Simple Summary
The discovery of actionable oncogenic driver mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has revolutionized the treatment and prognosis of this dreadful disease. New targeted therapies are being developed and tested in early phase clinical trials rapidly. We summarize emerging first-in-human clinical trials of targeted therapy that have been conducted or initiated in the past year. We hope this review will benefit our readers to be familiar with new advances in this field and create more opportunities for eligible patients to access clinical trials.
Abstract
Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide. Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type and is still incurable for most patients at the advanced stage. Targeted therapy is an effective treatment that has significantly improved survival in NSCLC patients with actionable mutations. However, therapy resistance occurs widely among patients leading to disease progression. In addition, many oncogenic driver mutations in NSCLC still lack targeted agents. New drugs are being developed and tested in clinical trials to overcome these challenges. This review aims to summarize emerging targeted therapy that have been conducted or initiated through first-in-human clinical trials in the past year.
1. Background
Lung cancer is the second-most diagnosed cancer and the leading cause of cancer death worldwide [1]. Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 85% of all lung cancer cases. Among NSCLC, the most common histological subtype is adenocarcinoma (LUAD), followed by squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC). For NSCLC patients at an advanced stage, tumor molecular profiling and biomarker testing are widely adopted as the standard of care that leads to a more individualized treatment plan tailored from multiple options including chemotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and targeted therapy. Targeted therapies, which are drugs interfering with tumor-specific molecules, are only suitable for NSCLC patients who are found to have actionable mutations by tumor genetic profiling, most commonly next-generation sequencing (NGS). With the advanced technique and decreased cost of NGS, all patients at advanced stages are recommended to test for tumor genetic alterations performed on the tumor tissue or by examining circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). So far, as of the time of this publication, the following genetic driver alterations have targeted agents approved by the U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA): EGFR mutations, ALK rearrangements, ROS1 rearrangements, RET rearrangements, NTRK fusions, MET exon 14 skipping mutation, KRAS G12C mutation, BRAF V600E mutation, and ERBB2 (HER2) mutation [2,3,4]. Newer agents are being developed for these molecular targets aiming to induce a more profound response and overcome treatment resistance. Additional translational studies are exploring novel driver mutations, turning traditionally undruggable mutations into therapeutic targets. Furthermore, common tumorigenic signaling pathways such as PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RAF/MEK/ERK have been the focus of targeted drug development for several years. Targeting such pathways along with tumor cell surface receptors by using combination therapy is a promising strategy.
In this review, we focus on new investigational targeted agents pipelined into human clinical trials for advanced NSCLC in the past year including trials for advanced LSCC. This is an update from a prior review of early-phase clinical trials on targeted therapy published in 2021 [4]. We identified references by searching the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) annual meeting abstracts, the World Conference on Lung Cancer (WCLC) abstracts, and information from clinicaltrials.gov over the past year. We only included first-in-human, phase I/II clinical trials in advanced/metastatic NSCLC. A total of 20 phase I, 16 phase I/II, and 10 phase II clinical trials were included in this review. A summary of included trials is shown in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 with a summary of molecular targets and involved pathways depicted in Figure 1. Each trial was individually reviewed. We excluded pre-clinical studies and phase III clinical trials. Other emerging systemic therapeutic strategies such as immune checkpoint inhibitors or adoptive cell therapy are beyond the scope of this review.

Table 1.
Recent first-in-human phase I/II clinical trials of EGFR targeted agents for NSCLC.

Table 2.
Recent first-in-human phase I/II clinical trials of non-EGFR targeted agents for NSCLC.

Table 3.
Summarizes recent first-in-human clinical trials of non-EGFR targeted agents for lung squamous cell carcinoma.
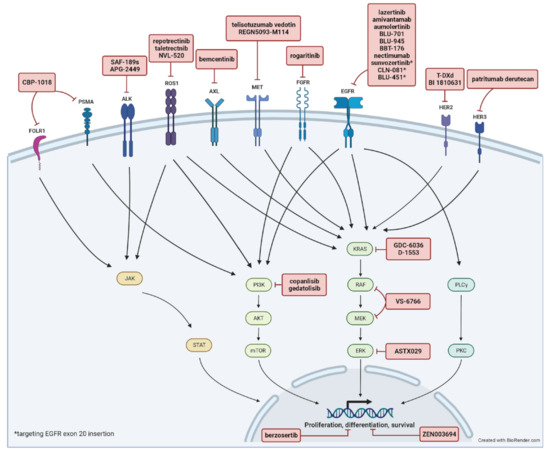
Figure 1.
Summary of molecular targets and involved pathways.
2. EGFR
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations are found in 15–20% of NSCLC in Western populations and in 45–50% of NSCLC in Asian populations [5]. The most common mutations are deletions in exon 19 and L858R point mutation in exon 21. EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) achieved great success in treating patients with advanced NSCLC harboring sensitizing EGFR mutations in the last decade. Osimertinib, a third-generation EGFR TKI, has become the first-line therapy for those patients including patients who carry T790M mutation resistant to first/second-generation TKIs. However, resistance to osimertinib inevitably occurs, leading to disease progression. For those patients who progress on osimertinib, chemotherapy remains as the subsequent therapy option unless enrolling in clinical trials. In addition to the lack of further effective targeted therapy, the value of immunotherapy in those patients is questionable. In a small subgroup analysis from the Impower150 trial, the combination of atezolizumab, bevacizumab, carboplatin, and paclitaxel (ABCP) was shown to have a survival benefit in patients with sensitizing EGFR mutations who had disease progression on TKI [6]. Whereas in a recent retrospective study, adding immunotherapy alone to chemotherapy is associated with a worse overall survival [7]. To overcome treatment resistance and develop more effective targeted therapies beyond osimertinib, recent early phase clinical trials focus on the following strategies: new EGFR TKI that are active against resistance mutations such as T790M or C797X, duo-blockade using two EGFR inhibitors, combine EGFR TKI with another targeted agent. Table 1 summarizes recent first-in-human clinical trials of EGFR targeted agents.
Lazertinib is a brain-penetrant EGFR TKI that targets typical EGFR mutations and T790M mutations but spares wild-type EGFR [8]. It was tested in a phase I/II trial of 127 patients with EGFR T790M-mutant NSCLC who had disease progression after TKI therapy (NCT03046992). The trial has an impressive ORR of 54% [9,10]. In another phase I trial, Lazertinib was assessed in the front-line setting for EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients and showed a favorable efficacy. The overall response rate (ORR) was 70% and the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 24.6 months in the optimal 240mg dosing cohort that contained 43 patients [11]. A phase III, randomized, double-blind trial (LASER301) is currently open to evaluate Lazertinib vs. gefitinib in the first-line setting of EGFR-mutant NSCLC treatment (NCT04248829).
Amivantamab is an EGFR-MET bispecific antibody that was approved to treat NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertions. The combination of amivantamab and lazertinib, targeting EGFR at both its extracellular and catalytic domains, was shown to have synergistic inhibition of tumor growth in preclinical [12]. This combination was recently evaluated in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC who had disease progression on EGFR TKI in the phase I CHRYSALIS-2 trial. The trial enrolled 116 patients who were heavily pre-treated (median prior lines of therapy was 3), and showed an encouraging response rate of 32% [13]. An updated result from cohort A that contains patients who had disease progression on osimertinib and chemotherapy was presented at ASCO 2022 [14]. The ORR was 33% with a median duration of response (DoR) of 9.6 months. The toxicity profile is manageable, and grade 3 or above treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) include infusion-related reactions (7%), acneiform dermatitis (5%), and hypoalbuminemia (4%) 2022 [14]. In the first-line setting, amivantamab plus lazertinib showed an ORR of 100% in 20 treatment-naïve patients who harbored EGFR exon 19 deletion or exon 21 L858R 2022 [15]. At a median follow-up of 22.3 months, the median DoR and PFS were not reached. The toxicity was consistent with previous trials [15]. The combination of amivantamab and lazertinib has demonstrated encouraging anti-tumor efficacy in both osimertinib-resistant and treatment-naïve subgroups of NSCLC patients in early phase clinical trials. The final results of those trials will be important to show whether there is a consistent trend. Moving forward, a phase III, randomized trial (MARIPOSA) is designed to compare the combination of amivantamab and lazertinib to osimertinib monotherapy as the first-line treatment for EGFR-mutant NSCLC [16]. It aims to enroll 1074 patients worldwide. Notably, this trial only includes patients with EGFR exon 19 deletion or L858R substitution, but not other less common mutations.
Aumolertinib is a third-generation EGFR TKI shown to be effective against T790M mutation. In a phase II APOLLO trial, 244 patients with T790M positive NSCLC who had disease progression on first- or second-generation EGFR TKIs received aumolertinib. The ORR was 68.9% and the median PFS was 12.4 months. The efficacy sustained in patients with CNS metastasis [17]. Icotinib is a first-generation EGFR TKI that is effective against CNS metastasis [18]. The combination of aumolertinib and icotinib is being tested as first-line therapy in NSCLC patients with brain metastasis in a phase I/II trial in China (ChiCTR2100044216). A total of 12 patients with brain metastasis were enrolled in the phase I arm. The ORR was 100%, and no grade 4 or 5 AEs were observed [19]. Long-term outcomes are yet to be determined and the phase II arm of the trial is undergoing.
BLU-945 is a next-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that is highly selective for on-target resistance EGFR mutations such as C797S and T790M, while sparing EGFR wildtype. Thus, it is potentially to be used in combination with other EGFR TKI to increase antitumor efficacy without increasing toxicity. BLU-945 has antitumor activity including intracranial response in osimertinib-resistant patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models [20]. It is currently being evaluated in the SYMPHONY trial (NCT04862780)–a phase I/II trial for patients with EGFR mutations who had received at least one EGFR TKI. Patients will receive either BLU-945 monotherapy or in combination with osimertinib. The primary endpoints are maximum tolerated dose, recommended phase II dose, safety in the phase I study, and overall response rate in the phase II study [21]. This trial is currently open for enrollment. The final results will help assess the role of BLU-945 in overcoming EGFR resistance and the potential clinical application of dual EGFR inhibitors.
