists of the σ-1 receptor cause selective release of the death program in tumor and self-reliant cells and inhibit tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 4875–4886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Tsai, S.Y.; Mori, T.; Fujimoto, M.; Su, T.P. Targeting ligand-operated chaperone sigma-1 receptors in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2011, 15, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Atta, M.S.M.; Mahmoud, S.; Oh-hashi, K.; Kiuchi, K. Chloroquine inhibits glutamate-induced death of a neuronal cell line by reducing reactive oxygen species through sigma-1 receptor. J. Neurochem. 2011, 119, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, R.R.; Bowen, W.D.; Tom, M.A.; Vo, V.N.; Truong, D.D.; De Costa, B.R. Characterization of two novel sigma receptor ligands: Antidystonic effects in rats suggest sigma receptor antagonism. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 280, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.; Romieu, P.; Maurice, T.; Su, T.P.; Maloteaux, J.M.; Hermans, E. Involvement of the sigma 1 receptor in the modulation of dopaminergic transmission by mamantadine. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 2212–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Muñoz, M.; Onetti, Y.; Cortés-Montero, E.; Garzón, J.; Sánchez-Blázquez, P. Cannabidiol enhances morphine antinociception, diminishes NMDA-mediated seizures and reduces stroke damage via the sigma 1 receptor. Mol. Brain 2018, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gris, G.; Portillo-Salido, E.; Aubel, B.; Darbaky, Y.; Deseure, K.; Vela, J.M.; Merlos, M.; Zamanillo, D. The selective sigma-1 receptor antagonist E-52862 attenuates neuropathic pain of different aetiology in rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.S.; Fukunaga, K. Stimulation of sigma-1 receptor signaling by dehydroepiandrosterone ameliorates pressure overload-induced hypertrophy and dysfunctions in ovariectomized rats. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2009, 13, 1253–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Fujita, Y.; Iyo, M. Phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficits in mice are improved by subsequent subchronic administration of fluvoxamine: Role of sigma-1 receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, A.; Kulkarni, S.K. Involvement of dopamine (DA)/serotonin (5-HT)/sigma (σ) receptor modulation in mediating the antidepressant action of ropinirole hydrochloride, a D2/D3 dopamine receptor agonist. Brain Res. Bull. 2007, 74, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, Y.; Terada, K.; Kamei, C.; Sugimoto, Y. Sertraline inhibits nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells via a mechanism involving the sigma-1 receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 853, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, B.H.; Park, Y.; Daudt, D.R.; Ma, H.-Y.; Akopova, I.; Stankowska, D.L.; Clark, A.F.; Yorio, T. Sigma-1 receptor stimulation attenuates calcium influx through activated L-type Voltage Gated Calcium Channels in purified retinal ganglion cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 107, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, Y.; Su, T.P. Potential Molecular Mechanisms on the Role of the Sigma-1 Receptor in the Action of Cocaine and Methamphetamine. J. Drug Alcohol Res. 2016, 5, 235970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brailoiu, E.; Chakraborty, S.; Brailoiu, G.C.; Zhao, P.; Barr, J.L.; Ilies, M.A.; Unterwald, E.M.; Abood, M.E.; Taylor, C. Choline is an intracellular messenger linking extracellular stimuli to IP3-evoked Ca2+ signals through sigma-1 receptors. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, J.; Ieni, J.; Maurice, T. The anti-amnesic and neuroprotective effects of donepezil against amyloid β25–35 peptide-induced toxicity in mice involve an interaction with the σ1 receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 149, 998–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurice, T.; Meunier, J.; Feng, B.; Ieni, J.; Monaghan, D.T. Interaction with sigma(1) protein, but not N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor, is involved in the pharmacological activity of donepezil. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 317, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.; Robson, M.J.; Healy, J.R.; Scandinaro, A.L.; Matsumoto, R.R. Involvement of sigma-1 receptors in the antidepressant-like effects of dextromethorphan. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontanilla, D.; Johannessen, M.; Hajipour, A.R.; Cozzi, N.V.; Jackson, M.B.; Ruoho, A.E. The hallucinogen N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is an endogenous sigma-1 receptor regulator. Science 2009, 323, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.S.; Tagashira, H.; Shioda, N.; Fukunaga, K. Targeting sigma-1 receptor with fluvoxamine ameliorates pressure-overload-induced hypertrophy and dysfunctions. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishima, T.; Hashimoto, K. Potentiation of nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells by ifenprodil: The role of sigma-1 and IP3 receptors. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xiao, H.; Barwick, S.R.; Smith, S.B. Comparison of sigma 1 receptor ligands SA4503 and PRE084 to (+)-pentazocine in the rd10 mouse model of RP. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuno, K.; Nakazawa, M.; Okamoto, K.; Kawashima, Y.; Mita, S. Binding properties of SA4503, a novel and selective sigma 1 receptor agonist. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 306, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K. Sigma-1 receptor chaperone and brain-derived neurotrophic factor: Emerging links between cardiovascular disease and depression. Prog. Neurobiol. 2013, 100, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Marwaha, R. Haloperidol; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mavlyutov, T.A.; Baker, E.M.; Losenegger, T.M.; Kim, J.R.; Torres, B.; Epstein, M.L.; Ruoho, A.E. The Sigma-1 Receptor–A Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of ALS? Sigma Recept. Role Dis. Ther. Targets 2017, 964, 255–265. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.S.; Zhu, H.J.; Markowitz, J.S.; Donovan, J.L.; Yuan, H.J.; Devane, C.L. Antipsychotic drugs inhibit the function of breast cancer resistance protein. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 103, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asong, G.M.; Amissah, F.; Voshavar, C.; Nkembo, A.T.; Ntantie, E.; Lamango, N.S.; Ablordeppey, S.Y. A mechanistic investigation on the anticancer properties of sya013, a homopiperazine analogue of haloperidol with activity against triple negative breast cancer cells. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 32907–32918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asong, G.M.; Voshavar, C.; Amissah, F.; Bricker, B.; Lamango, N.S.; Ablordeppey, S.Y. An Evaluation of the Anticancer Properties of SYA014, a Homopiperazine-Oxime Analog of Haloperidol in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Clevenger, C.V.; Kaklamani, V.; Lauriello, J.; Campbell, A.; Malwitz, K.; Kirkland, R.S. Antipsychotic treatment in breast cancer patients. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, V.J.; Osman, M.A. The Antipsychotic Drug Haldol Modulates IQGAP1-Signaling and Inhibits Cell Proliferation in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cell Lines. microPub Biol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oflaz, F.E.; Koshenov, Z.; Hirtl, M.; Rost, R.; Malli, R.; Graier, W.F. Sigma-1 receptor modulation by ligands coordinates cancer cell energy metabolism. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.D.; Longen, C.G.; Oyer, H.M.; Chen, N.; Maher, C.M.; Salvino, J.M.; Kania, B.; Anderson, K.N.; Ostrander, W.F.; Knudsen, K.E.; et al. Sigma1 targeting to suppress aberrant androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2439–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.C.; Mata, D.A.; Tay, T.K.; Traina, T.A.; Gucalp, A.; Chandarlapaty, S.; D’Alfonso, T.M.; Brogi, E.; Mullaney, K.; Ladanyi, M.; et al. Androgen receptor splice variant-7 in breast cancer: Clinical and pathologic correlations. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, T.E.; Irvine, C.M.; Dvinge, H.; Tarulli, G.A.; Hanson, A.R.; Ryan, N.K.; Pickering, M.A.; Birrell, S.N.; Hu, D.G.; Mackenzie, P.I.; et al. Expression of androgen receptor splice variants in clinical breast cancers. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 44728–44744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.K.; Mavlyutov, T.; Singh, D.; Biener, G.; Yang, J.; Oliver, J.A.; Ruoho, A.; Raicu, V. The sigma-1 receptors are present in monomeric and oligomeric forms in living cells in the presence and absence of ligands. Biochem. J. 2015, 466, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, U.B.; Ruoho, A.E. Biochemical pharmacology of the sigma-1 receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2016, 89, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramyan, A.M.; Yano, H.; Xu, M.; Liu, L.; Naing, S.; Fant, A.D.; Shi, L. The Glu102 mutation disrupts higher-order oligomerization of the sigma 1 receptor. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Thornton, J.M. Principles of protein-protein interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougan, D.A.; Reid, B.G.; Horwich, A.L.; Bukau, B. ClpS, a substrate modulator of the ClpAP machine. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirstein, J.; Zühlke, D.; Gerth, U.; Turgay, K.; Hecker, M. A tyrosine kinase and its activator control the activity of the CtsR heat shock repressor in B. subtilis. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3435–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, E.; Witt, E.; Ohlmeier, S.; Hanschke, R.; Hecker, M. The clp proteases of Bacillus subtilis are directly involved in degradation of misfolded proteins. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 3259–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlothauer, T.; Mogk, A.; Dougan, D.A.; Bukau, B.; Turgay, K. MecA, an adaptor protein necessary for ClpC chaperone activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 2306–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirstein, J.; Schlothauer, T.; Dougan, D.A.; Lilie, H.; Tischendorf, G.; Mogk, A.; Bukau, B.; Turgay, K. Adaptor protein controlled oligomerization activates the AAA+ protein ClpC. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1481–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Chen, F.; Chen, Z.; Yang, W.; Yue, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Sigma-1 receptor: A potential therapeutic target for traumatic brain injury. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 685201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsvlishvili, N.; Goguadze, N.; Zhuravliova, E.; Mikeladze, D. Sigma-1 receptor directly interacts with Rac1-GTPase in the brain mitochondria. BMC Biochem. 2015, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, E.E.; Mulloy, J.C.; Zheng, Y. Rac1 GTPase: A “Rac” of all trades. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2009, 66, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, M.A.; Cerione, R.A. Actin doesn’t do the locomotion. Secretion drives cell polarization. In Protein Trafficking: Mechanisms and Regulation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 388–399. [Google Scholar]
