TP53 Mutations in AML Patients Are Associated with Dismal Clinical Outcome Irrespective of Frontline Induction Regimen and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Treatment
2.2. Mutational Analysis and Determination of TP53 Allelic Status
2.3. Karyotype Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
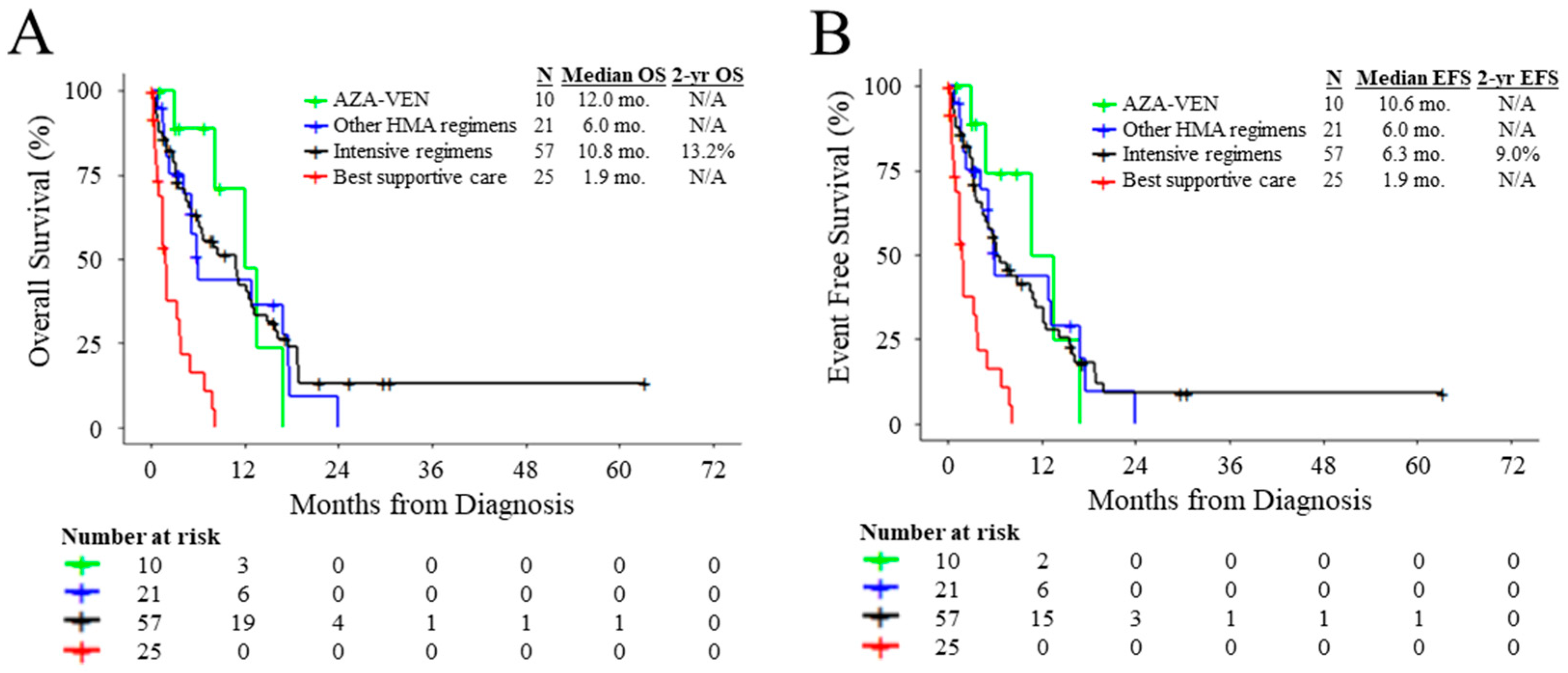
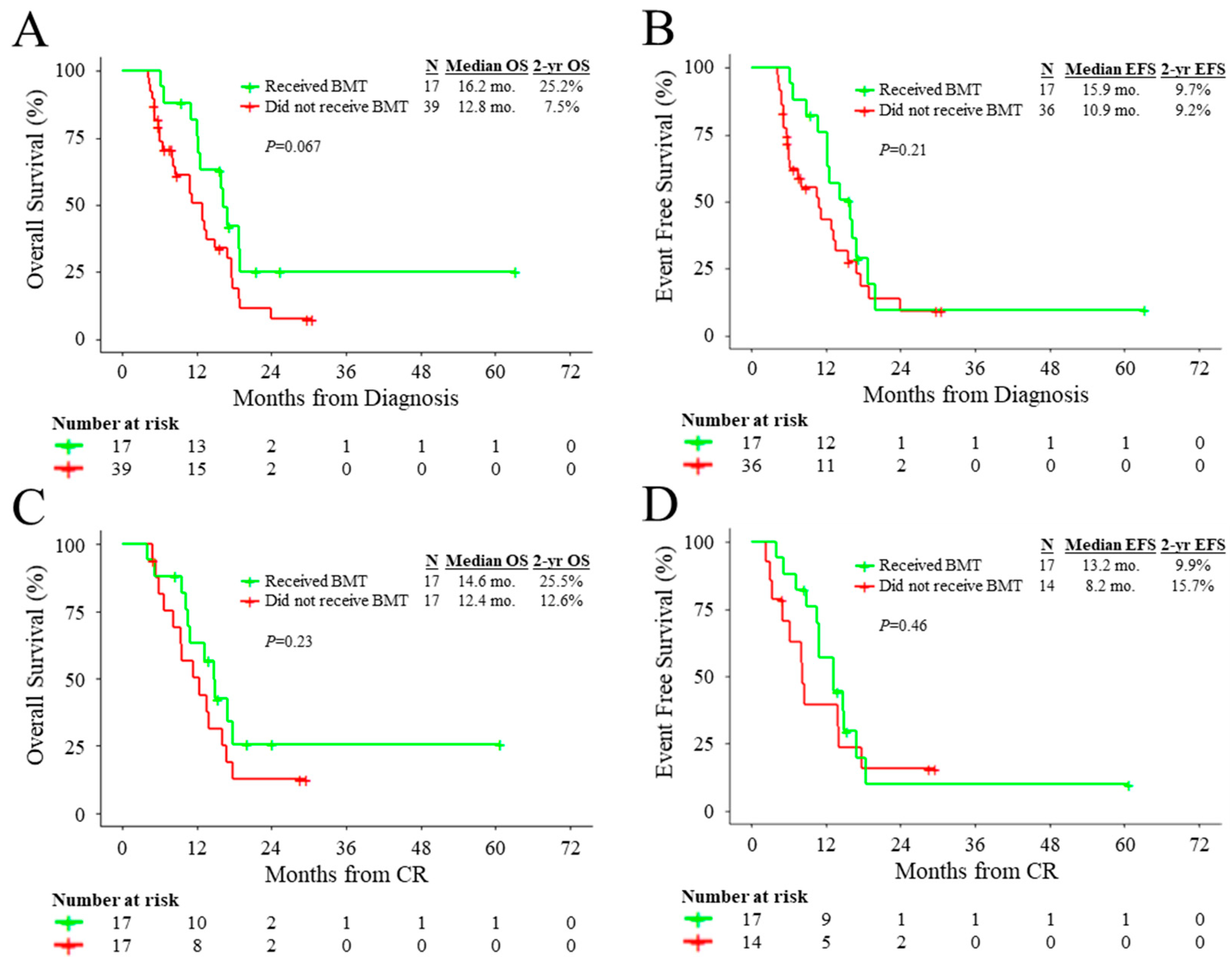
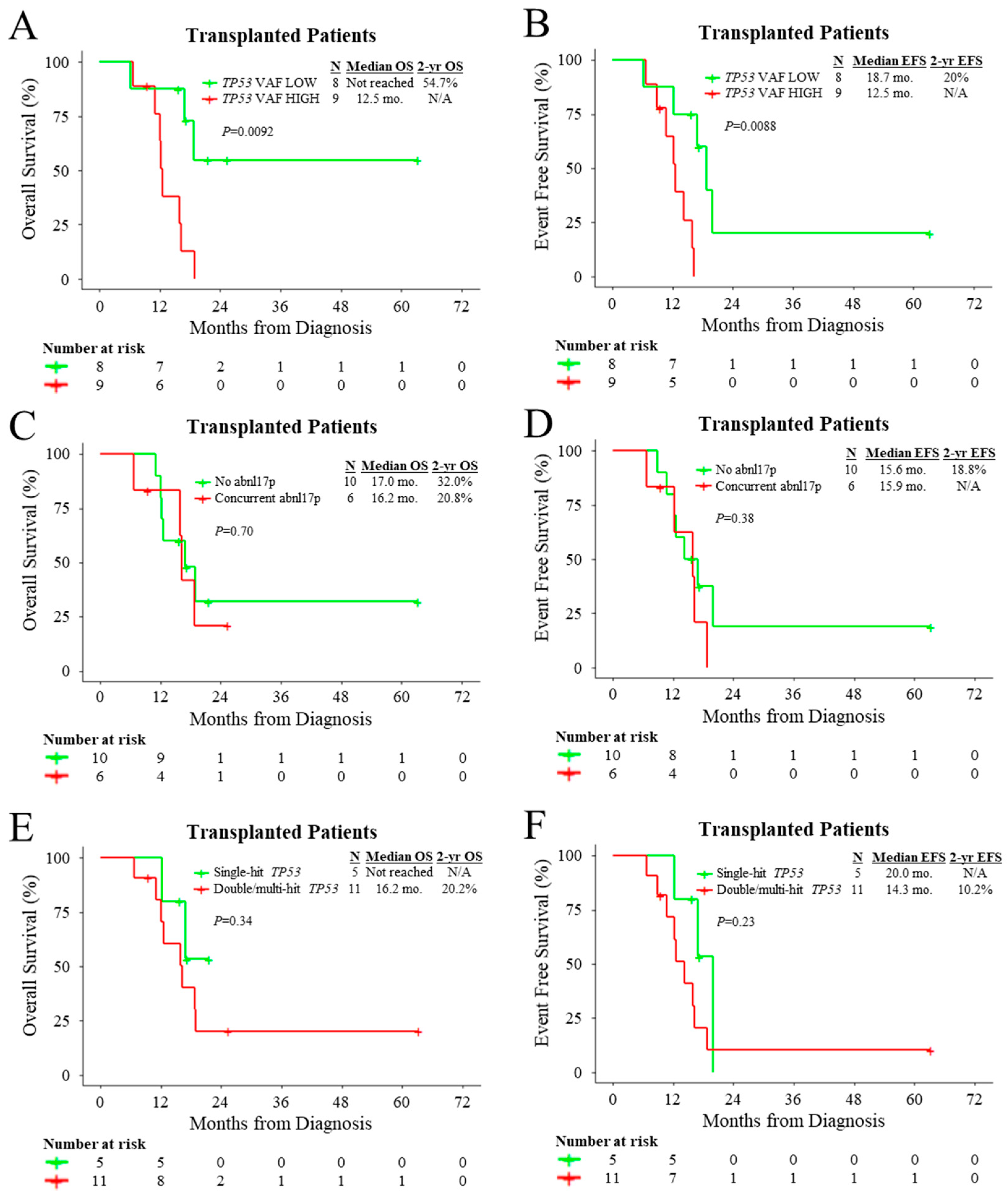
3.2. Outcomes of Patients According to Treatment and Molecular Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, J. The Cell-Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Functions of p53 in Tumor Initiation and Progression. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a026104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molica, M.; Mazzone, C.; Niscola, P.; de Fabritiis, P. TP53 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Still a Daunting Challenge? Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 3368. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33628731/ (accessed on 26 March 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döhner, H.; Wei, A.H.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Craddock, C.; DiNardo, C.D.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Godley, L.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood 2022, 140, 1345–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Borowitz, M.J.; Calvo, K.R.; Kvasnicka, H.M.; Wang, S.A.; Bagg, A.; Barbui, T.; Branford, S.; et al. International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemias: Integrating morphologic, clinical, and genomic data. Blood 2022, 140, 1200–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciurea, S.O.; Chilkulwar, A.; Saliba, R.M.; Chen, J.; Rondon, G.; Patel, K.P.; Khogeer, H.; Shah, A.R.; Randolph, B.V.; Ramos Perez, J.M.; et al. Prognostic factors influencing survival after allogeneic transplantation for AML/MDS patients with TP53 mutations. Blood 2018, 131, 2989–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poiré, X.; Labopin, M.; Maertens, J.; Yakoub-Agha, I.; Blaise, D.; Ifrah, N.; Socié, G.; Gedde-Dhal, T.; Schaap, N.; Cornelissen, J.J.; et al. Allogeneic stem cell transplantation in adult patients with acute myeloid leukaemia and 17p abnormalities in first