A Review of Herbal Resources Inducing Anti-Liver Metastasis Effects in Gastrointestinal Tumors via Modulation of Tumor Microenvironments in Animal Models
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
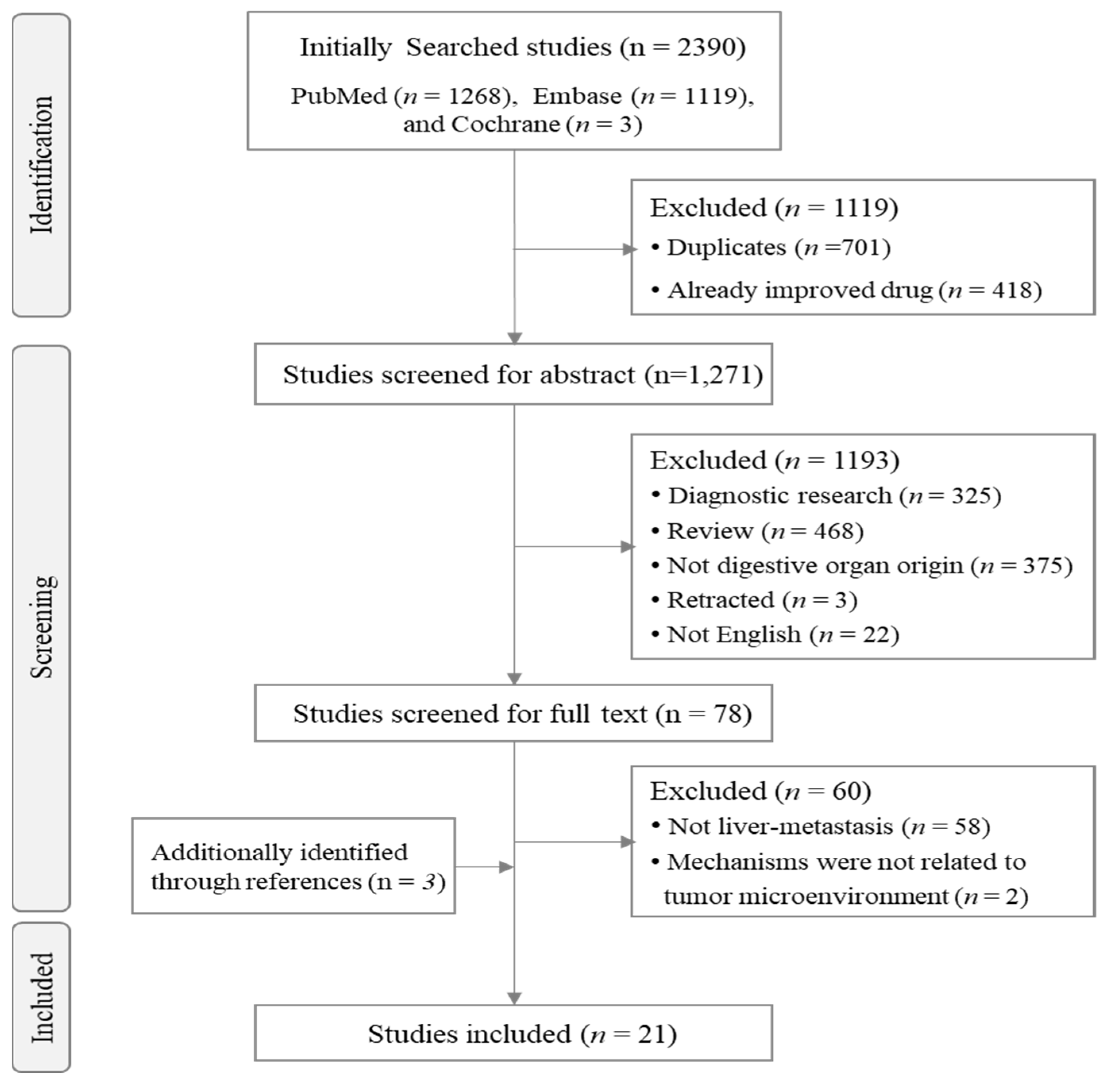
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Review and Selection of Relevant Articles
2.3. Analysis of Major Mechanisms Related to the Effects on Metastasis by Targeting the TME
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Selected Studies
3.2. Characteristics of the Herbal Candidates
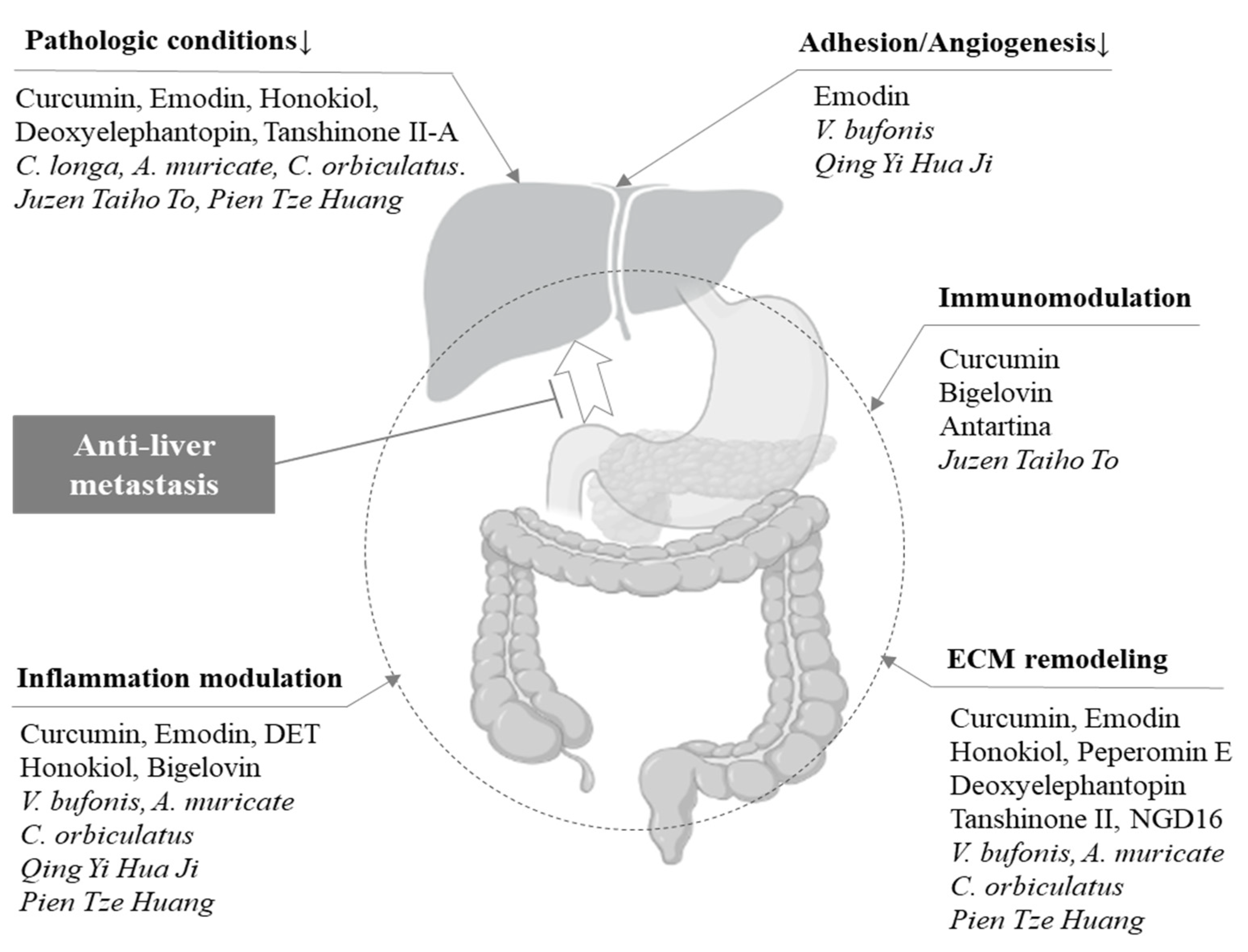
3.3. Anti-Liver Metastatic Effects on the TME
3.4. Effect of Herbal Candidates on the Liver Environment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Patel, N.; Zhang, H.-J. The progress of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as the risk of liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 1169–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, L. Curcumin inhibits liver metastasis of gastric cancer through reducing circulating tumor cells. Aging 2019, 11, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.-H.; Shi, W.-D.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.-M. Qingyihuaji formula inhibits progress of liver metastases from advanced pancreatic cancer xenograft by targeting to decrease expression of Cyr61 and VEGF. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, P.; Ouyang, H.; Yin, J.; Liu, A.; Ma, C.; Liu, L. Targeting cancer-related inflammation: Chinese herbal medicine inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, Y.; Fujii, H.; Hayakawa, Y.; Sakukawa, R.; Yamaura, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Tsukada, K.; Fujimaki, M.; Nunome, S.; Komatsu, Y. Oral administration of a Kampo (Japanese herbal) medicine Juzen-taiho-to inhibits liver metastasis of Colon 26-L5 carcinoma cells. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1998, 89, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Zhuang, Q.; Zheng, L.; Cao, Z.; Shen, A.; Li, Q.; Fu, C.; Feng, J.; Peng, J. Pien Tze Huang inhibits liver metastasis by targeting TGF-β signaling in an orthotopic model of colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1922–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Yue, G.G.-L.; Luo, L.; Tsui, S.K.-W.; Fung, K.-P.; Ng, S.S.-M.; Lau, C.B.-S. Turmeric Is therapeutic in vivo on patient-derived colorectal cancer xenografts: Inhibition of growth, metastasis, and tumor recurrence. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 574827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yue, G.G.-L.; Tsui, S.K.-W.; Fung, K.-P.; Bik-San Lau, C. Turmeric extract, with absorbable curcumin, has potent anti-metastatic effect in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine 2018, 46, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Chen, H.; Wei, W.; Ye, S.; Liao, W.; Gong, J.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, L.; Lin, S. Antiproliferative and antimetastatic effects of emodin on human pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Wang, C.; Zhang, P.; You, S. Emodin inhibits pancreatic cancer EMT and invasion by up-regulating microRNA-1271. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3366–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.