Identification of Tissue-Resident Natural Killer and T Lymphocytes with Anti-Tumor Properties in Ascites of Ovarian Cancer Patients
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Samples
2.2. Mice
2.3. Cell Lines
2.4. Functional Assays
2.5. Phenotyping
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
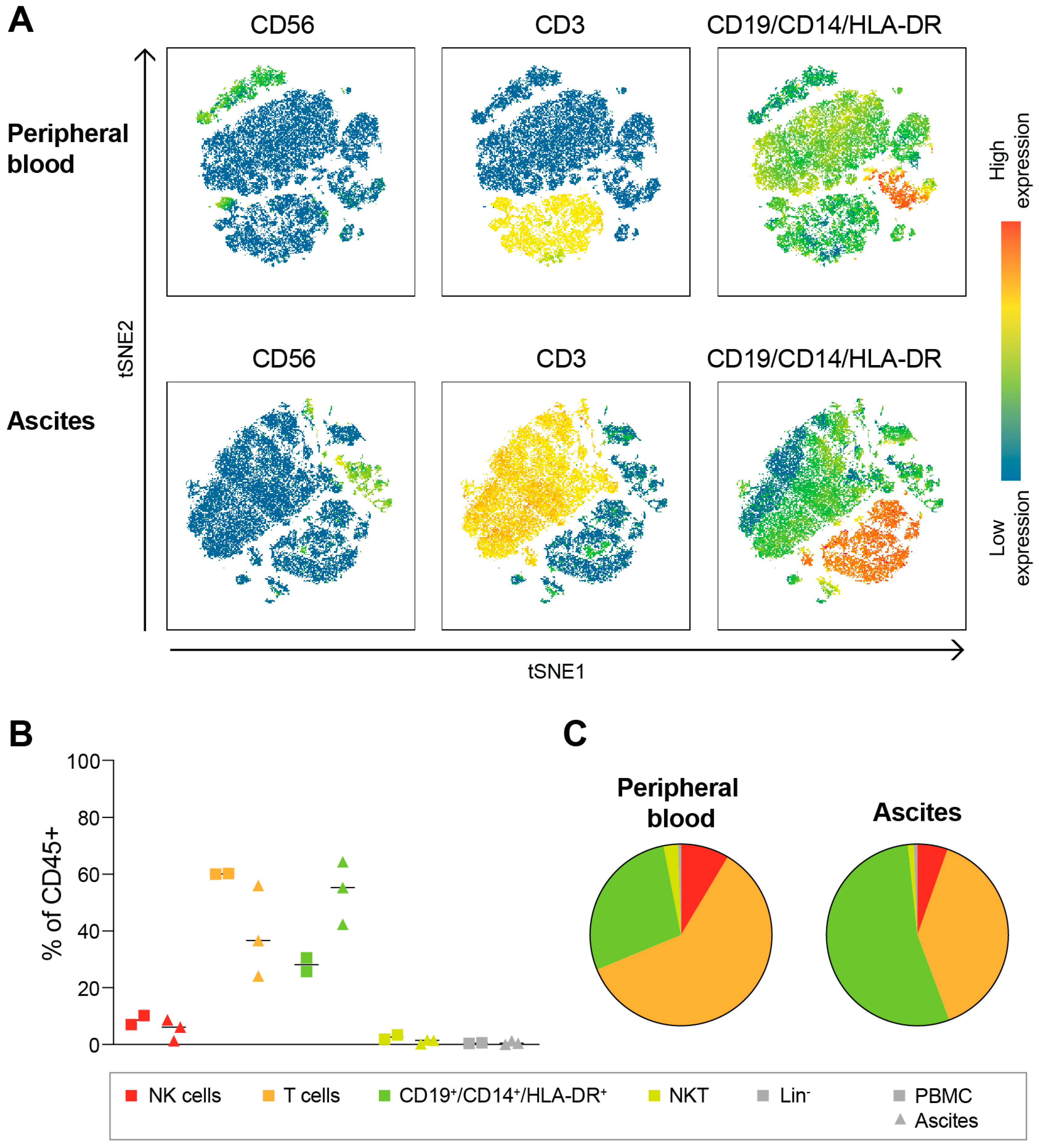
3.1. Ovarian Cancer Ascites Conatins a Large Subset of Tissue-Resident NK Cells
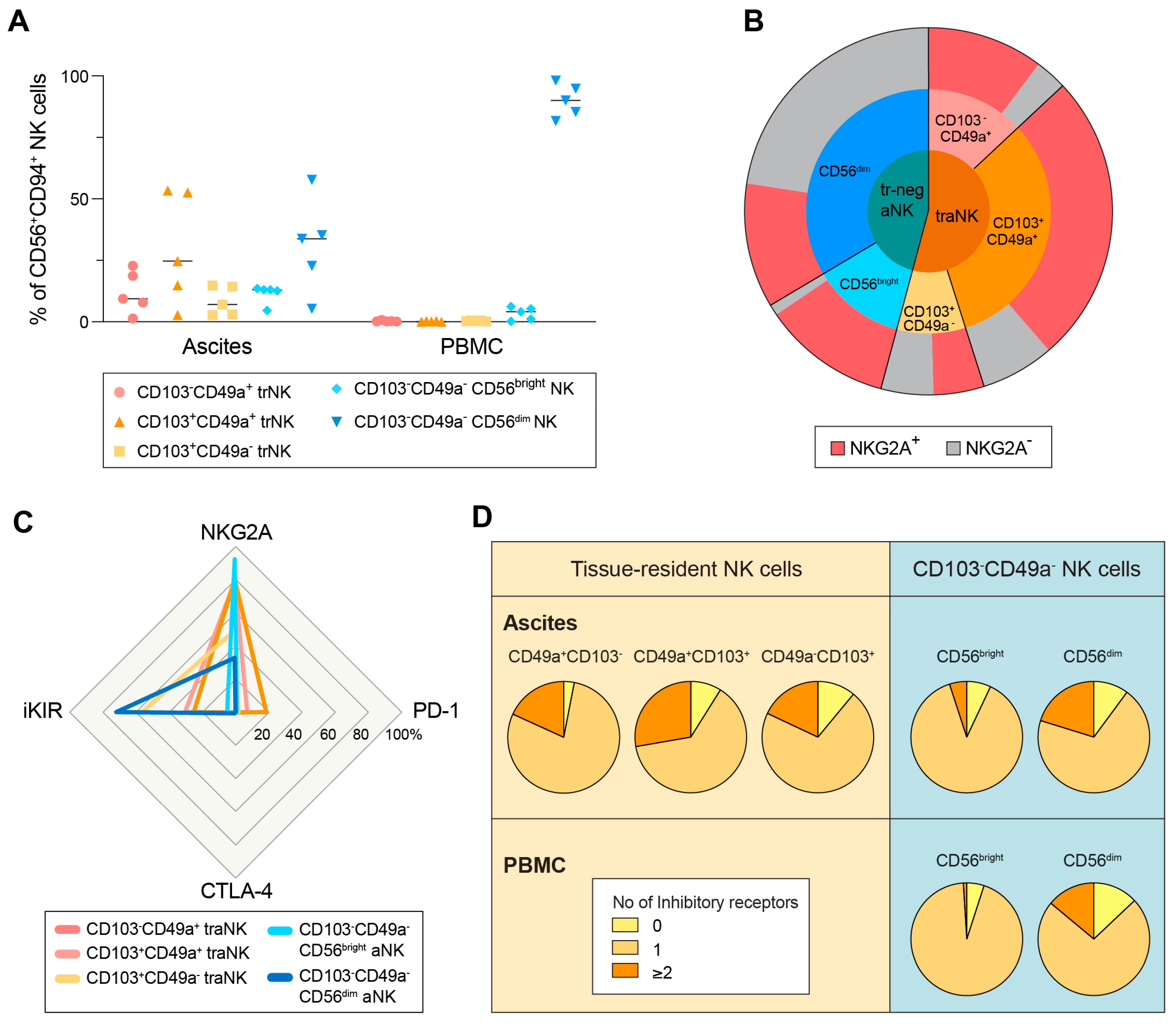
3.2. All Subsets of aNK Cells Are Highly NKG2A+
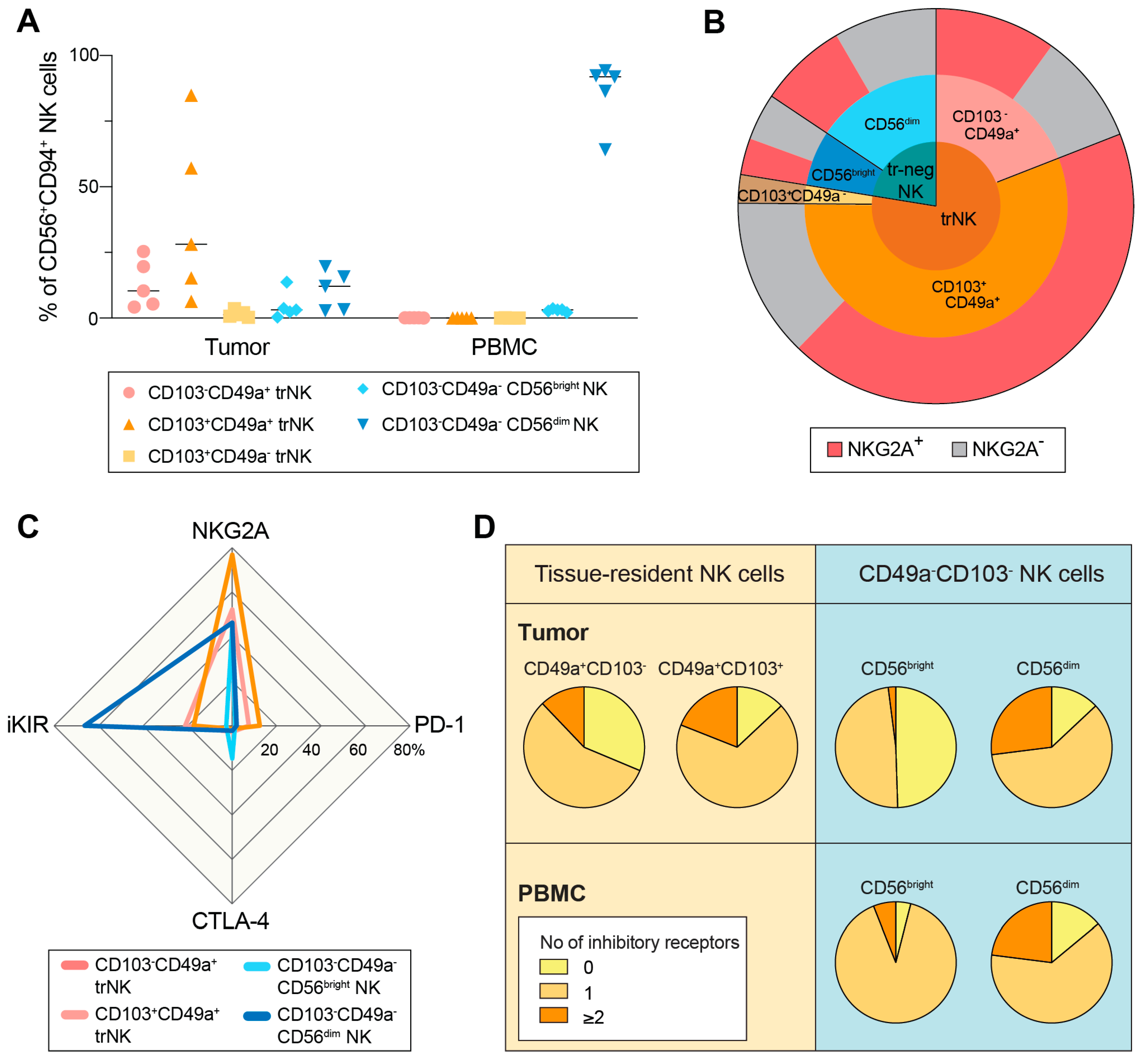
3.3. NKG2A+ trNK Cells Are Present also in the Primary Tumor Microenvironment in HGSC
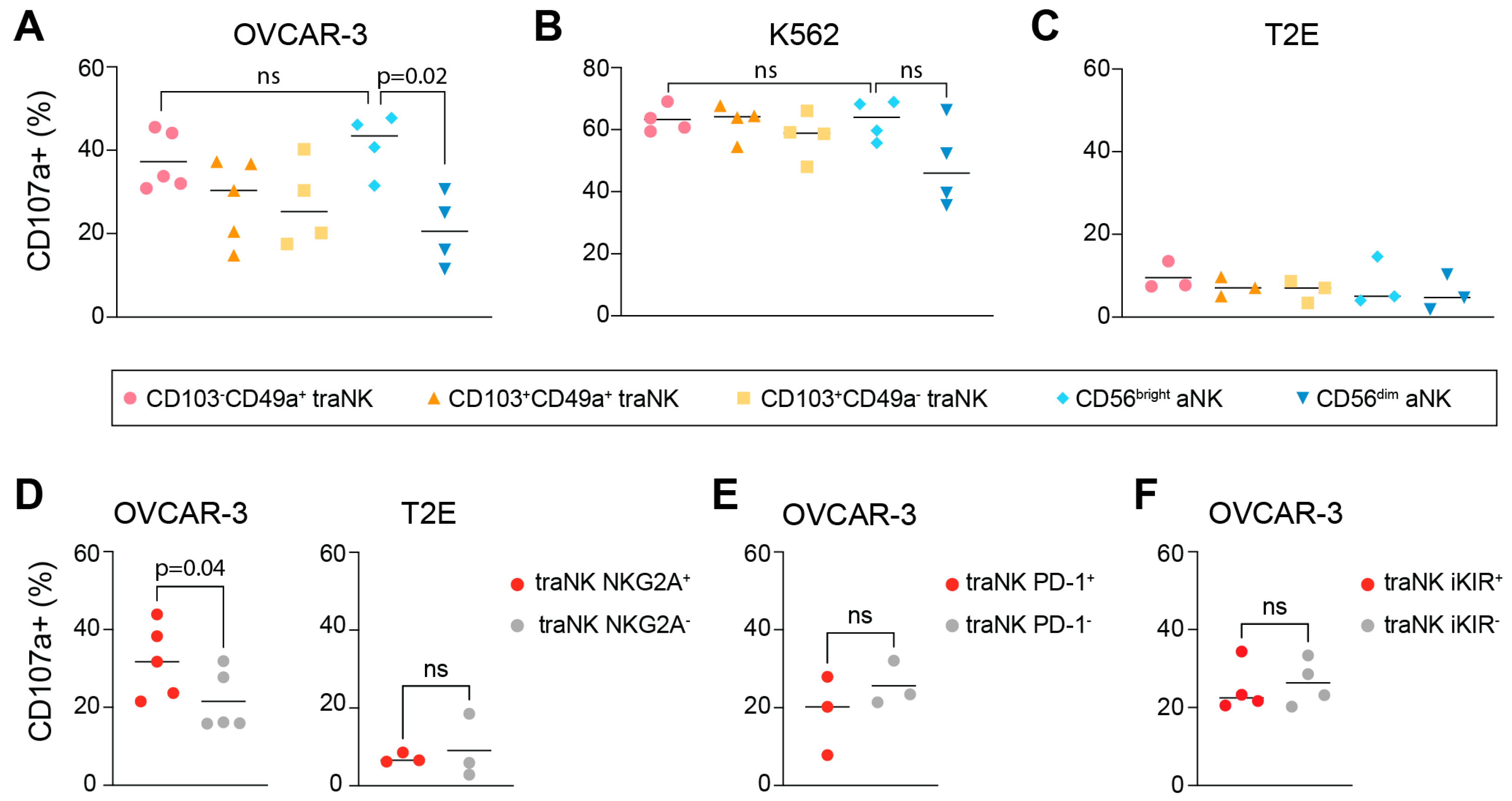
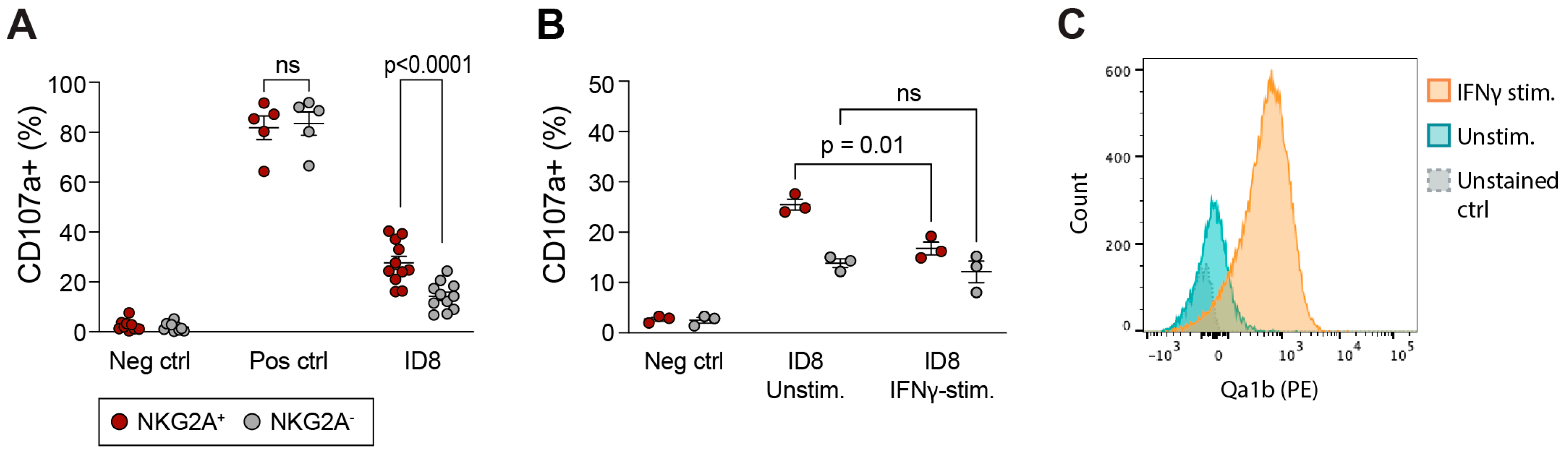
3.4. traNK Cells Respond to Ovarian Tumor Cells
3.5. Presence of Tissue-Resident CD8+ T Cells in Ascites and Tumor Environment of HGSC
3.6. In Vivo Phenotype of Mouse NK and T Cells in Ascites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sample Type 1 | Collection Site | Disease Stage | Age | Pharmacological Treatment 2 | Other Diseases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PB; A | Sahlgrenska University Hospital | 3C | 42 | No | No |
| PB; A | Sahlgrenska University Hospital | 3C | 73 | No | No |
| PB; A | Sahlgrenska University Hospital | 4 | 66 | Norvasc, Levothyroxine | Hypertension, Hypothyroidism |
| PB; A | Sahlgrenska University Hospital | 3A1 | 63 | No | No |
| PB; A | Sahlgrenska University Hospital | 4B | 58 | No | No |
| PB; T | Humanitas Research Hospital | 2B | 62 | No | Hypothyroidism, Osteoporosis |
| PB; T | Humanitas Research Hospital | 3C | 75 | Carboplatin, Paclitaxel, Gemcitabine, Bevacizumab | No |
| PB; T | Humanitas Research Hospital | 3B | 61 | No | Hypertension |
| PB; T | Humanitas Research Hospital | 4B | 82 | No | Arrythmia |
| PB; T | Humanitas Research Hospital | 2C | 58 | Carboplatin, Paclitaxel, Niraparib | Previous TEP (pulmonary thromboembolism) |
| PB; A | Addenbrooke’s Hospital | 3C | 75 | No | Restless legs syndrome, history of laminectomy, Meningioma, urge incontinence |
| PB; A | Addenbrooke’s Hospital | 3C | 70 | Taxol, Carboplatin, Bevacizumab, Caelyx | Hysterectomy 30 years ago for fibroids |
| PB; A | Addenbrooke’s Hospital | 3C | 89 | Taxol, Carboplatin | Oesophageal lichen planus, hearing loss |
| Reacts with | Antigen | Isotope | Clone | Source | Conjugated in-House | Used in tSNE Generation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | CD45 | 89Y | HI30 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | |
| CD3 | Qdot605/170Er | UCHT1 | Thermofisher | yes (not 2a) | ||
| CD14 | Qdot605/112Cd | Tük4 | Thermofisher | yes (not 2a) | ||
