Pleural Neoplasms—What Could MRI Change?
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Pleural Neoplasms and Their Classification
3.1. Mesothelial Tumours of the Pleura
3.1.1. Benign and Preinvasive Mesothelial Tumors
3.1.2. Mesothelioma
3.2. Mesenchymal Tumours of the Pleura
3.2.1. Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma
3.2.2. Angiosarcoma
3.2.3. Synovial Sarcoma
3.2.4. Solitary Fibrous Tumor and Malignant Solitary Fibrous Tumor
3.2.5. Desmoid-Type Fibromatosis
3.2.6. Calcifying Fibrous Tumor
3.2.7. Desmoplastic Round Cell Tumor
3.3. Lymphoproliferative Disorders of the Pleura
3.3.1. Primary Effusion Lymphoma
3.3.2. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Associated with Chronic Inflammation
3.4. Pleural Metastases
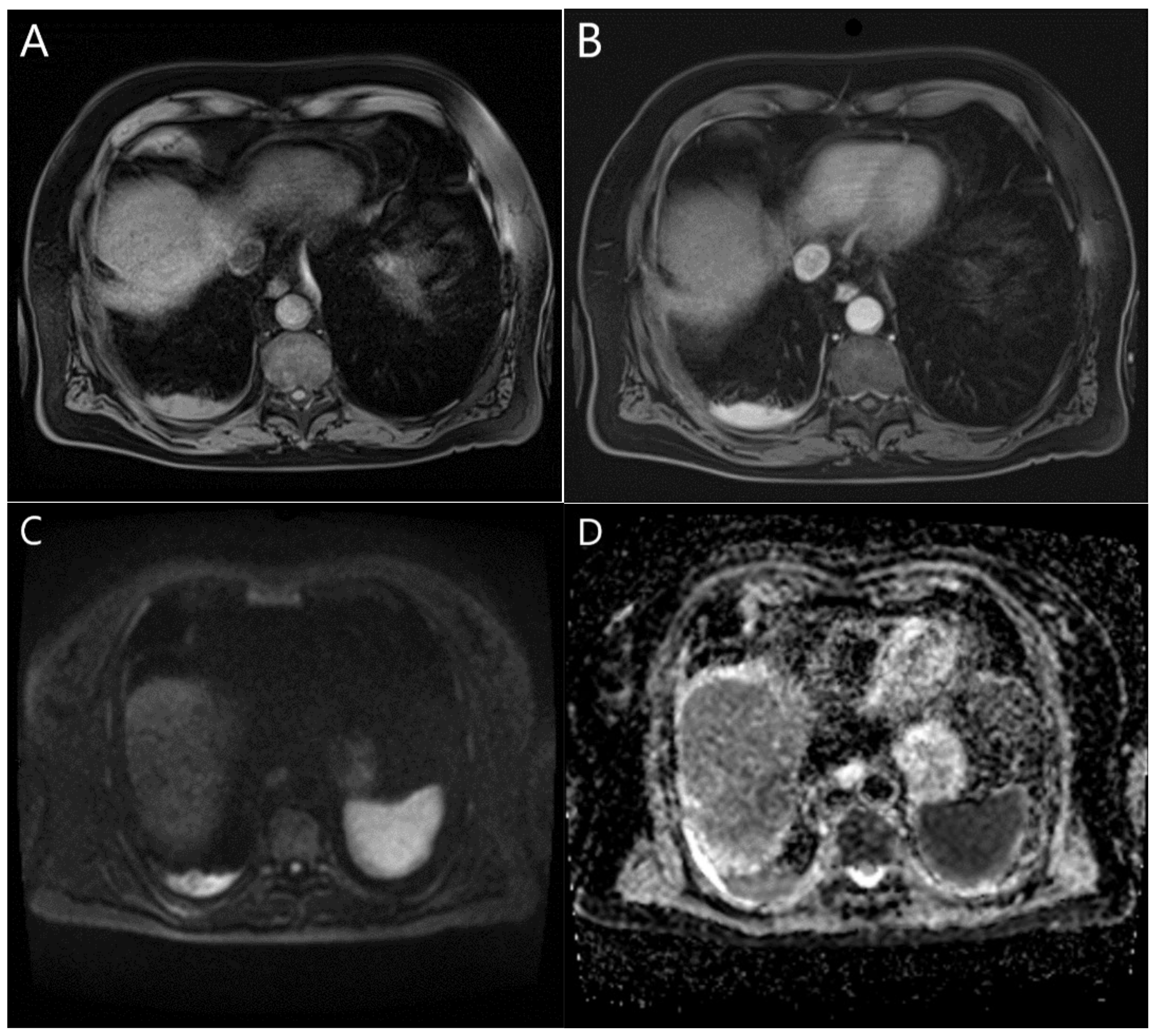
4. MRI as a Diagnostic Tool in Pleural Neoplasms
4.1. MRI and Its Potential as a Diagnostic Tool in Pleural Malignancies
4.2. MRI and Primary Pleural Tumours
4.2.1. MRI and MPM
4.2.2. MRI and SFT
4.2.3. MRI and Lymphomas
4.2.4. MRI and Pleural Lipoma and Liposarcoma
4.2.5. MRI and Pleural Leiomyoma and Leiomyosarcoma
4.2.6. MRI and Other Sarcomas of the Pleura
4.2.7. MRI and Pleural Hemangioma
4.2.8. MRI and Pleural Hemangioendothelioma
4.2.9. MRI and the Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors
4.2.10. MRI and DSRCT
4.3. MRI and Pleural Infiltration and Metastases
4.3.1. MRI and Thymoma
4.3.2. MRI and Bronchial and Lung Cancer
4.3.3. MRI and Pleural Metastases
4.4. MRI and Selected Pleural Pathologies That May Be Associated with Pleural Neoplasms
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gill, R.R. Imaging of Mesothelioma. In Malignant Mesothelioma; Recent Results in Cancer Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 189, pp. 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B.W.; Betancourt, S.L.; Shroff, G.S.; Lichtenberger, J.P., III. MR Imaging of Pleural Neoplasms. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2018, 27, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, M.T.; Viswanathan, C.; Godoy, M.B.; Carter, B.W.; Marom, E.M. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Role of CT, MRI, and PET/CT in Staging Evaluation and Treatment Considerations. Semin. Roentgenol. 2013, 48, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Han, Z.; Tang, X.; Yin, H.; Zhang, J. Diffusion-weighted imaging diagnostic algorithm in patients with suspected pleural malignancy. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 9038–9047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, R.R.; Umeoka, S.; Mamata, H.; Tilleman, T.R.; Stanwell, P.; Woodhams, R.; Padera, R.F.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; Hatabu, H. Diffusion-Weighted MRI of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Preliminary Assessment of Apparent Diffusion Coefficient in Histologic Subtypes. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 195, W125–W130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopar-Nieto, R.; Cabello-López, A.; Juárez-Pérez, C.A.; Haro-García, L.C.; Jiménez-Ramírez, C.; Aguilar-Madrid, G. Actual-ización sobre la epidemiología, fisiopatología, diagnóstico y tratamiento del mesotelioma maligno pleural. Update on epide-miology, pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Rev. Med. Inst. Mex. Seguro Soc. 2016, 54, 770–776. [Google Scholar]
- See, K.C.; Lee, P. Advances in the diagnosis of pleural disease in lung cancer. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2011, 5, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, E.J.; Matin, T.N.; Gleeson, F.V. Imaging of the pleura. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 32, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, S.; Bhalla, A.S.; Jana, M. Pediatric Chest MRI: A Review. Indian J. Pediatr. 2019, 86, 842–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Tunariu, N.; Collins, D.J.; Blackledge, M.D.; Riddell, A.M.; Leach, M.O.; Popat, S.; Koh, D.-M. Response evaluation in mesothelioma: Beyond RECIST. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittner, R.C. Diagnostic imaging in pleural diseases. Pneumologie 2004, 58, 238–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, V.; McCracken, D.J.; Rahman, N.M.; Epelbaum, O. Contemporary Approach to the Diagnosis of Malignant Pleural Effusion. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019, 16, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomo, L.; Feragalli, B.; Sacco, R.; Merlino, B.; Storto, M.L. Malignant pleural disease. Eur. J. Radiol. 2000, 34, 98–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y. New Applications of Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Thoracic Oncology. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 35, 027–040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena, E.; Ojiaku, M.; Inacio, J.R.; Gupta, A.; Macdonald, D.B.; Shabana, W.; Seely, J.M.; Rybicki, F.J.; Dennie, C.; Thornhill, R.E. Can CT and MR Shape and Textural Features Differentiate Benign Versus Malignant Pleural Lesions? Acad. Radiol. 2017, 24, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.S.C.; Seethamraju, R.T.; Bueno, R.; Gill, R.R. Clinical Implementation of a Free-Breathing, Motion-Robust Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI Protocol to Evaluate Pleural Tumors. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2020, 215, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallifax, R.; Talwar, A.; Wrightson, J.; Edey, A.; Gleeson, F. State-of-the-art: Radiological investigation of pleural disease. Respir. Med. 2017, 124, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibel, R.; Tuengerthal, S.; Schoenberg, S.O. The role of new imaging techniques in diagnosis and staging of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2003, 15, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, B.M.; Lee, H.