-H.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Shi, W.-D.; Liu, L.-M. Huachansu injection inhibits metastasis of pancreatic cancer in mice model of human tumor xenograft. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Cai, H.; Liu, Q.; Xia, Y.; Xing, L.; Zuo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, C.; Xu, K.; Yin, P. Cinobufacini inhibits colon cancer invasion and metastasis via suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and EMT. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2020, 48, 703–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Averett, C.; Bhardwaj, A.; Arora, S.; Srivastava, S.K.; Khan, M.A.; Ahmad, A.; Singh, S.; Carter, J.E.; Khushman, M.; Singh, A.P. Honokiol suppresses pancreatic tumor growth, metastasis and desmoplasia by interfering with tumor–stromal cross-talk. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.-C.; Lai, D.-W.; Lan, K.-H.; Shen, C.-C.; Wu, S.-M.; Chiu, C.-S.; Wang, K.-B.; Sheu, M.-L. Honokiol thwarts gastric tumor growth and peritoneal dissemination by inhibiting Tpl2 in an orthotopic model. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2568–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.-F.; Shen, X.; Xie, Y.-K.; Chen, J.-C.; Shi, H.-Q.; Yu, Z.-P.; Song, Q.-T.; Zhou, M.-T.; Zhang, Q.-Y. Inhibitory effects of tanshinone II-A on invasion and metastasis of human colon carcinoma cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2009, 30, 1537–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoch, A.; Suklabaidya, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Nayak, D.; Rasool, R.U.; Sharma, D.; Mukherjee, D.; Faheem, M.M.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, P.R. Dual role of Par-4 in abrogation of EMT and switching on mesenchymal to epithelial transition (MET) in metastatic pancreatic cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yue, G.G.-L.; Song, L.-H.; Huang, M.-B.; Lee, J.K.-M.; Tsui, S.K.-W.; Fung, K.-P.; Tan, N.-H.; Bik-San Lau, C. Natural small molecule bigelovin suppresses orthotopic colorectal tumor growth and inhibits colorectal cancer metastasis via IL6/STAT3 pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 150, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanga, X.-Z.; Gu, J.-L.; Gao, M.; Bian, Y.; Liang, J.-Y.; Wen, H.-M.; Wu, H. Peperomin E induces promoter hypomethylation of metastatic-suppressor genes and attenuates metastasis in poorly differentiated gastric cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 2341–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Zhong, X.; Huang, P.; Kang, P.; Leng, K.; Zheng, W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Cui, Y. Deoxyelephantopin induces apoptosis via oxidative stress and enhances gemcitabine sensitivity in vitro and in vivo through targeting the NF-κB signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer. Aging 2020, 12, 11116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qian, Y.; Dai, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Guo, S.; Hisamitsu, T. Antimetastatic Effects of Celastrus orbiculatus on Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma by Inhibiting Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and NF-κB/Snail Signaling Pathway. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.P.; Rachagani, S.; Purohit, V.; Pandey, P.; Joshi, S.; Moore, E.D.; Johansson, S.L.; Singh, P.K.; Ganti, A.K.; Batra, S.K. Graviola: A novel promising natural-derived drug that inhibits tumorigenicity and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo through altering cell metabolism. Cancer Lett. 2012, 323, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvicini, M.; Gutierrez-Moraga, A.; Rodriguez, M.M.; Gomez-Bustillo, S.; Salazar, L.; Sunkel, C.; Nozal, L.; Salgado, A.; Hidalgo, M.; Lopez-Casas, P.P. A tricin derivative from Deschampsia antarctica Desv. inhibits colorectal carcinoma growth and liver metastasis through the induction of a specific immune response. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Iwanowycz, S.; Wang, J.; Saaoud, F.; Yu, F.; Wang, Y.; Hu, J.; Chatterjee, S.; Wang, Q.; Fan, D. Emodin attenuates systemic and liver inflammation in hyperlipidemic mice administrated with lipopolysaccharides. Exp. Biol. Med. 2014, 239, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-A.; Chen, G.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Xiong, Y.; Tian, C.; Jia, B.; Wang, G.; Xia, J. Emodin alleviates liver fibrosis of mice by reducing infiltration of Gr1hi monocytes. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 5738101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, S.; Umemura, A.; Okuda, K.; Taketani, H.; Seko, Y.; Nishikawa, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Moriguchi, M.; Kanbara, Y.; Arbiser, J.L. Honokiol acts as a potent anti-fibrotic agent in the liver through Inhibition of TGF-β1/SMAD signaling and autophagy in hepatic stellate cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, T.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Qian, K.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, Y. Honokiol alleviates methionine-choline deficient diet-induced hepatic steatosis and oxidative stress in C57BL/6 mice by regulating CFLAR-JNK pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 2313641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-X.; Lu, X.-Y.; Zhang, S.-J.; Chiu, A.P.; Lo, L.H.; Largaespada, D.A.; Chen, Q.-B.; Keng, V.W. Sodium tanshinone IIA sulfonate ameliorates hepatic steatosis by inhibiting lipogenesis and inflammation. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.-J.; Yan, X.-L.; Dong, B.-S.; Yang, W.-N.; Su, S.-B.; Zhang, H. A network pharmacology approach to investigating the mechanism of Tanshinone IIA for the treatment of liver fibrosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 253, 112689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.T.; Cho, K.H.; Sharma, A.; Devi, S.; Park, T.S. Annona muricata leaf extract attenuates hepatic lipogenesis and adipogenesis. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4621–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Soejima, Y.; Kumagai, A.; Watanabe, M.; Uozaki, H.; Fukusato, T. Inhibitory effects of Japanese herbal medicines sho-saiko-to and juzen-taiho-to on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiraviriyakul, A.; Songjang, W.; Kaewthet, P.; Tanawatkitichai, P.; Bayan, P.; Pongcharoen, S. Honokiol-enhanced cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity against cholangiocarcinoma cells mediated by dendritic cells pulsed with damage-associated molecular patterns. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Lin, S.; Guo, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, X.; Jin, S.; Jin, L.; Li, Y. Identification of an Oleanane-Type Triterpene Hedragonic Acid as a Novel Farnesoid X Receptor Ligand with Liver Protective Effects and Anti-inflammatory Activity. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 93, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Si, Y.; Zhai, L.; Yang, N.; Yao, S.; Sang, H.; Zu, D.; Qin, S.; Wang, J. Celastrus orbiculatus Thunb. ameliorates high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in guinea pigs. Die Pharm.-Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 68, 850–854. [Google Scholar]
- Gezici, S.; Sekeroglu, N. Current Perspectives in the Application of Medicinal Plants Against Cancer: Novel Therapeutic Agents. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upreti, S.; Pandey, S.C.; Bisht, I.; Samant, M. Evaluation of the target-specific therapeutic potential of herbal compounds for the treatment of cancer. Mol. Divers. 2022, 26, 1823–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Hua, L.; Xu, W. Pien-Tze-Huang ameliorates hepatic fibrosis via suppressing NF-κB pathway and promoting HSC apoptosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 244, 111856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, F.; Dang, Y. Quantitative profiling of oxylipin reveals the mechanism of Pien-Tze-Huang on alcoholic liver disease. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 9931542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Wahab, S.M.; Jantan, I.; Haque, M.A.; Arshad, L. Exploring the leaves of Annona muricata L. as a source of potential anti-inflammatory and anticancer agents. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.-C.; Lin, K.-J.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Hsu, C.-A.; Yang, S.-S.; Shyur, L.-F. Hepatoprotective effect and mechanistic insights of deoxyelephantopin, a phyto-sesquiterpene lactone, against fulminant hepatitis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 516–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadati, S.; Sadeghi, A.; Mansour, A.; Yari, Z.; Poustchi, H.; Hedayati, M.; Hatami, B.; Hekmatdoost, A. Curcumin and inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, placebo controlled clinical trial. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Huang, W.; Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, P.; Zheng, S. Curcumin blunts epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocytes to alleviate hepatic fibrosis through regulating oxidative stress and autophagy. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, L.; Yu, Y.; Tian, J.; Xu, R.; Fang, Z.; Jiang, L.; et al. Chinese Herbal Prescription Fu-Zheng-Qu-Xie Prevents Recurrence and Metastasis of Postoperative Early-Stage Lung Adenocarcinoma: A Prospective Cohort Study Followed with Potential Mechanism Exploration. Oxid Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 6673828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeenk, H.G.; Incrocci, L.; Kazemier, G.; van