| CD19 | Qdot605/112Cd | SJ25-C1 | Thermofisher | yes (not 2a) | ||
| HLA-DR | Qdot605/112Cd | Tü36 | Thermofisher | yes (not 2a) | ||
| CD57 | 115In | HCD57 | BioLegend | yes | yes | |
| KIR2DS4 | 141Pr | FES172 | Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA | yes | yes | |
| CD103 | 142Nd | Ber-ACT8 | BioLegend | yes | yes | |
| CD117 | 143Nd | 104D2 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| CD69 | 144Nd | FN50 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| Granzyme B | 146Nd | CLB-GB11 | Novus, Singapore | yes | yes | |
| NKp30 | 148Nd | P30-15 | BioLegend | yes | yes | |
| KIR2DL2/L3/S2 | 149Sm | GL183 | Beckman Coulter | yes | yes | |
| CD107a | 151Eu | H4A3 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| Eomes | 152Sm | WD1928 | eBioscience | yes | yes | |
| MIP1a | 153Eu | 1.2_3E8-2H6-2B6 | Peprotech | |||
| CD96 | 154Sm | NK92.39 | BioLegend | yes | yes | |
| CD56 | 155Gd | B159 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| LILRB1 | 156Gd | GHI/75 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| NKG2C | 157Di | 134591 | R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA | yes | yes | |
| NKp44 | 160Gd | P44-8 | BioLegend | yes | yes | |
| Tbet | 161Dy | 4B10 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| NKp46 | 162Dy | BAB281 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| CD49a | 163Dy | TS2/7 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| CD161 | 164Dy | HP-3G10 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| CD127 | 165Ho | A019D5 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| NKG2D | 166Er | ON72 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| KIR3DL1 | 167Er | DX9 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| NKG2A | 169Tm | Z199 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| DNAM-1 | 171Yb | DX11 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| Ki-67 | 172Yb | B56 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| KIR2DL1 | 173Yb | 143211 | R&D Systems | yes | yes | |
| CD94 | 174Yb | HP-3D9 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| AhR | 175Lu | FF3399 | eBioscience | yes | yes | |
| KIR2DL3 | 176Yb | 180701 | R&D Systems | yes | yes | |
| CD16 | 209Bi | 3G8 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| CD7 | 147Sm | CD7-6B7 | Fluidigm Sciences | yes | ||
| CD9 | 159Tb | SN4 | Thermofisher | yes | yes | |
| EAT2 | 158Di | yes | yes | |||
| GzmA | 150Nd | yes | yes |
| Reacts with | Antigen | Isotope | Clone | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | CD3 | PerCp-Cy5.5 | SK7 | BD Biosciences |
| CD3 | BUV395 | UCHT1 | BD Horizon | |
| CD4 | PerCP-Cy5.5 | RPA-T4 | Biolegend | |
| CD8a | FITC | RPA-T8 | Biolegend | |