-S.; Raghuram, A.C.; Strange, C.; Mason, J.; Strange, T.; Delgado, J.; Sugarbaker, D.J. Preoperative prediction of unresectability in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 159, 2512–2520.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; Chirieac, L.R.; Dacic, S.; Duhig, E.; Flieder, D.B.; et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors: Impact of Genetic, Clinical and Radiologic Advances Since the 2004 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, J.L.; Dacic, S.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Attanoos, R.L.; Butnor, K.J.; Churg, A.; Husain, A.N.; Kadota, K.; Khoor, A.; Nicholson, A.G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Pleura: Advances Since the 2015 Classification. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpathiou, G.M.; Hiroshima, K.M.; Peoc’h, M.M. Adenomatoid Tumor: A Review of Pathology with Focus on Unusual Presentations and Sites, Histogenesis, Differential Diagnosis, and Molecular and Clinical Aspects with a Historic Overview of Its Description. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2020, 27, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minato, H.; Nojima, T.; Kurose, N.; Kinoshita, E. Adenomatoid tumor of the pleura. Pathol. Int. 2009, 59, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malpica, A.; Sant’ambrogio, S.; Deavers, M.T.; Silva, E.G. Well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma of the female peritoneum: A clinicopathologic study of 26 cases. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churg, A.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Roden, A.C.; Attanoos, R.; von der Thusen, J.H.; Tsao, M.-S.; Chang, N.; De Perrot, M.; Dacic, S. Malignant mesothelioma in situ: Morphologic features and clinical outcome. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dacic, S. Pleural mesothelioma classification—Update and challenges. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasley, M.B.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Dacic, S. Pleural mesothelioma classification update. Virchows Arch. 2021, 478, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strange, C.D.; Shroff, G.S.; Ahuja, J.; Vlahos, I.; Benveniste, M.F.; Truong, M.T. Imaging of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Pearls and Pitfalls. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2021, 42, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadowski, B.; De Rienzo, A.; Bueno, R. The Molecular Basis of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2020, 30, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attanoos, R.L.; Churg, A.; Galateau-Salle, F.; Gibbs, A.R.; Roggli, V.L. Malignant Mesothelioma and Its Non-Asbestos Causes. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, P.M.; Shroff, G.S.; Wu, C.C.; Rice, D.R.; Carter, B.W. Staging of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. In Diagnostic Imaging for Thoracic Surgery; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 189–199. ISBN 978-3-319-89893-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.K.; Bydder, S. Management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 3, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinn, K.; Mosleh, B.; Hoda, M.A. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: Recent developments. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2021, 33, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kindler, H.L.; Ismaila, N.; Armato, S.G., III; Bueno, R.; Hesdorffer, M.; Jahan, T.; Jones, C.M.; Miettinen, M.; Pass, H.; Rimner, A.; et al. Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1343–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Hamanaka, R.; Oiwa, K.; Nakazato, K.; Masuda, R.; Iwazaki, M. Localized malignant pleural mesothelioma. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 60, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Y.P.; Dong, F.; Dubuc, A.M.; Cin, P.D.; Bueno, R.; Chirieac, L.R. Molecular characterization of localized pleural mesothelioma. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fjaellegaard, K.; Petersen, J.K.; Stamp, I.M.; Hoegholm, A.; Clementsen, P.F.; Bodtger, U. Pleural epithelioid hemangioendothelioma mimicking pleural empyema: A case report. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 31, 101194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahrouqi, T.; Al-Baali, D.; Al-Sawafi, Y. Pleural epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: Clinical course and response to treatment. Saudi J. Med. Med. Sci. 2022, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenaka, M.; Ichiki, Y.; Nabe, Y.; Tsuda, Y.; Kuwata, T.; Chikaishi, Y.; Hirai, A.; Imanishi, N.; Yoneda, K.; Tanaka, F. Difficulty of treatment for pleural epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A report of a case. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 68, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hafez, A.A. Primary diagnosis of epithelioid hemangioendothelioma in pleural effusion based on cytologic features and vascular marker immunocytochemical staining. J. Cytol. 2021, 38, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Chung, M.J.; Jeong, K.C.; Hahn, C.H.; Hong, K.P.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, Y.T. Pleural Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma. Yonsei Med. J. 2008, 49, 1036–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Ye, C.; Ying, Y.; Mao, H. Pleural Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: A Case Report and Literature Review. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2016, 108, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.F.; Huang, Y.; Guo, J.H.; Zhang, W.; Hou, L.K.; Wu, C.Y.; Zhang, L.P. Often misdiagnosed primary pleural epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A clinicopathological analysis of five cases. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi Chin. J. Pathol. 2020, 49, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, A.; Chawla, M.; Cohen, P.J.; Kwon, J.S. Pleural Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma. Lung 2012, 190, 469–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedhai, Y.R.; Basnyat, S.; Golamari, R.; Koirala, A.; Yuan, M. Primary pleural angiosarcoma: Case report and literature review. SAGE Open Med. Case Rep. 2020, 8, 2050313X20904595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, G.; Orzes, N.; Uccelli, S.; Cettolo, F.; Arici, M.; Ciarfaglia, M.; Fisogni, S.; Marchetti, G.; Rocchetti, C. Spontaneous synchronous bilateral hemothorax as the only finding in primary pleural angiosarcoma: A case report and a literature review. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2021, 91, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zaid, A.; Mohammed, S. Primary Pleural Angiosarcoma in a 63-Year-Old Gentleman. Case Rep. Pulmonol. 2013, 2013, 974567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Cai, J.; Wei, J.; Liu, A.M.; Zeng, Z.M. Characteristics and outcomes of primary pleural angiosarcoma: A retrospective study of 43 published cases. Medicine 2022, 101, e28785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Goyal, K.; Bhatt, R.; Bansal, S.; Mishra, M. Primary Pleural Synovial Sarcoma: A Rare Cause of Hemorrhagic Pleural Effusion. Adv. Respir. Med. 2021, 89, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Li, L.; Shen, W.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Xin, T.; Huang, D.; Song, X.; Lv, Y.; et al. Pleural synovial sarcoma patient treated with combined chemotherapy and Endostar, plus sunitinib maintenance therapy: A case report and review of the literature. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 1141–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsurada, N.; Ohnishi, H.; Ikeda, M.; Jimbo, N.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Okamura, K. Primary pleural synovial sarcoma with repeated resection leading to long-term survival. Respirol. Case Rep. 2019, 7, e00480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lin, J.; Sun, H.; Xie, S. Primary pleural synovial sarcoma in an adolescent: A case report. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 3771–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimi, S.H.; Inam, H.; Chagan, F.K.; Choudry, U.K. Solitary fibrous pleural tumor. A rare and challenging case. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2020, 66, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savu, C.; Melinte, A.; Posea, R.; Galie, N.; Balescu, I.; Diaconu, C.; Cretoiu, D.; Dima, S.; Filipescu, A.; Balalau, C.; et al. Pleural Solitary Fibrous Tumors—A Retrospective Study on 45 Patients. Medicina 2020, 56, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, L.S.F.; Álvarez, D.F.; MurielRamos, M.; Alberca, A.H.; Simó, G.V. Fibroma pleural gigante. Giant pleural fibroma. An. Pediatr. 2003, 58, 604–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attanoos, R.L.; Pugh, M.R. The Diagnosis of Pleural Tumors Other Than Mesothelioma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 902–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarek, T.; Szpor, J.; Pankowski, J.; Okoń, K. Desmoid tumor of lung with pleural involvement—The case of unique location of aggressive fibromatosis. Folia Med. Crac. 2015, 55, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, T.; Mal, G.; Majeed, F.A.; Chai, S.M.; Lee, Y.C.G. A massive pleural-based desmoid tumour. Respirol. Case Rep. 2016, 5, e00205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permata, L.; Hayati, F. Pleural desmoid tumor: A rare site of presentation. Radiol. Case Rep. 2022, 17, 2837–2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, B. Multiple calcifying fibrous tumor of the pleura: A case report. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 2271–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrad, M.; LaFramboise, W.A.; Lyons, M.A.; Bittar, H.T.; Yousem, S.A. Whole-exome sequencing identifies unique mutations and copy number losses in calcifying fibrous tumor of the pleura: Report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 78, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mito, K.; Kashima, K.; Daa, T.; Kondoh, Y.; Miura, T.; Kawahara, K.; Nakayama, I.; Yokoyama, S. Multiple calcifying fibrous tumors of the pleura. Virchows Arch. 2005, 446, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeue, T.; Ohi, I.; Noguchi, S.; Fukao, A.; Terashita, S.; Horikawa, S.; Sugita, T. Desmoplastic Small Round Cell Tumor of the Pleura Successfully Treated with a Lower Dose of Pazopanib. Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 2463–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes-Jordan, A.; LaQuaglia, M.P.; Modak, S. Management of desmoplastic small round cell tumor. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2016, 25, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baburao, A.; Maurya, P.; Chakenahalli, A.; Narayanswamy, H. A rare cause of bilateral pleural effusion—Desmoplastic small round cell tumor. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2021, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, Z.; Shaohong, H.; Wenzhao, Z.; Lijia, G. Misdiagnosed desmoplastic small round cell tumor of the pleura: Case report and literature review. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 60–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, A.; Boerner, K.; Germer, C.-T.; Wiegering, A. Desmoplastic Small Round Cell Tumors: A review with focus on clinical management and therapeutic options. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 93, 102140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makis, W.; Stern, J. Hepatitis C–Related Primary Effusion Lymphoma of the Pleura and Peritoneum, Imaged With F-18 FDG PET/CT. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2010, 35, 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Xiao, P. Primary Effusion Lymphoma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2013, 137, 1152–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkhede, M.; Arora, S.; Ujjani, C. Primary effusion lymphoma: Current perspectives. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 3747–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakuwa, T.; Tresnasari, K.; Rahadiani, N.; Miwa, H.; Daibata, M.; Aozasa, K. Cell origin of pyothorax-associated lymphoma: A lymphoma strongly associated with Epstein–Barr virus infection. Leukemia 2008, 22, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loong, F.; Chan, A.C.; Ho, B.C.; Chau, Y.-P.; Lee, H.-Y.; Cheuk, W.; Yuen, W.-K.; Ng, W.-S.; Cheung, H.-L.; Chan, J.K.C. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with chronic inflammation as an incidental finding and new clinical scenarios. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuka, S.-I.; Yao, M.; Hoshida, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Iuchi, K.; Aozasa, K. Pyothorax-Associated Lymphoma: A Review of 106 Cases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 4255–4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres, J.; Gleeson, F. Imaging of the Pleura. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 31, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, R.R.; Gerbaudo, V.H.; Jacobson, F.L.; Trotman-Dickenson, B.; Matsuoka, S.; Hunsaker, A.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; Hatabu, H. MR Imaging of Benign and Malignant Pleural Disease. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. N. Am. 2008, 16, 319–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessôa, F.M.C.; De Melo, A.S.A.; Souza, A.S.; De Souza, L.S.; Hochhegger, B.; Zanetti, G.; Marchiori, E. Applications of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Thorax in Pleural Diseases: A State-of-the-Art Review. Lung 2016, 194, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyant, M.J.; Flores, R.M. Imaging of pleural and chest wall tumors. Thorac. Surg. Clin. 2004, 14, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, D.R.F.; Jones, K.D. Diagnosis of Mesothelioma. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2019, 13, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, N.R.; Gleeson, F.V. Imaging of Pleural Disease. Clin. Chest Med. 2006, 27, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plathow, C.; Klopp, M.; Thieke, C.; Herth, F.; Thomas, A.; Schmaehl, A.; Zuna, I.; Kauczor, H.-U. Therapy response in malignant pleural mesothelioma-role of MRI using RECIST, modified RECIST and volumetric approaches in comparison with CT. Eur. Radiol. 2008, 18, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eibschutz, L.S.; Flors, L.; Taravat, F.; Gholamrezanezhad, A. Imaging Approach to Disease of the Pleura. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2022, 52, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamuro, M.; Gerbaudo, V.H.; Gill, R.R.; Jacobson, F.L.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; Hatabu, H. Morphologic and functional imaging of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Eur. J. Radiol. 2007, 64, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Infante, B.; Michel, F.J. Mesotelioma pleural malign. Malign pleural mesothelioma. An. Sist. Sanit. Navar. 2005, 28 (Suppl. S1), 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marom, E.M.; Erasmus, J.J.; Pass, H.I.; Patz, E.F. The role of imaging in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Semin. Oncol. 2002, 29, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Reddy, G.P.; Gotway, M.B.; Higgins, C.B.; Jablons, D.M.; Ramaswamy, M.; Hawkins, R.A.; Webb, W.R. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Evaluation with CT, MR Imaging, and PET. RadioGraphics 2004, 24, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Hierholzer, J.; Bittner, R.C.; Chen, J.; Huang, L. Magnetic resonance imaging in distinguishing malignant from benign pleural disease. Chin. Med. J. 2001, 114, 645–649. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, D.; Mak, S.; Mallia, A.; Jeljeli, S.; Stirling, J.; Goh, V.; Bille, A.; Cook, G. Loco-regional staging of malignant pleural mesothelioma by integrated 18F-FDG PET/MRI. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 115, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsim, S.; Cowell, G.W.; Kidd, A.; Woodward, R.; Alexander, L.; Kelly, C.; Foster, J.E.; Blyth, K.G. A comparison between MRI and CT in the assessment of primary tumour volume in mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2020, 150, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, I.; Sharif, S.; Routledge, T.; Scarci, M. What is the best way to diagnose and stage malignant pleural mesothelioma? Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 12, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.D.; Lee, Y.G. Management of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Clin. Chest Med. 2006, 27, 335–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.