Dekken, H.; Tran, K.T.; Jeekel, J.; van Eijck, C.H. Adjuvant 5-FU-based chemoradiotherapy for patients undergoing R-1/R-2 resections for pancreatic cancer. Dig. Surg. 2005, 22, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, H.; Wang, P.; Meng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Yu, E.; Jin, H.; Chang, D.Z.; Liao, Z.; Cohen, L.; Liu, L. Multimodality treatment of pancreatic cancer with liver metastases using chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and/or Chinese herbal medicine. Pancreas 2011, 40, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, R.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, M.; Wei, S.; Ran, D.; Jin, W.; Wu, C. A Network Pharmacology Approach to Investigate the Anticancer Mechanism and Potential Active Ingredients of Rheum palmatum L. Against Lung Cancer via Induction of Apoptosis. Front. Pharm. 2020, 11, 528308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhou, B.; Liao, Y.; Wang, Z. Emodin Reverses Gemcitabine Resistance of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines Through Inhibition of IKKbeta/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Onco Targets 2020, 13, 9839–9848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, J.; Sheng, A.; Huang, S.; Tang, Y.; Ma, S.; Hong, G. Emodin Inhibits the proliferation of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells through activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 622046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, T. Expectations for and challenges in population-based endoscopic gastric and colorectal cancer screening. Dig. Endosc. 2022, 34, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.J.; Cosgrove, D.C.; Herman, J.M.; Pawlik, T.M. Advances in understanding of colorectal liver metastasis and implications for the clinic. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 9, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Chen, X.; Huang, L.; Du, Y.; Cheng, X. Treatment of synchronous liver metastases from gastric cancer: A single-center study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.-H.; Hu, Q.; Sui, H.; Ci, S.-J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, N.-N.; Yin, P.-H.; Qin, J.-M.; Li, Q. Tanshinone II-a inhibits angiogenesis through down regulation of COX-2 in human colorectal cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Jin, X.; Wan, X.; Yin, X.; Fang, M.; Liu, T.; Zhao, S. Effects and mechanism of tanshinone II A in proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of human colon cancer cells. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2019, 25, 4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeri, A.; Ward, N.; Panahi, Y.; Sahebkar, A. Anti-angiogenic activity of curcumin in cancer therapy: A narrative review. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 17, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Mok, S.; Xue, F.; Zhang, W. CXCL12/CXCR4: A symbiotic bridge linking cancer cells and their stromal neighbors in oncogenic communication networks. Oncogene 2016, 35, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neophytou, C.M.; Panagi, M.