| CD14 | PerCp-Cy5.5 | M5E2 | BD Biosciences | |
| CD19 | PerCp-Cy5.5 | HIB19 | BD Biosciences | |
| CD16 | BV786 | 3G8 | BD Biosciences | |
| CD56 | BV605 | HCD56 | Biolegend | |
| NKG2C | BUV737 | 134591 | BD Biosciences | |
| NKG2A | PE-Cy7 | Z199 | Beckman Coulter | |
| KIR3DL1 | FITC | DX9 | BD Biosciences | |
| Pan-KIR2D | FITC | NKVFS1 | Miltenyi Biotech | |
| HLA-E | PE | 3D12 | Biolegend | |
| CD103 | R718 | Ber-ACT8 | BD Biosciences | |
| CD49a | APC | TS2/7 | Biolegend | |
| CD94 | BV480 | HP-3D9 | BD Biosciences | |
| CD107a | BUV395 | H4A3 | BD Biosciences | |
| INFg | BV650 | 4S.b3 | Biolegend | |
| PD-1 | PE-CF594 | MIH4 | BD Biosciences | |
| CTLA-4 | BV421 | BNI3 | BD Biosciences | |
| Mouse | CD45 | AF700 | 30-F11 | Biolegend |
| CD45 | BUV395 | 30-F11 | BD Horizon | |
| CD3 | BV785 | 17A2 | Biolegend | |
| NK1.1 | BUV395 | PK136 | BD Horizon | |
| NK1.1 | PE-CF594 | PK136 | BD Pharmingen | |
| NKp46 | BUV737 | 29A1.4 | BD Pharmingen | |
| NKp46 | PerCp-eFluor710 | 29A1.4 | eBioscience | |
| NKG2A | PerCp-eFluor710 | 20d5 | eBioscience | |
| NKG2A | APC | 16A11 | Biolegend | |
| CD49a | PE | Ha31/8 | BD Pharmingen | |
| CD103 | APC | 2E7 | Biolegend | |
| CD103 | FITC | 2E7 | Biolegend | |
| PD-1 | PE-Cy7 | 29F.1A12 | Biolegend | |
| PD-1 | APC | J43 | eBioscience | |
| CTLA-4 | BV605 | UC0-4B9 | Biolegend | |
| Ly49A | FITC | YE1/48.10.6 | Biolegend | |
| EOMES | eFluor450 | Dan11mag | eBioscience | |
| CD8a | BV605 | 53-6.7 | Biolegend | |
| TIM-3 | BV510 | 5D12/TIM-3 | BD Biosciences | |
| LAG-3 | PE-Cy7 | C9B7W | Biolegend | |
| Granzyme B | Pacific Blue | GB11 | Biolegend | |
| CD107a | PE | ID4B | Biolegend |
References
- Stewart, C.; Ralyea, C.; Lockwood, S. Ovarian Cancer: An Integrated Review. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2019, 35, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. Cancer Stat Facts: Ovarian Cancer. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/ovary.html (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Hoogstad-van Evert, J.S.; Bekkers, R.; Ottevanger, N.; Jansen, J.H.; Massuger, L.; Dolstra, H. Harnessing natural killer cells for the treatment of ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 157, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisoni, E.; Imbimbo, M.; Zimmermann, S.; Valabrega, G. Ovarian Cancer Immunotherapy: Turning up the Heat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molgora, M.; Cortez, V.S.; Colonna, M. Killing the Invaders: NK Cell Impact in Tumors and Anti-Tumor Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greppi, M.; Tabellini, G.; Patrizi, O.; Candiani, S.; Decensi, A.; Parolini, S.; Sivori, S.; Pesce, S.; Paleari, L.; Marcenaro, E. Strengthening the AntiTumor NK Cell Function for the Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provinciali, N.; Greppi, M.; Pesce, S.; Rutigliani, M.; Briata, I.M.; Buttiron Webber, T.; Fava, M.; DeCensi, A.; Marcenaro, E. Case report: Variable response to immunotherapy in ovarian cancer: Our experience within the current state of the art. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1094017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, E.; Artis, D.; Colonna, M.; Diefenbach, A.; Di Santo, J.P.; Eberl, G.; Koyasu, S.; Locksley, R.M.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; Mebius, R.E.; et al. Innate Lymphoid Cells: 10 Years On. Cell 2018, 174, 1054–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiessling, R.; Klein, E.; Pross, H.; Wigzell, H. “Natural” killer cells in the mouse. II. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Characteristics of the killer cell. Eur. J. Immunol. 1975, 5, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Lei, Y.; Li, J.K.; Du, W.X.; Li, R.G.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Li, F.; Tan, H.B. Immune cells within the tumor microenvironment: Biological functions and roles in cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2020, 470, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducoin, K.; Oger, R.; Bilonda Mutala, L.; Deleine, C.; Jouand, N.; Desfrancois, J.; Podevin, J.; Duchalais, E.; Cruard, J.; Benlalam, H.; et al. Targeting NKG2A to boost anti-tumor CD8 T-cell responses in human colorectal cancer. Oncoimmunology 2022, 11, 2046931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, T.; Takeda, K.; Kaneda, H.; Matsumoto, H.; Hayakawa, Y.; Raulet, D.H.; Ikarashi, Y.; Kronenberg, M.; Yagita, H.; Kinoshita, K.; et al. NKG2A inhibits iNKT cell activation in hepatic injury. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzetta, V.; Bruni, E.; Terzoli, S.; Carenza, C.; Franzese, S.; Piazza, R.; Marzano, P.; Donadon, M.; Torzilli, G.; Cimino, M.; et al. NKG2A expression identifies a subset of human Vdelta2 T cells exerting the highest antitumor effector functions. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzetta, V.; Depierreux, D.; Colucci, F.; Mikulak, J.; Mavilio, D. NKG2A Immune Checkpoint in Vdelta2 T Cells: Emerging Application in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, S.; Greppi, M.; Grossi, F.; Del Zotto, G.; Moretta, L.; Sivori, S.; Genova, C.; Marcenaro, E. PD/1-PD-Ls Checkpoint: Insight on the Potential Role of NK Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Xin, Z.; Lin, M.; Hao, Z.; Chen, D.; He, T.; Zhao, L.; Wu, D.; Wu, P.; et al. Tissue-resident CD69(+) CXCR6(+) Natural Killer cells with exhausted phenotype accumulate in human non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Immunol. 