BBT-176 is a 4th generation EGFR TKI with high potency against C797S mutation. In a recent phase I trial (NCT04820023), 25 patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC who had cancer progression on at least one EGFR TKI were enrolled. Most of them (64%) received three or more lines of therapy. A total of 32% of them were found to have C797S mutation. TRAEs were mostly low grade including GI toxicities, dizziness, and platelet count decrease. Two patients with tumors harboring triple EGFR mutations of exon 19 del/T790M/C797S showed tumor shrinkage in both target and non-target lesions [22]. The trial is ongoing to further optimize BBT-176 dosing and evaluate clinical efficacy.
BLU-701 is a brain-penetrant EGFR TKI with high potency on common EGFR mutations plus C797X resistance mutations, while sparing wild-type EGFR [23]. It is being evaluated in a phase I/II first-in-human study (HARMONY trial) for patient with EGFR-mutant NSCLC. The phase I arm has three parts: 1A, 1B, and 1C, which are testing BLU-701 alone, BLU-701 plus osimertinib, and BLU-701 plus carboplatin and pemetrexed, respectively. The phase II arm will be using the recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) from phase I result, and has an designated group (part 2A) for NSCLC patients harboring EGFR C797X mutation [23]. The trial is currently recruiting and expected to finish in 2024.
Patritumab deruxtecan is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of an anti-HER3 antibody attached to a topoisomerase I inhibitor payload. It demonstrated clinical efficacy in treating advanced EGFR-mutant NSCLC after failure of EGFR TKI in a phase I trial (NCT03260491) [24]. The phase II and phase III trials, namely HERTHENA-Lung01 (NCT04619004) and HERTHENA-Lung02 (NCT05338970), are actively recruiting to further confirm the efficacy and safety of patritumab deruxtecan in patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC with disease progression on EGFR TKI. Additionally, Patritumab deruxtecan is also being tested for treating NSCLC with wild-type EGFR in one arm of the above phase I trial. A total of 47 patients who had received prior chemotherapy with or without immunotherapy were treated with patritumab deruxtecan. The ORR was 28% and the median PFS was 5.4 months [25]. Notably, in 17 patients with driver genomic alterations, 35% achieved objective response. The most common grade ≥ 3 TEAEs were neutropenia (26%), thrombocytopenia (15%), and fatigue (15%), and drug-related interstitial lung disease occurred in 4 pts (9%; 0 grade ≥ 3) [25].
3. EGFR TKI in Combination with Other Targeted Agents
Anlotinib is a multi-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that has anti-tumor activity in several solid tumors [26]. Adding anlotinib to osimertinib was able to overcome treatment resistance in EGFR T790M-positive NSCLC in an in vitro study and a retrospective clinical study [27,28]. This combination was recently tested in a first-line setting for NSCLC in a phase I/IIa trial (NCT04770688). A total of 25 treatment-naïve patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC were treated with anlotinib plus osimertinib [29]. The ORR was 65.2% and DCR was 95.7%. Median PFS was not reported. Grade 3 or higher AEs occurred in 20% patients, and the most common AEs were platelet count decreased (56.5%), thyroid-stimulating hormones increased (39.1%) and diarrhea (30.4%) [29]. Osimertinib in combination with anlotinib showed encouraging anti-tumor activity with an acceptable toxicity profile. Further randomized controlled trials are needed to assess the value of adding anlotinib to osimertinib in the first-line setting compared with standard-of-care osimertinib monotherapy.
Necitumumab is a monoclonal antibody against EGFR. It was initially tested in combination with cisplatin and gemcitabine as a first-line treatment for squamous NSCLC. The study showed 1.6 months OS benefit at the cost of increased toxicity [30]. It was hypothesized that duo blockade of EGFR by the combination of necitumumab and osimertinib may overcome EGFR-TKI resistance [31]. This combination was tested in a phase I dose escalation and expansion trial (NCT02496663). The trial recruited 101 EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients who developed resistance to first/second generation TKIs or osimertinib, or harbored EGFR ex20ins with disease progression on chemotherapy. The ORR among all patients was 19% (95% CI 11–27%). Grade 3 or higher TRAEs were seen in 38% patients, most commonly rash (21%) [31]. Necitumumab in combination with osimertinib is being tested in a phase II platform study (ORCHARD) for patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC who had cancer progression on osimertinib. The trial is recruiting and estimated to complete in 2025.
Aurora kinases are enzymes within the serine/threonine kinase family and play key roles in mammalian cell mitosis and meiosis [32]. Preclinical studies have shown that aurora kinases are responsible for EMT-associated EGFR-TKI resistance [33,34]. PI3K/AKT/mTOR is a downstream pathway of EGFR. Activation of this pathway is reported to be a mechanism of EGFR-TKI resistance [35]. Adding an aurora kinase inhibitor or a mTOR inhibitor to osimertinib was tested in a phase I clinical trial (NCT04479306). A total of 40 patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC who had cancer progression on osimertinib were assigned to two groups, and received osimertinib in combination with either alisertib, an aurora kinase inhibitor, or sapanisertib, an mTOR inhibitor. The osimertinib + sapanisertib arm showed ORR of 12.5%, DCR of 68.7%, and median PFS of 4.6 months; whereas the osimertinib + alisertib arm failed to show meaningful clinical efficacy [36]. The treatment was well tolerated. Grade 3 treatment emergent adverse events (TEAEs) occurred in 10% patients, most commonly hyperglycemia (45%) and stomatitis (40%). No grade 4 TEAEs were observed [36]. Further trials are needed to validate the clinical benefit of adding mTOR inhibitor to EGFR TKI.
A strategy of combining duo-EGFR blockade with HER2 blockade is being tested in a phase Ib/II trial. In the phase Ib dose escalation arm, 15 patients were treated with a triple therapy of osimertinib, necitumumab, and trastuzumab. The toxicities appear manageable (most commonly rash, headache, dry skin). It demonstrated a preliminary efficacy, as 5 of 10 evaluable patients achieved numerical reduction in tumor size [37]. The phase 2 arm is currently open for accrual.
Repotrectinib is a ROS1/TRK/ALK Inhibitor that was granted breakthrough therapy designation (BTD) for treating ROS1-postive or NTRK-positive NSCLC based on the results from TRIDENT-1 trial [38,39]. Additionally, as a pan-TRK inhibitor, repotrectinib can potentially overcome EGFR off-target resistance [39,40]. The combination of osimertinib and repotrectinib is being assessed in a phase I study (TOTEM trial). Eligible patients are required to have advanced EGFR-mutant NSCLC including those with brain metastasis or pre-treated with osimertinib [40]. The trial is conducted in Spain only. The trial is expected to finish recruitment by March 2023, and to be completed by June 2026 [40].
4. EGFR Exon 20 Insertions
EGFR exon 20 insertion (ex20ins) mutations, representing 4–12% of NSCLC EGFR mutations, are historically resistant to EGFR TKIs. In 2021, FDA approved amivantamab and mobocertinib for the treatment of patients with NSCLC who harbor EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations and have disease progression on or after platinum-based chemotherapy. The reported ORR and median PFS were 40% and 8.3 months for amivantamab, as well as 28% and 7.3 months for mobocertinib [41,42]. However, both drugs have significant toxicity (grade 3 or higher TRAEs 35–50%), and their effectiveness against CNS metastasis has not been established.
Sunvozertinib is a selective EGFR ex20ins inhibitor with weak activity against wild-type EGFR [43]. Its clinical efficacy is evaluated in the phase 1 WU-KONG1 and WU-KONG2 trials that contained 119 evaluable patients with EGFR ex20ins who had disease progression after platinum-based chemotherapy. The updated results were presented at WCLC 2022. In the RP2D 300 mg daily group, sunvozertinib achieved a prominent ORR of 52.4%, and the ORR in patients with brain metastasis remained high at 44% [44]. The toxicity appears manageable. Grade 3 or higher TRAEs most commonly were CPK elevation (11.2%), diarrhea (6.5%), and anemia (3%) [44]. The RP2D 300 mg daily dosing is further being tested in a phase II trial (WU-KONG6). The preliminary result was presented at ESMO 2022 (45). The clinical efficacy was similar to that in the phase I trial, with an ORR of 59.8% in all evaluable patients and 48.4% in patients with brain metastasis. The toxicity profile was similar to other EGFR TKIs [45]. Notably, 34% patients were pre-treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. It would be interesting to know the response rate in the subgroup, as EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients who received immunotherapy initially usually developed severe AEs on subsequent EGFR TKIs [46,47]. Sunvozertinib appears to have an impressive efficacy in NSCLC with EGFR ex20ins as a subsequent systemic therapy, although this trend needs to be proved in larger double blind, controlled clinical trials. Additionally, it will be important to examine the effectiveness of sunvozertinib as first-line therapy for advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR ex20ins.
CLN-081 is a new EGFR TKI selectively against ex20ins rather than wild-type EGFR [48]. Its clinical application is being evaluated in an ongoing phase I/IIa trial (NCT04036682). The trial enrolled 73 patients with EGFR ex20ins NSCLC. A total of 66% of patients received 2 or more prior lines of therapy. A total of 38% patients had a history of CNS metastasis at baseline [49]. At the optimal dose of 100 mg bid, ORR was encouraging 41% and median PFS was 12 months. A total of 2 of 3 patients who had CNS target lesions achieved partial response or stable disease for more than a year. Most common grade 3 or higher TRAEs were anemia (10%), increased ALT (4%), and increased AST (4%) [49]. Compared to the two FDA-approved ex20ins inhibitors, CLN-081 appears to have similar or better clinical efficacy with potential effect on CNS metastasis, and a more tolerated toxicity profile. Data from further larger trials are awaited, especially for those patients with CNS involvement.
BLU-451 is another new inhibitor of EGFR ex20ins and has activity against both typical and atypical EGFR mutations on exon 20 and 21. It was shown to be CNS-penetrant, resulting in CNS tumor regression in a xenograft lung cancer mouse model [50]. It is being tested in a phase I/II trial (NCT05241873). Eligible patients include those with EGFT ex20ins NSCLC who have been treated with platinum-based chemotherapy with or without an EGFR ex20ins-targeted agent. Active asymptomatic brain metastasis are permitted in special cohorts [51].
5. ALK Rearrangements
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) account for 3–7% of NSCLC patients [52,53]. Currently the FDA has approved five ALK inhibitors (ALKi) for NSCLC: crizotinib, ceritinib, alectinib, brigatinib, and lorlatinib. Treatment options after resistance to ALK inhibitors are limited.