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Papageorgis, P. The role of tumor microenvironment in cancer metastasis: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. Cancers 2021, 13, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Rahman, N.I.A.; Shimizu, A.; Ogita, H. Cell-to-cell contact-mediated regulation of tumor behavior in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 4005–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeke, S.; Mograbi, B.; Alix-Panabières, C.; Hofman, P. Never travel alone: The crosstalk of circulating tumor cells and the blood microenvironment. Cells 2019, 8, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, T.; Sultanpuram, N.; Sendi, H. The role of liver microenvironment in hepatic metastasis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, H.-J.; Kim, H.-G.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, H.-S.; Cho, J.-H.; Jo, I.-J.; Park, S.-J.; Son, C.-G. A preclinical model of chronic alcohol consumption reveals increased metastatic seeding of colon cancer cells in the liver. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1698–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkoc, Y.; Gozuacik, D. Autophagy and hepatic tumor microenvironment associated dormancy. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2021, 52, 1277–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Guo, L.; Gu, X.; Zhang, B.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Gao, B. Prevention of colorectal cancer liver metastasis by exploiting liver immunity via chitosan-TPP/nanoparticles formulated with IL-12. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3909–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Mizoguchi, I.; Morishima, N.; Chiba, Y.; Mizuguchi, J.; Yoshimoto, T. Regulation of antitumor immune responses by the IL-12 family cytokines, IL-12, IL-23, and IL-27. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2010, 2010, 832454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, P. Cohort study on fuzheng capsule and quxie capsule in reducing relapse and metastasis of cancer in patients with stage II and III colorectal carcinoma after operation. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi = Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Med. 2006, 26, 677–680. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S.; Baidoo, J.N.; Sampat, S.; Mancuso, A.; David, L.; Cohen, L.S.; Zhou, S.; Banerjee, P. Liposomal TriCurin, a synergistic combination of curcumin, epicatechin gallate and resveratrol, repolarizes tumor-associated microglia/macrophages, and eliminates glioblastoma (GBM) and GBM stem cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, L.; Xu, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Aa, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, B.; Xie, Y. Curcumin inhibits hepatic stellate cell activation via suppression of succinate-associated HIF-1α induction. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 476, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, H.; Bu, H.; Chen, H.; Tong, H.; Liu, D.; Guo, H.; Lin, S.-Z. Emodin inhibits the differentiation and maturation of dendritic cells and increases the production of regulatory T cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
| Classification | Total Number of Studies/Reference |
|---|---|
| Final number of included studies | 21 |