2022, 52, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnell, A.; Bod, L.; Madi, A.; Kuchroo, V.K. The yin and yang of co-inhibitory receptors: Toward anti-tumor immunity without autoimmunity. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munari, E.; Quatrini, L.; Ciancaglini, C.; Eccher, A.; Bogina, G.; Moretta, L.; Mariotti, F.R. Immunotherapy targeting inhibitory checkpoints: The role of NK and other innate lymphoid cells. Semin. Immunol. 2022, 61–64, 101660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, L.; van der Burg, S.H.; van Hall, T. The NKG2A-HLA-E Axis as a Novel Checkpoint in the Tumor Microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 5549–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felices, M.; Chu, S.; Kodal, B.; Bendzick, L.; Ryan, C.; Lenvik, A.J.; Boylan, K.L.M.; Wong, H.C.; Skubitz, A.P.N.; Miller, J.S.; et al. IL-15 super-agonist (ALT-803) enhances natural killer (NK) cell function against ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 145, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, M.A.; Cooley, S.; Judson, P.L.; Ghebre, R.; Carson, L.F.; Argenta, P.A.; Jonson, A.L.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Curtsinger, J.; McKenna, D.; et al. A phase II study of allogeneic natural killer cell therapy to treat patients with recurrent ovarian and breast cancer. Cytotherapy 2011, 13, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, D.L.; Bendzick, L.; Pribyl, L.; McCullar, V.; Vogel, R.I.; Miller, J.S.; Geller, M.A.; Kaufman, D.S. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Natural Killer Cells for Treatment of Ovarian Cancer. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppendahl, L.D.; Dahl, C.M.; Miller, J.S.; Felices, M.; Geller, M.A. Natural Killer Cell-Based Immunotherapy in Gynecologic Malignancy: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppendahl, L.D.; Felices, M.; Bendzick, L.; Ryan, C.; Kodal, B.; Hinderlie, P.; Boylan, K.L.M.; Skubitz, A.P.N.; Miller, J.S.; Geller, M.A. Cytokine-induced memory-like natural killer cells have enhanced function, proliferation, and in vivo expansion against ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 153, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caligiuri, M.A. Human natural killer cells. Blood 2008, 112, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrega, P.; Bonaccorsi, I.; Di Carlo, E.; Morandi, B.; Paul, P.; Rizzello, V.; Cipollone, G.; Navarra, G.; Mingari, M.C.; Moretta, L.; et al. CD56(bright)perforin(low) noncytotoxic human NK cells are abundant in both healthy and neoplastic solid tissues and recirculate to secondary lymphoid organs via afferent lymph. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3805–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjorkstrom, N.K.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Michaelsson, J. Emerging insights into natural killer cells in human peripheral tissues. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, S.; Tabellini, G.; Cantoni, C.; Patrizi, O.; Coltrini, D.; Rampinelli, F.; Matta, J.; Vivier, E.; Moretta, A.; Parolini, S.; et al. B7-H6-mediated downregulation of NKp30 in NK cells contributes to ovarian carcinoma immune escape. Oncoimmunology 2015, 4, e1001224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsten, M.; Norell, H.; Bryceson, Y.T.; Poschke, I.; Schedvins, K.; Ljunggren, H.G.; Kiessling, R.; Malmberg, K.J. Primary human tumor cells expressing CD155 impair tumor targeting by down-regulating DNAM-1 on NK cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4921–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukesova, S.; Vroblova, V.; Tosner, J.; Kopecky, J.; Sedlakova, I.; Cermakova, E.; Vokurkova, D.; Kopecky, O. Comparative study of various subpopulations of cytotoxic cells in blood and ascites from patients with ovarian carcinoma. Contemp. Oncol. 2015, 19, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhn, O.; Ivarsson, M.A.; Gardner, L.; Hollinshead, M.; Stinchcombe, J.C.; Chen, P.; Shreeve, N.; Chazara, O.; Farrell, L.E.; Theorell, J.; et al. Distinctive phenotypes and functions of innate lymphoid cells in human decidua during early pregnancy. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquardt, N.; Kekalainen, E.; Chen, P.; Lourda, M.; Wilson, J.N.; Scharenberg, M.; Bergman, P.; Al-Ameri, M.; Hard, J.; Mold, J.E.; et al. Unique transcriptional and protein-expression signature in human lung tissue-resident NK cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuff, A.O.; Sillito, F.; Dertschnig, S.; Hall, A.; Luong, T.V.; Chakraverty, R.; Male, V. The Obese Liver Environment Mediates Conversion of NK Cells to a Less Cytotoxic ILC1-like Phenotype. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, J.; Blagih, J.; Ennis, D.; Leung, E.; Dowson, S.; Farquharson, M.; Tookman, L.A.; Orange, C.; Athineos, D.; Mason, S.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Trp53 and Brca2 Knockout to Generate Improved Murine Models of Ovarian High-Grade Serous Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6118–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lau, M.C.; Wong, M.T.; Newell, E.W.; Poidinger, M.; Chen, J. Cytofkit: A Bioconductor Package for an Integrated Mass Cytometry Data Analysis Pipeline. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1005112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurioka, A.; Cosgrove, C.; Simoni, Y.; van Wilgenburg, B.; Geremia, A.; Bjorkander, S.; Sverremark-Ekstrom, E.; Thurnheer, C.; Gunthard, H.F.; Khanna, N.; et al. CD161 Defines a Functionally Distinct Subset of Pro-Inflammatory Natural Killer Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, V.D.; Huang, Y.-W.; Delgado-Gonzalez, A.; Chen, S.-Y.; Donoso, K.; Sachs, K.; Gentles, A.J.; Allard, G.M.; Kolahi, K.S.; Howitt, B.E.; et al. High-grade serous ovarian tumor cells modulate NK cell function to create an immune-tolerant microenvironment. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Nieves, U.Y.; Tay, J.K.; Saumyaa, S.; Horowitz, N.B.; Shin, J.H.; Mohammad, I.A.; Luca, B.; Mundy, D.C.; Gulati, G.S.; Bedi, N.; et al. Landscape of innate lymphoid cells in human head and neck cancer reveals divergent NK cell states in the tumor microenvironment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2101169118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, A.; Vermi, W.; Lee, J.S.; Lonardi, S.; Gilfillan, S.; Newberry, R.D.; Cella, M.; Colonna, M. Intraepithelial type 1 innate lymphoid cells are a unique subset of IL-12- and IL-15-responsive IFN-gamma-producing cells. Immunity 2013, 38, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nham, T.; Poznanski, S.M.; Fan, I.Y.; Shenouda, M.M.; Chew, M.V.; Lee, A.J.; Vahedi, F.; Karimi, Y.; Butcher, M.; Lee, D.A.; et al. Ex vivo-expanded NK cells from blood and ascites of ovarian cancer patients are cytotoxic against autologous primary ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, J.; Schmidt, D.; Böhme, M.; Morenz, J.; Weise, W. [Leukocyte and lymphocyte populations in peripheral blood and malignant ascites in patients with ovarian carcinoma]. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 1994, 54, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheuk, S.; Schlums, H.; Gallais Serezal, I.; Martini, E.; Chiang, S.C.; Marquardt, N.; Gibbs, A.; Detlofsson, E.; Introini, A.; Forkel, M.; et al. CD49a Expression Defines Tissue-Resident CD8(+) T Cells Poised for Cytotoxic Function in Human Skin. Immunity 2017, 46, 287–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernson, E. (Sahlgrenska Center for Cancer Research, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Institute of Clinical Sciences, University of Gothenburg, 405 30 Gothenburg, Sweden); Karlsson, V. (Sahlgrenska Center for Cancer Research, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Institute of Clinical Sciences, University of Gothenburg, 405 30 Gothenburg, Sweden). Personal Observation, 2022.