-A.; Bock, M.; Plathow, C.; Wasser, K.; Fink, C.; Zuna, I.; Schmähl, A.; Berger, I.; Kauczor, H.-U.; Schoenberg, S.O. Asbestos-related pleural disease: Value of dedicated magnetic resonance imaging techniques. Investig. Radiol. 2004, 39, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickell, L.T., Jr.; Lichtenberger, J.P., III; Khorashadi, L.; Abbott, G.F.; Carter, B.W. Multimodality Imaging for Characterization, Classification, and Staging of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Radiographics 2014, 34, 1692–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, A.S.; Mastronarde, J.G. Imaging of pleural masses: Which to choose? Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bittner, R.C.; Schnoy, N.; Schönfeld, N.; Grassot, A.; Loddenkemper, R.; Lode, H.; Kaiser, D.; Krumhaar, D.; Felix, R. Hochauflösende Magnetresonanztomographie (HR-MRT) von Pleura und Thoraxwand: Normalbefund und pathologische Veränderungen. High-resolution magnetic resonance tomography (HR-MRT) of the pleura and thoracic wall: Normal findings and pathological changes. Rofo 1995, 162, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heelan, R. Staging and response to therapy of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2004, 45, S59–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armato, S.G.; Francis, R.; Katz, S.I.; Ak, G.; Opitz, I.; Gudmundsson, E.; Blyth, K.G.; Gupta, A. Imaging in pleural mesothelioma: A review of the 14th International Conference of the International Mesothelioma Interest Group. Lung Cancer 2019, 130, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delourme, J.; Dhalluin, X.; Cortot, A.; Lafitte, J.-J.; Scherpereel, A. Prise en charge diagnostique et thérapeutique du mésothéliome pleural malin. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: Diagnosis and treatment. Rev. Pneumol. Clin. 2013, 69, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dynes, M.C.; White, E.M.; Fry, W.A.; Ghahremani, G.G. Imaging manifestations of pleural tumors. RadioGraphics 1992, 12, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payer, M.; Von Briel, T. Intradural pleural malignant mesothelioma. Acta Neurochir. 2007, 149, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downer, N.J.; Ali, N.J.; Au-Yong, I.T.H. Investigating pleural thickening. BMJ 2013, 346, e8376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paula, M.C.F.; Escuissato, D.L.; Belém, L.C.; Zanetti, G.; Souza, A.S.; Hochhegger, B.; Nobre, L.F.; Marchiori, E. Focal pleural tumorlike conditions: Nodules and masses beyond mesotheliomas and metastasis. Respir. Med. 2015, 109, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.O.; Hooper, C.E.; Searle, J.; Darby, M.; White, P.; Harvey, J.E.; Braybrooke, J.P.; Maskell, N.A.; Masani, V.; Lyburn, I.D. 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT and dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI as imaging biomarkers in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2018, 39, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, Y.; Yui, M.; Aoyagi, K.; Kishida, Y.; Seki, S.; Koyama, H.; Yoshikawa, T. Whole-Body MRI: Comparison of Its Capability for TNM Staging of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma with That of Coregistered PET/MRI, Integrated FDG PET/CT, and Conventional Imaging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, L.; Ardissone, F.; Gned, D.; Sverzellati, N.; Piacibello, E.; Veltri, A. Diagnostic Imaging and Workup of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Acta Bio Med. Atenei Parm. 2017, 88, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; David, S.J.; Skarin, A.T. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. In Thoracic Oncology. Cancer Treatment and Research; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2001; Volume 105, pp. 327–373. ISBN 978-1-4615-1589-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blyth, K.G.; Murphy, D.J. Progress and challenges in Mesothelioma: From bench to bedside. Respir. Med. 2018, 134, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomšič, M.V.; Korošec, P.; Kovač, V.; Bisdas, S.; Popovič, K. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Prediction of outcome based on DCE-MRI measurements in patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesel, F.L.; Bischoff, H.; von Tengg-Kobligk, H.; Weber, M.-A.; Zechmann, C.M.; Kauczor, H.-U.; Knopp, M.V. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of malignant pleural mesothelioma: A feasibility study of noninvasive assessment, therapeutic follow-up, and possible predictor of improved outcome. Chest 2006, 129, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grondin, S.C.; Sugarbaker, D.J. Malignant mesothelioma of the pleural space. Oncology 1999, 13, 919–932. [Google Scholar]
- Bonomi, M.; De Filippis, C.; Lopci, E.; Gianoncelli, L.; Rizzardi, G.; Cerchiaro, E.; Bortolotti, L.; Zanello, A.; Ceresoli, G.L. Clinical staging of malignant pleural mesothelioma: Current perspectives. Lung Cancer Targets Ther. 2017, 8, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entwisle, J. The use of magnetic resonance imaging in malignant mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2004, 45, S69–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armato, S.G.; Blyth, K.G.; Keating, J.J.; Katz, S.; Tsim, S.; Coolen, J.; Gudmundsson, E.; Opitz, I.; Nowak, A.K. Imaging in pleural mesothelioma: A review of the 13th International Conference of the International Mesothelioma Interest Group. Lung Cancer 2016, 101, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romei, C.; Fanni, S.C.; Volpi, F.; Milazzo, A.; D’amore, C.A.; Colligiani, L.; Neri, E.; De Liperi, A.; Stella, G.M.; Bortolotto, C. New Updates of the Imaging Role in Diagnosis, Staging, and Response Treatment of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botticella, A.; Defraene, G.; Nackaerts, K.; Deroose, C.M.; Coolen, J.; Nafteux, P.; Peeters, S.; Ricardi, U.; De Ruysscher, D. Optimal gross tumor volume definition in lung-sparing intensity modulated radiotherapy for pleural mesothelioma: An in silico study. Acta Oncol. 