SAF-189s is a novel next-generation ALK inhibitor with CNS penetration. Preclinical studies showed it can overcome most known resistance mutations of ALK [54]. It is being evaluated in a first-in-human phase I/II study in China (NCT04237805). The phase I data from 45 patients showed median PFS was 33.1 and 22.1 months (95% CI: 6.9–not reached and 13.8–26.6) in ALKi-naive and ALKi-pretreated patients, respectively. Most patients in phase II were ALKi-naive (n = 104, 69%), and the ORR was 92.3% and 65.4% (95% CI: 85.4–96.6 and 44.3–82.8) in ALKi-naive and ALKi-pretreated patients, respectively [54]. PFS data are not mature in phase II study yet. Common grade 3 or higher TRAEs were hyperglycemia (7%), hypertension (6%), and diarrhea (3%) [54]. The final results from this trial will help define the role of SAF-189s in ALK-altered NSCLC patients, particularly those who developed resistance to current ALK inhibitors.
APG-2449 is a TKI against ALK, ROS1, and focal adhesion kinase (FAK). It has been shown to have anti-tumor activity in ALK/ROS1-positive NSCLC mouse model [55]. It is being tested in a phase I dose escalation and expansion trial (NCT03917043) that enrolled 84 patients with ALK/ROS1 + NSCLC [56]. A total of 33% of them had received three or more lines of therapies. At the RP2D, it showed a good response rate in subsequent line setting (4 of 14 ALK+ patients resistant to second-generation TKIs achieved PR). The overall response rate was much higher in the first-line setting (80%, 8 of 10 patients). Four of eight patients with brain metastasis achieved objective response. Grade 3 or higher TRAEs only occurred in 7.1% patients [56]. APG-2449 appears to have a promising clinical efficacy with a favorable safety profile, although both need to be tested in further larger clinical trials.
6. ROS1
ROS1 rearrangements account for 1–2% of NSCLC. The ROS1 gene encodes a receptor tyrosine kinase belongs to the insulin receptor family [57]. Its fusion with other partner genes results in constant auto-phosphorylation and activates the downstream MAPK pathway that drive cancer cell proliferation [57,58]. The FDA has approved crizotinib and entrectinib for the treatment of ROS1-positive NSCLC. However, treatment resistance and disease progression inevitably occur in most patients [58]. In the TRIDENT-1 trial, repotrectinib demonstrated an ORR ranging from 40% to 67% in ROS1-positive NSCLC patients who had received one or more prior ROS1 TKI [39]. Taletrectinib, another ROS1 inhibitor, achieved an ORR of 90% in ROS1-positive, TKI-naïve, NSCLC patients in a phase II trial (NCT04395677) [59]. Both repotrectinib and taletrectinib were granted breakthrough therapy designation (BTD) by the FDA in 2022.
NVL-520 is a brain-penetrant, highly selective ROS1 inhibitor that is against ROS1 alterations including treatment-resistant G2032R solvent front mutation in preclinical studies [60]. ARROS-1 is a phase I/II trial (NCT05118789) designed to examine the pharmacokinetics, RP2D, safety, and preliminary clinical efficacy of NVL-520 in ROS1-positive solid tumors [61]. Patients are required to have received at least one ROS1 TKI therapy to be eligible for the trial. Patients with CNS metastasis are allowed. A most recent update was presented at the 34th EORTC-NCI-AACR (ENA) Symposium in Spain [62]. A total of 35 patients have enrolled and 34 of them have ROS1-positive NSCLC. Patients were heavily pre-treated, of which 71% had received two or more ROS1 TKIs. Among 21 evaluable patients, NVL-520 demonstrated an ORR of 48%, with no dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs) or treatment-related serious adverse events (SAEs) reported. In a smaller cohort of patients with CNS metastasis, the ORR was 73% (8/11). In patients with ROS1 G2032R-mutant cancers, 71.4% (5/7) achieved partial response [62]. The trial is continuing to recruit for the phase I part and the RP2D is yet to be determined.
7. KRAS
KRAS mutations had traditionally remained a pharmaceutical challenge because it does not have a deep binding pocket to fit in small molecule inhibitors [63]. The situation was changed in 2021 when FDA approved sotorasib, a first KRAS G12C inhibitor, for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic KRAS G12C-mutant NSCLC patients who received at least one line of systemic therapy. In a single-arm phase II trial (CodeBreaK 100), sotorasib showed an ORR of 37.1% and a median PFS of 6.8 months [64]. Adagrasib is the second G12C inhibitor that showed clinical benefit with an ORR of 42.9% and a median PFS of 8.5 months in the second line setting [65].
GDC-6036 is an oral, irreversible, selective KRAS G12C inhibitor. It is more potent and selective to inhibit G12C mutation than sotorasib and adagrasib in vitro [66]. A phase I dose-escalation and dose-expansion trial (NCT04449874) evaluated GDC-6036 in patients with solid tumors harboring KRAS G12C mutation. The study included 59 NSCLC patients who received at least one line of systemic therapy and were naïve to G12C inhibitors. GDC-6036 as monotherapy showed an unconfirmed overall response rate (ORR) of 53% (30 of 57 evaluable patients). Grade 3 or higher TRAEs occurred in 16.9% patients, most commonly ALT elevation (6.8%), AST elevation (5.1%), and diarrhea (3.4%). No dose-limiting toxicities were reported [67]. GDC-6036 as monotherapy showed a preliminary promising clinical efficacy with tolerable toxicity profile for NSCLC patients carrying KRAS G12C in the second line setting. A phase II/III study including a docetaxel control arm is currently recruiting NSCLC patients (NCT03178552). The results are awaited to see if similar outcomes are reproducible.
D-1553 is another oral KRAS inhibitor that selectively and irreversibly binds KRAS G12C mutated protein [68]. In a phase I dose escalation and expansion trial, 79 NSCLC patients carrying KRAS G12C who failed at least one prior line of systemic therapy were given D-1553. The ORR was 37.8% and the median PFS was 7.6 months [69]. The data were encouraging and still immature given the high censor rate (68%). Grade 3 or above TRAEs occurred in 35.4% patients, mainly liver enzyme elevation [69]. A phase II trial is currently recruiting (NCT05383898).
8. RAF/MEK
MAPK pathway is commonly upregulated in cancer, which is manifested by increased activity of RAS, RAF, MEK, ERK. BRAF V600E mutation occurs in 1–2% patients with lung adenocarcinoma and results in constitutive activation of downstream MEK/ERK signaling, leading to cancer cell proliferation [70]. The combination of a BRAF inhibitor, dabrafenib, and a MEK inhibitor, trametinib, was shown to be effective against BRAF V600E-mutant NSCLC in a phase II trial. It demonstrated a ORR of 64% and median PFS of 10.8 months in the treatment-naïve group and a similar efficacy in the pretreated group [71,72]. The FDA approved dabrafenib and trametinib for the treatment of BRAF V600E-mutant metastatic NSCLC in 2017.
VS-6766 is a RAF/MEK clamp that inhibits both RAF and MEK and therefore prevents compensatory activation of RAF-dependent MEK phosphorylation [73]. VS-6766 monotherapy was shown objective responses in KRAS mutant NSCLC patients in a phase I trial [74]. Focal adhesion kinase (FAK) activation is a resistance mechanism of RAF and MEK inhibition. Defactinib, a FAK inhibitor, is being tested in combination with VS-6766 in the phase I FRAME trial (NCT03875820). This combination was well tolerated and had 15% ORR and 65% DCR [75]. A phase II study (RAMP 202, NCT04620330) is being conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of VS-6766 monotherapy and VS-6766 in combination with defactinib in NSCLC. This trial is open for enrollment of patients with KRAS or BRAF mutant NSCLC who have received at least one prior systemic therapy [76].
RAMP 203 is a phase I/II trial to assess the safety and efficacy of VS-6766 in combination with sotorasib. It is currently open for enrollment of patients with KRAS G12C mutant NSCLC. Eligible patients are required to be G12C inhibitors-naïve (cohort 1), or have disease progression while receiving G12C inhibitors (cohort 2) [77].
Crosstalks between RAF-MEK-ERK and PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathways are well established in tumorigenesis [78]. A combination of VS-6766 and everolimus, a mTOR inhibitor, is being evaluated in the aforementioned phase I trial (NCT02407509) to evaluate its safety and MTD. A total of 28 patients with RAS or RAF mutant cancers were included in the study and the median lines of previous treatment was 3 (range 0–7). At the recommended phase II dose, Grade 3 or above TRAEs were rash (18%) and pruritus (7%). In the KRAS mutant NSCLC expansion cohort, 2 of 10 patients showed objective response. The KRAS mutation was G12D in these two patients, and PFS was 35.8 and 41.8 months with treatment ongoing. The median PFS was 6.35 months (95% CI 3.52–not reached), a promising result in this heavily pre-treated cohort [79]. The combination of VS-6766 and everolimus is tolerable and has an encouraging preliminary clinical efficacy across different KRAS mutation variants. Further phase II/III trials are needed to prove its effectiveness in this subgroup of NSCLC patients who have KRAS mutations other than G12C and are lack of available targeted therapies.
9. ERK 1/2
ERK is a downstream effector in the RAF-MEK-ERK pathway. Inhibition of ERK may overcome resistance mechanisms of BRAF and MEK inhibitors [80]. ASTX029 is a potent, selective dual-mechanism ERK inhibitor that inhibits both ERK catalytic activity and the phosphorylation of ERK itself by MEK, despite not directly inhibiting MEK activity [81]. It demonstrated anti-tumor activity previously in xenograft mouse models [81]. It is being evaluated in a phase I clinical trial including 76 patients who had relapsed/refractory solid tumors (NCT03520075). Adverse events were similar to those previously reported with MEK inhibitors. Grade 3 or above TRAEs included diarrhea (n = 1), rash (n = 1), and malaise (n = 1). A dose level of 200 mg daily continuously was selected for investigation in the phase II study [82]. Among 12 patients who had NSCLC, 3 of them achieved durable partial response. Interestingly, all three of them carried KRAS mutation (G12A, G12D, G12V) [82]. The results from phase II trial will help assess its efficacy in patients with MAPK-altered solid tumors, especially in NSCLC patients with KRAS mutations other than G12C.