- Kraemer, T.; Celik, A.A.; Huyton, T.; Kunze-Schumacher, H.; Blasczyk, R.; Bade-Doding, C. HLA-E: Presentation of a Broader Peptide Repertoire Impacts the Cellular Immune Response-Implications on HSCT Outcome. Stem Cells Int. 2015, 2015, 346714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingari, M.C.; Ponte, M.; Cantoni, C.; Vitale, C.; Schiavetti, F.; Bertone, S.; Bellomo, R.; Cappai, A.T.; Biassoni, R. HLA-class I-specific inhibitory receptors in human cytolytic T lymphocytes: Molecular characterization, distribution in lymphoid tissues and co-expression by individual T cells. Int. Immunol. 1997, 9, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hall, T.; Andre, P.; Horowitz, A.; Ruan, D.F.; Borst, L.; Zerbib, R.; Narni-Mancinelli, E.; van der Burg, S.H.; Vivier, E. Monalizumab: Inhibiting the novel immune checkpoint NKG2A. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salome, B.; Sfakianos, J.P.; Ranti, D.; Daza, J.; Bieber, C.; Charap, A.; Hammer, C.; Banchereau, R.; Farkas, A.M.; Ruan, D.F.; et al. NKG2A and HLA-E define an alternative immune checkpoint axis in bladder cancer. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 1027–1043.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roby, K.F.; Taylor, C.C.; Sweetwood, J.P.; Cheng, Y.; Pace, J.L.; Tawfik, O.; Persons, D.L.; Smith, P.G.; Terranova, P.F. Development of a syngeneic mouse model for events related to ovarian cancer. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.P.; Elstrand, M.B.; Holth, A.; Silins, I.; Berner, A.; Trope, C.G.; Davidson, B.; Risberg, B. NK- and B-Cell Infiltration Correlates with Worse Outcome in Metastatic Ovarian Carcinoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 125, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoni, Y.; Fehlings, M.; Kloverpris, H.N.; McGovern, N.; Koo, S.L.; Loh, C.Y.; Lim, S.; Kurioka, A.; Fergusson, J.R.; Tang, C.L.; et al. Human Innate Lymphoid Cell Subsets Possess Tissue-Type Based Heterogeneity in Phenotype and Frequency. Immunity 2017, 46, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, L.; Sluijter, M.; Sturm, G.; Charoentong, P.; Santegoets, S.J.; van Gulijk, M.; van Elsas, M.J.; Groeneveldt, C.; van Montfoort, N.; Finotello, F.; et al. NKG2A is a late immune checkpoint on CD8 T cells and marks repeated stimulation and cell division. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 150, 688–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre, P.; Denis, C.; Soulas, C.; Bourbon-Caillet, C.; Lopez, J.; Arnoux, T.; Blery, M.; Bonnafous, C.; Gauthier, L.; Morel, A.; et al. Anti-NKG2A mAb Is a Checkpoint Inhibitor that Promotes Anti-Tumor Immunity by Unleashing Both T and NK Cells. Cell 2018, 175, 1731–1743.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooden, M.; Lampen, M.; Jordanova, E.S.; Leffers, N.; Trimbos, J.B.; van der Burg, S.H.; Nijman, H.; van Hall, T. HLA-E expression by gynecological cancers restrains tumor-infiltrating CD8(+) T lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10656–10661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmberg, K.J.; Levitsky, V.; Norell, H.; de Matos, C.T.; Carlsten, M.; Schedvins, K.; Rabbani, H.; Moretta, A.; Soderstrom, K.; Levitskaya, J.; et al. IFN-gamma protects short-term ovarian carcinoma cell lines from CTL lysis via a CD94/NKG2A-dependent mechanism. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, J.G.; Doyle, A.D.P.; Graham, L.V.; Khakoo, S.I.; Blunt, M.D. Disruption of the NKG2A:HLA-E Immune Checkpoint Axis to Enhance NK Cell Activation against Cancer. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innate Pharma Provides Update on Astrazeneca-Sponsored Interlink-1 Phase 3 Study. Available online: https://www.innate-pharma.com/media/all-press-releases/innate-pharma-provides-update-astrazeneca-sponsored-interlink-1-phase-3-study (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?cond=&term=Monalizumab&cntry=&state=&city=&dist= (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Komdeur, F.L.; Wouters, M.C.A.; Workel, H.H.; Tiljans, A.M.; Terwindt, A.L.J.; Brunekreeft, K.L.; Plat, A.; Klip, H.G.; Eggink, F.A.; Leffers, N.; et al. CD103+ intraepithelial T cells in high-grade serous ovarian cancer are phenotypically diverse TCRαβ+ CD8αβ+ T cells that can be targeted for cancer immunotherapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 75130–75144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuntoli, R.L.; Webb, T.j.; Zoso, A.; Rogers, O.; Diaz-Montez, T.P.; Bristow, R.E.; Oelke, M. Ovarian Cancer-Associated Ascites Demonstrates Altered Immune Environment: Implications for Antitumor Immunity. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 2875–2884. [Google Scholar]
- Drakes, M.L.; Stiff, P.L. Regulation of Ovarian Cancer Prognosis by Immune Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2018, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, J.R.; Milne, K.; Watson, P.; Deleeuw, R.J.; Nelson, B.H. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes expressing the tissue resident memory marker CD103 are associated with increased survival in high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernson, E.; Huhn, O.; Karlsson, V.; Hawkes, D.; Lycke, M.; Cazzetta, V.; Mikulak, J.; Hall, J.; Piskorz, A.M.; Portuesi, R.; et al. Identification of Tissue-Resident Natural Killer and T Lymphocytes with Anti-Tumor Properties in Ascites of Ovarian Cancer Patients. Cancers 2023, 15, 3362. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133362
Bernson E, Huhn O, Karlsson V, Hawkes D, Lycke M, Cazzetta V, Mikulak J, Hall J, Piskorz AM, Portuesi R, et al. Identification of Tissue-Resident Natural Killer and T Lymphocytes with Anti-Tumor Properties in Ascites of Ovarian Cancer Patients. Cancers. 2023; 15(13):3362. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133362
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernson, Elin, Oisín Huhn, Veronika Karlsson, Delia Hawkes, Maria Lycke, Valentina Cazzetta, Joanna Mikulak, James Hall, Anna M. Piskorz, Rosalba Portuesi, and et al. 2023. "Identification of Tissue-Resident Natural Killer and T Lymphocytes with Anti-Tumor Properties in Ascites of Ovarian Cancer Patients" Cancers 15, no. 13: 3362. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133362
APA StyleBernson, E., Huhn, O., Karlsson, V., Hawkes, D., Lycke, M., Cazzetta, V., Mikulak, J., Hall, J., Piskorz, A. M., Portuesi, R., Vitobello, D., Fiamengo, B., Siesto, G., Horowitz, A., Ghadially, H., Mavilio, D., Brenton, J. D., Sundfeldt, K., & Colucci, F. (2023). Identification of Tissue-Resident Natural Killer and T Lymphocytes with Anti-Tumor Properties in Ascites of Ovarian Cancer Patients. Cancers, 15(13), 3362. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15133362