complete remission: A study from the Acute Leukemia Working Party (ALWP) of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher-Reyes, G.; Kim, T.H.; Novitzky-Basso, I.; Kim, K.H.; Smith, A.; Stockley, T.; Capochichi, J.M.; Al-Shaibani, Z.; Pasic, I.; Law, A.; et al. Prognostic impact of the adverse molecular-genetic profile on long-term outcomes following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in acute myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021, 56, 1908–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middeke, J.M.; Herold, S.; Rücker-Braun, E.; Berdel, W.E.; Stelljes, M.; Kaufmann, M.; Schäfer-Eckart, K.; Baldus, C.D.; Stuhlmann, R.; Ho, A.D.; et al. TP53 mutation in patients with high-risk acute myeloid leukaemia treated with allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 172, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, J.; Jentzsch, M.; Bill, M.; Goldmann, K.; Schulz, J.; Niederwieser, D.; Platzbecker, U.; Schwind, S. Prognostic impact of the ELN2017 risk classification in patients with AML receiving allogeneic transplantation. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 3864–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanate, A.S.; Majhail, N.S.; Savani, B.N.; Bredeson, C.; Champlin, R.E.; Crawford, S.; Giralt, S.A.; LeMaistre, C.F.; Marks, D.I.; Omel, J.L.; et al. Indications for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation and Immune Effector Cell Therapy: Guidelines from the American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dholaria, B.; Savani, B.N.; Hamilton, B.K.; Oran, B.; Liu, H.D.; Tallman, M.S.; Ciurea, S.O.; Holtzman, N.G.; II, G.L.P.; Devine, S.M.; et al. Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia: An Evidence-Based Review from the American Society of Transplantation and Cellular Therapy. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Kennedy, J.A.; Capo-Chichi, J.M.; Kim, S.; Hu, Z.H.; Alyea, E.P.; Popat, U.R.; Sobecks, R.M.; Scott, B.L.; Gerds, A.T.; et al. Genetic factors rather than blast reduction determine outcomes of allogeneic HCT in BCR-ABL-negative MPN in blast phase. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5562–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alduaij, W.; McNamara, C.J.; Schuh, A.; Arruda, A.; Sukhai, M.; Kanwar, N.; Thomas, M.; Spiegel, J.; Kennedy, J.A.; Stockley, T.; et al. Clinical Utility of Next-generation Sequencing in the Management of Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: A Single-Center Experience. HemaSphere 2018, 2, e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Sukhai, M.A.; Zhang, T.; Dolatshahi, R.; Harbi, D.; Garg, S.; Misyura, M.; Pugh, T.; Stockley, T.L.; Kamel-Reid, S. Integration of Technical, Bioinformatic, and Variant Assessment Approaches in the Validation of a Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Panel for Myeloid Malignancies. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 759–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Reumers, J.; Couceiro, J.R.; De Smet, F.; Gallardo, R.; Rudyak, S.; Cornelis, A.; Rozenski, J.; Zwolinska, A.; Marine, J.C.; et al. Gain of function of mutant p53 by coaggregation with multiple tumor suppressors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Niu, D.; Lam, T.H.; Xiao, Z.; Ren, E.C. Mapping the p53 transcriptome universe using p53 natural polymorphs. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaoun, L.; Sonkin, D.; Ardin, M.; Hollstein, M.; Byrnes, G.; Zavadil, J.; Olivier, M. TP53 Variations in Human Cancers: New Lessons from the IARC TP53 Database and Genomics Data. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 865–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grob, T.; Al Hinai, A.S.A.; Sanders, M.A.; Kavelaars, F.G.; Rijken, M.; Gradowska, P.L.; Biemond, B.J.; Breems, D.A.; Maertens, J.; van Marwijk Kooy, M.; et al. Molecular characterization of mutant TP53 acute myeloid leukemia and high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome. Blood 2022, 139, 2347–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalban-Bravo, G.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Benton, C.B.; Class, C.A.; Chien, K.S.; Sasaki, K.; Naqvi, K.; Alvarado, Y.; Kadia, T.M.; Ravandi, F.; et al. Genomic context and TP53 allele frequency define clinical outcomes in TP53-mutated myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hientz, K.; Mohr, A.; Bhakta-Guha, D.; Efferth, T. The role of p53 in cancer drug resistance and targeted chemotherapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 