| Original plant (only single compound or extract) | 12 |
| Medication | |
| Single compound | 12/[3,10,11,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,23] |
| Single-herb extract | 5/[8,9,12,21,22] |
| Herbal decoction | 4/[4,5,6,7] |
| Organ of origin | |
| Pancreas | 9/[4,5,10,11,12,14,17,20,22] |
| Colon | 8/[6,7,8,9,13,16,18,23] |
| Stomach | 4/[3,15,19,21] |
| Experimental design | |
| Lesion implantation area | |
| Pancreatic region | 4/[10,14,17,22] |
| Colon region | 4/[7,9,13,18] |
| Stomach region | 3/[3,15,19] |
| Spleen injection | 5/[4,5,11,12,15,20] |
| Subcutaneous injection | 1/[8] |
| Intraperitoneal injection | 1/[21] |
| Intrahepatic injection | 1/[23] |
| Intravenous injection (tail vein) | 2/[6,16] |
| Administration method | |
| Oral | 12/[4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,16,19,21,22] |
| Intraperitoneal injection | 7/[12,13,14,15,17,20,23] |
| Intravenous injection | 2/[3,18] |
| Positive control | |
| FOLFOX (5-FU, fluorouracil, and oxaliplatin) | 2/[8,9] |
| 5-FU | 1/[23] |
| Cisplatin | 1/[6] |
| Gemcitabine | 1/[20] |
| Mithramycin | 1/[19] |
| Capecitabine | 1/[21] |
| None | 14/[3,4,5,7,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,22] |
| Efficacy assessment tool | |
| Number of liver metastasis nodules | 15/[3,4,6,7,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,20,21,22] |
| Size of liver metastatic area | 5/[5,8,9,18,23] |
| Luciferase activity in liver | 1/[19] |
| Original Plant | Origin of Cancer (Method of Transplantation) and Drug Formulation (Route of Administration) | Main Mechanisms Related to the Tumor Microenvironment (Site of Tissue Taken for Assay) | Liver Environment Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Curcuma longa L. | Xenograft, colon ca. (sc), and ethanol ex (po) [8] | Regulates EMT and angiogenesis at the original site (rectum) | Steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis [24,25] |
| Colon 26-M01 (oi) and ethanol ex (po) [9,18] | Regulates immune components and the vascular endothelium at the original site (rectum) | ||
| Primary gastric cancer cell (sc) and curcumin (iv) [3] | Inhibits CXCL12/CXCR4 expression at the original site (limb) | ||
| Rheum palmatum L. | Pancreas SW1990 (oi) and emodin (po) [10] | Suppresses NF-κB and MMP-9 protein expression at the original site (pancreas) | Steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis [26,27] |
| Pancreas SW1990 (si) and emodin (po) [11] | Increases E-cadherin expression via miRNA-1271 at the metastasis site (liver) | ||
| Venenum bufonis | Pancreas SW1990 (si) and water ex (ip) [12] | Regulates MMP-2/9 and VEGF expression at the metastasis site (liver) | |
| Colon HCT116 (oi) and cinobufacini (ip) [13] | Regulates MMP-2/9 and increases E-cadherin expression at the original site (colon) | ||
| Magnolia acuminate L. | Pancreas MIA PaCa-2 (oi) and honokiol (ip) [14] | Interferes with tumor–stromal crosstalk at the original site (pancreas) | Steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis [28,29] |
| Stomach MKN45 (oi) and honokiol (ip) [15] | Increases E-cadherin and suppresses TGF-β expression at the original site (stomach) | ||
| Elephantopus scaber L. | Pancreas BxPC-3 (si) and deoxyelephantopin (ip) [20] | Increases E-cadherin and suppresses NF-κB expression at the original site (pancreas) | Inflammation [30] |