2016, 55, 1450–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giesel, F.L.; Choyke, P.L.; Mehndiratta, A.; Zechmann, C.M.; von Tengg-Kobligk, H.; Kayser, K.; Bischoff, H.; Hintze, C.; Delorme, S.; Weber, M.; et al. Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma—Initial Results of Tumor Microcirculation and its Correlation to Microvessel Density (CD-34). Acad. Radiol. 2008, 15, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomšič, M.V.; Bisdas, S.; Kovač, V.; Serša, I.; Popovič, K. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI of malignant pleural mesothelioma: A comparative study of pharmacokinetic models and correlation with mRECIST criteria. Cancer Imaging 2019, 19, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Rimner, A.; Deasy, J.; Hunt, M.A.; Tyagi, N. Dual-input tracer kinetic modeling of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in thoracic malignancies. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2019, 20, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usuda, K.; Iwai, S.; Funasaki, A.; Sekimura, A.; Motono, N.; Matoba, M.; Doai, M.; Yamada, S.; Ueda, Y.; Uramoto, H. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Can Differentiate between Malignant and Benign Pleural Diseases. Cancers 2019, 11, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razek, A.A. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging of chest tumors. Cancer Imaging 2012, 12, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inan, N.; Sarisoy, H.T.; Çam, I.; Sakçi, Z.; Arslan, A. Diffusion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in the Differential Diagnosis of Benign and Metastatic Malignant Pleural Thickening. J. Thorac. Imaging 2016, 31, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, F.; D’amore, C.A.; Colligiani, L.; Milazzo, A.; Cavaliere, S.; De Liperi, A.; Neri, E.; Romei, C. The Use of Chest Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Diagnosis. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginat, D.T.; Bokhari, A.; Bhatt, S.; Dogra, V. Imaging Features of Solitary Fibrous Tumors. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Arab, W. Solitary fibrous tumours of the pleura. Eur. J. Cardio Thorac. Surg. 2012, 41, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Perrot, M.; Fischer, S.; Bründler, M.-A.; Sekine, Y.; Keshavjee, S. Solitary fibrous tumors of the pleura. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2002, 74, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnemai-Azar, A.A.; Rahnemai-Aazr, A.A.; Robinson, P.; Pham, S. Solitary fibrous tumour of the pleura masquerading as catecholamine-secreting paraganglioma. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2013009939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-K.; Duddalwar, V.; Rouse, H.; Lau, E.; Bekhit, E.; Hennessy, O. Extranodal lymphoma in the thorax: Cross-sectional imaging findings. Clin. Radiol. 2009, 64, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bligh, M.P.; Borgaonkar, J.N.; Burrell, S.C.; MacDonald, D.A.; Manos, D. Spectrum of CT Findings in Thoracic Extranodal Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Radiographics 2017, 37, 439–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M. Pleural lipoma: Report of a case. Kyobu Geka Jpn. J. Thorac. Surg. 2005, 58, 1185–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Haratake, N.; Shoji, F.; Kozuma, Y.; Okamoto, T.; Maehara, Y. Giant Leiomyoma Arising from the Mediastinal Pleura: A Case Report. Ann. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 23, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Daraji, W.I.; Salman, W.D.; Nakhuda, Y.; Zaman, F.; Eyden, B. Primary Smooth Muscle Tumor of the Pleura: A Clinicopathological Case Report with Ultrastructural Observations and a Review of the Literature. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2005, 29, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzoyan, M.; Muslimani, A.; Setrakian, S.; Swedeh, M.; Daw, H.A. Primary Pleuropulmonary Synovial Sarcoma. Clin. Lung Cancer 2008, 9, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, A.A.; Franks, T.J.; Pugatch, R.D.; Galvin, J.R. From the archives of the AFIP: Pleuropulmonary synovial sarcoma. RadioGraphics 2006, 26, 923–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Xu, S. Imaging findings from a case of pleural low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma similar to mesothelioma with pleural effusion. Clin. Respir. J. 2016, 10, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matono, R.; Maruyama, R.; Ide, S.; Kitagawa, D.; Tanaka, J.; Saeki, H.; Shimokama, T.; Higashi, H. Extraskeletal osteosarcoma of the pleura: A case report. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2008, 56, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, G.; Agrawal, S.; Patil, P. Intrathoracic hemangioma. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2020, 16, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagi, K.; Matsutake, T.; Fukushima, K.; Mukae, H.; Kurohama, H.; Matsumoto, H. A refractory pleural effusion caused by a pleural capillary hemangioma. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2021, 33, 101384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoldi, L.A.S.; Vigil, L.V.; Solis, R.A. Pleural effusion caused by a capillary hemangioma in the pleural cavity. Derrame pleural secundario a un hemangioma capilar de localización pleural. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2016, 52, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, B.M.; Ben-Arie, G.; Samueli, B.; Azulay, A.A. Pleural hemangioma: A case report and review of the literature. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 228, 153650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotty, E.J.; McAdams, H.P.; Erasmus, J.J.; Sporn, T.A.; Roggli, V.L. Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the pleura: Clinical and radiologic features. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2000, 175, 1545–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askari, E.; Yaghmaei, S.; Haseli, S.; Totkaboni, M.P. Primary Pleural Hemangioendothelioma: A Case Report and Literature Review. Case Rep. Oncol. 2021, 14, 1201–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Saxena, S.; Seenivasagam, R.; Tarafdar, S.; Ilahi, I. A Rare Case of Primary Pleural Neurofibroma. Cureus 2021, 13, e17062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinam, S.; Rajesh, P.; Collins, F.; Langman, G. Pleural neurofibroma: Description of the first two cases of a rare pleural tumour. Lung Cancer 2009, 63, S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochtrop, T.A.; Szynaka, M.; Kopp, A.F. Pleurales Schwannom. Rofo 2016, 188, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, F.J.L.; Alfonso, L.G.; Rodríguez, A.I.E.; Rivas, H.E.T. Pleural Schwannoma Mimicking Metastatic Rectal Carcinoma. Schwannoma pleural que simula metástasis pleural de un carcinoma de recto. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2019, 55, 110–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibby, A.; Daly, R.; Internullo, E.; Edey, A.J.; Maskell, N.A. Benign pleural schwannoma presenting with a large, blood-stained pleural effusion. Thorax 2018, 73, 497–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, K.M.; Song, Q. Clinical and CT Manifestation of Pleural Schwannoma. Acta Radiol. 2012, 53, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavitakis, E.M.; Moschovi, M.; Stefanaki, K.; Karamolegou, K.; Dimitriadis, E.; Pandis, N.; Karakousis, C.P.; Tzortzatou-Stathopoulou, F. Desmoplastic small round cell tumor of the pleura. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2007, 49, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodalli, N.; Erzen, C.; Yüksel, M. Evaluation of parietal pleural invasion of lung cancers with breathhold inspiration and expiration MRI. Clin. Imaging 1999, 23, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kwon, W.; Lee, H.Y.; Ko, S.M.; Kim, S.-H.; Lee, W.-Y.; Yong, S.J.; Jung, S.-H.; Byun, C.S.; Lee, J.; et al. Imaging Assessment of Visceral Pleural Surface Invasion by Lung Cancer: Comparison of CT and Contrast-Enhanced Radial T1-Weighted Gradient Echo 3-Tesla MRI. Korean J. Radiol. 2021, 22, 829–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, J.; Nicholson, B.T.; Patrie, J.T.; Harvey, J.A. Incidental Pleural Effusions Detected on Screening Breast MRI. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2012, 199, W142–W145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coolen, J.; De Keyzer, F.; Nafteux, P.; De Wever, W.; Dooms, C.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Roebben, I.; Verbeken, E.; De Leyn, P.; Van Raemdonck, D.; et al. Malignant Pleural Disease: Diagnosis by Using Diffusion-weighted and Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MR Imaging—Initial Experience. Radiology 2012, 263, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, P.; Costantini, M.; Belli, P.; Giuliani, M.; Bufi, E.; Fubelli, R.; Distefano, D.; Romani, M.; Bonomo, L. Extra-mammary findings in breast MRI. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 2268–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knuuttila, A.; Halme, M.; Kivisaari, L.; Kivisaari, A.; Salo, J.; Mattson, K. The clinical importance of magnetic resonance imaging versus computed tomography in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 1998, 22, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coolen, J.; De Keyzer, F.; Nafteux, P.; De Wever, W.; Dooms, C.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Derweduwen, A.; Roebben, I.; Verbeken, E.; De Leyn, P.; et al. Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma: Visual Assessment by Using Pleural Pointillism at Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging. Radiology 2015, 274, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsim, S.; Humphreys, C.A.; Cowell, G.W.; Stobo, D.B.; Noble, C.; Woodward, R.; Kelly, C.A.; Alexander, L.; Foster, J.E.; Dick, C.; et al. Early Contrast Enhancement: A novel magnetic resonance imaging biomarker of pleural malignancy. Lung Cancer 2018, 118, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaarschmidt, B.M.; Sawicki, L.M.; Gomez, B.; Grueneisen, J.; Hoiczyk, M.; Heusch, P.; Buchbender, C. Malignant pleural mesothelioma: Initial experience in integrated 18F-FDG PET/MR imaging. Clin. Imaging 2016, 40, 956–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehndiratta, A.; Knopp, M.V.; Zechmann, C.M.; Owsijewitsch, M.; von Tengg-Kobligk, H.; Zamecnik, P.; Kauczor, H.U.; Choyke, P.L.; Giesel, F.L. Comparison of diagnostic quality and accuracy in color-coded versus gray-scale DCE-MR imaging display. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2009, 4, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Mesothelial Tumours | Lymphoproliferative Disorders | Mesenchymal Tumours | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign and Preinvasive Mesothelial Tumours | Mesothelioma | ||