- Rittmeyer, E.N.; Daniel, S.; Hsu, S.C.; Osman, M.A. A dual role for IQGAP1 in secretion. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanos, B.E.; Bay, A.E.P.; Salvarezza, S.; Vivanco, I.; Mellinghoff, I.; Osman, M.; Sacks, D.; Rodriguez-Boulan, E. IQGAP1 controls tight junction formation through differential regulation of claudin recruitment. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeprich, G.J.; Sinclair, A.N.; Shekhar, S.; Goode, B.L. Single-molecule imaging of IQGAP1 regulating actin filament dynamics. Mol. Biol. Cell 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, K.; Timson, D.J.; Ahmadian, M.R. New model for the interaction of IQGAP1 with CDC42 and RAC1. Small GTPases 2020, 11, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, C.-F.; Li, J.; Yang, S.-X.; Guo, H.-J.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X.-Y.; Wang, Y.-T.; Li, M.-H.; Li, J.-Y.; Zou, Q. IQGAP1 promotes anoikis resistance and metastasis through Rac1-dependent ROS accumulation and activation of Src/FAK signalling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrick, C.; Fischer, A.; Srivastava, D.P.; Tronson, N.C.; Penzes, P.; Radulovic, J. N-cadherin regulates cytoskeletally associated IQGAP1/ERK signaling and memory formation. Neuron 2007, 55, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Frausto, S.F.; Guedea, A.L.; Tronson, N.; Jovasevic, V.; Leaderbrand, K.; Corcoran, K.A.; Guzmán, Y.F.; Swanson, G.T.; Radulovic, J. IQGAP1 regulates NR2A signaling, spine density, and cognitive processes. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 8533–8542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martina, M.; Turcotte, M.E.B.; Halman, S.; Bergeron, R. The sigma-1 receptor modulates NMDA receptor synaptic transmission and plasticity via SK channels in rat hippocampus. J. Physiol. 2007, 578, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, M.A. Cytoskeleton dynamics in health and disease: Role of molecular switches and rheostats. In The Cytoskeleton in Health and Disease; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 11–62. [Google Scholar]

| Compound Name | Function | Clinical Use | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chloroquine | Anti-malarial drug | [45] | |
| BD1047 | Antagonist | Has antipsychotic properties, potential use as a neuropathic pain treatment (in phase II clinical trials) | [46,47] |
| BD1063 | Antagonist | Reduces effects of cocaine, MDMA | [46,47] |
| Cannabidiol (CBD) | Antagonist | Treatment for pain, cancer symptoms and holds potential for Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, stroke, epilepsy, neuropsychiatric disorders | [48] |
| E52862 | Antagonist | Potential treatment for neuropathic pain | [49] |
| Dehydroepiandrosterone | Agonist | Anti-aging therapy, used to treat depression and menopause symptoms | [50] |
| Haloperidol | Antagonist | Antipsychotic | [24] |
| NE-100 | Antagonist | Commonly used to study SigmaR1 | [51] |
| Progesterone | Antagonist | Important hormone of the menstrual cycle and helping maintain the early stages of pregnancy | [45,52] |
| Sertraline | Antagonist | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor used to treat depression, OCD, PTSD, and panic attacks | [53] |
| Verapamil | Antagonist | treats cardiac issues including angina, heart rhythm problems, and hypertension | [54] |
| Cocaine | Agonist | Central nervous system (CNS) stimulant | [11,12,34,55] |
| Choline | Agonist | Triggers IP3-evoked Ca2+ release | [56] |
| Donepezil | Agonist | Dementia medication | [57,58] |
| Dextromethorphan | Agonist | Cough suppressant | [59] |
| N, N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) | Agonist | hallucinogen | [60] |
| Fluvoxamine | Agonist | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor used to treat depression and OCD | [61] |
| Ifenprodil | Agonist | Cerebral vasodilator | [62] |
| Memantine | Agonist | Used to treat Alzheimer’s disease symptoms | [47] |
| Methamphetamine | Agonist | Central nervous system (CNS) stimulant | [45] |
| Pentazocine | Agonist | Opioid pain medication | [63] |
| SA4503 (Cutamesine) | Agonist | Anti-amnesia properties, inhibits angiotensin II-induces cardiomyocyte hypertrophy | [64] |
| SKF10,47 | Agonist | Opioid analgesic | [65] |
| 4-(N-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)-4-iodobenzamide (4-IBP) | Agonist | Decreases migration of human cancer cells in vitro | [36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robinson, T.S.; Osman, M.A. An Emerging Role for Sigma Receptor 1 in Personalized Treatment of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133464
Robinson TS, Osman MA. An Emerging Role for Sigma Receptor 1 in Personalized Treatment of Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2023; 15(13):3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133464
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobinson, Taylor S., and Mahasin A. Osman. 2023. "An Emerging Role for Sigma Receptor 1 in Personalized Treatment of Breast Cancer" Cancers 15, no. 13: 3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133464
APA StyleRobinson, T. S., & Osman, M. A. (2023). An Emerging Role for Sigma Receptor 1 in Personalized Treatment of Breast Cancer. Cancers, 15(13), 3464. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133464