10. HER2
HER2-mutant NSCLC is a rare subgroup (2–4%) of NSCLC. It is associated with poor outcomes and short survival compared with other subtypes of NSCLC. There is an unmet need for developing targeted therapy in this subgroup of patients. Recently, the FDA granted accelerated approval for fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki (T-DXd) as a second or further line of therapy for patients with HER2-mutant NSCLC, based on DESTINY-Lung01 and DESTINY-Lung02 trials. T-DXd showed promising ORR of 58% and median DOR of 8.7 months in this pre-treated subpopulation [83,84]. Drug-related interstitial lung disease, a notable TRAE, occurred less frequently in patients treated with a lower dose (5.9% vs. 14.0%, in dosing groups 5.4 mg/kg vs. 6.5 mg/kg) [83,84]. A phase III trial, DESTINY-Lung04, is currently evaluating the efficacy and safety of T-DXd in the first-line setting for the treatment of HER2-mutant NSCLC. Another HER-2 targeted agent, BI 1810631, selectively inhibits HER2 but spares wild-type EGFR, thus limiting the toxicities associated with off-target EGFR inhibition [85]. A phase Ia/Ib trial (NCT04886804) is open to recruit approximately 96 patients worldwide who have HER2+ advanced solid tumor, including about 30 patients who have HER2 ex20ins mutant, pretreated, advanced NSCLC in the Ib arm. The primary endpoints are MTD in phase Ia and ORR in phase Ib [85,86].
11. MET
The mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) gene is a proto-oncogene that regulates cell proliferation, cell adhesion, and angiogenesis [87]. MET genomic alterations occur in about 4% of patients with NSCLC [52]. The alterations consist of exon 14 skipping mutations, MET amplification, and MET fusions [88]. Capmatinib and tepotinib are the only two FDA-approved agents for patients with metastatic NSCLC harboring MET exon 14 skipping mutations, based on two phase II trials. The ORR was 68% for capmatinib and 43% for tepotinib in the treatment-naïve population [89,90].
Telisotuzumab vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of a c-Met antibody and a microtubule inhibitor. It is being evaluated in a phase II trial including patients with advanced c-MET-overexpressing NSCLC who had received less than two prior therapies. The ORR was 36.5% in the non-squamous EGFR wild-type cohort, but was less in the non-squamous EGFR-mutant and squamous cohorts [91]. Two patients developed grade 5 AEs (one sudden death and one pneumonitis, possibly related) raised a safety concern [91].
REGN5093 is a human bispecific antibody that binds to two distinct epitopes of MET and causes internalization and degradation of MET [92]. REGN5093-M114 is an antibody drug conjugate (ADC) that combines this bispecific antibody to a microtubule inhibitor. A phase I/II trial (NCT04982224) is open for enrollment to evaluate its safety, tolerability, recommended dosing, and preliminary antitumor activity [93]. Eligible patients need to have MET-overexpressing NSCLC and no further approved therapies are available.
12. AXL
AXL is a receptor tyrosine kinase that is known to be associated with treatment resistance in NSCLC [94,95]. BGB324 (bemcentinib), a selective oral AXL inhibitor, has shown synergistic anti-tumor activity with immune checkpoint inhibitor by overcoming immune suppression conferred by STK11 mutation in a NSCLC xenograft mouse model (96). In a phase II trial (NCT03184571) testing the combination of bemcentinib and pembrolizumab in advanced NSCLC patients, three of those were found to have STK11 mutations, and all of them demonstrated objective response [96]. In November 2021, the FDA granted a fast track designation to bemcentinib in combination with a PD-1/PD-L1 agent in the treatment of patients with STK11-altered advanced or metastatic NSCLC without actionable mutations. Given the promising results on subsequent lines of therapy, on 11 October 2022, a new phase Ib/IIa trial (NCT05469178) was initiated to test the combination of bemcentinib and chemo-immunotherapy in the first-line setting for the treatment of STK11 mutant NSCLC patients.
Additionally, bemcentinib was also shown synergistic anti-tumor activity with docetaxel in in vivo studies [97]. A phase I dose escalation and expansion trial (NCT02922777) is currently evaluating the combination of bemcentinib and docetaxel in patients with advanced NSCLC. The trial enrolled 21 patients who were heavily pre-treated (median number of prior therapy was 3, range 1–13). A total of 27% (4 of 15) patients had partial response, and 60% (9 of 15) patients had stable disease. Notably, 76% patient had grade 3 or above neutropenia, albeit received prophylactic G-CSF support [97].
13. IL1RAP
IL-1 dysregulation is implicated in tumorigenesis, tumor progression, and resistance to chemotherapy [98]. Interleukin-1 Receptor Accessory Protein (IL1RAP) is a co-receptor of IL-1R and is required for IL-1 signaling [99]. Nadunolimab (CAN04) is a humanized antibody targeting IL1RAP that has a synergetic anti-tumor effect in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy in an in vitro model [99]. Nadunolimab was evaluated in combination with chemotherapy in a phase I/IIa trial CANFOUR (NCT03267316). A total of 33 patients with advanced NSCLC received nadunolimab along with cisplatin and gemcitabine as first-line therapy or after progression on pembrolizumab. On an interim analysis, the ORR was 53% and the PFS was 6.8 months. TRAEs of grade 3 or higher included neutropenia (58%), febrile neutropenia (9%), thrombocytopenia (30%), and anemia (18%) [100]. In this study, nadunolimab combined with chemotherapy demonstrated clinical efficacy and the toxic profile was expected. However, the trial did not choose more commonly used chemo regimens for NSCLC such as pemetrexed or paclitaxel. Further studies are also needed to compare its clinical benefit to the current standard-of-care chemoimmunotherapy.
14. NRF2
NRF2 (encoded by NFE2L2) is a transcription factor that regulates oxidative stress response. It is negatively regulated by KEAP1. Genetic alterations to NFE2L2 and KEAP1 lead to constitutive activation of NRF2, that occurs in 30% of lung squamous cell carcinoma and 25% of lung adenocarcinoma [101,102,103]. Telaglenastat (CB-839) is a glutaminase inhibitor that has anti-tumor activity in KEAP1/NRF2-mutated NSCLC cell lines and xenograft models [104]. Sapanisertib, a mTOR inhibitor, was shown to have selective anti-tumor activity in NRF2-activating NSCLC in an in vivo xenograft model [105]. Therefore, the combination of telaglenastat and sapanisertib was hypothesized to have synergistic efficacy in treating NRF2/KEAP1-altered NSCLC [106]. This combination is being tested in a phase I trial (NCT04250545). A total of 13 patients were enrolled in the dose escalation portion, and the primary endpoint of identifying the recommended expansion dose (RED) was reached. Most patients achieved tumor shrinkage (5/8). This combination appears safe and tolerable at the RED [106]. The expansion portion of the study contains four cohorts suitable for patients with different KRAS or NFE2L2/KEAP1 mutation status. A separate phase 2 trial (NCT02417701) is also assessing the potential role of sapanisertib in patients with stage IV or recurrent LSCC.
15. ACSS2
Acyl-coenzyme A synthetase short-chain family member 2 (ACSS2) is an enzyme responsible for acetyl-CoA synthesis. Its gene expression promotes the growth of several human solid tumors [107]. MTB-9655, the first oral inhibitor of ACSS2, was shown to have anti-tumor effect in xenograft mouse model of ACSS2-high lung cancer [108]. In a phase I dose escalation and expansion trial (NCT04990739), 10 patients who had advanced solid tumors unamendable to standard therapies received this drug and demonstrated few toxicities. MTD has not been reached yet and the dose escalation is continuing [108].
16. FGFR
Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) alterations contribute to oncogenesis in multiple tumor types. Pemigatinib, a selective FGFR1-3 inhibitor, was showing response across several tumor types including NSCLC in the phase I FIGHT-101 study [109]. FIGHT-210 is a phase II single-arm multicenter trial aiming to recruit 125 patients with advanced NSCLC with FGFR1-3 alterations who progress on available therapies. It is currently recruiting. Futibatinib is an irreversible FGFR1-4 inhibitor, which demonstrates antitumor response in several solid tumors carrying FGFR aberrations [110]. Preclinical studies showed that futibatinib in combination with a MEK inhibitor had synergistic antitumor effect in KRAS-mutant NSCLC cell lines. A phase I/II open-label trial (NCT04965818) is being conducted to assess the safety and preliminary efficacy of futibatinib and binimetinib (MEK inhibitor) in patients with advanced NSCLC with KRAS mutation [111]. The trial is still ongoing, but has completed recruitment. Rogaratinib, a pan-FGFR inhibitor, was studied in patients with advanced and pretreated lung squamous cell carcinoma in the phase II SAKK 19/18 trial. It enrolled 15 patients with FGFR1-3 mRNA overexpression. However, the trial was closed prematurely due to futility observed from its initial results. Median PFS was 1.6 months, with median OS being 3.5 months. The majority of participants, 60%, discontinued the drug due to disease progression. Among all of them, 46.7% had stable disease and 33% showed disease progression [112].
17. Squamous Cell Carcinoma
As mentioned above, LSCC is the second-most common histologic type of NSCLC, accounting for approximately 20% of cases of lung cancer in the USA [113]. While many advancements with targeted therapy had positively impacted outcomes in patients with adenocarcinoma of the lung, the same has not been seen with LSCC, as the most common driver mutations seen on adenocarcinoma are infrequently observed in LSCC [114,115]. Despite that, LSCC still presents significant gene mutations affecting a diversity of cellular pathways that may be potential targets for cancer therapy [116]. This subtype of NSCLC is an active subject of ongoing research aiming at recognizing specific mutations and pharmacologic mechanisms to target them. Table 3 summarizes the trials presented below.
18. FOLR1/PSMA
Folate-receptor 1 (FOLR1) and prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) are overexpressed in solid tumors including lung cancer, prostate cancer, and renal cell carcinoma [117]. They are present both on tumor cells and on endothelial cells. CBP-1018 is the first bi-ligand drug conjugate targeting both FOLR1 and PSMA, with a monomethyl auristatin E drug payload [118]. A phase IA/IB open-label trial (NCT04928612) is currently enrolling patients that have relapsed after prior standard lines of therapy, with four different cohorts. One of them is comprised by patients with advanced LSCC. The primary objectives are safety, tolerability, dose limiting toxicity, and MTD assessment. Preliminary ORR, PFS, and duration of response data will also be assessed.