| Inula helianthus-aquatica | Colon HCT116 (oi) and bigelovin (iv) [18] | Decreases IL-6 and suppresses N-cadherin expression at the original site (colon) | |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza B. | Colon SW480 (iv) and tanshinone II-A (po) [16] | Regulates MMP-2/9 and TIMP-1/2 expression at the original site (colon) | Steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis [31,32] |
| Deschampsia Antarctica D. | Colon CT-26 (ih) and antartina (ip) [23] | Activates immunity, mainly via dendritic cells and CD8 T cells (blood) | |
| Peperomia dindygulensis M. | Stomach NCI-N87-luc (oi) and peperomin E (po) [19] | Activates E-cadherin and TIMP-3 at the original site (stomach) | |
| Cruciferous vegetables | Pancreas UN-KC-6141 (oi) and NGD16 (ip) [17] | Increases E-cadherin expression at the original site in a Par4-dependent manner (pancreas) | |
| Annona muricata L. | Pancreas CD18/HPAF (oi) and ethanol ex (po) [22] | Suppresses MMP-9 and MUC4 expression at the original site (pancreas) | Steatosis and inflammation [33,34] |
| Celastrus orbiculatus T. | Stomach SGC-7901 (ip) and acetate ex (po) [21] | Decreases NF-κB, increases E-cadherin, and suppresses N-cadherin expression at the original site (peritoneal) | Steatosis and inflammation [35,36] |
| Qing Yi Hua Ji | Pancreas SW1990HM (si) and decoction (po) [5] | Decreases IL-6 expression and increases tumor-associated macrophages at the original site (pancreas) | |
| Pancreas SW1990HM (si) and decoction (po) [4] | Suppresses VEGF releases at the metastasis site (liver) | ||
| Juzen-taiho-to | Colon 26-L5 (pv) and decoction (po) [6] | Regulates macrophages and/or T cells (blood) | Steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis [37,38] |
| Pientzehuang | Colon CT-26 (oi) and decoction (po) [7] | Decreases TGF-β, increases E-cadherin, and suppresses N-cadherin expression at the original site (colon) | Steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis [39,40] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-K.; Lee, N.-H.; Son, C.-G. A Review of Herbal Resources Inducing Anti-Liver Metastasis Effects in Gastrointestinal Tumors via Modulation of Tumor Microenvironments in Animal Models. Cancers 2023, 15, 3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133415
Kim S-K, Lee N-H, Son C-G. A Review of Herbal Resources Inducing Anti-Liver Metastasis Effects in Gastrointestinal Tumors via Modulation of Tumor Microenvironments in Animal Models. Cancers. 2023; 15(13):3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133415
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Sul-Ki, Nam-Hun Lee, and Chang-Gue Son. 2023. "A Review of Herbal Resources Inducing Anti-Liver Metastasis Effects in Gastrointestinal Tumors via Modulation of Tumor Microenvironments in Animal Models" Cancers 15, no. 13: 3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133415
APA StyleKim, S.-K., Lee, N.-H., & Son, C.-G. (2023). A Review of Herbal Resources Inducing Anti-Liver Metastasis Effects in Gastrointestinal Tumors via Modulation of Tumor Microenvironments in Animal Models. Cancers, 15(13), 3415. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133415