8921–8946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karran, P. Mechanisms of tolerance to DNA damaging therapeutic drugs. Carcinogenesis 2001, 22, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przespolewski, A.; Goldberg, A.D.; Talati, C.; Fazal, S.; Vachhani, P.; Sanikommu, S.R.R.; Thota, S.; Waksal, J.; Ball, B.; Famulare, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of CPX-351 in Younger Patients <60 Years Old with Secondary Acute Myeloid Leukemia: An Updated Analysis. Blood 2021, 138, 1264. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, A.D.; Talati, C.; Desai, P.; Famulare, C.; Devlin, S.M.; Farnoud, N.; Sallman, D.A.; Lancet, J.E.; Roboz, G.J.; Sweet, K.L.; et al. TP53 Mutations Predict Poorer Responses to CPX-351 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2018, 132, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiche, E.; Rahme, R.; Bertoli, S.; Dumas, P.Y.; Micol, J.B.; Hicheri, Y.; Pasquier, F.; Peterlin, P.; Chevallier, P.; Thomas, X.; et al. Real-life experience with CPX-351 and impact on the outcome of high-risk AML patients: A multicentric French cohort. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadia, T.M.; Jain, P.; Ravandi, F.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Andreef, M.; Takahashi, K.; Borthakur, G.; Jabbour, E.; Konopleva, M.; Daver, N.G.; et al. TP53 mutations in newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia: Clinicomolecular characteristics, response to therapy, and outcomes. Cancer 2016, 122, 3484–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, V.; Schnittger, S.; Kohlmann, A.; Eder, C.; Roller, A.; Dicker, F.; Schmid, C.; Wendtner, C.M.; Staib, P.; Serve, H.; et al. A novel hierarchical prognostic model of AML solely based on molecular mutations. Blood 2012, 120, 2963–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsley, R.C.; Gibson, C.J.; Murdock, H.M.; Stone, R.M.; Cortes, J.E.; Uy, G.L.; Lin, T.L.; Ritchie, E.K.; Prebet, T.; Ryan, R.J.; et al. Genetic Characteristics and Outcomes By Mutation Status in a Phase 3 Study of CPX-351 Versus 7 + 3 in Older Adults with Newly Diagnosed, High-Risk/Secondary Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). Blood 2019, 134, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Maiti, A.; Loghavi, S.; Pourebrahim, R.; Kadia, T.M.; Rausch, C.R.; Furudate, K.; Daver, N.G.; Alvarado, Y.; Ohanian, M.; et