19. ATR
Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein kinase (ATR) is one of the regulators of DNA damage response. It is potential target especially for cells that have lost ataxia-telangiectasia-mutated kinase (ATM) or p53. In this way, berzosertib has been studied in combination with DNA-damaging drugs. This compound is a first-in-calls inhibitor of ATR, with observed antitumor activity in preclinical studies [119]. A phase 1 study of bersozertib combined with gemcitabine with or without cisplatin in patients with advanced solid tumors (12% of patients with NSCLC) showed that this regimen was safe and well-tolerated [120]. When combined with gemcitabine alone, it led to partial response in 8.3% of patients, with 60.4% experiencing stable disease. In the group of berzosertib with gemcitabine and cisplatin, 14% experienced partial response, with 57% showing stable disease.
Berzosertib is now being studied in a phase IB and randomized open-label phase II study combining it with carboplatin, gemcitabine, and pembrolizumab in patients with LSCC that were never treated with chemotherapy (NCT04216316). Patients are currently being enrolled.
20. NSD3
NSD3 is a histone methyltransferase located on chromosomal region 8p 11–12. It has been demonstrated to participate in the tumorigenesis of LSCC. By depleting NSD3 from animal models with patient-derived xenografts, researchers have been able to slow down tumor growth in mice [57,121]. This study also demonstrated that LSCC with NSD3 may render cancer cells susceptible to bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) inhibitors. Similar effects have been already documented in acute myeloid leukemia [9,122]. As no NSD3 inhibitors are currently available, investigators started considering the role of BET inhibitors in this setting. A phase II trial of ZEN003694, a BET inhibitor, is currently enrolling patients with recurrent or metastatic LSCC with NSD3 amplification (NCT05607108).
21. PI3K Pathway
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/ protein kinase B (AKT)/ mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway is essential in cell cycle regulation and survival [123]. It is also commonly involved in the genesis of cancer cells, as it directly affects cell proliferation and apoptosis. As such, inhibitors of this pathway have been studied as potential anti-cancer drugs. Some have been approved, being potential therapeutic lines in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and follicular lymphoma, for example.
Copanlisib is a pan-class I PI3K inhibitor that has been studied in combination with nivolumab, a PD-1 inhibitor, in a phase IB trial (NCT03735628). The combination was used in patients with advanced solid tumors. It was demonstrated to be safe and well tolerated. Within the treated group, progression of disease was seen in 25% of patients, with the remaining 75% demonstrating some degree of disease control [124]. Results for the phase II of this trial have not yet been published.
Other combination strategies involving a PI3K inhibitor are also being assessed. Its use in association with a cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) inhibitors is being considered in a phase I trial (NCT03065062). This trial is employing palbociclib, a CDK4/6 inhibitor, in combination with gedatolisib, a PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, in patients with advanced LSCC and other solid tumors. CDK4/6 inhibitors are known to lead to cell cycle arrest, but are also found to indirectly affect other intracellular pathways. This mechanism has been described in breast cancer, the most common clinical indication that employs CDK4/6 inhibitors, but also in other malignancies such as pleural mesothelioma [125,126].
22. Conclusions
Targeted therapy has achieved tremendous success and revolutionized the treatment landscape of NSCLC. In advanced disease, however, treatment resistance and failure eventually occur in majority of patients, which remains the main challenge for NSCLC targeted treatment. This challenge is much attributed to the complexity of tumor biology including intratumor heterogeneity, cancer genome evolution, and resistance mutations due to selective pressure imposed by current therapy [127,128,129]. The development of more effective targeted therapies relies on a better understanding of NSCLC at the genome, transcriptome, and proteome levels [5,130]. New discovery of oncogenic driver alterations and treatment-resistant mechanisms are being transformed into new drug developments and being tested in early phase clinical trials. We are confident that targeted therapy continues to be an ever-changing field in NSCLC treatment, with a goal to achieve individualized precision medicine that further improves patients’ overall outcome.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L. and Y.L.; methodology, S.L.; data curation, S.L. and G.S.d.C.C.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L. and G.S.d.C.C.; writing—review and editing, S.L., G.S.d.C.C., J.W., R.M., Y.Z., and Y.L.; supervision, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
Rami Manochakian: Advisory boards: Turning Points, Janssen, Guardant Health, Takeda and Novocure. Consulting & advisory board: AstraZeneca. Yanyan Lou: Advisory boards: AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Lilly Oncology, Turning point therapeutics. Consultant: AstraZeneca. Honorarium: clarion health care. Research Funding Support: Merck, MacroGenics, Tolero Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Vaccinex, Blueprint Medicines, Harpoon Therapeutics, Sun Pharma Advanced Research, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Kyowa Pharmaceuticals, Tesaro, Bayer HealthCare, Mirati Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo.
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abughanimeh, O.; Kaur, A.; El Osta, B.; Ganti, A.K. Novel targeted therapies for advanced non-small lung cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2022, 49, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aisner, D.L.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.R.; Bharat, A.; Bruno, D.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A. Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 497–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeed, U.; Manochakian, R.; Zhao, Y.; Lou, Y. Targeted therapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: Current advances and future trends. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.C.; Tan, D.S.W. Targeted Therapies for Lung Cancer Patients With Oncogenic Driver Molecular Alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Mok, T.S.K.; Nishio, M.; Jotte, R.M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Orlandi, F.; Stroyakovskiy, D.; Nogami, N.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower150): Key subgroup analyses of patients with EGFR mutations or baseline liver metastases in a randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2019, 7, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.N.; Piper-Vallillo, A.J.; Gardner, R.M.; Cunanan, K.; Neal, J.W.; Das, M.; Padda, S.K.; Ramchandran, K.; Chen, T.T.; Sequist, L.V.; et al. Chemotherapy Plus Immunotherapy Versus Chemotherapy Plus Bevacizumab Versus Chemotherapy Alone in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC After Progression on Osimertinib. Clin. Lung Cancer 2022, 23, e210–e221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.; Hong, M.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Park, C.W.; Kim, S.; Yun, M.R.; Kang, H.N.; Pyo, K.H.; Lee, S.S.; Koh, J.S.; et al. YH25448, an Irreversible EGFR-TKI with Potent Intracranial Activity in EGFR Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 2575–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.J.; Han, J.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, Y.G.; Cho, E.K.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, G.W.; Lee, J.S.; et al. Lazertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from the dose escalation and dose expansion parts of a first-in-human, open-label, multicentre, phase 1-2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Han, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, E.K.; Lee, Y.-G.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, G.-W.; Lee, J.-S.; et al. A Phase 1/2 Study of Lazertinib 240 mg in Patients With Advanced EGFR T790M-Positive NSCLC After Previous EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.; Han, J.-Y.; Lee, K.; Lee, Y.-G.; Kim, D.-W.; Min, Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Cho, E.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, G.-W. EP08. 02-025 Lazertinib as a Frontline Treatment in Patients with EGFR Mutant Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results from the Phase I/II Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S408–S409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Lee, K.H.; Cho, E.K.; Kim, D.W.; Lee, J.S.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Spira, A.; Haura, E.B.; Sabari, J.K.; et al. 1258O Amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an EGFR-MET bispecific antibody, in combination with lazertinib, a 3rd-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), in advanced EGFR NSCLC. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.A.; Goto, K.; Ohe, Y.; Besse, B.; Park, K.; Wang, Y.; Griesinger, F.; Yang, J.C.H.; Felip, E.; Sanborn, R.E.; et al. 1193MO Amivantamab plus lazertinib in post-osimertinib, post-platinum chemotherapy EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Preliminary results from CHRYSALIS-2. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S952–S953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.A.; Goto, K.; Ohe, Y.; Besse, B.; Lee, S.-H.; Wang, Y.; Griesinger, F.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Felip, E.; Sanborn, R.E.; et al. Amivantamab and lazertinib in patients with EGFR-mutant non–small cell lung (NSCLC) after progression on osimertinib and platinum-based chemotherapy: Updated results from CHRYSALIS-2. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.; Lee, S.-H.; Han, J.-Y.; Cho, E.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, K.; Curtin, J.; Gao, G.; Xie, J.; Schnepp, R. P1. 