| Adenomatoid tumour | Localized mesothelioma | Primary effusion lymphoma | Epithelioid haemangioendothelioma |
| Differentiated papillary mesothelial tumour | Diffuse mesothelioma | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with chronic inflammation | Angiosarcoma |
| Mesothelioma in situ | Both have subtypes:Sarcomatoid mesothelioma | Synovial sarcoma | |
| Epithelioid mesothelioma | Solitary fibrous tumour | ||
| Biphasic mesothelioma | Calcifying fibrous tumour | ||
| Desmoplastic round cell tumour | |||
| Tumour Type | T1-Weighted MRI | Dynamic and DCE (Dynamic Contrast Enhanced) MRI | T2-Weighted MRI |
|---|---|---|---|
| MPM | Pleural thickening, nodules, masses—isointense/mildly hyperintense in relation to the chest wall muscle * [1,2,3,13,75,76,82,84,85,104]. Pleural effusions—low signal intensity [10,92]. | Moderately enhanced signal after gadolinium administration [75,76]. Pleural thickening—diffusely enhanced [92]. | Pleural thickening, nodules, masses—moderately hyperintense in relation to the chest wall muscle [1,2,3,13,75,76,77,84,85,104]. Unilateral pleural effusion—focal high signal intensity [2,9,82]. Pleural fluid—focal hyperintense areas [13]. Pleural effusions—high signal intensity [10,75,92]. |
| Solitary fibrous tumour | Tumour—low/intermediate intensity due to the fibrous tissue’s presence [2,13,17,75,79,123,124]. | After gadolinium—intense homogenous enhancement reflects the tumour’s vascularity [11,75,79,125]. | Tumour—low/intermediate intensity due to the mature fibrous tissue’s presence [2,11,17,75,79,123,128]. Highly intense heterogenous signal—possibly a reflection of the tumour’s high cellularity [2,13,55] **. High signal intensity in areas of necrosis and myxoid degeneration [11,75,79,123]. Internal septations—low signal intensity [2]. Tumour may have a low intensity margin [75,79]. Malignant fibrosis—high signal intensity caused by increased vascularity, cellularity and edema [124]. |
| Lipoma | High signal intensity [2,74,79,88]. Well-defined homogenous mass—hyperintense [17,74,79]. | Well-defined homogenous mass—moderate signal intensity [17,74,79,88]. | |
| Liposarcoma | Heterogenous signal—a mixture of fat and soft tissue [2]. Low signal intensity (myxoid degeneration) [17,74,75,79]. | Uneven enhancement [75]. | High signal intensity (myxoid degeneration) [17,74,75,79]. |
| PEL (primary effusion lymphoma) | Effusion -hyperintense signal [2,9]. Cystic/necrotic regions may occur after systemic therapy—high signal intensity [2]. Pleural thickening and nodules/masses may be observed. | ||
| Pleural lymphoma | Hypo or isointense in comparison to the chest wall muscle [126]. | Contrast enhancement present in fat suppressed T1 MRI [126]. | Hyperintense [126]. |
| Hemangioma | Mass—high signal intensity [135]. | Eccentric enhancement in the early-phase images and filling in in the delayed-phase scans [135]. | Mass—high signal intensity [135]. |
| Pleural Schwannoma | Tumour—hypo- to isointense in relation to muscle [143,144]. Split fat sign may be present [144]. | After gadolinium—uneven signal enhancement [143]. | Tumour—inhomogeneous areas with peripherally hyperintense and centrally hypointense structures [143]. Cystic degeneration with hyalinization—hyperintense (due to poor blood flow and degeneration) [143], may also be hypointense [144]. |
| Pleural neurofibroma | Low-intensity signal [141]. | Heterogenous high-intensity signal [141]. | |
| Primary pleuropulmonary synovial sarcoma | Tumour mass—heterogenous medium-intensity signal. Necrotic regions—hypointense. Hemorrhages—hyperintense [132]. | Heterogenous enhancement in T1 [132]. | Tumour mass—heterogenous medium-intensity signal. Necrotic regions—hyperintense. Hemorrhages—hypointense [132]. “Tripple sign” [131]. |
| Leiomyoma | Isointense signal [129]. | Heterogenous enhancement in T1 images [129]. | Heterogenously highly intense signal [129]. |
| Pleural low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma | Hypo- or isointense to muscle. Myxoid edges or hemorrhagic effusion—mild hyperintensity [133]. | Ring-shaped enhancement [133]. | Heterogenous highly intense signal. Myxoid tissue—hyperintense. Fibrous tissue—hypointense [133]. |
| Exudate | Transudate | |
|---|---|---|
| Diffusion in DWI | Low diffusion [74,75]. | High diffusion [74,75]. |
| Signal intensity in triple echo imaging | High signal intensity [74]. | Low signal intensity [74]. |
| Related conditions | Malignancy, infection, thromboembolic disease [75]. | Increased hydrostatic pressure, decreased colloid osmotic pressure [75]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szczyrek, M.; Bitkowska, P.; Jutrzenka, M.; Szudy-Szczyrek, A.; Drelich-Zbroja, A.; Milanowski, J. Pleural Neoplasms—What Could MRI Change? Cancers 2023, 15, 3261. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123261
Szczyrek M, Bitkowska P, Jutrzenka M, Szudy-Szczyrek A, Drelich-Zbroja A, Milanowski J. Pleural Neoplasms—What Could MRI Change? Cancers. 2023; 15(12):3261. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123261
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzczyrek, Michał, Paulina Bitkowska, Marta Jutrzenka, Aneta Szudy-Szczyrek, Anna Drelich-Zbroja, and Janusz Milanowski. 2023. "Pleural Neoplasms—What Could MRI Change?" Cancers 15, no. 12: 3261. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123261
APA StyleSzczyrek, M., Bitkowska, P., Jutrzenka, M., Szudy-Szczyrek, A., Drelich-Zbroja, A., & Milanowski, J. (2023). Pleural Neoplasms—What Could MRI Change? Cancers, 15(12), 3261. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123261