al. Outcomes of TP53-mutant acute myeloid leukemia with decitabine and venetoclax. Cancer 2021, 127, 3772–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bally, C.; Adès, L.; Renneville, A.; Sebert, M.; Eclache, V.; Preudhomme, C.; Mozziconacci, M.J.; de The, H.; Lehmann-Che, J.; Fenaux, P. Prognostic value of TP53 gene mutations in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia treated with azacitidine. Leuk. Res. 2014, 38, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollyea, D.A.; Pratz, K.W.; Wei, A.H.; Pullarkat, V.; Jonas, B.A.; Recher, C.; Babu, S.; Schuh, A.C.; Dail, M.; Sun, Y.; et al. Outcomes in Patients with Poor-risk Cytogenetics with or without TP53 Mutations Treated with Venetoclax and Azacitidine. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 5272–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, J.S.; Petti, A.A.; Miller, C.A.; Fronick, C.C.; O’Laughlin, M.; Fulton, R.S.; Wilson, R.K.; Baty, J.D.; Duncavage, E.J.; Tandon, B.; et al. TP53 and Decitabine in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2023–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, S.; Shoukier, M.; Konopleva, M.; Dinardo, C.D.; Ravandi, F.; Short, N.J.; Andreeff, M.; Borthakur, G.; Daver, N.; Pemmaraju, N.; et al. Outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed TP53-mutated acute myeloid leukemia with or without venetoclax-based therapy. Cancer 2021, 127, 3541–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, N.J.; Montalban-Bravo, G.; Hwang, H.; Ning, J.; Franquiz, M.J.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Patel, K.P.; DiNardo, C.D.; Ravandi, F.; Garcia-Manero, G.; et al. Prognostic and therapeutic impacts of mutant TP53 variant allelic frequency in newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5681–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Jonas, B.A.; Pullarkat, V.; Thirman, M.J.; Garcia, J.S.; Wei, A.H.; Konopleva, M.; Döhner, H.; Letai, A.; Fenaux, P.; et al. Azacitidine and Venetoclax in Previously Untreated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, R.; Diepstraten, S.T.; Moujalled, D.; Chew, E.; Flensburg, C.; Shi, M.X.; Dengler, M.A.; Litalien, V.; MacRaild, S.; Chen, M.; et al. Intact TP-53 function is