16-01 Amivantamab and Lazertinib in Treatment-Naive EGFR-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Felip, E.; Hayashi, H.; Thomas, M.; Lu, S.; Besse, B.; Sun, T.; Martinez, M.; Sethi, S.N.; Shreeve, S.M.; et al. MARIPOSA: Phase 3 study of first-line amivantamab + lazertinib versus osimertinib in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Dong, X.; Yang, C.T.; Song, Y.; Chang, G.C.; Lu, Y.; Pan, H.; Chiu, C.H.; et al. Efficacy of Aumolertinib (HS-10296) in Patients With Advanced EGFR T790M+ NSCLC: Updated Post-National Medical Products Administration Approval Results From the APOLLO Registrational Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Jiang, G.; Zhang, A.; Li, Z.; Jia, J. Icotinib is as efficacious as gefitinib for brain metastasis of EGFR mutated non-small-cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M. EP08.02-067 Concurrent Aumolertinib Plus Icotinib for First-Line Treatment of EGFR Mutated Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S431–S432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.; Park, C.W.; Zhang, Z.; Woessner, R.; Dineen, T.; Stevison, F.; Hsieh, J.; Eno, M.; Wilson, D.; Campbell, J.; et al. Abstract 1467: BLU-945, a fourth-generation, potent and highly selective epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) with intracranial activity, demonstrates robust in vivo antitumor activity in models of osimertinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shum, E.; Elamin, Y.Y.; Piotrowska, Z.; Spigel, D.R.; Reckamp, K.L.; Rotow, J.K.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Lim, S.M.; Kim, T.M.; Lin, C.-C.; et al. A phase 1/2 study of BLU-945 in patients with common activating EGFR-mutant non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): SYMPHONY trial in progress. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, TPS9156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.M.; Ahn, J.S.; Hong, M.H.; Kim, T.M.; Jung, H.A.; Jung, H.A.; Ou, S.H.I.; Jeong, S.; Lee, Y.H.; Yim, E.; et al. MA07.09 BBT-176, a 4th generation EGFR TKI, for Progressed NSCLC after EGFR TKI Therapy: PK, Safety and Efficacy from Phase 1 Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S70–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, C.; Campbell, J.; Woessner, R.; Guo, J.; Timsit, Y.; Iliou, M.; Wardwell, S.; Davis, A.; Chicklas, S.; Hsieh, J.; et al. Abstract 1262: BLU-701 is a highly potent, brain-penetrant and WT-sparing next-generation EGFR TKI for the treatment of sensitizing (ex19del, L858R) and C797S resistance mutations in metastatic NSCLC. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jänne, P.A.; Baik, C.; Su, W.C.; Johnson, M.L.; Hayashi, H.; Nishio, M.; Kim, D.W.; Koczywas, M.; Gold, K.A.; Steuer, C.E.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Patritumab Deruxtecan (HER3-DXd) in EGFR Inhibitor-Resistant, EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 74–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steuer, C.E.; Hayashi, H.; Su, W.-C.; Nishio, M.; Johnson, M.L.; Kim, D.-W.; Koczywas, M.; Felip, E.; Gold, K.A.; Murakami, H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of patritumab deruxtecan (HER3-DXd) in advanced/metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) without EGFR-activating mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Zheng, F.; Ren, D.; Du, F.; Dong, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Ahmad, R.; Zhao, J. Anlotinib: A novel multi-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor in clinical development. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhu, C.; Sun, M. 1813P Anlotinib plus osimertinib overcomes acquired resistance to osimertinib via FGFR and EGFR signaling in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Gong, Q.; Li, B.; Qie, H.L.; Li, W.; Jiang, H.T.; Li, H.F. Clinical outcomes and safety of osimertinib plus anlotinib for patients with previously treated EGFR T790M-positive NSCLC: A retrospective study. J. Clin. Pharm. 2022, 47, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Yan, B.; Gu, A.; Chu, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhong, H.; Shi, C.; Zhang, X. Phase Ib/IIa study evaluating the safety and clinical activity of osimeritinib combined with anlotinib in EGFRm, treatment-naive advanced NSCLC patients (AUTOMAN). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, e21140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatcher, N.; Hirsch, F.R.; Luft, A.V.; Szczesna, A.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Dediu, M.; Ramlau, R.; Galiulin, R.K.; Bálint, B.; Losonczy, G.; et al. Necitumumab plus gemcitabine and cisplatin versus gemcitabine and cisplatin alone as first-line therapy in patients with stage IV squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (SQUIRE): An open-label, randomised, controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, J.W.; Krailo, M.D.; Padda, S.K.; Groshen, S.G.; Wakelee, H.A.; Reckamp, K.L.; Koczywas, M.; Piotrowska, Z.; Steuer, C.E.; Kim, C.; et al. Osimertinib plus necitumumab in EGFR-mutant NSCLC: Final results from an ETCTN California Cancer Consortium phase I study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenson, B.; Crispino, J.D. The aurora kinases in cell cycle and leukemia. Oncogene 2015, 34, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.N.; Bhatt, R.; Rotow, J.; Rohrberg, J.; Olivas, V.; Wang, V.E.; Hemmati, G.; Martins, M.M.; Maynard, A.; Kuhn, J.; et al. Aurora kinase A drives the evolution of resistance to third-generation EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.B.; Sun, H.; Robichaux, J.; Pfeifer, M.; McDermott, U.; Travers, J.; Diao, L.; Xi, Y.; Tong, P.; Shen, L.; et al. A YAP/FOXM1 axis mediates EMT-associated EGFR inhibitor resistance and increased expression of spindle assembly checkpoint components. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaaz4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Wang, G.; Pei, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, W. Emerging strategies to overcome resistance to third-generation EGFR inhibitors. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamin, Y.Y.; Negrao, M.V.; Fossella, F.V.; Byers, L.A.; Zhang, J.; Gay, C.M.; Tu, J.C.; Pozadzides, J.V.; Tran, H.T.; Lu, C.; et al. Results of a phase 1b study of osimertinib plus sapanisertib or alisertib for osimertinib-resistant, EGFR-mutant non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.; Huang, H.K.T.; Cummings, A.; Noor, Z.; Slomowitz, S.; Kirimis, E.; Olevsky, O.; Arzoo, K.; Ashouri, S.; DiCarlo, B.; et al. MA07.05 Phase 1b/2 Study of Combined HER Inhibition in Refractory EGFR-mutated Metastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S68–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.C.; Doebele, R.C.; Lin, J.; Nagasaka, M.; Baik, C.; Van Der Wekken, A.; Velcheti, V.; Lee, K.H.; Liu, S.; Solomon, B.; et al. MA11.07 Phase 1/2 TRIDENT-1 Study of Repotrectinib in Patients with ROS1+ or NTRK+ Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S174–S175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Cho, B.C.; Springfeld, C.; Camidge, D.R.; Solomon, B.; Baik, C.; Velcheti, V.; Kim, Y.-C.; Moreno, V.; van der Wekken, A.J.; et al. Abstract P224: Update from the Phase 2 registrational trial of repotrectinib in TKI-pretreated patients with ROS1+ advanced non-small cell lung cancer and with NTRK+ advanced solid tumors (TRIDENT-1). Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, P224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, A.; Cobo, M.; Azkárate, A.; Calles, A.; Molina, M.Á.; Rosell, R. EP08.02-011 Design of a Phase I Trial (TOTEM) to Test Repotrectinib in Combination with Osimertinib in Advanced, Metastatic EGFR-Mutant NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S401–S402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Haura, E.B.; Leighl, N.B.; Mitchell, P.; Shu, C.A.; Girard, N.; Viteri, S.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, C.K.; et al. Amivantamab in EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Progressing on Platinum Chemotherapy: Initial Results From the CHRYSALIS Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Riely, G.J.; Mekhail, T.; Nguyen, D.; Garcia Campelo, M.R.; Felip, E.; et al. Treatment Outcomes and Safety of Mobocertinib in Platinum-Pretreated Patients With EGFR Exon 20 Insertion–Positive Metastatic Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 1/2 Open-label Nonrandomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, e214761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Mitchell, P.L.; Fang, J.; Camidge, D.R.; Nian, W.; Chiu, C.-H.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Su, W.-C.; et al. Sunvozertinib, a Selective EGFR Inhibitor for Previously Treated Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 1676–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-H.; Wang, M.; Mitchell, P.; Fang, J.; Nian, W.; Chiu, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Su, W.-C.; Camidge, R. EP08. 02-029 Sunvozertinib in NSCLC Patients with EGFR Exon20 Insertion Mutations: Effect of Prior Treatment. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S410–S411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, J.-H.; Mitchell, P.; Fang, J.; Nian, W.; Chiu, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.; Su, W.; Camidge, D. 987P Sunvozertinib for NSCLC patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations: Preliminary analysis of WU-KONG6, the first pivotal study. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1003–S1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Arbour, K.C.; Rizvi, H.; Iqbal, A.N.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Girshman, J.; Kris, M.G.; Riely, G.J.; Yu, H.A.; Hellmann, M.D. Severe immune-related adverse events are common with sequential PD-(L)1 blockade and osimertinib. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, K.K.W.; Fong, W.; Cho, W.C.S. Immunotherapy in Treating EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer: Current Challenges and New Strategies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 635007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasako, S.; Terasaka, M.; Abe, N.; Uno, T.; Ohsawa, H.; Hashimoto, A.; Fujita, R.; Tanaka, K.; Okayama, T.; Wadhwa, R.; et al. TAS6417, A Novel EGFR Inhibitor Targeting Exon 20 Insertion Mutations. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 1648–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.A.; Tan, D.S.-W.; Smit, E.F.; Spira, A.I.; Soo, R.A.; Nguyen, D.; Lee, V.H.-F.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Velcheti, V.; Wrangle, J.M.; et al. Phase (Ph) 1/2a study of CLN-081 in patients (pts) with NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations (Ins20). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, P.G.; Pandey, A.; Roth, B.; Saxton, T.; Estes, D.J.; Trivedi, R.; Agrawal, H.; Hallur, G.; Ahmad, I.; Jenkins, H. LNG-451 (BLU-451), a potent inhibitor of EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations with high CNS exposure. Available online: https://www.blueprintmedicines.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Blueprint-Medicines-AACR-2022-BLU-451-EGFR-Exon-20-Insertions-DMPK-Preclinical-Poster.pdf (accessed on 17 March 2023).
- Spira, A.I.; Yu, H.A.; Sun, L.; Nguyen, D.; Pearson, P.; Shim-Lopez, J.; Hausman, D.F.; Le, X. Phase 1/2 study of BLU-451, a central nervous system (CNS) penetrant, small molecule inhibitor of EGFR, in incurable advanced cancers with EGFR exon 20 insertion (ex20ins) mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, TPS9155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, G.; Miller, P.G.; Agarwala, V.; Li, G.; Kaushik, G.; Backenroth, D.; Gossai, A.; Frampton, G.M.; Torres, A.Z.; Lehnert, E.M.; et al. Association of Patient Characteristics and Tumor Genomics With Clinical Outcomes Among Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Using a Clinicogenomic Database. JAMA 2019, 321, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soda, M.; Choi, Y.L.; Enomoto, M.; Takada, S.; Yamashita, Y.; Ishikawa, S.; Fujiwara, S.; Watanabe, H.; Kurashina, K.; Hatanaka, H.; et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2007, 448, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-J.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zang, A.; Fan, Y.; Hui, A.-M.; Zhou, Y.; et al. SAF-189s in advanced, ALK-positive, non–small cell lung cancer: Results from a first-in-human phase 1/2, multicenter study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.D.; Tao, R.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Xu, C.; Zhai, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Tang, C.; et al. Discovery of a novel ALK/ROS1/FAK inhibitor, APG-2449, in preclinical non-small cell lung cancer and ovarian cancer models. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Song, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wu, G.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yu, X.; Gao, F.; et al. First-in-human phase I results of APG-2449, a novel FAK and third-generation ALK/ ROS1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), in patients (pts) with second-generation TKI-resistant ALK/ROS1+ non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) or mesothelioma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azelby, C.M.; Sakamoto, M.R.; Bowles, D.W. ROS1 Targeted Therapies: Current Status. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.D.; Doebele, R.C. Molecular Pathways: ROS1 Fusion Proteins in Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4040–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, N.; Ma, H.; Fan, H.; Li, K.; Wu, H.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Wang, X.; et al. The efficacy and safety of taletrectinib in patients with TKI-naïve or crizotinib-pretreated ROS1-positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 8572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangpeerachaikul, A.; Keddy, C.; Nicholson, K.; Davare, M.; Pelish, H.E. Abstract 3336: Preclinical activity of NVL-520 in ROS1-driven cancer models with diverse fusion partners and kinase-domain mutations. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A.; Ou, S.H.I.; Gadgeel, S.; Johnson, M.; Spira, A.; Lopes, G.; Besse, B.; Felip, E.; van der Wekken, A.J.; Calles, A.; et al. EP08.02-041 NVL-520, a Highly Selective ROS1 Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced ROS1-Positive Solid Tumors: The Phase 1/2 ARROS-1 Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drilon, A. Safety and preliminary clinical activity of NVL-520, a highly selective ROS1inhibitor, in patients with advanced ROS1 fusion-positive solid tumors. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 174, S3–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgia, R.; Pharaon, R.; Mambetsariev, I.; Nam, A.; Sattler, M. The improbable targeted therapy: KRAS as an emerging target in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoulidis, F.; Li, B.T.; Dy, G.K.; Price, T.J.; Falchook, G.S.; Wolf, J.; Italiano, A.; Schuler, M.; Borghaei, H.; Barlesi, F.; et al. Sotorasib for Lung Cancers with KRAS p.G12C Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jänne, P.A.; Riely, G.J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Heist, R.S.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Pacheco, J.M.; Johnson, M.L.; Sabari, J.K.; Leventakos, K.; Yau, E.; et al. Adagrasib in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring a KRASG12C Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purkey, H. Abstract ND11: Discovery of GDC-6036, a clinical stage treatment for KRAS G12C-positive cancers. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, ND11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacher, A.; Patel, M.R.; Miller, W.H., Jr.; Desai, J.; Garralda, E.; Bowyer, S.; Kim, T.W.; De Miguel, M.; Falcon, A.; Krebs, M.G.; et al. OA03.04 Phase I A Study to Evaluate GDC-6036 Monotherapy in Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) with KRAS G12C Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S8–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Weng, J.; Fan, X.; Wang, E.; Zhu, Q.; Tao, L.; Han, Z.; Wang, Z.; Niu, H.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Abstract 932: Discovery of D-1553, a novel and selective KRas-G12C Inhibitor with potent anti-tumor activity in a broad spectrum of tumor cell lines and xenograft models. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Jian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, P.; Jiang, L.; Gong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Dong, X.; et al. OA03.07 Safety and Efficacy of D-1553 in Patients with KRAS G12C Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 1 Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.T.C.; Garnett, M.J.; Roe, S.M.; Lee, S.; Niculescu-Duvaz, D.; Good, V.M.; Project, C.G.; Jones, C.M.; Marshall, C.J.; Springer, C.J.; et al. Mechanism of Activation of the RAF-ERK Signaling Pathway by Oncogenic Mutations of B-RAF. Cell 2004, 116, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Besse, B.; Groen, H.J.M.; Hashemi, S.M.S.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, T.M.; Quoix, E.; Souquet, P.J.; Barlesi, F.; Baik, C.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Dabrafenib Plus Trametinib in Patients With BRAF V600E-Mutant Metastatic NSCLC: Updated 5-Year Survival Rates and Genomic Analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Smit, E.F.; Groen, H.J.M.; Mazieres, J.; Besse, B.; Helland, Å.; Giannone, V.; D’Amelio, A.M., Jr.; Zhang, P.; Mookerjee, B.; et al. Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with previously untreated BRAFV600E-mutant metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, N.; Harada, N.; Joseph, E.W.; Ohara, K.; Miura, T.; Sakamoto, H.; Matsuda, Y.; Tomii, Y.; Tachibana-Kondo, Y.; Iikura, H.; et al. Enhanced Inhibition of ERK Signaling by a Novel Allosteric MEK Inhibitor, CH5126766, That Suppresses Feedback Reactivation of RAF Activity. Cancer Res 2013, 73, 4050–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Chénard-Poirier, M.; Roda, D.; de Miguel, M.; Harris, S.J.; Candilejo, I.M.; Sriskandarajah, P.; Xu, W.; Scaranti, M.; Constantinidou, A.; et al. Intermittent schedules of the oral RAF-MEK inhibitor CH5126766/VS-6766 in patients with RAS/RAF-mutant solid tumours and multiple myeloma: A single-centre, open-label, phase 1 dose-escalation and basket dose-expansion study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1478–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, M.G.; Shinde, R.; Rahman, R.A.; Grochot, R.; Little, M.; King, J.; Kitchin, J.; Parmar, M.; Turner, A.; Mahmud, M.; et al. Abstract CT019: A phase I trial of the combination of the dual RAF-MEK inhibitor VS-6766 and the FAK inhibitor defactinib: Evaluation of efficacy in KRAS mutated NSCLC. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, CT019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Reuss, J.E.; Spira, A.I.; Janne, P.A.; Rehman, M.; Pachter, J.A.; Patrick, G.; Denis, L.J.; Spigel, D.R. A phase 2 study of VS-6766 (RAF/MEK clamp) RAMP 202, as a single agent and in combination with defactinib (FAK inhibitor) in recurrent KRAS mutant (mt) and BRAF mt non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, TPS9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, R.; Awad, M.M.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Pachter, J.A.; Patrick, G.; Denis, L.J. A phase 1/2 study of VS-6766 (RAF/MEK clamp) in combination with sotorasib (G12C inhibitor) in patients with KRAS G12C mutant non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) (RAMP 203). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, TPS9148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, M.C.; Er, E.E.; Blenis, J. The Ras-ERK and PI3K-mTOR pathways: Cross-talk and compensation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchom, A.R.; Perez, V.S.; Morton, C.; Manickavasagar, T.; Nintos, G.; Lai-Kwon, J.E.; Guo, C.; Tunariu, N.; Parker, T.; Prout, T.; et al. Phase I trial of the RAF/MEK clamp VS-6766 in combination with everolimus using an intermittent schedule with expansion in NSCLC across multiple KRAS variants. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazar-Rethinam, M.; Kleyman, M.; Han, G.C.; Liu, D.; Ahronian, L.G.; Shahzade, H.A.; Chen, L.; Parikh, A.R.; Allen, J.N.; Clark, J.W.; et al. Convergent Therapeutic Strategies to Overcome the Heterogeneity of Acquired Resistance in BRAF(V600E) Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munck, J.M.; Berdini, V.; Bevan, L.; Brothwood, J.L.; Castro, J.; Courtin, A.; East, C.; Ferraldeschi, R.; Heightman, T.D.; Hindley, C.J.; et al. ASTX029, a Novel Dual-mechanism ERK Inhibitor, Modulates Both the Phosphorylation and Catalytic Activity of ERK. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 1757–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoRusso, P.; Rasco, D.W.; Shapiro, G.; Mita, A.C.; Azad, N.S.; Swiecicki, P.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Gandara, D.R.; Kummar, S.; Tanajian, H.; et al. A first-in-human, phase 1 study of ASTX029, a dual-mechanism inhibitor of ERK1/2, in relapsed/refractory solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.T.; Smit, E.F.; Goto, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Udagawa, H.; Mazières, J.; Nagasaka, M.; Bazhenova, L.; Saltos, A.N.; Felip, E.; et al. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan in HER2-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, K.; Sang-We, K.; Kubo, T.; Goto, Y.; Ahn, M.J.; Planchard, D.; Kim, D.W.; Yang, J.C.H.; Yang, T.Y.; Pereira, K.M.C.; et al. LBA55 Trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) in patients (Pts) with HER2-mutant metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Interim results from the phase 2 DESTINY-Lung02 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymach, J.; Opdam, F.; Barve, M.; Gibson, N.; Sadrolhefazi, B.; Serra, J.; Yamamoto, N. Abstract CT212: A phase I, open-label, dose escalation, confirmation, and expansion trial of BI 1810631 as monotherapy in patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors with HER2 aberrations. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, CT212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opdam, F.; Heymach, J.; Barve, M.; Gibson, N.; Sadrolhefazi, B.; Serra, J.; Yamamoto, N.; Yoh, K.; Wu, Y.L. EP08.02-049 A Phase I Trial of the HER2 Exon 20 Inhibitor, BI 1810631, In Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors With HER2 Aberrations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S421–S422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.S.; Salgia, R. MET Pathway as a Therapeutic Target. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2009, 4, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Jain, P.; Wang, F.; Ma, P.C.; Borczuk, A.; Halmos, B. MET alterations and their impact on the future of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) targeted therapies. Expert Opin. Targets 2021, 25, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, P.K.; Felip, E.; Veillon, R.; Sakai, H.; Cortot, A.B.; Garassino, M.C.; Mazieres, J.; Viteri, S.; Senellart, H.; Van Meerbeeck, J.; et al. Tepotinib in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer with MET Exon 14 Skipping Mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Seto, T.; Han, J.