essential for sustaining durable responses to BH3-mimetic drugs in leukemias. Blood 2021, 137, 2721–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimmer, R.R.; Kovtonyuk, L.V.; Klemm, N.; Fullin, J.; Stolz, S.M.; Mueller, J.; Caiado, F.; Kurppa, K.J.; Ebert, B.L.; Manz, M.G.; et al. TP53 mutations confer resistance to hypomethylating agents and BCL-2 inhibition in myeloid neoplasms. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 3201–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechiporuk, T.; Kurtz, S.E.; Nikolova, O.; Liu, T.; Jones, C.L.; D’alessandro, A.; Culp-Hill, R.; D’almeida, A.; Joshi, S.K.; Rosenberg, M.; et al. The TP53 Apoptotic Network Is a Primary Mediator of Resistance to BCL2 Inhibition in AML Cells. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 910–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daver, N.G.; Maiti, A.; Kadia, T.M.; Vyas, P.; Majeti, R.; Wei, A.H.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Craddock, C.; Sallman, D.A.; Kantarjian, H.M. TP53-Mutated Myelodysplastic Syndrome and Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Biology, Current Therapy, and Future Directions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 2516–2529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badar, T.; Atallah, E.; Shallis, R.M.; Goldberg, A.D.; Patel, A.; Abaza, Y.; Bewersdorf, J.P.; Saliba, A.N.; Correia, G.S.D.C.; Murthy, G.; et al. Outcomes of TP53-mutated AML with evolving frontline therapies: Impact of allogeneic stem cell transplantation on survival. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, E232–E235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, M.; Tariq, E.; Chaudhary, S.G.; Anwar, I.; Iqbal, Q.; Fatima, H.; Abdelhakim, H.; Ahmed, N.; Balusu, R.; Hematti, P.; et al. Outcomes with allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in TP53-mutated acute myeloid leukemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 3409–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Eladl, E.; Zarif, M.; Capo-Chichi, J.M.; Schuh, A.; Atenafu, E.; Minden, M.; Chang, H. Molecular characterization of AML-MRC reveals TP53 mutation as an adverse prognostic factor irrespective of MRC-defining criteria, TP53 allelic state, or TP53 variant allele frequency. Cancer Med. 2022, 12, 6511–6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Gelber, R.D.; Regan, M.M. Challenges of guarantee-time bias. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 2963–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najima, Y.; Sadato, D.; Harada, Y.; Oboki, K.; Hirama, C.; Toya, T.; Doki, N.; Haraguchi, K.; Yoshifuji, K.; Akiyama, M.; et al. Prognostic impact of TP53 mutation, monosomal karyotype, and prior myeloid disorder in nonremission acute myeloid leukemia at allo-HSCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021, 56, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loke, J.; Labopin, M.; Craddock, C.; Cornelissen, J.J.; Labussière-Wallet, H.; Wagner-Drouet, E.M.; Van Gorkom, G.; Schaap, N.P.M.; Kröger, N.M.; Veelken, J.H.; et al. Additional cytogenetic features determine outcome in patients allografted for TP53 mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 2022, 128, 2922–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashakori, M.; Kadia, T.; Loghavi, S.; Daver, N.; Kanagal-Shamanna, R.; Pierce, S.; Sui, D.; Wei, P.; Khodakarami, F.; Tang, Z.; et al. TP53 copy number and protein expression inform mutation status across risk categories in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2022, 140, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, M.J.; Boiocchi, L.; Fathi, A.T.; Brunner, A.M.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Nardi, V. Correlation of p53 immunohistochemistry with TP53 mutational status and overall survival in newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukaemia. Histopathology 2022, 81, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
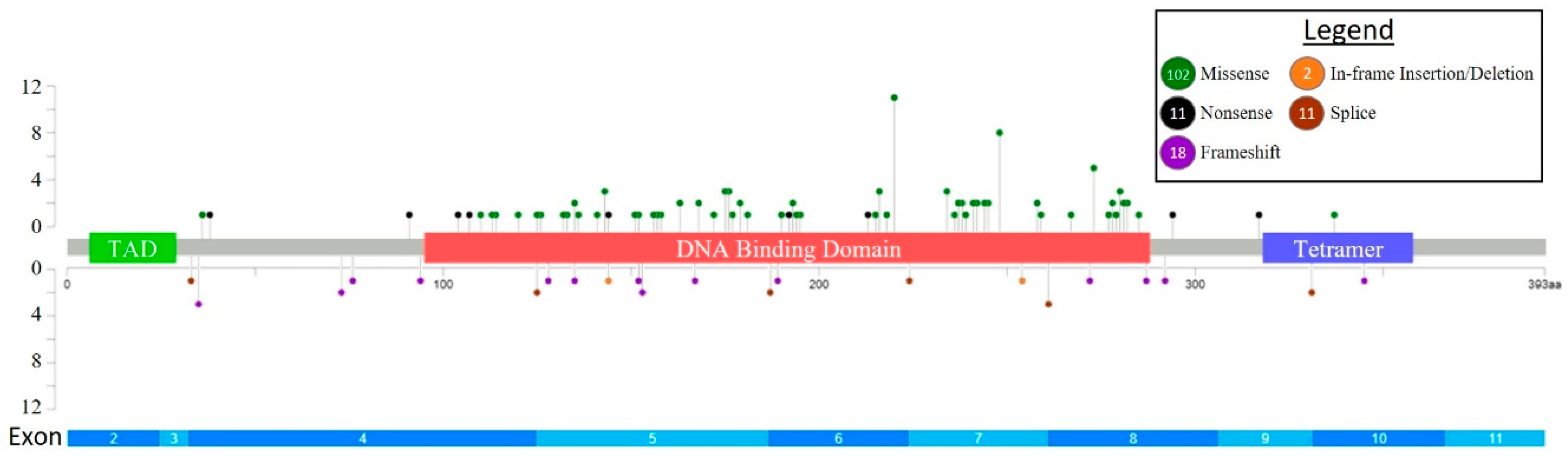
| Clinical Feature | Total (n = 113) | Intensive Induction (n = 57) | AZA-VEN (n = 10) | Other HMA Regimens (n = 21) | Supportive Care (n = 25) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (y), median [range] | 70.7 [34.3–91.7] | 63.7 [34.3–76.7] | 72.0 [55.2–83.1] | 78.8 [60.2–91.7] | 77.6 [53.8–91.6] | <0.0001 a |
| Male/Female gender | 52:61 | 32:25 | 6:4 | 6:15 | 8:17 | 0.052 b |
| WBC count ×109/L, median [range] | 2.9 [0.3–76.9] | 2.9 [0.3–76.9] | 2.6 [0.3–11.2] | 2.6 [1.1–16.8] | 4.0 [0.8–72.4] | 0.322 a |
| Platelets ×109/L, median [range] | 46 [5–782] | 46 [7–782] | 48 [10–162] | 68 [5–290] | 40 [6–338] | 0.981 a |