-Y.; Reguart, N.; Garon, E.B.; Groen, H.J.M.; Tan, D.S.W.; Hida, T.; de Jonge, M.; Orlov, S.V.; et al. Capmatinib in MET Exon 14–Mutated or MET-Amplified Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Bar, J.; Horinouchi, H.; Goldman, J.W.; Moiseenko, F.V.; Filippova, E.; Cicin, I.; Bradbury, P.A.; Daaboul, N.; Tomasini, P.; et al. Telisotuzumab vedotin (Teliso-V) monotherapy in patients (pts) with previously treated c-Met–overexpressing (OE) advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DaSilva, J.O.; Yang, K.; Perez Bay, A.E.; Andreev, J.; Ngoi, P.; Pyles, E.; Franklin, M.C.; Dudgeon, D.; Rafique, A.; Dore, A.; et al. A Biparatopic Antibody That Modulates MET Trafficking Exhibits Enhanced Efficacy Compared with Parental Antibodies in MET-Driven Tumor Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1408–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.E.; Awad, M.M.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Villaruz, L.C.; Sabari, J.K.; Perez, J.; Daly, C.; Patel, S.; Li, S.; Seebach, F.A.; et al. A phase 1/2 study of REGN5093-M114, a METxMET antibody-drug conjugate, in patients with mesenchymal epithelial transition factor (MET)-overexpressing NSCLC. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, TPS8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Bryan, J.P.; Frye, R.A.; Cogswell, P.C.; Neubauer, A.; Kitch, B.; Prokop, C.; Espinosa, R., 3rd; Le Beau, M.M.; Earp, H.S.; Liu, E.T. axl, a transforming gene isolated from primary human myeloid leukemia cells, encodes a novel receptor tyrosine kinase. Mol. Cell Biol. 1991, 11, 5016–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramkumar, K.; Stewart, C.A.; Cargill, K.R.; Della Corte, C.M.; Wang, Q.; Shen, L.; Diao, L.; Cardnell, R.J.; Peng, D.H.; Rodriguez, B.L.; et al. AXL Inhibition Induces DNA Damage and Replication Stress in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells and Promotes Sensitivity to ATR Inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Han, C.; Girard, L.; Park, H.; Zhang, A.; Dong, C.; Ye, J.; et al. AXL targeting restores PD-1 blockade sensitivity of STK11/LKB1 mutant NSCLC through expansion of TCF1(+) CD8 T cells. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, S.; Fattah, F.J.; Williams, J.N.; Macchiaroli, A.; Padro, J.; Pogue, M.; Dowell, J.; Brekken, R.A.; Putnam, W.C.; McCracken, N.W.; et al. Phase 1 dose escalation and expansion study of bemcentinib (BGB324), a first-in-class, selective AXL inhibitor, with docetaxel in patients with previously treated advanced NSCLC. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litmanovich, A.; Khazim, K.; Cohen, I. The Role of Interleukin-1 in the Pathogenesis of Cancer and its Potential as a Therapeutic Target in Clinical Practice. Oncol. Ther. 2018, 6, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millrud, C.R.; von Wachenfeldt, K.; Falk, H.H.; Forsberg, G.; Liberg, D. Abstract 2269: The anti-IL1RAP antibody CAN04 increases tumor sensitivity to platinum-based chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, A.; Cicenas, S.; Zvirbule, Z.; Paz-Ares, L.G.; Awada, A.; Garcia-Ribas, I.; Losic, N.; Zemaitis, M. Phase 1/2a trial of nadunolimab, a first-in-class fully humanized monoclonal antibody against IL1RAP, in combination with cisplatin and gemcitabine (CG) in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lignitto, L.; LeBoeuf, S.E.; Homer, H.; Jiang, S.; Askenazi, M.; Karakousi, T.R.; Pass, H.I.; Bhutkar, A.J.; Tsirigos, A.; Ueberheide, B.; et al. Nrf2 Activation Promotes Lung Cancer Metastasis by Inhibiting the Degradation of Bach1. Cell 2019, 178, 316–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Daemen, A.; Nickles, D.; Jeon, S.-M.; Foreman, O.; Sudini, K.; Gnad, F.; Lajoie, S.; Gour, N.; Mitzner, W.; et al. NRF2 Activation Promotes Aggressive Lung Cancer and Associates with Poor Clinical Outcomes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, Q.; He, X.; Yuan, X.; Chen, Y.; Chu, Q.; Wu, K. Emerging roles of Nrf2 signal in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, F.; Fan, N.; Zhou, C.; Li, D.; Macvicar, T.; Dong, Q.; Bruns, C.J.; Zhao, Y. Targeting Glutaminolysis: New Perspectives to Understand Cancer Development and Novel Strategies for Potential Target Therapies. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 589508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, P.K.; Fan, P.D.; Qeriqi, B.; Namakydoust, A.; Daly, B.; Ahn, L.; Kim, R.; Plodkowski, A.; Ni, A.; Chang, J.; et al. Targeting NFE2L2/KEAP1 mutations in advanced non-small cell lung cancer with the TORC1/2 inhibitor TAK-228. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 18, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, J.; Frankel, P.; Massarelli, E.; Nieva, J.; Lai, W.C.V.; Koczywas, M.; Shackelford, D.; Lanza, I.; Reid, J.M.; Gonsalves, W.I.; et al. MA13.08 A Phase 1 Trial of Sapanisertib and Telaglenastat (CB-839) in Patients with Advanced NSCLC (NCI 10327): Results from Dose Escalation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S91–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, Z.T.; Peck, B.; Jones, D.T.; Zhang, Q.; Grosskurth, S.; Alam, I.S.; Goodwin, L.M.; Smethurst, E.; Mason, S.; Blyth, K.; et al. Acetyl-CoA Synthetase 2 Promotes Acetate Utilization and Maintains Cancer Cell Growth under Metabolic Stress. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perets, R.; Geva, R.; McKean, M.; Goutopoulos, A.; Erez, O.; Phadnis, M.; Youssoufian, H.; Schwartz, B.E.; Kansra, V.; Fattaey, A. Phase 1 first-in-human trial of MTB-9655, the first oral inhibitor of ACSS2, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, e20609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, V.; Iannotti, N.O.; Gutierrez, M.; Smith, D.C.; Féliz, L.; Lihou, C.F.; Tian, C.; Silverman, I.M.; Ji, T.; Saleh, M. FIGHT-101, a first-in-human study of potent and selective FGFR 1-3 inhibitor pemigatinib in pan-cancer patients with FGFFGFR alterations and advanced malignancies. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meric-Bernstam, F.; Bahleda, R.; Hierro, C.; Sanson, M.; Bridgewater, J.; Arkenau, H.-T.; Tran, B.; Kelley, R.K.; Park, J.O.; Javle, M.; et al. Futibatinib, an Irreversible FGFR1–4 Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors Harboring FGF/FGFR Aberrations: A Phase I Dose-Expansion Study. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodon, J.; O’Neil, B.; Wacheck, V.; Liu, M.; Rosen, L.S. 1198TiP A phase Ib/II open-label, nonrandomized study of FGFR inhibitor futibatinib in combination with MEK inhibitor binimetinib in patients with advanced KRAS-mutant cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addeo, A.; Rothschild, S.I.; Holer, L.; Schneider, M.; Waibel, C.; Haefliger, S.; Mark, M.; Fernandez, E.; Mach, N.; Mauti, L.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) inhibitor rogaratinib in patients with advanced pretreated squamous-cell non-small cell lung cancer over-expressing FGFR mRNA: The SAKK 19/18 phase II study. Lung Cancer 2022, 172, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Ann. Glob. Health. 2019, 85, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liam, C.-K.; Mallawathantri, S.; Fong, K.M. Is Tissue Still the Issue in Detecting Molecular Alterations in Lung Cancer? Respirology 2020, 25, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbst, R.S.; Morgensztern, D.; Boshoff, C. The Biology and Management of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Nature 2018, 553, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heist, R.S.; Sequist, L.V.; Engelman, J.A. Genetic Changes in Squamous Cell Lung Cancer: A Review. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shannessy, D.J.; Yu, G.; Smale, R.; Fu, Y.S.; Singhal, S.; Thiel, R.P.; Somers, E.B.; Vachani, A. Folate Receptor AlphaE in Lung Cancer: Diagnostic and Prognostic Significance. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Shi, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhou, L.; Ye, S.; Lai, X.; Huang, R.; Teng, Y.; Yu, J.; Chia, X.; et al. An Open-label, Non-randomized, Multi-center Phase I Study Evaluating the safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Preliminary Efficacy of Bi-ligand-drug Conjugate CBP-1018 in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncology 2022, 40, TPS2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.B.; Newsome, D.; Wang, Y.; Boucher, D.M.; Eustace, B.; Gu, Y.; Hare, B.; Johnson, M.A.; Milton, S.; Murphy, C.E.; et al. Potentiation of tumor responses to DNA damaging therapy by the selective ATR inhibitor VX-970. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5674–5685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, M.R.; Dean, E.; Evans, T.R.J.; Shapiro, G.I.; Pollard, J.; Hendriks, B.S.; Falk, M.; Diaz-Padilla, I.; Plummer, R. Phase 1 study of the ATR inhibitor berzosertib (formerly M6620, VX-970) combined with gemcitabine ± cisplatin in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Flores, N.M.; Hausmann, S.; Lofgren, S.M.; Kharchenko, V.; Angulo-Ibanez, M.; Sengupta, D.; Lu, X.; Czaban, I.; Azhibek, D.; et al. Elevated NSD3 histone methylation activity drives squamous cell lung cancer. Nature 2021, 590, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Ipsaro, J.J.; Shi, J.; Milazzo, J.P.; Wang, E.; Roe, J.S.; Suzuki, Y.; Pappin, D.J.; Joshua-Tor, L.; Vakoc, C.R. NSD3-Short Is an Adaptor Protein that Couples BRD4 to the CHD8 Chromatin Remodeler. Mol. Cell. 2015, 60, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzahrani, A.S. PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: At the bench and bedside. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 59, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, B.A.; Jotte, R.; Gabrail, N.; Hamid, O.; Huang, F.; Chaturvedi, S.; Herpers, M.; Soler, L.M.; Childs, B.H.; Hansen, A. Abstract P239: Safety and efficacy of copanlisib in combination with nivolumab: A phase Ib study in patients with advanced solid tumors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, P239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonelli, M.A.; Digiacomo, G.; Fumarola, C.; Alfieri, R.; Quaini, F.; Falco, A.; Madeddu, D.; La Monica, S.; Cretella, D.; Ravelli, A.; et al. Combined Inhibition of CDK4/6 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathways Induces a Synergistic Anti-Tumor Effect in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Cells. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampioni Vinciguerra, G.L.; Sonego, M.; Segatto, I.; Dall’Acqua, A.; Vecchione, A.; Baldassarre, G.; Belletti, B. CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Combination Therapies: Better in Company Than Alone: A Mini Review. Front Oncol. 2022, 12, 891580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Wilson, G.A.; McGranahan, N.; Birkbak, N.J.; Watkins, T.B.; Veeriah, S.; Shafi, S.; Johnson, D.H.; Mitter, R.; Rosenthal, R. Tracking the Evolution of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2109–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Jänne, P.A.; Mok, T.; Peters, S. Overcoming therapy resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Cardona, A.F.; Caglevic, C.; Manca, P.; Ruiz-Patiño, A.; Arrieta, O.; Rolfo, C. Overcoming TKI resistance in fusion-driven NSCLC: New generation inhibitors and rationale for combination strategies. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 2581–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, M.A.; Satpathy, S.; Cao, S.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Vasaikar, S.V.; Krug, K.; Petralia, F.; Li, Y.; Liang, W.W.; Reva, B.; et al. Proteogenomic Characterization Reveals Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cell 2020, 182, 200–225.e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).