| Hemoglobin, ×1012/L, median [range] | 82 [57–125] | 85 [60–125] | 86 [68–118] | 82 [67–121] | 79 [57–106] | 0.358 a |
| BM blasts %, median [range] | 37 [20–90] | 44 [20–90] | 50 [23–90] | 32 [20–79] | 32 [20–83] | 0.285 a |
| LDH, IU/L, median [range] | 320 [128–3391] | 336 [128–2790] | 309 [157–770] | 285 [148–841] | 371 [199–3391] | 0.081 a |
| Clinical ontogeny | ||||||
| de novo AML | 83 (73) | 46 (81) | 7 (70) | 15 (71) | 15 (60) | 0.054 b |
| s-AML | 13 (12) | 7 (12) | 1 (10) | 0 (0) | 5 (20) | |
| t-AML | 17 (15) | 4 (7) | 2 (20) | 6 (29) | 5 (20) | |
| Complete remission | 36 (41) | 29 (51) | 5 (50) | 2 (10) | n/a | 0.0022 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Zarif, M.; Zhou, Q.; Capo-Chichi, J.-M.; Schuh, A.; Minden, M.D.; Atenafu, E.G.; Kumar, R.; Chang, H. TP53 Mutations in AML Patients Are Associated with Dismal Clinical Outcome Irrespective of Frontline Induction Regimen and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Cancers 2023, 15, 3210. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123210
Zhao D, Zarif M, Zhou Q, Capo-Chichi J-M, Schuh A, Minden MD, Atenafu EG, Kumar R, Chang H. TP53 Mutations in AML Patients Are Associated with Dismal Clinical Outcome Irrespective of Frontline Induction Regimen and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Cancers. 2023; 15(12):3210. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123210
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Davidson, Mojgan Zarif, Qianghua Zhou, José-Mario Capo-Chichi, Andre Schuh, Mark D. Minden, Eshetu G. Atenafu, Rajat Kumar, and Hong Chang. 2023. "TP53 Mutations in AML Patients Are Associated with Dismal Clinical Outcome Irrespective of Frontline Induction Regimen and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation" Cancers 15, no. 12: 3210. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123210
APA StyleZhao, D., Zarif, M., Zhou, Q., Capo-Chichi, J.-M., Schuh, A., Minden, M. D., Atenafu, E. G., Kumar, R., & Chang, H. (2023). TP53 Mutations in AML Patients Are Associated with Dismal Clinical Outcome Irrespective of Frontline Induction Regimen and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Cancers, 15(12), 3210. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers15123210









